- Table of Contents
-
- 17-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Information center configuration
- 02-Flow log configuration
- 03-Fast log output configuration
- 04-NetStream configuration
- 05-Mirroring configuration
- 06-Packet capture configuration
- 07-NQA configuration
- 08-Track configuration
- 09-BFD configuration
- 10-Monitor Link configuration
- 11-Smart Link configuration
- 12-Interface backup configuration
- 13-Interface collaboration configuration
- 14-System maintenance and debugging configuration
- 15-NTP configuration
- 16-EAA configuration
- 17-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 18-NETCONF configuration
- 19-CWMP configuration
- 20-SNMP configuration
- 21-RMON configuration
- 22-Event MIB configuration
- 23-Process placement configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-NetStream configuration | 160.47 KB |
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with NetStream
Configuring NetStream filtering
Configuring the NetStream data export format
Configuring the refresh rate for NetStream version 9 template
Configuring VXLAN-aware NetStream
Configuring NetStream flow aging
Configuring periodical flow aging
Setting the upper limit for cached NetStream entries
Configuring the NetStream data export
Configuring the NetStream traditional data export
Configuring the NetStream aggregation data export
Display and maintenance commands for NetStream
Configuring session-based NetStream
Session-based NetStream aggregation modes
Session-based NetStream data export
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with session-based NetStream
Restrictions and guidelines: Session-based NetStream configuration
Display and maintenance commands session-based NetStream
Configuring NetStream
About NetStream
NetStream is an accounting technology that provides statistics on a per-flow basis. An IPv4 flow is defined by the following 7-tuple elements:
· Destination IP address.
· Source IP address.
· Destination port number.
· Source port number.
· Protocol number.
· ToS.
· Inbound or outbound interface.
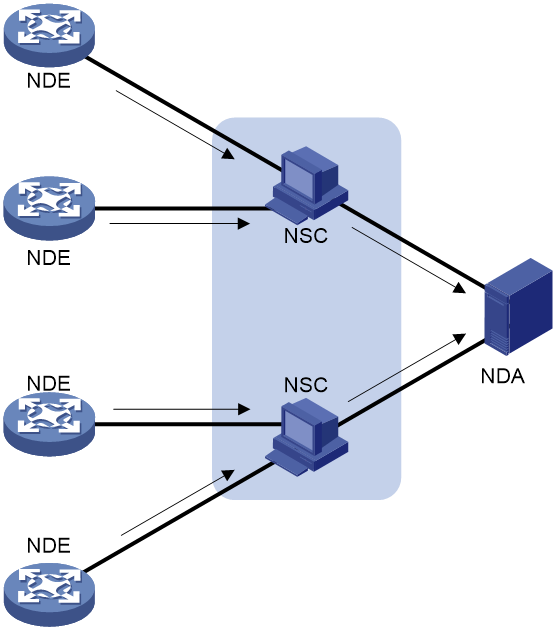
NetStream architecture
A typical NetStream system includes the following elements:
· NetStream data exporter—A device configured with NetStream. The NDE provides the following functions:
¡ Classifies traffic flows by using the 7-tuple elements.
¡ Collects data from the classified flows.
¡ Aggregates and exports the data to the NSC.
· NetStream collector—A program running on an operating system. The NSC parses the packets received from the NDEs, and saves the data to its database.
· NetStream data analyzer—A network traffic analyzing tool. Based on the data in NSC, the NDA generates reports for traffic billing, network planning, and attack detection and monitoring. The NDA can collect data from multiple NSCs. Typically, the NDA features a Web-based system for easy operation.
NSC and NDA are typically integrated into a NetStream server.
Figure 1 NetStream system
NetStream flow aging
NetStream uses flow aging to enable the NDE to export NetStream data to NetStream servers. NetStream creates a NetStream entry for each flow for storing the flow statistics in the cache.
When a flow is aged out, the NDE performs the following operations:
· Exports the summarized data to NetStream servers in a specific format.
· Clears NetStream entry information in the cache.
NetStream supports the following flow aging methods:
· Periodical aging.
· Forced aging.
