- Table of Contents
-
- 06-Network
- 01-Scanner
- 02-VRF
- 03-Interface
- 04-Interface pairs
- 05-Interface collaboration
- 06-Security zones
- 07-VLAN
- 08-MAC
- 09-DNS
- 10-ARP
- 11-ND
- 12-Forwarding advanced settings
- 13-ALG
- 14-GRE
- 15-IPsec
- 16-ADVPN
- 17-L2TP
- 18-SSL VPN
- 19-Routing table
- 20-Static routing
- 21-Policy-based routing
- 22-OSPF
- 23-BGP
- 24-IS-IS
- 25-RIP
- 26-IPv4 multicast routing
- 27-IPv6 multicast routing
- 28-PIM
- 29-IGMP
- 30-MLD
- 31-DHCP
- 32-HTTP
- 33-SSH
- 34-NTP
- 35-FTP
- 36-Telnet
- 37-MAC authentication
- 38-MAC address whitelist
- 39-MAC access silent MAC info
- 40-MAC access advanced settings
- 41-IP authentication
- 42-IPv4 whitelist
- 43-IPv6 whitelist
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 18-SSL VPN | 256.99 KB |
SSL VPN
This help contains the following topics:
¡ Restrictions and guidelines: SSL VPN gateway configuration
¡ Restrictions and guidelines: TCP access configuration
¡ Restrictions and guidelines: IP access configuration
¡ Restrictions and guidelines: Domain name configuration
¡ Restrictions and guidelines: Webpage template configuration
¡ Restrictions and guidelines: LDAP authentication configuration
¡ Restrictions and guidelines: SSO login configuration
¡ Restrictions and guidelines: WeChat Work authentication
¡ Configure basic settings in an SSL VPN context
¡ Configure authentication settings
· FAQ
Introduction
SSL VPN operating mechanism
To allow remote user access to protected resources behind an SSL VPN gateway, you must configure these resources on the gateway. Remote users can access only the resources authorized to them after they establish an SSL-encrypted connection to the gateway and pass the identity authentication.
SSL VPN operates as follows:
1. The remote user establishes an HTTPS connection to the SSL VPN gateway.
In this process, the remote user and the SSL VPN gateway perform SSL certificate authentication.
2. The remote user enters the username and password.
3. The SSL VPN gateway authenticates the credentials that the user entered, and authorizes the user to access a range of resources.
4. The user selects a resource to access.
An access request for that resource is sent to the SSL VPN gateway through the SSL connection.
5. The SSL VPN gateway resolves the request and forwards the request to the corresponding internal server.
6. The SSL VPN gateway forwards the server's reply to the user through the SSL connection.
SSL VPN networking modes
SSL VPN supports the following networking modes:
· Gateway mode—In gateway mode, the SSL VPN gateway acts as a gateway that connects remote users and the internal servers network. Because the SSL VPN gateway is deployed in line, it can provide full protection to the internal network but it affects data transmission performance.
· Single-arm mode—In single-arm mode, the SSL VPN gateway is attached to the network gateway. The gateway forwards user-to-server traffic to the SSL VPN gateway. The SSL VPN gateway processes the traffic and sends the processed traffic back to the gateway. The gateway forwards the traffic to the internal servers. The SSL VPN gateway is not a performance bottleneck in the network because it is not deployed on the key path. However, the SSL VPN gateway cannot provide full protection to the internal network.
SSL VPN access modes
Web access
In Web access mode, remote users use browsers to access Web resources allowed by an SSL VPN gateway through HTTPS. After login, a user can access any resources listed on the webpage. In Web access mode, all operations are performed on webpages.
The resources available for SSL VPN Web access users are Web servers only.
TCP access
In TCP access mode, users access TCP applications on internal servers by accessing the applications' open ports. Supported applications include remote access services (such as Telnet), desktop sharing services, mail services, Notes services, and other TCP services that use fixed ports.
In TCP access mode, a user installs the TCP access client software on the SSL VPN client (the terminal device that the user uses). The client software uses an SSL connection to transmit the application layer data.
IP access
IP access implements secured IP communications between remote users and internal servers.
To access an internal server in IP access mode, a user must install dedicated IP access client software. The client software will install a virtual network interface card (VNIC) on the SSL VPN client.
BYOD access
BYOD access enables secured access to internal resources through mobile clients.
For mobile clients to access internal resources in BYOD access mode:
· On the SSL VPN gateway, you must specify an Endpoint Mobile Office (EMO) server for mobile clients. Mobile clients access internal resources through the EMO server.
