- Table of Contents
-
- 09-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA configuration
- 02-802.1X configuration
- 03-MAC authentication configuration
- 04-Portal configuration
- 05-Web authentication configuration
- 06-Port security configuration
- 07-User profile configuration
- 08-Password control configuration
- 09-Keychain configuration
- 10-Public key management
- 11-PKI configuration
- 12-SSH configuration
- 13-SSL configuration
- 14-Object group configuration
- 15-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 16-TCP attack prevention configuration
- 17-IP source guard configuration
- 18-ARP attack protection configuration
- 19-ND attack defense configuration
- 20-uRPF configuration
- 21-SAVI configuration
- 22-SAVA configuration
- 23-MFF configuration
- 24-Crypto engine configuration
- 25-FIPS configuration
- 26-MACsec configuration
- 27-Microsegmentation configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 22-SAVA configuration | 242.62 KB |
Content
Enabling SAVA entry creation based on synchronized remote routes
Adding an interface to a SAVA access group
Display and maintenance commands for SAVA
Example: Configuring SAVA on border devices directly connected the LAN
Example: Configuring SAVA on border devices indirectly connected the LAN (OSPFv3)
Example: Configuring SAVA on border devices indirectly connected the LAN (IPv6 IS-IS)
Example: Configuring SAVA on inter-AS border devices indirectly connected the LAN
Configuring SAVA
About SAVA
Benefits
As shown in Figure 1, asymmetric routing might occur in an IPv6 multiple-access network. The outgoing interface for a return packet might be different from the incoming interface of the original packet. You can enable strict uRPF check on interface 1 of Device B to prevent attacks with spoofed source IPv6 addresses. However, strict uRPF check might determine that a valid packet from the LAN as an attack packet based on local routing information, which causes unexpected packet drop.
Figure 1 SAVA-enabled network
Mechanism
Obtaining prefixes of valid users
Creating SAVA entries
Filtering user packets based on SAVA entries
Application scenarios
Deployed on intra-AS border devices directedly connected to the LAN
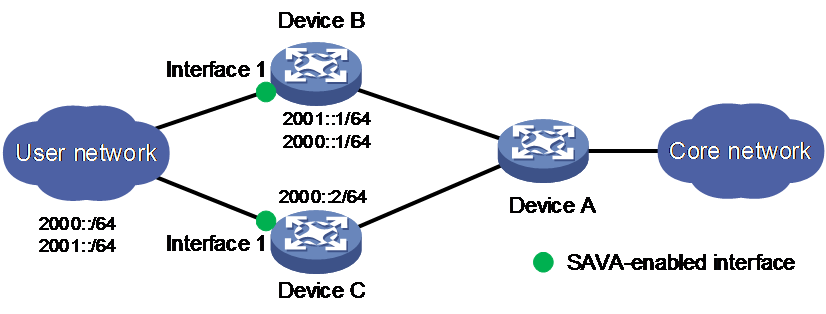
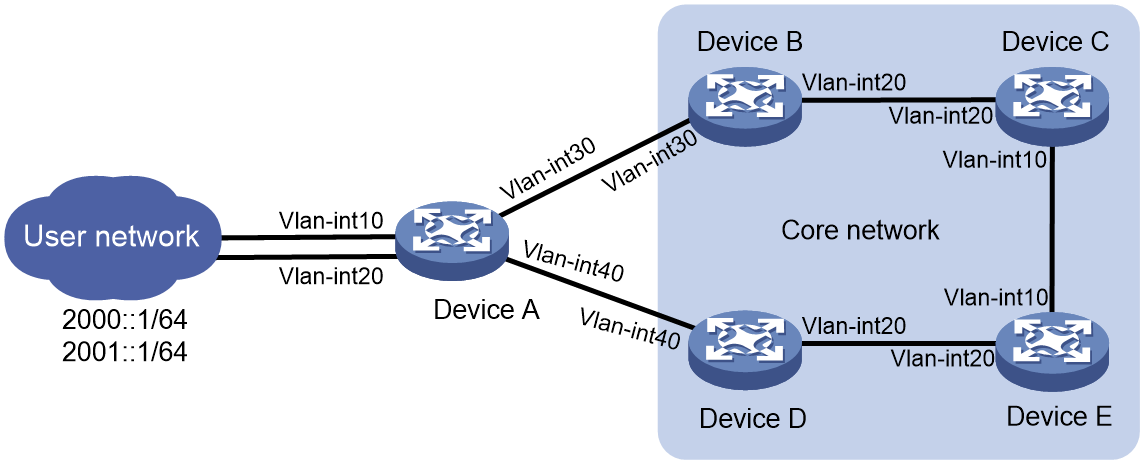
As shown in Figure 2, users in the LAN connect to the backbone network through Device B and Device C. Device B is configured with two gateways addresses (2000::1/64 and 2001::1/64). Device C is configured with the gateway address (2000::2/64).
