- Table of Contents
-
- 11-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Keychain configuration
- 02-Public key management
- 03-PKI configuration
- 04-Crypto engine configuration
- 05-SSH configuration
- 06-SSL configuration
- 07-Packet filter configuration
- 08-DHCP snooping configuration
- 09-DHCPv6 snooping configuration
- 10-ARP attack protection configuration
- 11-ND attack defense configuration
- 12-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 13-IP-based attack prevention configuration
- 14-uRPF configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 09-DHCPv6 snooping configuration | 139.45 KB |
Application of trusted and untrusted ports
Restrictions and guidelines: DHCPv6 snooping configuration
DHCPv6 snooping tasks at a glance
Configuring basic DHCPv6 snooping features
Configuring basic DHCPv6 snooping features in a common network
Configuring DHCP snooping support for Option 18
Configuring DHCP snooping support for Option 37
Configuring DHCPv6 snooping entry auto backup
Setting the maximum number of DHCPv6 snooping entries
Configuring DHCPv6 packet rate limit
Configuring a DHCPv6 packet blocking port
Enabling Relay-Forward packet check
Enabling client offline detection on the DHCPv6 snooping device
Enabling DHCPv6 snooping logging and alarm
Enabling DHCPv6 snooping logging
Verifying and maintaining DHCPv6 snooping
Displaying trusted port information
Displaying and clearing DHCPv6 snooping entries
Displaying and clearing DHCPv6 packet statistics for DHCPv6 snooping
DHCPv6 snooping configuration examples
Example: Configuring DHCPv6 snooping
Configuring DHCPv6 snooping
About DHCPv6 snooping
It guarantees that DHCPv6 clients obtain IPv6 addresses or prefixes from authorized DHCPv6 servers. Also, it records IP-to-MAC bindings of DHCPv6 clients (called DHCPv6 snooping address entries) and prefix-to-port bindings of DHCPv6 clients (called DHCPv6 snooping prefix entries) for security purposes.
DHCPv6 snooping defines trusted and untrusted ports to make sure that clients obtain IPv6 addresses only from authorized DHCPv6 servers.
· Trusted—A trusted port can forward DHCPv6 messages correctly to make sure the clients get IPv6 addresses from authorized DHCPv6 servers.
· Untrusted—An untrusted port discards received messages sent by DHCPv6 servers to prevent unauthorized servers from assigning IPv6 addresses.
DHCPv6 snooping reads DHCP-ACK messages received from trusted ports and DHCP-REQUEST messages to create DHCPv6 snooping entries. A DHCPv6 snooping entry can be an address entry or a prefix entry.
· A DHCPv6 address entry includes the MAC and IP addresses of a client, the port that connects to the DHCPv6 client, and the VLAN. You can use the display ipv6 dhcp snooping binding command to display the IP addresses of users for management.
· A DHCPv6 prefix entry includes the prefix and lease information assigned to the client, the port that connects to the DHCPv6 client, and the VLAN. You can use the display ipv6 dhcp snooping pd binding command to display the prefixes of the users for management.
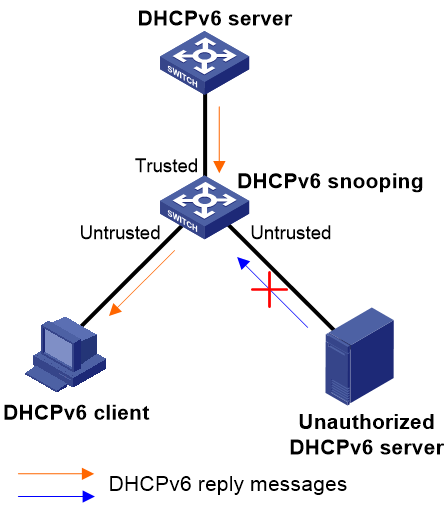
Application of trusted and untrusted ports
Configure ports facing the DHCPv6 server as trusted ports, and configure other ports as untrusted ports.
As shown in Figure 1, configure the DHCPv6 snooping device's port that is connected to the DHCPv6 server as a trusted port. The trusted port forwards response messages from the DHCPv6 server to the client. The untrusted port connected to the unauthorized DHCPv6 server discards incoming DHCPv6 response messages.
Figure 1 Trusted and untrusted ports
Restrictions and guidelines: DHCPv6 snooping configuration
DHCPv6 snooping works between the DHCPv6 client and server, or between the DHCPv6 client and DHCPv6 relay agent.
DHCPv6 snooping does not work between the DHCPv6 server and DHCPv6 relay agent.
