- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-Voice entity configuration | 190.27 KB |
Incoming voice entities and outgoing voice entities
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with voice entities
Restrictions: Licensing requirements for voice entities
Voice entities tasks at a glance
Creating a POTS entity and configuring basic parameters
Configuring codecs for a POTS entity
Configuring a POTS entity to register with the registrar
Configuring DTMF for a POTS entity
Setting a DSCP value for a POTS entity
Configuring the playout delay for a POTS entity
Enabling VAD for a POTS entity
Configuring a POTS entity to play ringback tones
Configuring options related to dial program
Creating a VoIP entity and configuring basic parameters
Configuring codecs for a VoIP entity
Configuring DTMF for a VoIP entity
Enabling VAD for a VoIP entity
Setting a DSCP value for a VoIP entity
Configuring the playout delay for a VoIP entity
Configuring a VoIP entity to play ringback tones
Configuring options related to dial program
Creating an IVR entity and configuring basic parameters
Configuring codecs for an IVR entity
Configuring an IVR entity to register with the registrar
Configuring DTMF for an IVR entity
Setting a DSCP value for an IVR entity
Enabling VAD for an IVR entity
Configuring options related to dial program
Setting the RTP timeout period
Setting the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data
Display and maintenance commands for voice entities
Configuring voice entities
About voice entities
Voice entities identify the originators and the terminators of calls, what protocols used to process the calls, and which routes used to forward the calls.
Types of voice entities
Voice entities include POTS entities, VoIP entities, and IVR entities. You can configure voice entities based on the types of connected devices.
Figure 1 Voice entities
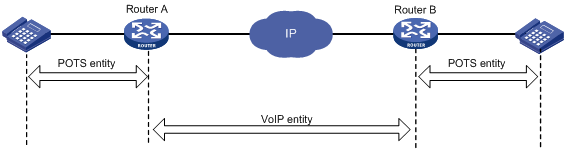
· POTS entity—A POTS entity connects to a local telephone or a PSTN network. When connecting to a local telephone, a POTS entity maintains local number information. When connecting to a PSTN network, a POTS entity maintains call destination information.
· VoIP entity—Connects to the IP side. A VoIP entity uses SIP to make VoIP calls. VoIP entities include the following categories:
¡ Dynamic and static VoIP entities.
¡ Incoming and outgoing VoIP entities.
A static incoming VoIP entity maintains the called information such as called number and call destination. Other types of VoIP entities are used in SRST. For more information, see "Configuring SRST."
· IVR entity—Sets a customizable IVR system. For more information about IVR entities, see "Configuring customizable IVR."
Incoming voice entities and outgoing voice entities
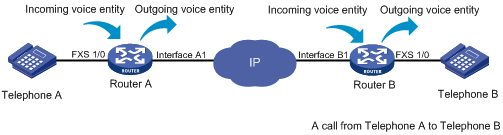
Each call has an incoming voice entity and an outgoing voice entity on the device.
· Incoming voice entity—Matches incoming calls. The device selects an incoming voice entity for an incoming call based on the calling number, the called number, or the PSTN interface. Incoming voice entities are used in the call pickup service and SIP register authentication.
· Outgoing voice entity—Matches outgoing calls. The device selects an outgoing voice entity for an outgoing call based on the called number. Outgoing voice entities are used to route calls to call destinations.
