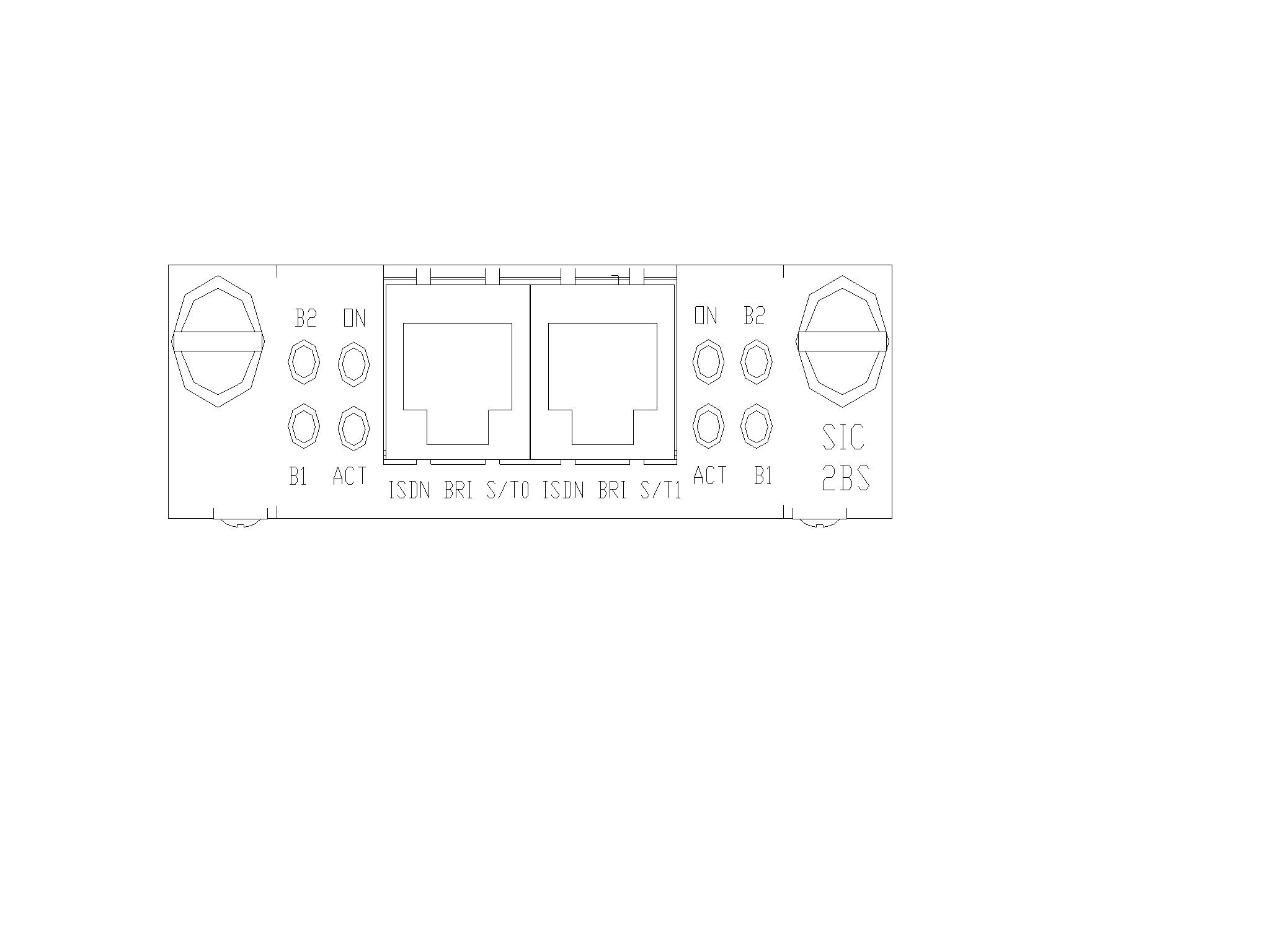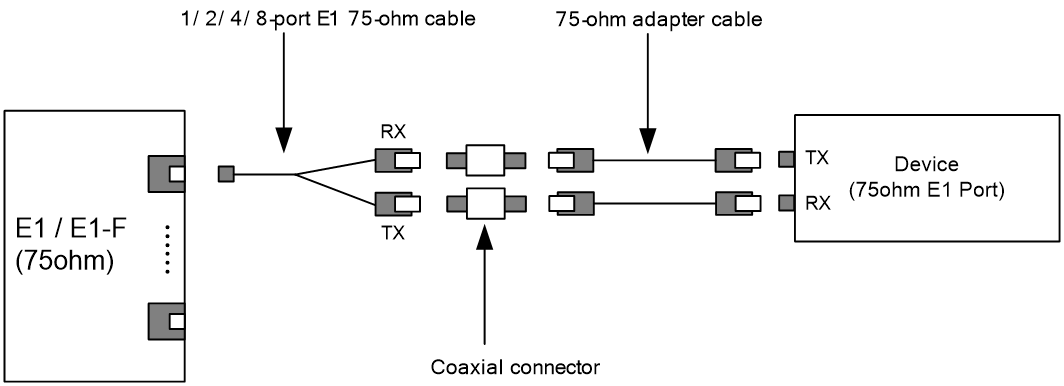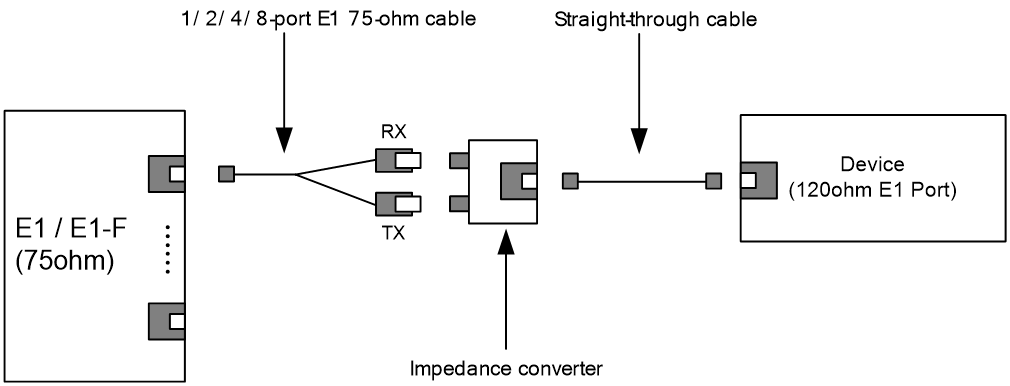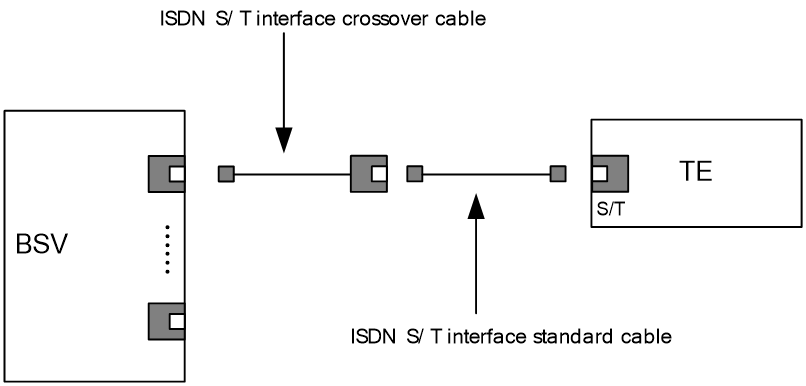- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-Text | 9.88 MB |
Contents
SIC-4FSW/SIC-4FSWP/DSIC-9FSW/DSIC-9FSWP
POS (SDH/SONET) interface modules
Analog modem interface modules
SIC-1FXS/SIC-1FXO/SIC-2FXS/SIC-2FXO
Network data encryption modules
POS (SDH/SONET) interface modules
MIM-1E1/MIM-2E1/MIM-4E1/MIM-1E1-F/MIM-2E1-F/MIM-4E1-F
POS terminal access interface modules
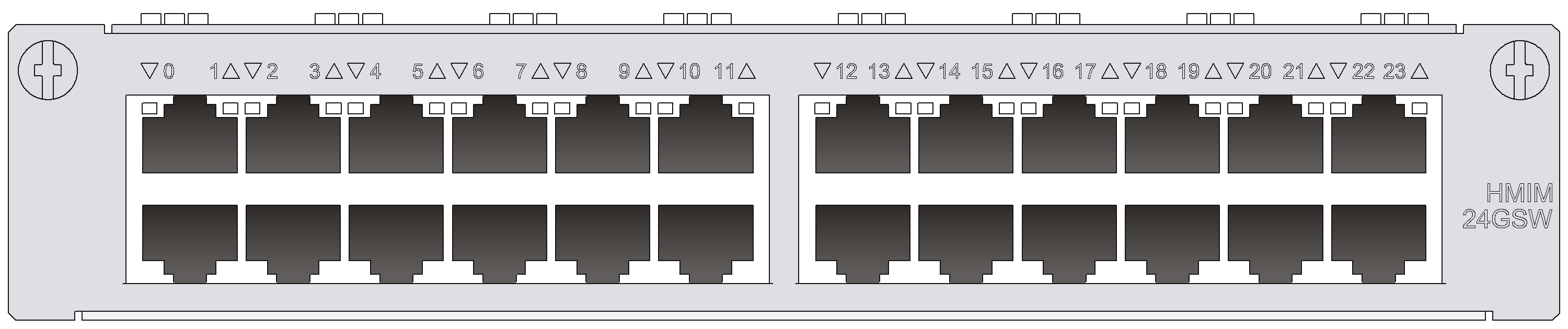
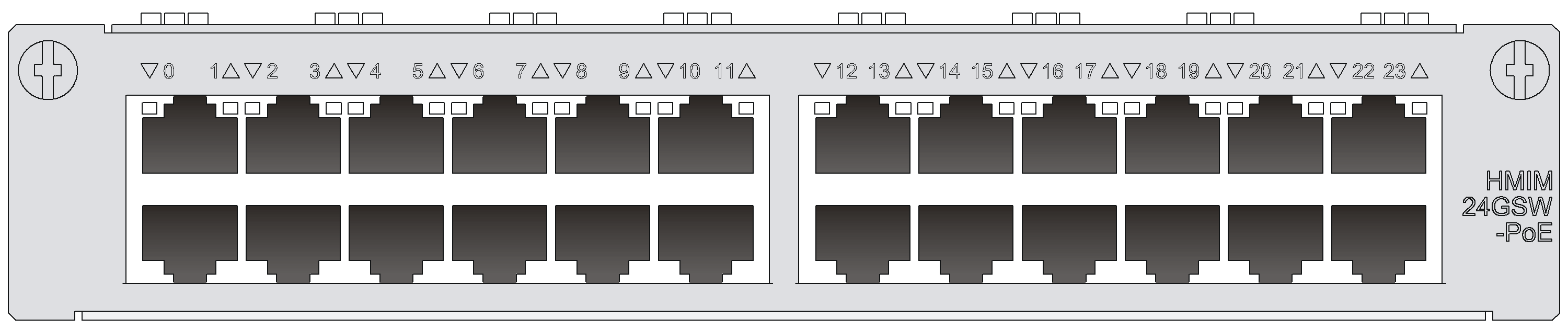
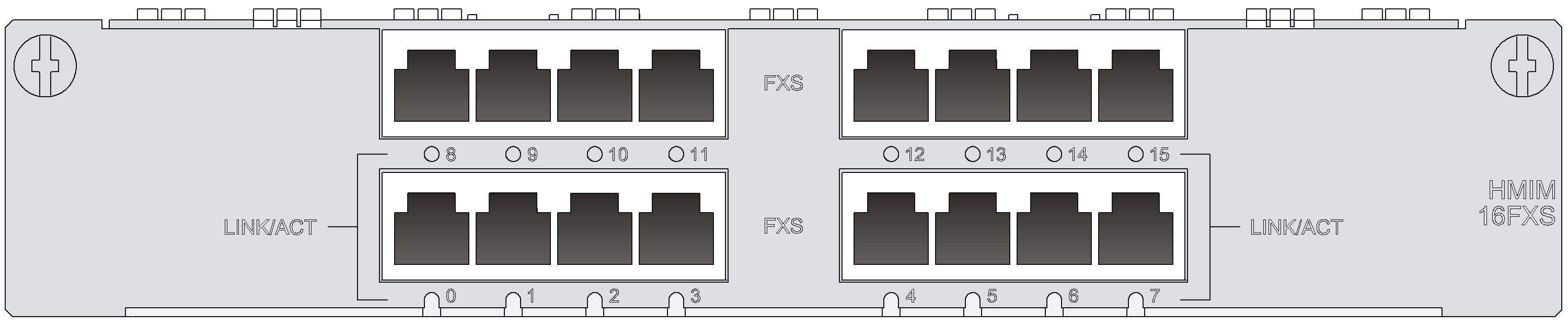
HMIM-8GSW/HMIM-24GSW/HMIM-24GSW-PoE
RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2/RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2
RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2/RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2
POS (SDH/SONET) interface modules
CPOS (SDH/SONET) interface modules
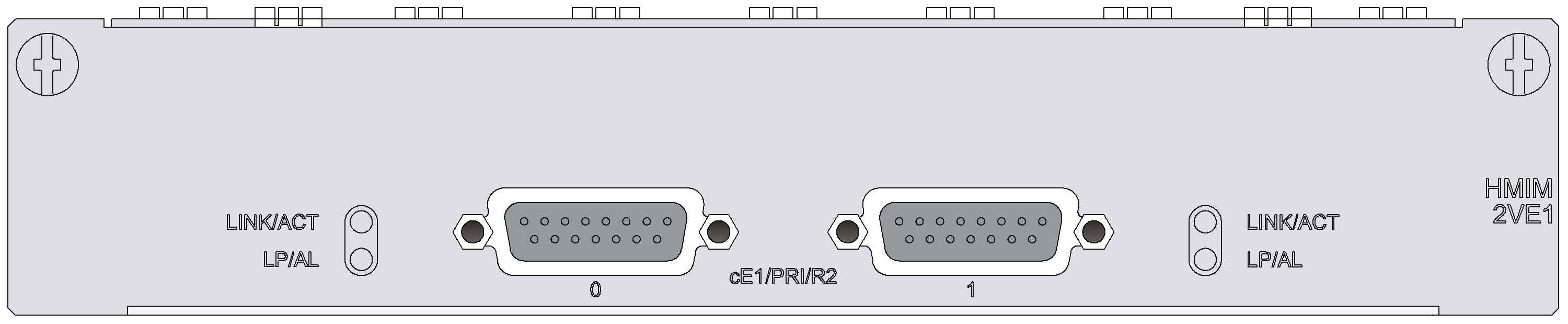
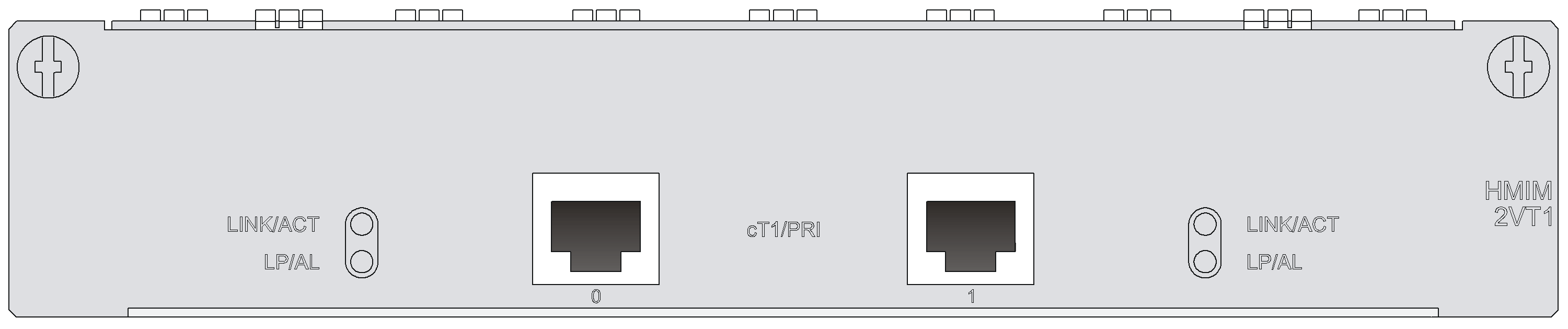
HMIM-1E1/HMIM-2E1/HMIM-4E1/HMIM-1E1-F/HMIM-2E1-F/HMIM-4E1-F
RT-HMIM-2E1-V3/RT-HMIM-4E1-V3/RT-HMIM-8E1-V3
HMIM-2E1T1/HMIM-4E1T1/HMIM-8E1T1/HMIM-2E1T1-F/HMIM-4E1T1-F/HMIM-8E1T1-F
RT-HMIM-4SAE-V2/RT-HMIM-8SAE-V2
RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2/RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2
POS terminal access interface modules
Digital modem interface modules
Network data encryption modules
Cables and the connection methods
Synchronous/asynchronous serial ports
ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface
Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules
Interface module power consumption
SIC/DSIC
MSR series routers use modular design and support a wide range of optional smart interface cards (SICs) and double smart interface cards (DSICs). A SIC occupies one SIC slot and a DSIC occupies two SIC slots. The SIC/DSIC series interface modules provide abundant interfaces, including synchronous/asynchronous serial interface, Ethernet interface, E1/T1, ISDN BRI/PRI, ADSL, audio interface, and Layer 2 switching interface.
Ethernet switching modules
· SIC-4FSW
· SIC-4FSWP
· DSIC-9FSW
· DSIC-9FSWP
· SIC-4GSW
· SIC-4GSWF
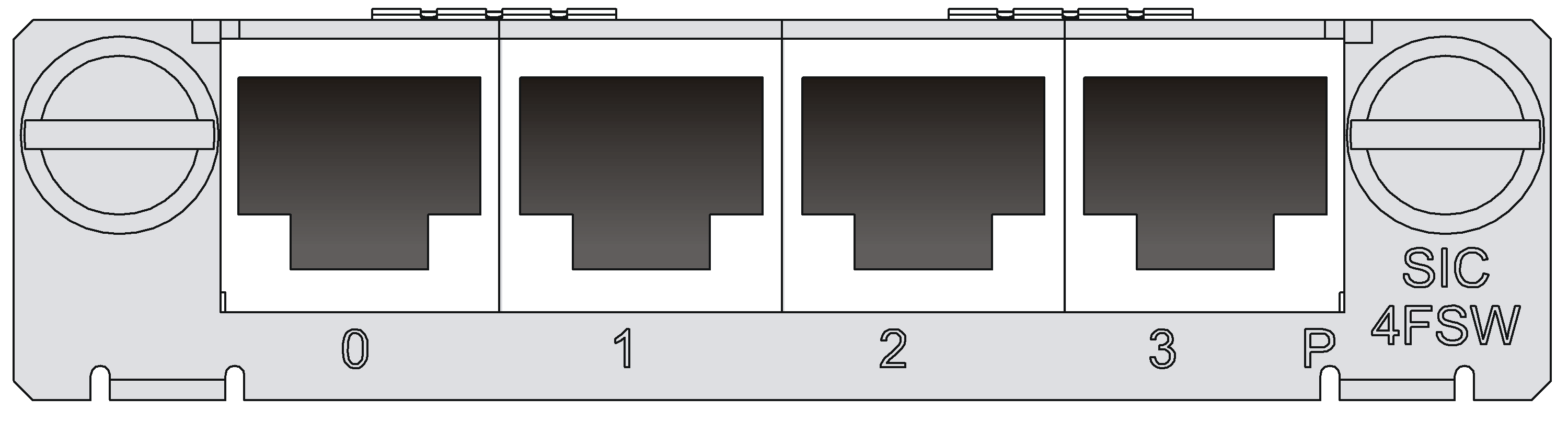
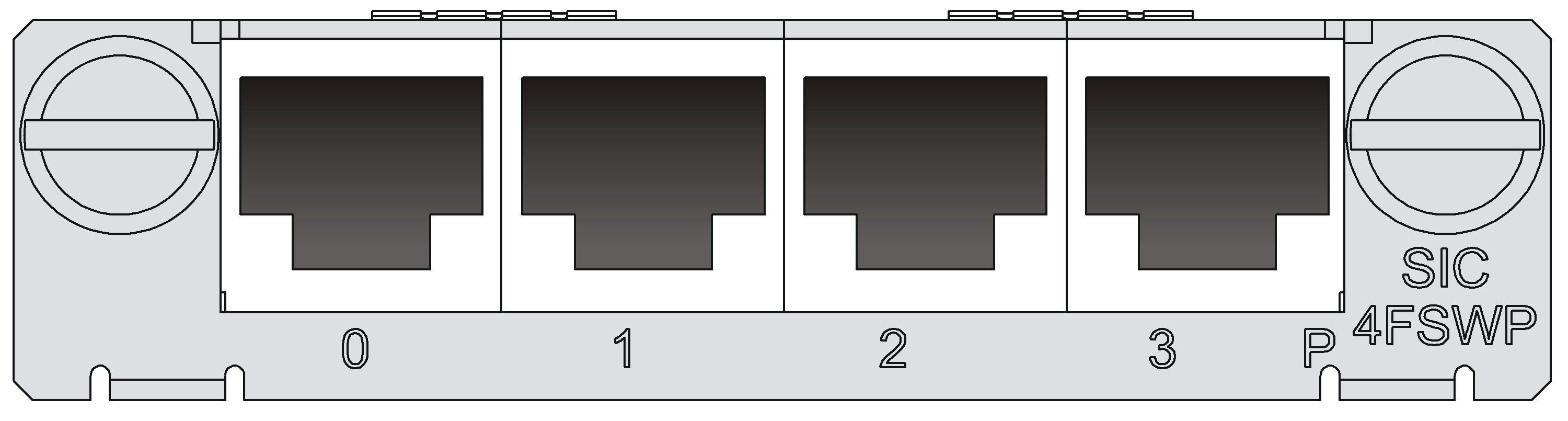
SIC-4FSW/SIC-4FSWP/DSIC-9FSW/DSIC-9FSWP
Introduction
The SIC-4FSW/SIC-4FSWP and DSIC-9FSW/DSIC-9FSWP interface modules are 4/9-port 10/100 Mbps Ethernet Layer 2 SIC interface modules that can be used on H3C MSR series routers. They provide up to 4/9 10/100 BASE-Tx Ethernet ports for Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching. A router installed with SIC-4FSW/SIC-4FSWP and DSIC-9FSW/DSIC-9FSWP modules can work as a switching/routing integrated device on a small-sized enterprise network to connect PCs and network devices inside the network directly. SIC-4FSWP/DSIC-9FSWP interface modules can supply power to powered devices (PDs) through power over Ethernet (PoE).
Functions supported by interface modules are as follows:
· Effective transmission distance of 100 m (328.08 ft) with category-5 twisted pair cables (both crossover and straight-through)
· Effective transmission distance of 100 m (328.08 ft) between any interfaces with category-5 twisted pair cables (both crossover and straight-through)
· Operating speeds of both 100 Mbps and 10 Mbps and autosensing
· Both full duplex (in common use) and half-duplex operating modes
Interface specifications
Table 1 describes the interface specifications of the SIC-4FSW, SIC-4FSWP, DSIC-9FSW, and DSIC-9FSWP interface modules. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 1 Interface specifications
|
Item |
SIC-4FSW/SIC-4FSWP |
DSIC-9FSW/DSIC-9FSWP |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
|
Interface type |
MDI/MDIX |
|
|
Number of connectors |
Four 100 Mbps RJ-45 connectors |
Nine 100 Mbps RJ-45 connectors |
|
Cable |
Standard (straight-through)/cross-over Ethernet cable |
|
|
Operation mode |
10/100 Mbps autosensing, full/half duplex |
|
|
|
NOTE: Ethernet interfaces on network adapters are usually medium dependent interfaces (MDIs). Medium dependent interfaces crossover (MDIXs) are another type of Ethernet interfaces, which are usually used on hubs and LAN switches. |
Interface LEDs
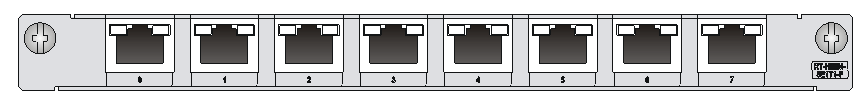
Figure 2 SIC-4FSWP panel
Figure 4 DSIC-9FSWP panel
On the panel, each port corresponds to one green LED. The following table describes the LEDs on the panel.
Table 2 LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Steady on |
A link is present, but no data is being transmitted or received. |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
|
Flashing |
A link is present and data is being transmitted and received (ACT). |
In addition, there is a PoE LED on each module, which is provided for the corresponding modules (SIC-4FSWP and DSIC-9FSWP) with the PoE function.
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about Ethernet interface cables and the connection methods, see "Ethernet interface."
SIC-4GSW
Introduction
The SIC-4GSW interface module is a 4-port 1000 Mbps Ethernet Layer 2 SIC interface module. The SIC-4GSW provides four 1000 Mbps RJ-45 ports. A router installed with SIC-4GSW modules can operate as a switching/routing integrated device on a small-sized enterprise network to connect PCs and network devices inside the network directly.
Functions supported by interface modules are as follows:
· Effective transmission distance of 100 m (328.08 ft) over category-5 twisted pair cables (both crossover and straight-through)
· Line rate of 1000 Mbps between any interfaces over category-5 twisted pair cables (both crossover and straight-through)
· Autosensing operating speeds of 1000 Mbps, 100 Mbps, and 10 Mbps
· Both full duplex (typically used) and half-duplex operating modes
Interface specifications
Table 3 describes the interface specifications of the SIC-4GSW interface module. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 3 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Interface type |
MDI/MDIX |
|
Number of connectors |
4 |
|
Cable |
Standard (straight-through)/cross-over Ethernet cable |
|
Operation mode |
10/100/1000 Mbps autosensing |
|
|
NOTE: Ethernet interfaces on network adapters are usually medium dependent interfaces (MDIs). Medium dependent interfaces crossover (MDIXs) are another type of Ethernet interfaces, which are usually used on hubs and LAN switches. |
Interface LEDs
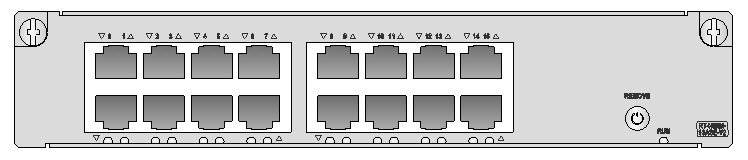
Figure 5 SIC-4GSW panel
The SIC-4GSW interface module provides a double-color (green/yellow) LED for each port to indicate the operating status of the port.
Table 4 LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
|
Steady green |
A 1000 Mbps link is present. |
|
Flashing green |
The port is sending and receiving data at 1000 Mbps. |
|
Steady yellow |
A 10/100 Mbps link is present. |
|
Flashing yellow |
The port is sending and receiving data at 10/100 Mbps. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For information about Ethernet interface cables and the connection methods, see "Ethernet interface."
SIC-4GSWF
Introduction
The 4-port 100/1000 Mbps Ethernet Layer 2/Layer 3 SIC interface module SIC-4GSWF provides four fiber ports. It is designed for switching/routing integrated routers on a small-sized enterprise network. You can use it to connect network devices inside the network.
The interface module has the following features:
· Support for multiple 100/1000 Mbps transceiver modules.
· 1000/100 Mbps interface rate.
· Full duplex operating mode.
Interface specifications
Table 5 describes the interface specifications of the SIC-4GSWF interface modules. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 5 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Number of interfaces |
4 |
|
Connector |
SFP/LC |
|
Standard |
802.3/802.3u/802.3ab |
|
Operating mode |
1000/100 Mbps, full duplex |
Interface LEDs
The SIC-4GSWF interface module provides a double-color (green/yellow) LED for each port to indicate the operating status of the port.
Table 6 LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
|
Steady green |
A link is present on the port and the port is operating at 1000 Mbps. |
|
Flashing green |
The port is sending and receiving data at 1000 Mbps. |
|
Steady yellow |
A link is present on the port and the port is operating at 100 Mbps. |
|
Flashing yellow |
The port is sending and receiving data at 100 Mbps. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods, see "Fiber port."
Ethernet interface modules
· SIC-1FEA
· SIC-1FEF
· SIC-1GEC-V2
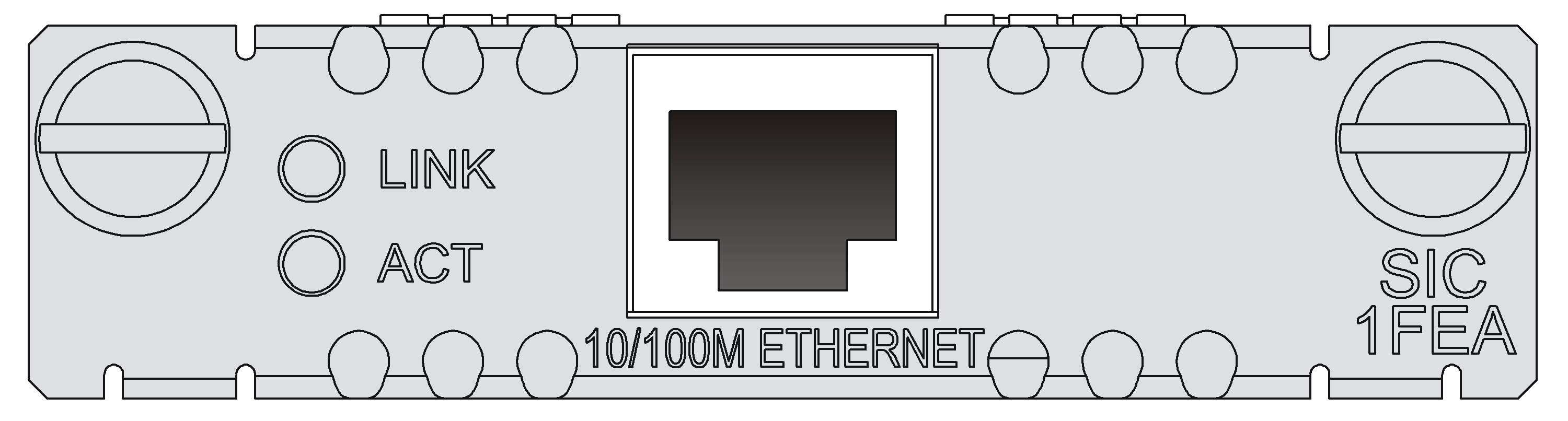
SIC-1FEA
Introduction
The 1-port 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Ethernet interface module (SIC-1FEA) is used for communication between the router and LAN. It supports:
· Effective transmission distance of 100 m (328.08 ft) with category-5 twisted pair cables
· Operating speeds of both 100 Mbps and 10 Mbps and autosensing
· Both full duplex (in common use) and half-duplex operating modes
Interface specifications
Table 7 describes the interface specifications of the SIC-1FEA interface module. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 7 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
|
Interface type |
MDI |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Cable type |
Straight-through Ethernet cable |
|
Operating mode |
10/100 Mbps autosensing Full duplex/half duplex |
|
|
NOTE: Ethernet interfaces on network adapters are usually medium dependent interfaces (MDIs). Medium dependent interfaces crossover (MDIXs) are another type of Ethernet interfaces, which are usually used on hubs and LAN switches. |
Interface LEDs
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: No link is present; · On: A link is present. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received; · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about the Ethernet interface cables and the connection methods, see "Ethernet interface".
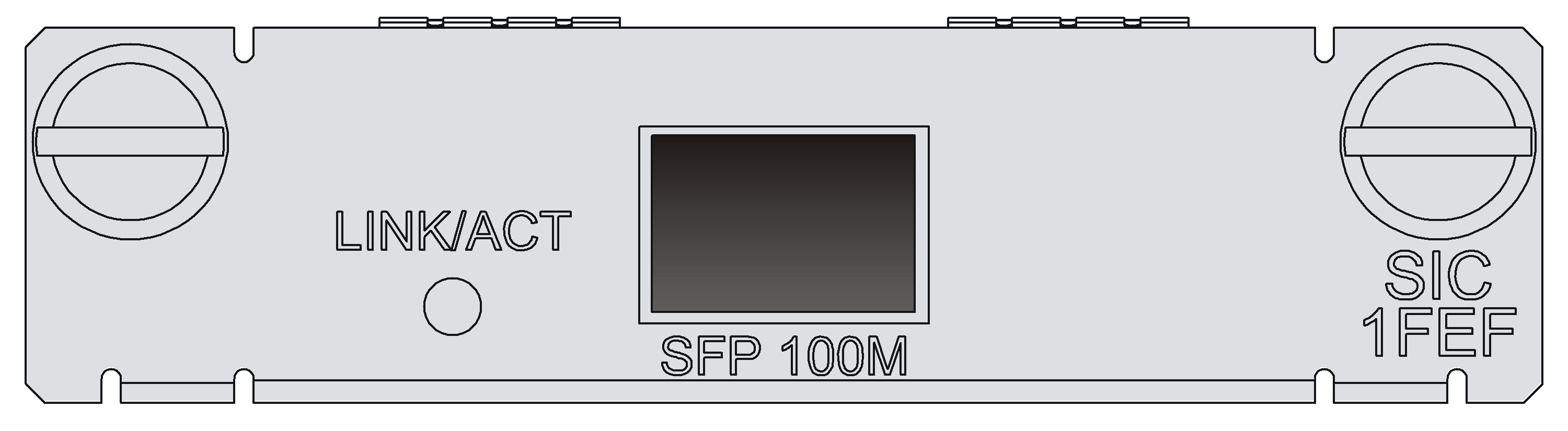
SIC-1FEF
Introduction
The 1-port 100 Mbps fiber Ethernet interface module (SIC-1FEF) is used for the communication between the router and LAN.
SIC-1FEF supports:
· Various types of transceiver modules.
· 100 Mbps interface rate.
· Full duplex.
Interface specifications
Table 9 describes the interface specifications of the SIC-1FEF interface module. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 9 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Connector |
SFP/LC |
|
Interface standard |
802.3, 802.3u, and 802.3ab |
|
Operating mode |
100 Mbps Full duplex |
Interface LEDs
Figure 8 SIC-1FEF panel
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
Off |
No link is present. |
|
Steady green |
The optical module has established a 100 Mbps link. |
|
|
Flashing green |
Data is being received and transmitted. |
|
|
Steady yellow |
Information detection failed. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods, see "Fiber port."
SIC-1GEC-V2
Introduction
The 1-port 10/100/1000 Mbps electrical and fiber Ethernet interface SIC module (SIC-1GEC-V2) has the following functions:
· Receipt, transmission and processing of GE data stream
· CE electrical and fiber port access
· 1000/100/10 Mbps on copper port
· 1000 Mbps on fiber port
Interface specifications
Table 11 describes the interface specifications of the SIC-1GEC-V2 interface module. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 11 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Interface type |
MDI |
|
Frame format |
· Ethernet_II · Ethernet_SNAP · IEEE 802.2 · IEEE 802.3 |
|
Operation mode |
10/100/1000 Mbps autosensing Full/half duplex |
|
|
NOTE: The SIC-1GEC-V2 provides combo interfaces. The fiber and copper ports of a combo interface cannot be used simultaneously. By default, the copper port is available. To use the fiber port, execute the related command. |
Interface LEDs
Table 12 LED description for the copper port on the SIC-1GEC-V2 panel
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. · Green: Data is being received and transmitted at a speed of 1000 Mbps. · Yellow: Data is being received and transmitted at a speed of 100/10 Mbps. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being received and transmitted; · Flashing: Data is being received and transmitted. |
Table 13 LED description for the fiber port on the SIC-1GEC-V2 panel
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. · Green: Data is being received and transmitted at a speed of 1000 Mbps. · Yellow: Fault. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being received and transmitted. · Flashing: Data is being received and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For information about Ethernet interface cables and the connection methods, see "Ethernet interface."
For information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
POS (SDH/SONET) interface modules
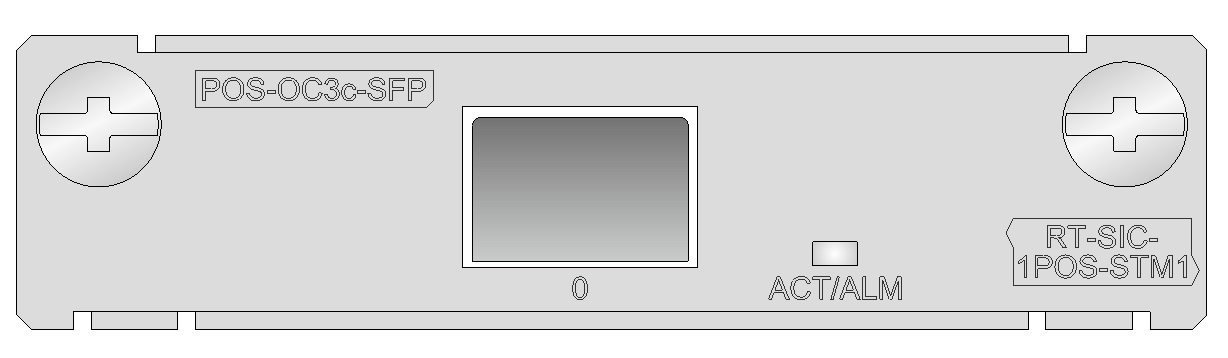
RT-SIC-1POS-STM1
|
CAUTION: The RT-SIC-1POS-STM1 interface module is not hot swappable. |
Introduction
The RT-SIC-1POS-STM1 1-port SDH/SONET interface module provides an interface transmission rate of 155.52 Mbps (STM-1/OC-3).
The RT-SIC-1POS-STM1 supports PPP, Frame Relay, and HDLC protocols at the data link layer and the IP protocol at the network layer. It allows direct transmission of packets over SONET/SDH. It provides a 155.52 Mbps fractional interface and supports various types of transceiver modules. You can purchase transceiver modules for it as required.
Interface specifications
Table 14 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
SFP/LC |
|
Number of interfaces |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
SONET OC-3/SDH STM-1 |
|
Interface rate |
155.52 Mbps |
Interface LEDs
Figure 10 RT-SIC-1POS-STM1 panel
Table 15 LED description
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
ACT/ALM |
Steady green |
A 155.52 Mbps link is present. |
|
Flashing green |
The port is receiving or sending data at 155.52 Mbps. |
|
|
Steady red |
An alarm has occurred. |
|
|
Off |
No transceiver module is present or the port is in shutdown state. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods, see "Fiber port."
E1/T1 interface modules
· SIC-E1-F
· SIC-2E1-F
· SIC-1EPRI
· SIC-T1-F
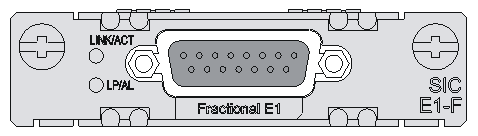
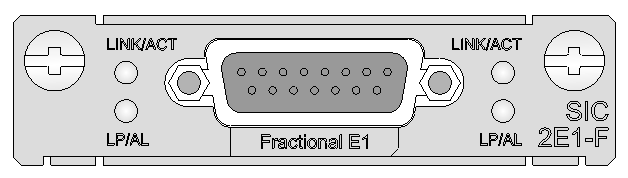
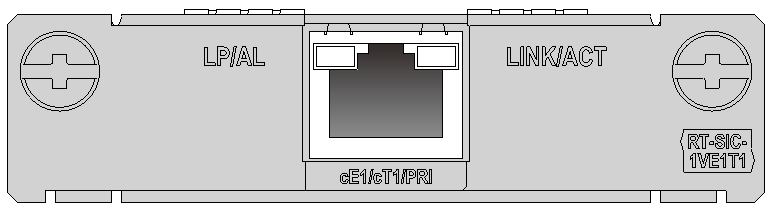
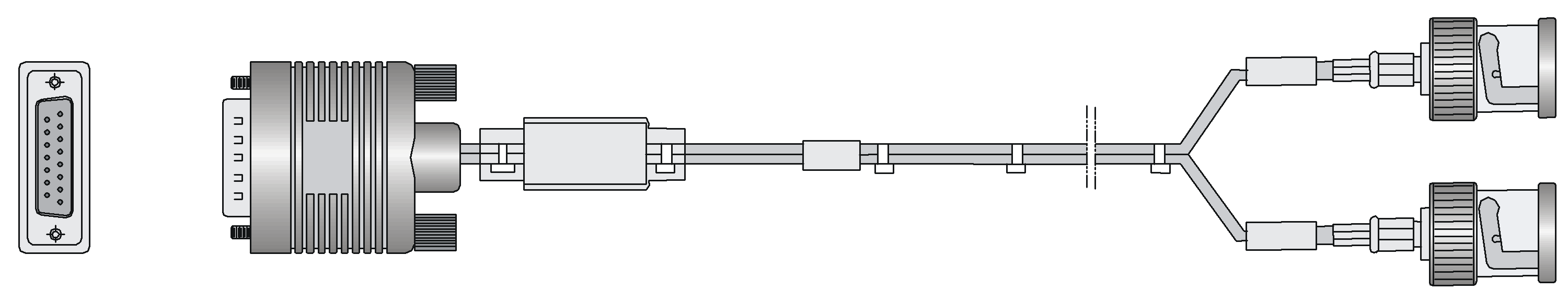
SIC-E1-F
Introduction
The 1-port fractional E1 interface module (SIC-E1-F) supports:
· Transmission/Receiving and handling of E1 data streams
· CE1 (channelized E1) access
· Remote loopback and local loopback functions, facilitating fault test and location.
The timeslots on an interface in FE1 mode on the SIC-E1-F can be bundled to form one interface (namely, can be bundled into one channel, and the rate of the interface is n No 64 Kbps, where n ranges from 1 to 31.)
