- Table of Contents
-
- 06-IP Multicast Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Multicast Overview
- 02-IGMP snooping configuration
- 03-PIM snooping configuration
- 04-Multicast VLAN configuration
- 05-Multicast routing and forwarding configuration
- 06-IGMP configuration
- 07-PIM configuration
- 08-MSDP configuration
- 09-MLD snooping configuration
- 10-IPv6 PIM snooping configuration
- 11-IPv6 multicast VLAN configuration
- 12-IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding configuration
- 13-MLD configuration
- 14-IPv6 PIM configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 13-MLD configuration | 234.01 KB |
Configuring basic MLD features
Configuring a static group member
Configuring an IPv6 multicast group policy
Configuring MLD query and response parameters
Enabling fast-leave processing
Displaying and maintaining MLD
Basic MLD features configuration example
MLD SSM mapping configuration example
No member information exists on the receiver-side router
Inconsistent membership information on the routers on the same subnet
Configuring MLD
Overview
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) establishes and maintains IPv6 multicast group memberships between a Layer 3 multicast device and hosts on the directly connected subnet.
MLD has the following versions:
· MLDv1 (defined by RFC 2710), which is derived from IGMPv2.
· MLDv2 (defined by RFC 3810), which is derived from IGMPv3.
The two MLD versions support the ASM model. MLDv2 can directly implement the SSM model, but MLDv1 must work with the MLD SSM mapping feature to implement the SSM model. For more information about the ASM and SSM models, see "Multicast overview."
The term "interface" in this chapter refers to VLAN interfaces.
How MLDv1 works
MLDv1 implements IPv6 multicast listener management based on the query and response mechanism.
Electing the MLD querier
All IPv6 multicast routers that run MLD on the same subnet can monitor MLD listener report messages (often called reports) from hosts. However, only one router can act as the MLD querier to send MLD query messages (often called queries). A querier election mechanism determines which router acts as the MLD querier on the subnet.
1. Initially, every MLD router assumes itself as the querier. Each router sends MLD general query messages (often called general queries) to all hosts and routers on the local subnet. The destination address of the general queriers is FF02::1.
2. After receiving a general query, every MLD router compares the source IPv6 address of the query with its own link-local interface address. The router with the lowest IPv6 address becomes the querier and all other routers become non-queriers.
3. All the non-queriers start the other querier present timer. If a router receives an MLD query from the querier before the timer expires, it resets this timer. Otherwise, it considers the querier has timed out and initiates a new querier election process.
Joining an IPv6 multicast group
Figure 1 MLD queries and reports
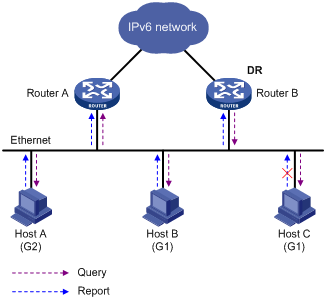
As shown in Figure 1, Host B and Host C are interested in the IPv6 multicast data addressed to IPv6 multicast group G1. Host A is interested in the IPv6 multicast data addressed to G2. The following process describes how the hosts join the IPv6 multicast groups and how the MLD querier (Router B in Figure 1) maintains the IPv6 multicast group memberships:
1. The hosts send unsolicited MLD reports to the IPv6 multicast groups they want to join without having to wait for the MLD queries from the MLD querier.
2. The MLD querier periodically multicasts MLD queries (with the destination address FF02::1) to all hosts and routers on the local subnet.
3. After receiving a query, the host whose report delay timer expires first sends an MLD report to the IPv6 multicast group G1 to announce its membership for G1. In this example, Host B sends the report. Host C, which is on the same subnet as Host B, suppresses its own report for G1 after receiving the report from Host B.
Because the MLD routers already know that G1 has at least one member, other members do not need to report their memberships. This mechanism, known as the MLD report suppression, helps reduce traffic on the local subnet.
