- Table of Contents
-
- 01-Fundamentals
- 00-Preface
- 01-CLI configuration
- 02-RBAC configuration
- 03-Login management configuration
- 04-FTP and TFTP configuration
- 05-File system management configuration
- 06-Configuration file management configuration
- 07-Software upgrade configuration
- 08-Device management configuration
- 09-Tcl configuration
- 10-Python configuration
- 11-License management
- 12-Automatic configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-FTP and TFTP configuration | 178.51 KB |
Contents
Using the device as an FTP server
Configuring authentication and authorization
Manually releasing FTP connections
Displaying and maintaining the FTP server
FTP server configuration example
FTP server configuration example (on an IRF fabric)
Using the device as an FTP client
Establishing an FTP connection
Managing directories on the FTP server
Working with files on the FTP server
Changing to another user account
Maintaining and troubleshooting the FTP connection
Terminating the FTP connection
Displaying command help information
Displaying and maintaining the FTP client
FTP client configuration example
FTP client configuration example (on an IRF fabric)
Configuring the device as an IPv4 TFTP client
Configuring the device as an IPv6 TFTP client
Configuring FTP
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is an application layer protocol for transferring files from one host to another over an IP network. It uses TCP port 20 to transfer data and TCP port 21 to transfer control commands. For more information about FTP, see RFC 959.
FTP is based on the client/server model. The AC can act as the FTP server or FTP client. Make sure the FTP server and the FTP client can reach each other before establishing the FTP connection.
Figure 1 FTP application scenario
FTP supports the following transfer modes:
· Binary mode—Used to non-text files, such as .app, .bin, and .btm files.
· ASCII mode—Used to transfer text files, such as .txt, .bat, and .cfg files.
When the device acts as the FTP client, you can set the transfer mode (binary by default). When the device acts as the FTP server, the transfer mode is determined by the FTP client.
FTP can operate in either of the following modes:
· Active mode (PORT)—The FTP server initiates the TCP connection. This mode is not suitable when the FTP client is behind a firewall, for example, when the FTP client resides in a private network.
· Passive mode (PASV)—The FTP client initiates the TCP connection. This mode is not suitable when the server does not allow the client to use a random unprivileged port greater than 1024.
FTP operation mode varies depending on the FTP client program.
Using the device as an FTP server
To use the device as an FTP server, you must enable the FTP server and configure authentication and authorization on the device. Other commands are optional.
Configuring basic parameters
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable the FTP server. |
ftp server enable |
By default, the FTP server is disabled. |
|
3. (Optional.) Use an ACL to control access to the FTP server. |
ftp server acl { acl-number | ipv6 acl-number6 } |
By default, no ACL is used for access control. |
|
4. (Optional.) Associate an SSL server policy with the FTP server to ensure data security. |
ftp server ssl-server-policy policy-name |
By default, no SSL server policy is associated with the FTP server. |
|
5. (Optional.) Configure the idle-timeout interval. |
ftp timeout minutes |
The default idle-timeout interval is 30 minutes. If no data is transferred between the FTP server and FTP client within the idle-timeout interval, the connection is terminated. |
|
6. (Optional.) Set the DSCP value for outgoing FTP packets. |
·
For an IPv4 FTP server: ·
For an IPv6 FTP server: |
By default, the DSCP value is 0. |
|
7. (Optional.) Set the maximum number of concurrent FTP users. |
aaa session-limit ftp max-sessions |
The default maximum number is 32. Changing this setting does not affect users who are currently online. If the new list is less than the number of online FTP users, no additional FTP users can log in until the number drops below the new limit. For more information about this command, see Security Command Reference. |
Configuring authentication and authorization
Perform this task on the FTP server to authenticate FTP clients and set the authorized directories that authenticated clients can access.
The following authentication modes are available:
· Local authentication—The device looks up the client's username and password in the local user account database. If a match is found, authentication succeeds.
· Remote authentication—The device sends the client's username and password to a remote authentication server for authentication. The user account is configured on the remote authentication server rather than the device.
The following authorization modes are available:
· Local authorization—The device assigns authorized directories to FTP clients based on the locally configured authorization attributes.
· Remote authorization—A remote authorization server assigns authorized directories on the device to FTP clients.
For information about configuring authentication and authorization, see Security Configuration Guide.