Periodical aging
Periodical aging uses the following methods:
· Inactive flow aging—A flow is inactive if no packet arrives for the NetStream entry within the inactive flow aging timer. When the timer expires, the following events occur:
¡ The inactive flow entry is aged out.
¡ The statistics of the flow are sent to NetStream servers and are cleared in the cache. The statistics can no longer be displayed by using the display ip netstream cache command.
This method ensures that inactive flow entries are cleared from the cache in a timely manner so new entries can be cached.
· Active flow aging—A flow is active if packets arrive for the NetStream entry within the active flow aging timer. When the timer expires, the statistics of the active flow are exported to NetStream servers. The device continues to collect active flow statistics.
This method periodically exports the statistics of active flows to NetStream servers.
Forced aging
To implement forced aging, use one of the following methods:
· Clear the NetStream cache immediately. All entries in the cache are aged out and exported to NetStream servers.
· Specify the upper limit for cached entries and configure the system to take either of the following actions when the limit is reached:
¡ Age out the oldest entries.
¡ Disable creation of a new entry in the cache.
NetStream data export
Traditional data export
Traditional NetStream collects the statistics of each flow and exports the statistics to NetStream servers.
This method consumes more bandwidth and CPU than the aggregation method, and it requires a large cache size.
Aggregation data export
NetStream aggregation merges the flow statistics according to the aggregation criteria of an aggregation mode, and it sends the summarized data to NetStream servers. The NetStream aggregation data export uses less bandwidth than the traditional data export.
Table 1 lists the available aggregation modes. In each mode, the system merges statistics for multiple flows into statistics for one aggregate flow if each aggregation criterion is of the same value. The system records the statistics for the aggregate flow. These aggregation modes work independently and can take effect concurrently.
For example, when the aggregation mode configured on the NDE is protocol-port, NetStream aggregates the statistics of flow entries by protocol number, source port, and destination port. Four NetStream entries record four TCP flows with the same destination address, source port, and destination port, but with different source addresses. In the aggregation mode, only one NetStream aggregation entry is created and sent to NetStream servers.
Table 1 NetStream aggregation modes
|
Aggregation mode |
Aggregation criteria |
|
AS aggregation |
· Source AS number · Destination AS number · Inbound interface index · Outbound interface index |
|
Protocol-port aggregation |
· Protocol number · Source port · Destination port |
|
Source-prefix aggregation |
· Source AS number · Source address mask length · Source prefix (source network address) · Inbound interface index |
|
Destination-prefix aggregation |
· Destination AS number · Destination address mask length · Destination prefix (destination network address) · Outbound interface index |
|
Source and destination prefix aggregation |
· Source AS number · Destination AS number · Source address mask length · Destination address mask length · Source prefix · Destination prefix · Inbound interface index · Outbound interface index |
|
Prefix-port aggregation |
· Source prefix · Destination prefix · Source address mask length · Destination address mask length · ToS · Protocol number · Source port · Destination port · Inbound interface index · Outbound interface index |
|
ToS-AS aggregation |
· ToS · Source AS number · Destination AS number · Inbound interface index · Outbound interface index |
|
ToS-source-prefix aggregation |
· ToS · Source AS number · Source prefix · Source address mask length · Inbound interface index |
|
ToS-destination-prefix aggregation |
· ToS · Destination AS number · Destination address mask length · Destination prefix · Outbound interface index |
|
ToS-prefix aggregation |
· ToS · Source AS number · Source prefix · Source address mask length · Destination AS number · Destination address mask length · Destination prefix · Inbound interface index · Outbound interface index |
|
ToS-protocol-port aggregation |
· ToS · Protocol type · Source port · Destination port · Inbound interface index · Outbound interface index |
|
ToS-BGP-nexthop |
· ToS · BGP next hop · Outbound interface index |
If packets are not forwarded according to the BGP routing table, the AS number or BGP next hop cannot be obtained.
NetStream export formats
NetStream exports data in UDP datagrams in one of the following formats:
· Version 5—Exports original statistics collected based on the 7-tuple elements and does not support the NetStream aggregation data export. The packet format is fixed and cannot be extended.
· Version 8—Supports the NetStream aggregation data export. The packet format is fixed and cannot be extended.
