- Table of Contents
-
- 07-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA configuration
- 02-802.1X configuration
- 03-MAC authentication configuration
- 04-Portal configuration
- 05-Web authentication configuration
- 06-Triple authentication configuration
- 07-Port security configuration
- 08-User profile configuration
- 09-Password control configuration
- 10-Public key management
- 11-PKI configuration
- 12-IPsec configuration
- 13-SSH configuration
- 14-SSL configuration
- 15-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 16-TCP attack prevention configuration
- 17-IP source guard configuration
- 18-ARP attack protection configuration
- 19-ND attack defense configuration
- 20-MFF configuration
- 21-Crypto engine configuration
- 22-FIPS configuration
- 23-802.1X client configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 06-Triple authentication configuration | 90.52 KB |
Configuring triple authentication
Typical network of triple authentication
Triple authentication mechanism
Triple authentication support for VLAN assignment
Triple authentication support for ACL authorization
Triple authentication support for online user detection
Restrictions and guidelines: Triple authentication
Triple authentication tasks at a glance
Triple authentication configuration examples
Example: Configuring basic triple authentication
Configuring triple authentication
About triple authentication
Triple authentication enables an access port to perform Web, MAC, and 802.1X authentication. A terminal can access the network if it passes one type of authentication. For more information about 802.1X authentication, MAC authentication, and Web authentication, see "Configuring 802.1X authentication", "Configuring MAC authentication", and "Configuring Web authentication."
Typical network of triple authentication
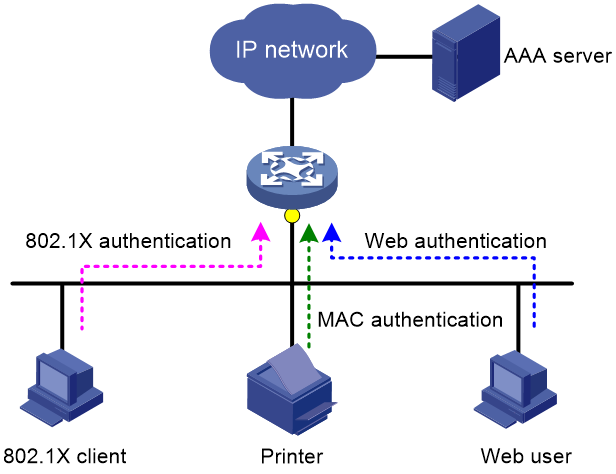
Triple authentication is suitable for a LAN that comprises terminals that require different authentication services, as shown in Figure 1. The triple authentication-enabled access port can perform MAC authentication for the printer, 802.1X authentication for the PC installed with the 802.1X client, and Web authentication for the Web user.
Figure 1 Triple authentication network diagram
Triple authentication mechanism
The three types of authentication are triggered by different packets:
· The access port performs MAC authentication for a terminal when it receives an ARP or DHCP broadcast packet from the terminal for the first time. If the terminal passes MAC authentication, the terminal can access the network. If the MAC authentication fails, the access port performs 802.1X or Web authentication.
· The access port performs 802.1X authentication when it receives an EAP packet from an 802.1X client or a third-party client. If the unicast trigger feature of 802.1X is enabled on the access port, any packet from the client can trigger an 802.1X authentication.
· The access port performs Web authentication when it receives an HTTP packet from a terminal.
If a terminal triggers different types of authentication, the authentications are processed at the same time. The failure of one type of authentication does not affect the others. When a terminal passes one type of authentication, the other types of authentication are processed as follows:
· If the terminal first passes MAC authentication, Web authentication is terminated immediately, but 802.1X authentication will proceed. If the terminal also passes 802.1X authentication, the 802.1X authentication information will overwrite the MAC authentication information for the terminal. If the terminal fails 802.1X authentication, the user stays online as a MAC authentication user, and only 802.1X authentication can be triggered again.
· If the terminal first passes 802.1X or Web authentication, the other types of authentication are terminated immediately and cannot be triggered again.
Triple authentication support for VLAN assignment
Authorization VLAN
After a user passes authentication, the authentication server assigns an authorization VLAN to the access port for the user. The user can then access the network resources in the authorized VLAN.
Authentication failure VLAN
The access port adds a user to an authentication failure VLAN configured on the port after the user fails authentication.
· For an 802.1X authentication user—Adds the user to the Auth-Fail VLAN configured for 802.1X authentication.
· For a Web authentication user—Adds the user to the Auth-Fail VLAN configured for Web authentication.
· For a MAC authentication user—Adds the user to the guest VLAN configured for MAC authentication.
The access port supports configuring all types of authentication failure VLANs at the same time. If a user fails more than one type of authentication, the authentication failure VLAN of the user changes as follows:
· If a user in the Web Auth-Fail VLAN fails MAC authentication, the user is moved to the MAC authentication guest VLAN.
