- Table of Contents
-
- 12-High Availability Configuration Guides
- 00-Preface
- 01-Ethernet OAM configuration
- 02-CFD configuration
- 03-DLDP configuration
- 04-RRPP configuration
- 05-ERPS configuration
- 06-Smart Link configuration
- 07-Monitor Link configuration
- 08-VRRP configuration
- 09-Error code detection configuration
- 09-Reth interface and redundancy group configuration
- 10-BFD configuration
- 11-Track configuration
- 13-Process placement configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 09-Reth interface and redundancy group configuration | 66.62 KB |
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
Displaying and maintaining Reth interfaces
Reth interface configuration example
Configuring Reth interfaces
About Reth interfaces
A redundant Ethernet (Reth) interface is a virtual Layer 3 interface that uses two member interfaces to ensure link availability. One member interface is active and the other is inactive. When the active interface fails, the inactive interface becomes active. The member interface switchover does not interrupt traffic.
|
|
NOTE: On the device, Reth member interfaces can only be management Ethernet ports. |
Applicable scenario
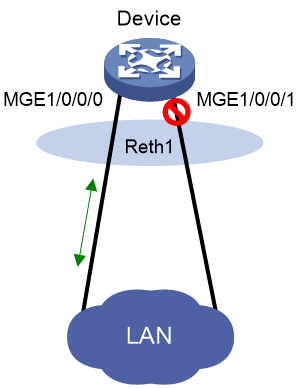
As shown in Figure 1, M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0 and M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/1 are member interfaces of a Reth interface. The Reth interface selects the member interface to forward traffic as follows:
· When both member interfaces are operating correctly, the Reth interface forwards traffic through M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0 and places M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/1 in inactive state.
· When M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0 fails, M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/1 becomes active and the Reth interface switches traffic over to M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/1.
Operating mechanism
A member interface of a Reth interface can be in either of the following states:
· Active—The interface can forward packets. A Reth interface can have only one active member interface.
· Inactive—The interface cannot forward packets.
A Reth interface determines the state of its member interfaces by using the following rules:
· When both member interfaces are physically up, the member interface with the higher priority is active and the member interface with lower priority is inactive. The priorities of the member interfaces are user configurable.
· When the active member interface goes down physically, the inactive interface automatically becomes active to forward packets.
· When both member interfaces are physically down, both interfaces are inactive.
The Reth interface uses the device bridge MAC address as its MAC address and can be configured with an IP address. For the upstream and downstream devices, they are connected to the Reth interface. The switchover between the Reth member interfaces is not visible to the network and does not cause network topology changes.
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
To use the Reth interface features, make sure the MPUs have a minimum of two management Ethernet ports.
The IP addresses of the management Ethernet ports become invalid after you assign them to a Reth interface. To log in to the device, you must use the IP address assigned to the Reth interface.
Configuring a Reth interface
When you configure a Reth interface, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· You can assign a maximum of two member interfaces to a Reth interface. The member interfaces must have different priorities.
· Before you delete a Reth interface, make sure all its member interfaces have been removed.
To configure a Reth interface:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Create a Reth interface and enter its view. |
interface reth interface-number |
By default, no Reth interfaces exist. |
|
3. Assign a member interface to the Reth interface. |
member interface interface-type interface-number priority priority |
By default, a Reth interface does not have member interfaces. |
|
4. (Optional.) Configure the expected bandwidth for the Reth interface. |
bandwidth bandwidth-value |
By default, the expected bandwidth is 10000 kbps. |
|
5. (Optional.) Configure the description of the Reth interface. |
description text |
The default description of a Reth interface is interface-name Interface (for example, Reth1 Interface). |
|
6. (Optional.) Set the MTU of the Reth interface. |
mtu size |
By default, the MTU of a Reth interface is 1500 bytes. |
|
7. Bring up the Reth interface. |
undo shutdown |
By default, a Reth interface is up. |
|
8. (Optional.) Restore the default settings for the Reth interface. |
default |
N/A |
Displaying and maintaining Reth interfaces
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display information about the member interfaces of a Reth interface. |
display reth interface interface-type interface-number |
|
Display Reth interface information. |
display interface [ reth [ interface-number ] ] [ brief [ description | down ] ] |
|
Clear statistics for Reth interfaces. |
reset counters interface [ reth [ interface-number ] ] |
Reth interface configuration example
Network requirements
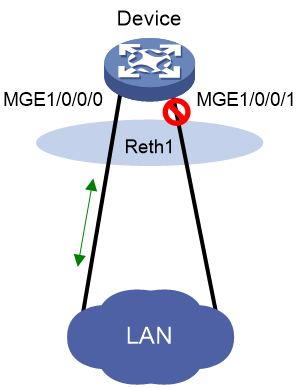
As shown in Figure 2, configure a Reth interface as follows:
· Assign M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0 and M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/1 to the Reth interface.
· Assign a higher priority to M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0 for it to be the active member interface.
Configuration procedure
# Create Reth 1, and assign an IP address to the interface.
[Sysname] interface reth 1
[Sysname-Reth-1] ip address 1.0.0.3 24
# Assign M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0 and M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/1 to Reth 1, and set their priority to 100 and 80, respectively.
[Sysname-Reth1] member interface M-GigabitEthernet1/0/0/0 priority 100
[Sysname-Reth1] member interface M-GigabitEthernet1/0/0/1 priority 80
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0 is active and M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/1 is inactive.
[Sysname-Reth1] display reth interface reth 1
Reth1 :
Redundancy group : N/A
Member Physical status Forwarding status Presence status
MGE1/0/0/0 UP Active Normal
MGE1/0/0/1 UP Inactive Normal
# Shut down M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0.
[Sysname-Reth1] quit
[Sysname] interface M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0
[Sysname-M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0] shutdown
# Verify that M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/1 becomes active and M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0 becomes inactive.
[Sysname-M-GigabitEthernet 1/0/0/0] display reth interface reth 1
Reth1 :
Redundancy group : N/A
Member Physical status Forwarding status Presence status
MGE1/0/0/0 DOWN Inactive Normal
MGE1/0/0/1 UP Active Normal