Manually releasing FTP connections
|
Task |
Command |
|
Manually release FTP connections. |
·
Release the FTP connection established
by using a specific user account: ·
Release the FTP
connection to a specific IP address: |
Displaying and maintaining the FTP server
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display FTP server configuration and status information. |
display ftp-server |
|
Display detailed information about online FTP users. |
display ftp-user |
FTP server configuration example
Network requirements
· Configure the AC as an FTP server.
· Create a local user account with the username abc and password 123456 on the FTP server.
· Use the user account to log in to the FTP server from the FTP client.
· Upload the file temp.bin from the FTP client to the FTP server.
· Download the configuration file startup.cfg from the FTP server to the FTP client for backup.
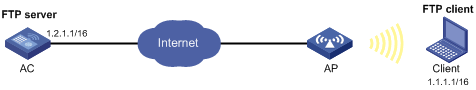
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses as shown in Figure 2. Make sure the AC and PC can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the AC (FTP server):
# Create a local user with the username abc and password 123456.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] local-user abc class manage
[Sysname-luser-abc] password simple 123456
# Assign the user role network-admin to the user. Set the working directory to the root directory of the flash memory.
[Sysname-luser-abc] authorization-attribute user-role network-admin work-directory flash:/
# Assign the service type FTP to the user.
[Sysname-luser-abc] service-type ftp
[Sysname-luser-abc] quit
# Enable the FTP server.
[Sysname] ftp server enable
[Sysname] quit
# Examine the storage space for space insufficiency and delete unused files for more free space.
<Sysname> dir
Directory of flash:
0 drw- - Jun 29 2016 18:30:38 logfile
1 drw- - Jun 21 2016 14:51:38 diagfile
2 drw- - Jun 21 2016 14:51:38 seclog
3 -rw- 2943 Jul 02 2016 08:03:08 startup.cfg
4 -rw- 63901 Jul 02 2016 08:03:08 startup.mdb
5 -rw- 716 Jun 21 2016 14:58:02 hostkey
6 -rw- 572 Jun 21 2016 14:58:02 serverkey
7 -rw- 6541264 Aug 04 2016 20:40:49 backup.bin
473664 KB total (467080 KB free)
<Sysname> delete /unreserved flash:/backup.bin
3. Perform FTP operations from the PC (FTP client):
# Log in to the FTP server at 1.2.1.1 using the username abc and password 123456.
c:\> ftp 1.2.1.1
Connected to 1.2.1.1.
220 FTP service ready.
User (1.2.1.1:(none)): abc
331 Password required for abc.
Password:
230 User logged in.
# Use the ASCII mode to download the configuration file startup.cfg from the AC to the PC for backup.
ftp> ascii
200 TYPE is now ASCII
ftp> get startup.cfg back-startup.cfg
# Use the binary mode to upload the file temp.bin to the AC.
ftp> binary
200 TYPE is now 8-bit binary
ftp> put temp.bin
# Exit FTP.
ftp> bye
FTP server configuration example (on an IRF fabric)
Network requirements
· Configure the IRF fabric as an FTP server.
· Create a local user account with the username abc and password 123456 on the FTP server.
· Use the user account to log in to the FTP server from the FTP client.
· Upload the file temp.bin from the FTP client to the FTP server.
· Download the configuration file config.cfg from the FTP server to the FTP client for backup.
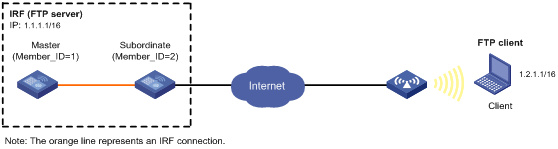
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses as shown in Figure 3. Make sure the IRF fabric and the PC can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the FTP server:
# Examine the storage space on the member devices. If the free space is insufficient, use the delete/unreserved file-url command to delete unused files. (Details not shown.)
# Create a local user with the username abc and password 123456.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] local-user abc class manage
[Sysname-luser-abc] password simple 123456
# Assign the user role network-admin to the user. Set the working directory to the root directory of the CF card on the master. (To set the working directory to the root directory of the CF card on the subordinate member, replace cfa0:/ with slot2#cfa0:/.)