· Version 9—Based on a template that can be configured according to the template formats defined in RFCs. Version 9 supports exporting the NetStream aggregation data and collecting statistics about BGP next hop packets.
NetStream filtering
NetStream filtering uses an ACL to identify packets. Whether NetStream collects data for identified packets depends on the action in the matching rule.
· NetStream collects data for packets that match permit rules in the ACL.
· NetStream does not collect data for packets that match deny rules in the ACL.
For more information about ACL, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
Protocols and standards
RFC 5101, Specification of the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol for the Exchange of IP Traffic Flow Information
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with NetStream
|
Hardware |
NetStream compatibility |
|
F5010, F5020, F5020-GM, F5030, F5030-6GW, F5040, F5060, F5080, F5000-AI-20, F5000-AI-40, F5000-V30, F5000-C, F5000-S, F5000-M, F5000-A |
No |
|
F1000-AI-20, F1000-AI-30, F1000-AI-50, F1000-AI-60, F1000-AI-70, F1000-AI-80, F1000-AI-90 |
No |
|
F1003-L, F1005-L, F1010-L |
No |
|
F1005, F1010 |
No |
|
F1020, F1020-GM, F1030, F1030-GM, F1050, F1060, F1070, F1070-GM, F1070-GM-L, F1080, F1090, F1000-V70 |
No |
|
F1000-AK1110, F1000-AK1120, F1000-AK1130, F1000-AK1140 |
No |
|
F1000-AK1212, F1000-AK1222, F1000-AK1232, F1000-AK1312, F1000-AK1322, F1000-AK1332 |
No |
|
F1000-AK1414, F1000-AK1424, F1000-AK1434, F1000-AK1514, F1000-AK1524, F1000-AK1534, F1000-AK1614 |
No |
|
F1000-AK108, F1000-AK109, F1000-AK110, F1000-AK115, F1000-AK120, F1000-AK125, F1000-AK710 |
No |
|
F1000-AK130, F1000-AK135, F1000-AK140, F1000-AK145, F1000-AK150, F1000-AK155, F1000-AK160, F1000-AK165, F1000-AK170, F1000-AK175, F1000-AK180, F1000-AK185, F1000-GM-AK370, F1000-GM-AK380, F1000-AK711 |
No |
|
LSU3FWCEA0, LSUM1FWCEAB0, LSX1FWCEA1 |
No |
|
LSXM1FWDF1, LSUM1FWDEC0, IM-NGFWX-IV, LSQM1FWDSC0, LSWM1FWD0, LSPM6FWD, LSQM2FWDSC0 |
No |
|
vFW1000, vFW2000 |
Yes |
NetStream tasks at a glance
To configure NetStream, perform the following tasks:
2. (Optional.) Configuring NetStream filtering
3. (Optional.) Configuring the NetStream data export format
4. (Optional.) Configuring the refresh rate for NetStream version 9 template
5. (Optional.) Configuring VXLAN-aware NetStream
6. (Optional.) Configuring NetStream flow aging
¡ Configuring periodical flow aging
¡ Setting the upper limit for cached NetStream entries
7. Configuring the NetStream data export
a. Configuring the NetStream traditional data export
b. (Optional.) Configuring the NetStream aggregation data export
Enabling NetStream
8. Enter system view.
system-view
9. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
10. Enable NetStream.
ip netstream { inbound | outbound }
By default, NetStream is disabled on an interface.
Configuring NetStream filtering
About this task
NetStream filtering uses an ACL to identify packets.
· To enable NetStream to collect statistics for specific flows, use the ACL permit statements to identify these flows
· To disable NetStream from collecting statistics for specific flows, use the ACL deny statements to identify these flows.
Restrictions and guidelines
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable NetStream filtering on the interface.
ip netstream { inbound | outbound } filter acl ipv4-acl-number
By default, NetStream filtering is disabled. NetStream collects statistics of all IPv4 packets passing through the interface.
Configuring the NetStream data export format
About this task
When you configure the NetStream data export format, you can also specify the following settings:
· Whether or not to export the BGP next hop information.
Exporting the BGP next hop information is supported only by the version 9 format.
· How to export the autonomous system (AS) information: origin-as or peer-as.