Figure 2 SAVA deployed on border devices directly connected to the LAN
Deployed on intra-AS border devices indirectedly connected to the LAN
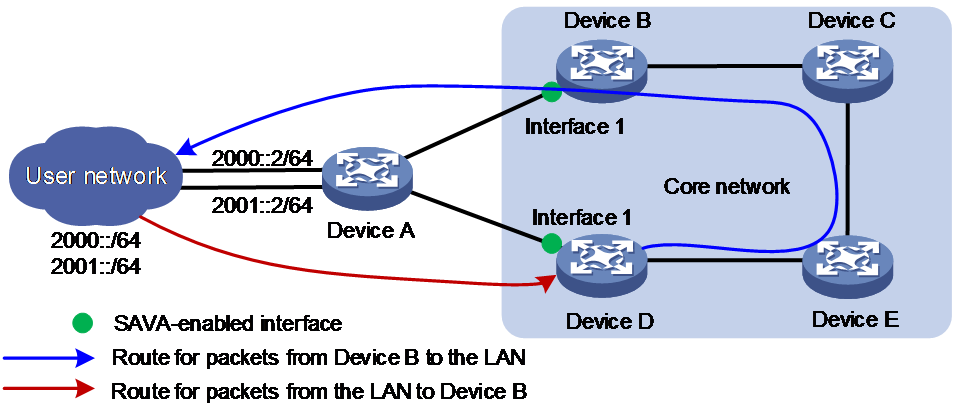
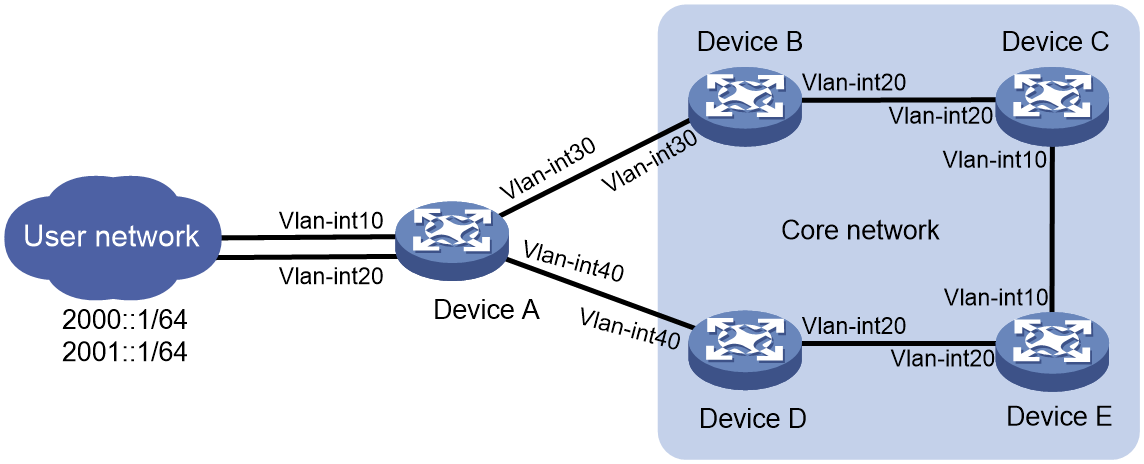
As shown in Figure 3, asymmetric traffic exists between Device D and the LAN after route convergence. Traffic from Device D to the LAN will traverse Device E, Device C, Device B, and Device A. Traffic from the LAN to Device D will traverse only Device A.