The SIC-E1-F does not support the PRI mode.
Interface specifications
Table 16 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
D15 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703 · G.704 |
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
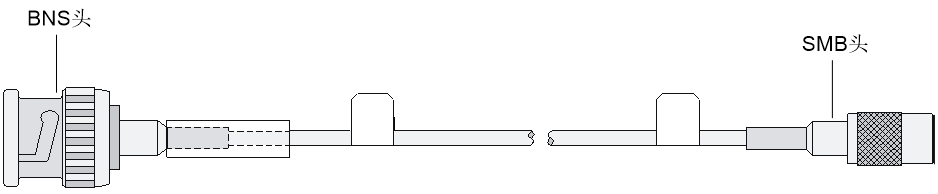
75-ohm unbalanced coaxial cable (D15 to BNC) |
|
Operating modes |
· E1 · CE1 |
|
Supported services |
· Backup · Terminal access |
Interface LEDs
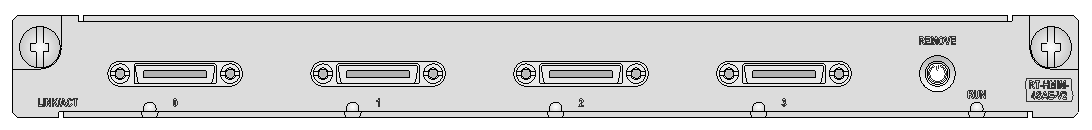
Figure 11 SIC-E1-F panel
Table 17 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted or received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: Neither loopback nor alarm is present. · Flashing: No cable is connected to the interface, the cable is damaged or not connected correctly, or the peer device is faulty. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
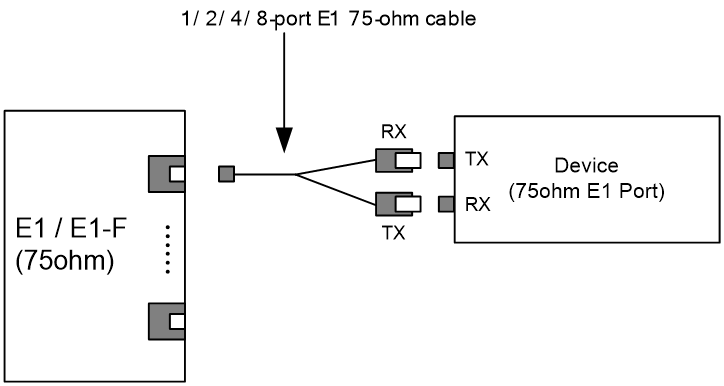
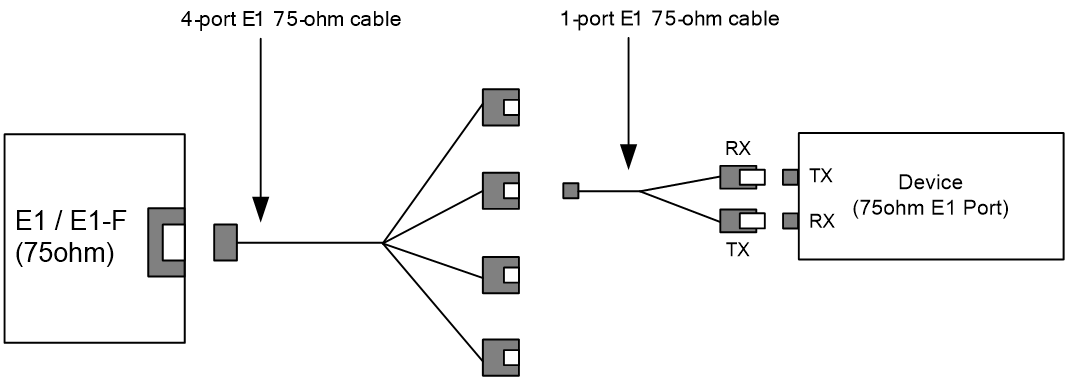
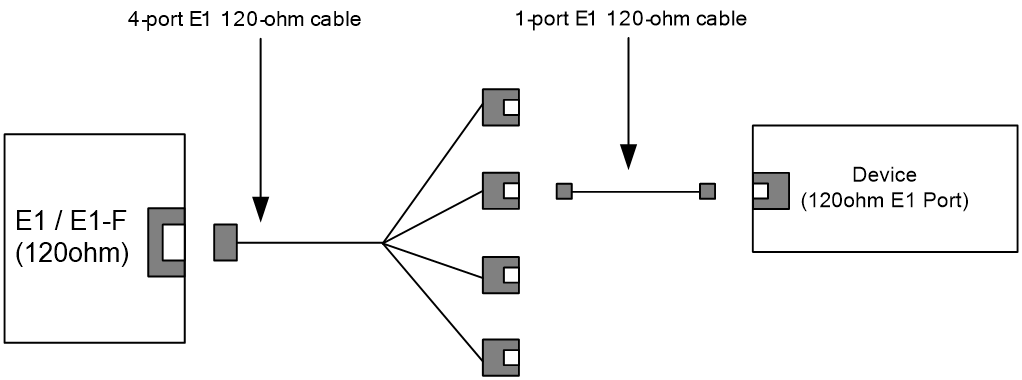
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E1 interface."
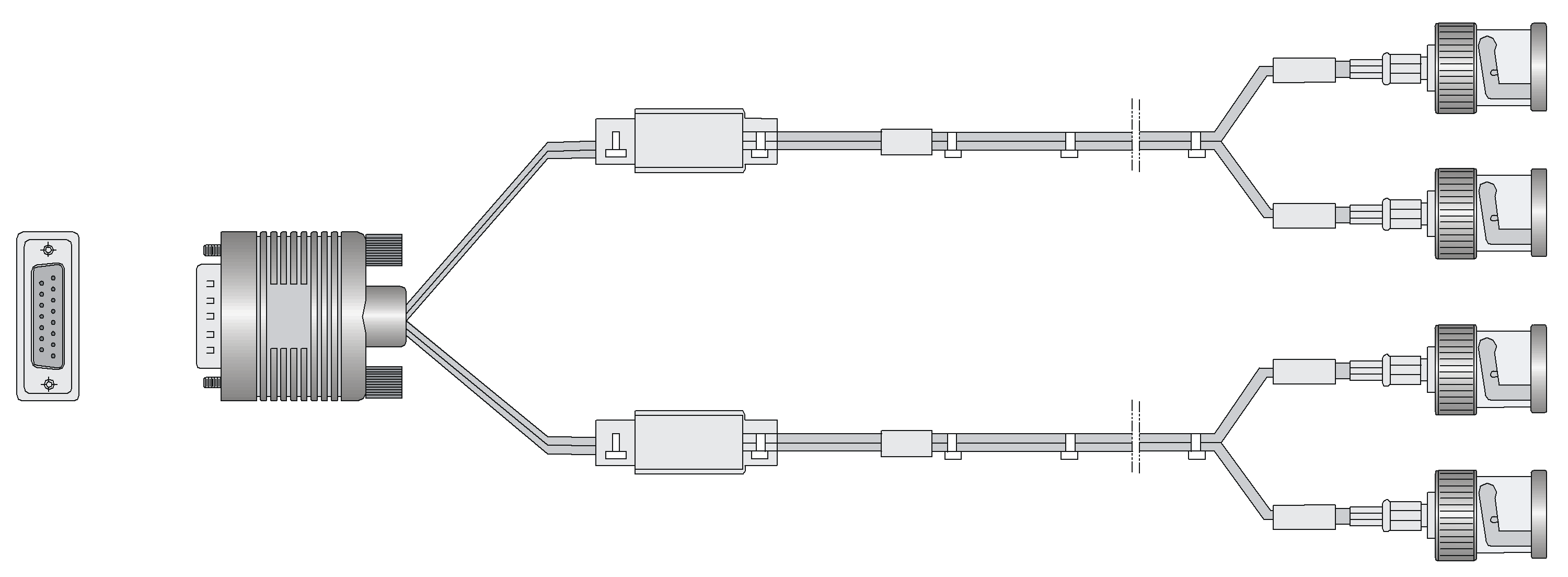
SIC-2E1-F
Introduction
The 2-port fractional E1 interface module (SIC-2E1-F), where F indicates fractional, supports:
· Transmission/Receiving and handling of E1 data streams
· CE1 (channelized E1) access
· Remote loopback and local loopback functions, facilitating fault test and location
Interface specifications
Table 18 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
D15 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703 · G.704 |
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
75-ohm unbalanced coaxial cable (D15 to BNC) |
|
Operating modes |
· E1 · CE1 |
|
Supported services |
· Backup · Terminal access |
Interface LEDs
Figure 12 SIC-2E1-F panel
Table 19 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT (left) |
· On: A carrier signal is received on line RX1. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted on line TX1 or received on line RX1. · Off: No carrier signal is received on line RX1. |
|
LP/AL (left) |
· On: The interface of lines TX1 and RX1 is in loopback mode. · Flashing: No cable is connected to the interface of lines TX1 and RX1, the cable is damaged or not connected correctly, or the peer device is faulty. · Off: Neither loopback nor alarm is present on the interface of lines TX1 and RX1. |
|
LINK/ACT (right) |
· On: A carrier signal is received on line RX2. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted on line TX2 or received on line RX2. · Off: No carrier signal is received on line RX2. |
|
LP/AL (right) |
· On: The interface of lines TX2 and RX2 is in loopback mode. · Flashing: No cable is connected to the interface of lines TX2 and RX2, the cable is damaged or not connected correctly, or the peer device is faulty. · Off: Neither loopback nor alarm is present on the interface of lines TX2 and RX2. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connections methods, see "E1 interface."
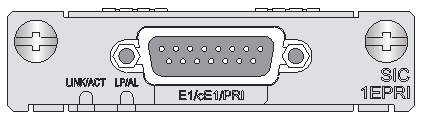
SIC-1EPRI
Introduction
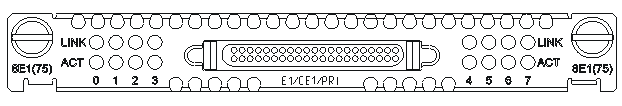
The SIC-1EPRI is a 1-port E1/CE1/PRI SIC interface module that provides the following features:
· Transmission/Receiving and handling of E1 data streams.
· CE1 (channelized E1) access.
· ISDN PRI function.
· Remote loopback and local loopback functions, facilitating fault test and location.
You can use the module for multiple purposes through different configurations.
Interface specifications
Table 20 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
D15 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703 · G.704 |
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
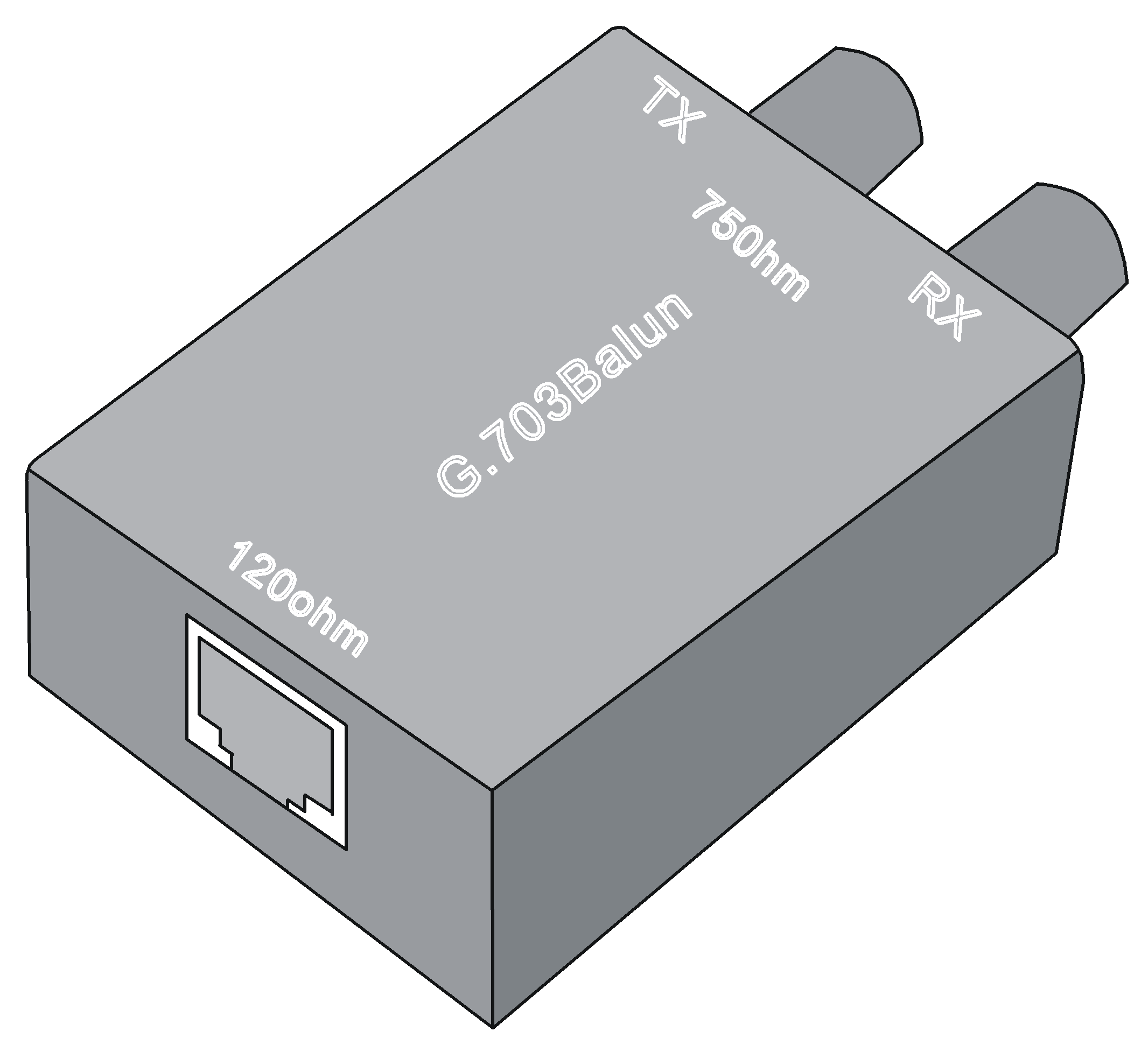
· 75-ohm unbalanced coaxial cable (D15 to BNC) · Coaxial connector, network interface connector, and 75-ohm to 120-ohm adapter NOTE: The default resister for the interface on the SIC-1EPRI is 75 ohm. A 75-ohm to 120-ohm adapter must be used when a 120-ohm cable is connected to the SIC-1EPRI. |
|
Operating mode |
· E1 · CE1 · ISDN PRI |
|
Supported service |
· Backup · Terminal access · ISDN |
Interface LEDs
Figure 13 SIC-1EPRI panel
Table 21 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted or received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Flashing: No cable is connected to the interface, the cable is damaged or not connected correctly, or the peer device is faulty. · Off: Neither loopback nor alarm is present. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connections methods, see "E1 interface."
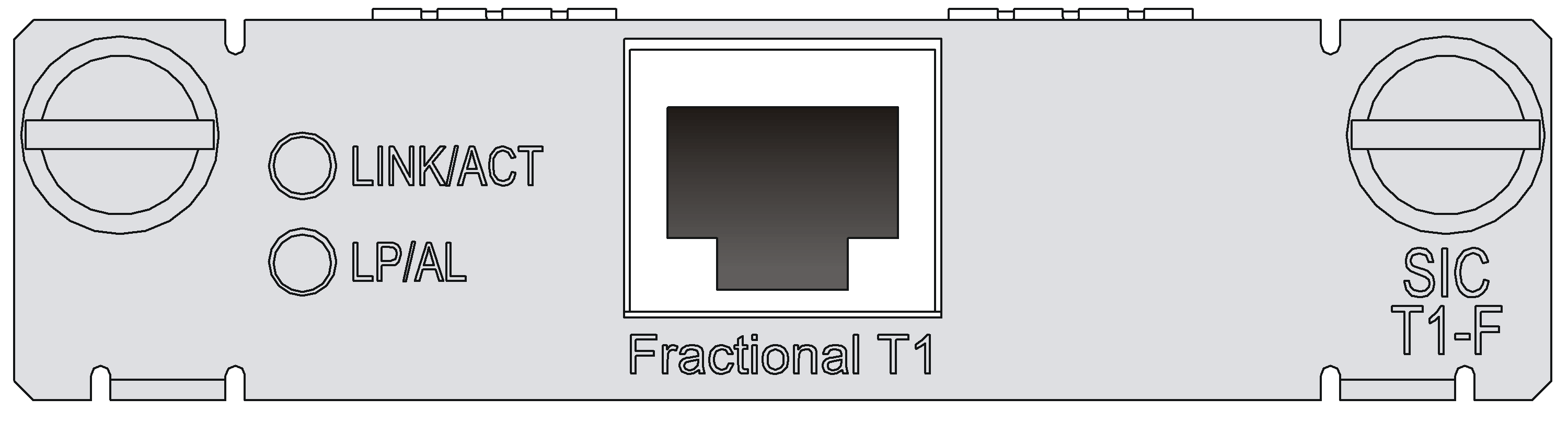
SIC-T1-F
Introduction
1-port Fractional T1 interface card (SIC-T1-F) has the following features:
· The timeslots on an interface in FT1 mode on the SIC-T1-F can be bundled to form one interface (namely, can be bundled into one channel, and the rate of the interface is n No 56 Kbps, where n ranges from 1 to 24.).
· The SIC-T1-F does not support the PRI mode.
Interface specifications
Table 22 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703/T1.102 · G.704 · AT&T TR 54016 · AT&T TR 62411 · ANSI T1.403 |
|
Interface rate |
1.544 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
T1 cable (100-ohm standard shielded network cable) |
|
Operating mode |
FT1 |
|
Supported service |
· Backup · Terminal access |
Interface LEDs
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted or/and received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: No cable is connected to the interface, the cable is damaged or not connected correctly, or the peer device is faulty. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about T1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "T1 interface."
Serial interface modules
· SIC-8AS
· SIC-16AS
· SIC-1SAE
· SIC-2SAE
· SIC-4SAE
· SIC-4RS
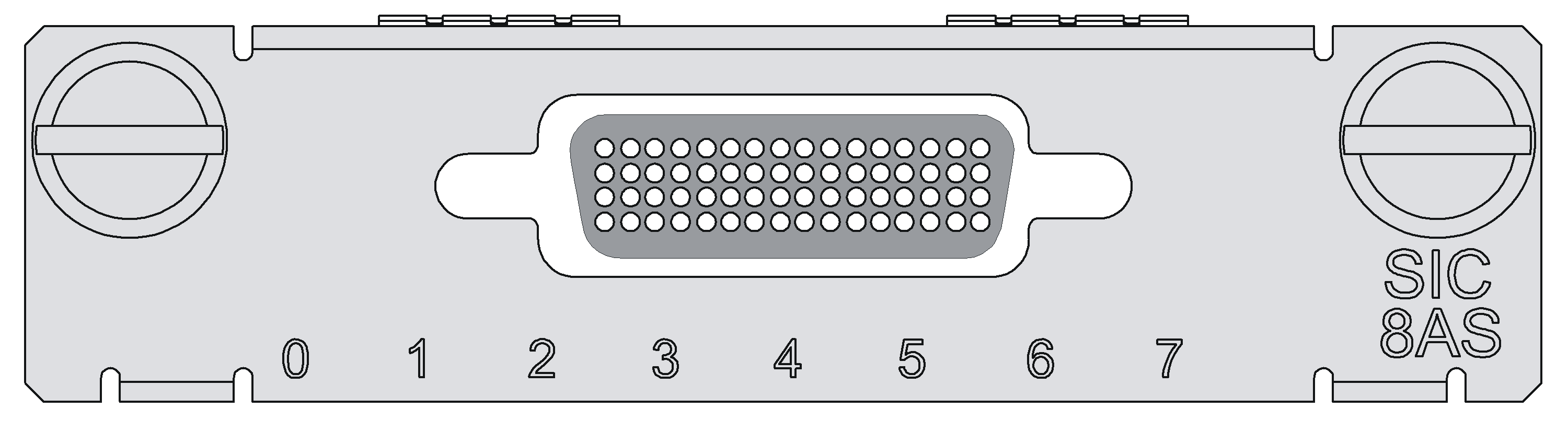
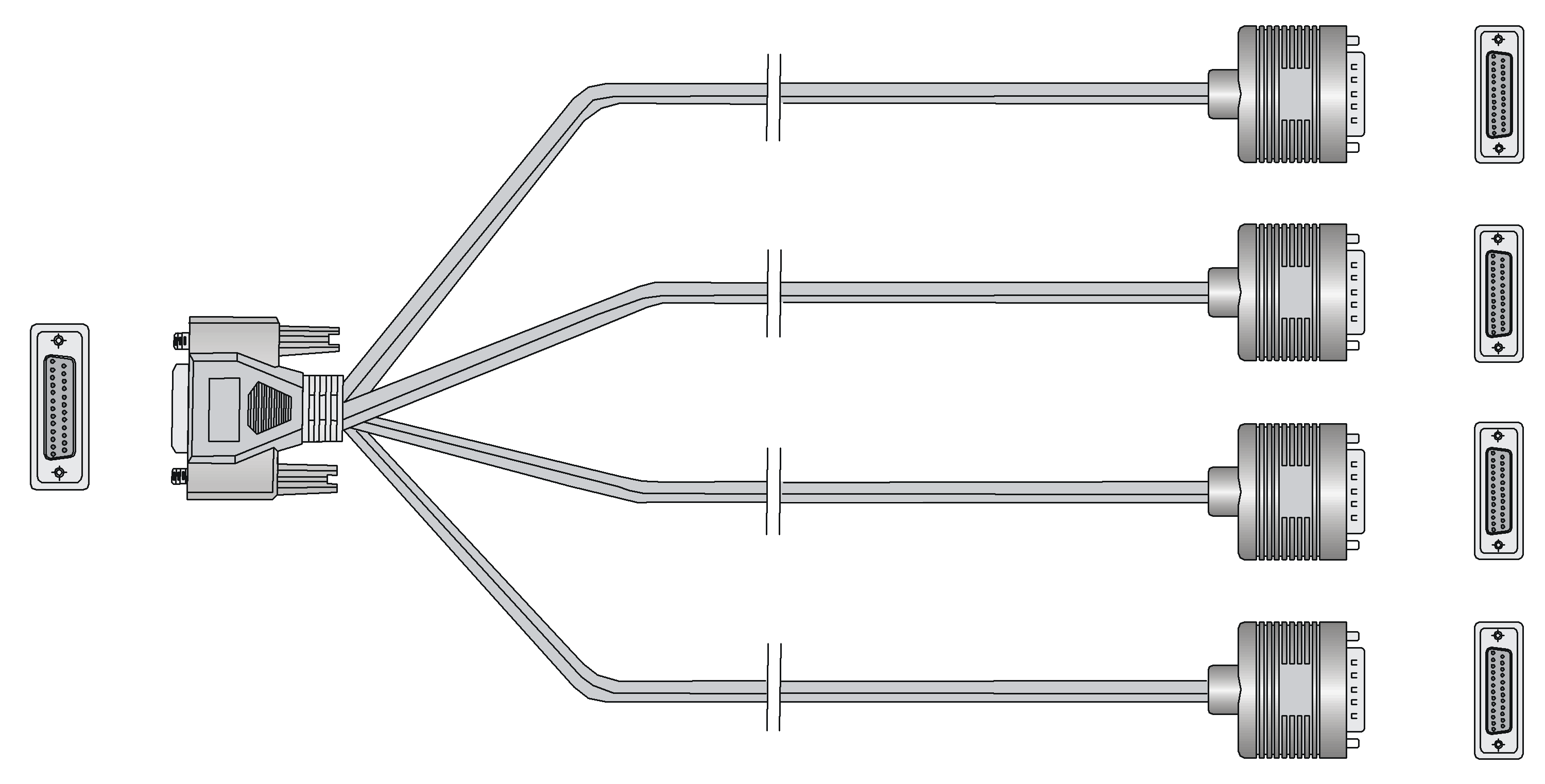
SIC-8AS
Introduction
The 8-port asynchronous serial interface module (SIC-8AS) mainly transmits and processes asynchronous data streams.
SIC-8AS has these features:
· Each asynchronous serial port provides a rate up to 115.2 Kbps.
· Supports the terminal access service and asynchronous dedicated line.
· Serves as the small-/medium-sized ISP dial-up access server when an asynchronous serial port is used for dial-up.
Interface specifications
Table 24 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
DB60 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Interface cable |
Customized cable with 8-port RJ-45 connector |
|
Interface standard |
RS-232 |
|
Minimum baud rate |
300 bps |
|
Maximum baud rate |
115.2 Kbps |
|
Supported services |
· Modem dial-up · Backup · Terminal access service · Asynchronous dedicated line |
Interface LEDs
Figure 15 SIC-8AS front panel
Table 25 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
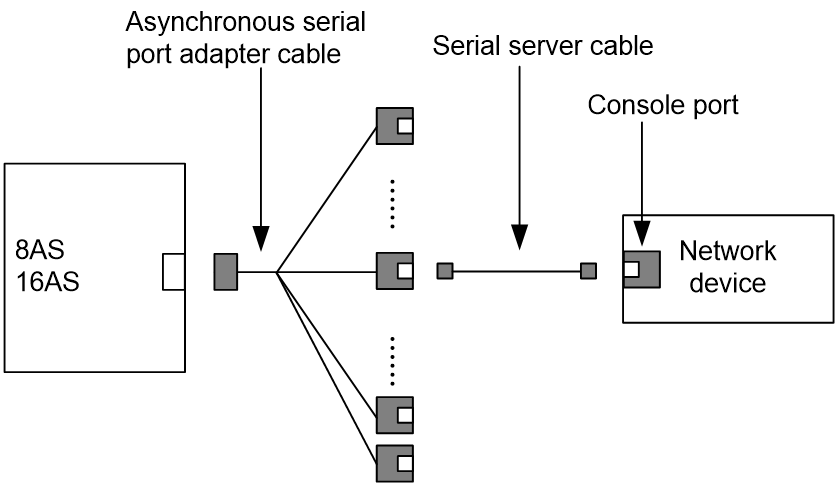
For more information about asynchronous serial port cables and the connection methods, see "Asynchronous serial ports."
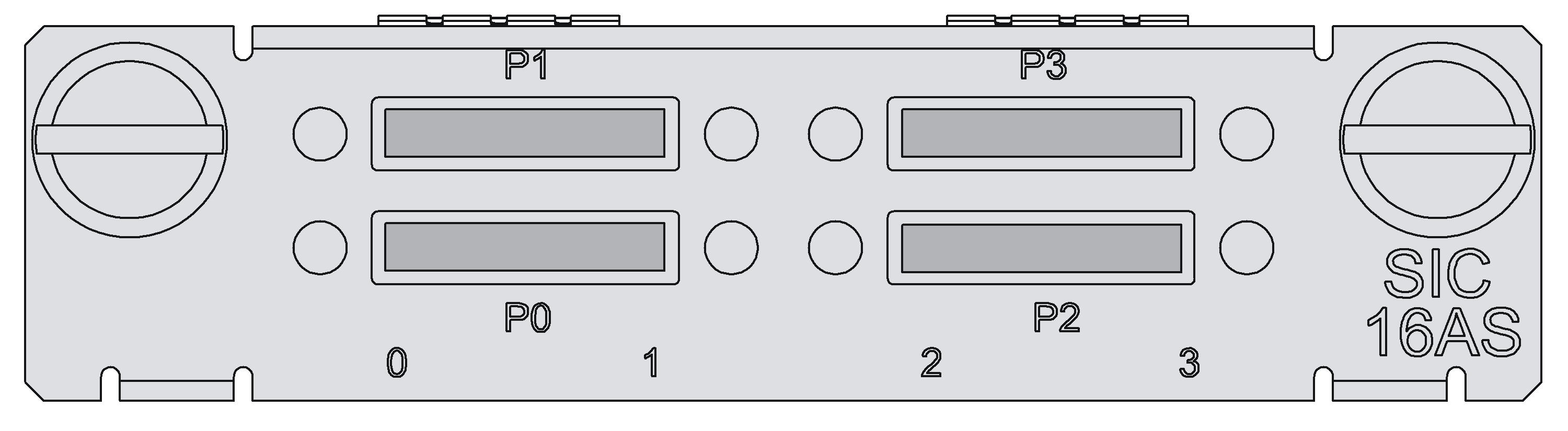
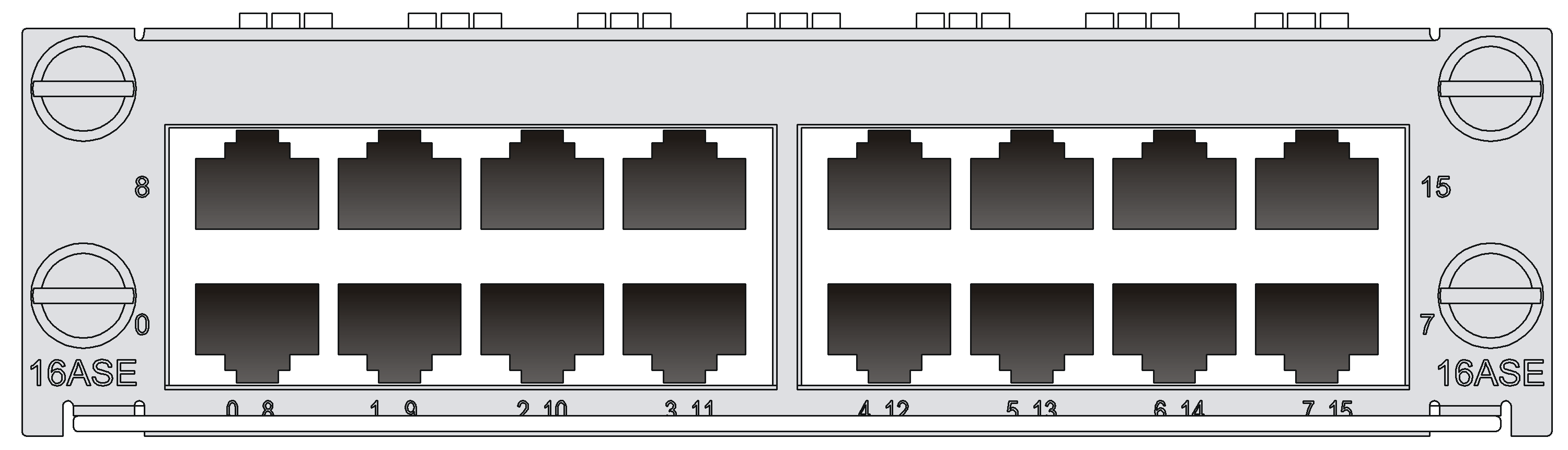
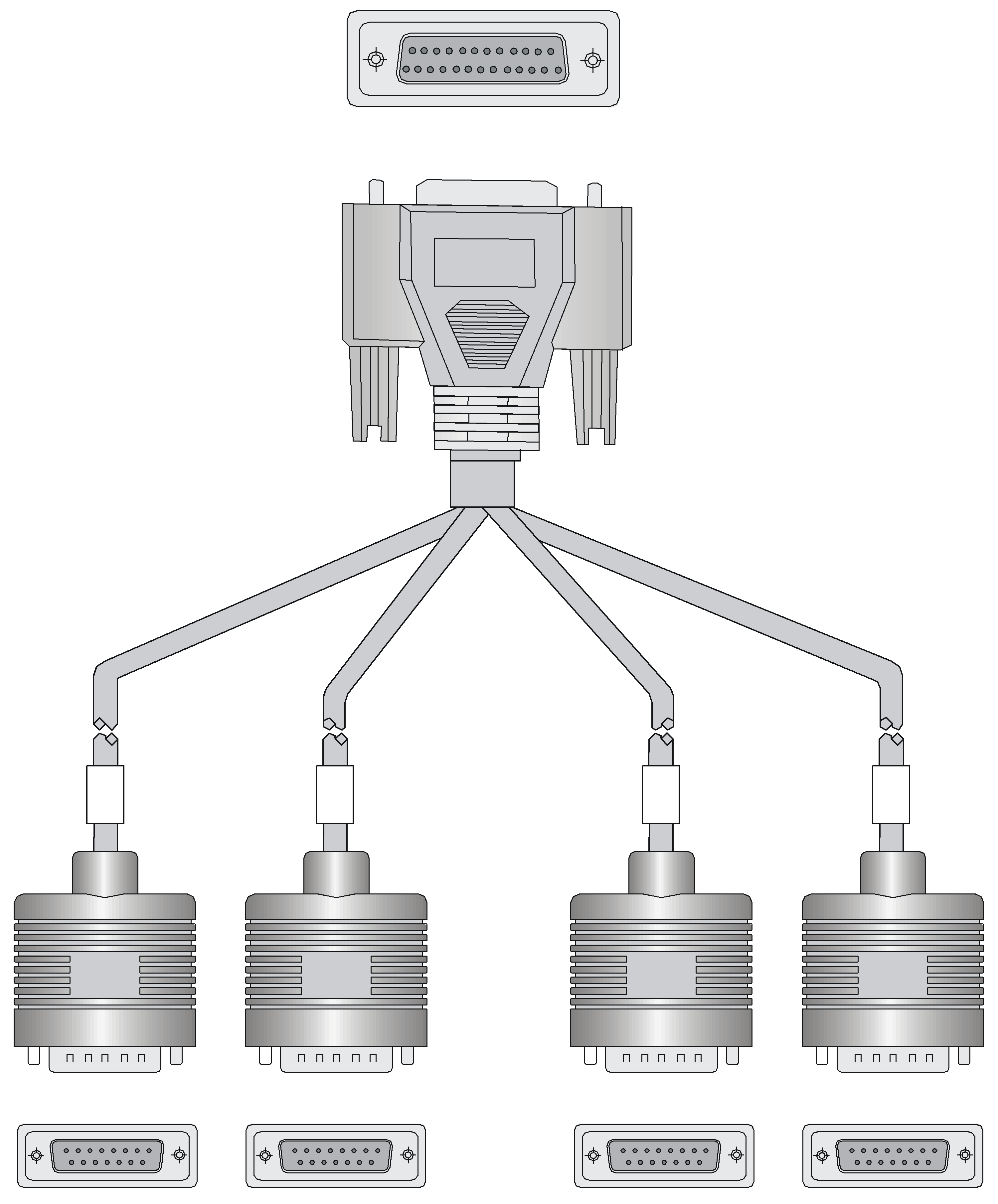
SIC-16AS
Introduction
The 16-port asynchronous serial interface module (SIC-16AS) mainly transmits and processes asynchronous data streams.
SIC-16AS features the following:
· Each asynchronous serial port provides a rate of up to 115.2 Kbps.
· Supports the terminal access service and asynchronous dedicated line.
· Serves as the small-/medium-sized ISP dial-up access server when an asynchronous serial port is used for dial-up.
Interface specifications
Table 26 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
D28 (male) |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Interface cable |
Customized cable with 16-port RJ-45 connector (female) |
|
Interface standard |
RS-232 |
|
Minimum baud rate |
300 bps |
|
Maximum baud rate |
115.2 Kbps |
|
Supported services |
· Modem dial-up · Backup · Terminal access service · Asynchronous dedicated line |
Interface LEDs
Figure 16 SIC-16AS panel
Table 27 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about asynchronous serial port cables and the connection methods, see "Asynchronous serial ports."
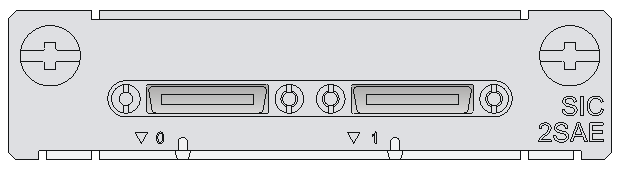
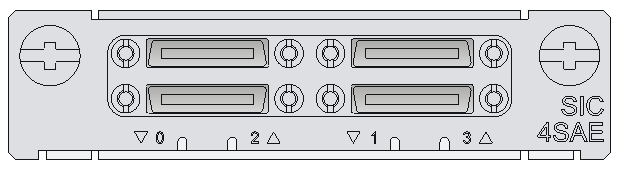
SIC-1SAE/SIC-2SAE/SIC-4SAE
Introduction
The SIC-1SAE/SIC-2SAE/SIC-4SAE is a 1-port/2-port/4-port enhanced high-speed synchronous/asynchronous serial interface module.
Interface specifications
Table 28 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Synchronous |
Asynchronous |
|
|
Connector |
D28 |
||
|
Number of connectors |
· 1 (SIC-1SAE) · 2 (SIC-2SAE) · 4 (SIC-4SAE) |
||
|
Interface standard and operating mode |
V.24 |
· V.35 · RS449 · X.21 · RS-530 |
RS-232 |
|
· DTE · DCE |
· DTE · DCE |
||
|
Minimum baud rate (bps) |
1200 |
1200 |
300 |
|
Maximum baud rate (bps) |
64 k |
2.048 M |
115.2 |
|
Cable |
· V.24 (RS-232) DTE cable · V.24 (RS-232) DCE cable · V.35 DTE cable · V.35 DCE cable · X.21 DTE cable · X.21 DCE cable · RS449 DTE cable · RS449 DCE cable · RS530 DTE cable · RS530 DCE cable |
||
|
Supported service |
· DDN leased line · Terminal access service |
· Dialup through modems · Backup · Asynchronous leased line · Terminal access |
|
Interface LEDs
Figure 18 SIC-2SAE panel
Figure 19 SIC-4SAE panel
The SIC-1SAE provides separate LINK and ACT LEDs for the port and the SIC-2SAE and SIC-4SAE provide one LINK/ACT LED for each port.
Table 29 LED description for the port on the SIC-1SAE
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received; · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Table 30 LED description for ports on the SIC-2SAE/SIC-4SAE
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
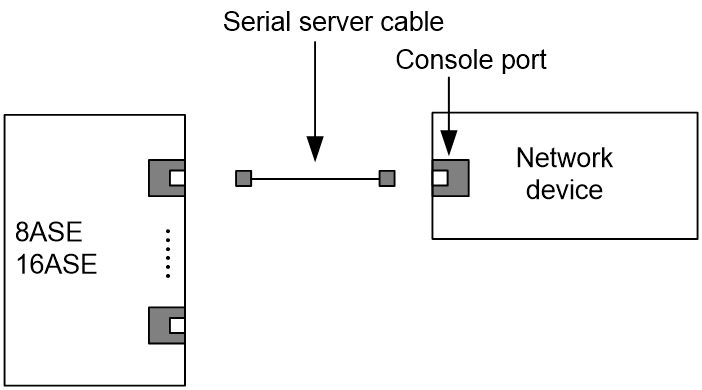
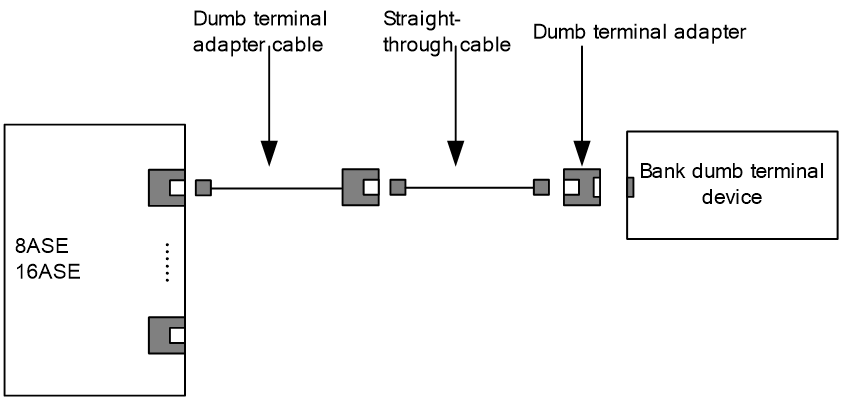
For more information about synchronous/asynchronous serial port cables and the connection methods, see "Synchronous/asynchronous serial ports."
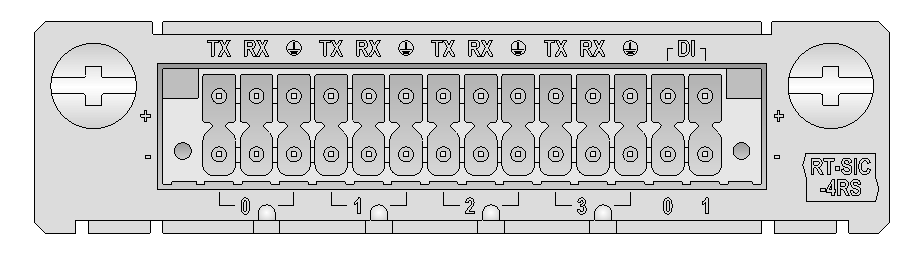
SIC-4RS
Introduction
The SIC-4RS is a 4-port asynchronous serial interface module.
The SIC-4RS has these features:
· Allows users to make matching wires connected to the terminal block themselves.
· Supports simultaneous connection to four asynchronous serial ports.