4. At the same time, because Host A is interested in G2, it sends a report to the IPv6 multicast group G2.
5. Through the query/report process, the MLD routers determine that G1 and G2 have members on the local subnet. The IPv6 multicast routing protocol (for example, IPv6 PIM) that is running on the routers generates (*, G1) and (*, G2) multicast forwarding entries. These entries are the basis for subsequent IPv6 multicast forwarding. The asterisk (*) represents any IPv6 multicast source.
6. When the IPv6 multicast data addressed to G1 or G2 reaches an MLD router, the router looks up the IPv6 multicast forwarding table. Based on the (*, G1) and (*, G2) entries, the router forwards the IPv6 multicast data to the local subnet. Then, the receivers on the subnet receive the data.
Leaving an IPv6 multicast group
When a host leaves an IPv6 multicast group, the following process occurs:
1. The host sends an MLD done message to all IPv6 multicast routers on the local subnet. The destination address is FF02::2.
2. After receiving the MLD done message, the querier sends a configurable number of multicast-address-specific queries to the group that the host is leaving. The IPv6 multicast addresses queried include both the destination address field and the group address field of the message.
3. One of the remaining members (if any on the subnet) in the group sends a report within the time of the maximum response time advertised in the multicast-address-specific queries.
4. If the querier receives a report for the group within the maximum response time, it maintains the memberships of the IPv6 multicast group. Otherwise, the querier assumes that no hosts on the subnet are interested in IPv6 multicast traffic addressed to that group and stops maintaining the memberships of the group.
MLDv2 enhancements
MLDv2 is based on and backwards-compatible with MLDv1. MLDv2 provides hosts with enhanced control capabilities and enhances the MLD state.
Enhancements in control capability of hosts
MLDv2 has introduced IPv6 multicast source filtering modes (Include and Exclude). These modes allow a host to choose whether to receive or reject multicast data from the specified IPv6 multicast sources. When a host joins an IPv6 multicast group, one of the following occurs:
· If the host expects IPv6 multicast data from specific IPv6 multicast sources like S1, S2, …, it sends a report with Filter-Mode denoted as "Include Sources (S1, S2, …)."
· If the host does not expect IPv6 multicast data from specific IPv6 multicast sources like S1, S2, …, it sends a report with Filter-Mode denoted as "Exclude Sources (S1, S2, …)."
As shown in Figure 2, the network has two IPv6 multicast sources, Source 1 (S1) and Source 2 (S2). Both of the sources can send IPv6 multicast data to IPv6 multicast group G. Host B wants to receive IPv6 multicast data addressed to G from Source 1 but not from Source 2.
Figure 2 Flow paths of multicast-address-and-source-specific multicast traffic
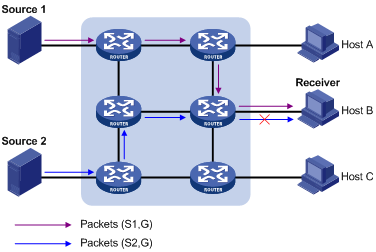
In MLDv1, Host B cannot select IPv6 multicast sources when it joins IPv6 multicast group G. The IPv6 multicast streams from both Source 1 and Source 2 flow to Host B whether it needs them or not.
In MLDv2, Host B can explicitly express its interest in the IPv6 multicast data addressed to G from Source 1 but not from Source 2. As a result, Host B receives only IPv6 multicast data from Source 1.
Enhancement in MLD state
A multicast router that is running MLDv2 maintains the multicast address state for each multicast address on each attached subnet. The multicast address state consists of the following information:
· Filter mode—Router keeps tracing the Include or Exclude state.
· List of sources—Router keeps tracing the newly added or deleted IPv6 multicast source.
· Timers—Filter timers, which include the time that the router waits before switching to the Include mode after an IPv6 multicast address times out, and the source timer for source recording.
MLD SSM mapping
An MLDv2 host can explicitly specify multicast sources in its MLDv2 reports. From the reports, the MLD router can obtain the multicast source addresses and directly provide the SSM service. However, an MLDv1 host cannot specify multicast sources in its MLDv1 reports.