Figure 3 SAVA deployed on intra-AS border devices indirectly connected to the LAN
Delpoyed on inter-AS border devices indirectedly connected to the LAN
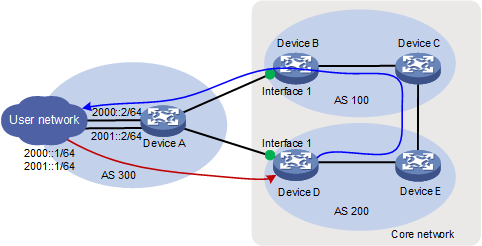
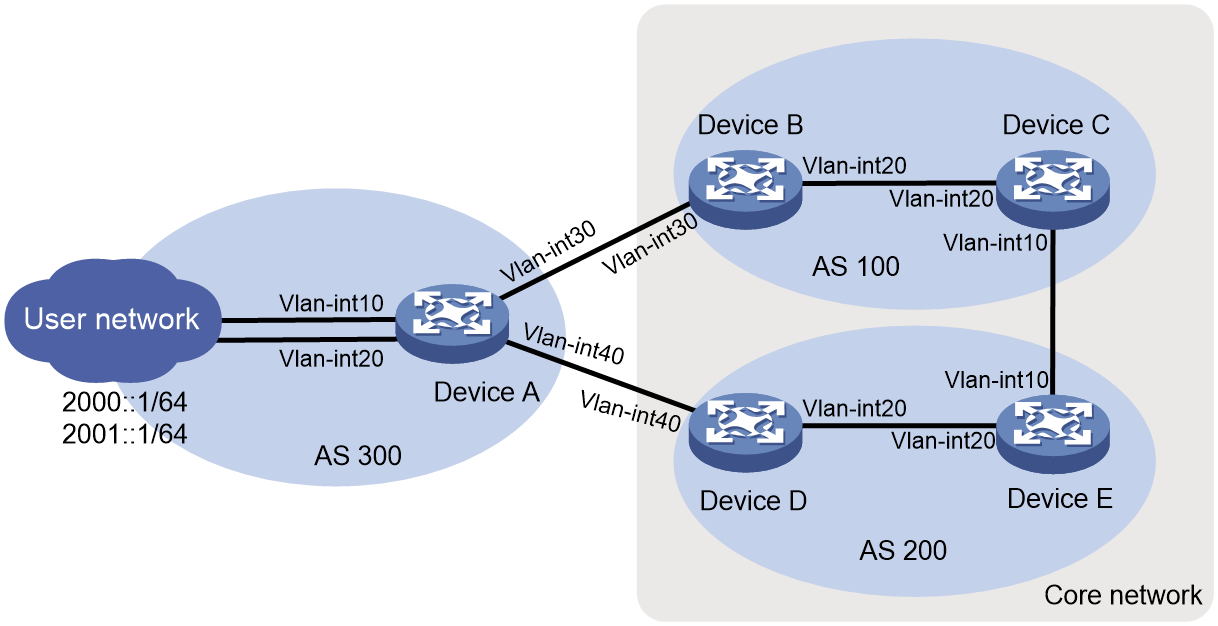
As shown in Figure 4, asymmetric traffic exists between Device D and the LAN after route convergence. Traffic from Device D to the LAN will traverse Device E, Device C, Device B, and Device A. Traffic from the LAN to Device D will traverse only Device A.
Figure 4 SAVA deployed on inter-AS border devices indirectly connected to the LAN
SAVA tasks at a glance
To configure SAVA, perform the following tasks:
2. Enabling SAVA entry creation based on synchronized remote routes
Perform this task if the LAN connects to the backbone network through multiple border devices and interfaces on the border devices do not have prefix information of all user in the LAN.
3. Adding an interface to a SAVA access group
Perform this task if a border device has multiple interfaces connected to the same LAN.
Enabling SAVA
Restrictions and guidelines
SAVA is not supported on tunnel endpoints.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable SAVA on the interface.
By default, SAVA is disabled.
Enabling SAVA entry creation based on synchronized remote routes
About this task
Prerequisites
· Configure OSPFv3 link tag inheritance
Perform this task if OSPFv3 runs on the network. For more information about OSPFv3 link tag inheritance, see OSPFv3 configuration in Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide.
· Configure IPv6 IS-IS link tag inheritance
Perform this task if IPv6 IS-IS runs on the network. For more information about IPv6 IS-IS link tag inheritance, see IS-IS configuration in Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable the device to create SAVA entries based on synchronized remote routes with the specified route tag.
ipv6 sava import remote-route-tag tag
By default, the device does not create SAVA entries based on synchronized remote routes.
Adding an interface to a SAVA access group
About this task
Restrictions and guidelines
All interfaces in a SAVA access group must belong to the public network or the same VPN instance.
You can add a maximum of eight interfaces to a SAVA access group.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Add the interface to a SAVA access group.
ipv6 sava access-group group-name
By default, an interface does not belong to a SAVA access group.
