- Table of Contents
-
- 10-MPLS Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Basic MPLS configuration
- 02-Static LSP configuration
- 03-LDP configuration
- 04-MPLS TE configuration
- 05-Static CRLSP configuration
- 06-RSVP configuration
- 07-Tunnel policy configuration
- 08-MPLS L3VPN configuration
- 09-MPLS L2VPN configuration
- 10-VPLS configuration
- 11-L2VPN access to L3VPN or IP backbone configuration
- 12-MPLS OAM configuration
- 13-MPLS protection switching configuration
- 14-MCE configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-Static CRLSP configuration | 90.59 KB |
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with static CRLSP
Restrictions and guidelines: Static CRLSP configuration
Prerequisites for static CRLSP configuration
Configuring the ingress node of a static CRLSP
Configuring a transit node of a static CRLSP
Configuring the egress node of a static CRLSP
Display and maintenance commands for static CRLSPs
Static CRLSP configuration examples
Example: Configuring a static CRLSP
Configuring a static CRLSP
About static CRLSP
A static Constraint-based Routed Label Switched Path (CRLSP) is established by manually specifying CRLSP setup information on the ingress, transit, and egress nodes of the forwarding path. The CRLSP setup information includes the incoming label, outgoing label, and required bandwidth. If the device does not have enough bandwidth resources required by a CRLSP, the CRLSP cannot be established.
Static CRLSPs consume fewer resources, but they cannot automatically adapt to network topology changes. Therefore, static CRLSPs are suitable for small and stable networks with simple topologies.
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with static CRLSP
|
Hardware |
Static CRLSP compatibility |
|
MSR810, MSR810-W, MSR810-W-DB, MSR810-LM, MSR810-W-LM, MSR810-10-PoE, MSR810-LM-HK, MSR810-W-LM-HK, MSR810-LM-CNDE-SJK, MSR810-CNDE-SJK |
Yes |
|
MSR810-LMS, MSR810-LUS |
No |
|
MSR810-LMS-EA, MSR810-LME |
Yes |
|
MSR2600-6-X1, MSR2600-10-X1 |
Yes |
|
MSR 2630 |
Yes |
|
MSR3600-28, MSR3600-51 |
Yes |
|
MSR3600-28-SI, MSR3600-51-SI |
No |
|
MSR3600-28-X1, MSR3600-28-X1-DP, MSR3600-51-X1, MSR3600-51-X1-DP |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-I-DP, MSR3610-IE-DP, MSR3610-IE-ES, MSR3610-IE-EAD |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-X1, MSR3610-X1-DP, MSR3610-X1-DC, MSR3610-X1-DP-DC |
Yes |
|
MSR 3610, MSR 3620, MSR 3620-DP, MSR 3640, MSR 3660 |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-G, MSR3620-G |
Yes |
|
Hardware |
Static CRLSP compatibility |
|
MSR810-W-WiNet, MSR810-LM-WiNet |
Yes |
|
MSR830-4LM-WiNet |
Yes |
|
MSR830-5BEI-WiNet, MSR830-6EI-WiNet, MSR830-10BEI-WiNet |
Yes |
|
MSR830-6BHI-WiNet, MSR830-10BHI-WiNet |
Yes |
|
MSR2600-6-WiNet, MSR2600-10-X1-WiNet |
Yes |
|
MSR2630-WiNet |
Yes |
|
MSR3600-28-WiNet |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-X1-WiNet |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-WiNet, MSR3620-10-WiNet, MSR3620-DP-WiNet, MSR3620-WiNet, MSR3660-WiNet |
Yes |
|
Hardware |
Static CRLSP compatibility |
|
MSR2630-XS |
Yes |
|
MSR3600-28-XS |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-XS |
Yes |
|
MSR3620-XS |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-I-XS |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-IE-XS |
Yes |
|
Hardware |
Static CRLSP compatibility |
|
MSR810-LM-GL |
Yes |
|
MSR810-W-LM-GL |
Yes |
|
MSR830-6EI-GL |
Yes |
|
MSR830-10EI-GL |
Yes |
|
MSR830-6HI-GL |
Yes |
|
MSR830-10HI-GL |
Yes |
|
MSR2600-6-X1-GL |
Yes |
|
MSR3600-28-SI-GL |
No |
Restrictions and guidelines: Static CRLSP configuration
The outgoing label specified on an LSR must be the same as the incoming label specified on the directly connected downstream LSR.