Figure 2 Incoming voice entities and outgoing voice entities
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with voice entities
|
Hardware |
Voice entity compatibility |
|
MSR810, MSR810-W, MSR810-W-DB, MSR810-LM, MSR810-W-LM, MSR810-10-PoE, MSR810-LM-HK, MSR810-W-LM-HK, MSR810-LMS-EA |
Yes for only VoIP entities and IVR entities |
|
MSR810-LMS, MSR810-LUS |
No |
|
MSR2600-6-X1 |
No |
|
MSR2600-10-X1 |
Yes |
|
MSR 2630 |
Yes |
|
MSR3600-28, MSR3600-51 |
Yes |
|
MSR3600-28-SI, MSR3600-51-SI |
No |
|
MSR3600-28-X1, MSR3600-28-X1-DP, MSR3600-51-X1, MSR3600-51-X1-DP |
No |
|
MSR3610-I-DP, MSR3610-IE-DP |
No |
|
MSR3610-X1, MSR3610-X1-DP, MSR3610-X1-DC, MSR3610-X1-DP-DC |
Yes |
|
MSR 3610, MSR 3620, MSR 3620-DP, MSR 3640, MSR 3660 |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-G, MSR3620-G |
No |
Restrictions: Licensing requirements for voice entities
To support voice entities, some device models require the Voice Software License. For more information, see license management in Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Voice entities tasks at a glance
To configure a voice entity, perform the following tasks:
1. Configure a voice entity
2. (Optional.) Setting the RTP timeout period
3. (Optional.) Setting the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data
4. (Optional.) Enabling SIP logging
Configuring a POTS entity
POTS entity tasks at a glance
To configure a POTS entity, perform the following tasks:
1. Creating a POTS entity and configuring basic parameters
2. (Optional.) Configuring codecs for a POTS entity
3. (Optional.) Configuring a POTS entity to register with the registrar
4. (Optional.) Configuring DTMF for a POTS entity
5. (Optional.) Setting a DSCP value for a POTS entity
6. (Optional.) Configuring the playout delay for a POTS entity
7. (Optional.) Enabling VAD for a POTS entity
8. (Optional.) Configuring a POTS entity to play ringback tones
9. (Optional.) Configuring options related to dial program
Creating a POTS entity and configuring basic parameters
About creating a POTS entity and configuring basic parameters
Upon receiving a call, the device selects an incoming POTS entity by comparing the call information with POTS entity attributes in the following order:
1. Called number with the called number string configured by the incoming called-number command.
2. Calling number with the calling number string configured by the answer-address command.
3. Calling number with the number template configured by the match-template command.
Once the call matches a POTS entity, the device stops matching and routes the call based on the attributes of the matching POTS entity.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Create a POTS entity and enter its view.
entity entity-number pots
By default, no POTS entities exist.
5. (Optional.) Configure a description for the POTS entity.
description text
6. Configure a number template for the POTS entity.
match-template match-string
The POTS entity uses the number template to match phone numbers. For example, the match-template 20 command matches all numbers beginning with 20.
7. Bind a voice interface to the POTS entity.
line line-number
By default, no voice interface is bound to a POTS entity.
8. (Optional.) Configure a number string for the POTS entity to match incoming calls. Choose the options to configure as needed:
¡ Configure a called number string.
incoming called-number called-number-string
If the called number string of a POTS entity matches the called number of a call, the device uses the POTS entity as the incoming voice entity of the call.
¡ Configure a calling number string.
answer-address calling-number-string
If the calling number string of a POTS entity matches the calling number of a call, the device uses the POTS entity as the incoming voice entity of the call.
By default, no number string is configured to match incoming calls. A call does not use a voice entity as an incoming voice entity.
9. Enable the POTS entity.
undo shutdown
By default, a POTS entity is enabled.
Configuring codecs for a POTS entity
About codecs of a POTS entity
By default, a POTS entity has four codecs g729r8, g711alaw, g711ulaw, and g723r53 in descending order of priority.
You can use one of the following methods to configure codecs for a POTS entity:
· Configure codecs for a POTS entity.
· Create a codec template, assign priorities to codecs in the codec template, and bind the codec template to a POTS entity.
Restrictions and guidelines
A call can be established only when the calling party and the called party use the same codec. You can use the display voice sip call command (see Voice Command Reference) to view the codec used by two parties.