· On the mobile client, the user must install SSL VPN client software dedicated for mobile clients.
Resource access control
SSL VPN controls user access to resources on a per-user basis.
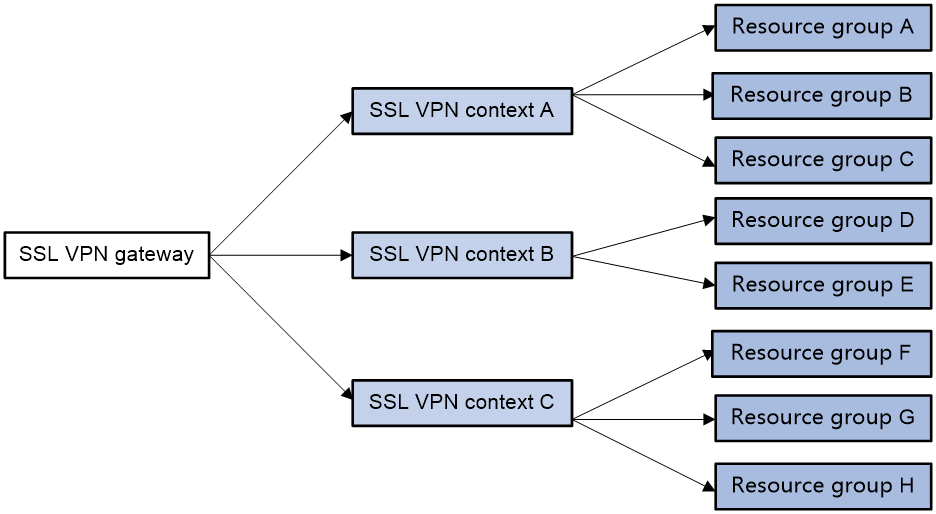
As shown in Figure 1, an SSL VPN gateway can be associated with multiple SSL VPN contexts. An SSL VPN context contains multiple resource groups. A resource group defines accessible Web resources, TCP resources, and IP resources.
Figure 1 SSL VPN resource access control
An SSL VPN user can access an SSL VPN gateway by using the following methods:
· Exclusive—If the SSL VPN gateway is associated with only one SSL VPN context, the user can access the SSL VPN context directly by entering the IP address and port number of the SSL VPN gateway.
· Domain name—The SSL VPN gateway can be associated with multiple SSL VPN contexts through different domain names. The user will be prompted to select a domain name from the domain list displayed on the SSL VPN gateway login page. The SSL VPN gateway determines the SSL VPN context to which the user belongs based on the selected domain name.
· Virtual host name—The SSL VPN gateway can be associated with multiple SSL VPN contexts through different virtual host names. The SSL VPN gateway determines the SSL VPN context to which the user belongs based on the virtual host name entered on the SSL VPN gateway login page.
After determining the SSL VPN context for a user, the SSL VPN gateway uses the authentication and authorization methods of the ISP domain specified for the context to perform authentication and authorization for the user.
· If the SSL VPN gateway authorizes the user to use a resource group, the user can access resources allowed by the resource group.
· If the SSL VPN gateway does not authorize the user to use a resource group, the user can access resources allowed by the default resource group.
|
The SSL VPN gateway uses AAA to perform user authentication and authorization. SSL VPN supports AAA protocols RADIUS and LDAP. RADIUS is most often used. |
Restrictions and guidelines
Disabling an SSL VPN AC interface might interrupt the IP access service. Please perform this operation with caution.
Restrictions and guidelines: SSL VPN gateway configuration
If the SSL server policy used by an SSL VPN gateway is changed, or the policy settings are changed, you must re-enable the gateway to make the configuration take effect.
Restrictions and guidelines: TCP access configuration
· When configuring the client address for a port forwarding item on the SSL VPN gateway, use an address in network segment 127.0.0.0/8, or use the host name or domain name.
· For a user to access TCP resources through a host, modifications to the hosts file on the host might be required. Make sure the user has the administrator privileges on the host.
· The host used for TCP access must have the Java Runtime Environment installed.
Restrictions and guidelines: IP access configuration
When you configure the IP access address pool for IP access clients, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· The IP access address pool and the IP address of the NIC used on an IP access client host must belong to different network segments.
· To avoid address conflicts, make sure the IP access pool does not contain the IP addresses of interfaces on the SSL VPN gateway device.
· Make sure the IP access address pool and the IP addresses of internal servers hosting accessible IP resources belong to different network segments.
