- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-PPP Troubleshooting Guide | 56.13 KB |
Troubleshooting Layer 2—WAN access
PPP issues
PPP interface in protocol down state
Symptom
After the physical PPP interfaces of two devices are connected, the link layer protocol state of the interfaces is displayed as down.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The physical layer state of the interface is not up.
· The PPP-related configuration is incorrect on the interfaces at both ends of the link.
· The PPP protocol packets are dropped.
· A loop exists on the link.
· The link latency is too high.
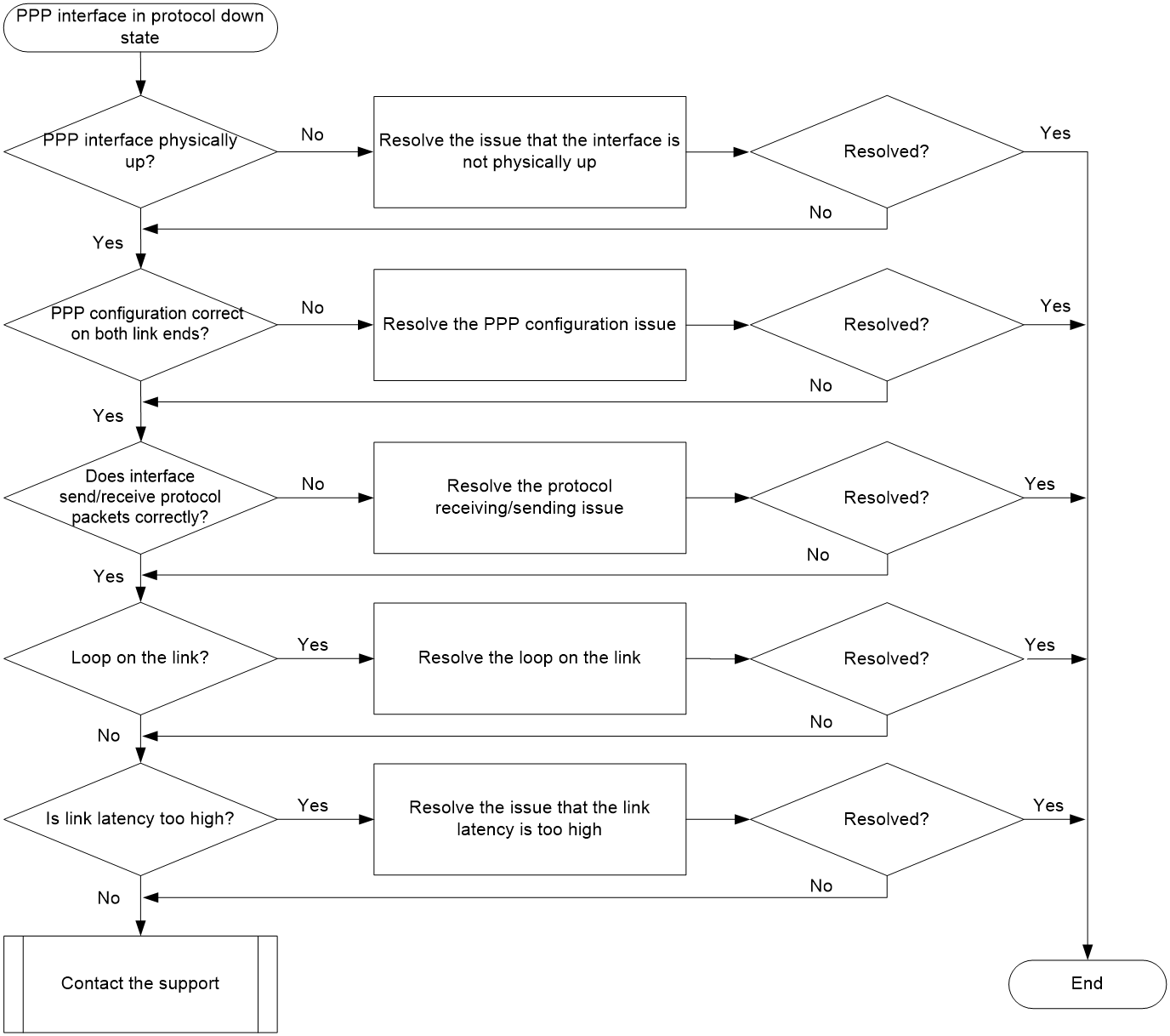
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting PPP interfaces in protocol down state
Solution
1. Identify whether the interface is up on the physical layer.
Execute the display interface interface-type interface-number command in any view to check the physical state of the local interface:
¡ If the physical state of the local interface is Administratively DOWN, the local interface is shut down by using the shutdown command. In this case, bring up the interface by executing the undo shutdown command on the local interface.
¡ If the physical state of the local interface is DOWN, identify whether the peer interface is shut down by using the shutdown command. If yes, bring up the peer interface by executing the undo shutdown command on the peer interface.
¡ Identify whether the optical fibers and transceiver modules are firmly installed at both ends, and whether the Rx/Tx optical fibers are correctly plugged. Resolve the issue that the interface is physically down.
¡ If the interface state is up, proceed to the next step.