Configuring a codec for a POTS entity
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter POTS entity view.
entity entity-number pots
5. Configure a codec for the POTS entity.
codec { g711alaw | g711ulaw | g723r53 | g723r63 | g726r16 | g726r24 | g726r32 | g726r40 | g729a | g729br8 | g729r8 } [ bytes payload-size ]
By default, no codec is configured for a POTS entity.
Binding a codec template to a POTS entity
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Create a codec template and enter its view.
voice class codec tag
4. Assign a priority to a codec in the codec template.
codec preference priority { g711alaw | g711ulaw | g723r53 | g723r63 | g726r16 | g726r24 | g726r32 | g726r40 | g729a | g729br8 | g729r8 } [ bytes payload-size ]
5. Return to voice view.
quit
6. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
7. Enter POTS entity view.
entity entity-number pots
8. Bind the codec template to the POTS entity.
voice-class codec tag
By default, no codec template is bound to a POTS entity.
Configuring a POTS entity to register with the registrar
About configuring a POTS entity to register with the registrar
Perform this task to configure a POTS entity to register with the registrar. If you do not want to register a number or you want to deregister a number from the registrar, you can use the undo register number command.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter POTS entity view.
entity entity-number pots
5. Configure the POTS entity to register with the registrar server.
register number
By default, a POTS entity initiates a registration to the registrar server after UA registration is configured.
For more information about this command, see SIP commands in Voice Command Reference.
Configuring DTMF for a POTS entity
About DTMF transmission
There are the following ways to transmit DTMF tones:
· Inband signaling—Sends DTMF tones in RTP packets.
· Out-of-band signaling—Sends DTMF tones in SIP messages or sends DTMF tones in RFC 2883-compliant RTP messages (NTE mode). To use NTE mode, configure the outband nte command and the same payload type value on the originating and terminating sides. Otherwise, the originating side might fail to transmit DTMF tones. For more information about out-of-band DTMF, see "Configuring SIP."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter POTS entity view.
entity entity-number pots
5. Configure DTMF transmission.
outband { nte | sip }
By default, inband transmission is adopted.
6. (Optional.) Set the value of the payload type used by NTE.
rtp payload-type nte value
By default, the value of the payload type used by NTE is 101.
When the device is connected to a device from another vendor, you cannot set the payload type field to any value forbidden by that device. A violation might cause an NTE negotiation failure.
Setting a DSCP value for a POTS entity
About setting a DSCP value for a POTS entity
You can set a DSCP value for IP packets carrying media streams to provide differentiated voice services.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can configure the ip qos dscp command both globally (in SIP view) and for a specific POTS entity (in POTS entity view). The configuration in POTS entity view takes precedence over the global configuration. A POTS entity uses the global configuration only when the ip qos dscp command is not configured in POTS entity view. For information about configuring a DSCP value in SIP view, see "Configuring SIP."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter POTS entity view.
entity entity-number pots
5. Set a DSCP value for IP packets carrying media streams.
ip qos dscp { dscp-value | dscp-value-set } media
The default value is ef (101110), the global default value.
Configuring the playout delay for a POTS entity
About the playout delay for a POTS entity
In an ideal voice network environment, the delay of each voice packet (time for each voice packet to travel from the sender to the receiver) is fixed. That is, the jitter is 0. In an actual voice network, the delay varies from packet to packet.
To smoothly play out voice packets received with different delay times, the receiver can buffer the voice packets for a period of time (playout delay time). By configuring playout delay, you can prevent delay variation (jitter) from affecting voice quality.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter POTS entity view.
entity entity-number pots
5. Configure the playout delay mode for the POTS entity.
playout-delay mode { adaptive | fixed }
The default mode is fixed.
6. Configure the playout delay time.
playout-delay { initial milliseconds | maximum milliseconds | minimum milliseconds }
By default, the initial playout delay time is 30 milliseconds, the maximum playout delay time is 160 milliseconds, and the minimum playout delay time is 10 milliseconds.