[Sysname-luser-abc] authorization-attribute user-role network-admin work-directory cfa0:/
# Assign the service type FTP to the user.
[Sysname-luser-abc] service-type ftp
[Sysname-luser-abc] quit
# Enable the FTP server.
[Sysname] ftp server enable
[Sysname] quit
3. Perform FTP operations from the FTP client:
# Log in to the FTP server at 1.1.1.1 using the username abc and password 123456.
c:\> ftp 1.1.1.1
Connected to 1.1.1.1.
220 FTP service ready.
User(1.1.1.1:(none)):abc
331 Password required for abc.
Password:
230 User logged in.
# Use the ASCII mode to download the configuration file config.cfg from the FTP server to the PC for backup.
ftp> ascii
200 TYPE is now ASCII
ftp> get config.cfg back-config.cfg
# Use the binary mode to upload the file temp.bin from the PC to the root directory of the CF card on the master.
ftp> binary
200 TYPE is now 8-bit binary
ftp> put temp.bin
# Exit FTP.
ftp> bye
Using the device as an FTP client
Establishing an FTP connection
To access the FTP server, you must establish a connection from the FTP client to the FTP server.
To establish an IPv4 FTP connection:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. (Optional.) Specify a source IP address for outgoing FTP packets. |
ftp client source { interface interface-type interface-number | ip source-ip-address } |
By default, no source IP address is specified. The device uses the primary IP address of the output interface as the source IP address. |
|
3. Return to user view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
4. Log in to the FTP server. |
·
(Method 1.) Log in to the FTP server from user view: · (Method 2.) Log in to the FTP server from FTP client view: a.
Enter FTP client view: b.
Log in to the FTP server: |
The source IP address specified in the ftp command takes precedence over the one set by the ftp client source command. |
To establish an IPv6 FTP connection:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. (Optional.) Specify the source IPv6 address for FTP packets sent by the FTP client. |
ftp client ipv6 source { interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6 source-ipv6-address } |
By default, no source IPv6 address is specified. The source address is automatically selected as defined in RFC 3484. |
|
3. Return to user view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
4. Log in to the FTP server. |
·
(Method 1.) Log in to the FTP server from user view: · (Method 2.) Log in to the FTP server from FTP client view: a.
Enter FTP client view: b.
Log in to the FTP
server: |
The source IP address specified in the ftp ipv6 command takes precedence over the one set by the ftp client ipv6 source command. |
Managing directories on the FTP server
Perform the following tasks in FTP client view:
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display directory and file information on the FTP server. |
·
Display the detailed information
of a directory or file on the FTP server: ·
Display the name of a directory
or file on the FTP server: |
|
Change the working directory on the FTP server. |
cd { directory | .. | / } |
|
Return to the upper level directory on the FTP server. |
cdup |
|
Display the working directory that is being accessed. |
pwd |
|
Create a directory on the FTP server. |
mkdir directory |
|
Delete a directory from the remote FTP server. |
rmdir directory |
Working with files on the FTP server
After you log in to the server, you can upload a file to or download a file from the authorized directory by following these steps:
1. Use the dir or ls command to display the directory and location of the file on the FTP server.
2. Delete unused files to get more free storage space.
3. Set the file transfer mode to ASCII for text files or to binary for non-text files.
4. Use the lcd command to change the local working directory of the FTP client. You can upload the file or save the downloaded file in this directory.
5. Upload or download the file.
To work with files on an FTP server, execute the following commands in FTP client view:
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display directory or file information on the FTP server. |
·
Display the
detailed information of a directory or file on the FTP server: ·
Display the name of a directory
or file on the FTP server: |
N/A |
|
Delete the specified file on the FTP server permanently. |
delete remotefile |
N/A |
|
Set the file transfer mode. |
·
Set the file transfer mode to
ASCII: ·
Set the file transfer mode to
binary: |
The default file transfer mode is binary. |
|
Set the FTP operation mode to passive. |
passive |
The default mode is passive. |
|
Display or change the local working directory of the FTP client. |
lcd [ directory | / ] |
N/A |
|
Upload a file to the FTP server. |
put localfile [ remotefile ] |
N/A |
|
Download a file from the FTP server. |
get remotefile [ localfile ] |
N/A |
|
Add the content of a file on the FTP client to a file on the FTP server. |
append localfile [ remotefile ] |
N/A |
|
Specify the retransmit marker. |
restart marker |
Use this command together with the put, get, or append command. |
|
Update the local file. |
newer remotefile |
N/A |
|
Get the missing part of a file. |
reget remotefile [ localfile ] |
N/A |
|
Rename the file. |
rename [ oldfilename [ newfilename ] ] |
N/A |
Changing to another user account
After you log in to the FTP server, you can initiate an FTP authentication to change to a new account. By changing to a new account, you can get a different privilege without re-establishing the FTP connection.