When you bind IP addresses to an SSL VPN user, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· If an IP access address pool is specified for the SSL VPN resource group authorized to the user, the IP addresses must exist in the address pool.
· If no address pool is specified for the SSL VPN resource group, the IP addresses must exist in the address pool specified for the SSL VPN context of the user.
· You can bind the same IP address to different SSL VPN users only when the SSL VPN contexts of the users are associated with different VPN instances.
Restrictions and guidelines: Domain name configuration
Make sure you specify valid domain names for SSL VPN configuration items such as Web resource URLs or port forwarding entries.
SSL VPN does not check the existence or validity of the specified domain names.
Restrictions and guidelines: Webpage template configuration
· The template files uploaded must be .zip files.
· An uploaded template .zip file must contain both home.html and login html files in the root directory of the .zip file.
Restrictions and guidelines: LDAP authentication configuration
If you configure LDAP authentication for SSL VPN users, you must also configure LDAP authorization. Configure LDAP authorization settings from the CLI on the device.
Restrictions and guidelines: SSO login configuration
For the auto-build SSO method, the following requirements must be met:
· If a user group name is specified as the SSO login parameter, only remote users are supported.
· SSO login is available only for accessing resources by clicking the URL links on the SSL VPN Web interface. SSO does not work if you access the resources by entering the URLs in a browser address bar or a URL input box.
· SSO login is not available for Web resources that require graphic verification codes.
· SSO login is not available for Web resources that require two-factor authentication or script invocation.
Restrictions and guidelines: WeChat Work authentication
If WeChat Work authentication is enabled in an SSL VPN context, the SSL VPN context supports only the Exclusive access mode for the associated gateway.
Configure SSL VPN
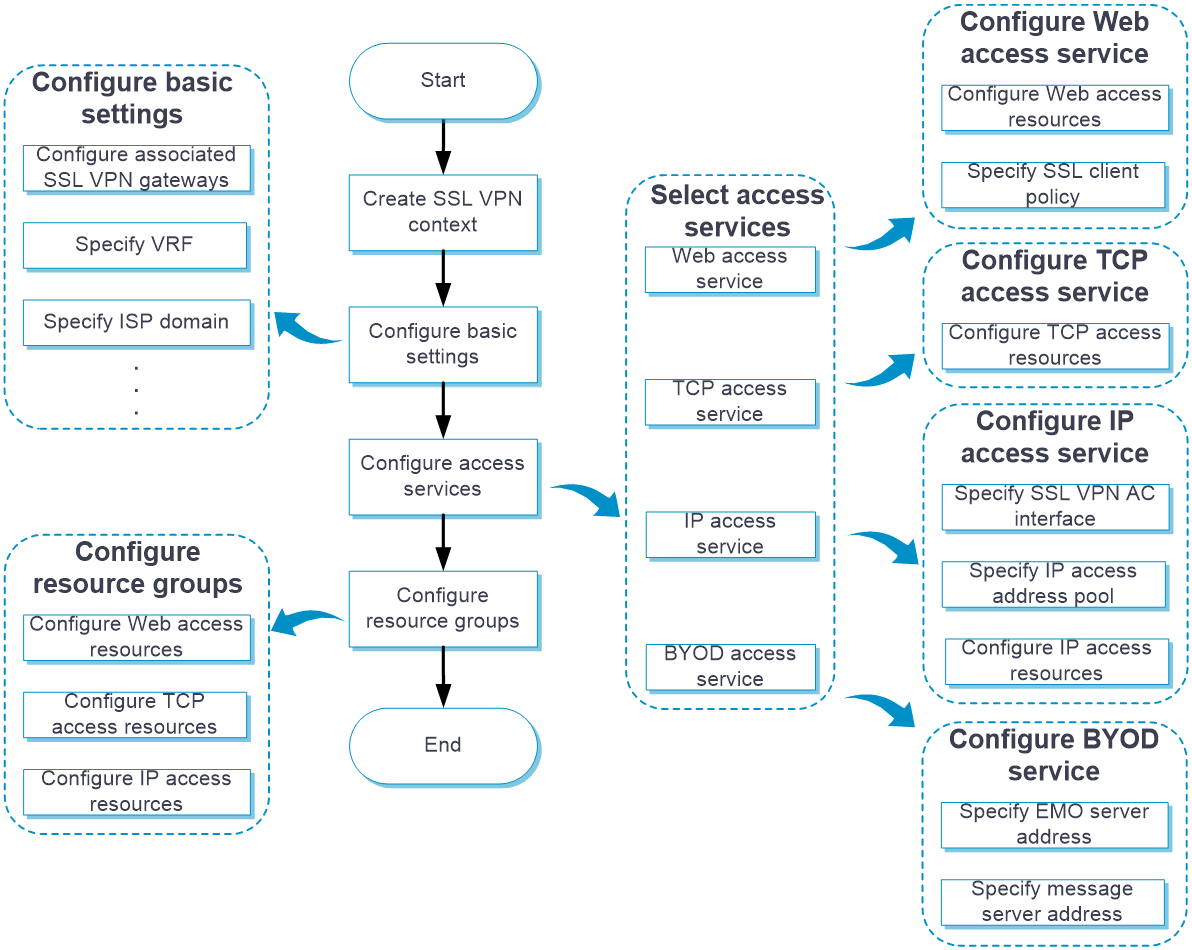
Configure an SSL VPN context as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 SSL VPN configuration procedure
In addition to the preceding configuration procedure, you can also perform the following tasks in SSL VPN:
· Create and edit SSL VPN gateways on the Network > SSL VPN > SSL VPN Gateways page.
