- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S12500X-AF & S12500-X & S9800 Switch Series Configuration Examples-Release 27xx-6W100
- 00-Preface
- 01-CLI configuration
- 02-RBAC configuration
- 03-Login management configuration
- 04-FTP and TFTP configuration
- 05-File system management configuration
- 06-Configuration file management configuration
- 07-Software upgrade configuration
- 08-Emergency shell configuration
- 09-Automatic configuration
- 10-Device management configuration
- 11-Tcl configuration
- 12-Python configuration
- 13-License management
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 06-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples | 184.15 KB |
|
H3C S12500X-AF & S12500-X & S9800 |
Ethernet Link Aggregation |
Configuration Examples |
S12500X-AF Switch Series
S12500-X Switch Series
S9800 Switch Series
Document version: 6W100-20190628
Copyright © 2019 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Contents
Example: Configuring Layer 2 link aggregation· 1
Restrictions and guidelines· 2
Verifying the configuration· 3
Example: Configuring Layer 2 link aggregation load sharing· 5
Restrictions and guidelines· 6
Verifying the configuration· 8
Example: Configuring Layer 2 link aggregation in an IRF fabric· 10
Restrictions and guidelines· 11
Verifying the configuration· 14
Example: Configuring Layer 3 link aggregation· 16
Restrictions and guidelines· 17
Verifying the configuration· 17
Example: Configuring Layer 3 link aggregation load sharing· 19
Restrictions and guidelines· 20
Verifying the configuration· 21
Introduction
This document provides Ethernet link aggregation configuration examples.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples in this document were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of Ethernet link aggregation.
Example: Configuring Layer 2 link aggregation
Network configuration
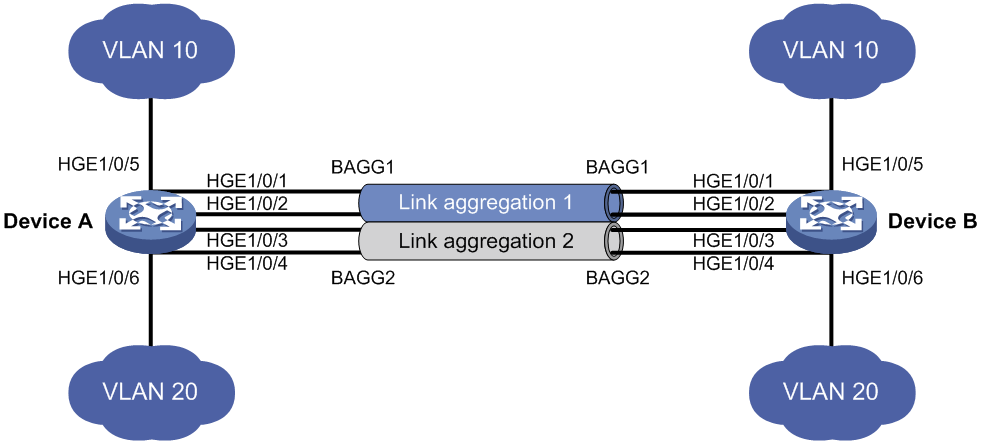
As shown in Figure 1, both Device A and Device B forward traffic from VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
Configure link aggregation on Device A and Device B to meet the following requirements:
· VLAN 10 on Device A can communicate with VLAN 10 on Device B.
· VLAN 20 on Device A can communicate with VLAN 20 on Device B.
Analysis
To enable traffic from VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 to pass through Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1, perform the following tasks:
· Configure Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1 as a trunk port.
· Assign the aggregate interface to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
Software versions used
Table 1 shows the software versions used in this configuration example.
Table 1 Product and software version compatibility
Product | Software version |
S12500X-AF Switch Series | S12500X-CMW710-R2712 |
S12500-X Switch Series | S12500X-CMW710-R2712 |
S9800 Switch Series | S9800-CMW710-R2712 |
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure Layer 2 link aggregation, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· When you assign a port to an aggregation group, the recommended configuration procedure is as follows:
a. Use the display this command in interface view to check the following attribute configurations of the port:
- Port isolation.
- VLAN.
