- Table of Contents
-
- 08-Radio Resources Management Command Reference
- 00-Preface
- 01-Radio management commands
- 02-WLAN radio load balancing commands
- 03-WLAN load balancing commands
- 04-WLAN radio resource measurement commands
- 05-Band navigation commands
- 06-WLAN RRM commands
- 07-Channel scanning commands
- 08-Spectrum management commands
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-Radio management commands | 316.67 KB |
Radio management commands
|
|
NOTE: · Support for the 6 GHz band depends on the AP model and local regulations. · Some tri-band APs support all three radios operating in the 5 GHz band (with radio 1 in 5.15 GHz to 5.35 GHz, radio 2 in 5.47 GHz to 5.85 GHz, and radio 3 in 5.15 GHz to 5.35 GHz or 5.47 GHz to 5.85 GHz). In this case, radio 3 is used only for scanning and is not recommended for service configuration. |
a-mpdu
Use a-mpdu enable to enable the A-MPDU aggregation method.
Use a-mpdu disable to disable the A-MPDU aggregation method.
Use undo a-mpdu to restore the default.
Syntax
a-mpdu { disable | enable }
undo a-mpdu
Default
The A-MPDU aggregation method is enabled.
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to 802.11n radios and radios of higher standards. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11g invalidates the command.
Examples
# Disable the A-MPDU aggregation method.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] type dot11an
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] a-mpdu disable
a-msdu
Use a-msdu enable to enable the A-MSDU aggregation method.
Use a-msdu disable to disable the A-MSDU aggregation method.
Use undo a-msdu to restore the default.
Syntax
a-msdu { disable | enable }
undo a-msdu
Default
The A-MSDU aggregation method is enabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to 802.11n radios and radios of higher standards. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11g invalidates the command.
Examples
# Disable the A-MSDU aggregation method.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] type dot11an
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] a-msdu disable
beacon-interval
Use beacon-interval to set the beacon interval.
Use undo beacon-interval to restore the default.
Syntax
beacon-interval interval
undo beacon-interval
Default
The beacon interval is 100 TUs.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
interval: Specifies the beacon interval in the range of 32 to 8191 TUs.
Examples
# Set the beacon interval to 1000 TUs.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] beacon-interval 1000
bss-color
Use bss-color enable to enable BSS coloring.
Use bss-color disable to disable BSS coloring.
Use undo bss-color to restore the default.
Syntax
bss-color { disable | enable }
undo bss-color
The following compatibility matrix shows the support of hardware platforms for this command:
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Command compatibility |
|
WA7200 series |
WA7220 WA7220-HI WA7220H WA7226-C WA7230 WA7230-LI |
No |
|
WA7300 series |
WA7320i WA7322H-HI WA7330X WA7338-HI |
Yes |
|
WA7500 series |
WA7538 WA7539 |
Yes |
|
WA7600 series |
WA7638 |
No |
Default
BSS coloring is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command takes effect only on 802.11ax radios and radios of higher standards. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a/b/g or a lower one removes the configuration.
BSS coloring enables the system to assign a color to each BSS and include the color ID in data packets for clients to identify if a packet comes from the associated AP. To avoid conflicts, clients that detect an 802.11ax data packet with the same color as its associated BSS will postpone transmission.
Enabling BSS coloring in a high density environment can improve system performance and channel usage.
Examples
# Enable BSS coloring.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] bss-color enable
Related commands
type dot11ax
channel
Use channel to specify a working channel for a radio interface.
Use undo channel to restore the default.
Syntax
channel { channel-number | auto }
undo channel
Default
The AP selects a working channel automatically.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
channel-number: Specifies a channel by its number. The value range for this argument varies by region code and radio mode.
auto: Configures the AP to automatically select a channel.
Usage guidelines
When radar signals are detected on the working channel of a radio, the AP changes its channel, and switches back to the specified channel after 30 minutes. Then the AP starts the quiet timer. If no radar signals are detected within the quiet time, the AP starts to use the channel. If radar signals are detected within the quiet time, the AP changes its channel.
Examples
# Specify channel 6 as the working channel.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] channel 6
channel band-width
Use channel band-width to set the bandwidth mode.
Use undo channel band-width to restore the default.
Syntax
channel band-width { 20 | 40 [ auto-switch ] | 80 | 160 | 320 }
undo channel band-width
Default
The bandwidth mode is 80 MHz for 802.11eax radios, 80 MHz for 802.11be radios, 160 MHz for 802.11eax radios, 80 MHz for 802.11abe radios, 80 MHz for 802.11ax radios, 20 MHz for 802.11gbe radios, 20 MHz for 802.11gax radios, 80 MHz for 802.11ac radios, 40 MHz for 802.11an radios, and 20 MHz for 802.11gn radios. The default bandwidth mode for 802.11be radios varies by device model.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
20: Sets the bandwidth mode to 20 MHz.
40: Sets the bandwidth mode to 40 MHz.
80: Sets the bandwidth mode to 80 MHz.
auto-switch: Allows a radio to switch its bandwidth mode between 20 MHz and 40 MHz. This keyword is applicable only to 802.11gn and 802.11gax radios.
160: Sets the bandwidth mode to 160 MHz. Support for this keyword depends on the AP model.
320: Sets the bandwidth mode to 320 MHz. Support for this keyword depends on the AP model.
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to the following radio types: 802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11ax, and 802.11gax 802.11eax, 802.11be, 802.11abe, and 802.11gbe. When you change the mode of a radio, the default setting of this command for the new radio mode is restored.
The radio uses the specified 40/80/160/320 MHz bandwidth if adjacent channels can be bound to form a 40/80/160/320 channel. If adjacent channels cannot form a 40/80/160/320 channel, the radio uses the next available bandwidth less than the specified one.
For example, the bandwidth mode is set to 80 MHz. The radio uses the 80 MHz bandwidth if adjacent channels that can be bound together exist. If adjacent channels that can be bound to an 80 MHz channel do not exist, but two adjacent channels that can be bound to a 40 MHz channel exist, the 40 MHz bandwidth is used. If no adjacent channels that can be bound together exist, the radio uses the 20 MHz bandwidth.
If the working channel is specified and the actual bandwidth is 160 MHz or 320 MHz, the device automatically selects a secondary channel.
Examples
# Set the bandwidth mode to 40 MHz.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] channel band-width 40
Related commands
channel
channel-usage measure
Use channel-usage measure to perform on-demand channel usage measurement.
Syntax
channel-usage measure
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This feature enables an AP to scan supported channels and display the channel usage after measurement. The measurement of each channel takes about one second.
Examples
# Perform on-demand channel usage measurement on radio interface 2.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface WLAN-Radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] channel-usage measure
Please wait..............Done.
Channel Usage
1 23%
2 34%
3 26%
4 36%
5 42%
6 39%
7 27%
8 45%
9 29%
10 38%
11 46%
12 30%
13 33%
client dot11ac-only
Use client dot11ac-only enable to enable the client dot11ac-only feature.
Use client dot11ac-only disable to disable the client dot11ac-only feature.
Use undo client dot11ac-only to restore the default.
