- Table of Contents
-
- 16-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Keychain configuration
- 02-Public key management
- 03-PKI configuration
- 04-Crypto engine configuration
- 05-SSH configuration
- 06-SSL configuration
- 07-Packet filter configuration
- 08-DHCP snooping configuration
- 09-DHCPv6 snooping configuration
- 10-ARP attack protection configuration
- 11-ND attack defense configuration
- 12-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 13-IP source guard configuration
- 14-uRPF configuration
- 15-MACsec configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 07-Packet filter configuration | 99.57 KB |
About packet filtering with ACLs
Packet filter tasks at a glance
Applying an ACL to filter packets globally
Applying an ACL to an interface for packet filtering
Configuring logging and SNMP notifications for packet filtering
Setting the packet filtering default action
Verifying and maintaining packet filter
Verifying the packet filter running status
Displaying packet filter statistics
Clearing packet filter statistics
Packet filter configuration examples
Example: Configuring interface-based packet filter
Configuring packet filter
About packet filtering with ACLs
This section describes procedures for using an ACL to filtering packets. For example, you can apply an ACL to an interface to filter incoming or outgoing packets.
Packet filter tasks at a glance
To configure packet filtering, perform the following tasks:
· Configure packet filtering with ACLs.
Choose one of the following tasks:
¡ Applying an ACL to filter packets globally
¡ Applying an ACL to an interface for packet filtering
· (Optional.) Configuring logging and SNMP notifications for packet filtering
· (Optional.) Setting the packet filtering default action
Applying an ACL to filter packets globally
Restrictions and guidelines
You can apply a maximum of four ACLs to the same direction globally: one IPv4 ACL, one IPv6 ACL, one Layer 2 ACL, and one user-defined ACL.
If you do not specify the ipv6 keyword for a basic or advanced ACL, you specify an IPv4 ACL.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Apply an ACL globally.
packet-filter [ ipv6 | mac | user-defined ] { acl-number | name acl-name } global { inbound | outbound } [ hardware-count ] [ share-mode ]
By default, global packet filtering is not configured.
Applying an ACL to an interface for packet filtering
Restrictions and guidelines
You can apply a maximum of four ACLs to the same direction of an interface: one IPv4 ACL, one IPv6 ACL, one Layer 2 ACL, and one user-defined ACL.
If you do not specify the ipv6 keyword for a basic or advanced ACL, you specify an IPv4 ACL.
In a scenario with a mixture of Layer 2 and Layer 3 traffic, when you apply ACLs to the outbound direction of a VLAN interface for packet filtering, the outbound traffic of Layer 3 aggregate subinterfaces with the same VLAN will also be matched.
For the sharing mode, only interfaces of the same type share one ACL resource.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Apply an ACL to the interface to filter packets.
packet-filter [ ipv6 | mac | user-defined ] { acl-number | name acl-name } { inbound | outbound } [ hardware-count ] [ share-mode ]
By default, an interface does not filter packets.
Configuring logging and SNMP notifications for packet filtering
About this task
You can configure the ACL module to generate log entries or SNMP notifications for packet filtering. The log entry or notification records the number of matching packets and the matched ACL rules. When the first packet of a flow matches an ACL rule, the output interval starts, and the device immediately outputs a log entry or notification for this packet. When the output interval ends, the device outputs a log entry or notification for subsequent matching packets of the flow.
The log entries are sent to the information center. For more information about the information center, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
The SNMP notifications are sent to SNMP. For more information about SNMP, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the interval for outputting packet filtering logs or notifications.
acl { logging | trap } interval interval
The default setting is 0 minutes. By default, the device does not generate log entries or SNMP notifications for packet filtering.
Setting the packet filtering default action
About this task
The packet filtering default action does not take effect on zone pair packet filtering. The default action for zone pair packet filtering is always deny.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the packet filtering default action to deny.
packet-filter default deny
By default, the packet filter permits packets that do not match any ACL rule to pass.
Verifying and maintaining packet filter
Verifying the packet filter running status
Perform display tasks in any view.
· Display ACL application information for packet filtering.
display packet-filter { global | interface [ interface-type interface-number ] | l2vpn-ac [ interface interface-type interface-number [ service-instance instance-id ] ] } [ inbound | outbound ] [ slot slot-number ]
· Display detailed ACL packet filtering information.
display packet-filter verbose { global | interface interface-type interface-number } { inbound | outbound } [ [ ipv6 | mac | user-defined ] { acl-number | name acl-name } ] [ slot slot-number ]
Displaying packet filter statistics
Perform display tasks in any view.