Enabling VAD for a POTS entity
About VAD
The voice activity detection (VAD) feature discriminates between silence and speech on a voice connection according to their energies. With VAD, a POTS entity does not generate traffic during periods of silence.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter POTS entity view.
entity entity-number pots
5. Enable VAD for the POTS entity.
vad-on [ g711 | g723r53 | g723r63 | g729a | g729r8 ] *
By default, VAD is disabled for a POTS entity.
The G.726 codec does not support VAD. The G.729br8 codec always supports VAD.
The G.711 codec is supported only the following interface modules:
¡ HMIM-1VE1.
¡ HMIM-1VT1.
¡ HMIM-2VE1.
¡ HMIM-2VT1.
¡ SIC-1BSV.
¡ SIC-1VE1T1.
¡ SIC-2BSV.
¡ SIC-2FXS1FXO.
The G.711 codec is supported only if the DSP image is configured as the Microsoft-verified version.
Configuring a POTS entity to play ringback tones
About configuring a POTS entity to play ringback tones
If the terminating side of a call cannot play ringback tones, configure a POTS entity on the originating side to play ringback tones.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature does not take effect if the POTS entity is bound to an FXS or FXO interface.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter POTS entity view.
entity entity-number pots
5. Configure the POTS entity to play ringback tones.
send-ring
By default, a POTS entity on the originating side does not play ringback tones.
Configuring options related to dial program
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter POTS entity view.
entity entity-number pots
For more information about the following commands in this view, see "Configuring dial programs."
5. Configure permitted calling numbers.
caller-permit calling-string
By default, a POTS entity permits all calling numbers.
6. Set the priority of the POTS entity.
priority priority-order
By default, the priority level is 0.
The smaller the number, the higher the priority.
7. Set the maximum number of calls allowed by the POTS entity.
max-conn max-number
By default, the number of calls allowed by a POTS entity is not limited.
8. Configure a dial prefix for the POTS entity
dial-prefix string
9. Bind a number substitution rule list to the POTS entity.
substitute { called | calling } list-number
By default, no number substitution rule list is bound to a POTS entity (no number substitution is performed).
10. Bind a subscriber group to the POTS entity.
caller-group { deny | permit } group-id
By default, no subscriber group is bound to a POTS entity (any calling number is allowed to originate calls).
11. Configure the number sending mode.
send-number { digit-number | all | truncate }
By default, the truncate mode is used.
Configuring a VoIP entity
VoIP entity tasks at a glance
To configure a VoIP entity, perform the following tasks:
1. Creating a VoIP entity and configuring basic parameters
2. (Optional.) Configuring codecs for a VoIP entity
3. (Optional.) Configuring DTMF for a VoIP entity
4. (Optional.) Enabling VAD for a VoIP entity
5. (Optional.) Setting a DSCP value for a VoIP entity
6. (Optional.) Configuring the playout delay for a VoIP entity
7. (Optional.) Configuring a VoIP entity to play ringback tones
8. (Optional.) Configuring options related to dial program
Creating a VoIP entity and configuring basic parameters
About basic parameters for a VoIP entity
Upon receiving a call, the device selects an incoming VoIP entity by comparing the call information with VoIP entity attributes in the following order:
1. Called number with the called number string configured by the incoming called-number command.
2. Calling number with the calling number string configured by the answer-address command.
3. Calling number with the number template configured by the match-template command. The VoIP entity uses the number template to match phone numbers. For example, the match-template 20 command matches all numbers beginning with 20.
Once the call matches a VoIP entity, the device stops matching and routes the call based on the attributes of the matching VoIP entity.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Create a VoIP entity and enter its view.
entity entity-number voip
5. (Optional.) Configure a description for the VoIP entity.
description text
6. Configure a number template for the VoIP entity.
match-template match-string
7. Configure the destination IP address.
address sip ip ip-address [ port port-number ]
For more information about this command, see Voice Command Reference.