- VLAN mapping.
b. If any of the above configurations exist, use the undo forms of the corresponding commands to remove these configurations. This enables the port to use the default attribute configurations.
c. Assign the port to the aggregation group.
· In a static aggregation group, the Selected state of a port is not affected by whether the peer port is added to an aggregation group and is Selected. As a result, the Selected state of a port might be different from the Selected state of the peer port. When both ends support static aggregation and dynamic aggregation, use dynamic aggregation.
· By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface.
Procedures
1. Configure Device A:
# Create VLAN 10, and assign port HundredGigE 1/0/4 to VLAN 10.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] vlan 10
[DeviceA-vlan10] port hundredgige 1/0/4
[DeviceA-vlan10] quit
# Create VLAN 20, and assign port HundredGigE 1/0/5 to VLAN 20.
[DeviceA] vlan 20
[DeviceA-vlan20] port hundredgige 1/0/5
[DeviceA-vlan20] quit
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1. Use one of the following methods as needed.
¡ Use the static aggregation mode to create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
¡ Use the dynamic aggregation mode to create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign ports HundredGigE 1/0/1 through HundredGigE 1/0/3 to aggregation group 1.
[DeviceA] interface range hundredgige 1/0/1 to hundredgige 1/0/3
[DeviceA-if-range] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceA-if-range] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-if-range] quit
# Configure Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1 as a trunk port.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] port link-type trunk
Configuring HundredGigE1/0/1 done.
Configuring HundredGigE1/0/2 done.
Configuring HundredGigE1/0/3 done.
# Assign the aggregate interface to VLANs 10 and 20.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] port trunk permit vlan 10 20
Configuring HundredGigE1/0/1 done.
Configuring HundredGigE1/0/2 done.
Configuring HundredGigE1/0/3 done.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
2. Configure Device B in the same way Device A is configured. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
# Display detailed information about the link aggregation groups on Device A.
· Link aggregation configuration information when the static aggregation mode is used:
[DeviceA] display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Aggregation Interface: Bridge-Aggregation1
Aggregation Mode: Static
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
Port Status Priority Oper-Key
HGE1/0/1(R) S 32768 1
HGE1/0/2 S 32768 1
HGE1/0/3 S 32768 1
The output shows that all member ports in the local aggregation group are in the Selected state. The Selected states of the local member ports are not affected by the Selected states of the peer member ports.
· Link aggregation configuration information when the dynamic aggregation mode is used:
[DeviceA] display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Aggregation Interface: Bridge-Aggregation1
Creation Mode: Manual
Aggregation Mode: Dynamic
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
System ID: 0x8000, 000f-e234-5678
Local:
Port Status Priority Index Oper-Key Flag
HGE1/0/1 S 32768 2 1 {ACDEF}
HGE1/0/2 S 32768 3 1 {ACDEF}
HGE1/0/3 S 32768 4 1 {ACDEF}
Remote:
Actor Priority Index Oper-Key SystemID Flag
HGE1/0/1(R) 32768 2 1 0x8000, a4e5-c316-0100 {ACDEF}
HGE1/0/2 32768 3 1 0x8000, a4e5-c316-0100 {ACDEF}
HGE1/0/3 32768 4 1 0x8000, a4e5-c316-0100 {ACDEF}
The output shows that the local member ports and the corresponding peer member ports are all Selected. In the dynamic link aggregation mode, each local member port and its peer member port have the same Selected state through exchanging LACPDUs. The user data traffic can be forwarded correctly.
Configuration files
· Device A:
#
vlan 10
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/5
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
¡ In the static aggregation mode:
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation1
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 10 20
¡ In the dynamic aggregation mode:
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation1
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 10 20
link-aggregation mode dynamic
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 10 20
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 10 20
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 10 20
port link-aggregation group 1
#
· Device B:
The configuration file on Device B is the same as the configuration file on Device A.
Example: Configuring Layer 2 link aggregation load sharing
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, both Device A and Device B forward traffic from VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
Configure link aggregation on Device A and Device B to meet the following requirements:
· VLAN 10 on Device A can communicate with VLAN 10 on Device B. VLAN 20 on Device A can communicate with VLAN 20 on Device B.