· Display match statistics for packet filtering ACLs.
display packet-filter statistics { global | interface interface-type interface-number } { inbound | outbound } [ [ ipv6 | mac | user-defined ] { acl-number | name acl-name } ] [ brief ]
· Display the accumulated statistics for packet filtering ACLs.
display packet-filter statistics sum { inbound | outbound } [ ipv6 | mac | user-defined ] { acl-number | name acl-name } [ brief ]
Clearing packet filter statistics
To clear match statistics for packet filtering ACLs, execute the following command in user view:
reset packet-filter statistics { global | interface [ interface-type interface-number ] } { inbound | outbound } [ [ ipv6 | mac | user-defined ] { acl-number | name acl-name } ]
Packet filter configuration examples
Example: Configuring interface-based packet filter
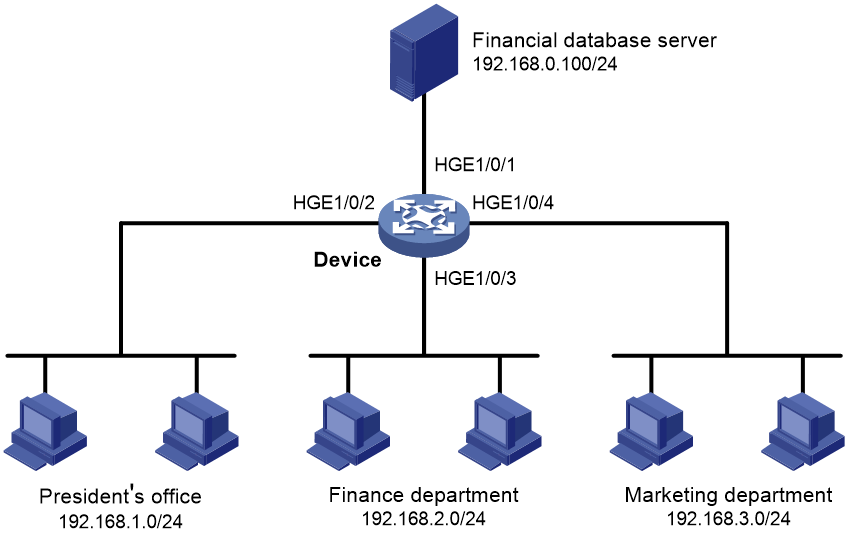
Network configuration
A company interconnects its departments through the device. Configure a packet filter to:
· Permit access from the President's office at any time to the financial database server.
· Permit access from the Finance department to the database server only during working hours (from 8:00 to 18:00) on working days.
· Deny access from any other department to the database server.
Figure 1 Network diagram
Prerequisites
By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface.
Procedure
# Create a periodic time range from 8:00 to 18:00 on working days.
<Device> system-view
[Device] time-range work 08:0 to 18:00 working-day
# Create an IPv4 advanced ACL numbered 3000.
[Device] acl advanced 3000
# Configure a rule to permit access from the President's office to the financial database server.
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] rule permit ip source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 destination 192.168.0.100 0
# Configure a rule to permit access from the Finance department to the database server during working hours.
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] rule permit ip source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 destination 192.168.0.100 0 time-range work
# Configure a rule to deny access to the financial database server.
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] rule deny ip source any destination 192.168.0.100 0
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] quit
# Apply IPv4 advanced ACL 3000 to filter outgoing packets on interface HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1] packet-filter 3000 outbound
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that a PC in the Finance department can ping the database server during working hours. (All PCs in this example use Windows XP).
C:\> ping 192.168.0.100
Pinging 192.168.0.100 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.0.100: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.0.100: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.0.100: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.0.100: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 192.168.0.100:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
# Verify that a PC in the Marketing department cannot ping the database server during working hours.
C:\> ping 192.168.0.100
Pinging 192.168.0.100 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Ping statistics for 192.168.0.100:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),
# Display configuration and match statistics for IPv4 advanced ACL 3000 on the device during working hours.
[Device] display acl 3000
Advanced IPv4 ACL 3000, 3 rules,
ACL's step is 5
rule 0 permit ip source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 destination 192.168.0.100 0
rule 5 permit ip source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 destination 192.168.0.100 0 time-range work (Active)
rule 10 deny ip destination 192.168.0.100 0
The output shows that rule 5 is active. Rule 5 and rule 10 have been matched four times as the result of the ping operations.