DHCPv6 snooping tasks at a glance
To configure DHCPv6 snooping, perform the following tasks:
1. Configuring basic DHCPv6 snooping features
2. (Optional.) Configuring DHCP snooping support for Option 18
3. (Optional.) Configuring DHCP snooping support for Option 37
4. (Optional.) Configuring DHCPv6 snooping entry auto backup
5. (Optional.) Setting the maximum number of DHCPv6 snooping entries
6. (Optional.) Configuring DHCPv6 packet rate limit
7. (Optional.) Enabling DHCPv6-REQUEST check
8. (Optional.) Configuring a DHCPv6 packet blocking port
9. Enabling Relay-Forward packet check
10. Enabling client offline detection on the DHCPv6 snooping device
11. (Optional.) Enabling DHCPv6 snooping logging and alarm
¡ Enabling DHCPv6 snooping logging
¡ Configuring packet drop alarm
Configuring basic DHCPv6 snooping features
Configuring basic DHCPv6 snooping features in a common network
Restrictions and guidelines
· To make sure DHCPv6 clients can obtain valid IPv6 addresses, specify the ports connected to authorized DHCPv6 servers as trusted ports. The trusted ports and the ports connected to DHCPv6 clients must be in the same VLAN.
· After a Layer 2 Ethernet interface join an aggregation group, the DHCPv6 snooping settings on the interface do not take effect unless the interface is removed from the aggregation group.
Enabling DHCPv6 snooping
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable DHCPv6 snooping.
ipv6 dhcp snooping enable
By default, DHCPv6 snooping is disabled.
Specifying a DHCPv6 snooping trusted port
1. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
This interface must connect to the DHCPv6 server.
2. Specify the port as a trusted port.
ipv6 dhcp snooping trust
By default, all ports are untrusted ports after DHCPv6 snooping is enabled.
Enabling recording DHCPv6 snooping entries
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
This interface must connect to the DHCPv6 clients.
3. Enable recording DHCPv6 snooping entries. Choose the following tasks as needed:
¡ Enable recording DHCPv6 snooping address entries.
ipv6 dhcp snooping binding record
By default, recording of DHCPv6 snooping address entries is disabled.
¡ Enable recording DHCPv6 snooping prefix entries.
ipv6 dhcp snooping pd binding record
By default, recording of DHCPv6 snooping prefix entries is disabled.
Configuring DHCP snooping support for Option 18
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable DHCP snooping support for Option 18.
ipv6 dhcp snooping option interface-id enable
By default, DHCP snooping support for Option 18 is disabled.
4. (Optional.) Specify the content as the interface ID.
ipv6 dhcp snooping option interface-id [ vlan vlan-id ] string interface-id
By default, the DHCPv6 snooping device uses its DUID as the content for Option 18.
Configuring DHCP snooping support for Option 37
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable DHCP snooping support for Option 37.
ipv6 dhcp snooping option remote-id enable
By default, DHCP snooping support for Option 37 is disabled.
4. (Optional.) Specify the content as the remote ID.
ipv6 dhcp snooping option remote-id [ vlan vlan-id ] string remote-id
By default, the DHCPv6 snooping device uses its DUID as the content for Option 37.
Configuring DHCPv6 snooping entry auto backup
About this task
The auto backup feature saves DHCPv6 snooping entries to a backup file, and allows the DHCPv6 snooping device to download the entries from the backup file at reboot. The entries on the DHCPv6 snooping device cannot survive a reboot. The auto backup helps the security features provide services if these features must use DHCPv6 snooping entries for user authentication.
Restrictions and guidelines
· If you disable DHCPv6 snooping with the undo ipv6 dhcp snooping enable command, the device deletes all DHCPv6 snooping entries, including those stored in the backup file.
· If you execute the ipv6 dhcp snooping binding database filename command, the DHCPv6 snooping device backs up DHCPv6 snooping entries immediately and runs auto backup. This command automatically creates the file if you specify a non-existent file.
· The waiting period starts when a DHCPv6 snooping entry is learned, updated, or removed. The DHCPv6 snooping device updates the backup file when the specified waiting period is reached. All changed entries during the period will be saved to the backup file. If no DHCPv6 snooping entry changes, the backup file is not updated.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the DHCPv6 snooping device to back up DHCPv6 snooping entries to a file.
ipv6 dhcp snooping binding database filename { filename | url url }
By default, the DHCPv6 snooping device does not back up the DHCPv6 snooping entries.
3. (Optional.) Manually save DHCPv6 snooping entries to the backup file.
ipv6 dhcp snooping binding database update now
4. (Optional.) Set the waiting time after a DHCPv6 snooping entry change for the DHCPv6 snooping device to update the backup file.
ipv6 dhcp snooping binding database update interval interval
By default, the DHCP snooping device waits 300 seconds to update the backup file after a DHCP snooping entry change. If no DHCP snooping entry changes, the backup file is not updated.