· The packets from VLAN 10 are load shared across the Selected ports of link aggregation group 1 by source MAC addresses. The packets from VLAN 20 are load shared across the Selected ports of link aggregation group 2 based on packet types.
Analysis
To meet the network requirements, you must perform the following tasks:
· To configure different load sharing modes for packets in different link aggregation groups, configure link aggregation load sharing modes in system view and Layer 2 aggregate interface view.
· To enable packets from VLAN 10 to pass through aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1, assign the aggregate interface to VLAN 10. To enable packets from VLAN 20 to pass through aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 2, assign the aggregate interface to VLAN 20.
Software versions used
Table 2 shows the software versions used in this configuration example.
Table 2 Product and software version compatibility
Product | Software version |
S12500X-AF Switch Series | S12500X-CMW710-R2712 |
S12500-X Switch Series | S12500X-CMW710-R2712 |
S9800 Switch Series | S9800-CMW710-R2712 |
Restrictions and guidelines
When you assign a port to an aggregation group, the recommended configuration procedure is as follows:
1. Use the display this command in interface view to check the following attribute configurations of the port:
¡ Port isolation.
¡ VLAN.
¡ VLAN mapping.
2. If any of the above configurations exist, use the undo forms of the corresponding commands to remove these configurations. This enables the port to use the default attribute configurations.
3. Assign the port to the aggregation group.
By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface.
Procedures
1. Configure Device A:
# Create VLAN 10, and assign port HundredGigE 1/0/5 to VLAN 10.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] vlan 10
[DeviceA-vlan10] port hundredgige 1/0/5
[DeviceA-vlan10] quit
# Create VLAN 20, and assign port HundredGigE 1/0/6 to VLAN 20.
[DeviceA] vlan 20
[DeviceA-vlan20] port hundredgige 1/0/6
[DeviceA-vlan20] quit
# Bring up HundredGigE 1/0/5.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/5
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/5] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/5] quit
# Bring up HundredGigE 1/0/6.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/6
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/6] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/6] quit
# Set the global load sharing mode to load share packets based on source MAC addresses.
[DeviceA] link-aggregation global load-sharing mode source-mac
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign ports HundredGigE 1/0/1 and HundredGigE 1/0/2 to aggregation group 1.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Assign Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1 to VLAN 10.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] port access vlan 10
Configuring HundredGigE1/0/1 done.
Configuring HundredGigE1/0/2 done.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 2.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 2
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation2] undo shutdown
# Configure Layer 2 aggregation group 2 to load share packets based on packet types.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation2] link-aggregation load-sharing mode flexible
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation2] quit
# Assign ports HundredGigE 1/0/3 and HundredGigE 1/0/4 to aggregation group 2.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/3
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/3] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/3] quit
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/4
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/4] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/4] port link-aggregation group 2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/4] quit
# Assign Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 2 to VLAN 20.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 2
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation2] port access vlan 20
Configuring HundredGigE1/0/3 done.
Configuring HundredGigE1/0/4 done.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation2] quit
2. Configure Device B in the same way Device A is configured. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
# Display the information about Selected ports in link aggregation groups on Device A.
[DeviceA] display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected , I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Aggregation Interface: Bridge-Aggregation1
Aggregation Mode: Static
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
Port Status Priority Oper-Key
HGE1/0/1(R) S 32768 1
HGE1/0/2 S 32768 1
Aggregation Interface: Bridge-Aggregation2
Aggregation Mode: Static
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
Port Status Priority Oper-Key
HGE1/0/3(R) S 32768 2
HGE1/0/4 S 32768 2
The output shows the following information:
· Link aggregation groups 1 and 2 are both Layer 2 static aggregation groups.
· Each aggregation group has two Selected ports for forwarding traffic.
# Display the link aggregation load sharing mode of Bridge-aggregation 1.
[DeviceA]display link-aggregation load-sharing mode interface Bridge-Aggregation 1
Bridge-Aggregation1 load-sharing mode:
source-mac address
The output shows that link aggregation group 1 load shares packets based on source MAC addresses.
# Display the link aggregation load sharing mode of Bridge-aggregation 2.
[DeviceA]display link-aggregation load-sharing mode interface Bridge-Aggregation 2
Bridge-Aggregation2 load-sharing mode:
packet type-based sharing
The output shows that link aggregation group 2 load shares packets based on packet types.