Syntax
client dot11ac-only { disable | enable }
undo client dot11ac-only
Default
The client dot11ac-only feature is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to 802.11ac radios and radios of higher standards. Changing the radio mode invalidates the command.
After you configure this command on a radio, the radio accepts only 802.11ac clients and clients of higher standards, and all lower-standard clients that are associated with the radio are logged off.
Examples
# Enable the client dot11ac-only feature.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] client dot11ac-only enable
Related commands
dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss
client dot11ax-only
Use client dot11ax-only enable to enable the client dot11ax-only feature.
Use client dot11ax-only disable to disable the client dot11ax-only feature.
Use undo client dot11ax-only to restore the default.
Syntax
client dot11ax-only { disable | enable }
undo client dot11ax-only
Default
The client dot11ax-only feature is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to 802.11ax radios and radios of higher standards. Changing the radio mode invalidates the command.
After you configure this command for a radio, the radio accepts only 802.11ax clients and clients of higher standards, and all lower-standard clients that are associated with the radio are logged off.
Examples
# Enable the client dot11ax-only feature.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] client dot11ax-only enable
Related commands
dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss
client dot11n-only
Use client dot11n-only enable to enable the client dot11n-only feature.
Use client dot11n-only disable to disable the client dot11n-only feature.
Use undo client dot11n-only to restore the default.
Syntax
client dot11n-only { disable | enable }
undo client dot11n-only
Default
The client dot11n-only feature is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to 802.11n radios and radios of higher standards. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11g invalidates the command.
After you configure this command on a radio, the radio accepts only 802.11n clients and clients of higher standards, and all 802.11a/b/g clients that are associated with the radio are logged off.
Examples
# Enable the client dot11n-only feature.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] client dot11n-only enable
client max-count
Use client max-count to set the maximum number of clients that can associate with an AP.
Use undo client max-count to restore the default.
Syntax
client max-count max-number
undo client max-count
Default
No limit is set for the number of clients that can associate with an AP.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
max-number: Specifies the maximum number of clients that can associate with an AP
Usage guidelines
When the maximum number of clients is reached on an AP, the AP stops accepting new clients.
Examples
# Set the maximum number of clients that can associate with an AP to 38.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] client max-count 38
display wlan ap radio
Use display wlan ap radio to display radio information.
Syntax
display wlan ap radio radio-id
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
Parameters
radio-id: Specifies a radio by its ID.
Examples
# Display information about radio 1.
<Sysname> display wlan ap radio 1
Radio 1:
BSSID : 74ea-cbdf-0640
State : Up
Type : 802.11acx(5GHz)
Antenna type : internal
Client dot11ac-only : Disabled
Client dot11n-only : Disabled
Channel band-width : 20/40/80MHz
Operating band-width : 20/40/80MHz
Secondary channel mode : SCA
Short GI for 20MHz : Supported
Short GI for 40MHz : Supported
Short GI for 80MHz : Supported
Short GI for 160MHz : Not supported
MIMO : Not Config
Green-Energy-Management : Disabled
A-MSDU : Enabled
A-MPDU : Enabled
LDPC : Not Supported
STBC : Supported
Operational VHT-MCS set:
Mandatory : Not configured
Supported : NSS1 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
NSS2 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
NSS3 0,1,2,3,4,5,7,8,9
NSS4 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
Multicast : Not configured
Operational HT MCS set:
Mandatory : Not configured
Supported : 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,
18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31
Multicast : Not configured
Channel : 36
Channel usage(%) : 0
Max power : 24 dBm
Operational rate:
Mandatory : 6, 12, 24 Mbps
Multicast : Auto
Supported : 9, 18, 36, 48, 54 Mbps
Disabled : Not configured
Distance : 1 km
ANI : Enabled
Fragmentation threshold : 2346 bytes
Beacon interval : 100 TU
Protection threshold : 2346 bytes
Long retry threshold : 4
Short retry threshold : 7
Frame aging time in cache : 2000 ms
Noise floor : -113 dBm
Protection mode : cts-to-self
MU-TxBF : Enabled
SU-TxBF : Enabled
Continuous mode : N/A
Client dot11ax-only : Disabled
Operational HE-MCS Set:
Mandatory : Not configured
Supported : NSS1 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11
NSS2 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11
Multicast : Not configured
OFDMA random access RUs : Not Supported
DL-OFDMA : Enabled
UL-OFDMA : Enabled
UL-MU-MIMO : Disabled
BSS-COLOR : Enabled
TWT negotiation : Enabled
ATF : Enabled
radar-detect switch : Enabled
HT protection mode : No protection
Table 1 Command output
|
Field |
Description |
|
State |
Radio state: · Up. · Down. |
|
Type |
Radio type: · 2.4GHz—802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n(2.4GHz), 802.11ax(2.4GHz), or 802.11be(2.4GHz) · 5GHz—802.11a, 802.11n(5GHz), 802.11ac(5GHz), 802.11ax(5GHz), or 802.11be(5GHz) · 6GHz—802.11ax(6GHz) or 802.11be(6GHz) |
|
Antenna type |
Antenna type. |
|
Client dot11ac-only |
· Disabled—Allows both 802.11ac and 802.11a/b/g/n clients to associate with the radio. · Enabled—Allows only 802.11ac clients to associate with the radio. |
|
Client dot11n-only |
· Disabled—Allows 802.11ac, 802.11n, and 802.11a/b/g clients to associate with the radio. · Enabled—Allows only 802.11n and 802.11ac clients to associate with the radio. |
|
Channel band-width |
Channel bandwidth: · 20MHz. · 20/40MHz. · 20/40/80MHz. · 20/40/80/160MHz. · 20/40/80/160/(80+80)/320MHz. |
|
Operating band-width |
Operating bandwidth of the radio. |
|
Secondary channel mode |
Secondary channel mode for 802.11n and 802.11ac radios: · SCA—Second Channel Above (SCA). The radio operates in 40 MHz bandwidth mode, and the secondary channel is above the primary channel. · SCB—Second Channel Below (SCB). The radio operates in 40 MHz bandwidth mode, and the secondary channel is below the primary channel. · SCN—The radio does not operate in 40 MHz bandwidth mode. This field is available only when the operating bandwidth is 20/40/80MHz. |
|
Short GI for 20MHz |
· Not supported. · Supported. |
|
Short GI for 40MHz |
· Not supported. · Supported. |
|
Short GI for 80MHz |
· Not supported. · Supported. |
|
Short GI for 160MHz |
· Not supported. · Supported. |
|
Short GI for 320MHz |
· Not supported. · Supported. |
|
MIMO |
MIMO mode: · 1x1—The radio sends and receives signals through one spatial stream. · 2x2—The radio sends and receives signals through two spatial streams. · 3x3—The radio sends and receives signals through three spatial streams. · 4x4—The radio sends and receives signals through four spatial streams. · Not configured—The radio sends and receives signals through the maximum number of spatial streams supported by the radio. If this field also displays (PowerLow) after any value option to indicate low power level, the radio can send and receive signals only through one spatial stream. |
|
Green-Energy-Management |
· Disabled. · Enabled. |
|
A-MSDU |
· Disabled. · Enabled. |
|