Interface specifications
Table 31 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
Terminal block |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Interface cable |
Allows users to make matching cables themselves. |
|
Interface standard and operating mode |
RS-232/485/422 |
|
Minimum baud rate (bps) |
300 |
|
Maximum baud rate (bps) |
115200 |
|
Supported service |
· 4 asynchronous serial port connection · 2-channel digital input (DI) detection |
Interface LEDs
Figure 20 SIC-4RS panel
Table 32 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
0 to 3 |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
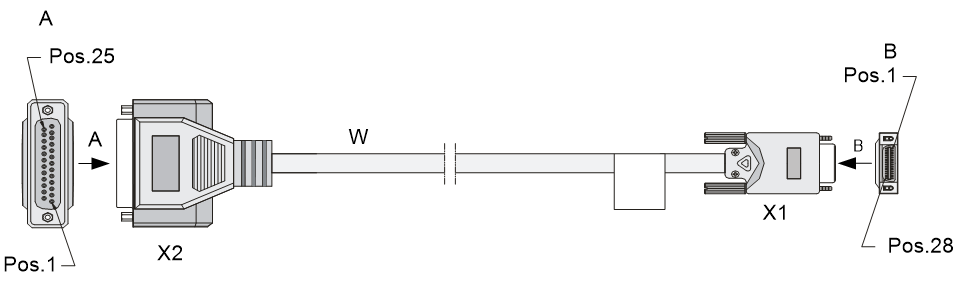
The SIC-4RS interface module allows users to make matching cables themselves for connection to it. Figure 21 and Table 33 describe the requirements for making matching cables.
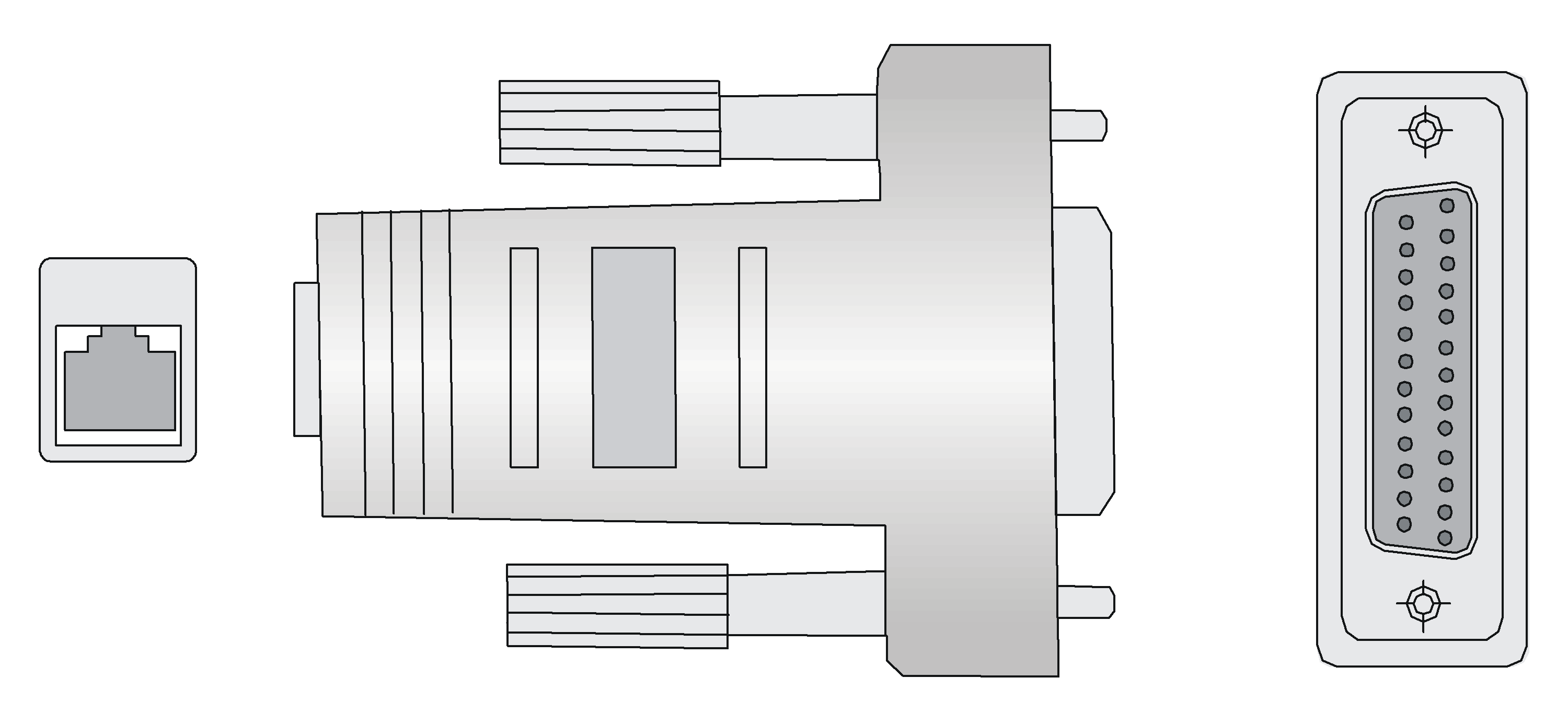
Figure 21 Pin numbering
|
Pin |
Interface standards and working modes |
||
|
RS-232 |
RS-422 |
RS-485 |
|
|
RTS0 |
TX0+ |
Data0+ |
|
|
2 |
TXD0 |
TX0- |
Data0- |
|
3 |
RXD0 |
RX0+ |
|
|
4 |
CTS0 |
RX0- |
|
|
5 |
GND |
||
|
6 |
GND |
||
|
7 |
RTS1 |
TX1+ |
Data1+ |
|
8 |
TXD1 |
TX1- |
Data1- |
|
9 |
RXD1 |
RX1+ |
|
|
10 |
CTS1 |
RX1- |
|
|
11 |
GND |
||
|
12 |
GND |
||
|
13 |
RTS2 |
TX2+ |
Data2+ |
|
TXD2 |
TX2- |
Data2- |
|
|
15 |
RXD2 |
RX2+ |
|
|
16 |
CTS2 |
RX2- |
|
|
17 |
GND |
||
|
18 |
GND |
||
|
19 |
RTS3 |
TX3+ |
Data3+ |
|
20 |
TXD3 |
TX3- |
Data3- |
|
21 |
RXD3 |
RX3+ |
|
|
22 |
CTS3 |
RX3- |
|
|
23 |
GND |
||
|
24 |
GND |
||
|
25 |
DN0_P |
||
|
26 |
DN0_N |
||
|
27 |
DN1_P |
||
|
28 |
DN1_N |
||
Analog modem interface modules
· SIC-1AM
· SIC-2AM
SIC-1AM/SIC-2AM
Introduction
The 1/2-port analog modem interface module (SIC-1AM/SIC-2AM) integrates the functions of asynchronous interface and external modem, that is, allowing 1/2 channel(s) of remote modem subscribers to directly access the Router. They support:
· Data rate of 56 kbps.
· Accessing and handling analog signals and transmitting the processed data to the Router host through the serial interface bus. And also, processing the data received from the host and then transmitting them to the PSTN via the telephone port.
Interface specifications
Table 34 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-11 |
|
Number of connectors |
· 1 (SIC-1AM) · 2 (SIC-2AM) |
|
Cable type |
Telephone cable with ferrite core |
|
Maximum speed |
56 kbps |
|
Supported standard |
· ITU-T V.90 · K56flex · V.34 (33.6 kbps) · V.FC · V.32 bis · V.32 · V.22 bis · V.22A/B · V.23 · V.21 · Bell 212A a · Bell 103 |
|
Supported service |
Modem dial-up |
Interface LEDs
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: The link is idle. · On: The connection has been established. · Flashing: The connection is being set up. |
|
ACT |
· Off: The link is idle. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted or received. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about the Ethernet interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
XDSL interface modules
· SIC-1ADSL
· SIC-1ADSL-I
SIC-1ADSL
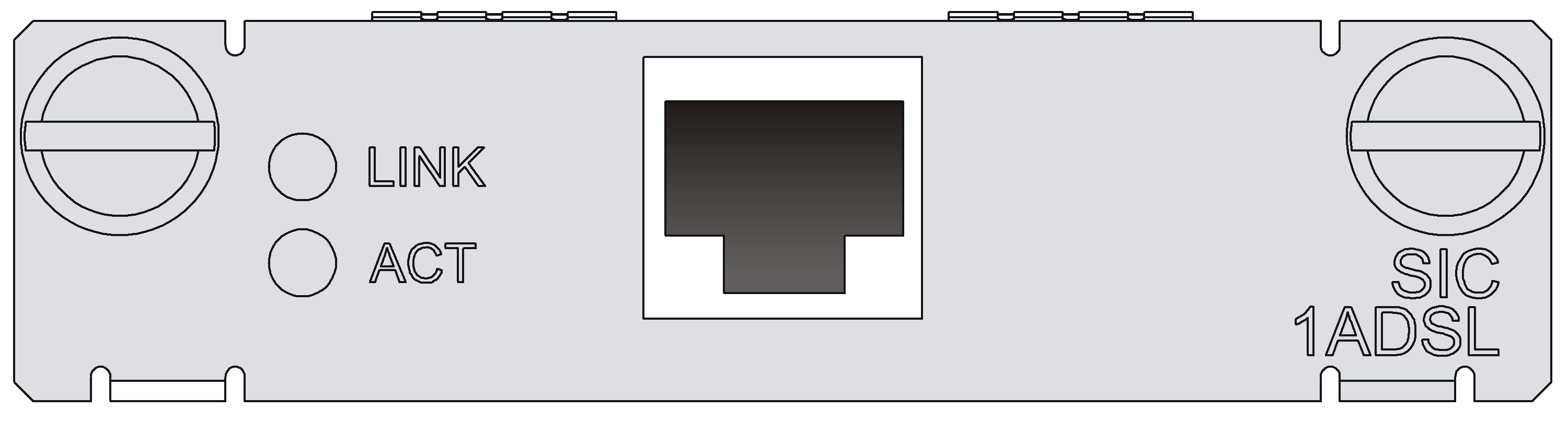
Introduction
The 1-port ADSL over PSTN interface module (SIC-1ADSL) provides an RJ-11 interface that can work as a WAN interface. It allows a LAN subscriber to connect to the digital subscriber's loop access multiplexer (DSLAM) at the central office over a regular analog subscriber line or telephone line. Thus, the subscriber can access the ATM/IP backbone or the Internet to enjoy services such as high-speed data communication and video on demand (VoD).
ADSL transmits data in the high frequency band above 26 kHz. Therefore, it can provide services without interfering with the voice service being provided in the low frequency band (0 to 4 kHz) on the same line. It provides downlink rates in the range 32 kbps to 8 Mbps and uplink rates in the range 32 kbps to 1 Mbps.
The SIC-1ADSL delivers these features:
· Manual ADSL line activation and deactivation, providing a convenient fault location means.
· Interface standards of G. DMT, G. Lite, and T1.413, autosensing.
· Trellis coding (except for G. Lite) on ADSL interfaces, enhancing the stability of ADSL connection.
Interface specifications
Table 36 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-11 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Interface rate |
· In ADSL full rate mode (ITU-T 992.1 G.DMT/ANSI T1.413): ¡ 8 Mbps (downlink rate) ¡ 1024 kbps (uplink rate) · In ADSL Lite mode (ITU-T 992.2 G.Lite): ¡ 64 kbps to 1 Mbps (downlink rate) ¡ 64 kbps to 512 kbps (uplink rate) · In ADSL2+ full rate mode (ITU-T 992.5): ¡ 24 Mbps (downlink rate) ¡ 1024 kbps (uplink rate) |
|
Interface standard |
· ITU-T 992.1 G.DMT · ITU-T 992.2 G.Lite · ANSI T1.413 Issue 2 · ITU-T 992.3 · ITU-T 992.5 |
|
Cable |
Telephone cable |
|
Supported service |
ADSL over the regular telephone line |
|
Maximum received and sent frame |
1700 bytes |
Interface LEDs
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: The loop is inactive. · On: The loop has been activated and has entered the data mode · Flashing: The loop is being activated. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about ADSL interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
SIC-1ADSL-I
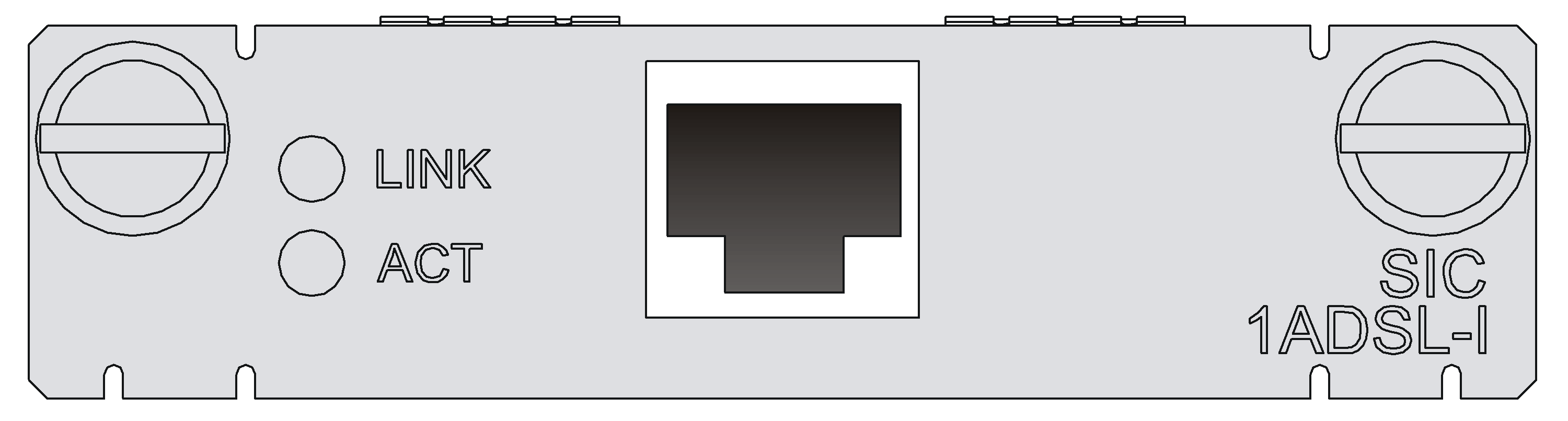
Introduction
The 1-port ADSL over ISDN interface module (SIC-1ADSL-I) uses the RJ-11 connector for the WAN interface. It allows a LAN subscriber to connect to the DSLAM at the central office over a regular analog subscriber line or telephone line. Thus, the subscriber can access the ATM/IP backbone or the Internet to enjoy services such as high-speed data communication and video on demand (VoD).
The module transmits data in the high frequency band above 138 kHz. Therefore, it can provide services on the same line without interfering with the ISDN service being provided on the same line. It provides downlink rates in the range 32 kbps to 8 Mbps and uplink rates in the range 32 kbps to 1 Mbps.
The SIC-1ADSL-I interface module delivers these features:
· Manual ADSL line activation and deactivation, providing a convenient fault location means
· A G.992.1-compliant interface, autosensing
· Trellis coding on ADSL interfaces, enhancing the stability of ADSL connection
Interface specifications
Table 38 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-11 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Interface rate |
· In ADSL full rate mode (ITU-T 992.1 G.DMT/ANSI T1.413): ¡ 8 Mbps (downlink rate) ¡ 1024 kbps (uplink rate) · In ADSL Lite mode (ITU-T 992.2 G.Lite): ¡ 64 kbps to 1 Mbps (downlink rate) ¡ 64 kbps to 512 kbps (uplink rate) · In ADSL2+ full rate mode (ITU-T 992.5): ¡ 24 Mbps (downlink rate) ¡ 1024 kbps (uplink rate) |
|
Interface standard |
· ITU-T 992.1 G.DMT · ITU-T 992.2 G.Lite · ANSI T1.413 Issue 2 · ITU-T 992.3 · ITU-T 992.5 |
|
Interface rate |
· Downlink: 8 Mbps · Uplink: 1024 kbps |
|
Interface cable |
Regular telephone cable |
|
Supported services |
ADSL over ISDN |
|
Maximum received and sent frame |
1700 bytes |
Interface LEDs
Figure 25 SIC-1ADSL-I panel
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: No link is present; · On: A link is present. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about ADSL interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
ISDN BRI interface modules
· SIC-1BS
· SIC-2BS
SIC-1BS/SIC-2BS
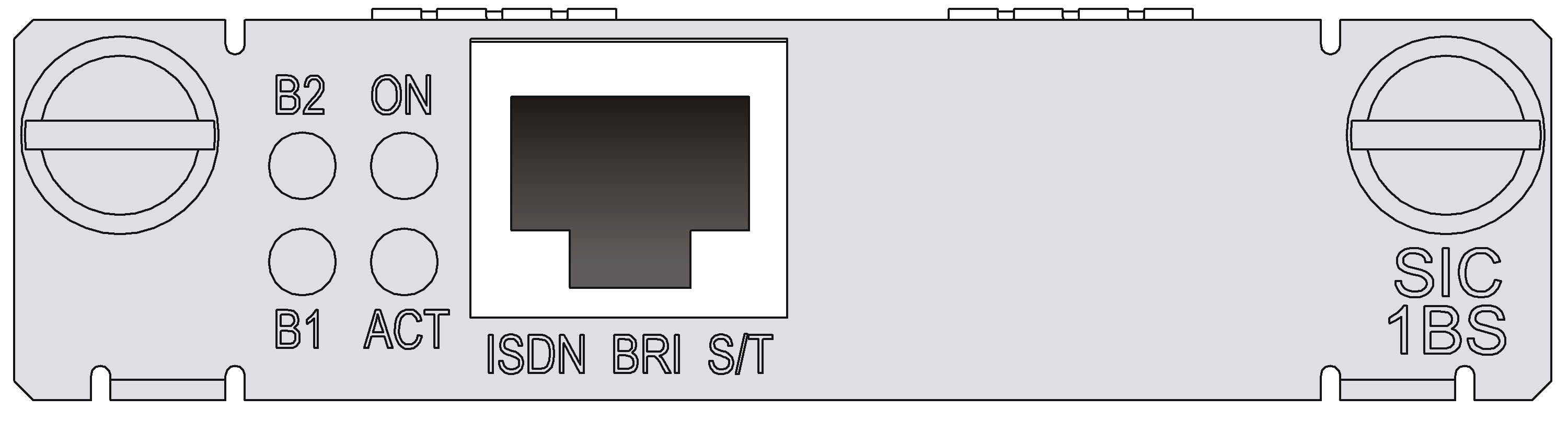
Introduction
The 1/2-port ISDN BRI S/T interface module (SIC-1BS/SIC-2BS) is mainly used to transmit, receive, and process ISDN BRI S/T traffic flows.
The SIC-1BS/SIC-2BS has two operating modes: dial-up and leased line.
Interface specifications
Table 40 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
· 1 (SIC-1BS) · 2 (SIC-2BS) |
|
Cable type |
Telephone cable with ferrite core |
|
Interface standard |
· ITU-T I.430 · Q.921 · Q.931 |
|
Operating mode |
· ISDN Dial-up · ISDN leased line |
|
Supported services |
· ISDN · ISDN supplementary services · Multi-subscriber number · Sub-address · Backup |
Interface LEDs
Figure 26 SIC-1BS panel
Table 41 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
B1 |
· Off indicates the B1 channel is idle. · Flashing indicates the B1 channel is being used for data communication. |
|
B2 |
· Off indicates the B2 channel is idle. · Flashing indicates the B1 channel is being used for data communication. |
|
ACT |
· Off indicates the inactive state. · Steady on indicates the active state. |
|
ON |
· Off indicates interface module is powered off. · On indicates the interface module is powered on. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about BS interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
Voice interface modules
· SIC-1FXS
· SIC-1FXO
· SIC-2FXS
· SIC-2FXO
· SIC-2FXS1FXO
· DSIC-4FXS1FXO
· SIC-1BSV
· SIC-2BSV
· SIC-1VE1
· SIC-1VT1
· SIC-1VE1T1
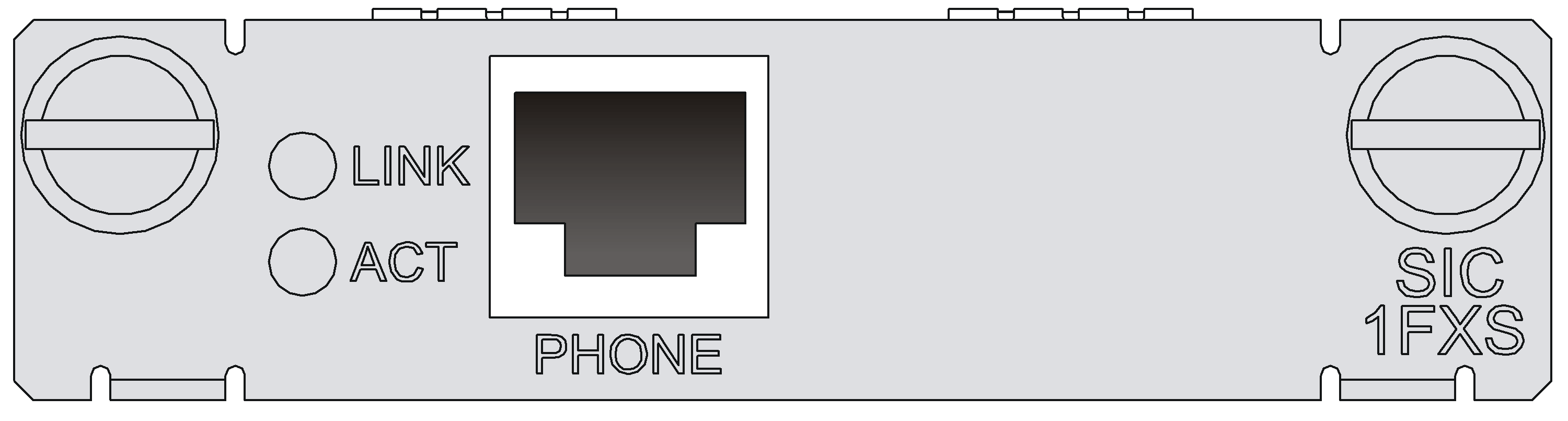
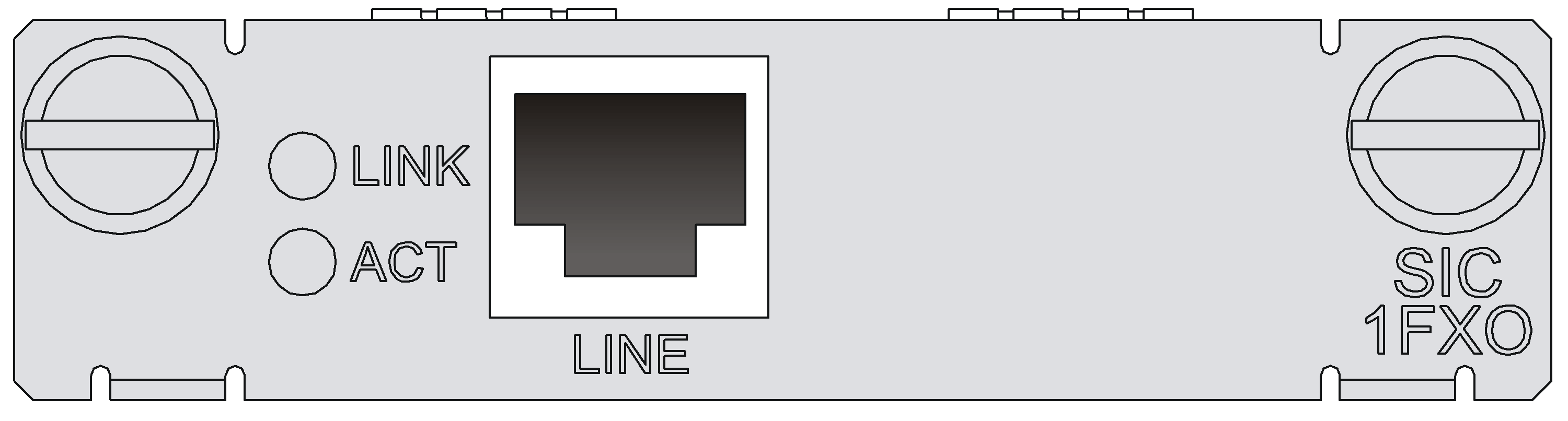
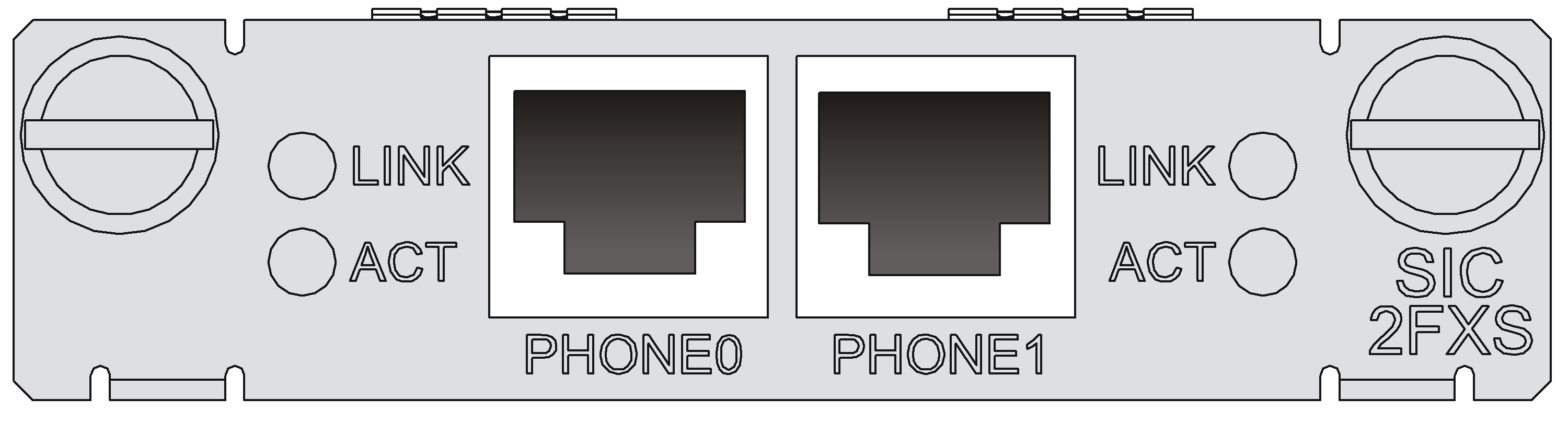
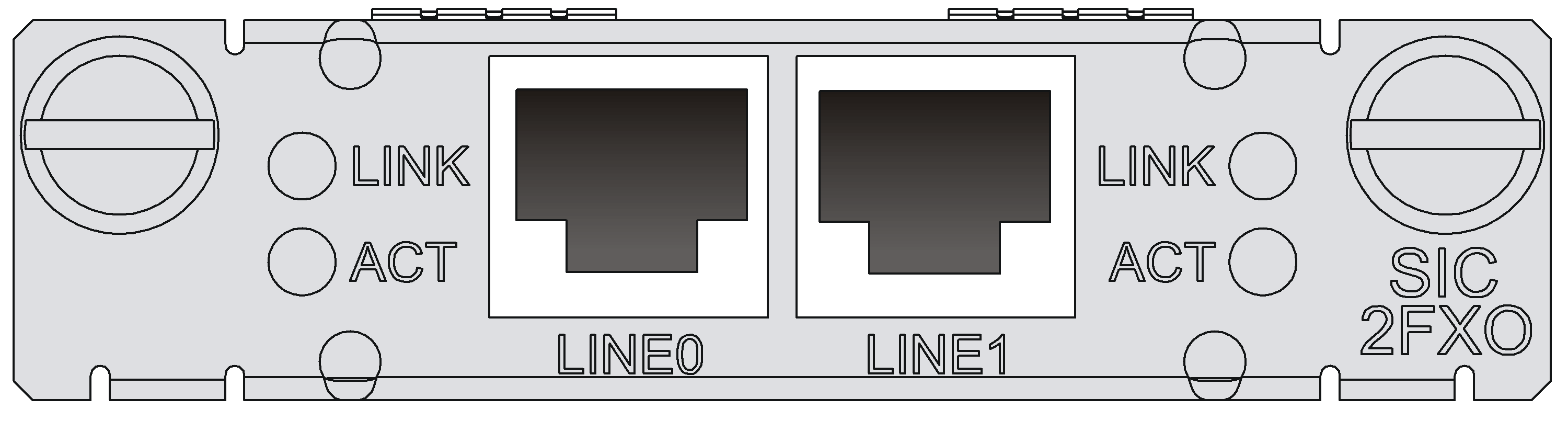
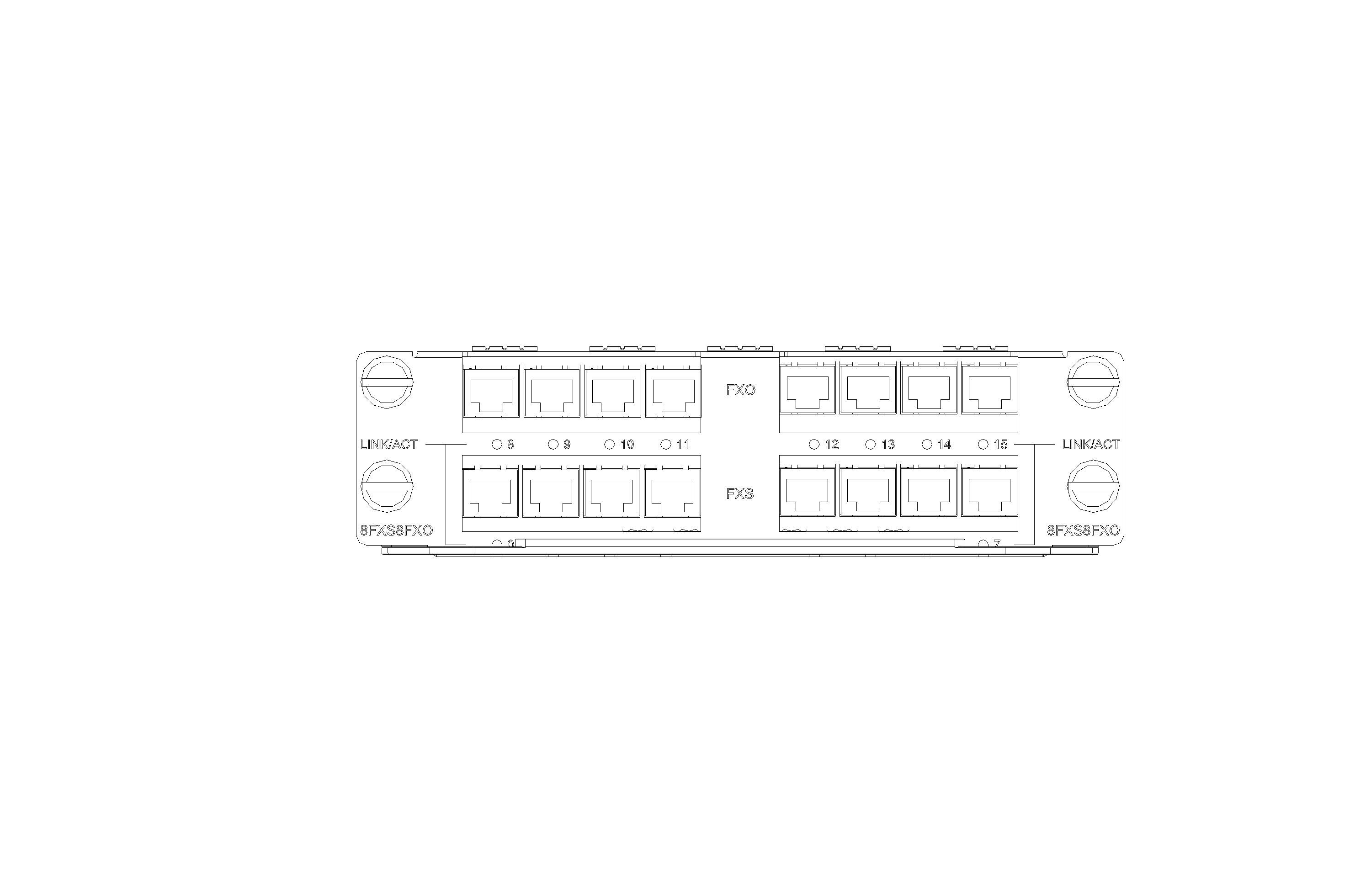
SIC-1FXS/SIC-1FXO/SIC-2FXS/SIC-2FXO
Introduction
The 1/2-port voice subscriber circuit interface module (SIC-1FXS/SIC-2FXS) and 1/2-port voice AT0 analog trunk interface module (SIC-1FXO/SIC-2FXO) serve to access and handle 1/2 channel(s) of analog voice signals over data communication networks. The differences between SIC-FXS and SIC-FXO are listed below:
· SIC-FXS modules are analog subscriber line modules that provide ordinary analog telephone and fax access and also can connect AT0 loop trunks of exchanges.
· SIC-FXO modules are loop trunk modules that provide access of common subscriber lines of exchanges.
Interface specifications
Table 42 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-11 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 (SIC-1FXS/SIC-1FXO) 2 (SIC-2FXS/SIC-2FXO) |
|
Interface standard |
· Subscriber circuit interface (SIC-1FXS/SIC-2FXS) compliant with ITU Q.512. · Loop trunk interface (SIC-1FXO/SIC-2FXO) compliant with ITU Q.552. · Over-current and over-voltage protection compliant with ITU K.20 |
|
Cable type |
Telephone cable with ferrite core. |
|
Dialing mode |
Supports DTMF, not supports pulse dial-up. |
|
Bandwidth |
300 Hz to 3400 Hz |
Interface LEDs
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: The link is idle. · On: The link is being occupied for call connection. |
|
ACT |
· Off: The link is idle. · On: The link is being occupied for communication. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about FXS/FXO interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
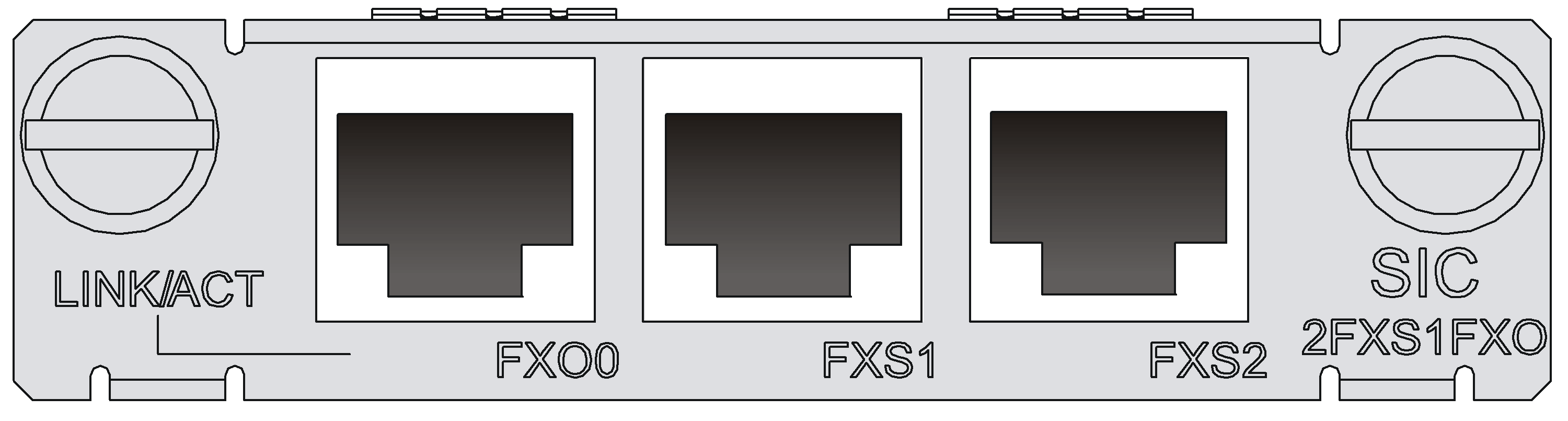
SIC-2FXS1FXO
Introduction
The 2-port analog subscriber circuit interface module and 1-port voice AT0 loop trunk interface module (SIC-2FXS1FXO) serve to access and handle three channels of analog voice signals over data communication networks. Two FXS interfaces and one FXO interface are available on a SIC-2FXS1FXO module:
· FXS interfaces are analog subscriber line interfaces that provide ordinary analog telephone and fax access and also can connect AT0 loop trunks of exchanges.
· FXO interfaces are loop trunk interfaces that provide access of common subscriber lines of exchanges.
Interface specifications
Table 44 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-11 |
|
Number of connectors |
2 FXS interfaces 1 FXO interface |
|
Interface standard |
· Supports subscriber circuit interface (FXS), compliant with ITU Q.512 · Supports loop trunk interface (FXO), compliant with ITU Q.552 · Over-current and over-voltage protection compliant with ITU K.20 |
|
Cable type |
Telephone cable with ferrite core |
|
Dial-up mode |
Supports DTMF, compliant with GB3378, but does not support pulse dial-up. |
|
Bandwidth |
300 Hz to 3400 Hz |
Interface LEDs
Figure 32 SIC-2FXS1FXO panel
Table 45 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Off: The link is idle. · Steady green: The link is being occupied for call connection. · Flashing yellow: The link is being occupied for communication. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about FXS/FXO interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
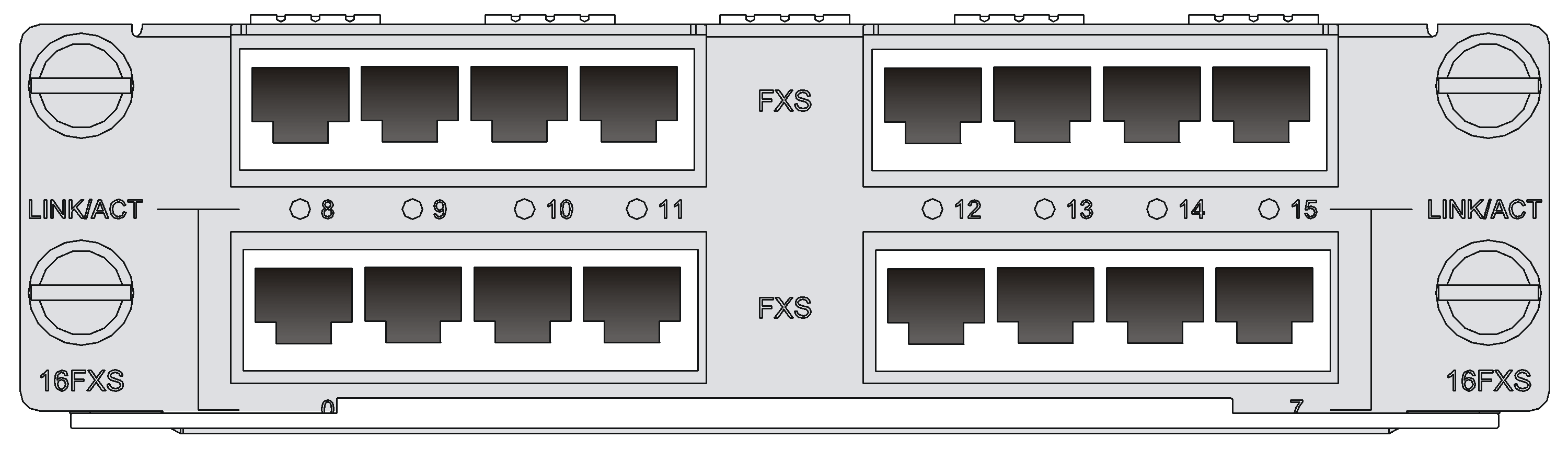
DSIC-4FXS1FXO
Introduction
The 4-port analog subscriber circuit interface module and 1-port voice AT0 loop trunk interface module (DSIC-4FXS1FXO) serve to access and handle five channels of analog voice signals over data communication networks.
· FXS interfaces are analog subscriber line interfaces that provide ordinary analog telephone and fax access and also can connect AT0 loop trunks of exchanges.
· FXO interfaces are loop trunk interfaces that provide access of common subscriber lines of exchanges.