Configuration files
· Device A:
#
link-aggregation global load-sharing mode source-mac
#
vlan 10
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/5
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/6
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation1
port access vlan 10
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation2
port access vlan 20
link-aggregation load-sharing mode flexible
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
port link-aggregation group 2
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
port link-aggregation group 2
· Device B:
The configuration file on Device B is the same as the configuration file on Device A.
Example: Configuring Layer 2 link aggregation in an IRF fabric
Network configuration
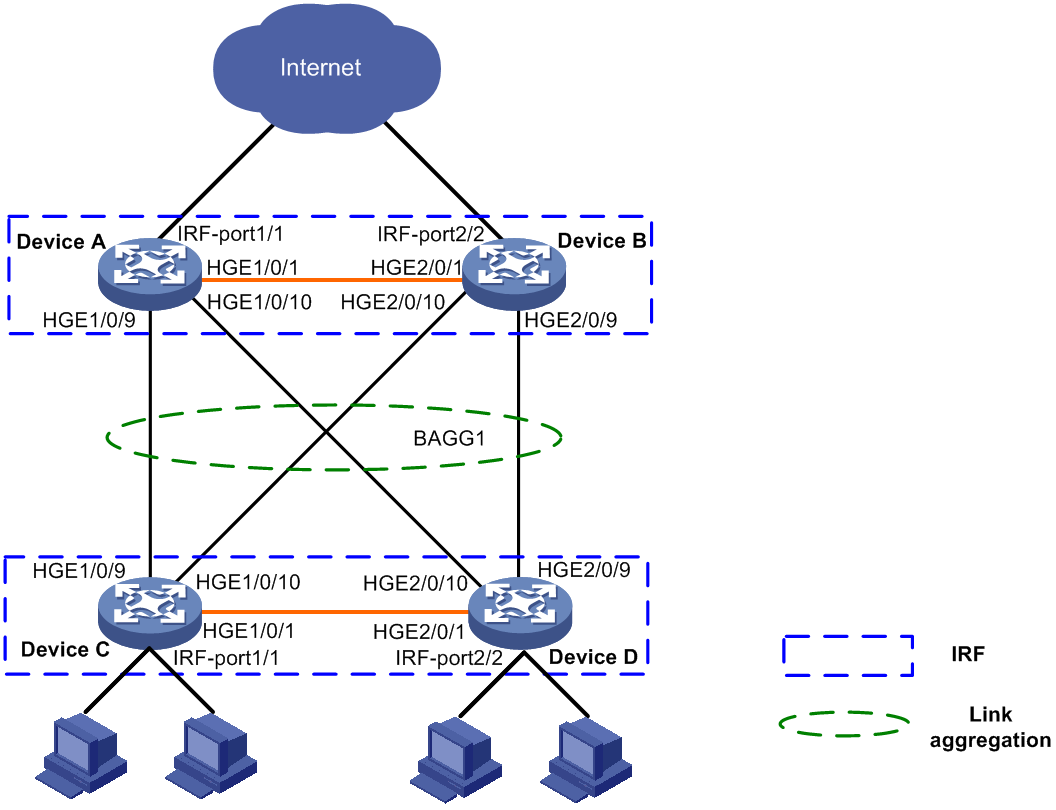
On the network as shown in Figure 3, perform the following tasks:
· Set up a two-chassis IRF fabric at the access layer and a two-chassis IRF fabric at the distribution layer of the enterprise network.
· Configure link aggregation to improve the reliability of the links between the access-layer and distribution-layer IRF fabrics and implement load sharing.
· Run LACP MAD on the two IRF fabrics to detect IRF split.
Software versions used
Table 3 shows the software versions used in this configuration example.
Table 3 Product and software version compatibility
Product | Software version |
S12500X-AF Switch Series | S12500X-CMW710-R2712 |
S12500-X Switch Series | S12500X-CMW710-R2712 |
S9800 Switch Series | S9800-CMW710-R2712 |
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure Layer 2 link aggregation in an IRF fabric, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· IRF physical ports must be set to the bridge mode.