A-MPDU |
· Disabled. · Enabled. |
|
LDPC |
· Supported. · Not Supported. |
|
STBC |
· Supported. · Not Supported. |
|
Operational VHT-MCS set |
· Supported—Supported VHT MCS set. · Mandatory—Mandatory VHT MCS set. · Multicast—Multicast VHT MCS set. |
|
Operational HT MCS set |
· Supported—Supported MCS set. · Mandatory—Mandatory MCS set. · Multicast—Multicast MCS set. |
|
Channel |
· Number<auto>—This field displays Number<auto> if the current channel is the optimal channel automatically selected by the AP. · Number—This field displays Number if the current 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz channel is manually configured. · Number<avoid radar>—This field displays Number<avoid radar> if the current channel is automatically selected by the AP to avoid radar signals. · 6G_Number—This field displays 6G_Number if the current 6 GHz channel is manually configured. |
|
Max power |
Maximum transmission power of the radio. |
|
Preamble type |
Preamble type: · Short. · Long. |
|
Operational rate |
· Mandatory. · Supported. · Multicast. · Disabled. · Not configured. |
|
Distance |
Maximum distance that the radio signal can reach. |
|
ANI |
· Enabled. · Disabled. |
|
Protection threshold |
Frame length threshold required for triggering the protection mechanism. |
|
Long retry threshold |
Maximum number of retransmission attempts for frames whose length exceeds the RTS threshold. |
|
Short retry threshold |
Maximum number of retransmission attempts for frames whose length is below the RTS threshold. |
|
Protection mode |
Conflict avoidance mode: · cts-to-self. · rts-cts. |
|
MU-TxBF |
· Enabled. · Disabled. Support for this field depends on the AP model. |
|
SU-TxBF |
· Enabled. · Disabled. Support for this field depends on the AP model. |
|
Continuous mode configuration: · Rate. · MCS index. · NSS index. · VHT-MCS index. · This field displays N/A if the continuous mode is not configured. |
|
|
Client dot11ax-only |
· Disabled—Allows both 802.11ax and 802.11a/b/g/n clients to associate with the radio. · Enabled—Allows only 802.11ax clients to associate with the radio. |
|
Operational EHT-MCS Set |
· Supported—Supported EHT-MCS set. · Mandatory—Mandatory EHT-MCS set. · Multicast—Multicast EHT-MCS set. |
|
OFDMA random access RUs |
OFDMA random access RUs: · Not supported. · Supported. |
|
DL-OFDMA |
DL-OFDMA: · Disabled. · Enabled. |
|
UL-OFDMA |
UL-OFDMA: · Disabled. · Enabled. |
|
UL-MU-MIMO |
UL-MU-MIMO: · Disabled. · Enabled. |
|
BSS-COLOR |
BSS-COLOR: · Disabled. · Enabled. |
|
TWT negotiation |
TWT negotiation: · Disabled. · Enabled. |
|
ATF |
ATF: · Disabled. · Enabled. |
|
radar-detect switch |
Radar detection: · Disabled. · Enabled. |
|
HT protection mode |
802.11n protection mode: · No protection. ¡ AP-associated clients and nearby wireless devices are operating in 802.11n mode and AP-associated clients are 802.11n clients with a bandwidth of 40 MHz. ¡ AP-associated clients are 802.11n clients with a bandwidth of 20 MHz. · Non-member protection. · 20 MHz protection. · Non-HT mixed. |
distance
Use distance to set the maximum transmission distance.
Use undo distance to restore the default.
Syntax
distance distance
undo distance
Default
The maximum transmission distance is 1 km (0.62 miles).
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
distance: Specifies the maximum transmission distance in the range of 1 to 40 km (0.62 to 24.86 miles).
Examples
# Set the maximum transmission distance to 5 km (3.11 miles).
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] type dot11g
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] distance 5
dl-ofdma
Use dl-ofdma enable to enable OFDMA.
Use dl-ofdma disable to disable OFDMA.
Use undo dl-ofdma to restore the default.
Syntax
dl-ofdma { disable | enable }
undo dl-ofdma
Default
Downlink OFDMA is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command takes effect only on 802.11ax and 802.11gax radios. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/gac removes the configuration.
OFDMA can provide the following benefits if enabled in a high density environment where small data packets are transmitted:
· Concurrent transmission to multiple users.
· Improved radio usage.
· Shortened transmission latency.
· Reduced conflict backoff.
Examples
# Enable downlink OFDMA.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] dl-ofdma enable
Related commands
type dot11ax
dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss
Use dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss to set the maximum mandatory NSS.
Use undo dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss nss-number
undo dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss
Default
No maximum mandatory NSS is set.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
nss-number: Specifies the maximum mandatory NSS in the range of 1 to 8.
Usage guidelines
Changing the radio mode to one lower than 802.11ac removes the configuration.
The maximum mandatory NSS cannot be greater than the maximum supported NSS.
After you modify the maximum mandatory NSS, clients that are associated with the radio and that do not support the modified NSS will go offline.
Examples
# Set the maximum mandatory NSS to 7.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss 7
Related commands
dot11ac support maximum-nss
dot11ac multicast-nss
Use dot11ac multicast-nss to set the multicast NSS and specify a VHT-MCS index.
Use undo dot11ac multicast-nss to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11ac multicast-nss nss-number vht-mcs index
undo dot11ac multicast-nss
Default
No multicast NSS is set.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
nss-number: Specifies the multicast NSS in the range of 1 to 8.
index: Specifies a VHT-MCS index in the range of 0 to 9.
Usage guidelines
Changing the radio mode to one lower than 802.11ac removes the configuration.
Before configuring this command, you must configure the dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss command.
The multicast NSS cannot be greater than the maximum mandatory NSS.
Examples
# Set the maximum mandatory NSS, multicast NSS, and VHT-MCS index to 2, 2, and 2, respectively.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss 2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11ac multicast-nss 2 vht-mcs 2
Related commands
dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss
dot11ac support maximum-nss
Use dot11ac support maximum-nss to set the maximum supported NSS.
Use undo dot11ac support maximum-nss to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11ac support maximum-nss nss-number
undo dot11ac support maximum-nss
Default
The maximum supported NSS is 8.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
nss-number: Specifies the maximum supported NSS in the range of 1 to 8.
Usage guidelines
Changing the radio mode to one lower than 802.11ac removes the configuration.
The maximum supported NSS cannot be smaller than the maximum mandatory NSS.
Examples
# Set the maximum supported NSS to 7.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11ac support maximum-nss 7
Related commands
dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss
dot11ax mandatory maximum-nss
Use dot11ax mandatory maximum-nss to set the maximum mandatory NSS for 802.11ax radios.
Use undo dot11ax mandatory maximum-nss to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11ax mandatory maximum-nss nss-number
undo dot11ax mandatory maximum-nss
Default
No maximum mandatory NSS is set for an 802.11ax radio interface.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
nss-number: Specifies the maximum mandatory NSS in the range of 1 to 8.
Usage guidelines
Changing the radio mode to one lower than 802.11ax removes the configuration.