Static CRLSPs are special static LSPs. They use the same label space as static LSPs. On a device, a static CRLSP and a static LSP cannot use the same incoming label. In addition, a static PW and a static LSP (or a static CRLSP) cannot use the same incoming label.
A static CRLSP can forward MPLS TE traffic only after you create an MPLS TE tunnel interface on the ingress node and specify the static CRLSP for the tunnel interface. For more information about MPLS TE, see "Configuring MPLS TE."
Prerequisites for static CRLSP configuration
Before you configure a static CRLSP, perform the following tasks:
1. Identify the ingress node, transit nodes, and egress node of the CRLSP.
2. Enable MPLS on all interfaces that participate in MPLS forwarding. For more information, see "Configuring basic MPLS."
3. Enable MPLS TE for each node and interface that the CRLSP traverses. For more information, see "Configuring MPLS TE."
Configuring the ingress node of a static CRLSP
About this task
The ingress node performs the following operations to forward MPLS TE traffic:
1. Adds the outgoing label of the static CRLSP to each packet.
2. Forwards the packet to the next hop or out of the outgoing interface.
On the ingress node, you must specify the outgoing label, the next hop or the outgoing interface, and the required bandwidth.
Restrictions and guidelines
Do not configure the next hop address as a local public IP address when configuring the ingress node.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the ingress node of a static CRLSP.
static-cr-lsp ingress lsp-name { nexthop ip-address | outgoing-interface interface-type interface-number } out-label out-label-value [ bandwidth [ ct0 | ct1 | ct2 | ct3 ] bandwidth-value ]
Configuring a transit node of a static CRLSP
About this task
A transit node swaps the label carried in a received packet with a label, and forwards the packet to the next hop or out of the outgoing interface.
On a transit node, you must specify the incoming label, the outgoing label, the next hop or the outgoing interface, and the required bandwidth.
Restrictions and guidelines
Do not configure the next hop address as a local public IP address when configuring a transit node.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure a transit node of a static CRLSP.
static-cr-lsp transit lsp-name in-label in-label-value { nexthop ip-address | outgoing-interface interface-type interface-number } out-label out-label-value [ bandwidth [ ct0 | ct1 | ct2 | ct3 ] bandwidth-value ]
Configuring the egress node of a static CRLSP
About this task
If PHP is not configured, the egress node processes a received packet as follows:
1. Pops the incoming label of a packet.
2. Performs label forwarding according to the inner label of the packet or performs IP forwarding.
Therefore, you must perform this task to specify the incoming label on the egress node.
You do not need to perform this task if PHP is configured. To configure PHP for a static CRLSP, set the outgoing label to 0 or 3 on the penultimate hop of the static CRLSP.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the egress node of a static CRLSP.
static-cr-lsp egress lsp-name in-label in-label-value
Display and maintenance commands for static CRLSPs
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display static CRLSP information. |
display mpls static-cr-lsp [ lsp-name lsp-name ] [ verbose ] |
Static CRLSP configuration examples
Example: Configuring a static CRLSP
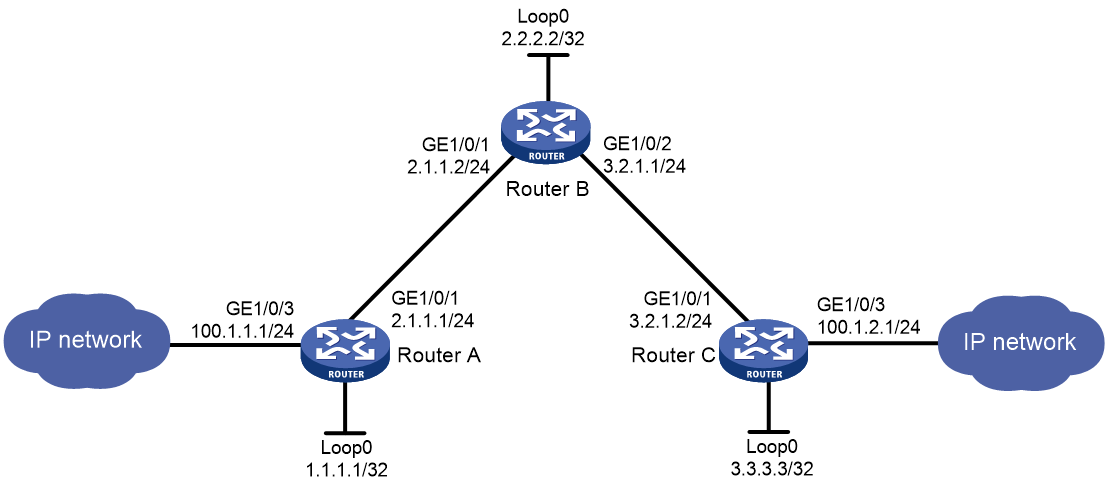
Network configuration
Router A, Router B, and Router C run IS-IS.