· When you bind physical ports to an IRF port, you must set all the physical ports to operate in either normal or enhanced mode.
· The physical ports of two connected IRF ports must operate in the same mode: normal or enhanced. For more information about the binding mode of the IRF physical ports, see IRF Configuration Guide.
· When you assign a port to an aggregation group, the recommended configuration procedure is as follows:
a. Use the display this command in interface view to check the following attribute configurations of the port:
- Port isolation.
- VLAN.
- VLAN mapping.
b. If any of the above configurations exist, use the undo forms of the corresponding commands to remove these configurations. This enables the port to use the default attribute configurations.
c. Assign the port to the aggregation group.
· In a static aggregation group, the Selected state of a port is not affected by whether the peer port is added to an aggregation group and is Selected. As a result, the Selected state of a port might be different from the Selected state of the peer port. When both ends support static aggregation and dynamic aggregation, use dynamic aggregation.
· By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface.
Procedures
1. Configure IRF on Device A:
# Shut down HundredGigE 1/0/1.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Bind HundredGigE 1/0/1 to IRF port 1/1.
[DeviceA] irf-port 1/1
[DeviceA-irf-port1/1] port group interface hundredgige 1/0/1
You must perform the following tasks for a successful IRF setup:
Save the configuration after completing IRF configuration.
Execute the "irf-port-configuration active" command to activate the IRF ports.
[DeviceA-irf-port1/1] quit
# Bring up HundredGigE1/0/1, and save the configuration.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] save
# Activate the IRF port configuration.
[DeviceA] irf-port-configuration active
2. Configure IRF on Device B:
# Change the member ID of Device B to 2, and reboot the device to validate the change.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] irf member 1 renumber 2
Renumbering the member ID may result in configuration change or loss. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[DeviceB] quit
<DeviceB> reboot
# Shut down HundredGigE 2/0/1.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 2/0/1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE2/0/1] shutdown
[DeviceB-HundredGigE2/0/1] quit
# Bind HundredGigE 2/0/1 to IRF port 2/2.
[DeviceB] irf-port 2/2
[DeviceB-irf-port2/2] port group interface hundredgige 2/0/1
You must perform the following tasks for a successful IRF setup:
Save the configuration after completing IRF configuration.
Execute the "irf-port-configuration active" command to activate the IRF ports.
[DeviceB-irf-port2/2] quit
# Bring up HundredGigE 2/0/1, and save the configuration.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 2/0/1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE2/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceB-HundredGigE2/0/1] quit
[DeviceB] save
# Activate the IRF port configuration.
[DeviceB] irf-port-configuration active
Device A and Device B perform master election, and the one that has lost the election reboots to form an IRF fabric with the master. In this example, Device B reboots.
# Use the display irf command to verify that Device A has become the Master device.
[DeviceA] display irf
MemberID Role Priority CPU-Mac Description
*+1 Master 1 00a0-fc00-5801 ---
2 Standby 1 00e0-fc58-1235 ---
--------------------------------------------------
* indicates the device is the master.
+ indicates the device through which the user logs in.
The bridge MAC of the IRF is: 00a0-fc00-5800
Auto upgrade : yes
Mac persistent : 6 min
Domain ID : 0
Auto merge : yes
3. Configure a Layer 2 aggregation group on Device A:
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 1, and configure the link aggregation mode as dynamic.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] link-aggregation mode dynamic
# Configure Layer 2 aggregation group 1 to load share packets based on packet types.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] link-aggregation load-sharing mode flexible
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign ports HundredGigE 1/0/9, HundredGigE1/0/10, HundredGigE 2/0/9, and HundredGigE 2/0/10 to link aggregation group 1.
[DeviceA] interface range hundredgige 1/0/9 to hundredgige 1/0/10
hundredgige 2/0/9 to hundredgige 2/0/10
[DeviceA-if-range] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceA-if-range] quit
[DeviceA]
Configure LACP MAD on the IRF fabric:
# Set the domain ID of the IRF fabric to 1.
# Enable LACP MAD on Bridge-Aggregation 1.
[DeviceA] interface Bridge-Aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] mad enable
You need to assign a domain ID (range: 0-4294967295)
[Current domain is: 1]:
The assigned domain ID is: 1
MAD LACP only enable on dynamic aggregation interface.