The MLD SSM mapping feature enables the MLD router to provide SSM support for MLDv1 receiver host. The router translates (*, G) in MLDv1 reports into (G, INCLUDE, (S1, S2...)) based on the configured MLD SSM mappings.
As shown in Figure 3, Host A and Host B on the IPv6 SSM network run MLDv1, and Host C runs MLDv2. To provide the SSM service for Host A and Host B, you must configure the MLD SSM mapping feature on Router A.
After MLD SSM mappings are configured, Router A checks the IPv6 multicast group address G carried in the message, and performs the following operations:
· If G is not in the IPv6 SSM group range, Router A provides the ASM service.
· If G is in the IPv6 SSM group range but does not match any MLD SSM mapping, Router A drops the report.
· If G is in the IPv6 SSM group range and matches MLD SSM mappings, Router A translates (*, G) in the report to (G, INCLUDE, (S1, S2...)) to provide SSM services.
|
|
NOTE: The MLD SSM mapping feature does not process MLDv2 reports. |
For more information about the IPv6 SSM group ranges, see "Configuring IPv6 PIM."
MLD support for VPNs
MLD maintains group memberships on a per-interface base. After receiving an MLD message on an interface, MLD processes the packet within the VPN to which the interface belongs. MLD only communicates with other multicast protocols within the same VPN instance.
Protocols and standards
· RFC 2710, Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) for IPv6
· RFC 3810, Multicast Listener Discovery Version 2 (MLDv2) for IPv6
MLD configuration task list
|
Tasks at a glance |
|
Configuring basic MLD features: · (Required.) Enabling MLD · (Optional.) Specifying an MLD version · (Optional.) Configuring a static group member · (Optional.) Configuring an IPv6 multicast group policy |
|
(Optional.) Adjusting MLD performance |
|
(Optional.) Configuring MLD SSM mappings |
|
(Optional.) Enabling MLD NSR |
Configuring basic MLD features
Before you configure basic MLD features, complete the following tasks:
· Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 unicast routing protocol so that all devices can interoperate at the network layer.
· Configure IPv6 PIM.
· Determine the MLD version.
· Determine the IPv6 multicast group address and IPv6 multicast source address for static group member configuration.
· Determine the ACL rule for IPv6 multicast group filtering.
Enabling MLD
Enable MLD on the interface on which IPv6 multicast group memberships are created and maintained.
To enable MLD:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable IPv6 multicast routing and enter IPv6 MRIB view. |
ipv6 multicast routing [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] |
By default, IPv6 multicast routing is disabled. |
|
3. Return to system view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
4. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
5. Enable MLD. |
mld enable |
By default, MLD is disabled. |
Specifying an MLD version
You must specify the same MLD version for all routers on the same subnet. Otherwise, MLD cannot operate correctly.
To specify an MLD version:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure an MLD version on the interface. |
mld version version-number |
The default setting is MLDv1. |
Configuring a static group member
You can configure an interface as a static group member of an IPv6 multicast group. The interface can always receive IPv6 multicast data for the group.
The static group member does not respond to MLD queries from the MLD querier. When you complete or cancel this configuration, the interface does not send an unsolicited MLD report or done message. This is because the interface is not a real member of the IPv6 multicast group.
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
The interface to be configured as a static group member of an IPv6 multicast group has the following restrictions:
· If the interface is MLD and IPv6 PIM-SM enabled, it must be an IPv6 PIM-SM DR.
· If the interface is MLD enabled but not IPv6 PIM-SM enabled, it must be an MLD querier.
For more information about IPv6 PIM-SM and DR, see "Configuring IPv6 PIM."
Configuration procedure
To configure a static group member:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the interface as a static group member. |
mld static-group ipv6-group-address [ source ipv6-source-address ] |
By default, the interface is not a static member of any IPv6 multicast groups. |
Configuring an IPv6 multicast group policy
This feature enables the switch to filter MLD reports based on the used ACL that specifies IPv6 multicast groups and the optional sources. It is used to control the IPv6 multicast groups that the hosts attached to an interface can join.