¡ origin-as—Records the original AS numbers for the flow source and destination.
¡ peer-as—Records the peer AS numbers for the flow source and destination.
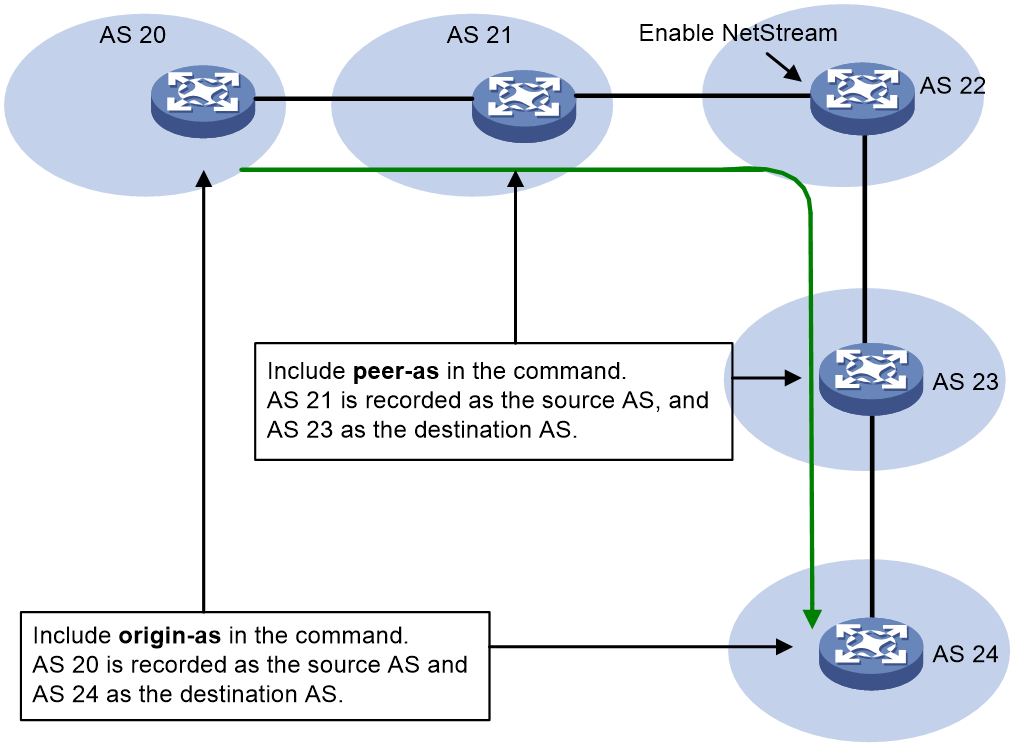
For example, as shown in Figure 2, a flow starts at AS 20, passes AS 21 through AS 23, and then reaches AS 24. NetStream is enabled on the device in AS 22.
· Specify the origin-as keyword to export AS 20 as the source AS and AS 24 as the destination AS.
· Specify the peer-as keyword to export AS 21 as the source AS and AS 23 as the destination AS.
Figure 2 Recorded AS information varies by different keyword configurations
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the NetStream data export format, and configure the AS and BGP next hop export attributes. Choose one option as needed:
¡ Set NetStream data export format to version 5 and configure the AS export attribute.
ip netstream export version 5 { origin-as | peer-as }
¡ Set NetStream data export format to version 9 and configure the AS and BGP export attributes.
ip netstream export version 9 { origin-as | peer-as } [ bgp-nexthop ]
By default:
¡ NetStream data export uses the version 9 format.
¡ The peer AS numbers for the flow source and destination are exported.
¡ The BGP next hop information is not exported.
Configuring the refresh rate for NetStream version 9 template
About this task
Version 9 is template-based and supports user-defined formats. A NetStream device must send the template to NetStream servers regularly, because the servers do not permanently save template.
For a NetStream server to use the correct version 9 template, configure the time-based or packet count-based refresh rate. If both settings are configured, the template is sent when either of the conditions is met.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the refresh rate for the NetStream version 9 template.
ip netstream export v9-template refresh-rate { packet packets | time minutes }
By default, the packet count-based refresh rate is 20 packets, and the time-based refresh interval is 30 minutes.