8. (Optional.) Configure number string for the VoIP entity to match incoming calls. Choose the options to configure as needed:
¡ Configure a called number string.
incoming called-number called-number-string
If the called number of a VoIP entity matches the called number of a call, the device uses the VoIP entity as the incoming voice entity of the call.
¡ Configure a calling number string.
answer-address calling-number-string
If the calling number of a VoIP entity matches the calling number of a call, the device uses the VoIP entity as the incoming voice entity of the call.
9. Enable the VoIP entity.
undo shutdown
By default, a VoIP entity is enabled.
Configuring codecs for a VoIP entity
About codecs for a VoIP entity
By default, a VoIP entity has four codecs g729r8, g711alaw, g711ulaw, and g723r53 in descending order of priority.
You can use one of the following methods to configure codecs for a VoIP entity:
· Configure codecs directly for a VoIP entity.
· Create a codec template, assign priorities to codecs in the codec template, and bind the codec template to a VoIP entity.
Restrictions and guidelines
A call can be established only when the calling party and the called party use the same codec. You can use the display voice sip call command (see Voice Command Reference) to view the codec used by two parties.
Configuring a codec for a VoIP entity
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter VoIP entity view.
entity entity-number voip
5. Configure a codec for the VoIP entity.
codec { g711alaw | g711ulaw | g723r53 | g723r63 | g726r16 | g726r24 | g726r32 | g726r40 | g729a | g729br8 | g729r8 } [ bytes payload-size ]
By default, no codec is configured for a VoIP entity.
Binding a codec template to a VoIP entity
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Create a codec template and enter its view.
voice class codec tag
4. Assign a priority to a codec in the codec template.
codec preference priority { g711alaw | g711ulaw | g723r53 | g723r63 | g726r16 | g726r24 | g726r32 | g726r40 | g729a | g729br8 | g729r8 } [ bytes payload-size ]
5. Return to voice view.
quit
6. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
7. Enter VoIP entity view.
entity entity-number voip
8. Bind the codec template to the VoIP entity.
voice-class codec tag
By default, no codec template is bound to a VoIP entity.
Configuring DTMF for a VoIP entity
About DTMF transmission
There are the following ways to transmit DTMF tones:
· Inband signaling—Sends DTMF tones in RTP packets
· Out-of-band signaling—Sends DTMF tones in SIP messages or sends DTMF tones in RFC 2883-compliant RTP packets (NTE mode). To use the NTE mode, configure command outband nte and the same payload type value on both the originating and terminating sides. Otherwise, the originating side might fail to transmit DTMF tones. For more information about out-of-band DTMF, see "Configuring SIP."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter VoIP entity view.
entity entity-number voip
5. Configure out-of-band DTMF signaling.
outband { nte | sip }
By default, inband DTMF signaling is used.
6. Set the value of the payload type used by NTE.
rtp payload-type nte value
By default, the value of the payload type used by NTE is 101.
When the device is connected to a device from another vendor, you cannot set the payload type field to any value forbidden by that device. A violation might cause an NTE negotiation failure.
Enabling VAD for a VoIP entity
About VAD
The voice activity detection (VAD) feature discriminates between silence and speech on a voice connection according to their energies. With VAD, a POTS entity does not generate traffic during periods of silence in an active voice connection.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter VoIP entity view.
entity entity-number voip
5. Enable VAD for a VoIP entity.
vad-on [ g711 | g723r53 | g723r63 | g729a | g729r8 ] *
By default, VAD is disabled for a VoIP entity.
The G.726 codec does not support VAD. The G.729br8 codec always supports VAD.
The G.711 codec is supported only the following interface modules:
¡ HMIM-1VE1.
¡ HMIM-1VT1.
¡ HMIM-2VE1.
¡ HMIM-2VT1.
¡ SIC-1BSV.
¡ SIC-1VE1T1.
¡ SIC-2BSV.
¡ SIC-2FXS1FXO.
The G.711 codec is supported only if the DSP image is configured as the Microsoft-verified version.