The maximum mandatory NSS cannot be greater than the maximum supported NSS.
Examples
# Set the maximum mandatory NSS to 8.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11ax mandatory maximum-nss 8
Related commands
type dot11ax
dot11ax multicast-nss
Use dot11ax multicast-nss to set the multicast NSS and specify an HE-MCS index for 802.11ax radios.
Use undo dot11ax multicast-nss to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11ax multicast-nss nss-number he-mcs index
undo dot11ax multicast-nss
Default
No multicast NSS is set for an 802.11ax radio interface.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
nss-number: Specifies the multicast NSS in the range of 1 to 8.
index: Specifies an HE-MCS index in the range of 0 to 11.
Usage guidelines
Before configuring this command, you must configure the dot11ax mandatory maximum-nss command.
The multicast NSS cannot be greater than the maximum mandatory NSS.
Changing the radio mode to one lower than 802.11ax removes the configuration.
Examples
# Set the maximum mandatory NSS, multicast NSS, and HE-MCS index to 2, 2, and 2, respectively.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11ax mandatory maximum-nss 2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11ax multicast-nss 2 he-mcs 2
Related commands
dot11ax mandatory maximum-nss
dot11ax support maximum-nss
Use dot11ax support maximum-nss to set the maximum supported NSS for 802.11ax radios.
Use undo dot11ax support maximum-nss to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11ax support maximum-nss nss-number
undo dot11ax support maximum-nss
Default
The maximum supported NSS is 8 for an 802.11ax radio interface.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
nss-number: Specifies the maximum supported NSS in the range of 1 to 8.
Usage guidelines
Changing the radio mode to one lower than 802.11ax removes the configuration.
Examples
# Set the maximum supported NSS to 8.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11ax support maximum-nss 8
Related commands
type dot11ax
dot11be mandatory maximum-nss
Use dot11be mandatory maximum-nss to set the maximum mandatory NSS for 802.11be.
Use undo dot11be mandatory maximum-nss to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11be mandatory maximum-nss nss-number
undo dot11be mandatory maximum-nss
Default
No maximum mandatory NSS is set.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
nss-number: Specifies the maximum mandatory NSS, in the range of 1 to 8.
Usage guidelines
Changing the radio mode to one lower than 802.11be removes the configuration.
The maximum mandatory NSS specified in this command for 802.11be cannot exceed the maximum supported NSS configured in the dot11be support maximum-nss command for 802.11be.
Examples
# Set the maximum mandatory NSS for 802.11be.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11be mandatory maximum-nss 8
Related commands
type dot11be
type dot11abe
type dot11gbe
dot11be multicast-nss
Use dot11be multicast-nss to set the multicast NSS and EHT-MCS for 802.11be.
Use undo dot11be multicast-nss to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11be multicast-nss nss-number eht-mcs index
undo dot11be multicast-nss
Default
No multicast NSS is set for 802.11ax radios.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
nss-number: Specifies the multicast NSS for 802.11be, in the range of 1 to 8.
index: Specifies the EHT-MCS index for the NSS, in the range of 0 to 13.
Usage guidelines
The dot11be mandatory maximum-nss command must be configured before this command can be configured.
The NSS for 802.11be multicast specified in this command cannot exceed the maximum mandatory NSS configured for 802.11be in the dot11be mandatory maximum-nss command.
Changing the radio mode to one lower than 802.11be removes the configuration.
Examples
# Set the maximum mandatory NSS to 2, the multicast NSS to 2, and the multicast EHT-MCS index to 2.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11be mandatory maximum-nss 2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11be multicast-nss 2 eht-mcs 2
Related commands
dot11be mandatory maximum-nss
dot11be support maximum-nss
Use dot11be support maximum-nss to set the maximum supported NSS for 802.11be.
Use undo dot11be support maximum-nss to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11be support maximum-nss nss-number
undo dot11be support maximum-nss
Default
The maximum supported NSS is 8.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Examples
nss-number: Specifies the maximum supported NSS for 802.11be, in the range of 1 to 8.
Usage guidelines
Changing the radio mode to one lower than 802.11be removes the configuration.
Examples
# Set the maximum supported NSS to 8.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11be support maximum-nss 8
Related commands
type dot11be
type dot11abe
type dot11gbe
dot11n mandatory maximum-mcs
Use dot11n mandatory maximum-mcs to set the maximum mandatory MCS index.
Use undo dot11n mandatory maximum-mcs to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11n mandatory maximum-mcs index
undo dot11n mandatory maximum-mcs
Default
No maximum mandatory MCS index is set.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
index: Specifies the maximum mandatory MCS index in the range of 0 to 76.
Usage guidelines
Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11g removes the configuration.
Before configuring the dot11n multicast-mcs command, you must set the maximum mandatory MCS index.
After you modify the maximum mandatory MCS index, clients that are associated with the radio and that do not support the modified MCS index will go offline.
Examples
# Set the maximum mandatory MCS index to 14.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11n mandatory maximum-mcs 14
dot11n multicast-mcs
Use dot11n multicast-mcs to set the multicast MCS index.
Use undo dot11n multicast-mcs to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11n multicast-mcs index
undo dot11n multicast-mcs
Default
No multicast MCS index is set.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
index: Specifies the multicast MCS index in the range of 0 to 76.
Usage guidelines
Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11g removes the configuration.
The multicast MCS index takes effect only when the radio associates only with 802.11n clients or clients of higher standards.
If 802.11a/b/g clients exist, the AP and clients use the 802.11a/b/g multicast rate to multicast packets.
The multicast MCS index maps to a rate in 20 MHz bandwidth mode regardless of whether the bandwidth mode is 20 MHz or 40 MHz.
Examples
# Set the multicast MCS index to 14.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11n mandatory maximum-mcs 15
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11n multicast-mcs 14
dot11n support maximum-mcs
Use dot11n support maximum-mcs to set the maximum supported MCS index.
Use undo dot11n support maximum-mcs to restore the default.
Syntax
dot11n support maximum-mcs index
undo dot11n support maximum-mcs
Default
The maximum supported MCS index is 76.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
index: Specifies the maximum supported MCS index in the range of 0 to 76.
Usage guidelines
Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11g removes the configuration.
The maximum supported MCS index cannot be smaller than the maximum mandatory MCS index.
Examples
# Set the maximum supported MCS index to 14.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dot11n support maximum-mcs 14
dtim
Use dtim to set the Delivery Traffic Indication Map (DTIM) interval.
Use undo dtim to restore the default.
Syntax
dtim counter
undo dtim
The following compatibility matrix shows the support of hardware platforms for this command:
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Command compatibility |
|
WA7200 series |
WA7220 WA7220-HI WA7220H WA7226-C WA7230 WA7230-LI |
No |
|
WA7300 series |
WA7320i WA7322H-HI WA7330X WA7338-HI |
Yes |
|
WA7500 series |
WA7538 WA7539 |
Yes |
|
WA7600 series |
WA7638 |
No |
Default
The DTIM interval is 1. The AP sends buffered broadcast and multicast frames after every beacon frame.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
counter: Specifies the DTIM interval in the range of 1 to 31.
