- Table of Contents
-
- 04-Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-MAC address table configuration
- 02-Ethernet link aggregation configuration
- 03-Port isolation configuration
- 04-VLAN configuration
- 05-QinQ configuration
- 06-Loop detection configuration
- 07-Spanning tree configuration
- 08-LLDP configuration
- 09-Layer 2 forwarding configuration
- 10-VLAN termination configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-QinQ configuration | 165.22 KB |
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with QinQ
Restrictions and guidelines: QinQ configuration
Configuring the TPID for VLAN tags
Configuring the global TPID value
Configuring an interface-specific TPID value
Setting the 802.1p priority in SVLAN tags
About the 802.1p priority in SVLAN tags
Prerequisites for setting the 802.1p priority in SVLAN tags
Creating a traffic class and configuring CVLAN match criteria
Creating a traffic behavior and configuring a priority marking action for SVLAN tags
Configuring QinQ
This document uses the following terms:
· CVLAN—Customer network VLANs, also called inner VLANs, refer to VLANs that a customer uses on the private network.
· SVLAN—Service provider network VLANs, also called outer VLANs, refer to VLANs that a service provider uses to transmit VLAN tagged traffic for customers.
About QinQ
802.1Q-in-802.1Q (QinQ) adds an 802.1Q tag to 802.1Q tagged customer traffic. It enables a service provider to extend Layer 2 connections across an Ethernet network between customer sites.
QinQ benefits
QinQ provides the following benefits:
· Enables a service provider to use a single SVLAN to convey multiple CVLANs for a customer.
· Enables customers to plan CVLANs without conflicting with SVLANs.
· Enables customers to keep their VLAN assignment schemes unchanged when the service provider changes its VLAN assignment scheme.
· Allows different customers to use overlapping CVLAN IDs. Devices in the service provider network make forwarding decisions based on SVLAN IDs instead of CVLAN IDs.
How QinQ works
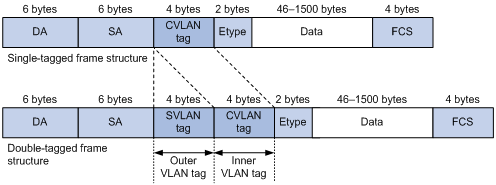
As shown in Figure 1, a QinQ frame transmitted over the service provider network carries the following tags:
· CVLAN tag—Identifies the VLAN to which the frame belongs when it is transmitted in the customer network.
· SVLAN tag—Identifies the VLAN to which the QinQ frame belongs when it is transmitted in the service provider network. The service provider allocates the SVLAN tag to the customer.
The devices in the service provider network forward a tagged frame according to its SVLAN tag only. The CVLAN tag is transmitted as part of the frame's payload.
Figure 1 Single-tagged Ethernet frame header and double-tagged Ethernet frame header
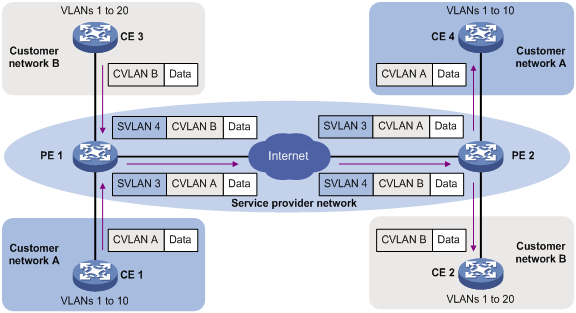
As shown in Figure 2, customer A has remote sites CE 1 and CE 4. Customer B has remote sites CE 2 and CE 3. The CVLANs of the two customers overlap. The service provider assigns SVLANs 3 and 4 to customers A and B, respectively.
When a tagged Ethernet frame from CE 1 arrives at PE 1, the PE tags the frame with SVLAN 3. The double-tagged Ethernet frame travels over the service provider network until it arrives at PE 2. PE 2 removes the SVLAN tag of the frame, and then sends the frame to CE 4.
Figure 2 Typical QinQ application scenario
QinQ implementations
QinQ is enabled on a per-port basis. The link type of a QinQ-enabled port can be access, hybrid, or trunk. The QinQ tagging behaviors are the same across these types of ports.
A QinQ-enabled port tags all incoming frames (tagged or untagged) with the PVID tag.
· If an incoming frame already has one tag, it becomes a double-tagged frame.
· If the frame does not have any 802.1Q tags, it becomes a frame tagged with the PVID.
QinQ provides the most basic VLAN manipulation method to tag all incoming frames (tagged or untagged) with the PVID tag.