Interface specifications
Table 46 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-11 |
|
Number of connectors |
4 FXS interfaces 1 FXO interface |
|
Interface standard |
· Supports subscriber circuit interface (FXS), compliant with ITU Q.512 · Supports loop trunk interface (FXO), compliant with ITU Q.552 · Over-current and over-voltage protection compliant with ITU K.20 |
|
Cable type |
Telephone cable with ferrite core |
|
Dial-up mode |
Supports DTMF, compliant with GB3378, but does not support pulse dial-up. |
|
Bandwidth |
300 Hz to 3400 Hz |
Interface LEDs
Figure 33 DSIC-4FXS1FXO panel
Table 47 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Off: The link is idle. · Steady green: The link is being occupied for call connection. · Flashing yellow: The link is being occupied for communication. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about FXS/FXO interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
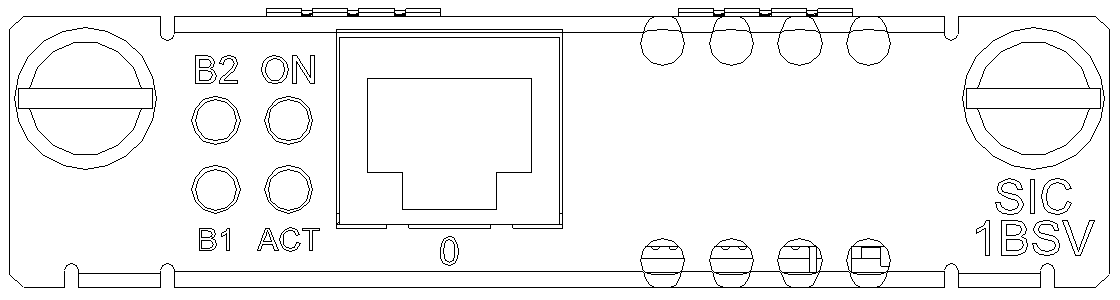
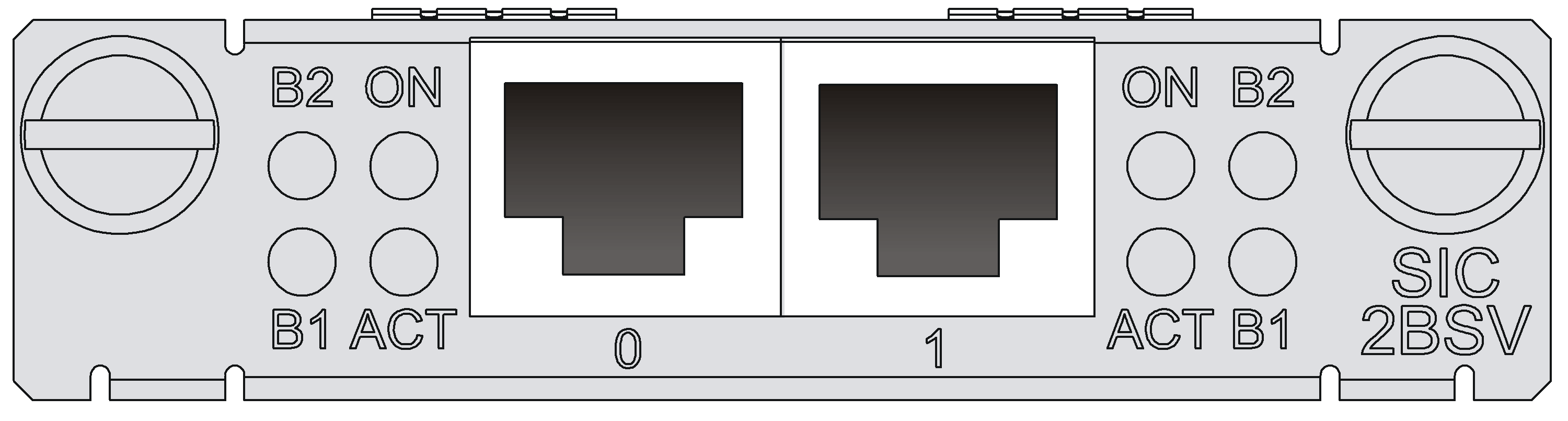
SIC-1BSV/SIC-2BSV
Introduction
The 1/2-port ISDN BRI S/T voice interface module (SIC-1BSV/SIC-2BSV) is mainly used to process (receive/transmit and compress/decompress) the ISDN interface voice traffic. The interface(s) on the SIC-1BSV/SIC-2BSV module is (are) ITU-T I.430-compliant, adopting pseudo-ternary coding, providing 192 Kbps interface rate, and allowing the maximum transmission distance of 1 km (0.6 miles) in point-to-point mode. In the upstream direction, the SIC-1BSV/SIC-2BSV module can be connected to a user interface on an ISDN switch to receive and decompress, compress and transmit ISDN BRI digital voice traffic. In the downstream direction, the module can be connected to a TE device to forward the voice packets from the TE device to the Internet through a WAN interface on the router, thus implementing VoIP. The module has the following features.
· A BSV interface supports two modes: user and network, respectively for connecting an ISDN network and a TE device.
· When a BSV interface works in network mode, traffic is processed as follows: The digital voice traffic received on the BSV interface is compressed and forwarded through the CPU on the main control board to a WAN interface. The IP voice traffic received on a WAN interface is forwarded through the CPU on the main control board to SIC-1BSV/SIC-2BSV, where the traffic is decompressed and sent to the TE device.
· When a BSV interface works in user mode, traffic is processed as follows: The digital voice traffic received from the B channels on the BSV interface is decompressed and forwarded through the CPU on the main control board to a local FXS or FXO analog voice interface. The voice signals received on the local FXS or FXO analog voice interface are processed by VoIP and forwarded through the CPU on the main control board to SIC-1BSV/SIC-2BSV, where the traffic is compressed and sent out of the BSV interface to the ISDN switch.
· Working in conjunction with the FXS or FXO analog voice interface modules, SIC-2BSV provides flexibility in voice call routing.
· The ISDN BRI D channel signaling is processed separately on CPU.
· A BSV interface supports remote power supply and thus can be connected directly to an ISDN phone, saving extra power supply device.
· The SIC-1BSV/SIC-2BSV is dedicated to voice applications, which is different from the BS interface modules where BRI data applications are supported.
Interface specifications
Table 48 Interface specifications
|
Item |
SIC-1BSV |
SIC-2BSV/ |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
2 |
|
Interface standard |
· ITU-T I.430 · Q.921 · Q.931 |
|
|
Interface rate |
192 Kbps |
|
|
Cable |
ISDN S interface cable |
|
|
Supported service |
Voice access over ISDN S interface cable |
|
Interface LEDs
Figure 35 SIC-2BSV panel
|
LED |
Description |
|
B1 |
Green Flashing indicates data is being transmitted or received on B1 channel. |
|
B2 |
Green Flashing indicates data is being transmitted or received on B2 channel. |
|
ACT |
Yellow · Flashing indicates the link is being activated. · Steady on indicates the link is active. |
|
ON |
Green, power LED. Steady on indicates the module is powered on. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about BSV interface cables and the connection methods, see "BSV/BSE interface."
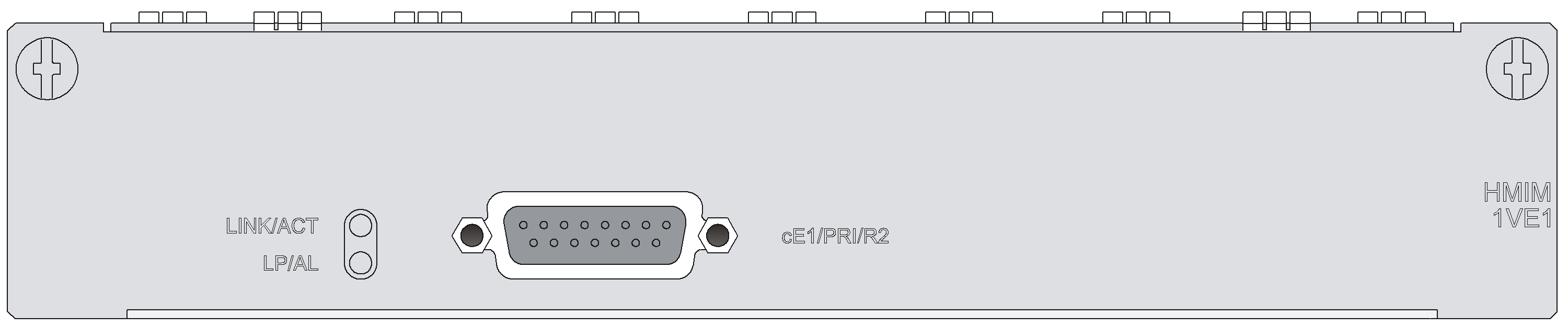
SIC-1VE1
Introduction
The 1-port E1 voice interface module (SIC-1VE1) can handle dense voice signals in VoIP system. It provides a CE1/PRI/R2 port, allowing the access of 30 channels of voice signals.
Interface specifications
Table 50 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
DB 15 |
|
Number of connector |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
G.703, G.704 |
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
|
Frame format |
· Ethernet_II · Ethernet_SNAP · IEEE 802.2 · IEEE 802.3 |
|
Cable type |
· 75-ohm unbalanced coaxial cable · 120-ohm balanced twisted pair cable · Coaxial connector, network interface connector and 75-ohm to 120-ohm adapter (with BNC connector) |
|
Operation mode |
CE1 ISDN PRI (only supported by SIC-1VE1) R2 |
|
Services |
· Backup · Terminal access · ISDN (only supported by SIC-1VE1) |
Interface LEDs
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: The link is idle. · On: The link is being occupied for call connection. |
|
ACT |
· Off: The link is idle. · On: The link is being occupied for communication. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E1 interface."
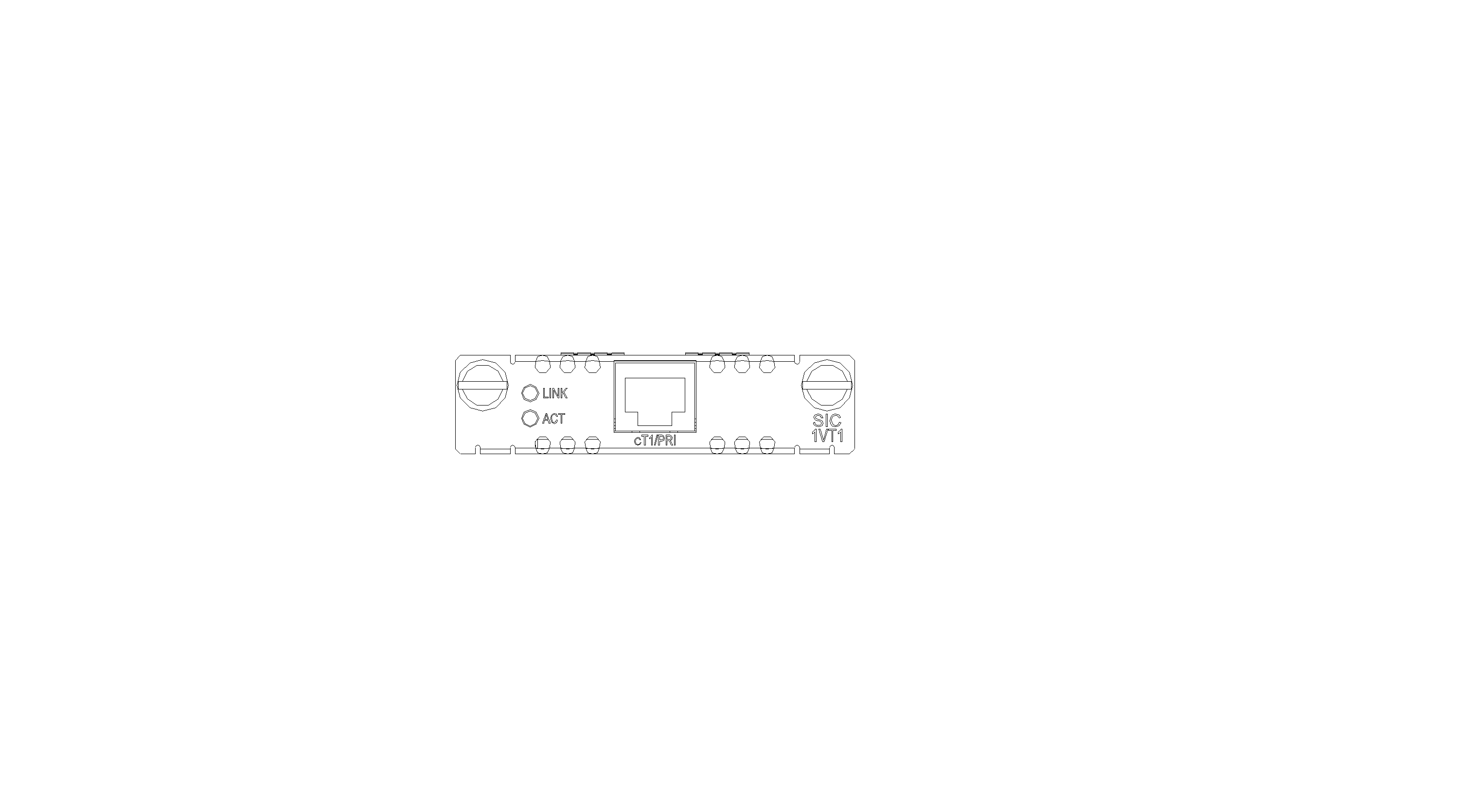
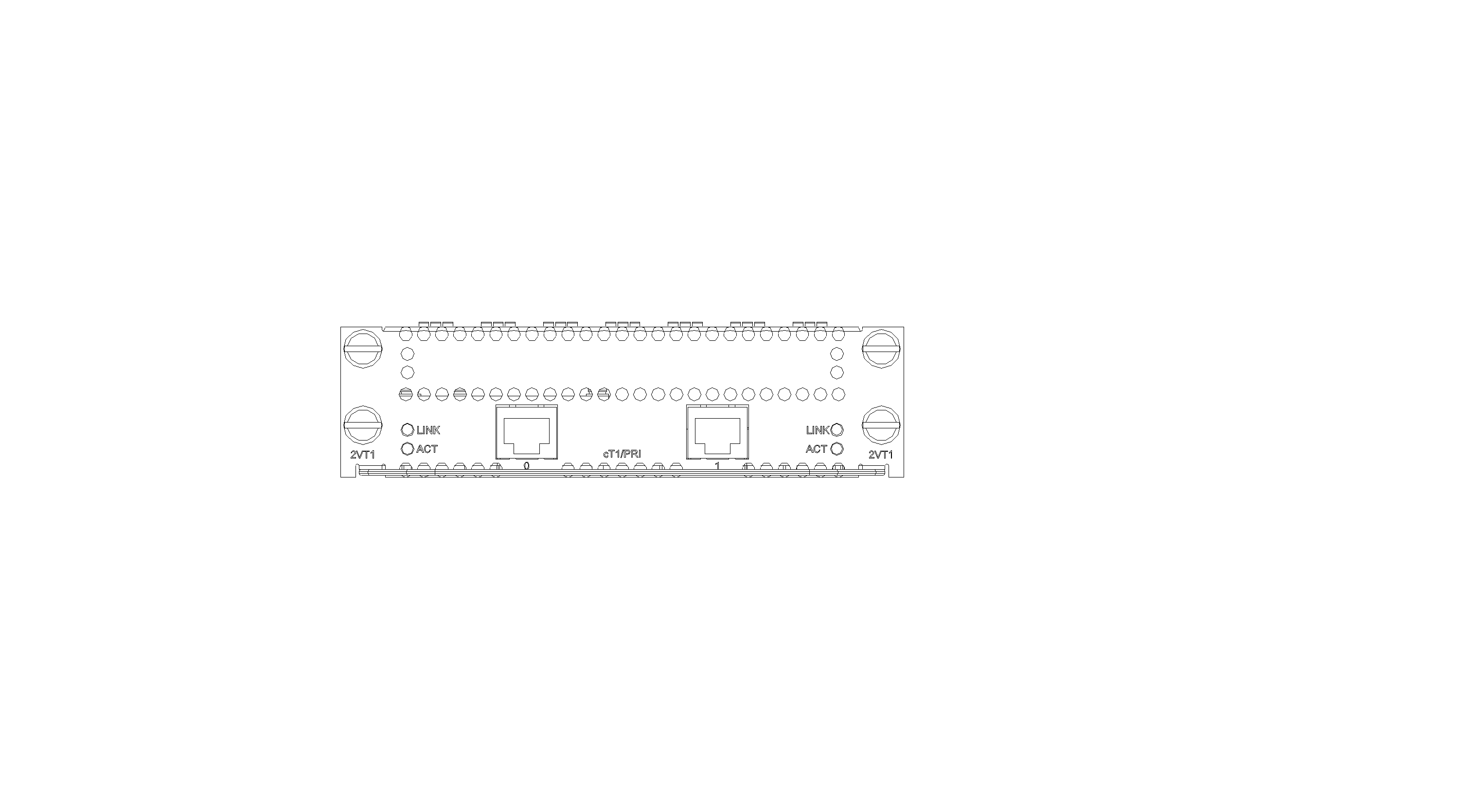
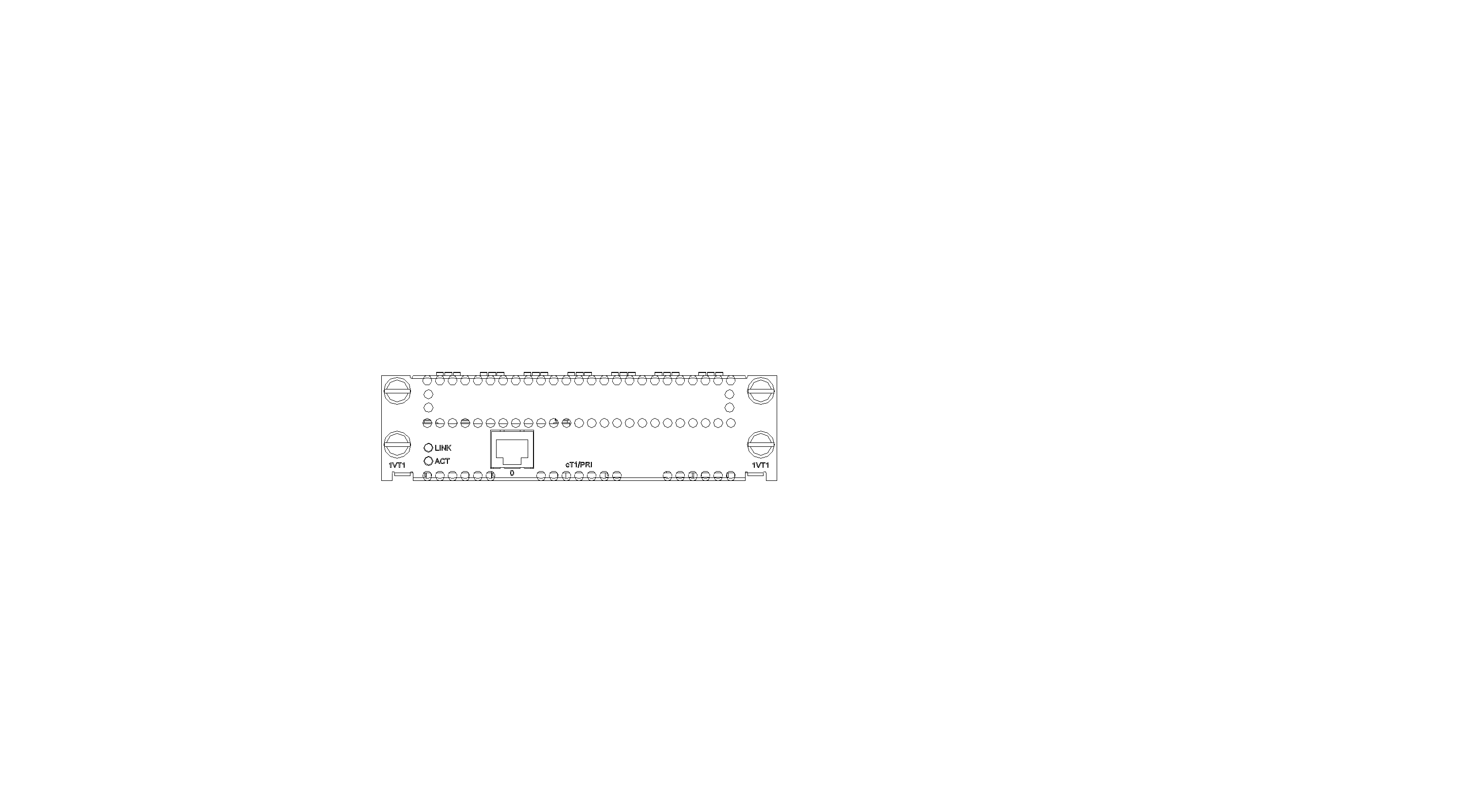
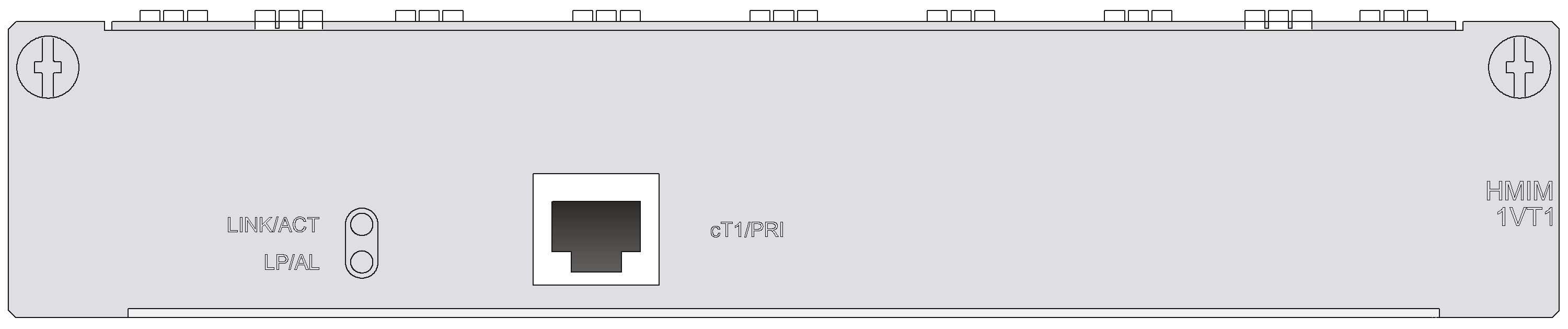
SIC-1VT1
Introduction
The 1-port T1 voice interface module (SIC-1VT1) can handle dense voice signals in VoIP system. It provides a CT1/PRI/R2 port, allowing the access of 23 channels of voice signals.
Interface specifications
Table 52 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connector |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703/T1.102 · G.704 · AT & T TR 54016 · AT & T TR 62411 · ANSI T1.403 |
|
Interface rate |
1.544 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
T1 cable (100-ohm standard shielded cable) |
|
Operation mode |
CT1 ISDN PRI |
|
Services |
Backup Terminal access ISDN |
Interface LEDs
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: The link is idle. · On: The link is being occupied for call connection. |
|
ACT |
· Off: The link is idle. · On: The link is being occupied for communication. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about T1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "T1 interface."
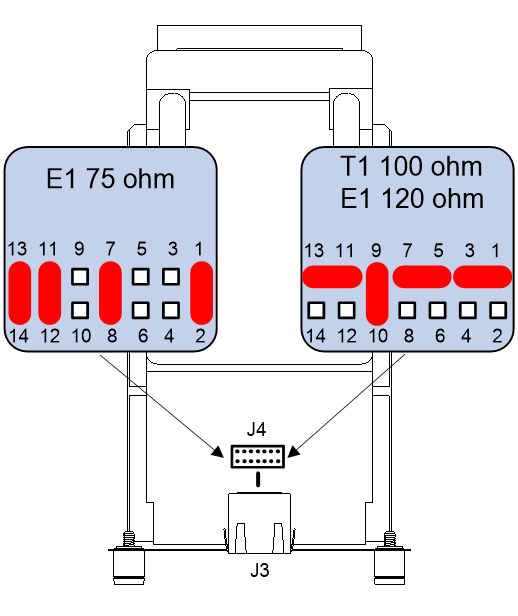
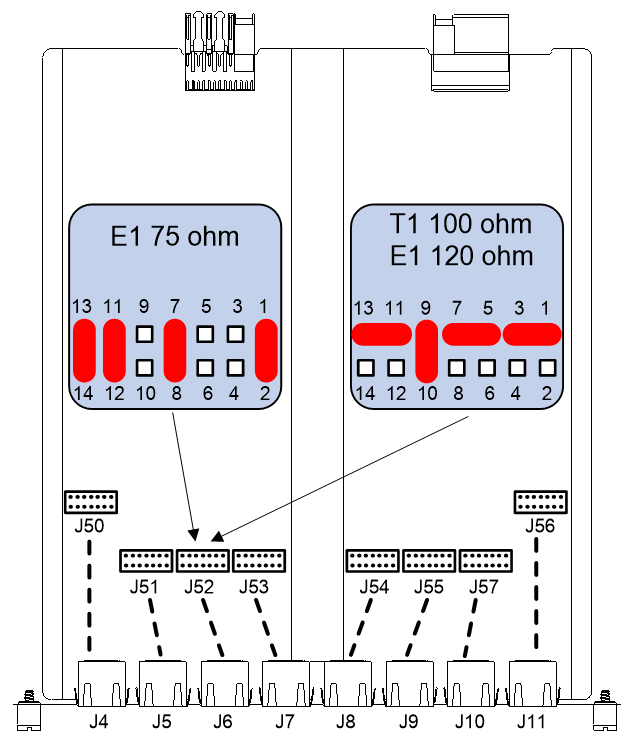
SIC-1VE1T1
Introduction
The 1-port E1/T1 voice interface module SIC-1VE1T1 handles dense voice signals in VoIP and FoIP systems. The E1 module transmits, receives, and processes E1 voice signals. It allows the interface to operate in CE1 mode or ISDN PRI mode to process a maximum of 30 channels of voice signals. The T1 module transmits, receives, and processes T1 voice signals. It allows the interface to operate in CT1 mode or ISDN PRI mode to process a maximum of 23 channels of voice signals.
You can use command lines and a jumper to configure the interface as a 75-ohm E1 interface, 100-ohm T1 interface, or 120-ohm E1 interface. By default, the interface is a 75-ohm E1 interface.
· To configure the interface as a 75-ohm E1 interface, connect the jumper to pins 1 and 2, pins 7 and 8, pins 11 and 12, and pins 13 and 14.
· To configure the interface as a 100-ohm T1 or 120-ohm E1 interface, connect the jumper to pins 1 to 3, pins 5 to 7, pins 9 and 10, and pins 11 to 13.
Figure 38 Jumper connecting methods
Interface specifications
Table 54 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connector |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703 · G.704 |
|
Interface rate |
· E1 interface: 2.048 Mbps · T1 interface: 1.544 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
· E1 75-ohm coaxial cable · E1 120-ohm twisted pair cable: 2 m (6.56 ft), 15 m (49.21 ft), or 30 m (98.43 ft) · T1 100-ohm standard shielded cable · Coaxial connector, network interface connector, or 75-to-120-ohm adapter (with BNC connector) |
|
Operating mode |
· E1 · T1 · CE1T1 · ISDN PRI |
|
Services |
Backup Terminal access ISDN PRI |
Interface LEDs
Figure 39 SIC-1VE1T1 panel
Table 55 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Steady green: Carrier signal has been received. · Flashing green at 4 Hz: Data is being transmitted or received. · Off: No carrier signals have been received. |
|
LP/AL |
· Steady yellow: The interface is in loopback mode. · Flashing yellow at 0.5 Hz: An AIS, LFA, or RAI alarm is present. · Off: Neither loopback nor alarm is present. |
Interface cables and connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E1 interface."
For more information about T1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "T1 interface."
3G interface modules
· SIC-3G-CDMA
· SIC-3G-TD
· SIC-3G-HSPA
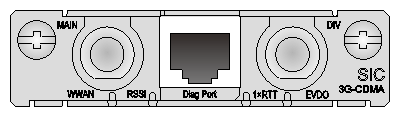
SIC-3G-CDMA
Introduction
The SIC-3G-CDMA module is used to access 3G WLANs. It supports:
· CDMA 2000 1x RTT
· 1x EV-DO Rev.0
· 1x EV-DO Rev.A
Interface specifications
Table 56 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
· TNC RF: Antenna for accessing WLANs. · RJ-45: For connecting to a third-party WLAN debugging and testing software such as CAIT of Qualcomm. |
|
Number of connectors |
· 2 TNC RF · 1 RJ-45 |
|
Interface standard |
· TNC RF: Omni antenna, supporting CDMA 2000 1 No RTT, 1 No EV-DO Rev.0, 1 No EV-DO Rev.A. · RJ-45: RS-232 |
|
Cable type |
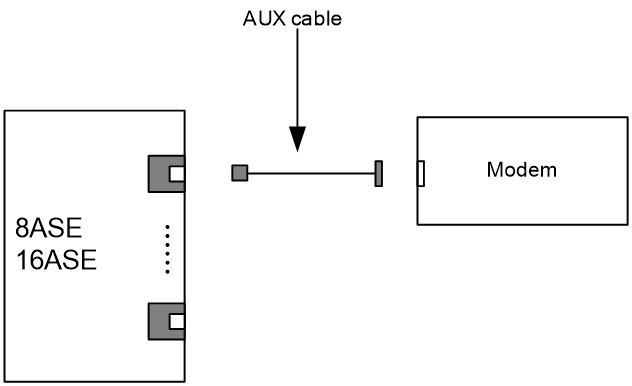
· TNC RF: None · RJ-45: AUX cable |
|
Rates |
Network standards: · 1 No EV-DO Rev.A (Downlink: 3.1 Mbps, uplink: 1.8 Mbps) · 1 No EV-DO Rev.0 (Downlink: 2.4 Mbps, uplink: 153.6 Kbps) · 1 No RTT (Downlink: 153.6 Kbps, uplink: 153.6 Kbps) |
|
Services |
· CDMA 2000 1x RTT · 1 No EV-DO Rev.0 · 1 No EV-DO Rev.A |
Interface LEDs
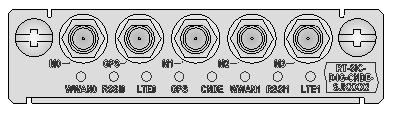
Figure 40 SIC-3G-CDMA panel
Table 57 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
WWAN |
· Steady green indicates that a link is present. · Flashing green indicates that data is being transmitted or received. |
|
RSSI |
· Steady green indicates strong signal. · Flashing green indicates middle or low signal. · Off indicates weak signal or no signal. |
|
1xRTT |
· Steady yellow indicates the service is valid. · Off indicates no service. |
|
EVDO |
· Steady yellow indicates the service is valid. · Off indicates no service. |
Antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods
For more information about SIC-3G-CDMA antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods, see "3G interface."
Installing a SIM card
|
CAUTION: Make sure the beveled corner of the SIM card fits into the beveled corner of the SIM socket. |
To installing a SIM card:
1. Open the SIM card socket in the direction marked OPEN so the holder projects upwards.
2. Insert the SIM card into the SIM card socket along the guide rails.
3. Close the SIM card socket in the direction marked LOCK to lock the card in position.
4. Execute the display cellular [ interface-number ] command after the router is started. When "SIM Status = OK" appears in the output information, the SIM card is identified.
SIC-3G-TD
Introduction
The SIC-3G-TD module provides access to 3 G WLANs. It supports the following features:
· GPRS
· EDGE
· TD-SCDMA
· HSDPA
Interface specifications
Table 58 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
TNC: For connecting an antenna and accessing WLANs. RJ-45: For connecting to a third-party WLAN debugging and testing software such as CAIT of Qualcomm. |
|
Number of connectors |
1 TNC RF 1 RJ-45 |
|
Interface standard |
TNC RF: Omni antenna, supporting GPRS/EDGE/TD-SCDMA//HSDPA RJ-45: RS-232 |
|
Cable type |
TNC RF: None RJ-45: AUX cable |
|
Rates |
· HSDPA (downlink: 2.8 Mbps, uplink: 384 Kbps) · TD-SCDMA (downlink: 384 Mbps, uplink: 384 Kbps) · EDGE (downlink: 236.8 Kbps, uplink: 236.8 Kbps) · GPRS (downlink: 85.6 Kbps, uplink: 85.6 Kbps) |
|
Services |
GPRS/EDGE/TD-SCDMA/HSDPA |
Interface LEDs
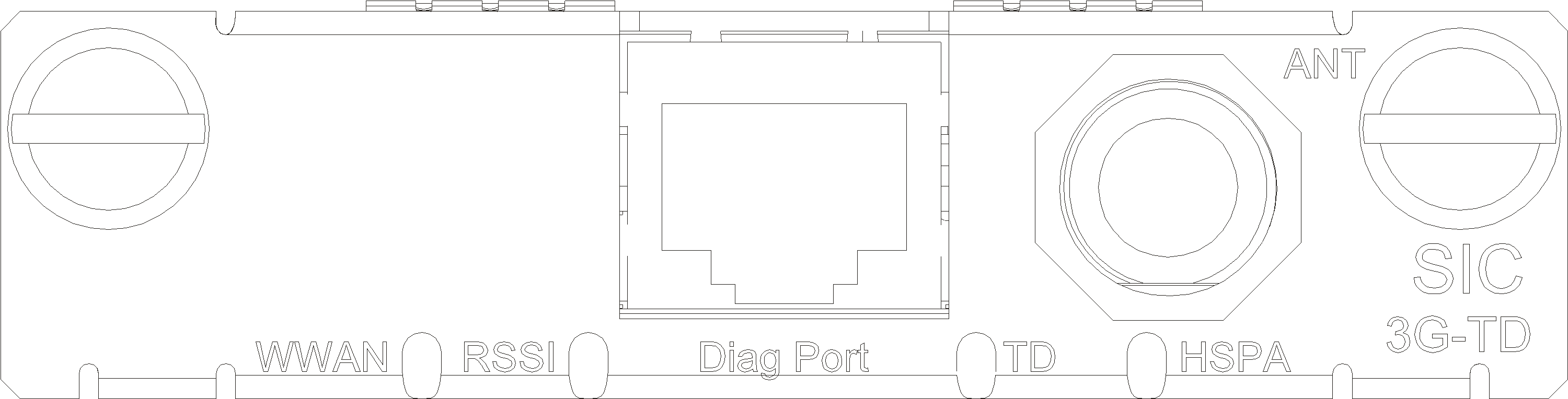
Figure 41 SIC-3G-TD panel
Table 59 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
WWAN |
· Steady green: A link is present. · Flashing green: Data is being transmitted or received. |
|
RSSI |
· Steady green: Strong signal. · Flashing green: Middle or low signal. · Off: Weak signal or no signal. |
|
TD |
· Steady yellow: The service is valid. · Off: No service. |
|
HSDPA |
· Steady yellow: The service is valid. · Off: No service. |
Antennas, interface cables, and the connection method
For more information about SIC-3G-GSM antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods, see "3G interface."
Installing a SIM card
|
CAUTION: Make sure the beveled corner of the SIM card fits into the beveled corner of the SIM socket. |
To install a SIM card:
1. Open the SIM card socket in the direction marked OPEN so the holder projects upwards.
2. Insert the SIM card into the SIM card socket along the guide rails.
3. Close the SIM card socket in the direction marked LOCK to lock the card in position.
4. Execute the display cellular [ interface-number ] command after the router is started. When "SIM Status = OK" appears in the output information, the SIM card is identified.
SIC-3G-HSPA
Introduction
The SIC-3G-HSPA module serves to access 3G networks. It supports:
· GPRS
· EDGE
· UMTS
· HSDPA
Interface specifications
Table 60 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
TNC: For connecting an antenna and accessing WLANs. RJ-45: For connecting to a third-party WLAN debugging and testing software such as CAIT of Qualcomm. |
|
Number of connectors |
2 TNC RF 1 RJ-45 |
|
Interface standard |
TNC RF: Omni antenna, supporting GPRS/EDGE/UMTS/HSDPA. RJ-45: RS-232 |
|
Cable type |
TNC RF: None RJ-45: AUX cable |
|
Rates |
· HSDPA (downlink: 7.2 Mbps) · HSUPA (uplink: 5.76 Mbps) · UMTS (downlink: 384 Mbps, uplink: 384 Kbps) · EDGE (downlink: 236.8 Kbps, uplink: 236.8 Kbps) · GPRS (downlink: 85.6 Kbps, uplink: 85.6 Kbps) |
|
Services |
GPRS/EDGE/UMTS/HSDPA |
|
Supported wireless band |
850/900/1900/2100 MHz WCDMA/HSDPA/HSUPA 850/900/1800/1900 MHz GPRS/EDGE |
Interface LEDs
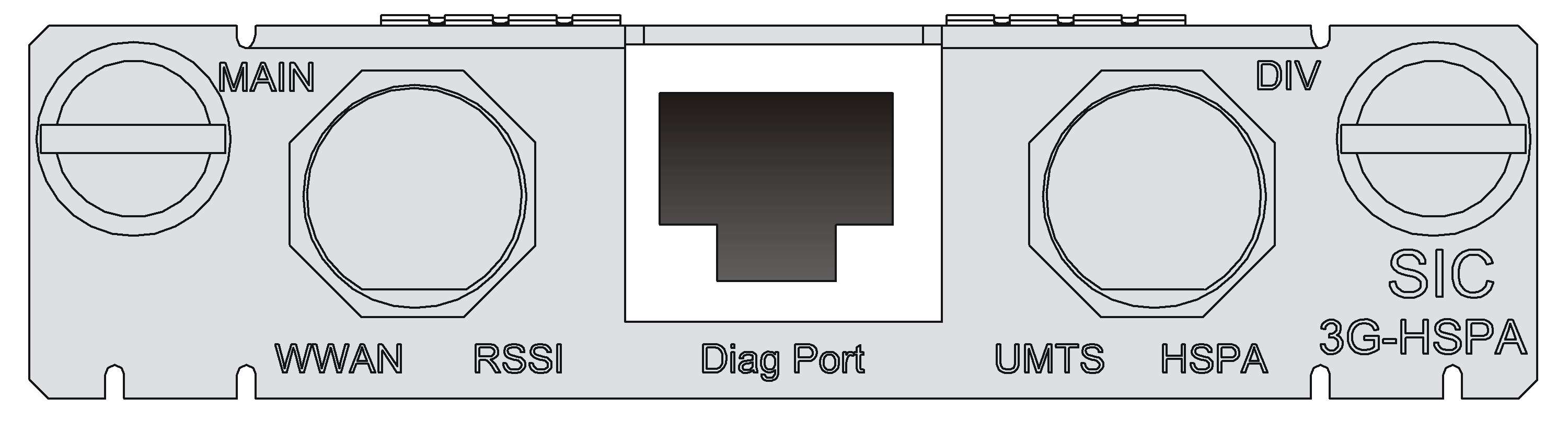
Figure 42 SIC-3G-HSPA panel
Table 61 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
WWAN |
· Steady green: A link is present. · Flashing green: Data is being transmitted or received. |
|
RSSI |
· Steady green: Strong signal. · Flashing green: Middle or low signal. · Off: Weak signal or no signal. |
|
UMTS |
· Steady yellow: The service is valid. · Off: No service. |
|
HSDPA |
· Steady yellow: The service is valid. · Off: No service. |
Antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods
|
CAUTION: The 3G antenna provided with the SIC-3G-HSPA must be installed on the antenna port that has a MAIN mark. |
For more information about SIC-3G-HSPA antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods, see "3G interface."
Installing a SIM card
|
CAUTION: Make sure the beveled corner of the SIM card fits into the beveled corner of the SIM socket. |
To install a SIM card:
1. Open the SIM card socket in the direction marked OPEN so the holder projects upwards.
2. Insert the SIM card into the SIM card socket along the guide rails.
3. Close the SIM card socket in the direction marked LOCK to lock the card in position.
4. Execute the display cellular [ interface-number ] command after the router is started. When "SIM Status = OK" appears in the output information, the SIM card is identified.
4G interface modules
· SIC-4G-LTE-M
· SIC-4G-CNDE
· RT-SIC-4G-CAT6
· SIC-D4G-CNDE
SIC-4G-LTE-M
Introduction
The SIC-4G-LTE-M module provides 4G WLAN access and supports the following features:
· LTE
· UMTS
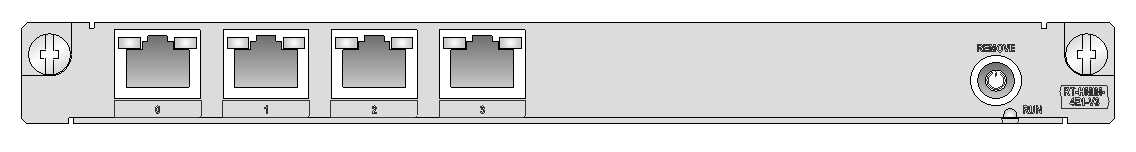
· HSPA+
· TD-SCDMA
· CDMA2000 1xRTT
· CDMA2000 1x-Ev-Do
· Quad-Band EDGE
· GPRS
· GSM
Interface specifications
Table 62 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
· TNC—For accessing WLANs. · SMA—For accessing GPS. · Mini USB Type AB—For connecting to third-party WLAN debugging and testing software such as CAIT of Qualcomm. |
|
Number of connectors |
· 2 TNCs · 1 SMA · 1 Mini USB Type AB |
|
Interface standard |
· TNC—Supports LTE, UMTS, HSPA+, CDMA 1x, EV-DO Rev A, Quad-Band EDGE, GPRS, and GSM · SMA—GPS · Mini USB Type AB—RS-232 |
|
Cable type |
· SMA—Flexible 174 sized cable · TNC—None · Mini USB Type AB—USB console cable |
|
Services |
· LTE · UMTS · HSPA+ · TD-SCDMA · CDMA2000 1xRTT · CDMA2000 1x-Ev-Do · Quad-Band EDGE · GPRS · GSM |
Interface LEDs
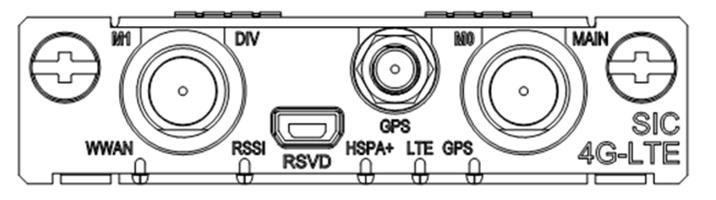
Figure 43 SIC-4G-LTE-M panel
Table 63 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
WWAN |
· Steady green indicates that a link is present. · Fast flashing green indicates that data is being transmitted or received. · Slowly flashing green indicates network searching. · Off indicates that no link is present. |
|
RSSI |
· Steady green indicates strong signal (RSSI ≥ –69 dBm). · Fast flashing green indicates middle signal (–89 dBm ≤ RSSI <–69 dBm). · Slowly flashing green indicates low signal (–99 dBm ≤ RSSI < –89 dBm). · Off indicates weak signal or no signal (RSSI < –99 dBm). |
|
HSPA+ |
· Steady green indicates that the HSPA+ service or HSDPA service is valid. · Flashing green indicates that the EVDO service is valid. · Off indicates no service. |
|
LTE |
· Steady green indicates that the LTE service is valid. · Off indicates no LTE service. |
|
GPS |
· Steady green indicates that the GPS service is valid. · Off indicates no GPS service. |
Antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods
For more information about SIC-4G-LTE-M interface module antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods, see "4G interface."
Installing a SIM card
|
CAUTION: Make sure the beveled corner of the SIM card fits into the beveled corner of the SIM socket. |
To install a SIM card:
1. Open the SIM card socket in the direction marked OPEN so the holder projects upwards.
2. Insert the SIM card into the SIM card socket along the guide rails.
3. Close the SIM card socket in the direction marked LOCK to lock the card in position.
4. Execute the display cellular [ interface-number ] command after the router is started. When "SIM Status = OK" appears in the output information, the SIM card is identified.