4. Configure IRF on Device C in the same way IRF is configured on Device A. (Details not shown.)
5. Configure IRF on Device D in the same way IRF is configured on Device B. (Details not shown.)
Device C and Device D perform master election, and the one that has lost the election reboots to form an IRF fabric with the master. In this example, Device C reboots.
6. Configure a Layer 2 dynamic aggregation group Bridge-Aggregation 1 on Device C in the same way Bridge-Aggregation 1 is configured on Device A. (Details not shown.)
7. Configure LACP MAD on the IRF fabric:
# Set the domain ID of the IRF fabric to 2.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] irf domain 2
# Enable LACP MAD on Bridge-Aggregation 1.
[DeviceC] interface Bridge-Aggregation 1
[DeviceC-Bridge-Aggregation1] mad enable
You need to assign a domain ID (range: 0-4294967295)
[Current domain is: 2]:
The assigned domain ID is: 2
MAD LACP only enable on dynamic aggregation interface.
Verifying the configuration
# Display the information about the link aggregation groups on Device A.
[DeviceA] display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Aggregate Interface: Bridge-Aggregation1
Creation Mode: Manual
Aggregation Mode: Dynamic
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
System ID: 0x8000, 00a0-fc00-5800
Local:
Port Status Priority Index Oper-Key Flag
HGE1/0/9(R) S 32768 10 1 {ACG}
HGE1/0/10 S 32768 11 1 {ACG}
HGE2/0/9 S 32768 138 1 {ACG}
HGE2/0/10 S 32768 139 1 {ACG}
Remote:
Actor Priority Index Oper-Key SystemID Flag
HGE1/0/9 32768 0 0 0x8000, 0000-0000-0000 {EF}
HGE1/0/10 32768 0 0 0x8000, 0000-0000-0000 {EF}
HGE2/0/9 32768 0 0 0x8000, 0000-0000-0000 {EF}
HGE2/0/10 32768 0 0 0x8000, 0000-0000-0000 {EF}
The output shows that the local member ports and the corresponding peer member ports are all Selected. In the dynamic link aggregation mode, each local member port and its peer member port have the same Selected state through exchanging LACPDUs. The user data traffic can be forwarded correctly.
# Display the load sharing mode of Layer 2 aggregation group 1 on Device A.
[DeviceA] display link-aggregation load-sharing mode interface Bridge-Aggregation 1
Bridge-Aggregation1 load-sharing mode:
packet type-based sharing
The output shows that Layer 2 aggregation group 1 load shares packets based on packet types.
# Shut down physical IRF port HundredGigE 2/0/1 on Device B.
A log message appears on Device A.
[DeviceA]%Jul 9 16:52:41:734 2016 DeviceA STM/3/STM_LINK_DOWN: -MDC=1; IRF port 1 went down.
%Jul 9 16:52:41:800 2016 DeviceA IFNET/3/PHY_UPDOWN: -MDC=1; Physical state on the interface HundredGigE1/0/1 changed to down.
%Jul 9 16:52:41:854 2016 DeviceA IFNET/5/LINK_UPDOWN: -MDC=1; Line protocol state on the interface HundredGigE1/0/1 changed to down.
%Jul 9 16:52:41:867 2016 DeviceA DEV/3/BOARD_REMOVED: -MDC=1; Board was removed from slot 2, type is Simware.
The output shows that IRF split occurs on the distribution layer because HundredGigE 2/0/1 that is bound to IRF port 2/2 is physically down.
Configuration files
· Device A:
#
irf domain 1
irf mac-address persistent timer
irf auto-update enable
irf auto-merge enable
undo irf link-delay
irf member 1 priority 1
irf member 2 priority 1
#
irf-port 1/1
port group interface HundredGigE1/0/1 mode enhanced
#
irf-port 2/2
port group interface HundredGigE1/0/1 mode enhanced
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation1
link-aggregation mode dynamic
link-aggregation load-sharing mode flexible
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/9
port link-mode bridge
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/10
port link-mode bridge
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface HundredGigE2/0/9
port link-mode bridge
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface HundredGigE2/0/10
port link-mode bridge
port link-aggregation group 1
#
· Device C:
The configuration file on Device C is similar as the configuration file on Device A.