Protocols and standards
· IEEE 802.1Q, IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks-Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
· IEEE 802.1ad, IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks-Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks-Amendment 4: Provider Bridges
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with QinQ
This feature is supported only on the following ports:
|
Hardware |
QinQ and port compatibility |
|
MSR3600-28, MSR3600-51 |
Fixed Layer 2 Ethernet ports. |
|
Routers installed with an Ethernet switching module |
Layer 2 Ethernet ports on the following modules: · HMIM-8GSW. · HMIM-8GSWF. · HMIM-24GSW. · HMIM-24GSW-PoE. For more information about the support of the routers for these modules, see H3C MSR Router Series Comware 7 Interface Module Guide. |
Restrictions and guidelines: QinQ configuration
When you configure QinQ, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· The inner 802.1Q tag of QinQ frames is treated as part of the payload. As a best practice to ensure correct transmission of QinQ frames, set the MTU to a minimum of 1504 bytes for each port on their forwarding path. This value is the sum of the default Ethernet interface MTU (1500 bytes) and the length (4 bytes) of a VLAN tag.
Enabling QinQ
About enabling QinQ
Enable QinQ on customer-side ports of PEs. A QinQ-enabled port tags an incoming frame with its PVID.
Hardware and feature compatibility
|
Hardware |
Feature and port compatibility |
|
MSR3600-28, MSR3600-51 |
Fixed Layer 2 Ethernet ports. |
|
MSR3600-X1 series |
Fixed Layer 2 Ethernet ports. |
|
MSR810-10-PoE |
Fixed Layer 2 Ethernet ports. |
|
Routers installed with an Ethernet switching module |
Layer 2 Ethernet ports on the following modules: · HMIM-8GSWF. · HMIM-24GSW. · HMIM-24GSW-PoE. For more information about the support of the routers for these modules, see H3C MSR Router Series Comware 7 Interface Module Guide. |
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Set the port link type.
port link-type { access | hybrid | trunk }
By default, the link type of a port is access.
¡ Assign the access port to the specified VLAN.
port access vlan vlan-id
By default, all access ports belong to VLAN 1.
By default, the hybrid port is an untagged member of the VLAN to which the port belongs when its link type is access.
port trunk permit vlan { vlan-id-list | all }
By default, a trunk port allows packets only from VLAN 1 to pass through.
4. Enable QinQ on the port.
qinq enable
By default, QinQ is disabled on the port.
Configuring the TPID for VLAN tags
About TPID
TPID identifies a frame as an 802.1Q tagged frame. The TPID value varies by vendor. On an H3C device, the TPID in the 802.1Q tag added on a QinQ-enabled port is 0x8100 by default, in compliance with IEEE 802.1Q. In a multi-vendor network, make sure the TPID setting is the same between directly connected devices so 802.1Q tagged frames can be identified correctly.
TPID settings include CVLAN TPID and SVLAN TPID.
A QinQ-enabled port uses the CVLAN TPID to match incoming tagged frames. An incoming frame is handled as untagged if its TPID is different from the CVLAN TPID.
SVLAN TPIDs are configurable on a per-port basis. A service provider-side port uses the SVLAN TPID to replace the TPID in outgoing frames' SVLAN tags and match incoming tagged frames. An incoming frame is handled as untagged if the TPID in its outer VLAN tag is different from the SVLAN TPID.
For example, a PE device is connected to a customer device that uses the TPID 0x8200 and to a provider device that uses the TPID 0x9100. For correct packet processing, you must set the CVLAN TPID and SVLAN TPID to 0x8200 and 0x9100 on the PE, respectively.
The TPID field is at the same position as the EtherType field in an untagged Ethernet frame. To ensure correct packet type identification, do not set the TPID value to any of the values listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Reserved EtherType values
|
Protocol type |
Value |
|
ARP |
0x0806 |
|
PUP |
0x0200 |
|
RARP |
0x8035 |
|
IP |
0x0800 |
|
IPv6 |
0x86dd |
|
PPPoE |
0x8863/0x8864 |
|
MPLS |
0x8847/0x8848 |
|
IPX/SPX |
0x8137 |
|
IS-IS |
0x8000 |
|
LACP |
0x8809 |
|
LLDP |
0x88cc |
|
802.1X |
0x888e |
|
802.1ag |
0x8902 |
|
Cluster |
0x88a7 |
|
Reserved |
0xfffd/0xfffe/0xffff |
Restrictions and guidelines
You can configure the TPID value in VLAN tags by using one of the following methods:
· In system view—The TPID value configuration made in system view takes effect on all ports of the device.
· In interface view—The TPID value configuration made in interface view takes effect only on the current interface. For a port, the TPID value configured in interface view has priority over that configured in system view. The TPID value in VLAN tags is typically configured on the service provider-side ports of PEs.
Configuring the global TPID value
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the global CVLAN TPID or SVLAN TPID.
qinq ethernet-type customer-tag hex-value
The default setting is 0x8100 for both CVLAN and SVLAN tags.
Configuring an interface-specific TPID value
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Set the interface-specific CVLAN TPID or SVLAN TPID.
qinq ethernet-type service-tag hex-value
By default, the interface-level TPID value in SVLAN and CVLAN tags equals the global TPID value.
Setting the 802.1p priority in SVLAN tags
About the 802.1p priority in SVLAN tags
By default, the 802.1p priority in the SVLAN tag added by a QinQ-enabled port depends on the priority trust mode on the port.
· If the 802.1p priority in frames is trusted, the device copies the 802.1p priority in the CVLAN tag to the SVLAN tag.