SIC-4G-CNDE
Introduction
The SIC-4G-CNDE module provides 4G WLAN access and supports the following technologies:
· LTE-TDD
· LTE-FDD
· TD-SCDMA
· UMTS
· GSM
· EVDO
· CDMA1x
Interface specifications
Table 64 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connectors |
3 SMA connectors |
|
Supported antenna types |
· GPS · Omnidirectional antenna, support for FDD-LTE/TDD-LTE/TD-SCDMA/UMTS/EDGE/GPRS/GSM/EVDO/CDMA |
|
Technologies and supported frequency bands |
· LTE-TDD band 38/39/40/41 · LTE-FDD band 1/3/5/7/8 · TD-SCDMA band 34/39 · UMTS band 1/8 · GSM band 2/3/5/8 · EVDO band BC0 · CDMA1x band BC0 |
Interface LEDs
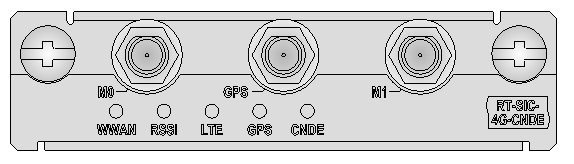
Figure 44 SIC-4G-CNDE panel
Table 65 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
WWAN |
· Steady green indicates that a link is present. · Fast flashing green indicates that data is being transmitted or received. · Slowly flashing green indicates network searching. · Off indicates that no link is present. |
|
RSSI |
· Steady green indicates strong signal (RSSI ≥ –69 dBm). · Fast flashing green indicates middle signal (–89 dBm ≤ RSSI <–69 dBm). · Slowly flashing green indicates low signal (–99 dBm ≤ RSSI < –89 dBm). · Steady yellow is reserved for future use. · Off indicates weak signal or no signal (RSSI < –99 dBm). |
|
LTE |
· Steady green indicates the 4G-LTE service is valid. · Flashing green (8 Hz) indicates the high-speed 3G service such as DC-HSPA+, HSPA+, HSDPA, HSUPA, or EVDO is valid. · Steady yellow indicates the 2G or low-speed 3G service such as UMTS, TD-SCDMA, CDMA2000-1xRTT, EDGE, GPRS, or GSM is valid. · Flashing yellow is reserved for future use. · Off indicates no LTE service. |
|
GPS |
· Steady green indicates that the GPS service is valid. · Off indicates no GPS service. |
|
CNDE |
· Steady green indicates that the module is operating correctly and is not sending or receiving data. · Flashing green indicates that the module is operating correctly and is sending or receiving data. · Steady yellow indicates that the module is faulty. · Off indicates that the module is not installed securely, or no power is present. |
Antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods
For more information about SIC-4G-CNDE interface module antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods, see "4G interface" and "GPS interface."
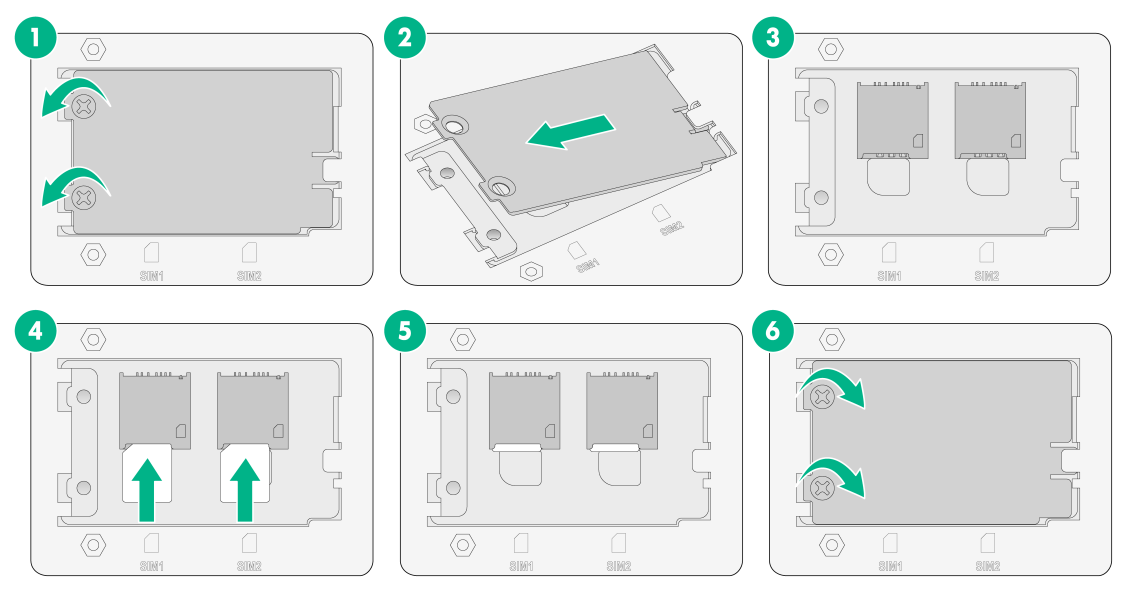
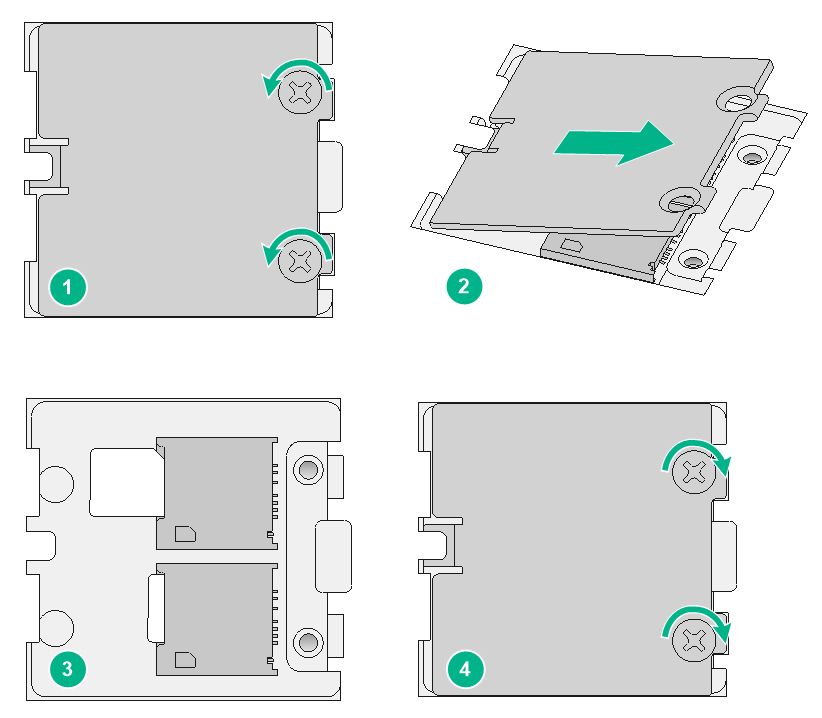
Installing Micro SIM card
|
CAUTION: Make sure the beveled corner of the Micro SIM card is oriented as indicated by the Micro SIM card icon. |
The SIC-4G-CNDE interface module supports Micro SIM cards.
The SIC-4G-CNDE has two Micro SIM card slots, but only one is active at a time. If you install SIM cards in both slots, the SIM1 slot 1 is active, the SIM2 slot is in standby state by default. To perform an active/standby switchover, execute the sim switch-to command. For more information about the command, see Layer 2—WAN Access Command Reference for the product.
To install a Micro SIM card:
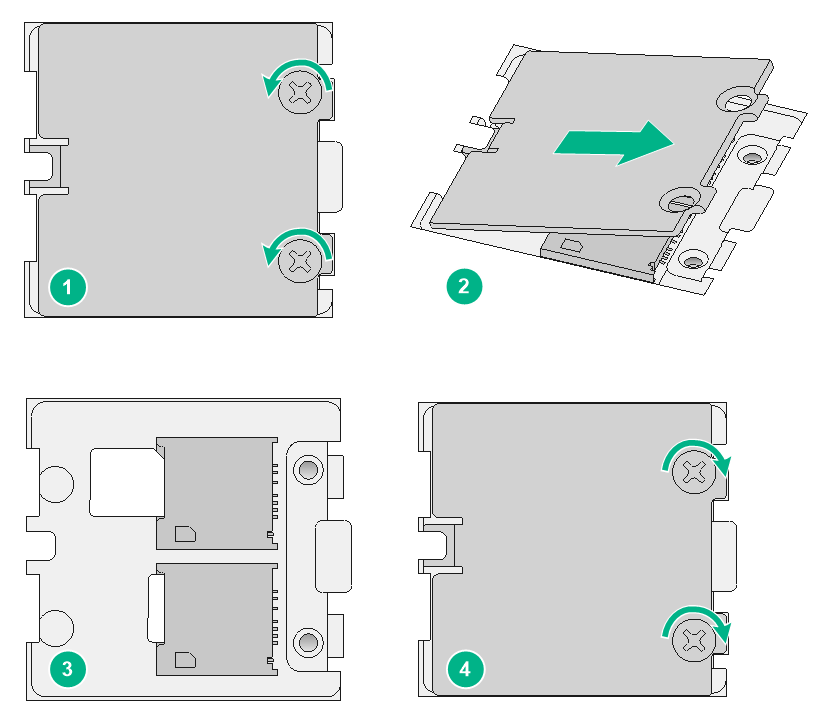
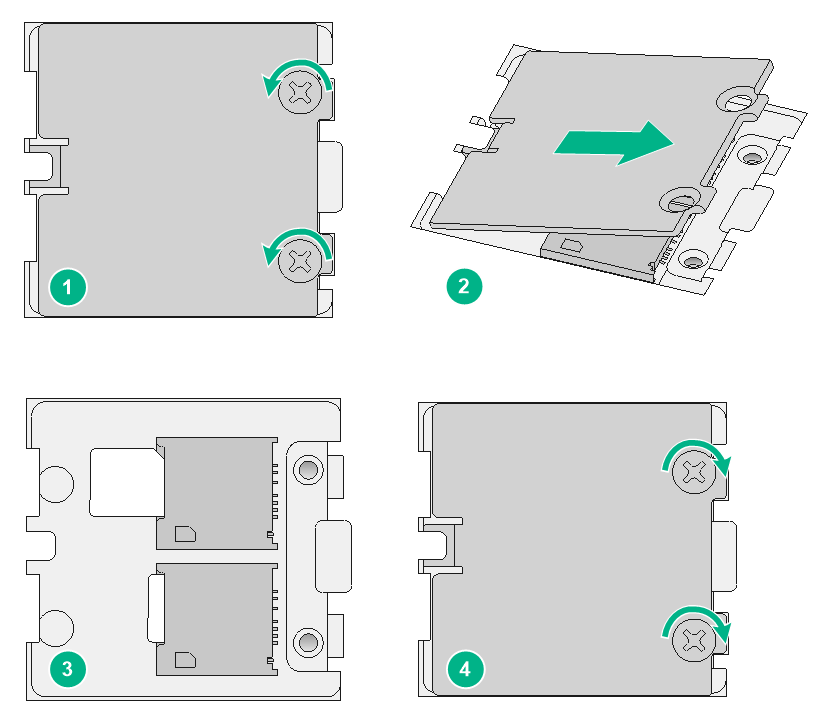
1. Use a Phillips screwdriver to remove the two screws on the SIM card retainer cover.
2. Lift the cover up and away from the retainer.
3. Insert SIM cards into the SIM card slots on the retainer.
4. Reattach the retainer cover and use the two screws to secure the cover.
5. Execute the display cellular [ interface-number ] command after the router is started. If "SIM Status = OK" is displayed in the output information, the Micro SIM card is identified.
Figure 45 Installing Micro SIM cards
RT-SIC-4G-CAT6
|
IMPORTANT: The RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module is hot swappable. However, to avoid unexpected reboot of the host, execute the remove command or press the remove button for over 3 seconds and wait for the remove LED to turn off before removing the module. |
Introduction
The RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module provides 4G WLAN access and supports the following technologies:
· LTE-TDD
· LTE-FDD
· WCDMA
Interface specifications
Table 66 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connectors |
3 SMA connectors |
|
Standard and operating mode |
· GNSS: GPS/GLONASS/BDS/Galileo · Omnidirectional antenna: FDD-LTE, TDD-LTE, WCDMA |
|
Supported services |
· LTE-TDD · LTE-FDD · WCDMA |
Interface LEDs
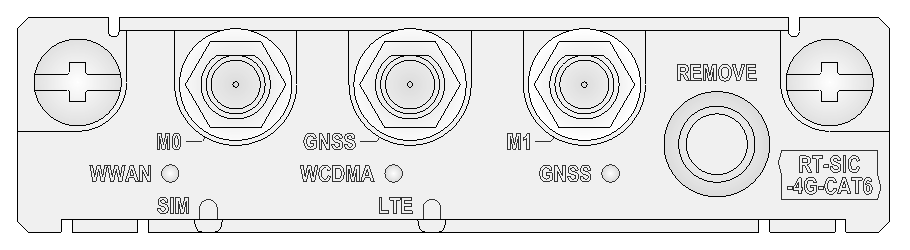
Figure 46 RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 panel
Table 67 LED description
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
WWAN |
Steady green |
A WWAN link is present. |
|
Fast flashing green |
Data is being transmitted or received on the WWAN link. |
|
|
Slow flashing green |
Searching and connecting to a WWAN network. |
|
|
Off |
Not connected to a WWAN. |
|
|
WCDMA |
Steady green |
Strong 3G signal strength (RSSI ≥ –70 dBm) |
|
Fast flashing green |
Medium 3G signal strength (–100 dBm ≤ RSSI < –70 dBm) |
|
|
Slow flashing green |
Low 3G signal strength (–125 dBm ≤ RSSI < –100 dBm) |
|
|
Off |
No 3G service (RSSI < –125 dBm) |
|
|
LTE |
Steady green |
The module is operating in 4G mode and the 4G signal strength is strong (RSSI ≥ –70 dBm). |
|
Fast flashing green |
The module is operating in 4G mode and the 4G signal strength is medium (–100 dBm ≤ RSSI < –70 dBm). |
|
|
Slow flashing green |
The module is operating in 4G mode and the 4G signal strength is low (–125 dBm ≤ RSSI < –100 dBm). |
|
|
Off |
No 4G service (RSSI < –125 dBm) |
|
|
SIM |
Steady green |
The SIM card in SIM card slot 0 is working. |
|
Steady yellow |
The SIM card in SIM card slot 1 is working. |
|
|
Off |
No SIM cards are present in the two SIM card slots. |
|
|
GNSS |
Steady green |
Valid GNSS service. |
|
Off |
No GNSS service. |
|
|
REMOVE |
Steady green |
The module is operating correctly. You can remove it. |
|
Fast flashing green |
The module is initializing. You cannot remove it. |
|
|
Off |
You can remove the module if all the other LEDs on the module are also off. |
Antennas, interface cables, and connection methods
For more information about RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods, see "4G interface" and "GNSS interface."
Installing Micro SIM card
|
CAUTION: Make sure the beveled corner of the Micro SIM card is oriented as indicated by the Micro SIM card icon. |
The RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module supports Micro SIM cards.
The RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 has two Micro SIM card slots, but only one is active at a time. If you install SIM cards in both slots, the SIM0 slot is active and the SIM1 slot is in standby state by default. To perform an active/standby switchover, execute the sim switch-to command. For more information about the command, see Layer 2—WAN Access Command Reference for the product.
To install a Micro SIM card:
1. Use a Phillips screwdriver to remove the two screws on the SIM card retainer cover.
2. Lift the cover up and away from the retainer.
3. Insert SIM cards into the SIM card slots on the retainer. Make sure the beveled corner of the Micro SIM card is oriented as indicated by the Micro SIM card icon.
4. Reattach the retainer cover and use the two screws to secure the cover.
5. Execute the display cellular [ interface-number ] command after the router is started. If "SIM Status = OK" is displayed in the output information, the Micro SIM card is identified.
Figure 47 Installing Micro SIM cards
SIC-D4G-CNDE
Introduction
The SIC-D4G-CNDE module provides 4G WLAN access and supports the following technologies:
· LTE-TDD
· LTE-FDD
· TD-SCDMA
· UMTS
· GSM
· EVDO
· CDMA1x
Interface specifications
Table 68 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connectors |
5 SMA connectors |
|
Supported antenna types |
· GPS · Omnidirectional antenna, support for FDD-LTE/TDD-LTE/TD-SCDMA/UMTS/EDGE/GPRS/GSM/EVDO/CDMA |
|
Technologies and supported frequency band |
· LTE-TDD band 38/39/40/41 · LTE-FDD band 1/3/5/7/8 · TD-SCDMA band 34/39 · UMTS band 1/8 · GSM band 2/3/5/8 · EVDO band BC0 · CDMA1x band BC0 |
Interface LEDs
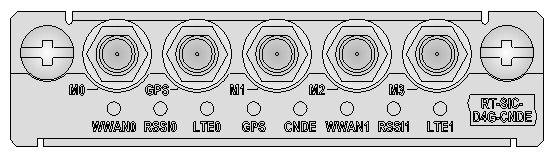
Figure 48 SIC-D4G-CNDE panel
Table 69 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
WWAN |
· Steady green indicates that a link is present. · Fast flashing green indicates that data is being transmitted or received. · Slowly flashing green indicates network searching. · Off indicates that no link is present. |
|
RSSI |
· Steady green indicates strong signal (RSSI ≥ –69 dBm). · Fast flashing green indicates middle signal (–89 dBm ≤ RSSI <–69 dBm). · Slowly flashing green indicates low signal (–99 dBm ≤ RSSI < –89 dBm). · Steady yellow is reserved for future use. · Off indicates weak signal or no signal (RSSI < –99 dBm). |
|
LTE |
· Steady green indicates the 4G-LTE service is valid. · Flashing green (8 Hz) indicates the high-speed 3G service such as DC-HSPA+, HSPA+, HSDPA, HSUPA, or EVDO is valid. · Steady yellow indicates the 2G or low-speed 3G service such as UMTS, TD-SCDMA, CDMA2000-1xRTT, EDGE, GPRS, or GSM is valid. · Flashing yellow is reserved for future use. · Off indicates no LTE service. |
|
GPS |
· Steady green indicates that the GPS service is valid. · Off indicates no GPS service. |
|
CNDE |
· Steady green indicates that the module is operating correctly and is not sending or receiving data. · Flashing green indicates that the module is operating correctly and is sending or receiving data. · Steady yellow indicates that the module is faulty. · Off indicates that the module is not installed securely, or no power is present. |
Antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods
For more information about SIC-D4G-CNDE interface module antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods, see "4G interface" and "GPS interface."
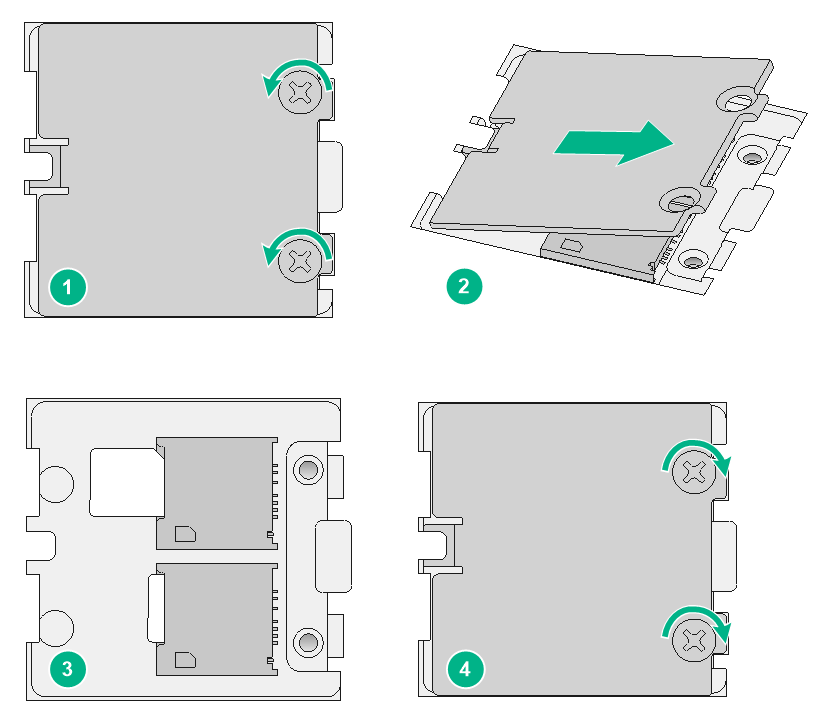
Installing Micro SIM card
|
CAUTION: Make sure the beveled corner of the Micro SIM card is oriented as indicated by the Micro SIM card icon. |
The SIC-D4G-CNDE interface module supports Micro SIM cards.
The SIC-D4G-CNDE has two Micro SIM card slots. The two slots can operate simultaneously. The SIM1 slot uses M0 and M1 antenna ports. M0 is the primary antenna port and M1 is the auxiliary antenna port. The SIM2 slot uses M2 and M3 antenna ports. M2 is the primary antenna port and M3 is the auxiliary antenna port. You must connect an antenna to the primary antenna port. An auxiliary antenna only cannot guarantee reliable connectivity. If the primary antenna fails, replace it immediately.
On the SIC-D4G-CNDE interface module, the space between adjacent antenna ports is insufficient for two antennas. To install 4G antennas for two adjacent ports, use a 4G antenna extension cable to connect one of the antennas.
To install a Micro SIM card:
1. Use a Phillips screwdriver to remove the two screws on the SIM card retainer cover.
2. Lift the cover up and away from the retainer.
3. Insert SIM cards into the SIM card slots on the retainer.
4. Reattach the retainer cover and use the two screws to secure the cover.
5. Execute the display cellular [ interface-number ] command after the router is started. If "SIM Status = OK" is displayed in the output information, the Micro SIM card is identified.
Figure 49 Installing Micro SIM cards
5G interface modules
RT-SIC-5G
|
CAUTION: Before removing an RT-SIC-5G module, execute the remove command or press and hold the remove button for more than 3 seconds and wait for the remove LED to turn off. The device might reboot unexpectedly if you remove a SIC-5G module with its remove LED on. |
Introduction
The RT-SIC-5G module provides 5G WLAN access and supports the following technologies:
· 5G NR
· LTE-A
· WCDMA
· FDD-LTE
· TDD-LTE
Interface specifications
Table 70 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connectors |
4 SMA connectors |
|
Standard and working mode |
· GNSS: GPS/GLONASS/BeiDou/Galileo · Omnidirectional antenna, support for WCDMA/FDD-LTE/TDD-LTE/5G NR |
|
Supported service |
· 5G/4G/3G networking · 5G and LTE-A full coverage · NSA and SA modes · Integrating multi-constellation GNSS receiver for fast and precise positioning in different environments |
Interface LEDs
Figure 50 RT-SIC-5G panel
Table 71 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
WWAN |
· Steady green indicates that a WWAN link is present. · Fast flashing green indicates that data is being transmitted or received on the WWAN link. · Slow flashing green indicates WWAN searching and building. · Off indicates that no WWAN link is present. |
|
5G |
· Steady green in SA mode indicates strong 5G signal (RSRP ≥ –85 dBm). · Fast flashing green in SA mode indicates middle 5G signal (–100 dBm ≤ RSSI <–85 dBm). · Slow flashing green in SA mode indicates low 5G signal (–115 dBm ≤ RSSI < –100 dBm). · Steady yellow in NSA mode indicates strong 5G signal (RSRP ≥ –85 dBm). · Fast flashing yellow in NSA mode indicates middle 5G signal (–100 dBm ≤ RSSI <–85 dBm). · Slow flashing yellow in NSA mode indicates low 5G signal (–115 dBm ≤ RSSI < –100 dBm). · Off indicates no 5G signal. |
|
LTE |
· Steady green indicates working in 4G mode with strong signal (RSSI ≥ –70 dBm). · Fast flashing green indicates working in 4G mode with middle signal (–100 dBm ≤ RSSI <–70 dBm). · Slow flashing green indicates working in 4G mode with low signal (–125 dBm ≤ RSSI <–100 dBm). · Steady yellow indicates working in 3G mode with strong signal (RSSI ≥ –70 dBm). · Fast flashing yellow indicates working in 3G mode with middle signal (–100 dBm ≤ RSSI <–70 dBm). · Slow flashing yellow indicates working in 3G mode with low signal (–125 dBm ≤ RSSI <–100 dBm) · Off indicates no 3G or 4G service. |
|
SIM |
· Steady green indicates that SIM card 1 is operating. · Steady yellow indicates that SIM card 2 is operating. · Off indicates that no SIM card is available. |
|
GNSS |
· Steady green indicates that the GNSS service is valid. · Off indicates no GNSS service. |
|
REMOVE |
· Steady green indicates that the SIC-5G module is operating normally and can be hot swapped. · Flashing green indicates that the SIC-5G module is being initialized and cannot be hot swapped. · Off indicates that you can remove the SIC-5G module if other LEDs are off. |
Antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods
For more information about RT-SIC-5G interface module antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods, see "5G interface."
Installing an RT-5G SIM card
|
CAUTION: To avoid damage to a SIM card or the 5G interface module, insert the SIM card into the slot with the cut corner oriented as shown in the illustration. |
The RT-SIC-5G interface module provides two SIM card slots. You can install one or two SIM cards as required. SIM card 1 is operating by default when two SIM cards are installed on the SIC-5G interface module. In Figure 51, two SIM cards are installed.
To install an RT-5G SIM card:
1. Use a screwdriver to remove the two screws on the SIM card retainer cover.
2. Lift the cover up and away from the retainer, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 51.
3. Orient the SIM card with the cut corner as shown in the illustration.
4. Insert the SIM card into the SIM card slot along the guide rails.
5. Slightly push SIM card edge to secure it into the slot.
6. Reattach the retainer cover and use the two screws to secure the cover.
7. Execute the display cellular [ interface-number ] command after the router is started. If "SIM Status = OK" is displayed in the output information, the SIM card is identified.
Figure 51 Installing 5G SIM cards
Network data encryption modules
· SIC-CNDE
· SIC-CNDE-SJK
· SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK
· SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK
SIC-CNDE
Introduction
The SIC-CNDE is a China Network Data Encryption (CNDE) module. The SIC-CNDE provides high performance and reliable data encryption features for routers by using the SM1 mechanism.
Insert SIC-CNDE module in the SIC slot. The main board forwards IP packets and implements VPN with the encryption feature, where SM1 encryption and decryption is implemented by the encryption module.
Interface specifications
Table 72 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Hardware algorithm |
Key algorithm: · SM1-128 · SM1-256 |
Interface LEDs
Figure 52 SIC-CNDE panel
Table 73 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
ACT |
· Flashing: Data is being transmitted or received between the module and the host. · Steady green: No data is being transmitted or received. |
SIC-CNDE-SJK
Introduction
The SIC-CNDE-SJK (CNDE is the acronym of China Network Data Encryption) supports SM1, SM2, and SM4 encryption algorithms and provides high performance and reliable data encryption features for routers.
LEDs
Figure 53 SIC-CNDE-SJK panel
Table 74 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
CNDE |
· Steady green: The module is operating correctly and is not sending or receiving data. · Flashing green: The module is operating correctly and is sending or receiving data. · Steady yellow: The module is faulty. · Off: The module is not installed securely, or no power is present. |
SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK
Introduction
The SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK (CNDE is the acronym of China Network Data Encryption) supports SM1, SM2, and SM4 encryption algorithms and provides high performance and reliable data encryption features for routers. The SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK module provides 4G WLAN access and supports the following technologies:
· LTE-TDD
· LTE-FDD
· TD-SCDMA
· UMTS
· GSM
· EVDO
· CDMA1x
Interface specifications
Table 75 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connectors |
3 × SMA connectors |
|
Supported antenna types |
· GPS antenna · Omnidirectional antenna, support for FDD-LTE/TDD-LTE/TD-SCDMA/UMTS/EDGE/GPRS/GSM/EVDO/CDMA |
|
Technologies and supported frequency bands |
· LTE-TDD band 38/39/40/41 · LTE-FDD band 1/3/5/7/8 · TD-SCDMA band 34/39 · UMTS band 1/8 · GSM band 2/3/5/8 · EVDO band BC0 · CDMA1x band BC0 |
Interface LEDs
Figure 54 SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK panel
Table 76 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
WWAN |
· Steady green: A link is present. · Fast flashing: Data is being transmitted or received. · Slowly flashing: The module is searching for wireless networks. · Off: No link is present. |
|
RSSI |
· Steady green: Strong signal strength (RSSI ≥ –69 dBm). · Fast flashing: Middle signal strength (–89 dBm ≤ RSSI <–69 dBm). · Slowly flashing green: Low signal strength (–99 dBm ≤ RSSI < –89 dBm). · Off: Weak or no signal strength (RSSI < –99 dBm). |
|
LTE |
· Steady green: The 4G-LTE service is running. · Flashing green (8 Hz): The high-speed 3G service such as DC-HSPA+, HSPA+, HSDPA, HSUPA, or EVDO is running. · Steady yellow: The 2G or low-speed 3G service such as UMTS, TD-SCDMA, CDMA2000-1xRTT, EDGE, GPRS, or GSM is running. · Off: No LTE service. |
|
GPS |
· Steady green: The GPS service is running. · Off: No GPS service. |
|
CNDE |
· Steady green: The module is operating correctly and is not sending or receiving data. · Flashing green: The module is operating correctly and is sending or receiving data. · Steady yellow: The module is faulty. · Off: The module is not installed securely, or no power is present. |
Antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods
For more information about SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK interface module antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods, see "4G interface" and "GPS interface."
Installing a Micro SIM card
|
CAUTION: Make sure the beveled corner of the Micro SIM card is oriented as indicated by the Micro SIM card icon. |
The SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK interface module supports Micro SIM cards.
The SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK has two Micro SIM card slots, but only one is active at a time. If you install SIM cards in both slots, the SIM1 slot 1 is active, the SIM2 slot is in standby state by default. To perform an active/standby switchover, execute the sim switch-to command. For more information about the command, see Layer 2—WAN Access Command Reference for the product.
To install a Micro SIM card:
1. Use a Phillips screwdriver to remove the two screws on the SIM card retainer cover.
2. Lift the cover up and away from the retainer.
3. Insert SIM cards into the SIM card slots on the retainer.
4. Reattach the retainer cover and use the two screws to secure the cover.
5. Execute the display cellular [ interface-number ] command after the router is started. If "SIM Status = OK" is displayed in the output information, the Micro SIM card is identified.
Figure 55 Installing Micro SIM cards
SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK
Introduction
The SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK (D4G indicates that the module supports two SIM cards that can operate simultaneously; CNDE is the acronym of China Network Data Encryption) supports SM1, SM2, and SM4 encryption algorithms and provides high performance and reliable data encryption features for routers. The SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK module provides 4G WLAN access and supports the following technologies:
· LTE-TDD
· LTE-FDD
· TD-SCDMA
· UMTS
· GSM
· EVDO
· CDMA1x
Interface specifications
Table 77 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connectors |
5 SMA connectors |
|
Supported antenna types |
· GPS antenna · Omnidirectional antenna, support for FDD-LTE/TDD-LTE/TD-SCDMA/UMTS/EDGE/GPRS/GSM/EVDO/CDMA |
|
Technologies and supported frequency bands |
· LTE-TDD band 38/39/40/41 · LTE-FDD band 1/3/5/7/8 · TD-SCDMA band 34/39 · UMTS band 1/8 · GSM band 2/3/5/8 · EVDO band BC0 · CDMA1x band BC0 |
Interface LEDs
Figure 56 SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK panel
Table 78 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
WWAN |
· Steady green: A link is present. · Fast flashing green: Data is being transmitted or received. · Slowly flashing green: The module is searching for wireless networks. · Off: No link is present. |
|
RSSI |
· Steady green: Strong signal strength (RSSI ≥ –69 dBm). · Fast flashing green: Middle signal strength (–89 dBm ≤ RSSI <–69 dBm). · Slowly flashing green: Low signal strength (–99 dBm ≤ RSSI < –89 dBm). · Off: Weak or no signal strength (RSSI < –99 dBm). |
|
LTE |
· Steady green: The 4G-LTE service is running. · Flashing green (8 Hz): The high-speed 3G service such as DC-HSPA+, HSPA+, HSDPA, HSUPA, or EVDO is running. · Steady yellow: The 2G or low-speed 3G service such as UMTS, TD-SCDMA, CDMA2000-1xRTT, EDGE, GPRS, or GSM is running. · Off: No LTE service is running. |
|
GPS |
· Steady green: The GPS service is running. · Off: No GPS service is running. |
|
CNDE |
· Steady green: The module is operating correctly and is not sending or receiving data. · Flashing green: The module is operating correctly and is sending or receiving data. · Steady yellow: The module is faulty. · Off: The module is not installed securely, or no power is present. |
Antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods
For more information about SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK interface module antennas, interface cables, and the connection methods, see "4G interface" and "GPS interface."
Installing a Micro SIM card
|
CAUTION: Make sure the beveled corner of the Micro SIM card is oriented as indicated by the Micro SIM card icon. |
The SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK has two Micro SIM card slots. The two slots can operate simultaneously. The SIM1 slot uses M0 and M1 antenna ports. M0 is the primary antenna port and M1 is the auxiliary antenna port. The SIM2 slot uses M2 and M3 antenna ports. M2 is the primary antenna port and M3 is the auxiliary antenna port. You must connect an antenna to the primary antenna port. An auxiliary antenna only cannot guarantee reliable connectivity. If the primary antenna fails, replace it immediately.
On the SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK interface module, the space between adjacent antenna ports is insufficient for two antennas. To install 4G antennas for two adjacent ports, use a 4G antenna extension cable to connect one of the antennas.
To install a Micro SIM card:
1. Use a Phillips screwdriver to remove the two screws on the SIM card retainer cover.
2. Lift the cover up and away from the retainer.
3. Insert SIM cards into the SIM card slots on the retainer.
4. Reattach the retainer cover and use the two screws to secure the cover.
5. Execute the display cellular [ interface-number ] command after the router is started. If "SIM Status = OK" is displayed in the output information, the Micro SIM card is identified.
Figure 57 Installing Micro SIM cards
WLAN interface modules
· SIC-AP220
· SIC-AP320
SIC-AP220
|
CAUTION: The SIC-AP220 WLAN interface module is not hot swappable. |
Introduction
The SIC-AP220 WLAN interface module receives and sends wireless data. Two external antennas can be installed on the module. The module supports the 802.11a/b/g/n/ac standard and can operate on both the 2.4 G and 5G frequency bands.
Interface specifications
Table 79 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
Two: one for the FE port and one for the console port |
|
Interface standard |
FE port: 802.3/802.3u, 10/100Mbps autosensing, full/half duplex Console port: RS/EIA-232 Radio interface: Radio 1 operates on the 5 GHz frequency band and supports the 1×1 MIMO technology. Radio 2 operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band and support the 2×2 MIMO technology. |
|
Cable type |
FE port: Standard (straight-through)/cross-over Ethernet cable Console port: Console cable |
Interface LEDs
Figure 58 SIC-AP220 panel
Table 80 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
SYS |
· Steady amber: The module is starting up. · Flashing green: Only the 2.4G radio has associated clients. · Flashing amber: Only the 5G radio has associated clients. · Flashing alternatively between amber and green: Both the 2.4G and 5G radios have associated clients. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about Ethernet interface cables and the connection methods, see "Ethernet interface."
For more information about asynchronous serial port cables and the connection methods, see "Asynchronous serial ports."
For more information about WLAN interface cables and the connection methods, see "WLAN interface."
SIC-AP320
|
CAUTION: The SIC-AP320 WLAN interface module is not hot swappable. |
Introduction
The SIC-AP320 WLAN interface module receives and sends wireless data. Two external antennas can be installed on the module. The module supports the 802.11a/b/g/n/ac standard and can operate on both the 2.4 G and 5G frequency bands.
Interface specifications
Table 81 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
1 RJ-45 connector for the console port |
|
Interface standard |
Console port: RS/EIA-232 Radio interface: Radio 1 operates on the 5 GHz frequency band and supports the 2×2 MIMO technology. Radio 2 operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band and support the 1×1 MIMO technology. |
|
Cable type |
Console cable for the console port |
Interface LEDs
Figure 59 SIC-AP320 panel
Table 82 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
SYS |
· Steady amber: The module is starting up. · Flashing green: Only the 2.4G radio has associated clients. · Flashing amber: Only the 5G radio has associated clients. · Flashing alternatively between amber and green: Both the 2.4G and 5G radios have associated clients. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about asynchronous serial port cables and the connection methods, see "Asynchronous serial ports."
For more information about WLAN interface cables and the connection methods, see "WLAN interface."
M.2 riser SIC modules
RT-SIC-M2-SATA
|
CAUTION: · The RT-SIC-M2-SATA module is hot swappable. To remove an RT-SIC-M2-SATA module, first press and hold the remove button for a minimum of three seconds. You can remove the module only when the remove LED is turned off. If the remove LED is flashing green, wait for the remove LED to turn off and then remove the module. · No M.2 SSD drive is provided with the RT-SIC-M2-SATA module. Purchase one as required. · To build a redundant array of independent disks (RAID), install two SSD drives of the same size in two RT-SIC-M2-SATA modules. |
Introduction
The RT-SIC-M2-SATA module is an M.2 SSD riser SIC module that provides high data availability through RAID. RAID combines multiple physical drives into one logical drive to provide better storage performance and data backup than a single drive.
Module specifications
Table 83 Module specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Drive type |
M.2 SATA SSD |
|
Drive dimensions (D × W) |
80 × 22 mm (3.15 × 0.87 in) |
|
Number of drives |
1 |
|
RAID level |
RAID 1 |
|
Theoretical transmission rate |
1.5/3/6 Gbps |
Interface LEDs
Figure 60 RT-SIC-M2-SATA panel
Table 84 LED description
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
PWR |
Steady green |
The module has normal power input. |
|
Off |
The module does not have power input. |
|
|
SSD |
Steady green |
A SSD drive is present. |
|
Steady yellow |
The SSD drive is damaged. |
|
|
Off |
No SSD drive is present. |
|
|
ACT |
Flashing green (8 Hz) |
The system is reading or writing data to the drive. |
|
Off |
The system is not reading or writing data to the drive. |
|
|
REMOVE |
Flashing green (8 Hz) |
· The module is being initialized. Pressing the remove button or removing the module is not allowed. · A removal operation is being performed. |
|
Steady green |
The module is operating correctly. Pressing the remove button to remove the module is allowed. |
|
|
Off |
The module can be removed. |
Installing an SSD drive on the module
|
CAUTION: To use the RT-SIC-M2-SATA module, install an SSD drive in it. |
To install an SSD drive on the module:
1. Insert the SSD drive into the M.2 slot on the module at a 45° angle.
2. Slightly press the SSD drive until it is level with the surface of the connector.
3. Use a Phillips screwdriver to screw the SSD drive into place.
Figure 61 Installing an SSD drive
MIM
For the modular MSR series routers, a wide range of optional multiple interface modules (MIMs) are available, which provide abundant interfaces, including synchronous/asynchronous serial interface, Ethernet interface, E1/T1, ISDN BRI/PRI, audio interface, and Layer 2 switching interface.
ATM interface modules
· MIM-1ATM-OC3
MIM-1ATM-OC3
Introduction
The 1-port ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) 155 Mbps optical interface module (MIM-1ATM-OC3) provides ATM interfaces for routers and supports:
· Two frame formats: SDH STM-1 and SONET OC-3
· Scrambling in data transmission
· Both line clock (when working as DTE interface), and internal clock (when working as DCE interface)
· Three types of test measures, that is, local cell loopback, local payload loopback, and remote loopback.
Interface specifications
Table 85 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Number of interfaces |
1 |
|
Connector |
SFP/LC |
|
Interface standard |
SONET OC-3/SDH STM-1 |
|
Operating mode |
155 Mbps |
Interface LEDs
Figure 62 MIM-1ATM-OC3 panel
Table 86 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. · Off: No carrier signal is received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: An alarm indication signal (AIS), loss of frame alignment (LFA) signal, or remote alarm indication (RAI) signal is present. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
POS (SDH/SONET) interface modules
· MIM-1POS
MIM-1POS
Introduction
The 1-port SDH/SONET interface module (MIM-1POS) supports interface rates up to 155.52 Mbps (STM-1/OC-3).
The MIM-1POS can use the protocols such as PPP, Frame Relay and HDLC at the data link layer and IP at the network layer. It allows direct transmission of packets over SONET/SDH. It supports:
· Various types of transceiver modules.
· 155.52 Mbps fractional interface.
Interface specifications
Table 87 Interface specifications
|
Item |
MIM-1POS |
|
Connector |
SFP/LC |
|
Interface standard |
SONET OC-3/SDH STM-1 |
|
Number of interfaces |
1 |
|
Interface rate |
155.52 Mbps |
Interface LEDs
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. · Off: No carrier signal is received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: An alarm indication signal (AIS), loss of frame alignment (LFA) signal, or remote alarm indication (RAI) signal is present. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
E1/T1 interface modules
· MIM-1E1
· MIM-2E1
· MIM-4E1
· MIM-1E1-F
· MIM-2E1-F
· MIM-4E1-F
· MIM-8E1
· MIM-8E1-F
· MIM-2T1
· MIM-4T1-F
MIM-1E1/MIM-2E1/MIM-4E1/MIM-1E1-F/MIM-2E1-F/MIM-4E1-F
Introduction
The 1-/2-/4-port channelized E1/PRI interface module (MIM-1E1/MIM-2E1/MIM-4E1) transmits, receives, and processes E1 data traffic. In addition, you can use the module for other purposes, such as CE1 access and the ISDN PRI function.