Setting the maximum number of DHCPv6 snooping entries
About this task
Perform this task to prevent the system resources from being overused.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Set the maximum number of DHCPv6 snooping entries for the interface to learn.
ipv6 dhcp snooping max-learning-num max-number
By default, the number of DHCPv6 snooping entries for an interface to learn is not limited.
Configuring DHCPv6 packet rate limit
About this task
This DHCPv6 packet rate limit feature discards exceeding DHCPv6 packets to prevent attacks that send large numbers of DHCPv6 packets.
Restrictions and guidelines
The rate set on the Layer 2 aggregate interface applies to all members of the aggregate interface. If a member interface leaves the aggregation group, it uses the rate set in its Ethernet interface view.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Set the maximum rate at which an interface can receive DHCPv6 packets.
ipv6 dhcp snooping rate-limit rate
By default, incoming DHCPv6 packets on an interface are not rate limited.
Enabling DHCPv6-REQUEST check
About this task
Perform this task to use the DHCPv6-REQUEST check feature to protect the DHCPv6 server against DHCPv6 client spoofing attacks. Attackers can forge DHCPv6-RENEW messages to renew leases for legitimate DHCPv6 clients that no longer need the IP addresses. The forged messages disable the victim DHCPv6 server from releasing the IP addresses. Attackers can also forge DHCPv6-DECLINE or DHCPv6-RELEASE messages to terminate leases for legitimate DHCPv6 clients that still need the IP addresses.
The DHCPv6-REQUEST check feature enables the DHCPv6 snooping device to check every received DHCPv6-RENEW, DHCPv6-DECLINE, or DHCPv6-RELEASE message against DHCPv6 snooping entries.
· If any criterion in an entry is matched, the device compares the entry with the message information.
¡ If they are consistent, the device considers the message valid and forwards it to the DHCPv6 server.
¡ If they are different, the device considers the message forged and discards it.
· If no matching entry is found, the device forwards the message to the DHCPv6 server.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable DHCPv6-REQUEST check.
ipv6 dhcp snooping check request-message
By default, DHCPv6-REQUEST check is disabled.
Configuring a DHCPv6 packet blocking port
About this task
Perform this task to configure a port as a DHCPv6 packet blocking port. The DHCPv6 packet blocking port drops all incoming DHCP requests.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Configure the port to block DHCPv6 requests.
ipv6 dhcp snooping deny
By default, the port does not block DHCPv6 requests.
|
CAUTION: To avoid IPv6 address and prefix acquisition failure, configure a port to block DHCPv6 packets only if no DHCPv6 clients are connected to it. |
Enabling Relay-Forward packet check
About this task
A DHCPv6 snooping device functions between DHCPv6 clients and a DHCPv6 server, or between DHCPv6 clients and a DHCPv6 relay agent. When a DHCPv6 relay agent receives a DHCPv6 request, it generates a Relay-Forward packet, adds client information to Option 79, and then forwards the packet to the DHCPv6 server. If the DHCPv6 snooping device receives a Relay-Forward packet, it indicates that the DHCPv6 snooping device location is not correct. In this case, the DHCPv6 snooping device cannot function correctly.
This feature enables the DHCPv6 snooping device to drop Relay-Forward packets. When the number of dropped Relay-Forward packets reaches or exceeds the threshold, the device generates a log for administrators to adjust locations of the DHCPv6 devices.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable the Relay-Forward packet check.
ipv6 dhcp snooping check relay-forward
By default, the Relay-Forward packet check is disabled.
Enabling client offline detection on the DHCPv6 snooping device
About this task
When a DHCPv6 client goes offline abnormally, it does not send a message to the DHCPv6 server to release its IPv6 address. As a result, the DHCPv6 server is not aware of the offline event and cannot release the address lease of the client timely.
With this feature enabled, the DHCPv6 snooping device performs the following operations when the ND entry of a client ages out:
1. Deletes the DHCPv6 snooping entry for the client.
2. Sends a release message to the DHCPv6 server to inform the server to release the address lease of the client.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable client offline detection.
ipv6 dhcp snooping client-detect
By default, client offline detection is disabled.
Enabling DHCPv6 snooping logging and alarm
Enabling DHCPv6 snooping logging
About this task
The DHCPv6 snooping logging feature enables the DHCPv6 snooping device to generate DHCPv6 snooping logs and send them to the information center. The information helps administrators locate and solve problems. For information about the log destination and output rule configuration in the information center, see information center configuration in System Management Configuration Guide.