Configuring SAVA logging
About this task
To identify and troubleshoot issues, enable SAVA logging.
This feature enables the device to generate SAVA logs when SAVA detects spoofing packets.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure SAVA logging.
ipv6 sava log enable spoofing-packet [ interval interval | number number ]*
By default, SAVA logging is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for SAVA
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display SAVA entries. |
display ipv6 sava [ interface interface-type interface-number | slot slot-number ] |
|
Display SAVA packet drop statistics. |
display ipv6 sava packet-drop statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
|
Clear SAVA packet drop statistics. |
reset ipv6 sava packet-drop statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
SAVA configuration examples
Example: Configuring SAVA on border devices directly connected the LAN
Network configuration
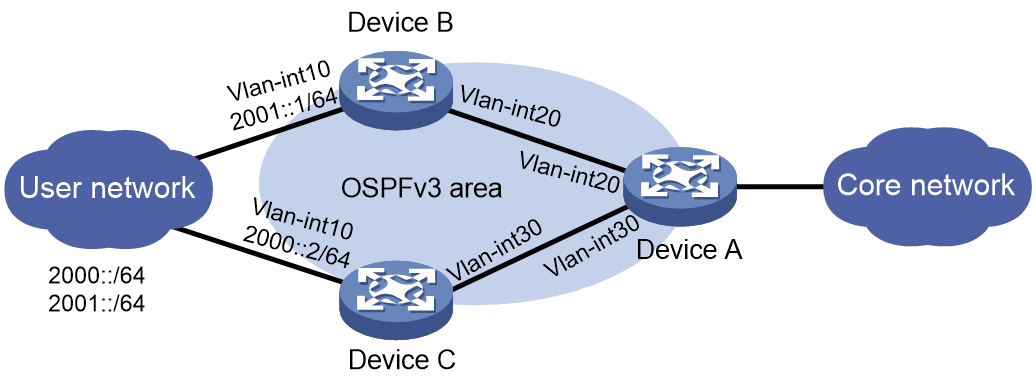
As shown in Figure 5, legal users in the LAN use prefixes 2000::/64 and 2001::/64. Configure SAVA on VLAN-interface 10 of Device B and Device C to meet the following requirements:
Device C creates a SAVA entry upon receiving an IPv6 route with prefix 2001::/64.
The LAN-side interface on Device C filters packets from users in the LAN based on SAVA entries.
Table 1 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::12:1/120 |
Device B |
Vlan-int10 |
2001::1/64 |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int30 |
192:168::22:1/120 |
Device B |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::22:2/120 |
|
Device C |
Vlan-int10 |
2000::2/64 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Device C |
Vlan-int30 |
192:168::12:2/120 |
— |
— |
— |
Prerequisites
1. Assign IPv6 addresses to interfaces on the devices.
2. Configure OSPFv3 on the backbone network. For more information, see OSPFv3 configuration in Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Configure Device B:
# Enable SAVA on VLAN-interface 10 (the LAN-side interface).
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface10] ipv6 sava enable
# Configure routing policy named ttt, configure node 10 in permit mode to permit routes with the output interface VLAN-interface 10 and to set a tag of 100 for IGP routes.
[DeviceB] route-policy ttt permit node 10
[DeviceB-route-policy-ttt-10] if-match interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceB-route-policy-ttt-10] apply tag 100
[DeviceB-route-policy-ttt-10] quit
# Configure OSPFv3 process 1 to redistribute direct routes permitted by routing policy ttt.
[DeviceB] ospfv3 100
[DeviceB-ospfv3-100] import-route direct route-policy ttt
[DeviceB-ospfv3-100] quit
2. Configure Device C:
# Enable SAVA on VLAN-interface 10 (the LAN-side interface).
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] ipv6 sava enable
# Configure VLAN-interface 10 to redistribute remote routes with route tag 100.
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] ipv6 sava import remote-route-tag 100
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display SAVA entries on Device C.
[DeviceC] display ipv6 sava
IPv6 SAVA entry count: 2
Destination: 2000:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int10 Flags: L
Destination: 2001:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int10 Flags: R
Example: Configuring SAVA on border devices indirectly connected the LAN (OSPFv3)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 6, OSPFv3 runs on the core network. Configure the devices to meet the following requirements:
Table 2 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int10 |
2001::2/64 |
Device B |
Vlan-int30 |
192:168::12:2/120 |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int20 |
2000::2/64 |
Device B |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::34:3/120 |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int30 |
192:168::12:1/120 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int40 |
192:168::22:1/120 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Device C |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::34:4/120 |
Device D |
Vlan-int40 |
192:168::22:2/120 |
|
Device C |
Vlan-int10 |
192:168::46:4/120 |
Device D |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::56:5/120 |
|
Device E |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::56:6/120 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Device E |
Vlan-int10 |
192:168::46:6/120 |
— |
— |
— |
Prerequisites
Assign IPv6 addresses to interfaces on the devices.