· MIM-1E1-F/MIM-2E1-F/MIM-4E1-F
The MIM-1E1-F/MIM-2E1-F/MIM-4E1-F module is different from the MIM-1E1/MIM-2E1/MIM-4E1 module in the sense that:
¡ The FE1 operating mode supported by the E1-F modules allows only one n No 64 kbps bundle to be formed on each interface, where n = 1 to 31. However, an E1 module allows arbitrary grouping of 31 channels and multiple bundles.
¡ The E1-F modules do not support PRI mode.
Interface specifications
Table 89 Interface specifications
|
Item |
MIM-1E1/1E1-F module |
MIM-2E1/2E1-F module |
MIM-4E1/4E1-F module |
|
|
Connector |
DB-15 |
DB-15 |
DB-25 |
|
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
2 |
1 |
|
|
Interface standard |
· G.703 · G.704 |
|||
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
|||
|
Cable type |
· E1 75-ohm unbalanced coaxial cable · E1 120-ohm balanced twisted pair cable · 120-ohm 4E1 conversion cable (MIM-4E1/MIM-4E1-F modules) · 75-ohm 4E1 conversion cable (MIM-4E1/MIM-4E1-F modules) · Coaxial connector, network interface connector and 75-ohm to 120-ohm adapter (with BNC connector) |
|||
|
Operating mode |
· E1, CE1, ISDN PRI (only supported by MIM-1E1/MIM-2E1/MIM-4E1) · FE1 (only supported by MIM-1E1-F/MIM-2E1-F/MIM-4E1-F) |
|||
|
Supported service |
· Backup · Terminal access service · ISDN PRI (only supported by MIM-1E1/MIM-2E1/MIM-4E1) |
|||
Interface LEDs
MIM-1E1 and MIM-1E1-F panels are similar. The following figure illustrates an MIM-1E1 panel.
Figure 64 MIM-1E1 panel
The panels of MIM-2E1 and MIM-2E1-F are similar. The following figure illustrates an MIM-2E1 panel.
Figure 65 MIM-2E1 panel
MIM-4E1 and MIM-4E1-F panels are similar. The following figure illustrates an MIM-4E1 module.
Figure 66 MIM-4E1 panel
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: The link is not set up. · On: The link has been set up. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received; · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connections methods, see "E1 interface."
MIM-8E1/MIM-8E1-F
Introduction
· MIM-8E1 module
The 8-port channelized E1/PRI interface module (MIM-8E1) transmits, receives, and processes eight channels of E1 data traffic. In addition, you can use the module for other purposes, such as CE1 access and the ISDN PRI function.
· MIM-8E1-F module
The 8-port fractional E1 interface module (MIM-8E1-F) is different from the MIM-8E1 module in the sense that:
¡ The FE1 operating mode supported by the MIM-8E1-F module allows only one n No 64 kbps bundle to be formed on each interface, where n = 1 to 31. However, an MIM-8E1 module allows arbitrary grouping of 31 channels and therefore multiple bundles.
¡ The MIM-8E1-F module does not support PRI mode.
|
|
NOTE: For a MIM-8E1 module, the system automatically creates a serial interface for each timeslot bundle formed on a controller E1 interface. |
Interface specifications
Table 91 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
D68 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
G.703 |
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
75-ohm 8E1 conversion cable |
|
Cable characteristic impedance |
75-ohm |
|
Operating mode |
· E1, CE1, ISDN PRI (only supported by MIM-8E1) · FE1 (only supported by MIM-8E1-F) |
|
Supported service |
· Backup · Terminal access service · ISDN PRI (only supported by MIM-8E1) |
Interface LEDs
MIM-8E1 and MIM-8E1-F panels are similar.
Figure 67 MIM-8E1 (75-ohm) panel
Figure 68 MIM-8E1-F (75-ohm) panel
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: The link is not set up. · On: The link has been set up. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received; · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connections methods, see "E1 interface."
MIM-2T1/MIM-4T1-F
Introduction
The 2-port channelized T1/PRI interface module (MIM-2T1) serves to transmit/receive and handle T1 data streams, provide CT1 access, and fulfill the function of ISDN PRI. Thereby, one module can be used for multiple purposes.
The 4-port fractional T1 interface module (MIM-4T1-F) provides the following features:
¡ FT1 operating mode supported by T1-F modules allows only one bundle. In other words, the time slots can only be bundled into one n x 64 kbps or 56 kbps channel, where n=1-24.
¡ T1-F does not support PRI mode.
|
|
NOTE: For a MIM-1T1 module, the system automatically creates a serial interface for each timeslot bundle formed on a controller T1 interface. |
Interface specifications
Table 93 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
||
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
|
|
Number of connectors |
· 2 (MIM-2T1 module) · 4 (MIM-4T1-F module) |
|
|
|
Interface standard |
· G.703/T1.102 · G.704 · AT & T TR 54016 · AT & T TR 62411 · ANSI T1.403 |
|
|
|
Interface rate |
1.544 Mbps |
|
|
|
Cable type |
T1 cable (100-ohm shielding network cable) |
|
|
|
Operating mode |
· CT1/ISDN PRI (MIM-2T1 module) · FT1 (MIM-4T1-F module) |
|
|
|
Supported service |
· Backup · Terminal access service · ISDN PRI (MIM-2T1 module) |
|
|
Interface LEDs
Figure 69 MIM-2T1 panel
Figure 70 MIM-4T1-F panel
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted or/and received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: No cable is connected to the interface, the cable is damaged or not connected correctly, or the peer device is faulty. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about T1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "T1 interface."
E3/T3 interface modules
· MIM-1CE3
MIM-1CE3
Introduction
The 1-port channelized E3 interface module (MIM-1CE3) serves to:
· Transmit/Receive and handle one channel of E3 fast traffic, as well as provide the accessing of E3 traffic when working in E3 mode.
· Provide the low-speed accessing service at the speed of n No 64 kbps, where n is smaller than or equal to 128, when working in CE3 mode.
|
|
NOTE: E3 represents the tertiary group rate of E system in the TDM system, that is, 34.368 Mbps. An E3 channel can be channelized into 16 E1 lines through the demultiplexing processes of E23 and E12, each E1 line supporting both the operating modes of E1 and CE1. E23 is used to indicate either E2-to-E3 multiplex or E3-to-E2 demultiplex, and E12 to indicate E1-to-E2 multiplex or E2-to-E1 demultiplex. "E23" and "E12" discussed here represent the demultiplex process. |
Interface specifications
Table 95 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
SMB |
|
Number of connectors |
2 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703 · G.704 · G.751 |
|
Interface rate |
34.368 Mbps |
|
Interface cable type |
E3 cable (75ohm coaxial cable) |
|
Operating mode |
E3 CE3 |
|
Supported service |
E3 leased line |
Interface LEDs
Figure 71 MIM-1CE3 panel
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: The link is not set up. · On: The link has been set up. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received; · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E3 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E3/T3 interface."
Serial interface modules
· MIM-2SAE
· MIM-4SAE
· MIM-8SAE
· MIM-8ASE
· MIM-16ASE
MIM-2SAE/MIM-4SAE/MIM-8SAE
Introduction
The MIM-2SAE/MIM-4SAE/MIM-8SAE stands for 2/4/8-port enhanced high-speed synchronous/asynchronous serial interface module. In terms of function, SAE modules are the same as SA modules except that SAE modules support more protocols, for example, RS449, X.21, and RS530.
Interface specifications
Table 97 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Synchronous |
Asynchronous |
|
|
Connector |
D28 |
||
|
Number of connectors |
2 (MIM-2SAE) 4 (MIM-4SAE) 8 (MIM-8SAE) |
||
|
Interface standard and operating mode |
V.24 |
V.35, RS449, X.21, RS530 |
RS-232 |
|
DTE, DCE |
DTE, DCE |
||
|
Minimum baud rate (bps) |
1200 |
1200 |
300 |
|
Maximum baud rate (bps) |
64 k |
2.048 M |
115.2 |
|
Cable |
· V.24 (RS-232) DTE cable · V.24 (RS-232) DCE cable · V.35 DTE cable · V.35 DCE cable · X.21 DTE cable · X.21 DCE cable · RS449 DTE cable · RS449 DCE cable · RS530 DTE cable · RS530 DCE cable |
||
|
Supported service |
· DDN leased line · Terminal access service |
· Dialup through modems · Backup · Asynchronous leased line · Dumb terminal access |
|
Interface LEDs
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: No link is present; · On: A link is present. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received; · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
The MIM-8SAE module provides a LED for each channel. When the LED is on, a link is present. When the LED is flashing, data is being transmitted or received.
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about synchronous/asynchronous serial port cables and the connection methods, see "Synchronous/asynchronous serial ports."
MIM-8ASE/MIM-16ASE
Introduction
The 8/16-port enhanced asynchronous serial interface module (MIM-8ASE/MIM-16ASE) transmits/receives and handles asynchronous serial interface data streams. ASE modules, however, use RJ-45 connectors and AUX cables.
Interface specifications
Table 99 Interface specifications
|
Item |
MIM-8ASE module |
MIM-16ASE module |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
|
Number of connectors |
8 (MIM-8ASE) 16 (MIM-16ASE) |
|
|
Interface standard and operating mode |
RS-232 |
|
|
Cable |
· AUX cable · Ethernet straight-through cable · MIM-8ASE/MIM-16ASE dumb terminal cable |
|
|
Minimum baud rate (bps) |
300 |
|
|
Maximum baud rate (bps) |
115.2 k |
|
|
Service supported |
· Dialup through Modem · Backup · Terminal access service · Asynchronous leased line service |
|
Interface LEDs
Each channel on the MIM-8ASE/MIM-16ASE has only one LED.
Table 100 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Off: No link is present; · On: A link is present. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted or received. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about asynchronous serial port cables and the connection methods, see "Asynchronous serial ports."
POS terminal access interface modules
· MIM-6FCM
Introduction
The 6-port fast connect modem interface module (FIC-6FCM) provides services for point of sale (POS) terminal devices to fast dial up to a bank card accounting system.
|
|
NOTE: The point of sale (POS) access service refers to a type of smart card service widely used in places such as shopping malls and gasoline service stations. It links a POS terminal device located in a shopping mall or a gasoline service station to a bank card accounting system to provide services. |
Interface specifications
Table 101 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
6 |
|
Cable |
Telephone cable with ferrite core |
|
Supported protocols |
· ITU-T-V.22 (PSK/QPSK) · V.22 BIS (QAM) |
Interface LEDs
Figure 77 MIM-6FCM panel
Each connector of the POS access port has two LEDs: carrier detect (CD) and ACT.
Table 102 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
CD |
· Off: No carrier signals are detected. · On: A carrier signal is detected. |
|
ACT |
· Flashing: Data is being received or transmitted. · Off: No data is being received or transmitted. |
Interface cable
The MIM-6FCM uses telephone cables with ferrite core.
|
|
NOTE: The standard equipment package for the MIM-6FCM includes the appropriate number of interface cables. |
Connecting the interface cable
|
CAUTION: · Before connecting a port, read its label carefully. A wrong connection might damage the interface module or the device. · Add a special lightning arrester at the input end of the telephone cable for better protection. |
To connect the interface cable:
1. Connect one end of a telephone cable to the RJ-11 or RJ-45 connector of the FCM interface.
2. Connect the other end of the telephone cable to the PSTN network.
3. Check the LED on the MIM-6FCM panel. When the LED is on, the self-test succeeds. The LED is off, the self-test failed. In the latter case, contact your agent.
Upgrading the FCM module software
1. Download the FCM module software to the CF module or flash of the router.
2. After the router that is inserted with the FCM module is powered on and starts up, input bootrom update file cfa0:/ filename slot slotnum all in the user mode to upgrade FCM module software.
3. Run the display version command to display the driver version. If the version number is changed, the upgrade is completed.
The driver version number is just like (Driver) 1.0 in the module information displayed as follows:
[SLOT 5]MIM-6FCM (Hardware)1.0, (Driver)1.0, (Cpld)1.0
Voice interface modules
· MIM-4FXS
· MIM-4FXO
· MIM-8FXS8FXO
· MIM-16FXS
· MIM-4E&M
· MIM-2VE1
· MIM-2VT1
· MIM-1VE1
· MIM-1VT1
MIM-8FXS8FXO
Introduction
The 8-port voice subscriber circuit and 8-port voice AT0 analog trunk interface module (MIM-8FXS8FXO) serves to access and handle 16 channels of analog voice signals over data communication networks. The module provides eight FXS interfaces and eight FXO interfaces:
· FXS interfaces are analog subscriber line interfaces that provide ordinary analog telephone and fax access and also can connect AT0 loop trunks of exchanges.
· FXO interfaces are loop trunk interfaces that provide access of common subscriber lines of exchanges.
|
CAUTION: While using MIM-8FXS8FXO, make sure the device can be connected to IP networks or other WANs. |
Interface specifications
Table 103 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-11 |
|
Number of connectors |
· 8 (FXS interfaces) · 8 (FXO interfaces) |
|
Interface standard |
· Subscriber circuit interface (FXS) compliant with ITU Q.512. · Loop trunk interface (FXO) compliant with ITU Q.552. · Over-current and over-voltage protection compliant with ITU K.20. |
|
Cable type |
Telephone cable with ferrite core |
|
Dial-up mode |
DTMF, compliant with GB3378 (Pulse dial-up is not available.) |
|
Bandwidth |
300 to 3400 Hz |
Interface LEDs
Figure 78 MIM-8FXS8FXO panel
Table 104 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Off: No link is present. · Steady green: A link is present and a call connection is being established. · Flashing yellow: A link is present and there is a call activity. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about FXS/FXO interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
MIM-16FXS
Introduction
The 16-port loop trunk interface module (MIM-16FXS) serves to access and handle 16 channels of analog voice signals over data communication networks. The module provides 16 FXS interfaces:
FXS interfaces are analog subscriber line interfaces that provide ordinary analog telephone and fax access and also can connect AT0 loop trunks of exchanges.
Interface specifications
Table 105 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-11 |
|
Number of connectors |
16 (FXS interfaces) |
|
Interface standard |
Subscriber circuit interface (FXS) compliant with ITU Q.512. Over-current and over-voltage protection compliant with ITU K.20. |
|
Cable type |
Telephone cable with ferrite core |
|
Dial-up mode |
DTMF, compliant with GB3378 (Pulse dial-up is not available.) |
|
Bandwidth |
300 to 3400 Hz |
Interface LEDs
Figure 79 MIM-16FXS panel
Table 106 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Off: No link is present. · Steady green: A link is present and a call connection is being established. · Flashing yellow: A link is present and there is a call activity. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about FXS interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
MIM-2VE1
Introduction
The 2-port E1 voice interface module (MIM-2VE1) handles dense voice signals in a VoIP system. It provides two CE1/PRI/R2 ports, allowing the access of 60 channels of voice signals.
Interface specifications
Table 107 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
D15 |
|
Number of connectors |
2 |
|
Operating mode |
CE1 ISDN PRI R2 |
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
|
Cable |
E1 120-ohm balanced twisted pair cable 75ohm-to-120ohm adapter |
|
Supported service |
· R2 signaling · DSS1 signaling · IP Fax · General VoIP features in Comware |
Interface LEDs
Figure 80 MIM-2VE1 panel
Table 108 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received on the interface. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted and/or received. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E1 interface."
MIM-2VT1
Introduction
The 2-port T1 voice interface module (MIM-2VT1) can handle dense voice signals in VoIP system. It provides two CT1/PRI ports, allowing the access of 48 channels of voice signals.
Interface specifications
Table 109 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connector |
2 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703/T1.102 · G.704 · AT & T TR 54016 · AT & T TR 62411 · ANSI T1.403 |
|
Interface rate |
1.544 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
T1 cable (100-ohm standard shielded cable) |
|
Operation mode |
· CT1 · ISDN PRI |
|
Services |
· Backup · Terminal access · ISDN |
Interface LEDs
Figure 81 MIM-2VT1 panel
Table 110 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received on the interface. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted and/or received. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about T1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "T1 interface."
MIM-1VE1
Introduction
The 1-port E1 voice interface module (MIM-1VE1) can handle dense voice signals in VoIP system. It provides a CE1/PRI/R2 port, allowing the access of 30 channels of voice signals.
Interface specifications
Table 111 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
D15 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Operating mode |
CE1 ISDN PRI R2 |
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
|
Cable |
E1 120-ohm balanced twisted pair cable 75-ohm-to-120-ohm adapter (with BNC connector) |
|
Supported service |
· R2 signaling · DSS1 signaling · IP Fax · General VoIP features in Comware |
Interface LEDs
Figure 82 MIM-1VE1 panel
Table 112 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received on the interface. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted and/or received. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E1 interface."
MIM-1VT1
Introduction
The 1-port T1 voice interface module (MIM-1VT1) can handle dense voice signals in VoIP system.
The MIM-1VT1 module is structured in the form of board plus VCPM module plus VPM strip. It provides a CT1/PRI port, allowing the access of 24 channels of voice signals.
Interface specifications
Table 113 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connector |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703/T1.102 · G.704 · AT & T TR 54016 · AT & T TR 62411 · ANSI T1.403 |
|
Interface rate |
1.544 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
T1 cable (100-ohm standard shielded cable) |
|
Operation mode |
CT1 ISDN PRI |
|
Services |
Backup Terminal access ISDN |
Interface LEDs
Figure 83 MIM-1VT1 panel
Table 114 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received on the interface. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted and/or received. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about T1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "T1 interface."
MIM-4FXS/MIM-4FXO
Introduction
· The 4-port voice subscriber circuit interface module (MIM-4FXS) serves to access and handle 4 channels of ordinary analog phone, fax, or AT0 loop trunk of telephone exchange.
· The 4-port voice AT0 analog trunk interface module (MIM-4FXO) serves to access and handle 4 channels of common user lines of telephone exchange.
These modules make it possible to transfer voice signals over data communication networks.
Interface specifications
Table 115 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
4 |
|
Cable |
· Telephone cable with ferrite core · E&M trunk (for E&M module, which should be made by users depending on the actual needs at the site.) |
|
Interface standard |
· ITU Q.512-compliant subscriber circuit interface (MIM-4FXS) · ITU Q.552-compliant loop trunk interface (MIM-4FXO) · ITU K.20-compliant overcurrent and overvoltage protection |
|
Dial-up mode |
DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) but not pulse dial-up |
|
Bandwidth |
300 Hz to 3400 Hz |
Interface LEDs
Figure 84 MIM-4FXS panel
Figure 85 MIM-4FXO panel
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. |
|
ACT |
· Off: The channel is idle. · On: There is call activity. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about FXS/FXO interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
MIM-4E&M
Introduction
The 4-port voice E&M analog trunk interface module (MIM-4E&M) serves to access and handle 2/4 channels of E&M analog trunks.
These modules make it possible to transfer voice signals over data communication networks.
Interface specifications
Table 117 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
4 |
|
Cable |
· Telephone cable with ferrite core · E&M trunk (for E&M module, which should be made by users depending on the actual needs at the site.) |
|
Interface standard |
· G.712-compliant E&M trunk interface, E&M interface (supporting Bell type I, II, III, V, and support 4-wire). · ITU K.20-compliant overcurrent and overvoltage protection |
|
Dial-up mode |
DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) but not pulse dial-up |
|
Bandwidth |
300 Hz to 3400 Hz |
Interface LEDs
Figure 86 MIM-4E&M panel
Table 118 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. |
|
ACT |
· Off: The channel is idle. · On: There is call activity. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E&M interface cables and the connection methods, see "E&M interface."
HMIMs/DHMIMs
For the modular MSR series routers, a wide range of optional high-performance multiplex interface modules (HMIMs) and double high-performance multiplex interface modules (DHMIMs) are available, which provide abundant interfaces, including synchronous/asynchronous serial interface, Ethernet interface, E1/T1, ISDN BRI/PRI, audio interface, and Layer 2 switching interface.
Ethernet switching modules
· HMIM-8GSW
· HMIM-24GSW
· HMIM-24GSW-PoE
· HMIM-8GSWF
HMIM-8GSW/HMIM-24GSW/HMIM-24GSW-PoE
Introduction
The HMIM-8GSW/HMIM-24GSW/HMIM-24GSW-PoE module is an 8/24/24 1000 Mbps Ethernet Layer 2 switching HMIM interface module. Each HMIM-8GSW/HMIM-24GSW module provides 8/24 1000 Mbps RJ-45 ports. HMIM-8GSW/HMIM-24GSW modules are suitable for a small enterprise network to act as a switching and routing device, which can be directly connected to PCs and network devices of the enterprise. The HMIM-24GSW-PoE can supply power to remote PDs.
The HMIM-8GSW/HMIM-24GSW/HMIM-24GSW-PoE supports the following functions:
· A transmission distance of 100 m (328.08 ft) over a category-5 twisted pair cable (crossover or straight-through cable).
· 1000 Mbps wire-speed forwarding between any two ports connected with a category-5 twisted pair cable (crossover or straight-through cable).
· Autosensing at a rate of 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 1000 Mbps.
· Full duplex (typically used) and half duplex operating modes.
Interface specifications
Table 119 describes the interface specifications of the HMIM-8GSW, HMIM-24GSW, and HMIM-24GSW-PoE interface modules. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 119 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
|
Interface type |
MDI/MDIX |
|
Number of connectors |
· 8 (HMIM-8GSW) · 24 (HMIM-24GSW and HMIM-24GSW-PoE) |
|
Cable type |
Standard (straight-through) Ethernet cable/crossover Ethernet cable |
|
Operation mode |
Autosensing 10/100/1000 Mbps, full duplex/half duplex |
|
|
NOTE: Ethernet interfaces on network adapters are usually medium dependent interfaces (MDIs). Cross medium dependent interfaces (MDIXs) are another type of Ethernet interfaces, which are usually used on hubs and LAN Switches. |
Interface LEDs
Figure 87 HMIM-8GSW panel
Figure 88 HMIM-24GSW panel
Figure 89 HMIM-24GSW-PoE panel
Each 1000 Mbps Ethernet interface on the panel has one LED.
Table 120 LED description
|
LED status |
Description |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
|
Steady green |
A 1000 Mbps link is present. |
|
Flashing green |
The port is sending and receiving data at 1000 Mbps. |
|
Steady yellow |
A 10/100 Mbps link is present. |
|
Flashing yellow |
The port is sending and receiving data at 10/100 Mbps. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about the Ethernet interface cables and the connection methods, see "Ethernet interface."
HMIM-8GSWF
Introduction
The 8-port 100/1000 Mbps Ethernet Layer 2/Layer 3 HMIM interface module HMIM-8GSWF provides four SFP fiber ports and four combo interfaces. It is designed for a switching/routing integrated device on a small-sized enterprise network. You can connect it to network devices inside the network.
Functions supported by interface modules are as follows:
· Various types of transceiver modules.
· Operating speeds of 1000 Mbps and 100 Mbps.
· Full duplex operating mode.
Interface specifications
Table 121 describes the interface specifications of the HMIM-8GSWF interface module. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 121 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Number of ports |
8 |
|
Connector type |
SFP/LC/RJ-45 |
|
Interface standard |
· 802.3 · 802.3u · 802.3ab |
|
Operation mode |
100/1000 Mbps, full duplex |
Interface LEDs
Figure 90 HMIM-8GSWF panel
Table 122 SFP fiber port LED description
|
LED status |
Description |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
|
Steady green |
A 1000 Mbps link is present. |
|
Flashing green |
The port is sending and receiving data at 1000 Mbps. |
|
Steady yellow |
A 100 Mbps link is present. |
|
Flashing yellow |
The port is sending and receiving data at 100 Mbps. |
Table 123 RJ-45 port LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
Green LED |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A 1000 Mbps link is present. · Flashing: The port is sending and receiving data at 1000 Mbps. |
|
Yellow LED |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A100 Mbps link is present. · Flashing: The port is sending and receiving data at 100 Mbps. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
Ethernet interface modules
· HMIM-2GEE
· HMIM-4GEE
· HMIM-8GEE
· RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2
· RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2
· HMIM-2GEF
· HMIM-4GEF
· HMIM-8GEF
· RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2
· RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2
· RT-HMIM-4XP
HMIM-2GEE/HMIM-4GEE/HMIM-8GEE
Introduction
The HMIM-GEE module is used to complete the communication between a router and a LAN, which includes the following types:
· HMIM-2GEE—2-port 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T Ethernet copper interface module
· HMIM-4GEE—4-port 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T Ethernet copper interface module
· HMIM-8GEE—8-port 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T Ethernet copper interface module
The HMIM-2GEE/HMIM-4GEE/HMIM-8GEE supports:
· 100 m (328.08 ft) of transmission distance over a category-5 twisted-pair cable.
· Operation at 10/100/1000 Mbps and autosensing.
· Full duplex and half-duplex, autonegotiation.
Interface specifications
Table 124 describes the interface specifications of the HMIM-2GEE, HMIM-4GEE, and HMIM-8GEE interface modules. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 124 Interface specifications
|
Item |
HMIM-2GEE |
HMIM-4GEE |
HMIM-8GEE |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
||
|
Number of connectors |
2 |
4 |
8 |
|
Interface type |
MDI/MDIX |
||
|
Interface standard |
· 802.3 · 802.3u · 802.3ab |
||
|
Supported cable |
Ethernet cable |
||
|
Operating mode |
· 10/100/1000 Mbps, autosensing · Full duplex/half-duplex, autonegotiation |
||
Interface LEDs
Figure 91 HMIM-2GEE panel
Figure 92 HMIM-4GEE panel
Figure 93 HMIM-8GEE panel
Table 125 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
Green LED |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A 1000 Mbps link is present. · Flashing: The port is sending and receiving data at 1000 Mbps. |
|
Yellow LED |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A 10/100 Mbps link is present. · Flashing: The port is sending and receiving data at 10/100 Mbps. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about the Ethernet interface cables and the connection methods, see "Ethernet interface."
RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2/RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2
|
CAUTION: The RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2/RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2 module is hot swappable. To remove it, first press and hold the remove button until the RUN LED is off. |
Introduction
The 4/8-port 10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T Ethernet copper interface module (RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2/RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2) is used to complete the communication between a router and a LAN.
The RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2/RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2 supports:
· 100 m (328.08 ft) of transmission distance over a category-5 twisted-pair cable.
· Operation at 10/100/1000 Mbps and autosensing.
· Full duplex and half-duplex, autonegotiation.
Interface specifications
Table 126 describes the interface specifications of the RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2 and RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2 interface modules. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 126 Interface specifications
|
Item |
RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2 |
RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2 |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
|
|
Number of connectors |
4 |
8 |
|
Interface type |
MDI/MDIX |
|
|
Interface standard |
· 802.3 · 802.3u · 802.3ab |
|
|
Supported cable |
Ethernet cable |
|
|
Operating mode |
· 10/100/1000 Mbps, autosensing · Full duplex/half-duplex, autonegotiation |
|
Interface LEDs
Figure 94 RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2 panel
Figure 95 RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2 panel
Table 127 LED description
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
Green |
A 1000 Mbps link is present on the port. |
|
Flashing green |
The port is sending and receiving data at 1000 Mbps. |
|
|
Yellow |
A 10/100 Mbps link is present on the port. |
|
|
Flashing yellow |
The port is sending and receiving data at 10/100 Mbps. |
|
|
Off |
No link is present on the port. |
|
|
RUN |
Steady green |
The interface module is operating correctly. You cannot remove it. |
|
Off |
The interface module is not recognized and you can remove it, or the interface module has been removed. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about the Ethernet interface cables and the connection methods, see "Ethernet interface."
HMIM-2GEF/HMIM-4GEF/HMIM-8GEF
Introduction
The HMIM-GEF module is used to complete the communication between a router and a LAN, which includes the following types:
· HMIM-2GEF—2-port 1000BASE-SX/1000BASE-LX Ethernet fiber interface module
· HMIM-4GEF—4-port 1000BASE-SX/1000BASE-LX Ethernet fiber interface module
· HMIM-8GEF—8-port 1000BASE-SX/1000BASE-LX Ethernet fiber interface module
The HMIM-2GEF/HMIM-4GEF/HMIM-8GEF supports:
· Various types of transceiver modules.
· Operation at 1000 Mbps.
· Full duplex.
Interface specifications
Table 128 describes the interface specifications of the HMIM-2GEF, HMIM-4GEF, and HMIM-8GEF interface modules. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 128 Interface specifications
|
Item |
HMIM-2GEF |
HMIM-4GEF |
HMIM-8GEF |
|
Number of connectors |
2 |
4 |
8 |
|
Connector type |
SFP/LC |
||
|
Interface standard |
· 802.3 · 802.3u · 802.3ab |
||
|
Operating mode |
· 1000 Mbps · Full duplex |
||
Interface LEDs
Figure 96 HMIM-2GEF panel
Figure 97 HMIM-4GEF panel
Figure 98 HMIM-8GEF panel
Table 129 LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Steady green |
A 1000 Mbps link is present. |
|
Flashing green |
Data is being transmitted and/or received at 1000 Mbps. |
|
Steady yellow |
A 100 Mbps link is present. |
|
Flashing yellow |
Data is being transmitted and/or received at 100 Mbps. |
|
Off |
No link is present on the port. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2/RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2
|
CAUTION: The RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2/RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2 module is hot swappable. To remove it, first press and hold the remove button until the RUN LED is off. |
Introduction
The 4/8-port 1000Base-SX/1000Base-LX Ethernet fiber interface module (RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2/RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2) is used to complete the communication between a router and a LAN.
The RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2/RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2 supports:
· Various types of transceiver modules.
· Operation at 1000 Mbps.
· Full duplex.
Interface specifications
Table 130 describes the interface specifications of the RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2 and RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2 interface modules. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 130 Interface specifications
|
Item |
RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2 |
RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2 |
|
Number of connectors |
4 |
8 |
|
Connector type |
SFP/LC |
|
|
Interface standard |
· 802.3 · 802.3u · 802.3ab |
|
|
Operating mode |
· 1000 Mbps · Full duplex |
|
Interface LEDs
Figure 99 RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2 panel
Figure 100 RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2 panel
Table 131 LED description
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
Green |
A 1000 Mbps link is present on the port. |
|
Flashing green |
The port is sending and receiving data at 1000 Mbps. |
|
|
Yellow |
A 100 Mbps link is present on the port. |
|
|
Flashing yellow |
The port is sending and receiving data at 100 Mbps. |
|
|
Off |
No link is present on the port. |
|
|
RUN |
Steady green |
The interface module is operating correctly. You cannot remove it. |
|
Off |
The interface module is not recognized and you can remove it, or the interface module has been removed. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
RT-HMIM-4XP
|
CAUTION: The RT-HMIM-4XP interface module is hot swappable. To remove it, first press and hold the remove button until the RUN LED is off. |
Introduction
The RT-HMIM-4XP is a 10GBASE-R Ethernet interface module that provides four SFP+ ports. Each port is a Layer 3 service port. The RT-HMIM-4XP module supports SFP transceiver modules and 10 Gbps SFP+ transceiver modules.
Interface specifications
Table 132 describes the interface specifications of the RT-HMIM-4XP interface module. For information about link mode of the interfaces, see "Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules."
Table 132 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Number of interfaces |
4 |
|
Connector |
SFP+/LC |
|
Interface standard |
10GBASE-R |
|
Interface rate and duplex mode |
1000 Mbps/10 Gbps autosensing, full duplex |
Interface LEDs
Figure 101 RT-HMIM-4XP panel
Table 133 LED description
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
RUN |
Steady green |
The interface module is operating correctly. |
|
Off |
The interface module is not recognized. |
|
|
LINK/ACT |
Steady green |
A 10 Gbps link is present on the port. |
|
Flashing green (12 Hz) |
Data is being transmitted and/or received at 10 Gbps on the port. |
|
|
Steady yellow |
A 1000 Mbps link is present on the port. |
|
|
Flashing yellow (12 Hz) |
Data is being transmitted and/or received at 1000 Mbps on the port. |
|
|
Off |
No link is present on the port. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
ATM interface modules
· HMIM-1ATM-OC3
HMIM-1ATM-OC3
Introduction
The 1-port ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) 155 Mbps optical interface module (HMIM-1ATM-OC3) provides ATM interfaces for routers and supports the following features:
· Two frame formats: SDH STM-1 and SONET OC-3
· Scrambling in data transmission
· Both line clock (when working as DTE interface), and internal clock (when working as DCE interface)
· Three types of test measures: local cell loopback, local payload loopback, and remote loopback.
Interface specifications
Table 134 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Number of interfaces |
1 |
|
Connector |
SFP/LC |
|
Interface standard |
· SONET OC-3 · SDH STM-1 |
|
Operating mode |
155 Mbps |
Interface LEDs
Figure 102 HMIM-1ATM-OC3 panel
Table 135 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. · Off: No carrier signal is received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: An alarm is present. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
POS (SDH/SONET) interface modules
· HMIM-1POS
· RT-HMIM-2POS-STM1
· RT-HMIM-4POS-STM1/4
HMIM-1POS
Introduction
The 1-port SDH/SONET interface module (HMIM-1POS) supports interface rates up to 155.52 Mbps (STM-1/OC-3).
The HMIM-1POS can use the protocols such as PPP, Frame Relay, and HDLC at the data link layer and IP at the network layer. It allows direct transmission of packets over SONET/SDH.
The HMIM-1POS provides 155.52 Mbps fractional interface and supports various types of transceiver modules.
Interface specifications
Table 136 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Interface standard |
SONET OC-3/SDH STM-1 |
|
Number of interfaces |
1 |
|
Connector type |
SFP/LC |
|
Interface rate |
155.52 Mbps |
Interface LEDs
Figure 103 HMIM-1POS front panel
Table 137 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. · Off: No carrier signal is received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: An alarm is present. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
RT-HMIM-2POS-STM1
|
CAUTION: The RT-HMIM-2POS-STM1 module is hot swappable. To remove it, first press and hold the remove button until the RUN LED is off. |
Introduction
The RT-HMIM-2POS-STM1 2-port SDH/SONET interface module provides an interface transmission rate of 155.52 Mbps (STM-1/OC-3).
The RT-HMIM-2POS-STM1 module supports the PPP, Frame Relay, and HDLC protocols at the data link layer and the IP protocol at the network layer. It allows direct transmission of packets over SONET/SDH.
The RT-HMIM-2POS-STM1 module provides 155.52 Mbps fractional interface and supports various types of transceiver modules.
Interface specifications
Table 138 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Interface standard |
SONET OC-3/SDH STM-1 |
|
Number of interfaces |
2 |
|
Connector type |
SFP/LC |
|
Interface rate |
155.52 Mbps |
Interface LEDs
Figure 104 RT-HMIM-2POS-STM1 front panel
Table 139 LED description
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
ACT/ALM |
Steady green |
A 155.52 Mbps link is present on the port. |
|
Flashing green |
Data is being transmitted and/or received at 155.52 Mbps on the port. |
|
|
Steady red |
An alarm has occurred on the port. |
|
|
Off |
No transceiver module is present on the port or the port is in shutdown state. |
|
|
RUN |
Steady green |
The interface module is operating correctly. You cannot remove it. |
|
Flashing green |
The interface module is upgrading firmware. |
|
|
Steady red |
The interface module is faulty. |
|
|
Off |
The interface module is not recognized. You can remove it. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
RT-HMIM-4POS-STM1/4
|
CAUTION: The RT-HMIM-4POS-STM1/4 module is hot swappable. To remove it, first press and hold the remove button until the RUN LED is off. |
Introduction
The RT-HMIM-4POS-STM1/4 4-port SDH/SONET interface module provides an interface transmission rate of 155.52 Mbps (STM-1/OC-3) or 622.08 Mbps ( STM-4/OC-12).
The RT-HMIM-4POS-STM1/4 module supports the PPP, Frame Relay, and HDLC protocols at the data link layer and the IP protocol at the network layer. It allows direct transmission of packets over SONET/SDH.
You can use command lines to configure the POS ports on the RT-HMIM-4POS-STM1/4 module to operate at STM-1/OC-3 POS or STM-4/OC-12 POS mode. The operation mode configuration applies to the ports rather than the whole interface module.
Interface specifications
Table 140 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Interface standard |
· SONET OC-3/SDH STM-1 · SONET OC-12/SDH STM-4 |
|
Number of interfaces |
4 |
|
Connector type |
SFP/LC |
|
Interface rate |
· 155.52 Mbps · 622.08 Mbps |
Interface LEDs
Figure 105 RT-HMIM-4POS-STM1/4 front panel
Table 141 LED description
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
ACT/ALM |
Steady green |
A 155.52 or 622.08 Mbps link is present on the port. |
|
Flashing green |
Data is being transmitted and/or received at 155.52 or 622.08 Mbps on the port. |
|
|
Steady red |
An alarm has occurred on the port. |
|
|
Off |
No transceiver module is present on the port or the port is in shutdown state. |
|
|
RUN |
Steady green |
The interface module is operating correctly. You cannot remove it. |
|
Flashing green |
The interface module is upgrading firmware. |
|
|
Steady red |
The interface module is faulty. |
|
|
Off |
The interface module is not recognized. You can remove it. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
CPOS (SDH/SONET) interface modules
· HMIM-1CPOS
· HMIM-2CPOS
HMIM-1CPOS/HMIM-2CPOS
Introduction
The HMIM-1CPOS/HMIM-2CPOS is a 1-port/2-port channelized SDH/SONET interface module. C stands for channelized, and POS for Packet over SDH/SONET. The HMIM-1CPOS/HMIM-2CPOS provides one/two STM-1/OC3-compliant multi-channel interfaces and supports communication speeds up to 155.52 Mbps.
HMIM-1CPOS/HMIM-2CPOS can change between the E1 system and T1 system.
HMIM-1CPOS is inserted in an HMIM slot of a modular router and communicates with the CPU through the PCI interface to receive and transmit data on STM-1 channelized POS interface. It supports:
· Various types of transceiver modules.
· Clear channel (unframed) E1 or T1
· Fractional (framed) E1 or T1
· Up to 256 64 kbps logical channels
Interface specifications
Table 142 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
SFP/LC |
|
Number of Connectors |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
SONET OC-3/SDH STM-1 |
|
Interface rate |
155.52 Mbps |
|
IMPORTANT: If the interface receives signal over a long-haul optical fiber, make sure the transmission distance is longer than 25 km (15.53 miles). If the transmission distance is shorter than 25 km (15.53 miles), use an optical attenuator to reduce the optical power. |
Interface LEDs
Figure 106 HMIM-1CPOS front panel
Figure 107 HMIM-2CPOS front panel
Table 143 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. · Off: No carrier signal is received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: An alarm is present. |
Transceiver modules, optical fibers, and connection methods
For more information about transceiver modules, optical fibers, and the connection methods, see "Fiber port."
Interface mode switchover
You can switch the HMIM-1CPOS/HMIM-2CPOS to operate in E1 and T1 interface modes at the command line interface (CLI).
To switch the interface mode:
1. Insert the HMIM-1CPOS/HMIM-2CPOS into the HMIM slot of the router and then power on the router.
2. Use the card-mode command in system view to set the interface mode. The HMIM-1CPOS/HMIM-2CPOS module is inserted in slot 4 of the router in the following example.
# Enter system view.
<Sysname> system-view
# Set the HMIM-1CPOS/HMIM-2CPOS to operate in E1 interface mode.
[Sysname] module-mode slot 4 e1
# Set the HMIM-1CPOS/HMIM-2CPOS to operate in T1 interface mode.
[Sysname] module-mode slot 4 t1
E1/T1 interface modules
· HMIM-1E1
· HMIM-2E1
· HMIM-4E1
· HMIM-1E1-F
· HMIM-2E1-F
· HMIM-4E1-F
· HMIM-8E1
· HMIM-8E1-F
· RT-HMIM-2E1-V3
· RT-HMIM-4E1-V3
· RT-HMIM-8E1-V3
· HMIM-2T1
· HMIM-4T1-F
· HMIM-2E1T1
· HMIM-4E1T1
· HMIM-8E1T1
· HMIM-2E1T1-F
· HMIM-4E1T1-F
· HMIM-8E1T1-F
HMIM-1E1/HMIM-2E1/HMIM-4E1/HMIM-1E1-F/HMIM-2E1-F/HMIM-4E1-F
Introduction
The 1-port channelized E1/PRI interface module (HMIM-1E1), 2-port channelized E1/PRI interface module (HMIM-2E1), and 4-port channelized E1/PRI interface module (HMIM-4E1) transmit, receive, and process E1 data traffic. In addition, you can use these modules for other purposes, such as CE1 access and the ISDN PRI function.
The HMIM-1E1-F/HMIM-2E1-F/HMIM-4E1-F module is different from the HMIM-1E1/HMIM-2E1/HMIM-4E1 module in the sense that:
· The FE1 operating mode supported by the E1-F modules allows only one n No 64 Kbps bundle to be formed on each interface, where the value range of n is 1 to 31. However, an E1 module allows arbitrary grouping of 31 channels and multiple bundles.
· The E1-F modules do not support PRI mode.
