- Table of Contents
-
- 02-Layer 2-LAN Switching Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Ethernet interface configuration
- 02-Loopback and null interface configuration
- 03-Bulk interface configuration
- 04-MAC address table configuration
- 05-Ethernet link aggregation configuration
- 06-Port isolation configuration
- 07-Spanning tree configuration
- 08-BPDU tunneling configuration
- 09-VLAN configuration
- 10-GVRP configuration
- 11-LLDP configuration
- 12-Service loopback group configuration
- 13-MVRP configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 12-Service loopback group configuration | 115.91 KB |
Configuring service loopback groups
Service types of service loopback groups
States of service loopback ports
Displaying and maintaining service loopback groups
Service loopback group configuration example
This chapter describes how to configure service loopback groups.
Overview
A service loopback group contains one or multiple Ethernet ports for looping packets sent out by the device back to the device. This feature must work with other features, such as GRE. Member ports in a service loopback group are load balanced.
Service types of service loopback groups
A service loopback group provides one of the following services:
· Tunnel—Supports unicast tunnel traffic.
· Multicast tunnel—Supports multicast tunnel traffic.
The device supports only one service loopback group for each service type. However, you can use one service loopback group with multiple features.
States of service loopback ports
A service loopback group member port is placed in one of the following states:
· Selected—A selected port can loop back user traffic.
· Unselected—An unselected port cannot loop back user traffic.
The system sets the state of each member port in a service loopback group to selected or unselected by using the following workflow.
1. Selects the full-duplex port with the highest rate as the reference port. If two ports have the same duplex mode and speed, the one with the lower port number is selected.
2. Sets the state of each member port in the service loopback group, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Setting the state of each member port in a service loopback group
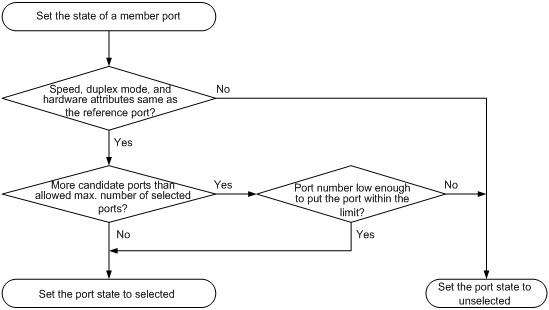
Each time a new port is assigned to the service loopback group, the system sets the state of all the member ports all over again.
Configuration procedure
When you configure a service loopback group, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· Make sure the ports you are assigning to a service loopback group meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Requirements |
|
Link type |
Access. |
|
Aggregation membership |
The ports are not members of link aggregation groups or any other service loopback group. |
|
Support for services |
The ports support the service type of the service loopback group. |
|
Feature compatibility |
The following features are not configured on the ports: · 802.1X · Isolate-user-VLAN · MAC authentication · MSTP · NDP · Port security · Uplink/downlink ports of a port isolation group NOTE: On service loopback group member ports, you can only configure port attributes (including port rate and duplex mode), ACL, and QoS. |
· To change the service type of a service loopback group successfully, make sure the following requirements are met:
¡ The service group has not been referenced by a feature.
¡ The attributes of all member ports are not conflict with the target service type.
¡ No service group has been created for the target service type.
· For correct traffic processing, make sure a service loopback group has at least one member port when it is being used by a feature.
To configure a service loopback group:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Create a service loopback group and specify its service type. |
service-loopback group number type { multicast-tunnel | tunnel } * |
N/A |
|
3. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
4. Assign the port to a service loopback group. |
port service-loopback group number |
By default, a port does not belong to any service loopback group. Repeat this command to assign multiple ports to a service loopback group. |
Displaying and maintaining service loopback groups
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display information about service loopback groups. |
display service-loopback group [ number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
Service loopback group configuration example
Network requirements
All Ethernet ports of Device A support tunnel service. Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to a service loopback group for tunnel traffic loopback.
Configuration procedure
# Create service loopback group 1, and specify the service type as Tunnel (unicast tunnel service).
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] service-loopback group 1 type tunnel
# Disable MSTP and NDP on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/3, and then assign them to service loopback group 1.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo stp enable
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo ndp enable
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port service-loopback group 1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo ndp enable
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port service-loopback group 1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] undo stp enable
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo ndp enable
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Create logical interface Tunnel 1 and reference service loopback group 1 on Tunnel 1.
[DeviceA] interface tunnel 1
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] service-loopback-group 1