Procedure
1. Configure Device A:
# Configure OSPFv3.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] ospfv3 1
[DeviceA-ospfv3-1] router-id 1.1.1.1
[DeviceA-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface10] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface10] quit
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 30
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface30] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface130] quit
2. Configure Device B:
# Configure OSPFv3.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] ospfv3 1
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1] router-id 2.2.2.2
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 30
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceB- Vlan-interface20] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceB- Vlan-interface20] quit
# Enable OSPFv3 link tag inheritance.
[DeviceB] ospfv3 1
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1] link-tag inherit enable
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1] quit
# Set the OSPFv3 link tag for VLAN-interface 30 to 100.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 30
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] ospfv3 link-tag 100
# Enable SAVA on VLAN-interface 30.
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] ipv6 sava enable
# Configure VLAN-interface 30 to redistribute remote routes with route tag 100.
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] ipv6 sava import remote-route-tag 100
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] quit
3. Configure Device D:
# Configure a static route, whose destination address is 2000:: /64, next hop address is FE80::1 (a link-local IPv6 address on Device A), and tag value is 100.
<DeviceD> system-view
[DeviceD] ipv6 route-static 2000:: 64 vlan-interface 40 FE80::1 tag 100
# Configure routing policy named sava, configure node 10 in permit mode to permit routes with the output interface VLAN-interface 40.
[DeviceD] route-policy sava permit node 10
[DeviceD-route-policy-sava-10] if-match interface vlan-interface 40
[DeviceD-route-policy-sava-10] quit
# Configure OSPFv3.
[DeviceD] ospfv3 1
[DeviceD-ospfv3-1] router-id 4.4.4.4
[DeviceD-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface20] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceD- Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure OSPFv3 process 1 to redistribute direct routes permitted by routing policy sava.
[DeviceD] ospfv3 1
[DeviceD-ospfv3-1] import-route static route-policy sava
# Enable OSPFv3 link tag inheritance.
[DeviceD-ospfv3-1] link-tag inherit enable
[DeviceD-ospfv3-1] quit
# Enable SAVA on VLAN-interface 40.
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 40
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface40] ipv6 sava enable
# Configure VLAN-interface 40 to redistribute remote routes with route tag 100.
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface40] ipv6 sava import remote-route-tag 100
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface40] quit
4. Configure Device C:
# Configure OSPFv3.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] ospfv3 1
[DeviceC-ospfv3-1] router-id 3.3.3.3
[DeviceC-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 40
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface40] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface40] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] quit
5. Configure Device E:
# Configure OSPFv3.
<DeviceE> system-view
[DeviceE] ospfv3 1
[DeviceE-ospfv3-1] router-id 5.5.5.5
[DeviceE-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceE] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceE-Vlan-interface20] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceE-Vlan-interface20] quit
[DeviceE] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceE-Vlan-interface10] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceE-Vlan-interface10] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display SAVA entries on Device D.
[DeviceD] display ipv6 sava
IPv6 SAVA entry count: 4
Destination:192:168::12:0 Prefix length: 120
Interface: Vlan-int40 Flags: R
Destination:192:168::22:0 Prefix length: 120
Interface: Vlan-int40 Flags: L
Destination: 2000:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int40 Flags: L
Destination: 2001:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int40 Flags: R
# Display SAVA entries on Device B.
[DeviceB] display ipv6 sava
IPv6 SAVA entry count: 3
Destination:192:168::12:0 Prefix length: 120
Interface: Vlan-int30 Flags: L
Destination: 2000:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int30 Flags: R
Destination: 2001:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int30 Flags: L
Example: Configuring SAVA on border devices indirectly connected the LAN (IPv6 IS-IS)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 7, IPv6 IS-IS runs on the core network. Configure the devices to meet the following requirements:
Table 3 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int10 |
2001::2/64 |
Device B |
Vlan-int30 |
192:168::12:2/120 |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int20 |
2000::2/64 |
Device B |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::34:3/120 |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int30 |
192:168::12:1/120 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int40 |
192:168::22:1/120 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Device C |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::34:4/120 |
Device D |
Vlan-int40 |
192:168::22:2/120 |
|
Device C |
Vlan-int10 |
192:168::46:4/120 |
Device D |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::56:5/120 |
|
Device E |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::56:6/120 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Device E |
Vlan-int10 |
192:168::46:6/120 |
— |
— |
— |
Prerequisites
Assign IPv6 addresses to interfaces on the devices.