Interface specifications
Table 144 Interface specifications
|
Item |
HMIM-1E1/HMIM-1E1-F |
HMIM-2E1/HMIM-2E1-F |
HMIM-4E1/HMIM-4E1-F |
|
Connector type |
DB15 |
DB15 |
DB25 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
2 |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
G.703 and G.704 |
||
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
||
|
Cable type |
· E1 75-ohm unbalanced coaxial cable · E1 120-ohm balanced twisted pair cable · 120-ohm 4E1 conversion cable (only supported by the HMIM-4E1/HMIM-4E1-F) · 75-ohm 4E1 conversion cable (only supported by the HMIM-4E1/HMIM-4E1-F) · Coaxial connector, network interface connector, and 75-ohm to 120-ohm adapter (with BNC connector) |
||
|
Operating mode |
· E1, CE1, ISDN PRI (only supported by the HMIM-1E1/HMIM-2E1/HMIM-4E1) · FE1 (only supported by the HMIM-1E1-F/HMIM-2E1-F/HMIM-4E1-F) |
||
|
Supported services |
· Backup · Terminal access service · ISDN PRI (only supported by the HMIM-1E1/HMIM-2E1/HMIM-4E1) |
||
Interface LEDs
Figure 108 HMIM-E1 panel
Figure 109 HMIM-E1-F panel
Figure 110 HMIM-2E1 panel
Figure 111 HMIM-2E1-F panel
Figure 112 HMIM-4E1 panel
Figure 113 HMIM-4E1-F panel
Table 145 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. · Off: No carrier signal is received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: No cable is connected to the interface, the cable is damaged or not connected correctly, or the peer device is faulty. |
|
LINK |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. |
|
ACTIVE |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E1 interface."
HMIM-8E1/HMIM-8E1-F
Introduction
The 8-port channelized E1/PRI interface module (HMIM-8E1) transmits, receives, and processes eight channels of E1 data traffic. In addition, you can use the module for other purposes, such as CE1 access and the ISDN PRI function.
The 8-port fractional E1 interface module (HMIM-8E1-F) is different from the HMIM-8E1 module in the sense that:
· The FE1 operating mode supported by the HMIM-8E1-F module allows only one n No 64 Kbps bundle to be formed on each interface, where the value range of n is 1 to 31. However, an HMIM-8E1 module allows arbitrary grouping of 31 channels and therefore multiple bundles.
· The HMIM-8E1-F module does not support PRI mode.
|
|
NOTE: For an HMIM-8E1 module, the system automatically creates a serial interface for each timeslot bundle formed on a controller E1 interface. |
Interface specifications
Table 146 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
D68 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
G.703 |
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
75-ohm 8E1 conversion cable |
|
Cable characteristic impedance |
75 ohm |
|
Operating mode |
· E1, CE1, ISDN PRI (only supported by the HMIM-8E1) · FE1 (only supported by the HMIM-8E1-F) |
|
Supported services |
· Backup · Terminal access service · ISDN PRI (only supported by the HMIM-8E1) |
Interface LEDs
Figure 114 HMIM-8E1 (75-ohm) panel
Figure 115 HMIM-8E1-F (75-ohm) panel
Table 147 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. · Off: No carrier signal is received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: No cable is connected to the interface, the cable is damaged or not connected correctly, or the peer device is faulty. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E1 interface."
RT-HMIM-2E1-V3/RT-HMIM-4E1-V3/RT-HMIM-8E1-V3
|
CAUTION: The RT-HMIM-2E1-V3/RT-HMIM-4E1-V3/RT-HMIM-8E1-V3 module is hot swappable. To remove it, first press and hold the remove button until the RUN LED is off. |
Introduction
The RT-HMIM-2E1-V3/RT-HMIM-4E1-V3/RT-HMIM-8E1-V3 module stands for 2/4/8-port channelized CE1/PRI and fractional E1 (E1-F) interface module.
The module provides the following features:
· Channelized CE1/PRI mode—The module allows arbitrary grouping of 31 channels and multiple bundles. It transmits/receives and handles E1 data streams, provides CE1 access, and supports ISDN PRI.
· Unchannelized E1 mode—Interfaces on the module are 2048 Mbps synchronous serial interfaces without timeslot division.
· Fractional E1 (E1-F) mode—The time slots can only be bundled into one n x 64 kbps channel, where the value range of n is 1 to 31. The module does not support PRI mode.
Interface specifications
Table 148 Interface specifications
|
Item |
RT-HMIM-2E1-V3 |
RT-HMIM-4E1-V3 |
RT-HMIM-8E1-V3 |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
RJ-45 |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
2 |
4 |
8 |
|
Interface standard |
G.703 |
||
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
||
|
Cable type |
· E1 120-ohm balanced twisted pair cable: 2 m (6.56 ft), 15 m (49.21 ft), or 30 m (98.43 ft) · E1 75-ohm unbalanced coaxial cable · 75-ohm adapter cable · Coaxial connector, network interface connector, and 75-ohm to 120-ohm adapter (with BNC connector) |
||
|
Operating mode |
· Unchannelized E1 (G.703) · Channelized E1 (CE1/PRI) · Fractional E1 (E1-F) |
||
|
Supported services |
· Backup · Terminal access service · ISDN PRI |
||
Interface LEDs
Figure 116 RT-HMIM-2E1-V3 panel
Figure 117 RT-HMIM-4E1-V3 panel
Figure 118 RT-HMIM-8E1-V3 panel
On the panel, each port corresponds to one green LED and one yellow LED. Table 149 describes the LEDs on the panel.
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
Steady green |
A carrier signal has been received. |
|
Flashing green |
Data is being transmitted or/and received. |
|
|
Off |
No carrier signal has been received. |
|
|
LP/AL |
Steady yellow |
The interface is in loopback mode. |
|
Flashing yellow |
No cable is connected to the interface, the cable is damaged or not connected correctly, or the peer device is faulty. |
|
|
Off |
No loopback or alarm is present. |
|
|
RUN |
Steady green |
The module is operating correctly. You cannot remove it. |
|
Off |
The module is not recognized and you can remove it, or the module has been removed. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E1 interface."
HMIM-2T1/HMIM-4T1-F
Introduction
The 2-port channelized CT1/PRI interface module (HMIM-2T1) serves to transmit/receive and handle T1 data streams, provide CT1 access, and fulfill the function of ISDN PRI. Thereby, one module can be used for multiple purposes.
The 4-port fractional T1 interface module (HMIM-4T1-F) is different from the HMIM-CT1 module in the sense that:
· FT1 operating mode supported by T1-F modules allows only one bundle. In other words, the time slots can only be bundled into one n x 64 Kbps/56 Kbps channel, where the value range of n is 1 to 24. However, a CT1 module allows of arbitrary grouping of the 24 channels.
· T1-F does not support PRI mode.
|
|
NOTE: For a T1 module, the system automatically creates a serial interface for each timeslot bundle formed on a controller T1 interface. |
Interface specifications
Table 150 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
· 2 (HMIM-2T1) · 4 (HMIM-4T1-F) |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703/T1 102 · G.704 · AT & T TR 54016 · AT & T TR 62411 · ANSI T1.403 |
|
Interface rate |
1.544 Mbps |
|
cable type |
T1 cable (100-ohm shielding network cable) |
|
Operating mode |
CT1, ISDN PRI (only supported by the HMIM-2T1) FT1 (only supported by the HMIM-4T1-F) |
|
Supported services |
· Backup · Terminal access service · ISDN PRI (only supported by the HMIM-2T1) |
Interface LEDs
Figure 119 HMIM-2T1 panel
Figure 120 HMIM-4T1-F panel
Table 151 LED description
|
LEDs |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted or/and received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: No cable is connected to the interface, the cable is damaged or not connected correctly, or the peer device is faulty. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about T1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "T1 interface."
HMIM-2E1T1/HMIM-4E1T1/HMIM-8E1T1/HMIM-2E1T1-F/HMIM-4E1T1-F/HMIM-8E1T1-F
Introduction
· HMIM-2E1T1/HMIM-4E1T1/HMIM-8E1T1 module
The 2/4/8-port channelized E1/CE1/T1/CT1/PRI interface module transmits/receives and handles T1 data streams, provides CT1 access, and supports ISDN PRI. The module allows arbitrary grouping of 31 channels.
· HMIM-2E1T1-F/HMIM-4E1T1-F/HMIM-8E1T1-F module
The 2/4/8-port fractional T1 interface module allows only one bundle. The time slots can only be bundled into one n x 64 Kbps/56 Kbps channel, where the value range of n is 1 to 31. The module does not support PRI mode.
· HMIM-2E1T1/HMIM-4E1T1/HMIM-8E1T1(-F) jumper settings
You can use command lines and a jumper to configure an interface on the interface module as a 75-ohm E1 interface, 100-ohm T1 interface, or 120-ohm E1 interface. By default, an interface is a 75-ohm E1 interface.
¡ To configure an interface on the interface module as a 75-ohm E1 interface, connect the jumper to pins 1 and 2, pins 7 and 8, pins 11 and 12, and pins 13 and 14.
¡ To configure an interface on the interface module as a 100-ohm T1 or 120-ohm E1 interface, connect the jumper to pins 1 to 3, pins 5 to 7, pins 9 and 10, and pins 11 to 13.
Figure 121 Jumper connecting methods
|
|
NOTE: · An interface corresponds to a jumper connector. Pin settings for the jumper connectors are the same. · Each interface comes with four jumper caps. · All interfaces must operate in the same mode. |
Interface specifications
Table 152 Interface specifications
|
Item |
HMIM-2E1T1/ |
HMIM-4E1T1/ |
HMIM-8E1T1/ |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
RJ-45 |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
2 |
4 |
8 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703/G.704 · T1 102 · AT&T TR 54016 · AT&T TR 62411 · ANSI T1.403 |
||
|
Interface rate |
· 1.544 Mbps · 2.048 Mbps |
||
|
Supported cable |
· E1 75-ohm unbalanced twisted pair cable · E1 120-ohm balanced twisted pair cable · T1 cable (100-ohm shielding network cable) · Coaxial connector, network connector, 75-to-120-ohm adapter (with BNC connector) |
||
|
Operating mode |
· E1/T1/CE1T1/ISDN PRI (only supported by the HMIM-2E1T1/HMIM-4E1T1/HMIM-8E1T1 module) · FE1T1 (only supported by the HMIM-2E1T1-F/HMIM-4E1T1-F/HMIM-8E1T1-F module) |
||
|
Supported services |
· Backup · Terminal access service · ISDN PRI (only supported by the HMIM-2E1T1/HMIM-4E1T1/HMIM-8E1T1 module) |
||
Interface LEDs
Figure 122 HMIM-2E1T1 panel
Figure 123 HMIM-2E1T1-F panel
Figure 124 HMIM-4E1T1 panel
Figure 125 HMIM-4E1T1-F panel
Figure 126 HMIM-8E1T1 panel
Figure 127 HMIM-8E1T1-F panel
Table 153 LED description
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
Steady green |
A carrier signal has been received. |
|
Flashing green |
Data is being transmitted or/and received. |
|
|
Off |
No carrier signal has been received. |
|
|
LP/AL |
Steady yellow |
The interface is in loopback mode. |
|
Flashing yellow |
No cable is connected to the interface, the cable is damaged or not connected correctly, or the peer device is faulty. |
|
|
Off |
No loopback or alarm is present. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E1 interface."
For more information about T1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "T1 interface."
E3/T3 interface modules
· HMIM-1CE3
HMIM-1CE3
Introduction
The 1-port channelized E3 interface module (HMIM-1CE3) serves to:
· Transmit/receive and handle one channel of E3 fast traffic, as well as provide the accessing of E3 traffic when operating in E3 mode.
· Provide the low-speed accessing service at the speed of n No 64 kbps, where "n" is smaller than or equal to 128, when operating in CE3 mode.
|
|
NOTE: E3 represents the tertiary group rate of E system in the TDM system, that is, 34.368 Mbps. An E3 channel can be channelized into 16 E1 lines through the demultiplexing processes of E23 and E12, each E1 line supporting both the operating modes of E1 and CE1. E23 is used to indicate either E2-to-E3 multiplex or E3-to-E2 demultiplex, and E12 to indicate E1-to-E2 multiplex or E2-to-E1 demultiplex. "E23" and "E12" discussed here represent the demultiplex process. |
Interface specifications
Table 154 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
SMB |
|
Number of connectors |
2 |
|
Interface standard |
G.703, G.704, and G.751 |
|
Interface rate |
34.368 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
E3 cable (75-ohm coaxial cable) |
|
Operating mode |
· E3 · CE3 |
|
Supported services |
E3 leased line |
Interface LEDs
Figure 128 HMIM-1CE3 panel
Table 155 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. · Off: No carrier signal is received. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: An alarm indication signal (AIS), loss of frame alignment (LFA) signal, or remote alarm indication (RAI) signal is present. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E3 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E3/T3 interface."
Serial interface modules
· HMIM-2SAE
· HMIM-4SAE
· HMIM-8SAE
· RT-HMIM-4SAE-V2
· RT-HMIM-8SAE-V2
· HMIM-8ASE
· HMIM-16ASE
· RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2
· RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2
HMIM-2SAE/HMIM-4SAE/HMIM-8SAE
Introduction
The 2-port SAE module (HMIM-2SAE), 4-port SAE module (HMIM-4SAE), and 8-port SAE module (HMIM-8SAE) are enhanced high-speed synchronous/asynchronous serial interface modules. In terms of function, SAE modules are the same as SA modules except that SAE modules support more protocols, for example, RS449, X.21, and RS530.
Interface specifications
Table 156 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Synchronous |
Asynchronous |
|
|
Connector type |
D28 |
||
|
Number of connectors |
2 (HMIM-2SAE) 4 (HMIM-4SAE) 8 (HMIM-8SAE) |
||
|
Interface standard and operating mode |
V.24 |
V.35, RS449, X.21, and RS530 |
RS-232 |
|
DTE and DCE |
DTE and DCE |
||
|
Minimum baud rate (bps) |
1200 |
1200 |
300 |
|
Maximum baud rate (bps) |
64000 |
2048000 |
115200 |
|
cable type |
V.24 DTE cable V.24 DCE cable V.35 DTE cable V.35 DCE cable X.21 DTE cable X.21 DCE cable RS449 DTE cable RS449 DCE cable RS530 DTE cable RS530 DCE cable |
||
|
Supported services |
· DDN leased line · Terminal access service |
· Dialup through modems · Backup · Asynchronous leased line · Dumb terminal access |
|
Interface LEDs
Figure 129 HMIM-2SAE panel
Figure 130 HMIM-4SAE panel
Table 157 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· Off: No link is present. · On: A link is present. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received. · Flashing: Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
Figure 131 HMIM-8SAE panel
On the HMIM-8SAE module, each link corresponds to a LED. The LED state indicates the link state as follows:
· On—A link is present.
· Flashing—Data is being transmitted or received.
· Off—No data is being transmitted or received.
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about synchronous/asynchronous serial port cables and the connection methods, see "Synchronous/asynchronous serial ports."
RT-HMIM-4SAE-V2/RT-HMIM-8SAE-V2
|
CAUTION: The RT-HMIM-4SAE-V2/RT-HMIM-8SAE-V2 module is hot swappable. To remove it, first press and hold the remove button until the RUN LED is off. |
Introduction
The 4-port SAE module (RT-HMIM-4SAE-V2) and 8-port SAE module (RT-HMIM-8SAE-V2) are enhanced high-speed synchronous/asynchronous serial interface modules. In terms of function, SAE modules are the same as SA modules except that SAE modules support more protocols, for example, RS449, X.21, and RS530.
Interface specifications
Table 158 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Synchronous |
Asynchronous |
|
|
Connector type |
D28 |
||
|
Number of connectors |
4 (RT-HMIM-4SAE-V2) 8 (RT-HMIM-8SAE-V2) |
||
|
Interface standard and operating mode |
V.24 |
V.35, RS449, X.21, and RS530 |
RS-232 |
|
DTE and DCE |
DTE and DCE |
||
|
Minimum baud rate (bps) |
1200 |
1200 |
300 |
|
Maximum baud rate (bps) |
64000 |
2048000 |
115200 |
|
Cable type |
V.24 DTE cable V.24 DCE cable V.35 DTE cable V.35 DCE cable X.21 DTE cable X.21 DCE cable RS449 DTE cable RS449 DCE cable RS530 DTE cable RS530 DCE cable |
||
|
Supported services |
· DDN leased line · Terminal access service |
· Backup · Asynchronous leased line · Terminal access |
|
Interface LEDs
Figure 132 RT-HMIM-4SAE-V2 panel
Figure 133 RT-HMIM-8SAE-V2 panel
Table 159 LED description
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
RUN |
Steady green |
The module is operating correctly. You cannot remove it. |
|
Off |
The module is not recognized and you can remove it, or the module has been removed. |
|
|
LINK/ACT |
Steady green |
A link is present. |
|
Flashing green |
Data is being received or/and transmitted. |
|
|
Off |
No link is present. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about synchronous/asynchronous serial port cables and the connection methods, see "Synchronous/asynchronous serial ports."
HMIM-8ASE/HMIM-16ASE
Introduction
The 8-port ASE module (HMIM-8ASE) and the 16-port ASE module (HMIM-16ASE) are enhanced asynchronous serial interface modules that are used to transmit, receive, and handle asynchronous serial interface data streams. ASE modules use RJ-45 connectors and AUX cables.
Interface specifications
Table 160 Interface specifications
|
Item |
HMIM-8ASE |
HMIM-16ASE |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
|
|
Number of connectors |
8 (HMIM-8ASE) 16 (HMIM-16ASE) |
|
|
Interface standard and operating mode |
RS-232 |
|
|
cable type |
· AUX cable · Standard (straight-through) Ethernet cable · HMIM-8ASE/HMIM-16ASE dumb terminal cable |
|
|
Minimum baud rate (bps) |
300 |
|
|
Maximum baud rate (bps) |
115.2 k |
|
|
Supported services |
· Dialup through a modem · Backup · Terminal access service · Asynchronous leased line service |
|
Interface LEDs
Figure 134 HMIM-8ASE panel
Figure 135 HMIM-16ASE panel
Each channel on HMIM-8ASE/HMIM-16ASE has only one LED. The LED state indicates the link state as follows:
· On—A link is present.
· Flashing—Data is being transmitted or received.
· Off—No link is present.
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about asynchronous serial port cables and the connection methods, see "Asynchronous serial ports."
RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2/RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2
|
CAUTION: The RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2/RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2 module is hot swappable. To remove it, first press and hold the remove button until the RUN LED is off. |
Introduction
The 8-port ASE module (RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2) and the 16-port ASE module (RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2) are enhanced asynchronous serial interface modules that are used to transmit, receive, and handle asynchronous serial interface data streams. ASE modules use RJ-45 connectors and AUX cables.
Interface specifications
Table 161 Interface specifications
|
Item |
RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2 |
RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2 |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
|
|
Number of connectors |
· 8 (RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2) · 16 (RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2) |
|
|
Interface standard and operating mode |
RS-232 |
|
|
cable type |
· AUX cable · Standard (straight-through) Ethernet cable · Dumb terminal cable |
|
|
Minimum baud rate (bps) |
300 |
|
|
Maximum baud rate (bps) |
115.2 k |
|
|
Supported services |
· Dialup through a modem · Backup · Terminal access service · Asynchronous leased line service |
|
Interface LEDs
Figure 136 RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2 panel
Figure 137 RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2 panel
Each channel on RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2/RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2 has only one LED. The LED state indicates the link state as follows:
· On—A link is present.
· Flashing—Data is being transmitted or received.
· Off—No link is present.
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about asynchronous serial port cables and the connection methods, see "Asynchronous serial ports."
POS terminal access interface modules
· HMIM-1E1POS
· DHMIM-1E1POS1DM
HMIM-1E1POS
Introduction
The HMIM-1E1POS is a 1-port channelized E1 high-density POS access interface module. Each E1 port can deal with incoming calls from 30 POS terminals at the same time. The HMIM-1E1POS is applicable to the bank data transaction center for smart card accounting management.
|
|
NOTE: The POS access service is a type of smart card service widely used in places such as shopping malls and gasoline service stations. It links a POS terminal device located in a shopping mall or a gasoline service station to a bank card accounting system to provide services. |
|
|
NOTE: · The HMIM-1E1POS uses the PRI voice protocol, but cannot be used for regular voice calling. The voice subscriber lines that the HMIM-1E1POS generates cannot be used as regular voice interfaces, and cannot be bound to the voice entities. · The PRI interface is used for transmitting service data. The interfaces Diag Port0 and Diag Port1 are used only for device debugging. |
Interface specifications
Table 162 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Cable |
120-ohm standard non-shield cable |
|
Operating mode |
PRI |
|
Supported protocols |
Synchronous mode: · ITU-T-V.22 (PSK/QPSK) · V.22 BIS (QAM) |
|
Supported services |
POS call in PRI mode |
Interface LEDs
Figure 138 HMIM-1E1POS panel
Table 163 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Steady green: A carrier signal is detected. · Flashing green: Data is being received or transmitted. · Off: No carrier signals are detected. |
|
LP/AL |
· Steady yellow: The interface is in loopback. · Flashing yellow: An alarm is present. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. |
Interface cable
The HMIM-1E1POS uses the 120-ohm unshielded E1 cable with RJ-45 connecters at both ends.
Figure 139 HMIM-1E1POS interface cable
|
|
NOTE: The HMIM-1E1POS does not come with the interface cable. You need to order for the E1 cable. |
Connecting the interface cable
|
CAUTION: · Before connecting a port, read its label carefully. A wrong connection can cause damages to the interface module and even the device. · As a best practice, add a lightning arrester between an interface cable and interface module for better lightning protection when the cable is routed outdoors. |
To connect the interface cable:
1. Connect one end of the interface cable to the RJ-45 port on the HMIM-1E1POS.
2. Connect the other end of the interface cable to the peer device.
3. Examine the status of the LINK LED on the HMIM-1E1POS. If the LINK LED is off, examine the cable connection and cable condition.
DHMIM-1E1POS1DM
Introduction
The DHMIM-1E1POS1DM is a 1-port channelized E1 high-density POS access interface module. Each E1 port can deal with incoming calls from 30 POS terminals at the same time. The DHMIM-1E1POS1DM is applicable to the bank data transaction center for smart card accounting management.
The DHMIM-1E1POS1DM can operate as the HMIM-1E1POS or the DHMIM-1DM. When the E1 port of the DHMIM-1E1POS1DM operates in asynchronous mode, you can upgrade the POS device remotely.
|
|
NOTE: The PRI interface is used for transmitting service data. The interfaces Diag Port0 and Diag Port1 are used only for device debugging. |
Interface specifications
Table 164 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
|
Cable |
120-ohm standard non-shielded cable |
|
|
Operation mode |
PRI |
|
|
Supported protocols |
· Synchronous mode: ¡ ITU-T-V.22 (PSK/QPSK) ¡ V.22 BIS (QAM) · Asynchronous mode: ¡ ITU-T V.92 ¡ V.90 ¡ V.34 ¡ V.32 bis ¡ V.32 ¡ V.23 ¡ V.22 bis ¡ V.22 ¡ V.21 ¡ Bell 212a ¡ Bell 103 |
|
|
Supported services |
POS call in PRI mode |
|
Interface LEDS
Figure 140 DHMIM-1E1POS1DM panel
Table 165 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Steady green: The carrier signal is detected. · Flashing green (8 Hz): Data is being received or transmitted. · Off: No carrier signals are detected. |
|
LP/AL |
· Steady yellow: The interface is in loopback. · Flashing yellow (1 Hz): An alarm is present. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. |
Connecting the interface cable
|
CAUTION: · As a best practice, add a lightning arrester between an interface cable and interface module for better lightning protection when the cable is routed outdoors. · Before connecting a port, read its label carefully. A wrong connection might cause damages to the interface module and even the device. |
If the interface module has been properly installed, follow these steps to connect the cable:
1. Connect one end of the interface cable to the RJ-45 port on the DHMIM-1E1POS1DM.
2. Connect the other end of the interface cable to the peer device.
3. Examine the status of the LINK LED on the DHMIM-1E1POS1DM. If the LINK LED is off, examine the cable connection and cable condition.
Digital modem interface modules
· DHMIM-1DM
DHMIM-1DM
Introduction
The DHMIM-1DM is a 1-port channelized E1 high-density digital modem interface module. You can upgrade the POS device remotely.
|
|
NOTE: The PRI interface is used for transmitting service data. The interfaces Diag Port0 and Diag Port1 are used only for device debugging. |
Interface specifications
Table 166 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Cable |
120-ohm standard non-shielded cable |
|
Operation mode |
PRI |
|
Supported protocols |
Asynchronous mode: · ITU-T V.92 · V.90 · V.34 · V.32 bis · V.32 · V.23 · V.22 bis · V.22 · V.21 · Bell 212a · Bell 103 |
|
Supported services |
POS call in PRI mode |
Interface LEDs
Figure 141 DHMIM-1DM panel
Table 167 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Steady green: The carrier signal is detected. · Flashing green (8 Hz): Data is being received or transmitted. · Off: No carrier signals are detected. |
|
LP/AL |
· Steady yellow: The interface is in loopback. · Flashing yellow (1 Hz): An alarm is present. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. |
Connecting the interface cable
|
CAUTION: · As a best practice, add a lightning arrester between an interface cable and interface module for better lightning protection when the cable is routed outdoors. · Before connecting a port, read its label carefully. A wrong connection might cause damages to the interface module and even the device. |
If the interface module has been properly installed, follow these steps to connect the cable:
1. Connect one end of the interface cable to the RJ-45 port on the DHMIM-1DM.
2. Connect the other end of the interface cable to the peer device.
3. Examine the status of the LINK LED on the DHMIM-1DM. If the LINK LED is off, examine the cable connection and cable condition.
Voice interface modules
· HMIM-16FXS
· HMIM-8FXS8FXO
· HMIM-2VE1
· HMIM-2VT1
· HMIM-1VE1
· HMIM-1VT1
· HMIM-4FXS
· HMIM-4FXO
· HMIM-4E&M
HMIM-16FXS
Introduction
The 16-port loop trunk interface module (HMIM-16FXS) serves to access and handle 16 channels of analog voice signals over data communication networks. The module provides 16 FXS interfaces.
FXS interfaces are analog subscriber line interfaces that provide ordinary analog telephone and fax access and also can connect AT0 loop trunks of exchanges.
Interface specifications
Table 168 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-11 |
|
Number of connectors |
16 (FXS interfaces) |
|
Interface standard |
· ITU Q.512-compliant subscriber circuit interface (FXS) · ITU K.20-compliant over-current and over-voltage protection |
|
Cable type |
Telephone cable with ferrite core |
|
Dial-up mode |
DTMF, compliant with GB3378 (Pulse dial-up is not available.) |
|
Bandwidth |
300 to 3400 Hz |
|
Ringing voltage |
40 V |
Interface LEDs
Figure 142 HMIM-16FXS front panel
Table 169 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Steady green: A link is present and a call connection is being established. · Off: No link is present. · Flashing yellow: A link is present and there is a call activity. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about FXS interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
HMIM-8FXS8FXO
Introduction
The 8-port analog subscriber circuit interface module and 8-port voice AT0 loop trunk interface module (HMIM-8FXS8FXO) serve to access and handle 16 channels of analog voice signals over data communication networks. Eight FXS interfaces and eight FXO interfaces are available on an HMIM-8FXS8FXO module:
· FXS interfaces are analog subscriber line interfaces that provide ordinary analog telephone and fax access and also can connect AT0 loop trunks of exchanges;
· FXO interfaces are loop trunk interfaces that provide access of common subscriber lines of exchanges.
When you use the HMIM-8FXS8FXO module in a device, make sure the device has been connected to the IP network or other WAN.
Interface specifications
Table 170 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector type |
RJ-11 |
|
Number of connectors |
· 8 FXS interfaces · 8 FXO interfaces |
|
Interface standard |
· ITU Q.512-compliant subscriber circuit interface (FXS) · ITU Q.552-compliant loop trunk interface (FXO) · ITU K.20-compliant over-current and over-voltage protection |
|
Cable type |
Telephone cable with ferrite core |
|
Dial-up mode |
DTMF, compliant with GB3378 (Pulse dial-up is not available.) |
|
Bandwidth |
300 Hz to 3400 Hz |
|
Ringing voltage |
40 V |
Interface LEDs
Figure 143 HMIM-8FXS8FXO front panel
Table 171 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· Steady green: The link is being occupied for a call connection. · Off: The link is idle. · Flashing yellow: The link is being occupied for communication. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about FXS interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
HMIM-2VE1
Introduction
The 2-port E1 voice interface module (HMIM-2VE1) can handle dense voice signals in VoIP system. It provides two CE1/PRI/R2 ports, allowing the access of 60 channels of voice signals.
Interface specifications
Table 172 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
D15 |
|
Number of connectors |
2 |
|
Operating mode |
· CE1 · ISDN PRI · R2 |
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
· E1 75-ohm unbalanced coaxial cable · E1 120-ohm balanced twisted pair cable · Coaxial connector, network interface connector, and 75-to-120-ohm adapter (with BNC connector) |
|
Supported service |
· R2 signaling · DSS1 signaling · IP Fax · General VoIP features in Comware |
Interface LEDs
Figure 144 HMIM-2VE1 panel
Table 173 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received and/or transmitted. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: An alarm indication signal (AIS), loss of frame alignment (LFA) signal, or remote alarm indication (RAI) signal is present. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E1 interface."
HMIM-2VT1
Introduction
The 2-port T1 voice interface module (HMIM-2VT1) can handle dense voice signals in VoIP system. It provides two CT1/PRI ports, allowing the access of 48 channels of voice signals.
Interface specifications
Table 174 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connector |
2 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703/T1.102 · G.704 · AT & T TR 54016 · AT & T TR 62411 · ANSI T1.403 |
|
Interface rate |
1.544 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
T1 cable (100-ohm standard shielded cable) |
|
Operation mode |
· CT1 · ISDN PRI |
|
Services |
· Backup · Terminal access · ISDN |
Interface LEDs
Figure 145 HMIM-2VT1 panel
Table 175 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received and/or transmitted. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: An alarm indication signal (AIS), loss of frame alignment (LFA) signal, or remote alarm indication (RAI) signal is present. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about T1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "T1 interface."
HMIM-1VE1
Introduction
The 1-port E1 voice interface module (HMIM-1VE1) can handle dense voice signals in VoIP system. It provides a CE1/PRI/R2 port, allowing the access of 30 channels of voice signals.
Interface specifications
Table 176 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
D15 |
|
Number of connectors |
1 |
|
Operating mode |
· CE1 · ISDN PRI · R2 |
|
Interface rate |
2.048 Mbps |
|
Cable |
· E1 75-ohm unbalanced coaxial cable · E1 120-ohm balanced twisted pair cable · Coaxial connector, network interface connector, and 75ohm-to-120ohm adapter (with BNC connector) |
|
Supported service |
· R2 signaling · DSS1 signaling · IP Fax · General VoIP features in Comware |
Interface LEDs
Figure 146 HMIM-1VE1 panel
Table 177 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received and/or transmitted. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: An alarm indication signal (AIS), loss of frame alignment (LFA) signal, or remote alarm indication (RAI) signal is present. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "E1 interface."
HMIM-1VT1
Introduction
The 1-port T1 voice interface module (HMIM-1VT1) can handle dense voice signals in VoIP system. It provides a CT1/PRI port, allowing the access of 24 channels of voice signals.
Interface specifications
Table 178 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connector |
1 |
|
Interface standard |
· G.703/T1.102 · G.704 · AT & T TR 54016 · AT & T TR 62411 · ANSI T1.403 |
|
Interface rate |
1.544 Mbps |
|
Cable type |
T1 cable (100-ohm standard shielded cable) |
|
Operation mode |
· CT1 · ISDN PRI |
|
Services |
· Backup · Terminal access · ISDN |
Interface LEDs
Figure 147 HMIM-1VT1 panel
Table 179 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK/ACT |
· On: A carrier signal is received. · Off: No carrier signal is received. · Flashing: Data is being received and/or transmitted. |
|
LP/AL |
· On: The interface is in loopback mode. · Off: No loopback or alarm is present. · Flashing: An alarm indication signal (AIS), loss of frame alignment (LFA) signal, or remote alarm indication (RAI) signal is present. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about T1 interface cables and the connection methods, see "T1 interface."
HMIM-4FXS/HMIM-4FXO
Introduction
The 4-port voice subscriber circuit interface module (HMIM-4FXS) processes and transmits over data communications networks voice signals for 2/4 regular analog phones, faxes, or AT0 loop trunks of telephone exchanges.
The 4-port voice AT0 analog trunk interface module (HMIM-4FXO) processes and transmits over data communications networks voice signals for 2/4 loops of telephone exchanges.
Interface specifications
Table 180 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
4 |
|
Cable |
· Telephone cable with ferrite core · E&M trunk cable (only for E&M modules, made on site) |
|
Interface standard |
· ITU Q.512-compliant subscriber circuit interface (HMIM-4FXS) · ITU Q.552-compliant loop trunk interface (HMIM-4FXO) · ITU K.20-compliant over-current and over-voltage protection |
|
Dial-up mode |
DTMF, compliant with GB3378 (Pulse dial-up is not available.) |
|
Bandwidth |
300 Hz to 3400 Hz |
Interface LEDs
Figure 148 HMIM-4FXS panel
Figure 149 HMIM-4FXO panel
Table 181 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· On: A link is present. · Off: No link is present. |
|
ACT |
· On: There is call activity. · Off: The channel is idle. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about FXS/FXO interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
HMIM-4E&M/HMIM-8E&M
Introduction
The 4/8-port voice E&M analog trunk interface module (HMIM-4E&M/HMIM-8E&M) provides and transmits over data communications networks voice signals for 4/8 E&M analog trunks.
Interface specifications
Table 182 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
· 4 (HMIM-4E&M) · 8 (HMIM-8E&M) |
|
Cable type |
· Telephone cable with ferrite core · E&M trunk cable (only for E&M modules, made on site) |
|
Interface standard |
· G.712-compliant E&M trunk interface (HMIM-4E&M/HMIM-8E&M), E&M interface (supporting Bell type I, II, III, V, and support 2-wire and 4-wire) · ITU K.20-compliant over-current and over-voltage protection |
|
Dial-up mode |
DTMF, compliant with GB3378 (Pulse dial-up is not available.) |
|
Bandwidth |
300 Hz to 3400 Hz |
Interface LEDs
Figure 150 HMIM-4E&M panel
Figure 151 HMIM-8E&M panel
Table 183 LED description
|
LED |
Status |
Description |
|
LINK |
Steady green |
A link is present. |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
|
|
ACT |
Steady yellow |
There is call activity.. |
|
Off |
The channel is idle. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about E&M interface cables and the connection methods, see "E&M interface."
Analog modem modules
· HMIM-6AM
· HMIM-6FCM
HMIM-6AM
Introduction
The 6-port analog modem interface module (HMIM-6AM) provides six channels of user dial-in and dial-out, and provides a connection speed of 56 kbps when ITU-T V.90 is applied. Working with the MSR routers, it provides medium-density RAS functions.
Interface specifications
Table 184 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
6 |
|
Cable |
Telephone cable |
|
Interface rate |
56 kbps |
|
Interface standard |
ITU-T V.90, K56flex, V.34 (33.6 kbps), V.FC, V.32 bis, V.32, V.22 bis, V.22A/B, V.23, V.21, Bell 212A a, and Bell 103 |
|
Supported service |
Dialup through modem |
Interface LEDs
Figure 152 HMIM-6AM panel
|
LED |
Description |
|
LINK |
· On: A link is present. · Off: No link is present. · Flashing: A link is being established. |
|
ACT |
· Off: No data is being transmitted or received. · Flashing: Data is being transmitted and/or received. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about AM interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
HMIM-6FCM
Introduction
The 6-port fast connect modem interface module (HMIM-6FCM) provides POS terminal devices to fast dial up to a bank card accounting system.
|
|
NOTE: The POS access service refers to a type of smart card service widely used in places such as shopping malls and gasoline service stations. It links a POS terminal device located in a shopping mall or a gasoline service station to a bank card accounting system to provide services. |
Interface specifications
Table 186 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Connector |
RJ-45 |
|
Number of connectors |
6 |
|
Cable |
Telephone cable with ferrite core |
|
Supported protocols |
ITU-T V.22 |
Interface LEDs
Figure 153 HMIM-6FCM panel
Table 187 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
CD |
· Off: No carrier signals are detected. · On: A carrier signal is detected. |
|
ACT |
· Flashing: Data is being received or transmitted. · Off: No data is being received or transmitted. |
Interface cables and the connection methods
For more information about FCM interface cables and the connection methods, see "ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface."
Network data encryption modules
HMIM-CNDE-SJK
Introduction
The HMIM-CNDE-SJK (CNDE is the acronym of China Network Data Encryption) supports SM1, SM2, and SM4 encryption algorithms and provides high performance and reliable data encryption features for routers.
Interface LEDs
Figure 154 HMIM-CNDE-SJK panel
Table 188 LED description
|
LED |
Description |
|
RUN |
· Steady green: The module is operating correctly and is not sending or receiving data. · Flashing green: The module is operating correctly and is sending or receiving data. · Steady yellow: The module is faulty. · Off: The module is not installed securely, or no power is present. |
HMIM adapters
· HMIM-Adapter
· HMIM-Adapter-H
HMIM-Adapter/HMIM-Adapter-H
Introduction
The HMIM-Adapter/HMIM-Adapter-H is designed for MIM-to-HMIM conversions. Some MIMs can operate as HMIMs with an HMIM-Adapter/HMIM-Adapter-H adapter installed. For the MIM-to-HMIM conversion relations, see "Appendix B Purchase guide."
Views
Figure 155 HMIM-Adapter view
Figure 156 HMIM-Adapter-H view
VPMs
VPM purchase guide
· The HMIM-1VE1/HMIM-1VT1 module provides a voice processing module (VPM) slot. The HMIM-2VE1/HMIM-2VT1 module provides two VPM slots. Each VPM slot is installed with a VPM when the HMIM-1VE1/HMIM-1VT1 module or HMIM-2VE1/HMIM-2VT1 module is shipped from the factory.
· The main board of the MSR 36-20 router provides a VPM slot. The main boards of the MSR 36-40, MSR 36-60, MSR 56-60, and MSR 56-80 routers provide two VPM slots. The routers do not provide VPMs when shipped from the factory. The number and specifications of VPMs needed depend on the number of calls.
· The SIC-1VE1/SIC-1VT1 module does not provide any VPM slot, and can only use the VPMs installed on the main board of MSR.
· The MIM-1VE1/MIM-1VT1 module provides a VPM slot, and the MIM-2VE1/MIM-2VT1 module provides two VPM slots. No VPM is installed when the MIM-1VE1/MIM-1VT1 or MIM-2VE1/MIM-2VT1 module is shipped from the factory.
· The MIM-1VE1/MIM-1VT1 module must be used with VPM installed. The number of VPMs needed depends on the number of calls.
· Because the initiator of a three-party conference is responsible for audio mixing, so when using MSR as the initiator of a three-party conference, the main board of MSR must have VPM installed.
Introduction
The voice processing module (VPM) functions encoding/decoding, echo cancellation (EC) and comfortable noise generation (CNG) of voices.
Interface specifications
Table 189 Interface specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Number of calls supported |
· 8 · 16 · 24 · 32 · 128 · 256 · 512 |
Cables and the connection methods
Ethernet interface
Ethernet cable appearance and applicable models
Table 190 Ethernet cable appearance and applicable models
|
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
1 × RJ-45 < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
SIC-4FSW SIC-4FSWP SIC-4GSW DSIC-9FSW DSIC-9FSWP SIC-1FEA SIC-1GEC-V2 SIC-AP220 HMIM-8GSW HMIM-24GSW HMIM-24GSW-PoE HMIM-2GEE HMIM-4GEE HMIM-8GEE HMIM-1E1POS DHMIM-1DM DHMIM-1E1POS1DM |
10/100 Mbps Ethernet uses category-5 twisted pair cables, and 1000 Mbps Ethernet uses category-5 enhanced or category-6 twisted pair cables. Twisted pair cables include straight-through cables and crossover cables.
Category-5 cables provide a transmission frequency of 100 MHz for voice and data transmission; they are mainly used in 100BASE-T and 10BASE-T networks. Category-5 cables are common Ethernet cables, which can also be used to transmit 1000 Mbps Ethernet data.
Category-5 enhanced cables feature low attenuation and crosstalk, providing higher attenuation to crosstalk ratio (ACR), less delay error and higher performance than category-5 cables. Category-5 enhanced cables are mainly used in 1000 Mbps Ethernet networks.
Category-6 cables provide a transmission frequency of 1 MHz to 250 MHz, and improve the performance on crosstalk and return loss. A fine better return loss performance is extremely important for new-generation full-duplex high-speed networks. Category-6 cables have sufficient power sum ACR (PS-ACR) when working at 200 MHz. They provide a bandwidth two times than that of category-5 enhanced cables, thus featuring a higher transmission performance. Therefore, category-6 cables are suitable for applications requiring a transmission speed of more than 1 Gbps.
The 10/100 Mbps Ethernet uses two pairs of cables, orange/white, orange, green/white and green cables, to transmit and receive data, while the 1000 Mbps Ethernet uses four pairs of cables to transmit and receive data.
For the pinouts of common twisted pair cables, see the following tables. (A and B represent the two ends of a cable respectively.)
Table 191 Straight-through cable pinouts
|
Pinout No. |
A |
B |
|
1 |
Orange/white |
Orange/white |
|
2 |
Orange |
Orange |
|
3 |
Green/white |
Green/white |
|
4 |
Blue |
Blue |
|
5 |
Blue/white |
Blue/white |
|
6 |
Green |
Green |
|
7 |
Brown/white |
Brown/white |
|
8 |
Brown |
Brown |
Table 192 Crossover cable pinouts
|
Pinout No. |
A |
B |
|
1 |
Orange/white |
Green/white |
|
2 |
Orange |
Green |
|
3 |
Green/white |
Orange/white |
|
4 |
Blue |
Blue |
|
5 |
Blue/white |
Blue/white |
|
6 |
Green |
Orange |
|
7 |
Brown/white |
Brown/white |
|
8 |
Brown |
Brown |
|
|
NOTE: Strictly follow the pinouts in the above tables when identifying or making the two types of Ethernet cables; otherwise, the communication quality may be affected. |
Connecting an Ethernet cable
1. Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to an Ethernet interface on the module and the other end to the Ethernet interface on the peer device. Because the Ethernet interface of the module supports MDI/MDIX autosensing, you can use a straight-through cable or crossover cable to connect the interface.
