- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-Password Control Troubleshooting Guide | 90.88 KB |
Troubleshooting user access and authentication
Password control issues
Password change required upon admin login
Symptom
When an administrator logs in to the device through local authentication, the system identifies that the password strength does not meet the requirements and prompts the administrator to change the current login password.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The password control configured in local user view has a high password strength check.
· The password control configured in local user group view has a high password strength check.
· The password control configured in system view has a high password strength check.
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
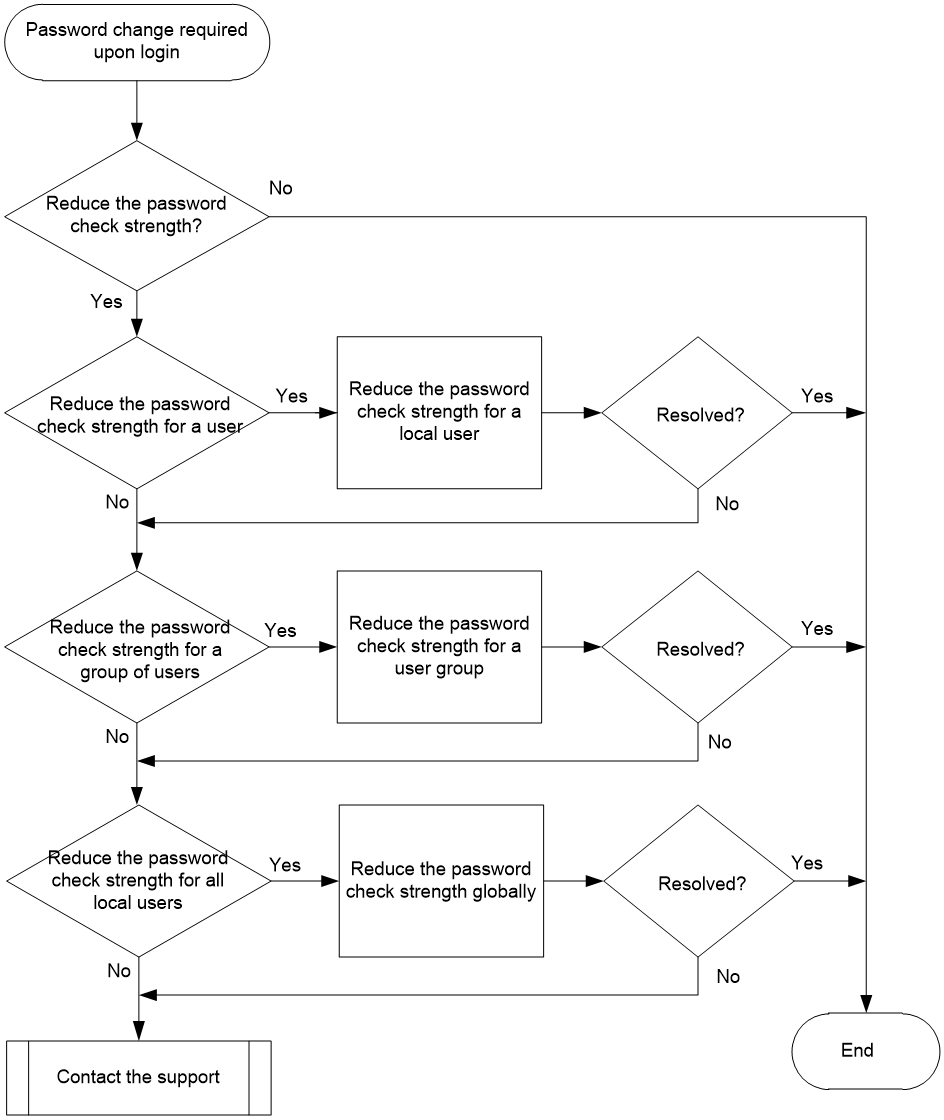
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting password change upon the login of an administrator
Solution
1. Identify whether to reduce the current password check strength.
With the global password control feature enabled, when a device management user that log in via Telnet, SSH, HTTP, and HTTPS enters the login password, the system will check the user's login password according to password restrictions. The password restrictions include the current password composition policy, minimum password length, and password complexity policy. If the password does not meet the above password restrictions, the system considers the password weak. For information about password control, see User Access and Authentication Configuration Guide.