Procedure
1. Configure Device A:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] isis 1
[DeviceA-isis-1] is-level level-2
[DeviceA-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[DeviceA-isis-1] cost-style wide
[DeviceA-isis-1] address-family ipv6
[DeviceA-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[DeviceA-isis-1] quit
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface10] isis ipv6 enable 1
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface10] quit
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 30
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface30] isis ipv6 enable 1
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface30] quit
2. Configure Device B:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] isis 1
[DeviceB-isis-1] is-level level-2
[DeviceB-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[DeviceB-isis-1] cost-style wide
[DeviceB-isis-1] address-family ipv6
[DeviceB-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[DeviceB-isis-1] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 30
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] isis ipv6 enable 1
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface20] isis ipv6 enable 1
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Enable IPv6 IS-IS link tag inheritance.
[DeviceB] isis 1
[DeviceB-isis-1] address-family ipv6
[DeviceB-isis-1-ipv6] link-tag inherit enable
[DeviceB-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[DeviceB-isis-1] quit
# Set the IPv6 IS-IS link tag for VLAN-interface 30 to 100.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 30
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] isis ipv6 link-tag 100
# Enable SAVA on VLAN-interface 30.
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] ipv6 sava enable
# Configure VLAN-interface 30 to redistribute remote routes with route tag 100.
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] ipv6 sava import remote-route-tag 100
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] quit
3. Configure Device D:
# Configure a static route, whose destination address is 2000:: /64, next hop address is FE80::1 (a link-local IPv6 address on Device A), and tag value is 100.
<DeviceD> system-view
[DeviceD] ipv6 route-static 2000:: 64 vlan-interface 40 FE80::1 tag 100
# Configure routing policy named sava, configure node 10 in permit mode to permit routes with the output interface VLAN-interface 40.
[DeviceD] route-policy sava permit node 10
[DeviceD-route-policy-sava-10] if-match interface vlan-interface 40
[DeviceD-route-policy-sava-10] quit
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[DeviceD] isis 1
[DeviceD-isis-1] is-level level-2
[DeviceD-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[DeviceD-isis-1] cost-style wide
[DeviceD-isis-1] address-family ipv6
[DeviceD-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[DeviceD-isis-1] quit
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface20] isis ipv6 enable 1
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure IS-IS process 1 to redistribute direct routes permitted by routing policy sava.
[DeviceD] isis 1
[DeviceD-isis-1] address-family ipv6
[DeviceD-isis-1-ipv6] import-route static route-policy sava level-2
# Enable IPv6 IS-IS link tag inheritance.
[DeviceD-isis-1-ipv6] link-tag inherit enable
[DeviceD-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[DeviceD-isis-1] quit
# Enable SAVA on VLAN-interface 40.
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 40
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface40] ipv6 sava enable
# Configure VLAN-interface 40 to redistribute remote routes with route tag 100.
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface40] ipv6 sava import remote-route-tag 100
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface40] quit
4. Configure Device C:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] isis 1
[DeviceC-isis-1] is-level level-2
[DeviceC-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[DeviceC-isis-1] cost-style wide
[DeviceC-isis-1] address-family ipv6
[DeviceC-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[DeviceC-isis-1] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 40
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface40] isis ipv6 enable 1
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface40] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] isis ipv6 enable 1
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] quit
5. Configure Device E:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
<DeviceE> system-view
[DeviceE] isis 1
[DeviceE-isis-1] is-level level-2
[DeviceE-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[DeviceE-isis-1] cost-style wide
[DeviceE-isis-1] address-family ipv6
[DeviceE-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[DeviceE-isis-1] quit
[DeviceE] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceE-Vlan-interface20] isis ipv6 enable 1
[DeviceE-Vlan-interface20] quit
[DeviceE] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceE-Vlan-interface10] isis ipv6 enable 1
[DeviceE-Vlan-interface10] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display SAVA entries on Device D.