2. Check the status of the LED of the Ethernet interface after power-on. For the status of the LED, see the relevant part in this manual.
Fiber port
Appearances and applicable models of transceiver modules and optical fibers
Optical interfaces must work with SFP or SFP+ transceiver modules and optical fibers with LC connectors. For more information about interface module and transceiver module compatibility, see H3C MSR Router Series Transceiver Module Compatibility Matrix.
Connecting an optical fiber
|
CAUTION: · Never stare into an open optical Ethernet interface, because invisible rays may be emitted from the optical Ethernet interface. · Cover the dust cover if no optical fiber connector is connected to the optical Ethernet interface. |
To connect an optical fiber:
1. Insert the transceiver module to the interface on the interface module or service module.
2. Identify the Rx and Tx ports on the transceiver module. Plug the LC connector at one end of one fiber cable into the Rx port of the router and the LC connector at the other end into the Tx port of the peer device. Plug the LC connector at one end of another fiber cable into the Tx port of the router and the LC connector at the other end to the Rx port of the peer device.
3. View the LINK LED after connection.
¡ If the LED is on, the optical fiber link is present.
¡ If the LED is off, no link is present. This may be because the TX and Rx port of the optical fiber are not connected correctly. In this case, connect the optical fiber again.
E1 interface
To verify the impedance value of the E1 cable, view the label on the cable. The label location in Figure 157 is for illustration only.
E1 cable appearance and applicable models
Table 193 E1 cable appearance and applicable models
|
Cable |
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
1-port E1 75-ohm cable |
1 × D15 < ---- > 2 × BNC |
SIC-E1-F SIC-1EPRI MIM-1E1 MIM-1E1-F MIM-2E1 MIM-2E1-F HMIM-1E1 HMIM-1E1-F HMIM-2E1 HMIM-2E1-F SIC-1VE1 MIM-1VE1 MIM-2VE1 HMIM-1VE1 HMIM-2VE1 |
|
1-port E1 120-ohm cable |
1 × D15 < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
MIM-1E1 MIM-1E1-F MIM-2E1 MIM-2E1-F HMIM-1E1 HMIM-1E1-F HMIM-2E1 HMIM-2E1-F SIC-1VE1 MIM-1VE1 MIM-2VE1 HMIM-1VE1 HMIM-2VE1 |
|
1-port E1 120-ohm cable (2 m, 15 m, 30 m)-RJ-45 |
1 × RJ-45 < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
RT-HMIM-2E1-V3 RT-HMIM-4E1-V3 RT-HMIM-8E1-V3 HMIM-2E1T1 HMIM-4E1T1 HMIM-8E1T1 HMIM-2E1T1-F HMIM-4E1T1-F HMIM-8E1T1-F SIC-1VE1T1 |
|
2-port E1 75-ohm cable |
1 × D15 < ---- > 4 × BNC |
SIC-2E1-F |
|
4-port E1 75-ohm cable |
1 × D25 < ---- > 4 × D15 |
MIM-4E1 MIM-4E1-F HMIM-4E1 HMIM-4E1-F |
|
4-port E1 120-ohm cable |
1 × D25 < ---- > 4 × D15 |
MIM-4E1 MIM-4E1-F HMIM-4E1 HMIM-4E1-F |
|
8-port E1 75-ohm cable |
1 × D68 < ---- > 16 × BNC |
MIM-8E1 MIM-8E1-F HMIM-8E1 HMIM-8E1-F |
|
1-port E1 75-ohm cable-RJ-45 |
RT-HMIM-2E1-V3 RT-HMIM-4E1-V3 RT-HMIM-8E1-V3 HMIM-2E1T1 HMIM-4E1T1 HMIM-8E1T1 HMIM-2E1T1-F HMIM-4E1T1-F HMIM-8E1T1-F SIC-1VE1T1 |
|
|
75-ohm adapter cable |
1 × BNC < ---- > 1 × BNC |
Use as needed |
|
Coaxial connector |
1 × BNC < ---- > 1 × BNC |
Use as needed |
|
Impedance converter |
2 × BNC < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
Use as needed |
Dual inline package switch
E1 / E1-F / VE1 interface module provides a dual inline package (DIP) switch. The DIP switch setting defines the interface impedance and the grounding method.
Table 194 DIP switch-to-interface map
|
DIP switch |
E1 interface |
Applicable models |
|
S1 |
Interface 0 |
MIM-1E1 MIM-1E1-F MIM-2E1 MIM-2E1-F MIM-4E1 MIM-4E1-F HMIM-1E1 HMIM-1E1-F HMIM-2E1 HMIM-2E1-F HMIM-4E1 HMIM-4E1-F SIC-1VE1 MIM-1VE1 MIM-2VE1 HMIM-1VE1 HMIM-2VE1 |
|
S2 |
Interface1 |
MIM-1E1 MIM-1E1-F MIM-2E1 MIM-2E1-F MIM-4E1 MIM-4E1-F HMIM-1E1 HMIM-1E1-F HMIM-2E1 HMIM-2E1-F HMIM-4E1 HMIM-4E1-F MIM-2VE1 HMIM-2VE1 |
|
S3 |
Interface2 |
MIM-4E1 MIM-4E1-F HMIM-4E1 HMIM-4E1-F |
|
S4 |
Interface3 |
MIM-4E1 MIM-4E1-F HMIM-4E1 HMIM-4E1-F |
By default, all DIP switches are ON, and the E1 interface impedance is 70 ohms, as shown in the following figure:
Figure 158 Default DIP switch settings
H3C recommends that you use the DIP switch as follows: When the interface is connected to a 70-ohm cable, turn on switches BIT1 through 8; when the interface is connected to a 120-ohm cable, turn off switches BIT1 through 8. Description for DIP switch settings is shown in the following table:
Table 195 Description for DIP switch settings
|
DIP |
Description |
Configuration of 75-ohm impedance |
Configuration of 120-ohm impedance |
|
1BIT |
75-ohm/120-ohm selection switch |
ON |
Off |
|
2BIT |
ON |
Off |
|
|
3BIT |
ON |
Off |
|
|
4BIT |
ON |
Off |
|
|
5BIT |
ON |
Off |
|
|
6BIT |
RxRing grounding mode selection switch |
Off: RxRing is grounded via capacitance. ON: RxRing is grounded directly. |
N/A |
|
7BIT |
RxShield grounding mode selection switch |
N/A |
ON: RxShield is grounded. Off: RxShield is not grounded. |
|
8BIT |
SxShield grounding mode selection switch |
N/A |
Off: RxShield is grounded via capacitance ON: RxShield is grounded directly. |
Connecting a 1/2/8-port E1 75-ohm cable (D15/D68 <----> BNC)
|
CAUTION: Make sure you insert the cable into the right interface so as to avoid damages to the interface module or the chassis. |
· If you do not need to extend the cable, you can directly connect the BNC connectors of the E1 75-ohm cable to the remote network device as follows:
a. Connect the D15/D68 connector of the E1 75-ohm cable to the D15/D68 interface of the interface module and fasten the bolts to fix the cable.
b. The other end of the cable provides one pair or multiple pairs of 75-ohm BNC connectors. Connect the TX connectors and the RX connectors on this end to the RX connectors and the TX connectors on the remote device respectively.
Figure 159 Connect an E1 75-ohm cable
· If you want to extend the cable, connect each BNC connector of the E1 75-ohm cable to one end of a coaxial connector, and connect the remote device to the other end of the coaxial connector through an E1 75-ohm adapter cable.
Figure 160 Connect an E1 75-ohm cable
· If the impedance of the E1 interface on the remote device is 120 ohms, you must use an impedance converter to adapt the impedance.
Figure 161 Connect an impedance converter
Connecting a 4-port E1 75-ohm cable (D25 <----> D15)
1. Connect the D25 connector of the 4-port E1 75-ohm cable to the D25 interface of the interface module and fasten the bolts to fix the cable.
2. The other end of the cable provides four D15 connectors. Connect them to the D15 interfaces on the remote device as needed.
Figure 162 Connect an 4-port E1 75-ohm cable
Connecting a 1-port E1 120-ohm cable (D15 <----> RJ-45)
1. Connect the D15 connector of the E1 120-ohm cable to the D15 interface on the interface module and fasten the bolts to fix the cable.
2. The other end of the cable provides one or multiple RJ-45 connectors. Connect them to the RJ-45 interface on the remote device as needed.
Figure 163 Connecting an E1 120-ohm cable
Connecting a 4-port E1 120-ohm cable (D25 <----> D15)
1. Connect the D25 connector of the 4-port E1 120-ohm cable to the D25 interface on the interface module and fasten the bolts to fix the cable.
2. The other end of the cable provides four D15 connectors. Connect them to the D15 interface on the remote device as needed.
Figure 164 Connecting a 4-port E1 120-ohm cable
T1 interface
|
CAUTION: To avoid damages to the interface module or the chassis, make sure you insert the cable into the right interface. |
T1 cable appearance and applicable models
Table 196 T1 cable appearance and applicable models
|
Cable |
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
1-port T1 cable (100- ohm standard shielded cable) |
1 × RJ-45 < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
SIC-T1-F MIM-2T1 MIM-4T1-F HMIM-2T1 HMIM-4T1-F SIC-1VT1 SIC-1VE1T1 MIM-1VT1 MIM-2VT1 HMIM-1VT1 HMIM-2VT1 HMIM-2E1T1 HMIM-4E1T1 HMIM-8E1T1 HMIM-2E1T1-F HMIM-4E1T1-F HMIM-8E1T1-F |
|
RJ-45 connector |
1 × RJ-45 < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
Use as needed |
Connecting a 1-port T1 cable
The two ends of the 1-port T1 cable are RJ-45 connectors. Connect one end of the cable to the T1 connector (RJ-45) of the interface module and the other end of the cable to the T1 connector (RJ-45) on the remote device.
Connecting a 4/8-port T1 cable
· Connect the D68 connector of the 4/8-port T1 cable to the D68 interface on the interface module and fasten the bolts to fix the cable.
· The other end of the cable provides four or eight RJ-45 connectors. Connect them to the RJ-45 interface on the remote device as needed.
E3/T3 interface
E3/T3 cable appearance and applicable models
Table 197 E3/T3 cable appearance and applicable models
|
Cable |
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
E3/T3 interface cable |
1 × BNS < ---- > 1 × SMB |
MIM-1CE3 HMIM-1CE3 |
Connecting the cable
1. Connect the SMB connector of an E3/T3 cable to the Tx port on the interface module and the other end to the Rx port on the device to be connected.
2. Connect the SMB connector of another E3/T3 cable to the Rx port of interface module and the other end to the Tx port on the device to be connected;
3. Check the LINK LED on the module panel. It is off when fault has occurred on the link and signal is out of synchronization. In this case, check the link.
Synchronous/asynchronous serial ports
Appearance and applicable models of synchronous/asynchronous serial port cables
Table 198 Appearance and applicable models of synchronous/asynchronous serial port cables
|
Cable |
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
1 × D25 (male) < ---- > 1 × D28 |
SIC-1SAE SIC-2SAE SIC-4SAE MIM-2SAE MIM-4SAE MIM-8SAE HMIM-2SAE HMIM-4SAE HMIM-8SAE RT-HMIM-4SAE-V2 RT-HMIM-8SAE-V2 |
|
|
1 × D25 (female) < ---- > 1 × D28 |
||
|
1 × D28 < ---- > 1 × D34 (male) |
||
|
1 × D28 < ---- > 1 × D34 (female) |
||
|
1 × D15 (male) < ---- > 1 × D28 |
||
|
1 × D15 (female) < ---- > 1 × D28 |
||
|
1 × D28 < ---- > 1 × D37 (male) |
||
|
1 × D28 < ---- > 1 × D37 (female) |
||
|
1 × D25 (male) < ---- > 1 × D28 |
||
|
1 × D25 (female) < ---- > 1 × D28 |
Connecting the cable
1. Check port type of the peer device and choose the synchronous serial interface cable of correct type.
2. Plug the D28 end of the synchronous serial interface cable into the D28 interface of the SAE interface module.
3. If the WAN uses DDN line, connect the cable to the port of CSU/DSU.
4. Check the LINK LED on the SAE panel.
· If the LED is on, a link is present.
· If the LED is off, a fault has occurred on the link and signal is out of synchronization. In this case, check the link.
Asynchronous serial ports
Appearance and applicable models of asynchronous serial port cables
Table 199 Appearance and applicable models of asynchronous serial port cables
|
Cable |
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
8-port asynchronous serial port adapter cable |
1 × D60 < ---- > 8 × RJ-45 (female) |
SIC-8AS |
|
4-port asynchronous serial port adapter cable |
1 × D28 < ---- > 4 × RJ-45 (female) |
SIC-16AS |
|
Serial server cable |
1 × RJ-45 < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
MIM-8ASE MIM-16ASE HMIM-8ASE HMIM-16ASE RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2 RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2 |
|
Dumb terminal adapter cable |
1 × RJ-45 (female) < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 (male) |
MIM-8ASE MIM-16ASE HMIM-8ASE HMIM-16ASE RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2 RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2 |
|
AUX cable |
1 × D25 & 1 × D9 < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
MIM-8ASE MIM-16ASE HMIM-8ASE HMIM-16ASE RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2 RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2 |
|
Dumb terminal adapter |
1 × D25 < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
MIM-8ASE MIM-16ASE HMIM-8ASE HMIM-16ASE RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2 RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2 |
|
Console cable |
1 × DB-9 < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
SIC-AP220 SIC-AP320 |
Connecting a SIC-8AS/SIC-16AS interface module
To connect the SIC-8AS interface module, connect the D60 connector of the 8-port asynchronous serial port adapter cable to the SIC-8AS interface module.
To connect the SIC-16AS interface module, connect the D28 connector of the 4-port asynchronous serial port adapter cable to the SIC-16AS interface module, which allows up to four such cables.
Choose the cable connection type according to the remote device type:
· If the remote device is a network device with a console port, connect the console port to the RJ-45 interface of the asynchronous serial port adapter cable by using a serial server cable. The sequence is shown in the following figure:
Figure 165 Connecting a network device
· If the remote device is a bank dumb terminal device, connect the RJ-45 connector (male) on one end of the dumb terminal cable to the RJ-45 interface on the asynchronous serial port adapter cable. Connect the RJ-45 connector (female) on the other end of the dumb terminal cable to the RJ-45 interface on one end of the dumb terminal adapter by a straight-through cable. The other end of the dumb terminal adapter is a D25 interface and can be connected to the bank dumb terminal device. The sequence is shown in the following figure:
Figure 166 Connecting the dumb terminal device
· If the interface of the remote device, usually a modem, is a D25/D9 interface, use the AUX cable to connect the asynchronous serial port adapter cable to the interface:
Figure 167 Connecting a modem
Connecting a MIM-8ASE/MIM-16ASE/HMIM-8ASE/HMIM-16ASE/RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2/RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2 interface module
|
WARNING! To avoid damage to the device and the ports, do not plug or unplug the MIM-8ASE/MIM-16ASE module interface cable when the router is powered on. |
|
CAUTION: To avoid damages to the interface module or the chassis, make sure you insert the cable into the right interface. |
Choose the cable connection type according to the remote device type:
· If the remote device is a network device with a console port, connect the console port to the RJ-45 interface of the interface module by using a serial server cable. The sequence is shown in the following figure:
Figure 168 Connecting a network device
· If the remote device is a bank dumb terminal device, connect the RJ-45 connector (male) on one end of the dumb terminal cable to the RJ-45 interface on the interface module. Connect the RJ-45 connector (female) on the other end of the dumb terminal cable to the RJ-45 interface on one end of the dumb terminal adapter by a straight-through cable. The other end of the dumb terminal adapter is a D25 interface and can be connected to the bank dumb terminal device. The sequence is shown in the following figure:
Figure 169 Connecting a bank dumb terminal device
· If the interface of the remote device, usually a modem, is a D25/D9 interface, use the AUX cable to connect the RJ-45 interface on the interface module. The sequence is shown in the following figure:
Figure 170 Connecting a modem
Connecting a SIC-AP220/SIC-AP320 WLAN interface module
To connect the interface module to a configuration terminal (for example, a PC) through the serial console cable:
1. Connect the DB-9 female connector of the console cable to the serial port of the PC
2. Connect the RJ-45 connector to the console port on the module.
To disconnect the console cable, remove the RJ-45 connector end first.
ADSL/BS/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface
Appearance and applicable models of the magnetic-core telephone cable
Table 200 Appearance and applicable models of magnetic-core telephone cable
|
Cable |
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
Magnetic-core telephone cable |
1 × RJ-11 < ---- > 1 × RJ-11 |
SIC-1ADSL SIC-1ADSL-I SIC-1BS SIC-2BS SIC-1FXS SIC-1FXO SIC-2FXS SIC-2FXO SIC-2FXS1FXO DSIC-4FXS1FXO SIC-1AM SIC-2AM MIM-4FXS MIM-4FXO MIM-16FXS MIM-8FXS8FXO HMIM-4FXS HMIM-4FXO HMIM-16FXS HMIM-8FXS8FXO HMIM-6AM HMIM-6FCM |
Connecting an ADSL/FXS/FXO/AM/FCM interface module
1. Connect one end of the magnetic-core telephone cable to the RJ-11 or RJ-45 interface of the interface module.
2. Connect the other end of the magnetic-core telephone cable to the remote device interface.
Connecting a BS/BU interface module cable
1. If the service provider provides an ISDN U interface cable, you must use an NT1 device for adaptation. Connect one end of the magnetic-core telephone cable to the RJ-45 interface of the SIC-1BS interface module. Connect the other end of the magnetic-core telephone cable to the S/T interface of the NT1 device. Connect the ISDN U interface cable to the U interface on the NT1 device.
Figure 171 Connecting the U interface cable to the SIC-1BS interface module
2. If the service provider provides an ISDN S/T interface cable, directly connect the cable to the RJ-45 interface of the SIC-1BS interface module.
Figure 172 Connecting the S/T interface cable to the SIC-1BS interface module
E&M interface
E&M interface appearance and the applicable model
MIM-4E&M and FIC-4E&M modules support Bell I, II, III, V switches, and 2-wire & 4-wire voice signals.
As a best practice, use Bell V 4-wire voice signal to communicate with the router in practice.
The sequence of E&M RJ-45 pins is shown in the following figure, numbered 1 to 8 from left to right:
Figure 173 Sequence of RJ-45 pins
Table 201 Pinouts of E&M interface cable (Bell V 4-wire)
|
E&M interface |
||
|
RJ-45 Pin |
Signal |
Signal direction |
|
1 |
— |
— |
|
2 |
E |
IN |
|
3 |
RING0 |
IN |
|
4 |
RING1 |
OUT |
|
5 |
TIP1 |
OUT |
|
6 |
TIP0 |
IN |
|
7 |
M |
OUT |
|
8 |
SG |
Ground |
|
|
NOTE: Because the 4E&M modules cannot determine the interface types (Bell I/II/III/V), cable types (2-wire or 4-wire), and pinouts (E/M/Tx/Rx) of the peer switch, you must prepare the interface cables of the 4E&M modules according to the on-site conditions. To ensure the EMC of the router, install a ferrite core near the connector of the E&M module interface cable at the router side. |
The connection method
1. Connect one end of the magnetic-core telephone cable to the RJ-11 or RJ-45 interface of the interface module.
2. Connect the other end of the magnetic-core telephone cable to the remote device interface.
BSV/BSE interface
BSV/BSE interface cable appearance and applicable models
Table 202 BSV/BSE interface cable appearance and applicable models
|
Cable |
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
ISDN S/T interface standard cable |
1 × RJ-45 < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
SIC-1BSV SIC-2BSV |
|
ISDN S/T interface crossover cable |
1 × RJ-45 (female) < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 (male) |
SIC-1BSV SIC-2BSV |
Connecting a SIC-1BSV / SIC-2BSV / MIM-4BSV interface module cable
BSV interface supports the User and Network operating modes. The BSV interface works in User mode when connecting to an ISDN network, or works in Network mode when connecting to TE devices such as the digital telephones or the BSV interfaces working in User mode.
Choose the cable connection type according to the operating mode:
· When the BSV interface works in User mode, choose the connection method according to the type of the cable provided by the service provider:
¡ If the service provider provides an ISDN U interface cable, you must use an NT1 device for adaptation. Connect one end of the standard ISDN S/T interface cable to the RJ-45 interface of the BSV interface module. Connect the other end of the standard ISDN S/T interface cable to the S/T interface of the NT1 device. Connect the ISDN U interface cable to the U interface on the NT1 device.
Figure 174 Connecting a service provider U interface cable to a BSV interface module
¡ If the service provider provides an ISDN S/T interface cable, directly connect the service provider cable to the BSV interface.
Figure 175 Connecting a service provider S/T interface cable to a BSV interface module
· When the BSV interface works in Network mode, you must use an ISDN S/T interface crossover cable to connect the BSV interface to a TE device such as a digital telephone or a BSV interface working in User mode:
Connect the RJ-45 connector (male) of the ISDN S/T interface crossover cable to the RJ-45 interface on the BSV interface module. Connect the RJ-45 interface (female) of the standard ISDN S/T interface cable to one end of the standard ISDN S/T interface cable. Connect the S/T interface on the TE device to the other end of the standard ISDN S/T interface cable.
Figure 176 Connecting a TE device to a BSV interface module
3G interface
Appearance and applicable models of the SIC-3G-CDMA/SIC-3G-TD/SIC-3G-HSPA interface module antenna
Table 203 Appearance and applicable models of the SIC-3G-CDMA/SIC-3G-TD/SIC-3G-HSPA interface module antenna
|
Cable |
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
SIC-3G-CDMA/SIC-3G-TD/SIC-3G-HSPA interface module antenna |
|
SIC-3G-CDMA SIC-3G-TD SIC-3G-HSPA |
|
AUX cable |
1 × D25 & 1 × D9 < ---- > 1 × RJ-45 |
Table 204 The detailed specifications for the SIC-3G-CDMA/SIC-3G-TD/SIC-3G-HSPA interface module antenna
|
Item |
Description |
|
Frequency scope |
824-960 MHz / 1710-2170 MHz |
|
Voltage standing wave ratio |
≤ 2 |
|
Input impedance |
50 ohms |
|
Gain |
1.5 dBi |
|
Polarization type |
Vertical |
|
Maximum input power |
10 W |
|
Interface |
TNC-Male |
|
Lightning protection |
Direct current grounding |
|
Height |
153 mm (6.02 in) |
|
Weight |
26 g (0.92 oz) |
|
Length |
None |
|
Color |
Black |
|
Operating temperature |
–30 °C to +60 °C (–22°F to +140°F) |
Connecting a SIC-3G-CDMA/SIC-3G-TD/SIC-3G-HSPA interface module antenna
1. To install an antenna, adjust the angle of the antenna to 180º.
2. Fasten the antenna onto the antenna port that has a MAIN mark. Avoid over-tightening. Make sure the antenna is vertical to the ground or ceiling to achieve the optimal coverage.
Connecting a SIC-3G-CDMA/SIC-3G-TD/SIC-3G-HSPA interface debug antenna
To debug and test the SIC-3G-CDMA/SIC-3G-TD/SIC-3G-HSPA, connect the RJ-45 interface of the AUX cable to the Diag Port interface and connect the D25/D9 connector to a peer device, which is usually a PC.
4G interface
Appearance and applicable models of 4G antennas and extension cables
Table 205 Appearance and applicable models of the 4G antennas and extension cables
|
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
|
SIC-4G-LTE-M |
|
SIC-4G-CNDE/SIC-D4G-CNDE/SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK/SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK |
|
|
RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 |
|
|
SIC-4G-CNDE/SIC-D4G-CNDE/SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK/SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK |
|
|
|
RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 |
Table 206 Antenna specifications
|
Item |
Specification |
||
|
SIC-4G-LTE-M |
SIC-4G-CNDE/SIC-D4G-CNDE/SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK/SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK |
RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 |
|
|
Frequency scope |
698 to 960 MHz 1.71 to 2.7 GHz |
791 to 960 MHz 1710 to 2690 MHz |
617 to 960 MHz 1400 to 1612 MHz 1710 to 2170 MHz 2300 to 2700 MHz 3300 to 3800 MHz 4400 to 5000 MHz 5150 to 5850 MHz |
|
Voltage standing wave ratio |
2.5 |
≤ 3.5 |
≤ 4 |
|
Input impedance |
50 ohms |
50 ohms |
50 ohms |
|
Gain |
2 dBi |
791 to 960 MHz @ 3.1 dBi 1710 to 2690 MHz @ 7.2dBi |
617 to 960 MHz/0.59 dBi 1400 to 1612 MHz/1.87 dBi 1710 to 2170 MHz/3.74 dBi 2300 to 2700 MHz/3.51 dBi 3300 to 3800 MHz/3.7 dBi 4400 to 5000 MHz/4.0 dBi 5150 to 5850 MHz/4.87 dBi |
|
Polarization type |
Vertical |
Vertical |
Vertical |
|
Maximum input power |
5 W |
1 W |
1 W |
|
Interface |
TNC |
SMA |
SMA, male |
|
Height |
21.4 cm (8.43 in) |
16.6 cm (6.54 in) |
20.3 cm (7.99 in) |
|
Weight |
50.5 g (1.78 oz) |
22 g (0.78 oz) |
19.63 g (0.69 oz) |
|
Color |
Black |
Black |
Black |
|
Operating temperature |
–40°C to +85°C (–40°F to +185°F) |
–10°C to +60°C (14°F to 140°F) |
–20°C to +60°C (–4°F to +140°F) |
Table 207 4G antenna extension cable specifications for the SIC-4G-CNDE/SIC-D4G-CNDE/SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK/SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK module
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Frequency scope |
698 to 960 MHz 1710 to 2700 MHz |
|
Voltage standing wave ratio |
≤ 2.0 |
|
Input impedance |
50 ohms |
|
Gain |
2.0 dBi |
|
Polarization type |
Vertical |
|
Interface |
SMA |
|
Height |
16.4 ± 0.2 cm (6.46 ± 0.08 in) |
|
Weight |
134 ± 5 g (4.73 ± 0.18 oz) |
|
Color |
Black |
|
Cable length |
200 ± 2 cm (78.74 ± 0.79 in) |
|
Operating temperature |
–40°C to +60°C (–40°F to +140°F) |
Table 208 4G antenna extension cable specifications for the RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Frequency range |
DC to 6 GHz |
|
Voltage standing wave ratio |
≤ 5 |
|
Input impedance |
50 ohms |
|
Cable type |
RG-174 |
|
Max input power |
1 W |
|
Interface |
SMA |
|
Cable length |
3000 mm (118.11 in) |
|
Weight |
65.3 g (2.30 oz) |
|
Color |
Black |
|
Operating temperature |
–40°C to +85°C (–40°F to +185°F) |
Installing a 4G antenna for the SIC-4G-LTE-M, SIC-4G-CNDE, SIC-D4G-CNDE, SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK, SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK, or RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module
1. Change the angle of the antenna orientation from vertical to horizontal.
2. Fasten the antenna onto the antenna port. Avoid over-tightening.
Change the antenna orientation to vertical to achieve better signal coverage.
Connecting a 4G antenna extension cable for the SIC-4G-LTE-M, SIC-4G-CNDE, SIC-D4G-CNDE, SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK, SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK, or RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module
1. Fasten the SMA connector onto the antenna port on the module.
2. Attach the magnetic cradle on the other end of the extension cable to the rack.
Connecting a 4G antenna extension cable for the RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module
1. Fasten the SMA connector of the cable onto the antenna port on the module.
2. Connect the SMA female connector at the other end of the cable to the rod antenna. Place the antenna to a location near outdoors.
Installing a 4G interface debugging antenna
A 4G interface module has a Mini USB port to connect to the peer device through the USB console cable for third-party software to debug the 4G interface module. When the interface module is operating correctly, you do not need to connect the USB console cable.
To debug a 4G interface module, connect the port at one end of the USB console cable to the peer device (PC), and connect the other end to the Mini USB port on the interface module.
5G interface
Appearance and applicable models of 5G antennas and extension cables
Table 209 Appearance and applicable models of the 5G antennas and extension cables
|
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
|
RT-SIC-5G |
|
|
RT-SIC-5G |
Table 210 5G antenna specifications
|
Item |
Description |
|
Frequency range |
698 to 960 MHz 1710 to 2170 MHz 2300 to 2700 MHz 3300 to 3800 MHz 4400 to 5000 MHz 5150 to 5850 MHz |
|
Voltage standing wave ratio |
≤ 4 |
|
Input impedance |
50 ohms |
|
Gain |
617 MHz to 960 MHz, 0.59 dBi 1710 MHz to 2170 MHz, 3.74 dBi 2300 MHz to 2700 MHz, 3.51 dBi 3300 MHz to 3800 MHz, 3.7 dBi 4400 MHz to 5000 MHz, 4.0 dBi 5150 MHz to 5850 MHz, 4.87 dBi |
|
Polarization type |
Vertical |
|
Maximum input power |
1 W |
|
Interface |
SMA male |
|
Height |
203 mm (7.99 in) |
|
Weight |
19.63 g (0.69 oz) |
|
Color |
Black |
|
Operating temperature |
–20 °C to +65 °C (–4°F to +149°F) |
Table 211 5G antenna extension cable specifications
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Frequency range |
DC to 6 GHz |
|
Voltage standing wave ratio |
≤ 5 |
|
Input impedance |
50 ohms |
|
Cable type |
RG-174 |
|
Max input power |
1 W |
|
Interface |
SMA |
|
Cable length |
3000 mm (118.11 in) |
|
Weight |
65.3 g (2.30 oz) |
|
Color |
Black |
|
Operating temperature |
–40°C to +85°C (–40°F to +185°F) |
GPS interface
Appearance and applicable models of the SIC-4G-CNDE/SIC-D4G-CNDE/SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK/SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK interface module GPS antenna
Table 212 Appearance and applicable models of the 4G interface module GPS antenna
|
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
SIC-4G-CNDE SIC-D4G-CNDE SIC-4G-CNDE-SJK SIC-D4G-CNDE-SJK |
Table 213 Antenna specifications
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Frequency scope |
1575.42 ± 3 MHz |
|
Voltage standing wave ratio |
≤ 1.92 |
|
Input impedance |
50 ohms |
|
Gain |
1.5 dBic Typ |
|
Echo return loss |
10 dB Min |
|
Interface |
SMA |
|
Extension cable length |
5 m (16.40 ft) |
|
Extension cable type |
RG-174 Coaxial Cable |
|
Color |
Black |
|
Operating temperature |
–30°C to +80°C (–22°F to +176°F) |
Connecting an antenna extension cable
1. Fasten the SMA connector onto the GPS antenna port on the module.
2. Put the other end of the extension cable outdoor to achieve better signal coverage.
GNSS interface
Appearance and applicable models of the RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module GNSS antenna
Table 214 Appearance and applicable models of the RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module GNSS antenna
|
Antenna |
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module GNSS antenna |
RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 |
Table 215 RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 module GNSS antenna specifications
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Frequency scope |
· 1561±3 MHz · 1575.42±3 MHz · 1602±0.5 MHz |
|
Operating mode |
· GPS · GLONASS · BDS · Galileo |
|
Input impedance |
50 ohms |
|
Gain |
–2.91 dBic Typ |
|
Interface |
SMA male |
|
Extension cable length |
5 m (16.40 ft) |
|
Extension cable type |
RG-174 coaxial cable |
|
Color |
Black |
|
Operating temperature |
–40°C to +85°C (–40°F to +185°F) |
Connecting a GNSS antenna
1. Fasten the SMA male connector of the antenna extension cable onto the GNSS antenna port on the module.
2. Connect the other end of the extension cable to the antenna. Place the antenna outdoors for better signal receipt.
WLAN interface
Appearance and applicable models of the WLAN interface module antenna
Table 216 Appearance and applicable models of the WLAN interface module antenna
|
Antenna |
Appearance |
Applicable models |
|
WLAN interface module antenna |
SIC-AP220 SIC-AP320 |
Connecting a WLAN interface module antenna
1. Unfold the antenna.
2. Attach the antenna to the antenna connector on the interface module. To avoid damage, do not over-tighten the antenna.
3. Fold the antenna to a 90-degree angle so that it is vertical to the ground or ceiling to achieve optimal coverage.
Link mode of interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules
An interface can operate in bridge or route link mode. You can use the port link-mode command to change the link mode of an interface. Interfaces that operate in bridge mode are called Layer 2 interfaces. Interfaces that operate in route mode are called Layer 3 interfaces.
Some interfaces on Ethernet switching modules and interface modules can operate only as Layer 3 interfaces, as shown in Table 217. Some interfaces operate as Layer 2 interfaces by default but can be changed to Layer 3 interfaces by using the port link-mode command, as shown in Table 218.
|
IMPORTANT: · By default, the nine Ethernet interfaces on the DSIC-9FSW and DSIC-9FSWP interface modules operate in bridge mode. You can execute the port link-mode command to change the operating mode of any four interfaces to route. The remaining five interfaces can operate only in bridge mode. · When the SIC-4FSW, SIC-4FSWP, DSIC-9FSW, or DSIC-9FSWP interface module is installed on an MSR2600-10 or MSR2600-17 router, you can change the operating mode of any two interfaces to route. The remaining interfaces can operate only in bridge mode. · When the SIC-4FSW, SIC-4FSWP, DSIC-9FSW, or DSIC-9FSWP interface module is installed on other routers than MSR2600-10 and MSR2600-17 routers, you can change the operating mode of any four interfaces to route. The remaining interfaces can operate only in bridge mode. · For the interface module compatibility with router models, see "Appendix B Purchase guide." |
Table 217 Ethernet interfaces that can operate only as Layer 3 interfaces
|
Ethernet switching module/Ethernet interface module |
Interfaces that can operate only as Layer 3 interfaces |
|
SIC-4FSW |
N/A |
|
SIC-4FSWP |
N/A |
|
DSIC-9FSW |
N/A |
|
DSIC-9FSWP |
N/A |
|
SIC-4GSW |
N/A |
|
SIC-4GSWF |
N/A |
|
SIC-1FEA |
FE0 |
|
SIC-1FEF |
SFP0 |
|
SIC-1GEC-V2 |
Combo 0 (GE0, SFP0) |
|
HMIM-8GSW |
N/A |
|
HMIM-24GSW |
N/A |
|
HMIM-24GSW-PoE |
N/A |
|
HMIM-8GSWF |
N/A |
|
HMIM-2GEE |
GE0 and GE1 |
|
HMIM-4GEE |
GE0 to GE3 |
|
HMIM-8GEE |
GE0 to GE7 |
|
RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2 |
GE0 to GE3 |
|
RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2 |
GE0 to GE7 |
|
HMIM-2GEF |
SFP0 and SFP1 |
|
HMIM-4GEF |
SFP0 to SFP3 |
|
HMIM-8GEF |
SFP0 to SFP7 |
|
RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2 |
SFP0 to SFP3 |
|
RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2 |
SFP0 to SFP7 |
|
RT-HMIM-4XP |
SFP+0 to SFP+3 |
|
Ethernet switching module/Ethernet interface module |
Interfaces that operate as Layer 2 interfaces by default and can be changed to Layer 3 interfaces |
|
SIC-4FSW |
FE0 to FE3 |
|
SIC-4FSWP |
FE0 to FE3 |
|
DSIC-9FSW |
Any four interfaces |
|
DSIC-9FSWP |
Any four interfaces |
|
SIC-4GSW |
GE0 to GE3 |
|
SIC-4GSWF |
SFP0 to SFP3 |
|
SIC-1FEA |
N/A |
|
SIC-1FEF |
N/A |
|
SIC-1GEC-V2 |
N/A |
|
HMIM-8GSW |
GE0 to GE5, Combo 6 (GE6, SFP6), Combo 7 (GE7, SFP7) |
|
HMIM-24GSW |
GE0 to GE23 |
|
HMIM-24GSW-PoE |
GE0 to GE23 |
|
HMIM-8GSWF |
SFP0 to SFP3, Combo 4 (GE4, SFP4), Combo 5 (GE5, SFP5), Combo 6 (GE6, SFP6), Combo 7 (GE7, SFP7) |
|
HMIM-2GEE |
N/A |
|
HMIM-4GEE |
N/A |
|
HMIM-8GEE |
N/A |
|
RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2 |
N/A |
|
RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2 |
N/A |
|
HMIM-2GEF |
N/A |
|
HMIM-4GEF |
N/A |
|
HMIM-8GEF |
N/A |
|
RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2 |
N/A |
|
RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2 |
N/A |
|
RT-HMIM-4XP |
N/A |
Interface module power consumption
Table 219 Interface module power consumption
|
Interface module model |
Max power consumption |
|
DSIC-9FSW |
3.20 W |
|
SIC-4GSW |
3.80 W |
|
SIC-4GSWF |
4.20 W |
|
SIC-1GEC-V2 |
0.82 W |
|
RT-SIC-1POS-STM1 |
8.35 W |
|
SIC-E1-F |
0.43 W |
|
SIC-2E1-F |
0.43 W |
|
SIC-8AS |
3.35 W |
|
SIC-16AS |
0.75 W |
|
SIC-1SAE |
0.42 W |
|
SIC-2SAE |
3.35 W |
|
SIC-4SAE |
3.35 W |
|
SIC-4RS |
0.96 W |
|
SIC-2FXS |
2 W |
|
SIC-2FXO |
2 W |
|
SIC-2FXS1FXO |
2.44 W |
|
SIC-3G-CDMA |
3.40 W |
|
SIC-3G-TD |
3.40 W |
|
SIC-3G-HSPA |
3.40 W |
|
SIC-4G-LTE-M |
5 W |
|
SIC-4G-CNDE |
4.18 W |
|
SIC-D4G-CNDE |
6.61 W |
|
SIC-CNDE |
5.50 W |
|
RT-SIC-4G-CAT6 |
4.68 W |
|
RT-SIC-5G |
7.60 W |
|
HMIM-8GSW |
9.26 W |
|
HMIM-24GSW |
22.40 W |
|
HMIM-24GSW-PoE |
22.40 W |
|
HMIM-2GEE |
6.68 W |
|
HMIM-4GEE |
6.88 W |
|
HMIM-8GEE |
11.20 W |
|
RT-HMIM-4GEE-V2 |
9.09 W |
|
RT-HMIM-8GEE-V2 |
9.36 W |
|
HMIM-2GEF |
6.80 W |
|
HMIM-4GEF |
6.80 W |
|
HMIM-8GEF |
12.20 W |
|
RT-HMIM-4GEF-V2 |
9.09 W |
|
RT-HMIM-8GEF-V2 |
13.68 W |
|
HMIM-8GSWF |
10.30 W |
|
RT-HMIM-4XP |
5.12 W |
|
HMIM-1ATM-OC3 |
5.80 W |
|
HMIM-1POS |
5.07 W |
|
RT-HMIM-2POS-STM1 |
17.76 W |
|
RT-HMIM-4POS-STM1/4 |
17.76 W |
|
HMIM-1CPOS |
10 W |
|
HMIM-2CPOS |
11.54 W |
|
HMIM-1E1 |
4.50 W |
|
HMIM-2E1 |
4.61 W |
|
HMIM-4E1 |
4.71 W |
|
HMIM-1E1-F |
4.50 W |
|
HMIM-2E1-F |
4.61 W |
|
HMIM-4E1-F |
4.71 W |
|
HMIM-8E1 |
4.90 W |
|
HMIM-8E1-F |
4.90 W |
|
RT-HMIM-2E1-V3 |
4.34 W |
|
RT-HMIM-4E1-V3 |
4.56 W |
|
RT-HMIM-8E1-V3 |
4.91 W |
|
HMIM-2T1 |
5.10 W |
|
HMIM-4T1-F |
5.30 W |
|
HMIM-2E1T1 |
4.60 W |
|
HMIM-4E1T1 |
5.65 W |
|
HMIM-8E1T1 |
5.65 W |
|
HMIM-2E1T1-F |
4.60 W |
|
HMIM-4E1T1-F |
4.70 W |
|
HMIM-8E1T1-F |
4.90 W |
|
HMIM-1CE3 |
11.30 W |
|
HMIM-2SAE |
6.71 W |
|
HMIM-4SAE |
6.90 W |
|
HMIM-8SAE |
7.29 W |
|
RT-HMIM-4SAE-V2 |
4.19 W |
|
RT-HMIM-8SAE-V2 |
4.69 W |
|
HMIM-8ASE |
3.60 W |
|
HMIM-16ASE |
4.30 W |
|
RT-HMIM-8ASE-V2 |
3 W |
|
RT-HMIM-16ASE-V2 |
3.12 W |
|
HMIM-16FXS |
21.19 W |
|
HMIM-8FXS8FXO |
15.22 W |
|
HMIM-2VE1 |
10.75 W |
|
HMIM-2VT1 |
10.75 W |
|
HMIM-1VE1 |
9.50 W |
|
HMIM-1VT1 |
9.50 W |
|
HMIM-4FXS |
6.30 W |
|
HMIM-4FXO |
3.54 W |
|
HMIM-4E&M |
7.17 W |
|
HMIM-8E&M |
7.17 W |
|
HMIM-6AM |
12 W |
|
HMIM-6FCM |
9.90 W |
|
HMIM-CNDE-SJK |
14 W |
|
HMIM-Adapter |
2 W |
|
DHMIM-1DM |
49 W |
|
DHMIM-1E1POS1DM |
58.56 W |
|
VPM2 512 |
10 W |
|
VPM2 256 |
6.12 W |
|
VPM2 128 |
5.76 W |