By default, when a user logs in to the device with a weak password, the system will generate an alarm message. If the current password strength check is higher than the actual login control requirements, identify the scope of changes (local user, user group, or all local users). Then, perform the subsequent steps to reduce the password check strength in the corresponding view.
2. Reduce the password check strength of password control for the local user.
Execute the local-user command to enter local user view and perform the following operations:
¡ Execute the password-control composition command to configure the password composition policy. In this example, a password must contain a minimum of four character types and a minimum of five characters for each type.
¡ Execute the password-control length command to set the minimum password length. In this example, the minimum password length is 16 characters.
¡ Execute the password-control complexity command to configure the password complexity policy. In this example, the device will identify whether a password contains the username.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] local-user test class manage
[Sysname-luser-manage-test] password-control composition type-number 4 type-length 5
[Sysname-luser-manage-test] password-control length 16
[Sysname-luser-manage-test] password-control complexity user-name check
3. Reduce the password check strength of password control for the user group.
Execute the user-group command to enter user group view and perform the following operations:
¡ Execute the password-control composition command to configure the password composition policy for the user group.
¡ Execute the password-control length command to set the minimum password length.
¡ Execute the password-control complexity command to configure the password complexity policy.
4. Reduce the password check strength of password control for all local users.
In system view, perform the following operations:
¡ Execute the password-control composition command to configure the password composition policy.
¡ Execute the password-control length command to set the minimum password length.
¡ Execute the password-control complexity command to configure the password complexity policy.
5. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration files, diagnostics information, and prompt messages of the device.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A
Failure to create a local user or configure a user password
Symptom
When you fail to create a local user, the system generates the Add user failed message.
When you fail to configure the local user password, the system generates the Operation failed message.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The memory usage of the device has reached the specified threshold.
· The local file system of the device is running out of memory space.
· An anomaly occurs on the local lauth.dat file of the device.
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 2 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