· If port priority is trusted, the port priority (0 by default) is used as the 802.1p priority in the SVLAN tag.
For more information about QoS policies and priority trust mode, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
Prerequisites for setting the 802.1p priority in SVLAN tags
1. Enable QinQ. For more information, see "Enabling QinQ."
To use the CVLAN ID or 802.1p priority of the CVLAN tag to set the 802.1p priority of the SVLAN tag, you must first enable QinQ on the port.
2. Use the qos trust dot1p command to configure the port to trust the 802.1p priority in incoming frames. For more information, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
This setting is required if the remark dot1p command is configured. It is optional if the remark dot1p customer-dot1p-trust command is configured.
Tasks at a glance
To use QoS policies to set the 802.1p priority in SVLAN tags, perform the following tasks:
1. Creating a traffic class and configuring CVLAN match criteria
2. Creating a traffic behavior and configuring a priority marking action for SVLAN tags
Creating a traffic class and configuring CVLAN match criteria
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a traffic class and enter its view.
traffic classifier classifier-name [ operator { and | or } ]
3. Configure CVLAN match criteria.
Choose one option as needed:
¡ Match CVLAN IDs.
if-match customer-vlan-id vlan-id-list
¡ Match 802.1p priority.
if-match customer-dot1p dot1p-value&<1-8>
Creating a traffic behavior and configuring a priority marking action for SVLAN tags
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a traffic behavior and enter its view.
traffic behavior behavior-name
3. Configure a priority marking action for SVLAN tags.
Choose one option as needed:
¡ Replace the priority in the SVLAN tags of matching frames with the configured priority.
remark dot1p dot1p-value
¡ Copy the 802.1p priority in the CVLAN tag to the SVLAN tag.
remark dot1p customer-dot1p-trust
Creating a QoS policy
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a QoS policy and enter its view.
qos policy policy-name
3. Specify the traffic behavior for the traffic class in the QoS policy.
classifier classifier-name behavior behavior-name
Applying the QoS policy
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Apply the QoS policy to the inbound direction of the port.
qos apply policy policy-name inbound
Display and maintenance commands for QinQ
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display QinQ-enabled ports. |
display qinq [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
QinQ configuration examples
Example: Configuring basic QinQ
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3:
· The service provider assigns VLAN 100 to Company A's VLANs 10 through 70.
· The service provider assigns VLAN 200 to Company B's VLANs 30 through 90.
· The devices between PE 1 and PE 2 in the service provider network use a TPID value of 0x8200.
Configure QinQ on PE 1 and PE 2 to transmit traffic in VLANs 100 and 200 for Company A and Company B, respectively.
For the QinQ frames to be identified correctly, set the SVLAN TPID to 0x8200 on the service provider-side ports of PE 1 and PE 2.
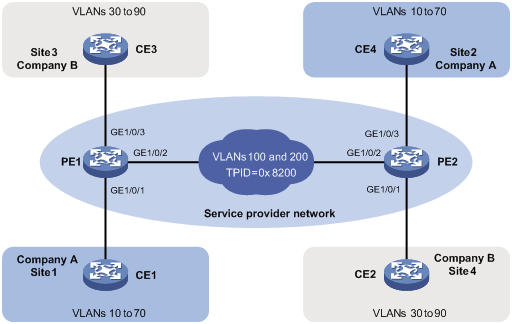
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port, and assign it to VLAN 100 and VLANs 10 through 70.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 100 10 to 70
# Set the PVID of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to VLAN 100.
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port trunk pvid vlan 100
# Enable QinQ on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] qinq enable
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 as a trunk port, and assign it to VLANs 100 and 200.
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 100 200
# Set the TPID value in the SVLAN tags to 0x8200 on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] qinq ethernet-type service-tag 8200
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 as a trunk port, and assign it to VLAN 200 and VLANs 30 through 90.
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 200 30 to 90
# Set the PVID of GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 200.
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port trunk pvid vlan 200
# Enable QinQ on GigabitEthernet 1/0/3.
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] qinq enable
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 as a trunk port, and assign it to VLAN 200 and VLANs 30 through 90.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 200 30 to 90
# Set the PVID of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to VLAN 200.
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port trunk pvid vlan 200
# Enable QinQ on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] qinq enable
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 as a trunk port, and assign it to VLANs 100 and 200.
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 100 200
# Set the TPID value in the SVLAN tags to 0x8200 on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] qinq ethernet-type service-tag 8200
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 as a trunk port, and assign it to VLAN 100 and VLANs 10 through 70.
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 100 10 to 70
# Set the PVID of GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 100.
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port trunk pvid vlan 100
# Enable QinQ on GigabitEthernet 1/0/3.
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] qinq enable
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
3. Configure the devices between PE 1 and PE 2:
# Set the MTU to a minimum of 1504 bytes for each port on the path of QinQ frames. (Details not shown.)
# Configure all ports on the forwarding path to allow frames from VLANs 100 and 200 to pass through without removing the VLAN tag. (Details not shown.)