Configuring VXLAN-aware NetStream
About this task
A VXLAN flow is identified by the same destination UDP port number. VXALN-aware NetStream collects statistics on the VNI information in the VXLAN packets.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Collect statistics on VXLAN packets.
ip netstream vxlan udp-port port-number
By default, statistics about VXLAN packets are not collected.
Configuring NetStream flow aging
Configuring periodical flow aging
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the aging timer for active flows.
ip netstream timeout active minutes
By default, the aging timer for active flows is 30 minutes.
3. Set the aging timer for inactive flows.
ip netstream timeout inactive seconds
By default, the aging timer for inactive flows is 30 seconds.
Setting the upper limit for cached NetStream entries
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the upper limit for cached entries.
ip netstream max-entry max-entries
By default, a maximum of 100000 NetStream entries can be cached.
3. Return to user view.
quit
4. Clear the cache, including the cached NetStream entries and the related statistics.
reset ip netstream statistics
Configuring the NetStream data export
Configuring the NetStream traditional data export
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify a destination host for NetStream traditional data export.
ip netstream export host ip-address udp-port [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no destination host is specified.
3. (Optional.) Specify the source interface for NetStream data packets sent to NetStream servers.
ip netstream export source interface interface-type interface-number
By default, NetStream data packets take the IP address of their output interface (interface that is connected to the NetStream device) as the source IP address.
As a best practice, connect the management Ethernet interface to a NetStream server, and configure the interface as the source interface.
4. (Optional.) Limit the data export rate.
ip netstream export rate rate
By default, the data export rate is not limited.
Configuring the NetStream aggregation data export
About this task
By default, NetStream aggregation uses software to merge flow statistics according to the aggregation mode criteria, and stores the data in the cache.
Restrictions and guidelines
Configurations in NetStream aggregation mode view apply only to the NetStream aggregation data export, and those in system view apply to the NetStream traditional data export. If configurations in NetStream aggregation mode view are not provided, the configurations in system view apply to the NetStream aggregation data export.
If the version 5 format is configured to export NetStream data, NetStream aggregation data export uses the version 8 format.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify a NetStream aggregation mode and enter its view.
ip netstream aggregation { as | destination-prefix | prefix | prefix-port | protocol-port | source-prefix | tos-as | tos-bgp-nexthop | tos-destination-prefix | tos-prefix | tos-protocol-port | tos-source-prefix }
By default, no NetStream aggregation mode is configured.
3. Enable the NetStream aggregation mode.
enable
By default, all NetStream aggregation modes are disabled.
4. Specify a destination host for NetStream aggregation data export.
ip netstream export host ip-address udp-port [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no destination host is specified.
If you expect only NetStream aggregation data, specify the destination host only in the related NetStream aggregation mode view.
5. (Optional.) Specify the source interface for NetStream data packets sent to NetStream servers.
ip netstream export source interface interface-type interface-number
By default, no source interface is specified for NetStream data packets. The packets take the IP address of the output interface as the source IP address.
Source interfaces in different NetStream aggregation mode views can be different.
If no source interface is configured in NetStream aggregation mode view, the source interface configured in system view applies.
Display and maintenance commands for NetStream
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display NetStream entry information. |
display ip netstream cache [ verbose ] [ type { ip | ipl2 | l2 } ] [ destination destination-ip | destination-port destination-port | interface interface-type interface-number | protocol protocol | source source-ip | source-port source-port ] * [ arrived-time start-date start-time end-date end-time ] [ slot slot-number ] |
|
Display information about the NetStream data export. |
display ip netstream export |
|
Display NetStream template information. |
display ip netstream template [ slot slot-number ] |
|
Age out and export all NetStream data, and clear the cache. |
reset ip netstream statistics |
Configuring session-based NetStream
About session-based NetStream
Session-based NetStream provides statistics for session-based services and exports the statistics in NetStream v9 format to NetStream servers.
For information about sessions, see session management in Security Configuration Guide.
Session-based NetStream aggregation modes
Session-based NetStream aggregates session statistics according to the aggregation criteria of an aggregation mode and exports the statistics to NetStream servers.