· If a user in the Web Auth-Fail VLAN or MAC authentication guest VLAN fails 802.1X authentication, the user is moved to the 802.1X Auth-Fail VLAN.
· If a user in the 802.1X Auth-Fail VLAN fails MAC authentication or Web authentication, the user is still in the 802.1X Auth-Fail VLAN.
Server-unreachable VLAN
If a user fails authentication due to the unreachable server, the access port adds the user to an server-unreachable VLAN.
· For an 802.1X authentication user—Adds the user to the critical VLAN configured for 802.1X authentication.
· For a Web authentication user—Adds the user to the Auth-Fail VLAN configured for Web authentication.
· For a MAC authentication user—Adds the user to the critical VLAN configured for MAC authentication.
The access port supports configuring all types of server-unreachable VLANs at the same time. A user is added to the server-unreachable VLAN as follows:
· If the user does not undergo 802.1X authentication, the user is added to the server-unreachable VLAN configured for the last authentication.
· If the user in the Web Auth-Fail VLAN or the MAC authentication critical VLAN also fails 802.1X authentication, the user is added to the 802.1X authentication critical VLAN.
Triple authentication support for ACL authorization
After a user passes authentication, the authentication server assigns an authorization ACL to the access port for the user. The access port uses the ACL to filter traffic for the user.
To use ACL authorization, you must specify authorization ACLs on the authentication server and configure the ACLs on the access device. You can change the user's access authorization by changing the authorization ACL on the authentication server or changing rules of the authorization ACL on the access device.
Triple authentication support for online user detection
You can configure the following features to detect the online status of users:
· Enable online user detection for Web authentication users.
· Enable the online user handshake or periodic online user reauthentication feature for 802.1X users.
· Enable offline detection for MAC authentication users.
Restrictions and guidelines: Triple authentication
In triple authentication, 802.1X authentication must use the MAC-based access control method.
If Web authentication is enabled on a port, configure the subnets of the authentication failure VLANs and server-unreachable VLANs of the port as Web authentication-free subnets. This ensures that an authentication-failed user can access the authentication failure VLAN or server-unreachable VLAN.
Do not configure both Web authentication-free IPs and 802.1X free IPs. If you do so, only 802.1X free IPs take effect.
Triple authentication tasks at a glance
Choose the following tasks as needed:
· Configure 802.1X authentication
For more information, see "Configuring 802.1X."
· Configure MAC authentication
For more information, see "Configuring MAC authentication."
· Configure Web authentication
For more information, see "Configuring Web authentication."
Triple authentication configuration examples
Example: Configuring basic triple authentication
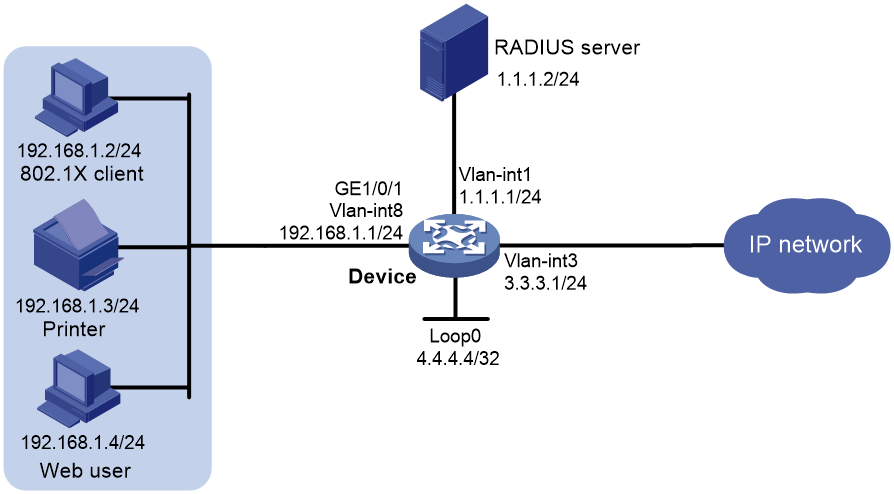
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, the terminals are connected to the device to access the IP network. Configure triple authentication on the device's Layer 2 interface that connects to the terminals. A terminal passing one of the three authentication methods, 802.1X authentication, Web authentication, and MAC authentication, can access the IP network.
· Assign IP addresses on subnet 192.168.1.0/24 to the terminals.
· Use the remote RADIUS server to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting. Configure the device to send usernames carrying no ISP domain names to the RADIUS server.
· Configure the local Web authentication server on the device to use listening IP address 4.4.4.4. Configure the device to send a default authentication page to the Web user and forward authentication data by using HTTP.
Procedure
1. Make sure that the terminals, the server, and the device can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the RADIUS server to provide normal authentication, authorization, and accounting for users. In this example, configure the following on the RADIUS server:
¡ An 802.1X user with username userdot.
¡ A Web authentication user with username userpt.
¡ A MAC authentication user with a username and password both being the MAC address of the printer f07d6870725f.