Example: Configuring Layer 3 link aggregation
Network configuration
On the network as shown in Figure 4, perform the following tasks:
· Configure a Layer 3 dynamic aggregation group on both Device A and Device B.
· Configure IP addresses and subnet masks for the corresponding Layer 3 aggregate interfaces.
Software versions used
Table 4 shows the software versions used in this configuration example.
Table 4 Product and software version compatibility
Product | Software version |
S12500X-AF Switch Series | S12500X-CMW710-R2712 |
S12500-X Switch Series | S12500X-CMW710-R2712 |
S9800 Switch Series | S9800-CMW710-R2712 |
Restrictions and guidelines
In a static aggregation group, the Selected state of a port is not affected by whether the peer port is added to an aggregation group and is Selected. As a result, the Selected state of a port might be different from the Selected state of the peer port. When both ends support static aggregation and dynamic aggregation, use dynamic aggregation.
By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface.
Procedures
# Create Layer 3 aggregate interface Route-Aggregation 1. Use one of the following methods as needed.
¡ Use the static aggregation mode to create Layer 3 aggregate interface Route-Aggregation 1.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface route-aggregation 1
¡ Use the dynamic aggregation mode to create Layer 3 aggregate interface Route-Aggregation 1.
[DeviceA] interface route-aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Route-Aggregation1] link-aggregation mode dynamic
# Configure an IP address and subnet mask for Layer 3 aggregate interface Route-Aggregation 1.
[DeviceA-Route-Aggregation1] ip address 192.168.1.1 24
[DeviceA-Route-Aggregation1] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-Route-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign ports HundredGigE 1/0/1 through HundredGigE 1/0/3 to aggregation group 1.
[DeviceA] interface range hundredgige 1/0/1 to hundredgige 1/0/3
[DeviceA-if-range] port link-mode route
[DeviceA-if-range] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-if-range] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceA-if-range] quit
Configure Device B in the same way Device A is configured. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
# Display detailed information about the link aggregation groups on Device A.
· Link aggregation configuration information when the static aggregation mode is used:
[DeviceA] display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Aggregate Interface: Route-Aggregation1
Aggregation Mode: Static
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
Port Status Priority Oper-Key
HGE1/0/1 S 32768 1
HGE1/0/2 S 32768 1
HGE1/0/3 S 32768 1
The output shows that all member ports in the local aggregation group are in Selected state. The Selected states of the local member ports are not affected by the Selected states of the peer member ports.
· Link aggregation configuration information when the dynamic aggregation mode is used:
[DeviceA] display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Aggregate Interface: Route-Aggregation1
Creation Mode: Manual
Aggregation Mode: Dynamic
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
System ID: 0x8000, 000f-e267-6c6a
Local:
Port Status Priority Index Oper-Key Flag
HGE1/0/1(R) S 32768 2 1 {ACDEF}
HGE1/0/2 S 32768 3 1 {ACDEF}
HGE1/0/3 S 32768 4 1 {ACDEF}
Remote:
Actor Priority Index Oper-Key SystemID Flag
HGE1/0/1 32768 2 1 0x8000, 68fa-34f2-0200 {ACDEF}
HGE1/0/2 32768 3 1 0x8000, 68fa-34f2-0200 {ACDEF}
HGE1/0/3 32768 4 1 0x8000, 68fa-34f2-0200 {ACDEF}
The output shows that the local member ports and the corresponding peer member ports are all Selected. In the dynamic link aggregation mode, each local member port and its peer member port have the same Selected state through exchanging LACPDUs. The user data traffic can be forwarded correctly.
Configuration files
· Device A:
#
¡ In the static aggregation mode:
#
interface route-aggregation1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
¡ In the dynamic aggregation mode:
#
interface route-aggregation1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
link-aggregation mode dynamic
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode route
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode route
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/3
port link-mode route
port link-aggregation group 1
#
Device B:
The configuration file on Device B is similar as the configuration file on Device A.