To configure an IPv6 multicast group policy:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure an IPv6 multicast group policy on an interface. |
mld group-policy acl6-number [ version-number ] |
By default, the interface is not configured with an IPv6 multicast group policy. The hosts attached to the interface can join any IPv6 multicast groups. |
|
|
NOTE: If you configure the interface as a static group member for an IPv6 multicast group or an IPv6 multicast source and group, this configuration is not effective on the IPv6 multicast group or the IPv6 multicast source and group. |
Adjusting MLD performance
Before adjusting MLD performance, complete the following tasks:
· Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 unicast routing protocol so that all devices can interoperate at the network layer.
· Configure basic MLD features.
Configuring MLD query and response parameters
The following are MLD query and response parameters:
· MLD querier's robustness variable—Number of times for retransmitting MLD queries in case of packet loss. A higher robustness variable makes the MLD querier more robust, but increases the timeout time for IPv6 multicast groups.
· MLD startup query interval—Interval at which an MLD querier sends MLD general queries at startup.
· MLD startup query count—Number of MLD general queries that an MLD querier sends at startup.
· MLD general query interval—Interval at which an MLD querier sends MLD general queries to check for IPv6 multicast group members on the network.
· MLD last listener query interval—In MLDv1, it sets the interval at which a querier sends multicast-address-specific queries after receiving a done message. In MLDv2, it sets the interval at which a querier sends multicast-address-and-source-specific queries after receiving a report that changes IPv6 multicast source and group mappings.
· MLD last listener query count—In MLDv1, it sets the number of multicast-address-specific queries that the querier sends after receiving a done message. In MLDv2, it sets the number of multicast-address-and-source-specific queries that the querier sends after receiving a report that changes IPv6 multicast group and source mappings.
· MLD maximum response time—Maximum time before a receiver responds with a report to an MLD general query. This per-group timer is initialized to a random value in the range of 0 to the maximum response time specified in the MLD query. When the timer value decreases to 0, the receiver sends an MLD report to the group.
· MLD other querier present timer—Lifetime for an MLD querier after a non-querier receives an MLD general query. If the non-querier does not receive a new query when this timer expires, the non-querier considers that the querier has failed and starts a new querier election.
Configuration guidelines
When you configure the MLD query and response parameters, follow these guidelines:
· You can configure the MLD query and response parameters for the current interface in interface view or globally for all interfaces in MLD view. The configuration made in interface view takes priority over the configuration made in MLD view.
· To avoid frequent MLD querier changes, set the MLD other querier present timer greater than the MLD general query interval.
· To speed up the response to MLD queries and avoid simultaneous timer expirations that cause MLD report traffic bursts, you must set an appropriate maximum response time.
¡ For MLD general queries, the maximum response time is set by the max-response-time command.
¡ For MLD multicast-address-specific queries or MLD multicast-address-and-source-specific queries, the maximum response time equals the MLD last listener query interval.
Configuring the MLD query and response parameters globally
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
N/A |
|
|
2. Enter MLD view. |
N/A |
|
|
3. Set the MLD querier's robustness variable. |
By default, the MLD querier's robustness variable is 2. |
|
|
4. Set the MLD startup query interval. |
By default, the MLD startup query interval equals one quarter of the MLD general query interval. |
|
|
5. Set the MLD startup query count. |
By default, the MLD startup query count equals the MLD querier's robustness variable. |
|
|
6. Set the MLD general query interval. |
By default, the MLD general query interval is 125 seconds. |
|
|
7. Set the MLD last listener query interval. |
By default, the MLD last listener query interval is 1 second. |
|
|
8. Set the MLD last listener query count. |
By default, the MLD last listener query count equals the MLD querier's robustness variable. |
|
|
9. Set the maximum response time for MLD general queries. |
By default, the maximum response time for MLD general queries is 10 seconds. |
|
|
10. Set the MLD other querier present timer. |