[DeviceD] display ipv6 sava
IPv6 SAVA entry count: 3
Destination:192:168::22:0 Prefix length: 120
Interface: Vlan-int40 Flags: L
Destination: 2000:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int40 Flags: L
Destination: 2001:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int40 Flags: R
# Display SAVA entries on Device B.
[DeviceB] display ipv6 sava
IPv6 SAVA entry count: 3
Destination:192:168::12:0 Prefix length: 120
Interface: Vlan-int30 Flags: L
Destination: 2000:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int30 Flags: R
Destination: 2001:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int30 Flags: L
Example: Configuring SAVA on inter-AS border devices indirectly connected the LAN
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 8, configure the devices to meet the following requirements:
Table 4 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int10 |
2001::2/64 |
Device B |
Vlan-int30 |
192:168::12:2/120 |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int20 |
2000::2/64 |
Device B |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::23:2/120 |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int30 |
192:168::12:1/120 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Device A |
Vlan-int40 |
192:168::22:1/120 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Device C |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::23:3/120 |
Device D |
Vlan-int40 |
192:168::22:2/120 |
|
Device C |
Vlan-int10 |
192:168::34:3/120 |
Device D |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::45:4/120 |
|
Device E |
Vlan-int20 |
192:168::45:5/120 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Device E |
Vlan-int10 |
192:168::34:4/120 |
— |
— |
— |
Prerequisites
Assign IPv6 addresses to interfaces on the devices.
Procedure
1. Configure Device B:
# Configure a static route, whose destination address is 2001:: 64, next hop address is FE80::1 (a link-local IPv6 address on Device A), and tag value is 100.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] ipv6 route-static 2001:: 64 vlan-interface 30 FE80::1 tag 100
# Configure routing policy sava and configure node 10 in permit mode for the routing policy to permit routes with the output interface VLAN-interface 30.
[DeviceB] route-policy sava permit node 10
[DeviceB-route-policy-sava-10] if-match interface vlan-interface 30
[DeviceB-route-policy-sava-10] quit
# Configure OSPFv3.
[DeviceB] ospfv3 1
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1] router-id 2.2.2.2
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface20] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure OSPFv3 to redistribute remote routes with route tag 100.
[DeviceB] ospfv3 1
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1] import-route static route-policy sava
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1] quit
# Enable SAVA on VLAN-interface 30.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 30
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] ipv6 sava enable
# Configure VLAN-interface 30 to redistribute remote routes with route tag 100.
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] ipv6 sava import remote-route-tag 100
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface30] quit
2. Configure Device D:
# Configure a static route, whose destination address is 2000:: 64, next hop address is FE80::1 (a link-local IPv6 address on Device A), and tag value is 100.
<DeviceD> system-view
[DeviceD] ipv6 route-static 2000:: 64 vlan-interface 40 FE80::1 tag 100
# Configure routing policy named sava, configure node 10 in permit mode to permit routes with the output interface VLAN-interface 40.
[DeviceD] route-policy sava permit node 10
[DeviceD-route-policy-sava-10] if-match interface vlan-interface 40
[DeviceD-route-policy-sava-10] quit
# Configure OSPFv3.
[DeviceD] ospfv3 1
[DeviceD-ospfv3-1] router-id 4.4.4.4
[DeviceD-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface20] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure OSPFv3 process 1 to redistribute remote routes permitted by routing policy sava.
[DeviceD] ospfv3 1
[DeviceD-ospfv3-1] import-route static route-policy sava
[DeviceD-ospfv3-1] quit
# Enable SAVA on VLAN-interface 40.
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 40
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface40] ipv6 sava enable
# Configure VLAN-interface 40 to redistribute remote routes with route tag 100.
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface40] ipv6 sava import remote-route-tag 100
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface40] quit
3. Configure Device C:
# Configure routing policy named sava-exp, configure node 0 in permit mode to permit routes with tag 100 and to set the 10:10 community attribute for BGP.
[DeviceC] route-policy sava-exp permit node 0
[DeviceC-route-policy-sava-exp-0] if-match tag 100
[DeviceC-route-policy-sava-exp-0] apply community 10:10
[DeviceC-route-policy-sava-exp-0] quit
# Enable BGP to exchange routing information for IPv6 address family with peer 192:168::34:4 in AS 200.
[DeviceC] bgp 100
[DeviceC-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[DeviceC-bgp-default] peer 192:168::34:4 as 200
[DeviceC-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[DeviceC-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 192:168::34:4 enable
[DeviceC-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 192:168::34:4 advertise-community
# Configure BGP to redistribute routes from OSPFv3 process 1, and apply routing policy sava-exp to routes outgoing to peer 192:168::34:4.