Restrictions and guidelines
As a best practice, disable this feature if the log generation affects the device performance.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable DHCPv6 snooping logging.
ipv6 dhcp snooping log enable
By default, DHCPv6 snooping logging is disabled.
Configuring packet drop alarm
About this task
After you enable the packet drop alarm for a feature, the device generates an alarm log when the number of packets dropped by this feature reaches or exceeds the threshold. The alarm log is sent to the information center. You can set log message filtering and output rules by configuring the information center. For more information about the information center, see information center configuration in System Management Configuration Guide.
To set the alarm threshold, use the ipv6 dhcp snooping alarm threshold command.
Restrictions and guidelines
For this feature to take effect, you must first execute the ipv6 dhcp snooping log enable command to enable DHCPv6 snooping logging.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable the packet drop alarm.
ipv6 dhcp snooping alarm { relay-forward | request-message } enable
By default, the packet drop alarm is disabled.
3. Set a packet drop alarm threshold.
ipv6 dhcp snooping alarm { relay-forward | request-message } threshold threshold
By default, the packet drop alarm threshold is 100.
Verifying and maintaining DHCPv6 snooping
Displaying trusted port information
To display information about trusted ports, execute the following command in any view:
display ipv6 dhcp snooping trust
Displaying and clearing DHCPv6 snooping entries
Perform display tasks in any view.
· Display DHCPv6 snooping address entries.
display ipv6 dhcp snooping binding [ address ipv6-address [ vlan vlan-id ] ]
· Display DHCPv6 snooping prefix entries.
display ipv6 dhcp snooping pd binding [ prefix prefix/prefix-length [ vlan vlan-id ] ]
· Display information about DHCPv6 snooping entry auto backup.
display ipv6 dhcp snooping binding database
Perform clear tasks in user view.
· Clear DHCPv6 snooping address entries.
reset ipv6 dhcp snooping binding { all | address ipv6-address [ vlan vlan-id ] }
· Clear DHCPv6 snooping prefix entries.
reset ipv6 dhcp snooping pd binding { all | prefix prefix/prefix-length [ vlan vlan-id ] }
Displaying and clearing DHCPv6 packet statistics for DHCPv6 snooping
To display DHCPv6 packet statistics for DHCPv6 snooping, execute the following command in any view:
display ipv6 dhcp snooping packet statistics [ slot slot-number ]
To clear DHCPv6 packet statistics for DHCPv6 snooping, execute the following command in user view:
reset ipv6 dhcp snooping packet statistics [ slot slot-number ]
DHCPv6 snooping configuration examples
Example: Configuring DHCPv6 snooping
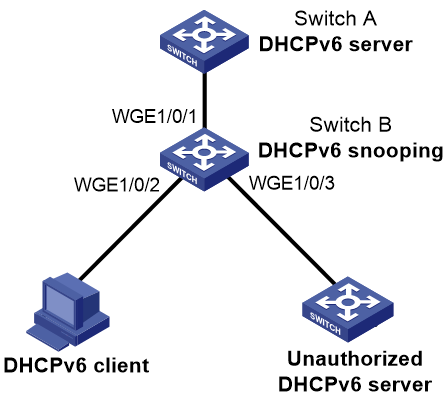
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, Switch B is connected to the authorized DHCPv6 server through Twenty-FiveGigE 1/0/1, to the unauthorized DHCPv6 server through Twenty-FiveGigE 1/0/3, and to the DHCPv6 client through Twenty-FiveGigE 1/0/2.
Configure only the port connected to the authorized DHCPv6 server to forward the responses from the DHCPv6 server. Enable the DHCPv6 snooping device to record DHCPv6 snooping address entries.
Procedure
# Enable DHCPv6 snooping.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ipv6 dhcp snooping enable
# Specify Twenty-FiveGigE 1/0/1 as a trusted port.
[SwitchB] interface twenty-fivegige 1/0/1
[SwitchB-Twenty-FiveGigE1/0/1] ipv6 dhcp snooping trust
[SwitchB-Twenty-FiveGigE1/0/1] quit
# Enable recording DHCPv6 snooping address entries on Twenty-FiveGigE 1/0/2.
[SwitchB]interface twenty-fivegige 1/0/2
[SwitchB-Twenty-FiveGigE1/0/2] ipv6 dhcp snooping binding record
[SwitchB-Twenty-FiveGigE1/0/2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the DHCPv6 client obtains an IPv6 address and all other configuration parameters only from the authorized DHCPv6 server. (Details not shown.)
# Display DHCPv6 snooping address entries on the DHCPv6 snooping device.
[SwitchB] display ipv6 dhcp snooping binding