Example: Configuring Layer 3 link aggregation load sharing
Network configuration
On the network as shown in Figure 5, perform the following tasks:
· Configure Layer 3 static aggregation groups 1 and 2 on Device A and Device B.
· Configure IP addresses and subnet masks for the corresponding Layer 3 aggregate interfaces.
· Configure link aggregation group 1 to load share packets based on source IP addresses.
· Configure link aggregation group 2 to load share packets based on packet types.
Software versions used
Table 5 shows the software versions used in this configuration example.
Table 5 Product and software version compatibility
Product | Software version |
S12500X-AF Switch Series | S12500X-CMW710-R2712 |
S12500-X Switch Series | S12500X-CMW710-R2712 |
S9800 Switch Series | S9800-CMW710-R2712 |
Restrictions and guidelines
You can configure global or group-specific link aggregation load sharing mode. A link aggregation group preferentially uses the group-specific load sharing mode.
By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface.
Procedures
1. Configure Device A:
# Configure the global load sharing mode to load share packets based on source IP addresses.
[DeviceA] link-aggregation global load-sharing mode source-ip
# Create Layer 3 aggregate interface Route-Aggregation 1.
[DeviceA] interface route-aggregation 1
# Configure an IP address and subnet mask for Layer 3 aggregate interface Route-Aggregation 1.
[DeviceA-Route-Aggregation1] ip address 192.168.1.1 24
[DeviceA-Route-Aggregation1] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-Route-Aggregation1] quit
# Create Layer 3 aggregate interface Route-Aggregation 2.
[DeviceA] interface route-aggregation 2
# Configure Layer 3 aggregation group 2 to load share packets based on packet types.
[DeviceA-Route-Aggregation2] link-aggregation load-sharing mode flexible
# Configure an IP address and subnet mask for Layer 3 aggregate interface Route-Aggregation 2.
[DeviceA-Route-Aggregation2] ip address 192.168.2.1 24
[DeviceA-Route-Aggregation2] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-Route-Aggregation2] quit
# Assign Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces HundredGigE 1/0/1 and HundredGigE 1/0/2 to aggregation group 1.
[DeviceA] interface range hundredgige 1/0/1 hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceA-if-range] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceA-if-range] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-if-range] quit
# Assign Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces HundredGigE 1/0/3 and HundredGigE 1/0/4 to aggregation group 2.
[DeviceA] interface range hundredgige 1/0/3 hundredgige 1/0/4
[DeviceA-if-range] port link-aggregation group 2
[DeviceA-if-range] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-if-range] quit
2. Configure Device B in the same way Device A is configured. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
# Display detailed information about all aggregation groups on Device A.
[DeviceA] display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Aggregate Interface: Route-Aggregation1
Aggregation Mode: Static
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
Port Status Priority Oper-Key
HGE1/0/1(R) S 32768 1
HGE1/0/2 S 32768 1
Aggregate Interface: Route-Aggregation2
Aggregation Mode: Static
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
Port Status Priority Oper-Key
HGE1/0/3(R) S 32768 2
HGE1/0/4 S 32768 2
The output shows that:
· Link aggregation groups 1 and 2 are both load-shared Layer 3 static aggregation groups.
· Each aggregation group contains two Selected ports.
# Display the group-specific load sharing modes of all aggregation groups on Device A.
[DeviceA] display link-aggregation load-sharing mode interface
Route-Aggregation1 load-sharing mode:
source-ip address
Route-Aggregation2 load-sharing mode:
packet type-based sharing
The output shows that:
· Link aggregation group 1 load shares packets based on source IP addresses.
· Link aggregation group 2 load shares packets based on packet types.
Configuration files
· Device A:
#
link-aggregation global load-sharing mode source-mac
#
interface Route-Aggregation1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Route-Aggregation2
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
link-aggregation load-sharing mode destination-ip
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode route
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode route
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/3
port link-mode route
port link-aggregation group 2
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/4
port link-mode route
port link-aggregation group 2
#
· Device B:
The configuration file on Device B is similar as the configuration file on Device A.
Related documentation
· H3C S12500X-AF & S12500-X & S9800 Switch Series Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide (R27xx)
· H3C S12500X-AF & S12500-X & S9800 Switch Series Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference (R27xx)