· Create and edit IP access address pools on the Network > SSL VPN > IP Access Address Pools page.
· Create and edit SSL VPN AC interfaces on the Network > SSL VPN > SSL VPN AC Interfaces page.
· Edit the webpage template, title, login welcome message, hide-password-box setting, and logo for the SSL VPN Webpage on the Webpage settings tab of the Edit SSL VPN Context page.
· Edit the following settings on the Webpage settings tab of the Edit SSL VPN Context page:
¡ Chinese and English notices on the SSL VPN gateway login page and resource page.
¡ Chinese and English webpage files.
¡ Chinese and English password complexity descriptions.
¡ Server reply messages rewriting.
· Upload the custom IP access client file on the Network > SSL VPN > Global Settings page. Users can download the client and use it to log in to the SSL VPN gateway. On this page, you can also select a webpage template as the global SSL VPN webpage template.
· Configure the port for user data transport in HA group on the Network > SSL VPN > Global Settings page. The device uses this port and the peer IP address (configured on the High Availability page) to establish an SSL VPN backup channel with the HA peer device. The SSL VPN backup channel is dedicatedly used for backup of SSL VPN user information. Support for the HA group port configuration on the SSL VPN global settings page depends on the device model.
· Add user-defined SSL VPN webpage templates:
a. Navigate to the Network > SSL VPN > TempManagement page, and then click Create.
b. On the opened page, upload a user-defined webpage template.
You can use the uploaded templates on the Network > SSL VPN > Global Settings or Edit SSL VPN Context page.
· View the online user information and IP access statistics on the Network > SSL VPN > Statistics page.
· For SSO login, you can export and import the user custom configuration on the Network > SSL VPN > Global Settings page:
¡ Click Export user custom configuration to export the custom username and password for the current user to perform SSO login.
¡ Click Import user custom configuration to import the custom username and password for the current user to perform SSO login.
Configure basic settings in an SSL VPN context
Configure the basic settings, including the associated SSL VPN gateways, VRF (VPN instance) to which the SSL VPN context belongs, the enabling status of user login logging, and the enabling status of the SSL VPN context.
Procedure
1. Click the Network tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select SSL VPN > SSL VPN Contexts.
The SSL VPN Contexts page opens.
3. Click Create.
The Create SSL VPN Context page opens.
