- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-Multicast VLAN Configuration | 125.32 KB |
Contents
Introduction to multicast VLAN
Multicast VLAN configuration task list
Configuring user port attributes
Configuring multicast VLAN ports
Displaying and maintaining multicast VLAN
Multicast VLAN configuration example
This chapter includes these sections:
· Introduction to multicast VLAN
· Multicast VLAN configuration task list
· Displaying and maintaining multicast VLAN
· Multicast VLAN configuration example
|
|
NOTE: · The term "switch" or "device" in this chapter refers to the switching engine on a WX3000E wireless switch. · The WX3000E series comprises WX3024E and WX3010E wireless switches. · The port numbers in this chapter are for illustration only. |
Introduction to multicast VLAN
In the traditional multicast programs-on-demand mode shown in Figure 1, , when hosts— Host A, Host B and Host C—that belong to different VLANs require multicast programs-on-demand service, the Layer 3 device—Router A—must forward a separate copy of the multicast traffic in each user VLAN to the Layer 2 device—Switch A. This results in not only waste of network bandwidth but also extra burden on the Layer 3 device.
Figure 1 Multicast transmission without multicast VLAN
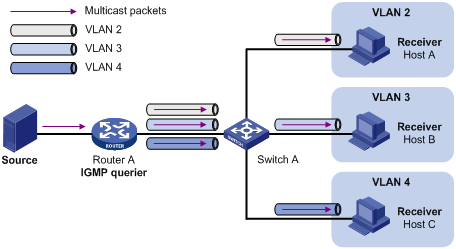
The multicast VLAN feature configured on the Layer 2 device is the solution to this issue. With the multicast VLAN feature, the Layer 3 device replicates the multicast traffic only in the multicast VLAN instead of making a separate copy of the multicast traffic in each user VLAN. This saves network bandwidth and lessens the burden on the Layer 3 device.
As shown in Figure 2, Host A, Host B and Host C are in three different user VLANs. All the user ports (ports with attached hosts) on Switch A are hybrid ports. On Switch A, configure VLAN 10 as a multicast VLAN, assign all the user ports to this multicast VLAN, and enable IGMP snooping in the multicast VLAN and all the user VLANs.
Figure 2 Port-based multicast VLAN
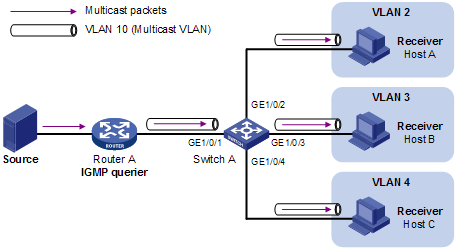
After the configuration, if Switch A receives an IGMP message on a user port, it tags the message with the multicast VLAN ID and relays it to the IGMP querier, so that IGMP snooping can uniformly manage the router ports and member ports in the multicast VLAN. When forwarding multicast data to Switch A, Router A needs to send only one copy of multicast traffic to Switch A in the multicast VLAN, and Switch A distributes the traffic to all the member ports in the multicast VLAN.
Multicast VLAN configuration task list
Complete the following tasks to configure multicast VLAN:
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
Required |
|
|
Required |
Configuring multicast VLAN
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure port-based multicast VLAN, complete the following tasks:
· Create VLANs as required
· Enable IGMP snooping in the VLAN to be configured as a multicast VLAN
· Enable IGMP snooping in all the user VLANs
Configuring user port attributes
Configure the user ports as hybrid ports that permit packets of the specified user VLAN to pass, and configure the user VLAN to which the user ports belong as the default VLAN.
Configure the user ports to permit packets of the multicast VLAN to pass and untag the packets. Thus, after receiving multicast packets tagged with the multicast VLAN ID from the upstream device, the Layer 2 device untags the multicast packets and forwards them to its downstream device.