Establish an MPLS TE tunnel over a static CRLSP from Router A to Router C to transmit data between the two IP networks. The required bandwidth for the tunnel is 2000 kbps.
The maximum bandwidth for MPLS TE traffic is 10000 kbps, and the maximum reservable bandwidth is 5000 kbps.
Figure 1 Network diagram
Procedure
1. Configure IP addresses and masks for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure IS-IS to advertise interface addresses, including the loopback interface address:
# Configure Router A.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] isis 1
[RouterA-isis-1] network-entity 00.0005.0000.0000.0001.00
[RouterA-isis-1] quit
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] isis enable 1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterA] interface loopback 0
[RouterA-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[RouterA-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure Router B.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] isis 1
[RouterB-isis-1] network-entity 00.0005.0000.0000.0002.00
[RouterB-isis-1] quit
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] isis enable 1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] isis enable 1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
[RouterB] interface loopback 0
[RouterB-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[RouterB-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure Router C.
<RouterC> system-view
[RouterC] isis 1
[RouterC-isis-1] network-entity 00.0005.0000.0000.0003.00
[RouterC-isis-1] quit
[RouterC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] isis enable 1
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterC] interface loopback 0
[RouterC-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[RouterC-LoopBack0] quit
# Execute the display ip routing-table command on each router to verify that the routers have learned the routes to one another, including the routes to the loopback interfaces. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure an LSR ID, and enable MPLS and MPLS TE:
# Configure Router A.
[RouterA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1
[RouterA] mpls te
[RouterA-te] quit
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls enable
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls te enable
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Configure Router B.
[RouterB] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
[RouterB] mpls te
[RouterB-te] quit
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls enable
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls te enable
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] mpls enable
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] mpls te enable
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Configure Router C.
[RouterC] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
[RouterC] mpls te
[RouterC-te] quit
[RouterC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls enable
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls te enable
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
4. Configure MPLS TE attributes:
# On Router A, set the maximum bandwidth and the maximum reservable bandwidth.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 10000
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 5000
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# On Router B, set the maximum bandwidth and the maximum reservable bandwidth.
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 10000
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 5000
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 10000
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 5000
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# On Router C, set the maximum bandwidth and the maximum reservable bandwidth.
[RouterC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 10000
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 5000
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
5. Configure an MPLS TE tunnel on Router A:
# Configure the MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 0.
[RouterA] interface tunnel 0 mode mpls-te
[RouterA-Tunnel0] ip address 6.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# Specify the tunnel destination address as the LSR ID of Router C.
[RouterA-Tunnel0] destination 3.3.3.3
# Configure MPLS TE to use a static CRLSP to establish the tunnel.
[RouterA-Tunnel0] mpls te signaling static
[RouterA-Tunnel0] quit
6. Create a static CRLSP:
# Configure Router A as the ingress node of the static CRLSP, and specify the next hop address as 2.1.1.2, outgoing label as 20, and required bandwidth as 2000 kbps.
[RouterA] static-cr-lsp ingress static-cr-lsp-1 nexthop 2.1.1.2 out-label 20 bandwidth 2000
# On Router A, configure tunnel 0 to use the static CRLSP static-cr-lsp-1.
[RouterA] interface tunnel 0
[RouterA-Tunnel0] mpls te static-cr-lsp static-cr-lsp-1
[RouterA-Tunnel0] quit
# Configure Router B as the transit node of the static CRLSP, and specify the incoming label as 20, next hop address as 3.2.1.2, outgoing label as 30, and required bandwidth as 2000 kbps.