For successful account change, you must enter the new username and password correctly. A wrong username or password can cause the FTP connection to be disconnected.
To change to another user account, execute the following command in user view:
|
Task |
Command |
|
Initiate an FTP authentication on the current FTP connection. |
user username [ password ] |
Maintaining and troubleshooting the FTP connection
Perform the following tasks in FTP client view:
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display FTP commands on the FTP server. |
rhelp |
N/A |
|
Display FTP commands help information on the FTP server. |
rhelp protocol-command |
N/A |
|
Display FTP server status. |
rstatus |
N/A |
|
Display detailed information about a directory or file on the FTP server. |
rstatus remotefile |
N/A |
|
Display FTP connection status. |
status |
N/A |
|
Display the system information of the FTP server. |
system |
N/A |
|
Enable or disable FTP operation information display. |
verbose |
By default, this function is enabled. |
|
Enable or disable FTP client debugging. |
debug |
By default, FTP client debugging is disabled. |
|
Clear the reply information in the buffer. |
reset |
N/A |
Terminating the FTP connection
Execute one of the following commands in FTP client view:
|
Task |
Command |
|
Terminate the connection to the FTP server without exiting FTP client view. |
· disconnect · close |
|
Terminate the connection to the FTP server and return to user view. |
· bye · quit |
Displaying command help information
Execute one of the following commands in FTP client view:
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display command help information. |
· help [ command-name ] · ? [ command-name ] |
Displaying and maintaining the FTP client
Execute the display command in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display source IP address information on the FTP client. |
display ftp client source |
FTP client configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 4, the PC is acting as an FTP server. A user account with the username abc and password 123456 has been created on the PC.
· Use the AC as an FTP client to log in to the FTP server.
· Download the file temp.bin from the PC to the AC.
· Upload the configuration file startup.cfg from the AC to the PC for backup.
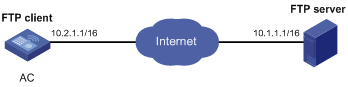
Configuration procedure
# Configure IP addresses as shown in Figure 4. Make sure the AC and PC can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
# Examine the storage space on the AC. If the free space is insufficient, use the delete/unreserved file-url command to delete unused files. (Details not shown.)
# Log in to the FTP server at 10.1.1.1 using the username abc and password 123456.
<Sysname> ftp 10.1.1.1
Press CTRL+C to abort.
Connected to 10.1.1.1 (10.1.1.1).
220 WFTPD 2.0 service (by Texas Imperial Software) ready for new user
User (10.1.1.1:(none)): abc
331 Give me your password, please
Password:
230 Logged in successfully
Remote system type is MSDOS.
ftp>
# Set the file transfer mode to binary.
ftp> binary
200 TYPE is now 8-bit binary
# Download the file temp.bin from the PC to the AC.
ftp> get temp.bin
local: temp.bin remote: temp.bin
150 Connecting to port 47457
226 File successfully transferred
23951480 bytes received in 95.399 seconds (251.0 kbyte/s)
# Use the ASCII mode to upload the configuration file startup.cfg from the AC to the PC for backup.
ftp> ascii
200 TYPE is now ASCII
ftp> put startup.cfg back-startup.cfg
local: startup.cfg remote: back-startup.cfg
150 Connecting to port 47461
226 File successfully transferred
3494 bytes sent in 5.646 seconds (618.00 kbyte/s)
ftp> bye
221-Goodbye. You uploaded 2 and downloaded 2 kbytes.
221 Logout.
<Sysname>
FTP client configuration example (on an IRF fabric)
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 5, the PC is acting as an FTP server. A user account with the username abc and password 123456 has been created on the PC.
· Use the IRF fabric as an FTP client to log in to the FTP server.
· Download the file temp.bin from the FTP server to the FTP client.
· Upload the configuration file config.cfg from the FTP client to the FTP server for backup.