Follow these steps to configure user port attributes:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter interface view or port group view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Required Use either command |
|
port-group { manual port-group-name | aggregation agg-id } |
||
|
Configure the user port link type as hybrid |
port link-type hybrid |
Required Access by default |
|
Specify the user VLAN that comprises the current user port or ports as the default VLAN |
port hybrid pvid vlan vlan-id |
Required VLAN 1 by default |
|
Configure the current user port or ports to permit packets of the specified multicast VLAN or VLANs to pass and untag the packets |
port hybrid vlan vlan-id-list untagged |
Required By default, a hybrid port permits only packets of VLAN 1 to pass. |
|
|
NOTE: For more information about the port link-type, port hybrid pvid vlan, and port hybrid vlan commands, see the Layer 2 Command Reference. |
Configuring multicast VLAN ports
Configuring multicast VLAN ports in multicast VLAN view
Follow these steps to configure multicast VLAN ports in multicast VLAN view:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure the specified VLAN as a multicast VLAN and enter multicast VLAN view |
multicast-vlan vlan-id |
Required Not a multicast VLAN by default |
|
Assign ports to the multicast VLAN |
port interface-list |
Required By default, a multicast VLAN has no ports. |
Configuring multicast VLAN ports in interface view or port group view
Follow these steps to configure multicast VLAN ports in interface view or port group view:
|
To do… |
Use this command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure the specified VLAN as a multicast VLAN and enter multicast VLAN view |
multicast-vlan vlan-id |
Required Not a multicast VLAN by default. |
|
Return to system view |
quit |
— |
|
Enter interface view or port group view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Required Use either command. |
|
port-group manual port-group-name |
||
|
Assign the current port or ports to the multicast VLAN |
port multicast-vlan vlan-id |
Required By default, a user port does not belong to any multicast VLAN. |
|
|
NOTE: · You cannot configure multicast VLAN on a device with multicast routing enabled. · The VLAN to be configured as a multicast VLAN must exist. · A port can belong to only one multicast VLAN. |
Displaying and maintaining multicast VLAN
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display multicast VLAN information |
display multicast-vlan [ vlan-id ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
Multicast VLAN configuration example
Network requirements
· As shown in Figure 3, Router A connects to a multicast source (Source) through GigabitEthernet1/0/1, and to Switch A through GigabitEthernet1/0/2. IGMPv2 is required on Router A. IGMPv2 Snooping is required on Switch A. Router A acts as the IGMP querier.
· The multicast source sends multicast data to multicast group 224.1.1.1. Host A, Host B, and Host C are receivers of the multicast group, and the hosts belong to VLAN 2 through VLAN 4 respectively.
· Configure the port-based multicast VLAN feature on Switch A so that Router A just sends multicast data to Switch A through the multicast VLAN and Switch A forwards the multicast data to the receivers that belong to different user VLANs.
Figure 3 Network diagram for port-based multicast VLAN configuration
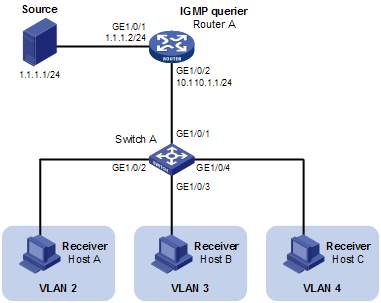
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses
Configure the IP address and subnet mask for each interface as per Figure 3. The detailed configuration steps are omitted here.
2. Configure Router A
# Enable IP multicast routing, enable PIM-DM on each interface, and enable IGMP on the host-side interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] multicast routing-enable
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] pim dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] pim dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] igmp enable
3. Configure Switch A
# Enable IGMP snooping globally.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] igmp-snooping
[SwitchA-igmp-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 10, assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to VLAN 10, and enable IGMP snooping in this VLAN.
[SwitchA] vlan 10
[SwitchA-vlan10] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchA-vlan10] igmp-snooping enable
[SwitchA-vlan10] quit
# Create VLAN 2 and enable IGMP snooping in the VLAN.
[SwitchA] vlan 2
[SwitchA-vlan2] igmp-snooping enable
[SwitchA-vlan2] quit
The configuration for VLAN 3 and VLAN 4 is similar. The detailed configuration steps are omitted.
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 as a hybrid port. Configure VLAN 2 as the default VLAN. Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to permit packets of VLAN 2 and VLAN 10 to pass and untag the packets when forwarding them.
[SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-type hybrid
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port hybrid pvid vlan 2
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port hybrid vlan 2 untagged
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port hybrid vlan 10 untagged
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
The configuration for GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 is similar. The detailed configuration steps are omitted.
# Configure VLAN 10 as a multicast VLAN.
[SwitchA] multicast-vlan 10
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 10.
[SwitchA-mvlan-10] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchA-mvlan-10] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to VLAN 10.
[SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] port multicast-vlan 10
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
4. Verify the configuration
# View the multicast VLAN information on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display multicast-vlan
Total 1 multicast-vlan(s)
Multicast vlan 10
port list:
GE1/0/2 GE1/0/3 GE1/0/4
# View the IGMP snooping multicast group information on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display igmp-snooping group
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Port flags: D-Dynamic port, S-Static port, C-Copy port
Subvlan flags: R-Real VLAN, C-Copy VLAN
Vlan(id):10.
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Router port(s):total 1 port(s).
GE1/0/1 (D)
IP group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group.
IP group address:224.1.1.1
(0.0.0.0, 224.1.1.1):
Host port(s):total 3 port(s).
GE1/0/2 (D)
GE1/0/3 (D)
GE1/0/4 (D)
MAC group(s):
MAC group address:0100-5e01-0101
Host port(s):total 3 port(s).
GE1/0/2
GE1/0/3
GE1/0/4
The output shows that IGMP snooping is maintaining the router ports and member ports in VLAN 10.