Usage guidelines
An AP periodically broadcasts a beacon compliant with the DTIM. After the AP broadcasts the beacon, it sends buffered broadcast and multicast frames based on the value of the DTIM interval. For example, if you set the DTIM interval to 5, the AP sends buffered broadcast and multicast frames every five beacon frames.
Examples
# Set the DTIM interval to 5.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] dtim 5
green-energy-management
Use green-energy-management enable to enable the energy-saving feature.
Use green-energy-management disable to disable the energy-saving feature.
Use undo green-energy-management to restore the default.
Syntax
green-energy-management { disable | enable }
undo green-energy-management
Default
The energy saving feature is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to 802.11n radios and radios of higher standards. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11g invalidates the command.
After you enable the energy-saving feature, the multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) mode of a radio automatically changes to 1x1 if no clients associate with the radio and the radio is not enabled with WIPS. This reduces power consumption.
Examples
# Enable the energy-saving feature.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] green-energy-management enable
ldpc
Use ldpc enable to enable LDPC.
Use ldpc disable to disable LDPC.
Use undo ldpc to restore the default.
Syntax
ldpc { disable | enable }
undo ldpc
Default
LDPC is enabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to 802.11n radios and radios of higher standards. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11g invalidates the command.
The device can receive but cannot send LDPC packets.
For 802.11ax radios, LDPC is enabled by default and cannot be disabled. The ldpc disable configuration does not take effect on 802.11ax radios.
Examples
# Disable LDPC.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] type dot11an
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] ldpc disable
max-power
Use max-power to set the maximum transmit power.
Use undo max-power to restore the default.
Syntax
max-power radio-power
undo max-power
Default
The AP uses the maximum supported transmit power.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
radio-power: Specifies the maximum transmit power. The value range depends on the region code, channel, AP model, radio mode, antenna type, and bandwidth.
Usage guidelines
The transmit power range supported by a radio varies by region code, channel, AP model, radio mode, antenna type, and bandwidth mode. If you change these attributes for a radio after you set the maximum transmit power, the configured maximum transmit power might be out of the supported transmit power range. If this happens, the system automatically adjusts the maximum transmit power to a valid value.
Examples
# Set the maximum transmit power to 15 dBm.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] type dot11g
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] max-power 15
mimo
Use mimo to specify a MIMO mode for a radio.
Use undo mimo to restore the default.
Syntax
mimo { 1x1 | 2x2 | 3x3 | 4x4 | 5x5 | 6x6 | 7x7 | 8x8}
undo mimo
Default
The default setting for this command varies by AP model.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
1x1: Sends and receives signals through one spatial stream.
2x2: Sends and receives signals through two spatial streams.
3x3: Sends and receives signals through three spatial streams.
4x4: Sends and receives signals through four spatial streams.
5x5: Sends and receives signals through five spatial streams.
6x6: Sends and receives signals through six spatial streams.
7x7: Sends and receives signals through seven spatial streams.
8x8: Sends and receives signals through eight spatial streams.
Usage guidelines
MIMO enables a radio to send and receive wireless signals through multiple spatial streams. This improves system capacity and spectrum usage without requiring higher bandwidth.
With green AP enabled, when no users are associated with a radio, the radio operates in 1x1 mode to reduce radiation and save power.
Examples
# Set the MIMO mode to 2x2.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] mimo 2x2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] undo mimo
mru
Use mru enable to enable MRU.
Use mru disable to disable MRU.
Use undo mru to restore the default.
Syntax
mru { disable | enable }
undo mru
The following compatibility matrix shows the support of hardware platforms for this command:
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Command compatibility |
|
WA7200 series |
WA7220 WA7220-HI WA7220H WA7226-C WA7230 WA7230-LI |
No |
|
WA7300 series |
WA7320i WA7322H-HI WA7330X WA7338-HI |
Yes |
|
WA7500 series |
WA7538 WA7539 |
Yes |
|
WA7600 series |
WA7638 |
No |
Default
MRU is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
Operating mechanism
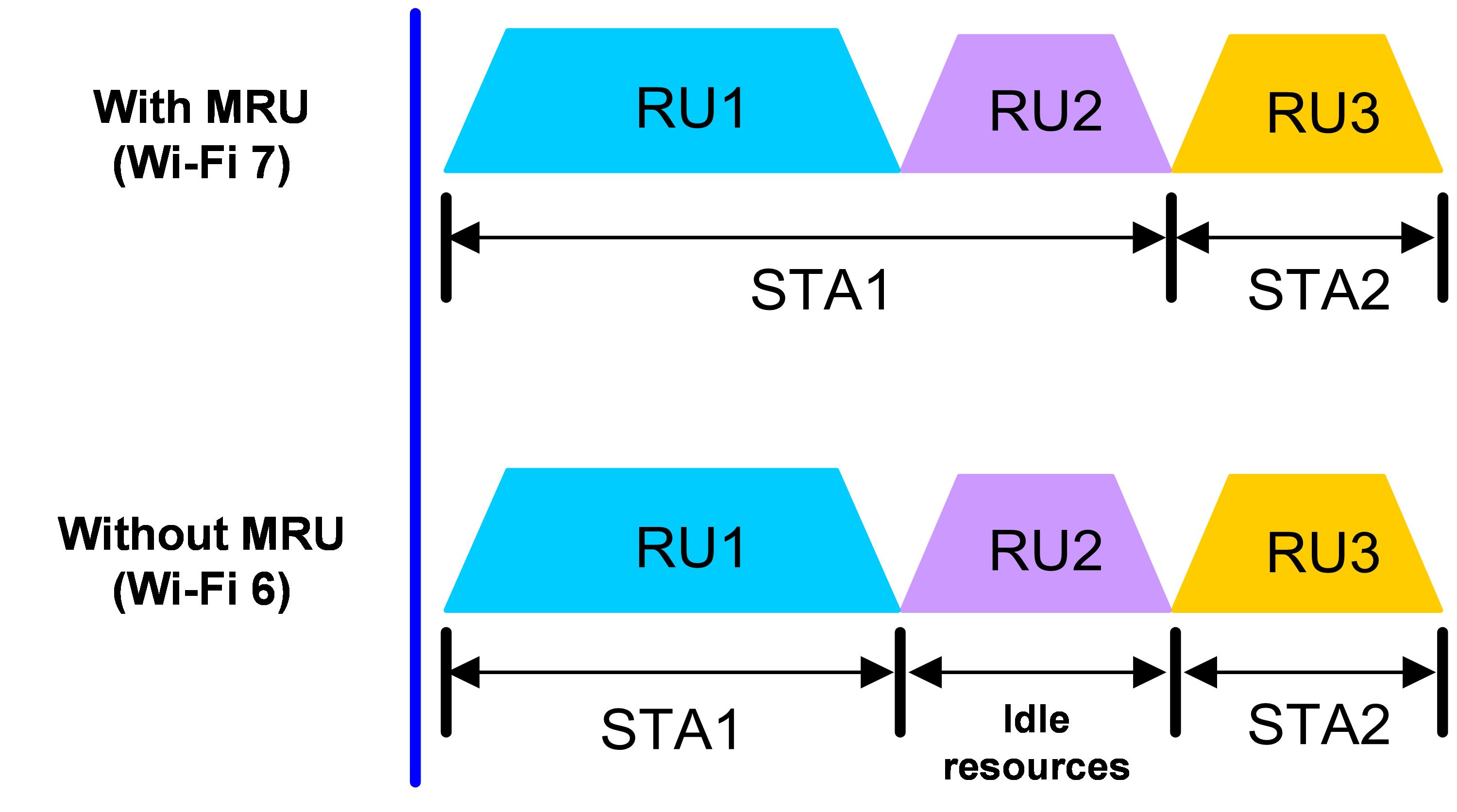
Multiple Resource Unit (MRU) is a technology that increases the spectral resource usage rate, mainly used in multi-user scenarios.