[DeviceC-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route ospfv3 1
[DeviceC-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 192:168::34:4 route-policy sava-exp export
[DeviceC-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[DeviceC-bgp-default] quit
# Configure basic community list 1 to permit routes with the 10:10 community attribute.
[DeviceC] ip community-list 1 permit 10:10
# Configure a routing policy named sava-imp, and configure node 10 in permit mode for the routing policy to use community list 1 to match BGP routes and to set the tag to 100.
[DeviceC] route-policy sava-imp permit node 0
[DeviceC-route-policy-sava-imp-0] if-match community 1
[DeviceC-route-policy-sava-imp-0] apply tag 100
[DeviceC-route-policy-sava-imp-0] quit
# Apply routing policy sava-imp to routes incoming from peer 192:168::34:4.
[DeviceC] bgp 100
[DeviceC-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[DeviceC-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 192:168::34:4 route-policy sava-imp import
[DeviceC-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[DeviceC-bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPFv3.
[DeviceC] ospfv3 1
[DeviceC-ospfv3-1] router-id 3.3.3.3
[DeviceC-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface20] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure OSPFv3 process 1 to redistribute routes from IPv6 BGP.
[DeviceC] ospfv3 1
[DeviceC-ospfv3-1] import-route bgp4+
[DeviceC-ospfv3-1] quit
4. Configure Device E:
# Configure routing policy named sava-exp, configure node 0 in permit mode to permit routes with tag 100 and to set the 10:10 community attribute for BGP.
[DeviceE] route-policy sava-exp permit node 0
[DeviceE-route-policy-sava-exp-0] if-match tag 100
[DeviceE-route-policy-sava-exp-0] apply community 10:10
[DeviceE-route-policy-sava-exp-0] quit
# Enable BGP to exchange routing information for IPv6 address family with peer 192:168::34:3 in AS 100.
[DeviceE] bgp 200
[DeviceE-bgp-default] router-id 5.5.5.5
[DeviceE-bgp-default] peer 192:168::34:3 as 100
[DeviceE-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[DeviceE-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 192:168::34:3 enable
[DeviceE-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 192:168::34:3 advertise-community
# Configure BGP to redistribute routes from OSPFv3 process 1, and apply routing policy sava-exp to routes outgoing to peer 192:168::34:3.
[DeviceE-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route ospfv3
[DeviceE-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 192:168::34:3 route-policy sava-exp export
[DeviceE-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[DeviceE-bgp-default] quit
# Configure basic community list 1 to permit routes with the 10:10 community attribute.
[DeviceE] ip community-list 1 permit 10:10
# Configure a routing policy named sava-imp, and configure node 10 in permit mode for the routing policy to use community list 1 to match BGP routes and to set the tag to 100.
[DeviceE] route-policy sava-imp permit node 0
[DeviceE-route-policy-sava-imp-0] if-match community 1
[DeviceE-route-policy-sava-imp-0] apply tag 100
[DeviceE-route-policy-sava-imp-0] quit
# Apply routing policy sava-imp to routes incoming from peer 192:168::34:4.
[DeviceE] bgp 200
[DeviceE-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[DeviceE-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 192:168::34:3 route-policy sava-imp import
[DeviceE-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[DeviceE-bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPFv3.
[DeviceE] ospfv3 1
[DeviceE-ospfv3-1] router-id 5.5.5.5
[DeviceE-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceE] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceE-Vlan-interface20] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceE- Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure OSPFv3 process 1 to redistribute routes from IPv6 BGP.
[DeviceE] ospfv3 1
[DeviceE-ospfv3-1] import-route bgp4+
[DeviceE-ospfv3-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display SAVA entries on Device D.
[DeviceD] display ipv6 sava
IPv6 SAVA entry count: 3
Destination:192:168::22:0 Prefix length: 120
Interface: Vlan-int40 Flags: L
Destination: 2000:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int40 Flags: L
Destination: 2001:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int40 Flags: R
# Display SAVA entries on Device B.
[DeviceB] display ipv6 sava
IPv6 SAVA entry count: 3
Destination:192:168::12:0 Prefix length: 120
Interface: Vlan-int30 Flags: L
Destination: 2000:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int30 Flags: R
Destination: 2001:: Prefix length: 64
Interface: Vlan-int30 Flags: L