By default, the MLD other querier present timer is [ MLD general query interval ] × [ MLD robustness variable ] + [ maximum response time for MLD general queries ] / 2. |
Configuring the MLD query and response parameters on an interface
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
N/A |
|
|
2. Enter interface view. |
N/A |
|
|
3. Set the MLD querier's robustness variable. |
By default, the MLD querier's robustness variable is 2. |
|
|
4. Set the MLD startup query interval. |
By default, the MLD startup query interval equals one quarter of the MLD general query interval. |
|
|
5. Set the MLD startup query count. |
By default, the MLD startup query count equals the MLD querier's robustness variable. |
|
|
6. Set the MLD general query interval. |
By default, the MLD general query interval is 125 seconds. |
|
|
7. Set the MLD last listener query interval. |
By default, the MLD last listener query interval is 1 second. |
|
|
8. Set the MLD last listener query count. |
By default, the MLD last listener query count equals the MLD querier's robustness variable. |
|
|
9. Set the maximum response time for MLD general queries. |
By default, the maximum response time for MLD general queries is 10 seconds. |
|
|
10. Set the MLD other querier present timer. |
By default, the MLD other querier present timer is [ MLD general query interval ] × [ MLD robustness variable ] + [ maximum response time for MLD general queries ] / 2. |
Enabling fast-leave processing
This feature enables the MLD querier to send a leave notification directly to the upstream without sending multicast-address-specific queries or multicast-address-and-source-specific queries after receiving a done message. This feature reduces leave latency and preserves the network bandwidth.
To enable fast-leave processing:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable fast-leave processing. |
mld fast-leave [ group-policy acl6-number ] |
By default, fast-leave processing is disabled. |
Configuring MLD SSM mappings
This feature enables the switch to provide SSM services for MLDv1 hosts.
This feature does not process MLDv2 messages. As a best practice, enable MLDv2 on the receiver-side interface to ensure that MLDv2 reports can be processed.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure MLD SSM mappings, complete the following tasks:
· Configure an IPv6 unicast routing protocol so that all devices in the domain can interoperate at the network layer.
· Configure basic MLD features.
Configuration procedure
To configure MLD SSM mappings:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter MLD view. |
N/A |
|
|
3. Configure MLD SSM mappings. |
By default, MLD SSM mappings are not configured. |
Enabling MLD NSR
This feature enables the switch to back up information about MLD interfaces and MLD forwarding entries to the standby process. After an active/standby switchover, the switch can recover the information without cooperation of other devices. This prevents an active/standby switchover from affecting the multicast service.
To enable MLD NSR:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable MLD NSR. |
mld non-stop-routing |
By default, MLD NSR is disabled. |
Displaying and maintaining MLD
|
|
CAUTION: The reset mld group command might cause IPv6 multicast data transmission failures. |
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display MLD group information. |
display mld [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] group [ ipv6-group-address | interface interface-type interface-number ] [ static | verbose ] |
|
Display MLD information. |
display mld [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] interface [ interface-type interface-number ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display MLD SSM mappings. |
display mld [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] ssm-mapping ipv6-group-address |
|
Clear dynamic group entries. |
reset mld [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] group { all | interface interface-type interface-number { all | ipv6-group-address [ prefix-length ] [ ipv6-source-address [ prefix-length ] ] } } |
MLD configuration examples
Basic MLD features configuration example
Network requirements
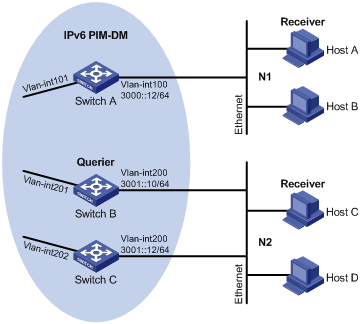
As shown in Figure 4:
· OSPFv3 and IPv6 PIM-DM run on the network.
· VOD streams are sent to receiver hosts in multicast. Receiver hosts of different organizations form stub networks N1 and N2. Host A and Host C are multicast receiver hosts in N1 and N2, respectively.
· MLDv1 runs between Switch A and N1, and between the other two switches (Switch B and Switch C) and N2. Switch A acts as the MLD querier in N1.
· Switch B acts as the MLD querier in N2 because it has a lower IPv6 address.