3. Configure Web authentication:
# Configure VLANs and IP addresses for the VLAN interfaces, and add ports to specific VLANs. (Details not shown.)
# Edit authentication pages, compress the pages to a .zip file named abc, and upload the .zip file to the device by FTP. (Details not shown.)
# Create an HTTP-based local portal Web service, and specify file abc.zip as the default authentication page file of the local portal Web service.
<Device> system-view
[Device] portal local-web-server http
[Device-portal-local-websvr-http] default-logon-page abc.zip
[Device-portal-local-websvr-http] quit
# Assign IP address 4.4.4.4 to Loopback 0.
[Device] interface loopback 0
[Device-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[Device-LoopBack0] quit
# Create a Web authentication server named webserver and enter its view.
[Device] web-auth server webserver
# Configure the redirection URL for the Web authentication server as http://4.4.4.4/portal/.
[Device-web-auth-server-webserver] url http://4.4.4.4/portal/
# Specify 4.4.4.4 as the IP address and 80 as the port number of the Web authentication server.
[Device-web-auth-server-webserver] ip 4.4.4.4 port 80
[Device-web-auth-server-webserver] quit
# Enable Web authentication on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and specify Web authentication server webserver on the interface.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] web-auth enable apply server webserver
[Device–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
4. Configure 802.1X authentication:
# Enable 802.1X authentication globally.
[Device] dot1x
# Enable 802.1X authentication (MAC-based access control required) on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dot1x port-method macbased
[Device–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dot1x
[Device–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
5. Configure MAC authentication:
# Enable MAC authentication globally.
[Device] mac-authentication
# Enable MAC authentication on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mac-authentication
[Device–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
6. Configure a RADIUS scheme:
# Create a RADIUS scheme named rs1.
[Device] radius scheme rs1
# Specify the primary authentication and accounting servers and keys.
[Device-radius-rs1] primary authentication 1.1.1.2
[Device-radius-rs1] primary accounting 1.1.1.2
[Device-radius-rs1] key authentication simple radius
[Device-radius-rs1] key accounting simple radius
# Specify usernames sent to the RADIUS server to carry no domain names.
[Device-radius-rs1] user-name-format without-domain
[Device-radius-rs1] quit
7. Configure an ISP domain:
# Create an ISP domain named triple.
[Device] domain triple
# Configure the domain to use RADIUS scheme rs1 for authentication, authorization and accounting of LAN access users.
[Device-isp-triple] authentication lan-access radius-scheme rs1
[Device-isp-triple] authorization lan-access radius-scheme rs1
[Device-isp-triple] accounting lan-access radius-scheme rs1
[Device-isp-triple] quit
# Configure domain triple as the default domain. If a username entered by a user includes no ISP domain name, the AAA method of the default domain is used.
[Device] domain default enable triple
Verifying the configuration
1. Verify that the Web user can pass Web authentication.
# On the Web user terminal, use a Web browser to access an external network and then enter the correct username and password on the authentication page http://4.4.4.4/portal/logon.html. (Details not shown.)
# Display information about online Web authentication users.
[Device] display web-auth user
Total online web-auth users: 1
User Name: localuser
MAC address: acf1-df6c-f9ad
Access interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Initial VLAN: 8
Authorization VLAN: N/A
Authorization ACL ID: N/A
Authorization user profile: N/A
2. Verify that the printer can pass MAC authentication.
# Connect the printer to the network. (Details not shown.)
# Display information about online MAC authentication users.
[Device] display mac-authentication connection
Total connections: 1
Slot ID: 1
User MAC address: f07d-6870-725f
Access interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Username: f07d6870725f
User access state: Successful
Authentication domain: triple
Initial VLAN: 8
Authorization untagged VLAN: N/A
Authorization tagged VLAN: N/A
Authorization VSI: N/A
Authorization ACL ID: N/A
Authorization user profile: N/A
Authorization CAR: N/A
Authorization URL: N/A
Termination action: Default
Session timeout period: N/A
Online from: 2015/01/04 18:01:43
Online duration: 0h 0m 2s
3. Verify that the 802.1X client can pass 802.1X authentication.
# On the 802.1X client, initiate 802.1X authentication and then enter the correct username and password. (Details not shown.)
# Display information about online 802.1X users.
[Device] display dot1x connection
Total connections: 1
Slot ID: 1
User MAC address: 7446-a091-84fe
Access interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Username: userdot
User access state: Successful
Authentication domain: triple
IPv4 address: 192.168.1.2
Authentication method: CHAP
Initial VLAN: 8
Authorization untagged VLAN: N/A
Authorization tagged VLAN list: N/A
Authorization VSI: N/A
Authorization ACL ID: N/A
Authorization user profile: N/A
Authorization CAR: N/A
Authorization URL: N/A
Termination action: Default
Session timeout period: N/A
Online from: 2015/01/04 18:13:01
Online duration: 0h 0m 14s