Setting a DSCP value for a VoIP entity
About setting a DSCP value for a VoIP entity
You can set a DSCP value for IP packets carrying media streams to provide differentiated voice services.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can configure the ip qos dscp command both globally (in SIP view) and for a specific VoIP entity (in VoIP entity view).The configuration in VoIP entity view takes precedence over the global configuration. A VoIP entity uses the global configuration only when the ip qos dscp command is not configured in VoIP entity view. For information about configuring a DSCP value in SIP view, see "Configuring SIP."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter VoIP entity view.
entity entity-number voip
5. Set a DSCP value for IP packets carrying media streams.
ip qos dscp { dscp-value | dscp-value-set } media
The default value is ef (101110), the global default value.
Configuring the playout delay for a VoIP entity
About the playout delay for a VoIP entity
In an ideal voice network environment, the delay of each voice packet (time for each voice packet to transmit from the sender to the receiver) is fixed. That is, the jitter is 0. In an actual voice network, the delay varies from packet to packet.
To smoothly play out voice packets received with different delay times, the receiver can buffer the voice packets for a period of time (playout delay time). By configuring playout delay, you can prevent delay variation (jitter) from affecting voice quality.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter VoIP entity view.
entity entity-number voip
5. Configure the playout delay mode for the VoIP entity.
playout-delay mode { adaptive | fixed }
By default, the playout delay mode is fixed.
6. Set the playout delay time.
playout-delay { initial milliseconds | maximum milliseconds | minimum milliseconds }
By default, the initial playout delay time is 30 milliseconds, the maximum playout delay time is 160 milliseconds, and the minimum playout delay time is 10 milliseconds.
Configuring a VoIP entity to play ringback tones
About configuring a VoIP entity to play ringback tones
If the terminating side of a call cannot play ringback tones, configure a VoIP entity on the originating side to play ringback tones.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter VoIP entity view.
entity entity-number voip
5. Configure the VoIP entity to play ringback tones.
send-ring
By default, a VoIP entity on the originating side does not play ringback tones.
Configuring options related to dial program
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter VoIP entity view.
entity entity-number voip
For more information about the following commands in this view, see "Configuring dial programs."
5. Configure the permitted calling numbers.
caller-permit calling-string
By default, a voice entity permits all calling numbers.
6. Set the maximum number of calls allowed by the VoIP entity.
max-conn max-number
By default, the number of calls allowed by a VoIP entity is not limited.
7. Set the priority of the VoIP entity.
priority priority-order
By default, the priority level is 0.
The smaller the number, the higher the priority.
8. Bind a number substitution rule list to the VoIP entity.
substitute { called | calling } list-number
By default, no number substitution rule list is bound to a VoIP entity.
9. Bind a subscriber group to the VoIP entity.
caller-group { deny | permit } group-id
By default, no subscriber group is bound to a VoIP entity.
Configuring an IVR entity
IVR entity tasks at a glance
To configure an IVR entity, perform the following tasks:
1. Creating an IVR entity and configuring basic parameters
2. (Optional.) Configuring codecs for an IVR entity
3. (Optional.) Configuring an IVR entity to register with the registrar
4. (Optional.) Configuring DTMF for an IVR entity
5. (Optional.) Setting a DSCP value for an IVR entity
6. (Optional.) Enabling VAD for an IVR entity
7. (Optional.) Configuring options related to dial program
Creating an IVR entity and configuring basic parameters
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Create an IVR entity and enter its view.
entity entity-number ivr
5. (Optional.) Configure a description for the IVR entity.
description text
6. Configure a number template for the IVR entity.
match-template match-string
7. Configure a root node for the IVR entity.
ivr-root node-id
8. Enable the IVR entity.
undo shutdown
By default, an IVR entity is enabled.
Configuring codecs for an IVR entity
About codecs for an IVR entity
By default, an IVR entity has four codecs g729r8, g711alaw, g711ulaw, and g723r53 in descending order of priority.