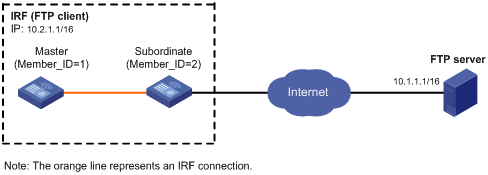
Configuration procedure
# Configure IP addresses as shown in Figure 5. Make sure the IRF fabric and PC can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
# Examine the storage space on the member devices. If the free space is insufficient, use the delete/unreserved file-url command to delete unused files. (Details not shown.)
# Log in to the FTP server at 10.1.1.1 using the username abc and password 123456.
<Sysname> ftp 10.1.1.1
Press CTRL+C to abort.
Connected to 10.1.1.1 (10.1.1.1).
220 WFTPD 2.0 service (by Texas Imperial Software) ready for new user
User (10.1.1.1:(none)): abc
331 Give me your password, please
Password:
230 Logged in successfully
Remote system type is MSDOS.
ftp>
# Set the file transfer mode to binary.
ftp> binary
200 TYPE is now 8-bit binary
# Download the file temp.bin from the PC to the root directory of the CF card on the master device.
ftp> get temp.bin
local: temp.bin remote: temp.bin
150 Connecting to port 47457
226 File successfully transferred
23951480 bytes received in 95.399 seconds (251.0 kbyte/s)
# Download the file temp.bin from the PC to the root directory of the CF card on the subordinate member (with member ID of 2).
ftp> get temp.bin slot2#cfa0:/temp.bin
# Use the ASCII mode to upload the configuration file config.cfg from the IRF fabric to the PC for backup.
ftp> ascii
200 TYPE is now ASCII
ftp> put config.cfg back-config.cfg
local: config.cfg remote: back-config.cfg
150 Connecting to port 47461
226 File successfully transferred
3494 bytes sent in 5.646 seconds (618.00 kbyte/s)
ftp> bye
221-Goodbye. You uploaded 2 and downloaded 2 kbytes.
221 Logout.
<Sysname>
Configuring TFTP
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is a simplified version of FTP for file transfer over secure reliable networks. TFTP uses UDP port 69 for data transmission. In contrast to TCP-based FTP, TFTP does not require authentication or complex message exchanges, and is easier to deploy. TFTP is suited for reliable network environments.
The device can only operate as a TFTP client. You can upload a file from the device to the TFTP server or download a file from the TFTP server to the device. If you download a file with a file name that exists in the target directory, the device deletes the existing file and saves the new one. If file download fails due to network disconnection or other reasons, the original file cannot be restored. Therefore, use a nonexistent file name instead.
Figure 6 TFTP application scenario

Configuring the device as an IPv4 TFTP client
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. (Optional.) Use an ACL to control the client's access to TFTP servers. |
tftp-server acl acl-number |
By default, no ACL is used for access control. |
|
3. Specify the source IP address for TFTP packets sent by the TFTP client. |
tftp client source { interface interface-type interface-number | ip source-ip-address } |
By default, no source IP address is specified. The device uses the primary IP address of the output interface as the source IP address. |
|
4. Return to user view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
5. Download or upload a file in an IPv4 network. |
tftp tftp-server { get | put | sget } source-filename [ destination-filename ] [ dscp dscp-value | source { interface interface-type interface-number | ip source-ip-address } ] * |
The source IP address specified in this command takes precedence over the one set by the tftp client source command. Use this command in user view. |
Configuring the device as an IPv6 TFTP client
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. (Optional.) Use an ACL to control the client's access to TFTP servers. |
tftp-server ipv6 acl acl-number |
By default, no ACL is used for access control. |
|
3. Specify the source IPv6 address for TFTP packets sent by the TFTP client. |
tftp client ipv6 source { interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6 source-ip-address } |
By default, no source IPv6 address is specified. The source address is automatically selected as defined in RFC 3484. |
|
4. Return to user view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
5. Download or upload a file in an IPv6 network. |
tftp ipv6 tftp-server [ -i interface-type interface-number ] { get | put | sget } source-filename [ destination-filename ] [ dscp dscp-value | source { interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6 source-ipv6-address } ] * |
The source IP address specified in this command takes precedence over the one set by the tftp client ipv6 source command. Use this command in user view. |