In Wi-Fi6, each user can only use one RU. In Wi-Fi7, the concept of MRU is introduced to allow a single user to use multiple RUs. As shown in Figure 1, under the same bandwidth, MRU allows a single client to occupy multiple RUs simultaneously when data is being transmitted to two users at the same time. This improves spectral resource usage and reduces latency. In Wi-Fi 6, a single client can only use the single RU resource allocated to it, resulting in a waste of spectral resources.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature takes effect only on 802.11be, 802.11gbe, and 802.11abe radios. Changing the radio mode to another mode cancels the configuration.
Examples
# Enable MRU.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] type dot11abe
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] mru enable
mu-txbf
Use mu-txbf enable to enable multi-user transmit beamforming (TxBF).
Use mu-txbf disable to disable multi-user TxBF.
Use undo mu-txbf to restore the default.
Syntax
mu-txbf { disable | enable }
undo mu-txbf
Default
Multi-user TxBF is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to 802.11ac radios and radios of higher standards. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, or 802.11n removes the configuration.
TxBF enables an AP to adjust transmitting parameters based on the channel information to focus RF signals on intended clients. This feature improves the RF signal quality.
Multi-user TxBF is part of 802.11ac Wave2. Multi-user TxBF enables an AP to focus different RF signals on their intended clients to reduce interference and transmission delay. This improves traffic throughput and bandwidth usage. Multi-user TxBF is applicable to WLANs that have a large number of clients and require high bandwidth usage and low transmission delay.
Multi-user TxBF takes effect only when single-user TxBF is enabled.
As a best practice, do not modify the default MIMO settings for an AP enabled with multi-user TxBF.
Examples
# Enable multi-user TxBF.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] su-txbf enable
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] mu-txbf enable
Related commands
mimo
su-txbf
pre-puncture
Use pre-puncture enable to enable preamble puncturing.
Use pre-puncture disable to disable preamble puncturing.
Use undo pre-puncture to restore the default.
Syntax
pre-puncture static { disable | enable }
undo pre-puncture static
The following compatibility matrix shows the support of hardware platforms for this command:
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Command compatibility |
|
WA7200 series |
WA7220 WA7220-HI WA7220H WA7226-C WA7230 WA7230-LI |
No |
|
WA7300 series |
WA7320i WA7322H-HI WA7330X WA7338-HI |
Yes |
|
WA7500 series |
WA7538 WA7539 |
Yes |
|
WA7600 series |
WA7638 |
No |
Default
Preamble puncturing is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
static: Specifies static preamble puncturing.
Usage guidelines
Operating mechanism
The preamble puncturing technology enables data transmission using discontinuous channels to improve channel utilization efficiency. It is mainly used in scenarios with channel interference.