Configure IPv6 multicast group filtering on Switch A to achieve the following goals:
· The hosts in N1 can join only IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101.
· The hosts in N2 can join any IPv6 multicast groups.
Configuration procedure
1. Assign an IPv6 address and prefix length to each interface as shown in Figure 4. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPFv3 on the switches in the IPv6 PIM-DM domain. (Details not shown.)
3. Enable the IPv6 multicast routing, MLD, and IPv6 PIM-DM:
# On Switch A, enable IPv6 multicast routing globally.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ipv6 multicast routing
[SwitchA-mrib6] quit
# Enable MLD on VLAN-interface 100.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] mld enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Enable IPv6 PIM-DM on VLAN-interface 101.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 101
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] ipv6 pim dm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] quit
# On Switch B, enable IPv6 multicast routing globally.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ipv6 multicast routing
[SwitchB-mrib6] quit
# Enable MLD on VLAN-interface 200.
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 200
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface200] mld enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface200] quit
# Enable IPv6 PIM-DM on VLAN-interface 201.
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 201
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface201] ipv6 pim dm
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface201] quit
# On Switch C, enable IPv6 multicast routing globally.
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] ipv6 multicast routing
[SwitchC-mrib6] quit
# Enable MLD on VLAN-interface 200.
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 200
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] mld enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] quit
# Enable IPv6 PIM-DM on VLAN-interface 202.
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 202
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface202] ipv6 pim dm
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface202] quit
4. Configure an IPv6 multicast group policy on Switch A so that the hosts connected to VLAN-interface 100 can join IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101 only.
[SwitchA] acl ipv6 number 2001
[SwitchA-acl6-basic-2001] rule permit source ff1e::101 128
[SwitchA-acl6-basic-2001] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] mld group-policy 2001
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display MLD information on VLAN-interface 200 of Switch B.
[SwitchB] display mld interface vlan-interface 200
Vlan-interface200(FE80::200:5EFF:FE66:5100):
MLD is enabled.
MLD version: 1
Query interval for MLD: 125s
Other querier present time for MLD: 255s
Maximum query response time for MLD: 10s
Querier for MLD: FE80::200:5EFF:FE66:5100 (This router)
MLD groups reported in total: 1
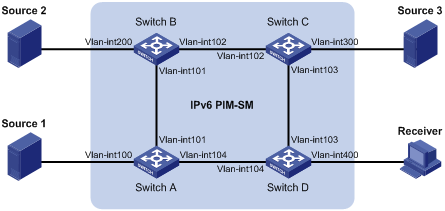
MLD SSM mapping configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 5:
· OSPFv3 runs on the network.
· The IPv6 PIM-SM domain uses both the ASM model and SSM model for IPv6 multicast delivery. VLAN-interface 104 of Switch D acts as the C-BSR and C-RP. The SSM group range is FF3E::/64.
· MLDv2 runs on VLAN-interface 400 of Switch D. The receiver host runs MLDv1, and does not support MLDv2. Therefore, the Receiver host cannot specify expected multicast sources in its membership reports.
· Source 1, Source 2, and Source 3 send IPv6 multicast packets to multicast groups in the IPv6 SSM group range.
Configure the MLD SSM mapping feature on Switch D so that the receiver host will receive IPv6 multicast data only from Source 1 and Source 3.
Table 1 Interface and IPv6 address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IPv6 address |
Device |
Interface |
IPv6 address |
|
— |
— |
||||
|
— |
— |
||||
|
Switch A |
Switch C |
||||
|
Switch A |
Switch C |
||||
|
Switch B |
Switch D |
||||
|
Switch B |
Switch D |
Configuration procedure
1. Assign an IPv6 address and prefix length to each interface according to Table 1. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPFv3 on the switches in the IPv6 PIM-SM domain. (Details not shown.)