[RouterB] static-cr-lsp transit static-cr-lsp-1 in-label 20 nexthop 3.2.1.2 out-label 30 bandwidth 2000
# Configure Router C as the egress node of the static CRLSP, and specify the incoming label as 30.
[RouterC] static-cr-lsp egress static-cr-lsp-1 in-label 30
7. Configure a static route on Router A to direct traffic destined for subnet 100.1.2.0/24 to MPLS TE tunnel 0.
[RouterA] ip route-static 100.1.2.0 24 tunnel 0 preference 1
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the tunnel interface is up on Router A.
[RouterA] display interface tunnel
Tunnel0
Current state: UP
Line protocol state: UP
Description: Tunnel0 Interface
Bandwidth: 64kbps
Maximum transmission unit: 1496
Internet address: 6.1.1.1/24 (primary)
Tunnel source unknown, destination 3.3.3.3
Tunnel TTL 255
Tunnel protocol/transport CR_LSP
Output queue - Urgent queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/100/0
Output queue - Protocol queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/500/0
Output queue - FIFO queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/75/0
Last clearing of counters: Never
Last 300 seconds input rate: 0 bytes/sec, 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Last 300 seconds output rate: 0 bytes/sec, 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Input: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 drops
Output: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 drops
# Display detailed information about the MPLS TE tunnel on Router A.
[RouterA] display mpls te tunnel-interface
Tunnel Name : Tunnel 0
Tunnel State : Up (Main CRLSP up)
Tunnel Attributes :
LSP ID : 1 Tunnel ID : 0
Admin State : Normal
Ingress LSR ID : 1.1.1.1 Egress LSR ID : 3.3.3.3
Signaling : Static Static CRLSP Name : static-cr-lsp-1
Resv Style : -
Tunnel mode : -
Reverse-LSP name : -
Reverse-LSP LSR ID : - Reverse-LSP Tunnel ID: -
Class Type : - Tunnel Bandwidth : -
Reserved Bandwidth : -
Setup Priority : 0 Holding Priority : 0
Affinity Attr/Mask : -/-
Explicit Path : -
Backup Explicit Path : -
Metric Type : TE
Record Route : - Record Label : -
FRR Flag : - Backup Bandwidth Flag: -
Backup Bandwidth Type: - Backup Bandwidth : -
Route Pinning : -
Retry Limit : 3 Retry Interval : 2 sec
Reoptimization : - Reoptimization Freq : -
Backup Type : - Backup LSP ID : -
Auto Bandwidth : - Auto Bandwidth Freq : -
Min Bandwidth : - Max Bandwidth : -
Collected Bandwidth : - Service Class : -
# Display static CRLSP information on each router.
[RouterA] display mpls lsp
FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE
1.1.1.1/0/1 StaticCR -/20 GE1/0/1
2.1.1.2 Local -/- GE1/0/1
[RouterB] display mpls lsp
FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE
- StaticCR 20/30 GE1/0/2
3.2.1.2 Local -/- GE1/0/2
[RouterC] display mpls lsp
FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE
- StaticCR 30/- -
[RouterA] display mpls static-cr-lsp
Name LSR Type In/Out Label Out Interface State
static-cr-lsp-1 Ingress Null/20 GE1/0/1 Up
[RouterB] display mpls static-cr-lsp
Name LSR Type In/Out Label Out Interface State
static-cr-lsp-1 Transit 20/30 GE1/0/2 Up
[RouterC] display mpls static-cr-lsp
Name LSR Type In/Out Label Out Interface State
static-cr-lsp-1 Egress 30/Null - Up
# Verify that Router A has a static route entry with interface Tunnel 0 as the output interface.
[RouterA] display ip routing-table
Destinations : 12 Routes : 12
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
2.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 2.1.1.1 GE1/0/1
2.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 2.1.1.1 GE1/0/1
2.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
2.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 2.1.1.1 GE1/0/1
2.2.2.2/32 IS_L1 15 10 2.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
100.1.2.0/24 Static 1 0 0.0.0.0 Tun0
3.3.3.3/32 IS_L1 15 20 2.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
6.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 6.1.1.1 Tun0
6.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 6.1.1.1 Tun0
6.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
6.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 6.1.1.1 Tun0