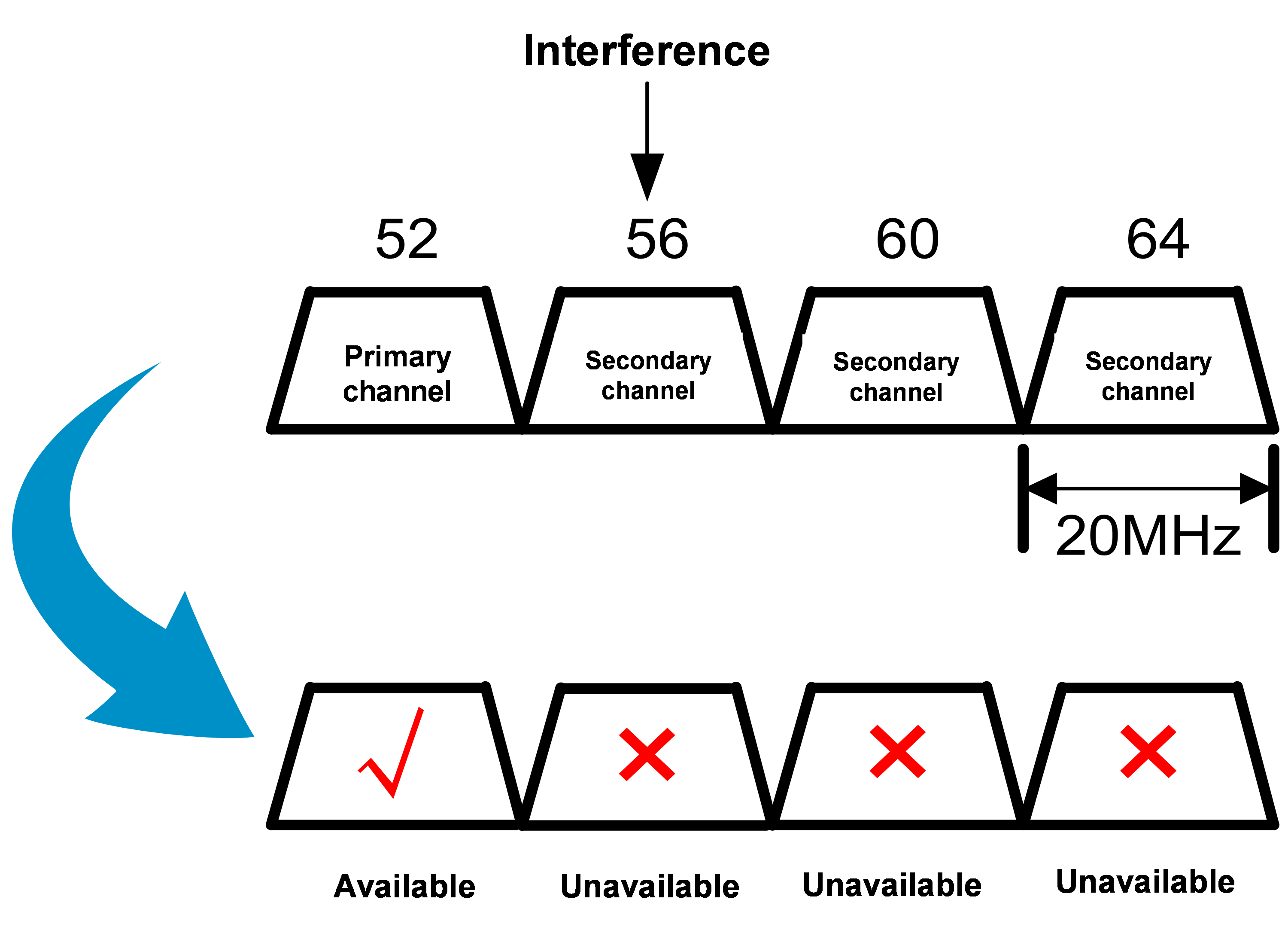
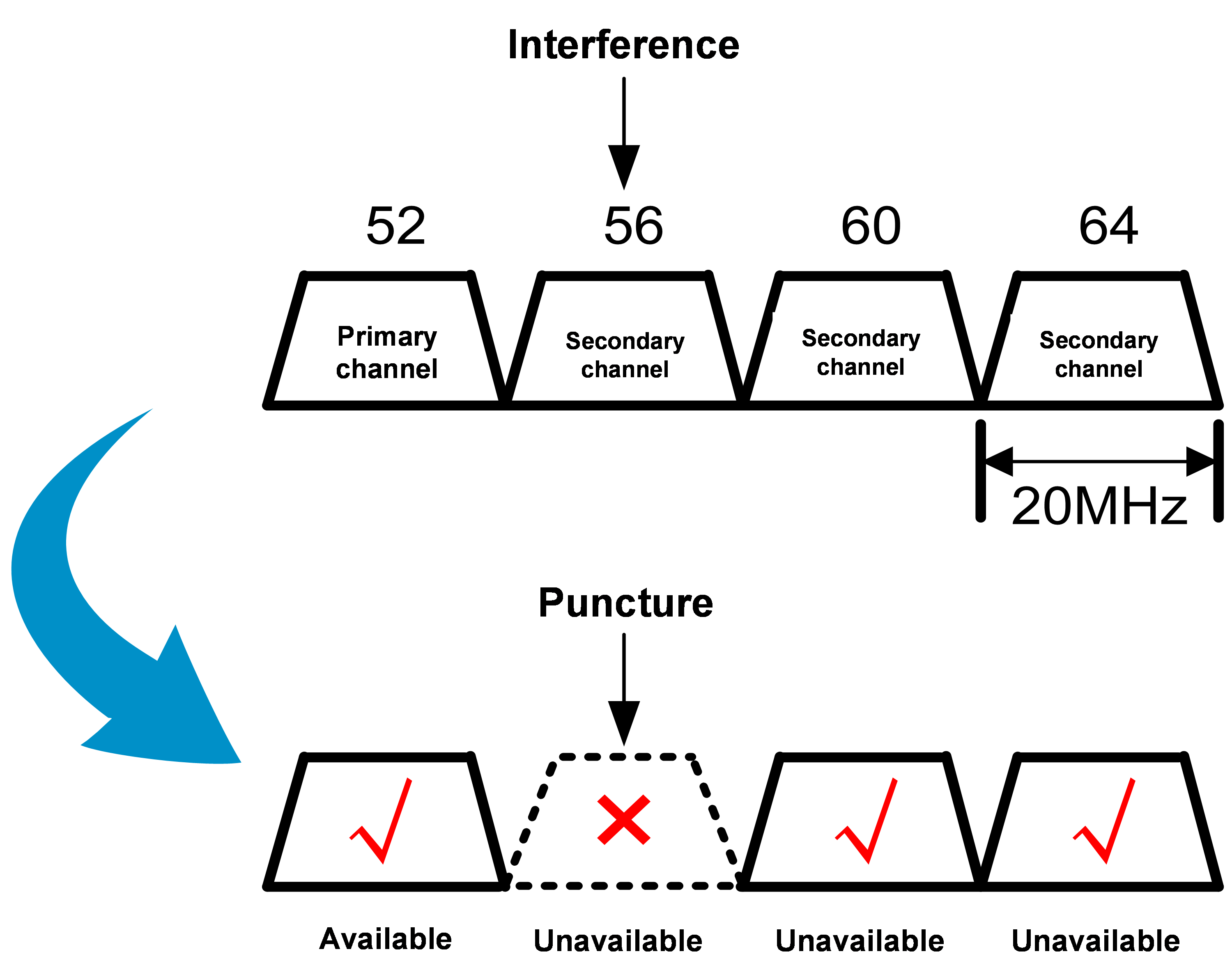
Without preamble puncturing, as shown in Figure 2, if the bandwidth mode is 80 MHz and interference is encountered on channel 56, the system uses the 20 MHz bandwidth mode instead for transmission. With preamble puncturing enabled, as shown in Figure 3, the interfered portion (channel 56) is punctured and shielded, and the remaining channels 52, 60, and 64 are bundled together for information transmission. Although the AP is still working in the 80 MHz bandwidth mode, the interfered channel is put in Null state (idle state) in actual transmission.
Preamble static puncturing refers to the software designating the puncturing positions based on the bandwidth mode and the position of the primary channel.
Figure 2 Without preamble puncturing
Figure 3 With preamble puncturing
Restrictions and guidelines
Preamble puncturing takes effect only when the bandwidth mode is 80 MHz or higher.
This feature takes effect only on 802.11be and 802.11abe radios. Changing the radio mode to another mode cancels the configuration.
Examples
# Enable preamble puncturing.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] type dot11abe
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] pre-puncture static enable
radar-detect disable
Use radar-detect disable to disable radar avoidance.
Use undo radar-detect to restore the default.
Syntax
radar-detect disable
undo radar-detect
Default
Radar avoidance is enabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
Radar avoidance enables a radio to change its working channel or keep silent when radar signals are detected on the working channel, avoiding interference on radars. After 30 minutes, the radio switches back to the previous working channel or restarts transmission. If radar signals can still be detected, the radio changes its working channel or keeps silent again.
With this feature disabled, radios continue to transmit or receive traffic on the working channels even if radar signals are detected on the channels.
Disable radar avoidance only when you perform device debugging.
Examples
# Disable radar avoidance.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] radar-detect disable
rate
Use rate to set the transmission rates for a radio.
Use undo rate to restore the default.
Syntax
rate { multicast { auto | rate-value } | { disabled | mandatory | supported } rate-value }
undo rate
Default
In radio interface view:
· 802.11be/802.11eax:
¡ Prohibited rates—None.
¡ Mandatory rates—6, 12, 24, 18, and 36.
¡ Multicast rate—Selected from the mandatory rates.
¡ Supported rates—9, 18, 36, 48, and 54.
· 802.11a/802.11an/802.11ac/802.11ax/802.11abe:
¡ Prohibited rates—None.
¡ Mandatory rates—6, 12, and 24.
¡ Multicast rate—Selected from the mandatory rates.
¡ Supported rates—9, 18, 36, 48, and 54.
· 802.11b:
¡ Prohibited rates—None.
¡ Mandatory rates—1 and 2.
¡ Multicast rate—Selected from the mandatory rates.
¡ Supported rates—5.5 and 11.
· 802.11g/802.11gn/802.11gax/802.11gbe:
¡ Prohibited rates—None.
¡ Mandatory rates—1, 2, 5.5, and 11.
¡ Multicast rate—Selected from the mandatory rates.