3. Enable IPv6 multicast routing, and enable IPv6 PIM-SM and MLD:
# On Switch D, enable IPv6 multicast routing.
<SwitchD> system-view
[SwitchD] ipv6 multicast routing
[SwitchD-mrib6] quit
# Enable MLDv2 on the receiver-side interface (VLAN-interface 400).
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 400
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface400] mld enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface400] mld version 2
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface400] quit
# Enable IPv6 PIM-SM on the other interfaces.
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 103
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface103] ipv6 pim sm
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface103] quit
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 104
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface104] ipv6 pim sm
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface104] quit
# On Switch A, enable IPv6 multicast routing.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ipv6 multicast routing
[SwitchA-mrib6] quit
# Enable IPv6 PIM-SM on each interface.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 pim sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 101
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] ipv6 pim sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 104
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface104] ipv6 pim sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface104] quit
# Configure Switch B and Switch C in the same way Switch A is configured. (Details not shown.)
4. Configure a C-BSR and a C-RP on Switch D.
[SwitchD] pim ipv6
[SwitchD-pim6] c-bsr 1003::2
[SwitchD-pim6] c-rp 1003::2
[SwitchD-pim6] quit
5. Configure the IPv6 SSM group range:
# Configure the IPv6 SSM group range FF3E::/64 on Switch D.
[SwitchD] acl ipv6 number 2000
[SwitchD-acl6-basic-2000] rule permit source ff3e:: 64
[SwitchD-acl6-basic-2000] quit
[SwitchD] ipv6 pim
[SwitchD-pim6] ssm-policy 2000
[SwitchD-pim6] quit
# Configure Switch A, Switch B, and Switch C in the same way Switch D is configured. (Details not shown.)
6. Configure MLD SSM mappings on Switch D.
[SwitchD] mld
[SwitchD-mld] ssm-mapping 1001::1 2000
[SwitchD-mld] ssm-mapping 3001::1 2000
[SwitchD-mld] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display MLD SSM mappings for IPv6 multicast group FF3E::101 on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display mld ssm-mapping ff3e::101
Group: FF3E::101
Source list:
1001::1
3001::1
# Display MLD information for IPv6 multicast groups on Switch D.
MLD groups in total: 1
Vlan-interface400(FE80::101):
MLD groups reported in total: 1
Group address: FF3E::101
Last reporter: FE80::1
Uptime: 00:02:04
Expires: Off
# Display IPv6 PIM routing table information on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display ipv6 pim routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 2 (S, G) entry
(1001::1, FF3E::101)
RP: 1003::2
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag:
UpTime: 00:13:25
Upstream interface: Vlan-interface104
Upstream neighbor: 1003::1
RPF prime neighbor: 1003::1
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface400
Protocol: mld, UpTime: 00:13:25, Expires: -
(3001::1, FF3E::101)
RP: 1003::2
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag:
UpTime: 00:13:25
Upstream interface: Vlan-interface103
Upstream neighbor: 3002::1
RPF prime neighbor: 3002::1
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface400
Protocol: mld, UpTime: 00:13:25, Expires: -
Troubleshooting MLD
No member information exists on the receiver-side router
Symptom
When a host sends a message to announce that it is joining IPv6 multicast group G, no member information of multicast group G exists on the immediate router.
Solution
To resolve the problem:
1. Use the display mld interface command to verify that the networking, interface connections, and IP address configuration are correct.
2. Use the display current-configuration command to verify that the IPv6 multicast routing is enabled. If it is not enabled, use the ipv6 multicast routing command in system view to enable IPv6 multicast routing. In addition, verify that MLD is enabled on the associated interfaces.
3. Use the display mld interface command to verify that the MLD version on the interface is lower than that on the host.
4. Use the display current-configuration interface command to verify that no ACL rule has been configured to filter the reports sent by the host to the IPv6 multicast group G.
5. If the problem persists, contact H3C Support.
Inconsistent membership information on the routers on the same subnet
Symptom
Different memberships are maintained on different MLD routers on the same subnet.
Solution
To resolve the problem:
1. Use the display current-configuration command to verify the MLD information on the interface.
2. Use the display mld interface command on all routers on the same subnet to check the MLD timers for inconsistent configurations.
3. Use the display mld interface command to verify that the routers are running the same MLD version.
4. If the problem persists, contact H3C Support.