2. Identify whether the PPP configuration is correct at both ends of the link.
Execute the display this command on the interface where the PPP protocol is down to check the PPP-related configuration on the interface.
[Sysname-Serial3/0/5] display this
#
interface Serial3/0/5
ip address 12.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
return
¡ Verify that the link layer protocol is PPP on both interfaces of the link. More specifically: In any view on the devices at both ends, execute the display interface interface-type interface-number command to identify whether the value for the Link layer protocol field in the command output is PPP on both interfaces. If it is not PPP on an interface, execute the link-protocol ppp command on the interface to configure the link layer protocol as PPP.
¡ If PPP authentication has been configured, identify whether the authentication type and the authentication username/password of the authenticator are the same as those of the authenticatee. If they are different, modify the configuration as described in the PPP configuration guide.
¡ If interfaces on both ends are assigned to an MP group, identify whether the MP-group interface is shut down by using the shutdown command. If yes, bring up the MP-group interface by executing the undo shutdown command on the MP-group interface.
¡ If the interface on one end has the remote address command executed, make sure the interface on the other end has either the ip address ppp-negotiate command executed or the ip address command executed to manually configure the IP address specified by using the remote address command on the peer interface.
If PPP is configured correctly but the link layer protocol state is still down on the PPP interface, proceed to the next step.
3. Identify whether the protocol packets are received and sent normally on the interface.
Execute the display ppp packet statistics command in any view to view the statistics of PPP protocol packets and identify whether the packets are sent and received normally.
<Sysname> display ppp packet statistics slot 3
PPP packet statistics in slot 3:
-----------------------------------LCP--------------------------------------
SEND_LCP_CON_REQ : 4 RECV_LCP_CON_REQ : 5
SEND_LCP_CON_NAK : 0 RECV_LCP_CON_NAK : 0
SEND_LCP_CON_REJ : 0 RECV_LCP_CON_REJ : 0
SEND_LCP_CON_ACK : 4 RECV_LCP_CON_ACK : 4
SEND_LCP_CODE_REJ : 0 RECV_LCP_CODE_REJ : 0
SEND_LCP_PROT_REJ : 0 RECV_LCP_PROT_REJ : 0
SEND_LCP_TERM_REQ : 2 RECV_LCP_TERM_REQ : 1
SEND_LCP_TERM_ACK : 1 RECV_LCP_TERM_ACK : 0
SEND_LCP_ECHO_REQ : 25 RECV_LCP_ECHO_REQ : 0
SEND_LCP_ECHO_REP : 0 RECV_LCP_ECHO_REP : 25
SEND_LCP_FAIL : 0 SEND_LCP_CON_REQ_RETRAN : 0
-----------------------------------IPCP-------------------------------------
SEND_IPCP_CON_REQ : 38 RECV_IPCP_CON_REQ : 2
SEND_IPCP_CON_NAK : 0 RECV_IPCP_CON_NAK : 0
SEND_IPCP_CON_REJ : 0 RECV_IPCP_CON_REJ : 0
SEND_IPCP_CON_ACK : 2 RECV_IPCP_CON_ACK : 2
SEND_IPCP_CODE_REJ : 0 RECV_IPCP_CODE_REJ : 0
SEND_IPCP_PROT_REJ : 0 RECV_IPCP_PROT_REJ : 0
SEND_IPCP_TERM_REQ : 0 RECV_IPCP_TERM_REQ : 0
SEND_IPCP_TERM_ACK : 0 RECV_IPCP_TERM_ACK : 0
SEND_IPCP_FAIL : 0
-----------------------------------IPV6CP-----------------------------------
SEND_IPV6CP_CON_REQ : 0 RECV_IPV6CP_CON_REQ : 0
SEND_IPV6CP_CON_NAK : 0 RECV_IPV6CP_CON_NAK : 0
SEND_IPV6CP_CON_REJ : 0 RECV_IPV6CP_CON_REJ : 0
SEND_IPV6CP_CON_ACK : 0 RECV_IPV6CP_CON_ACK : 0
SEND_IPV6CP_CODE_REJ : 0 RECV_IPV6CP_CODE_REJ : 0
SEND_IPV6CP_PROT_REJ : 0 RECV_IPV6CP_PROT_REJ : 0
SEND_IPV6CP_TERM_REQ : 0 RECV_IPV6CP_TERM_REQ : 0
SEND_IPV6CP_TERM_ACK : 0 RECV_IPV6CP_TERM_ACK : 0
SEND_IPV6CP_FAIL : 0
-----------------------------------OSICP------------------------------------
SEND_OSICP_CON_REQ : 0 RECV_OSICP_CON_REQ : 0
SEND_OSICP_CON_NAK : 0 RECV_OSICP_CON_NAK : 0
SEND_OSICP_CON_REJ : 0 RECV_OSICP_CON_REJ : 0
SEND_OSICP_CON_ACK : 0 RECV_OSICP_CON_ACK : 0
SEND_OSICP_CODE_REJ : 0 RECV_OSICP_CODE_REJ : 0
SEND_OSICP_PROT_REJ : 0 RECV_OSICP_PROT_REJ : 0
SEND_OSICP_TERM_REQ : 0 RECV_OSICP_TERM_REQ : 0