You can use one of the following methods to configure codecs for an IVR entity:
· Configure codecs directly for an IVR entity.
· Create a codec template, assign priorities to codecs in the codec template, and bind the codec template to an IVR entity.
Restrictions and guidelines
A call can be established only when the calling party and the called party use the same codec. You can use the display voice sip call command (see Voice Command Reference) to view the codec used by two parties.
Configuring a codec for an IVR entity
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter IVR entity view.
entity entity-number ivr
5. Specify a codec for the IVR entity.
codec { g711alaw | g711ulaw | g723r53 | g723r63 | g726r16 | g726r24 | g726r32 | g726r40 | g729a | g729br8 | g729r8 } [ bytes payload-size ]
By default, no codec is configured for an IVR entity.
Binding a codec template to an IVR entity
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Create a codec template and enter its view.
voice class codec tag
4. Assign a priority to a codec in the codec template.
codec preference priority { g711alaw | g711ulaw | g723r53 | g723r63 | g726r16 | g726r24 | g726r32 | g726r40 | g729a | g729br8 | g729r8 } [ bytes payload-size ]
5. Return to voice view.
quit
6. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
7. Enter IVR entity view.
entity entity-number ivr
8. Bind the codec template to the IVR entity.
voice-class codec tag
By default, no codec template is bound to an IVR entity.
Configuring an IVR entity to register with the registrar
About configuring an IVR entity to register with the registrar
Perform this task to configure an IVR entity to register with the registrar. If you do not want to register a number or you want to deregister a number from the registrar, you can use the undo register number command.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter IVR entity view.
entity entity-number ivr
5. Configure the IVR entity to register with the registrar.
register-number
By default, an IVR entity initiates a registration to the registrar after UA registration is configured.
For more information about this command, see SIP commands in Voice Command Reference.
Configuring DTMF for an IVR entity
About DTMF transmission
There are two ways to transmit DTMF tones:
· Inband signaling—Sends DTMF tones in RTP packets.
· Out-of-band signaling—Sends DTMF tones in SIP messages or RFC 2883-compliant RTP packets (NTE mode). To use the NTE mode, configure the outband nte command and the same payload type value on both the originating and terminating sides. Otherwise, the originating side might fail to transmit DTMF tones.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter IVR entity view.
entity entity-number ivr
5. Configure out-of-band DTMF by using NTE mode.
outband nte
By default, inband DTMF signaling is used.
6. Configure the value of the NTE payload type.
rtp payload-type nte value
By default, the value of the NTE payload type is 101.
When the device is connected to a device from another vendor, you cannot set the payload type field to any value forbidden by that device. Otherwise, an NTE negotiation failure might occur.
Setting a DSCP value for an IVR entity
About setting a DSCP value for an IVR entity
You can set a DSCP value for IP packets carrying media streams to provide differentiated voice services.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can configure the ip qos dscp command both globally (in SIP view) and for a specific IVR entity (in IVR entity view).The configuration in IVR entity view takes precedence over the global configuration. An IVR entity uses the global configuration only when the ip qos dscp command is not configured in IVR entity view. For information about configuring a DSCP value in SIP view, see "Configuring SIP."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter IVR entity view.
entity entity-number ivr
5. Set a DSCP value for IP packets carrying media streams.
ip qos dscp { dscp-value | dscp-value-set } media
The default value is ef (101110), the global default value.
Enabling VAD for an IVR entity
About VAD
The voice activity detection (VAD) feature discriminates between silence and speech on a voice connection according to their energies. With VAD, an IVR entity does not generate traffic during periods of silence in an active voice connection.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter IVR entity view.
entity entity-number ivr
5. Enable VAD for the IVR entity.
vad-on [ g711 | g723r53 | g723r63 | g729a | g729r8 ] *
By default, VAD is disabled for an IVR entity.
The G.726 codec does not support VAD. The G.729br8 codec always supports VAD.