¡ Supported rates—6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
disabled: Specifies rates that cannot be used by an AP.
mandatory: Specifies rates that the clients must support to associate with an AP.
multicast: Specifies the rate at which an AP multicasts packets. The multicast rate must be selected from the mandatory rates.
supported: Specifies rates that an AP supports. After a client associates with an AP, the client can select a higher or lower rate from the supported rates to communicate with the AP.
auto: Automatically selects a mandatory rate as the multicast rate.
rate-value: Specifies the rate value in Mbps. You can set multiple rates and separate them by spaces. The available values for this argument are as follows:
· 802.11be/802.11eax—6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54.
· 802.11a/802.11an/802.11ac/802.11ax/802.11abe—6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54.
· 802.11b—1, 2, 5.5, and 11.
· 802.11g/802.11gn/802.11gbe—1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54.
Usage guidelines
The mandatory rates and multicast rate cannot be null. When there is only one mandatory rate, you cannot specify the mandatory rate as a supported rate or prohibited rate.
Examples
# Set the mandatory rates to 6 Mbps, 12 Mbps, and 24 Mbps.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] type dot11g
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] rate mandatory 6 12 24
short-gi
Use short-gi enable to enable short Guard Interval (GI).
Use short-gi disable to disable short GI.
Use undo short-gi to restore the default.
Syntax
short-gi { disable | enable }
undo short-gi
Default
Short GI is enabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to 802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11gac, 802.11ax, and 802.11gax radios. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11g invalidates the command.
Examples
# Disable short GI.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] short-gi disable
stbc
Use stbc enable to enable Space-Time Block Coding (STBC).
Use stbc disable to disable STBC.
Use undo stbc to restore the default.
Syntax
stbc { disable | enable }
undo stbc
Default
STBC is enabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to 802.11n radios and radios of higher standards. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11g removes the configuration.
Examples
# Enable STBC.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] stbc enable
su-txbf
Use su-txbf enable to enable single-user TxBF.
Use su-txbf disable to disable single-user TxBF.
Use undo su-txbf to restore the default.
Syntax
su-txbf { disable | enable }
undo su-txbf
Default
Single-user TxBF is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command is applicable only to 802.11ac radios and radios of higher standards. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, or 802.11n removes the configuration.
Single-user TxBF enables an AP to improve the signal to one intended client. Single-user TxBF is applicable to WLANs that have widely spread clients, poor network quality, and serious signal attenuation.
Examples
# Enable single-user TxBF.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] su-txbf enable
Related commands
mimo
mu-txbf
twt negotiate
Use twt negotiate enable to enable Target Wake Time (TWT) negotiation.
Use twt negotiate disable to disable TWT negotiation.
Use undo twt negotiate to restore the default.
Syntax
twt negotiate { disable | enable }
undo twt negotiate
The following compatibility matrix shows the support of hardware platforms for this command:
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Command compatibility |
|
WA7200 series |
WA7220 WA7220-HI WA7220H WA7226-C WA7230 WA7230-LI |
No |
|
WA7300 series |
WA7320i WA7322H-HI WA7330X WA7338-HI |
Yes |
|
WA7500 series |
WA7538 WA7539 |
Yes |
|
WA7600 series |
WA7638 |
No |
Default
The default setting varies by AP model.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
TWT negotiation enables clients and APs to exchange data packets only in service periods and schedules client hibernation to reduce client power consumption and wireless resource competition.
With TWT negotiation enabled, clients send negotiation requests that carry the service period, TWT interval, and first wake time (calculated by clients) to APs. Upon receiving such a request, an AP sends a response. Then, the clients wake up as scheduled and wait for trigger frames from that AP. Upon receiving a trigger frame, clients enter a service period and start to exchange data packets with that AP. When a service period expires, clients enter hibernation mode even if data packet exchange is not finished.
A radio can provide the TWT service to a maximum of eight clients. After responding to the TWT negotiation requests of eight clients, the radio rejects the requests from the other clients.
This feature takes effect only on 802.11ax and 802.11gax radios. Changing the radio mode to a non-802.11ax or non-802.11gax mode removes the configuration.
Examples
# Enable TWT negotiation.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] type dot11ax
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] twt negotiate enable
Related commands
type
type
Use type to specify a radio mode.
Use undo type to restore the default.
Syntax
type { dot11a | dot11abe | dot11ac | dot11an | dot11ax | dot11b | dot11be | dot11eax | dot11g | dot11gax | dot11gbe | dot11gn }
undo type
Default
The default setting varies by AP model.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
dot11a: Specifies the 802.11a radio mode.
dot11abe: Specifies the 802.11be (5 GHz) radio mode.
dot11ac: Specifies the 802.11ac (5 GHz) radio mode.
dot11an: Specifies the 802.11n (5 GHz) radio mode.
dot11ax: Specifies the 802.11ax (5 GHz) radio mode.
dot11b: Specifies the 802.11b radio mode.
dot11be: Specifies the 802.11be (6 GHz) radio mode.
dot11eax: Specifies the 802.11ax (6 GHz) radio mode.
dot11g: Specifies the 802.11g radio mode.
dot11gax: Specifies the 802.11ax (2.4 GHz) radio mode.
dot11gbe: Specifies the 802.11be (2.4 GHz) radio mode.
dot11gn: Specifies the 802.11n (2.4 GHz) radio mode.
Usage guidelines
|
CAUTION: Modifying the mode of an enabled radio logs off all associated clients. |
Examples
# Set the radio mode to 802.11n (5 GHz).
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] type dot11an
ul-mu-mimo
Use ul-mu-mimo enable to enable uplink MU-MIMO.
Use ul-mu-mimo disable to disable uplink MU-MIMO.
Use undo ul-mu-mimo to restore the default.
Syntax
ul-mu-mimo { disable | enable }
undo ul-mu-mimo
Default
Uplink MU-MIMO is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command takes effect only on 802.11ax and 802.11gax radios. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/gac removes the configuration.
Uplink MU-MIMO enables an AP to receive data packets from multiple clients concurrently. With this feature enabled, an AP sends an HE_Trig message to all associated clients to inform the transmission time, frequency, sampling clock, and power requirements. Upon receiving the message, clients send data packets to the AP as required at the same time.
This feature is applicable to scenarios that have a large number of clients and high AP bandwidth usage and transmission latency requirements.
Only radios enabled with the client mode support this feature.
Examples
# Enable uplink MU-MIMO.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] ul-mu-mimo enable
Related commands
mu-txbf
ul-ofdma
Use ul-ofdma enable to enable uplink OFDMA.
Use ul-ofdma disable to disable uplink OFDMA.
Use undo ul-ofdma to restore the default.
Syntax
ul-ofdma { disable | enable }
undo ul-ofdma
Default
Uplink OFDMA is disabled.
Views
Radio interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
This command takes effect only on 802.11ax and 802.11gax radios. Changing the radio mode to 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/gac removes the configuration.
OFDMA can provide the following benefits if enabled in a high density environment where small data packets are transmitted:
· Concurrent transmission to multiple users.
· Improved radio usage.
· Shortened transmission latency.
· Reduced conflict backoff.
Examples
# Enable uplink OFDMA.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio 1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] ul-ofdma enable
Related commands
type dot11ax