SEND_OSICP_TERM_ACK : 0 RECV_OSICP_TERM_ACK : 0
SEND_OSICP_FAIL : 0
-----------------------------------MPLSCP-----------------------------------
SEND_MPLSCP_CON_REQ : 0 RECV_MPLSCP_CON_REQ : 0
SEND_MPLSCP_CON_NAK : 0 RECV_MPLSCP_CON_NAK : 0
SEND_MPLSCP_CON_REJ : 0 RECV_MPLSCP_CON_REJ : 0
SEND_MPLSCP_CON_ACK : 0 RECV_MPLSCP_CON_ACK : 0
SEND_MPLSCP_CODE_REJ : 0 RECV_MPLSCP_CODE_REJ : 0
SEND_MPLSCP_PROT_REJ : 0 RECV_MPLSCP_PROT_REJ : 0
SEND_MPLSCP_TERM_REQ : 0 RECV_MPLSCP_TERM_REQ : 0
SEND_MPLSCP_TERM_ACK : 0 RECV_MPLSCP_TERM_ACK : 0
SEND_MPLSCP_FAIL : 0
-----------------------------------AUTH-------------------------------------
SEND_PAP_AUTH_REQ : 0 RECV_PAP_AUTH_REQ : 0
SEND_PAP_AUTH_ACK : 0 RECV_PAP_AUTH_ACK : 0
SEND_PAP_AUTH_NAK : 0 RECV_PAP_AUTH_NAK : 0
SEND_CHAP_AUTH_CHALLENGE: 0 RECV_CHAP_AUTH_CHALLENGE: 0
SEND_CHAP_AUTH_RESPONSE : 0 RECV_CHAP_AUTH_RESPONSE : 0
SEND_CHAP_AUTH_ACK : 0 RECV_CHAP_AUTH_ACK : 0
SEND_CHAP_AUTH_NAK : 0 RECV_CHAP_AUTH_NAK : 0
SEND_PAP_AUTH_FAIL : 0 SEND_CHAP_AUTH_FAIL : 0
¡ If the number of received or sent packets is 0 or does not increase after you execute this command multiple times, it indicates that protocol packets are lost during transmission. Verify that the interfaces, optical fibers, and transceiver modules are operating correctly to resolve the packet loss issue. If the issue persists, proceed to step 6.
¡ If packets are received and sent normally, proceed to the next step.
4. Identify whether a loop exists on the link.
Execute the debugging ppp all interface interface-type interface-number command in user view on the local device to enable debugging for PPP packets. Identify whether the local end has received and sent packets that are completely the same (such as in the packet type, packet ID, and magic number.)
*Apr 7 19:38:04:384 2022 Sysname PPP/7/FSM_PACKET_0: -MDC=1-Slot=3;
PPP Packet:
Ser3/0/5(109) Output LCP(c021) Packet, PktLen 14
Current State reqsent, code ConfReq(01), id 0, len 10
MagicNumber(5), len 6, val c5 ae e7 03
*Apr 7 19:38:04:390 2022 Sysname PPP/7/FSM_PACKET_0: -MDC=1-Slot=3;
PPP Packet:
Ser3/0/5(109) Input LCP(c021) Packet, PktLen 14
Current State reqsent, code ConfReq(01), id 0, len 10
MagicNumber(5), len 6, val c5 ae e7 03
¡ If yes, a loop exists on the link. Check the cause of the loop (for example, an incorrect fiber connection), and remove the loop. If the issue persists, proceed to step 6.
¡ If not, no loop exists on the link. Proceed to the next step.
5. Identify whether the link latency is too high.
Execute the debugging ppp all interface interface-type interface-number command in user view on the local device to enable debugging for PPP packets. Determine the link latency by checking the time interval between the transmit timestamp and the receive timestamp of the PPP negotiation packets.
*Apr 7 19:38:04:384 2022 Sysname PPP/7/FSM_PACKET_0: -MDC=1-Slot=3;
PPP Packet:
Ser3/0/5(109) Output LCP(c021) Packet, PktLen 14
Current State reqsent, code ConfReq(01), id 0, len 10
MagicNumber(5), len 6, val c5 ae e7 03
*Apr 7 19:38:04:387 2022 Sysname PPP/7/FSM_PACKET_0: -MDC=1-Slot=3;
PPP Packet:
Ser3/0/5(109) Input LCP(c021) Packet, PktLen 14
Current State acksent, code ConfAck(02), id 0, len 10
MagicNumber(5), len 6, val c5 ae e7 03
Identify whether the link latency is longer than the negotiation timeout interval for PPP protocol packets configured on the current interface. The negotiation timeout interval for PPP protocol packets is configured by using the ppp timer negotiate command on the interface, and is 3 seconds by default.
¡ If the link latency is too high, execute the ppp timer negotiate command to appropriately increase the negotiation timeout interval. Alternatively, replace the corresponding device or link and retest the link latency until the link latency is less than the negotiation timeout interval for PPP protocol packets configured on the interface.
¡ If the link latency is small, proceed to the next step.
6. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A