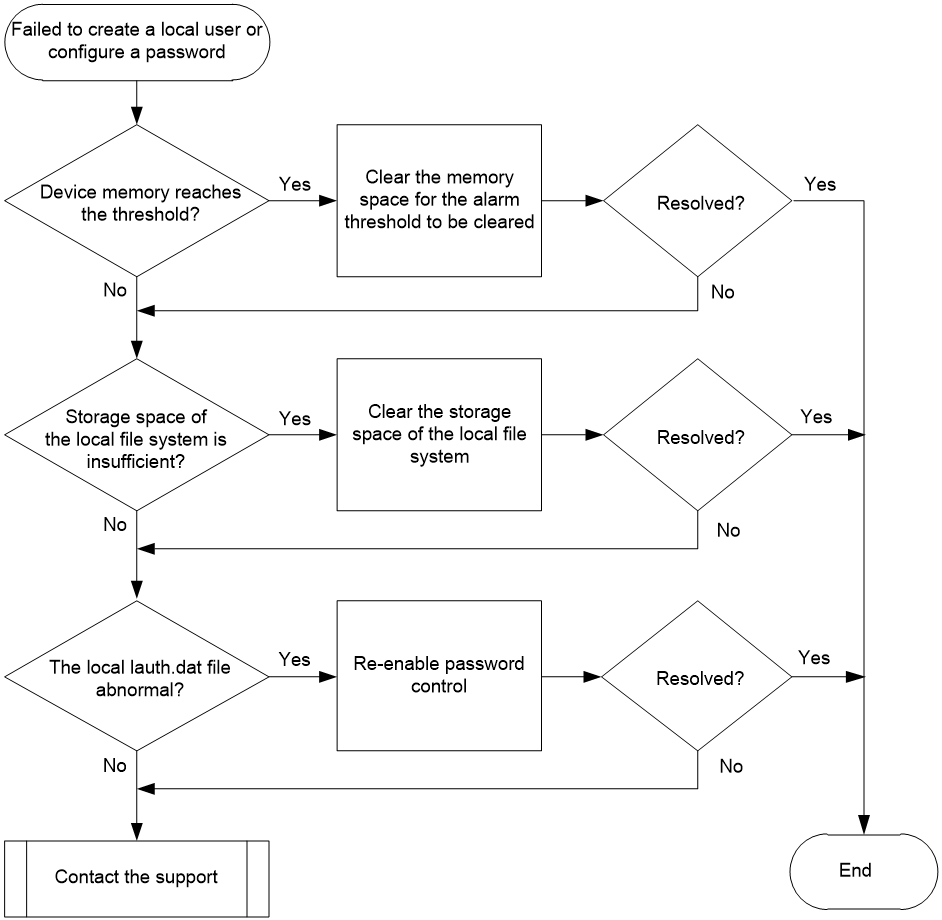
Figure 2 Flowchart for troubleshooting failure to create a local user or configure a user password
Solution
1. Identify whether the amount of the free memory space of the device has reached the specified memory alarm threshold.
If you fail to change the local user's password, directly proceed to step 2.
Execute the display memory-threshold command to view memory alarm thresholds and statistics. You can obtain the current state of the free memory in the system. During the period when the system memory is in the minor, severe, and critical alarm threshold states, creating local users is not allowed.
<Sysname> display memory-threshold
Memory usage threshold: 100%
Free-memory thresholds:
Minor: 96M
Severe: 64M
Critical: 48M
Normal: 128M
Early-warning: 144M
Secure: 160M
Current free-memory state: Normal (secure)
...
You can execute the monitor process command to check the process statistics in any view. Enter m to locate the processes that are consuming excessive memory resources, sorted by memory usage. If necessary, clean up the memory space. After the memory alarm state is cleared, try again to create local users.
2. Identify whether the storage space of the local file system on the device is insufficient.
If any of the following types of log messages are output on the device, a file system error causes this issue:
¡ PWDCTL/3/PWDCTL_FAILED_TO_OPENFILE: Failed to create or open the password file.
¡ PWDCTL/3/PWDCTL_FAILED_TO_WRITEPWD: Failed to write the password records to file.
¡ PWDCTL/3/PWDCTL_NOENOUGHSPACE: Not enough free space on the storage media where the file is located.
Execute the dir command in user view to check the remaining capacity information of local storage media (such as flash). If no enough remaining space is available, delete unnecessary files.
3. Identify whether the local lauth.dat file is operating properly.
After the global password control feature is enabled, the device will automatically generate the lauth.dat file to record the local user's authentication and login information. If this file is manually deleted or edited, an anomaly occurs on local authentication. Execute the dir command in user view to check the presence of the lauth.dat file in the local storage media, such as flash.
<Sysname> dir
Directory of flash: (EXT4)
0 drw- - Aug 16 2021 11:45:37 core
1 drw- - Aug 16 2021 11:45:42 diagfile
2 drw- - Aug 16 2021 11:45:57 dlp
3 -rw- 713 Aug 16 2021 11:49:41 ifindex.dat
4 -rw- 12 Sep 01 2021 02:40:01 lauth.dat
...
If this file is absent, is 0 in size, or is very small (less than 20B when an anomaly might occur), contact Technical Support. If the current configuration is required urgently, you can try to resolve this issue by enabling the global password control feature.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] undo password-control enable
[Sysname] password-control enable
If this issue is resolved, you can try to re-create the local user or configure the user password.
4. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration files, diagnostics information, and prompt messages of the device.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
· PWDCTL/3/PWDCTL_FAILED_TO_WRITEPWD
· PWDCTL/3/PWDCTL_FAILED_TO_OPENFILE
· PWDCTL/3/PWDCTL_NOENOUGHSPACE
Admin login failure due to idle timeout
Symptom
When an administrator uses local authentication to log in to the device, the login might fail due to account idle timeout. The system generates the prompt message of Failed to login because the idle timer expired.
Common causes
The main reason for this issue is that when a user has not logged in successfully within the configured idle time since their last login, their account is immediately invalidated once the idle time expires. Then, the system no longer permits the user to log in using that account.
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 3 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
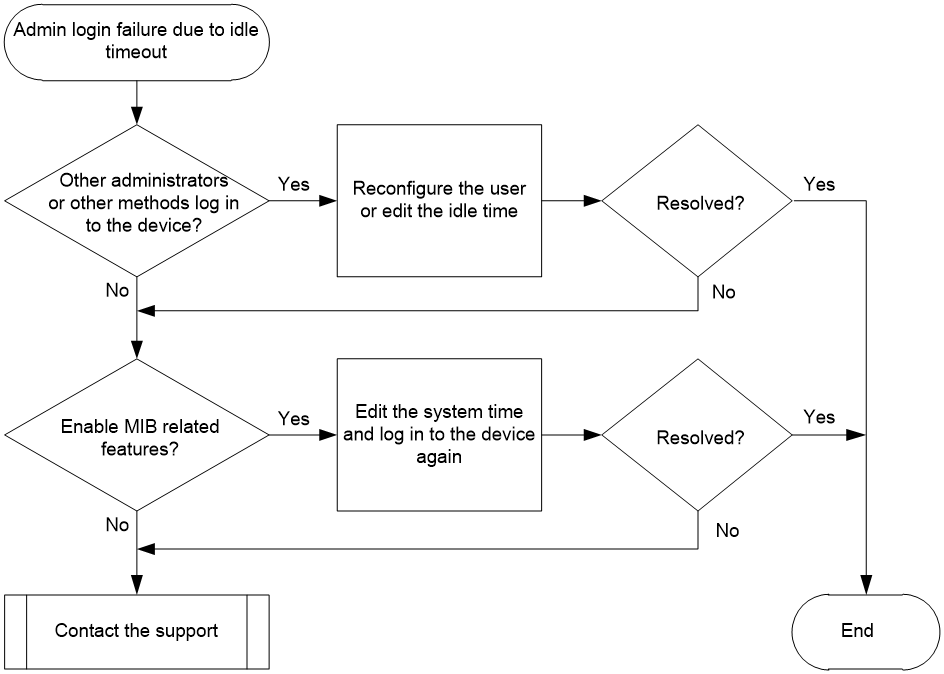
Figure 3 Flowchart for troubleshooting login failure of an administrator due to idle timeout
Solution
1. Identify whether other administrators or methods can log in to the device.
¡ If other administrators or methods (such as console login) can log in to the device, only the target user is prevented from logging in to the device. Therefore, after other administrators log in, they can delete this local user and re-create it, or edit the idle time of the user account (by the password-control login idle-time command). If the idle time is set to 0, the system disables the account idle time restriction.
¡ If no other administrators or methods can log in to the device, proceed to step 2.
2. Identify whether the device is enabled with SNMP.
You can attempt to log in to the device through the network management system (NMS):
¡ If SNMP is enabled, use the MIB to change the system time to a point before the idle time, and then log in to the device with this administrator account. The MIB node for changing system time is hh3cSysLocalClock (1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.3.1.1.1) in HH3C-SYS-MAN-MIB.
After a successful re-login by the administrator, restore the system time and disable the idle timeout check for user accounts.
¡ If you disable SNMP, the MIB is not available. You can try to restart the device and enter the EXTENDED-BOOTWARE menu. Then, select either the option to bypass console authentication or bypass the configuration file option to access the system. As a best practice, contact Technical Support to perform this step.
3. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, diagnostics information, and prompt messages of the device.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A