The G.711 codec is supported only the following interface modules:
¡ HMIM-1VE1.
¡ HMIM-1VT1.
¡ HMIM-2VE1.
¡ HMIM-2VT1.
¡ SIC-1BSV.
¡ SIC-1VE1T1.
¡ SIC-2BSV.
¡ SIC-2FXS1FXO.
The G.711 codec is supported only if the DSP image is configured as the Microsoft-verified version.
Configuring options related to dial program
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enter dial program view.
dial-program
4. Enter IVR entity view.
entity entity-number ivr
For more information about the following commands in this view, see "Configuring dial programs."
5. Configure the permitted calling numbers.
caller-permit calling-string
By default, an IVR entity permits all calling numbers.
6. Configure the priority of the IVR entity.
priority priority-order
By default, the priority level is 0.
The smaller the number, the higher the priority.
7. Configure the maximum number of calls allowed by the IVR entity.
max-conn max-number
By default, the number of calls allowed by an IVR entity is not limited.
8. Bind a number substitution rule list to the IVR entity.
substitute { called | calling } list-number
By default, no number substitution rule list is bound to an IVR entity.
9. Bind a subscriber group to the IVR entity.
caller-group { deny | permit } group-id
By default, no subscriber group is bound to an IVR entity.
Setting the RTP timeout period
About setting the RTP timeout period
The device disconnects a call if it does not receive RTP traffic during the set timeout period.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Set the RTP timeout period.
rtp-detect timeout value
By default, the RTP timeout period is 120 seconds.
Setting the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data
About the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data
VoIP voice data is buffered in the DSP buffer if a network latency or jitter exists. When the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data is reached, the device clears the DSP buffer to improve the quality of VoIP calls. You can adjust the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data.
Hardware and feature compatibility
|
Model |
Feature compatibility |
|
MSR810, MSR810-W, MSR810-W-DB, MSR810-LM, MSR810-W-LM, MSR810-10-PoE, MSR810-LM-HK, MSR810-W-LM-HK, MSR810-LMS-EA |
No |
|
MSR810-LMS, MSR810-LUS |
No |
|
MSR2600-6-X1, MSR2600-10-X1 |
No |
|
MSR 2630 |
No |
|
MSR3600-28, MSR3600-51 |
No |
|
MSR3600-28-SI, MSR3600-51-SI |
No |
|
MSR3600-28-X1, MSR3600-28-X1-DP, MSR3600-51-X1, MSR3600-51-X1-DP |
No |
|
MSR3610-I-DP, MSR3610-IE-DP |
No |
|
MSR3610-X1, MSR3610-X1-DP, MSR3610-X1-DC, MSR3610-X1-DP-DC |
No |
|
MSR 3610, MSR 3620, MSR 3620-DP, MSR 3640, MSR 3660 |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-G, MSR3620-G |
No |
Restrictions and guidelines
When PCM pass-through is enabled, the set maximum duration of DSP-buffered data takes effect.
When PCM pass-through is disabled, one of the following rules applies:
· If the set maximum duration of DSP-buffered data is in the range of 10 to 179 milliseconds, the default value (270 milliseconds) takes effect.
· If the set maximum duration of DSP-buffered data is 0 or in the range of 180 to 480 milliseconds, the set value takes effect.
For more information about PCM pass-through, see "Configuring voice interfaces."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Set the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data.
vqa-dsp-buffer maximum-time time
By default, the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data is 270 milliseconds.
Enabling SIP logging
About SIP logging
SIP logging enables the device to log SIP call events and send the log messages to the information center. With the information center, you can set log message filtering and output rules, including output destinations. For more information about using the information center, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter voice view.
voice-setup
3. Enable SIP logging.
sip log enable
By default, SIP logging is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for voice entities
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display voice call information. |
display voice call-info { tag | all } |
|
Display the configuration of voice entities. |
display voice entity { entity-tag | all | ivr | pots | voip } |
|
Display control information about calls in progress. |
display voice call |