Table 2 lists the available aggregation modes. In each mode, the system merges statistics for multiple sessions if each aggregation criterion is of the same value.
Table 2 Session-based NetStream aggregation modes
|
Aggregation mode |
Aggregation criteria |
|
App aggregation |
Application layer protocol ID. |
|
App-profile aggregation |
· Application layer protocol ID. · Traffic rule ID. |
|
App-user aggregation |
· Application layer protocol ID. · User IP address. |
Session-based NetStream data export
Session-based NetStream uses an aging mechanism to export flow entry statistics to NetStream servers.
When the aging timer for a session-based NetStream entry expires, statistics about the entry is cleared from the cache and exported to the NetStream servers.
When the session-based NetStream cache is full, the device stops generating new flow entries. Statistics collection for existing flow entries is not affected.
A session-based NetStream entry is also exported in the following situations:
· The session itself ages out.
· The session is manually deleted by the administrator.
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with session-based NetStream
|
Hardware |
NetStream compatibility |
|
F5010, F5020, F5020-GM, F5030, F5030-6GW, F5040, F5060, F5080, F5000-AI-20, F5000-AI-40, F5000-V30, F5000-C, F5000-S, F5000-M, F5000-A |
Yes |
|
F1000-AI-20, F1000-AI-30, F1000-AI-50, F1000-AI-60, F1000-AI-70, F1000-AI-80, F1000-AI-90 |
Yes |
|
F1003-L, F1005-L, F1010-L |
Yes |
|
F1005, F1010 |
Yes |
|
F1020, F1020-GM, F1030, F1030-GM, F1050, F1060, F1070, F1070-GM, F1070-GM-L, F1080, F1090, F1000-V70 |
Yes |
|
F1000-AK1110, F1000-AK1120, F1000-AK1130, F1000-AK1140 |
Yes |
|
F1000-AK1212, F1000-AK1222, F1000-AK1232, F1000-AK1312, F1000-AK1322, F1000-AK1332 |
Yes |
|
F1000-AK1414, F1000-AK1424, F1000-AK1434, F1000-AK1514, F1000-AK1524, F1000-AK1534, F1000-AK1614 |
Yes |
|
F1000-AK108, F1000-AK109, F1000-AK110, F1000-AK115, F1000-AK120, F1000-AK125, F1000-AK710 |
Yes |
|
F1000-AK130, F1000-AK135, F1000-AK140, F1000-AK145, F1000-AK150, F1000-AK155, F1000-AK160, F1000-AK165, F1000-AK170, F1000-AK175, F1000-AK180, F1000-AK185, F1000-GM-AK370, F1000-GM-AK380, F1000-AK711 |
Yes |
|
LSU3FWCEA0, LSUM1FWCEAB0, LSX1FWCEA1 |
Yes |
|
LSXM1FWDF1, LSUM1FWDEC0, IM-NGFWX-IV, LSQM1FWDSC0, LSWM1FWD0, LSPM6FWD, LSQM2FWDSC0 |
Yes |
|
vFW1000, vFW2000 |
No |
Restrictions and guidelines: Session-based NetStream configuration
For session-based NetStream to work, DPI must be enabled on the device. For more information about DPI, see DPI Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable session-based NetStream.
session-based netstream enable
By default, session-based NetStream is disabled.
3. Enable session-based NetStream aggregation modes.
session-based netstream aggregation { app | app-profile | app-user } *
By default, all session-based NetStream aggregation modes are disabled.
4. Specify a destination host for session-based NetStream data export.
session-based netstream export host ip-address udp-port [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no destination host is specified for session-based NetStream data export.
5. (Optional.) Specify a source IP address for session-based NetStream packets.
session-based netstream export source ip ip-address
By default, the source IP address of session-based NetStream packets is the primary IP address of the output interface.
6. (Optional.) Set the aging timer for cached session-based NetStream entries.
session-based netstream timeout minutes
By default, a session-based NetStream entry is can be cached for 5 minutes before being aged out.
Display and maintenance commands session-based NetStream
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display session-based NetStream statistics in the cache. |
display session-based netstream aggregation-cache { app | app-profile | app-user } * |