4. On the Basic settings tab, configure the basic settings for the SSL VPN context, and then click Next.
Table 1 Basic configuration items for an SSL VPN context
|
Item |
Description |
|
Context name |
Enter an SSL VPN context name. |
|
Associated gateways |
Configure the gateways associated with the SSL VPN context. To add an associated gateway for the SSL VPN context: 1. Click Create in the Associated gateways field. 2. In the dialog box that opens, select a gateway from the GateWay list. If no gateways are available, click SSL VPN Gateway to create a gateway. 3. Select an access method. Options include Exclusive, Domain name, and Virtual host name. You must specify a domain name or virtual host name if the SSL VPN gateway is or will be also associated with other SSL VPN contexts. For the context to use the gateway exclusively, select the Exclusive access method. |
|
VRF |
Select the VPN instance to which the SSL VPN context belongs. |
|
Max sessions |
Specify the maximum number of SSL VPN sessions for the SSL VPN context. If the limit is reached, new users cannot access the SSL VPN gateway. |
|
Login control |
Specify the maximum number of concurrent logins per account. A user cannot log in if the number of logins using the same account reaches the limit. You can enable force logout so when a login is attempted but logins using the account reach the maximum, the user with the longest idle time will be logged out to allow the new login. |
|
Max connt per session |
Select whether to enable or disable limiting the number of connections in a session. If the number of connections in a session has reached the limit, new connection requests for the session will be rejected with a 503 Service Unavailable message. |
|
Session idle timeout |
Specify the maximum idle time of an SSL VPN session. If the idle time of an SSL VPN session exceeds the specified idle timeout time, the session is terminated. |
|
Idle-cut traffic threshold |
Specify the idle-cut traffic threshold in kilobytes. An SSL VPN session will be disconnected if the session traffic observed within the session idle timeout time is below the idle-cut traffic threshold. |
|
Rate limit per session |
When the packet transmission rate in a direction of the SSL VPN session exceeds the specified limit, subsequent packets in that direction will be dropped. Uplink traffic refers to the traffic sent from users to the server. Downlink traffic refers to the traffic sent from the server to users. |
|
User login logging |
Select this item to enable logging for user login and logout events. |
|
Resource access logging |
Select this item to enable logging for resource access. After you enable resource access logging, you can select a logging method. Options include Log filtering and Summary log. If log filtering is enabled, the device generates only one log for accesses of the same user to the same resource in a minute. When log filtering is disabled, the device generates a log for each resource access. |
|
Online password change |
Select this item to enable password modification. An SSL VPN user is able to modify the password only when this feature is enabled in both SSL VPN user view and SSL VPN context view. |
|
Enable SSL VPN context |
Select this item to enable the SSL VPN context. |
|
Global URL Masking |
Select this item to enable URL masking for all Web resources in the SSL VPN context. |
|
Allowed clients |
Select the client types allowed. Client types include browsers, PC iNode clients, and mobile iNode clients. If browsers are denied (not selected), no users can use browsers to access the SSL VPN. If iNode clients are denied, new users cannot use iNode clients to access the SSL VPN. Online users will not be affected. |
Configure authentication settings
The authentication mode for users to log in to an SSL VPN context includes password authentication, certificate authentication, and IMC SMS verification.
Procedure
On the AuthN Config tab, configure the authentication settings.
Table 2 Authentication configuration items for an SSL VPN context
|
Item |
Description |
|
ISP domain |
Select the ISP domain used for authentication, authorization, and accounting. |
|
Code verification |
Select this item to enable code verification. After code verification is enabled, a user must enter a correct verification code to log in to the SSL VPN Web interface. |
|
Certificate auth |
Select this item to enable certificate authentication. To use certificate authentication, make sure client authentication is enabled in the SSL server policy. The SSL VPN gateway uses the digital certificate sent by an SSL VPN client to authenticate the client. |
|
Username attribute |
Select the certificate attribute to be used as the SSL VPN username. By default, the CN attribute in the Subject field of a certificate is used as the username. |
|
Enable password |
Select this item to enable password authentication. After password authentication is enabled, a user can use the username and password to log in to the SSL VPN Web interface. |
|
Certificate and pwdN |
Select the authentication mode for users if both certificate and password authentication methods are enabled. To require users to pass both certificate and password authentications, select Use all methods. To require users to pass either certificate or password authentication, select Use any method. |
|
IMC user pwd modify |
Select this item to enable password modification for IMC authentication users. You must specify the IMC server's IP address and port number, and the VRF instance to which the IMC server belongs. For this feature to take effect, make sure the online password change feature is enabled. |
|
IMC SMS verification |
Select this item to enable IMC SMS verification. To use this feature, make sure SMS message verification has been configured on the IMC server. After SMS message verification is enabled, an SSL VPN client can dynamically obtain a verification code from the IMC server for SSL VPN gateway login authentication. |
|
Enable WeChat Work authN |
Select this item to enable WeChat Work authentication. To use this feature, make sure the following tasks have been completed: · Configuring the company Apps on the WeChat Work management platform. · Configuring the App homepage redirect link and the trusted domain name of the SSL VPN gateway for each App on the WeChat Work management platform. · Completing the domain name ownership verification: download the domain name ownership verification file from the WeChat Work management platform, and then upload the file on the Network > SSL VPN > Global Settings page. After the WeChat Work authentication is enabled, the device obtains user information from the third party of WeChat Work and uses the user information for authentication and authorization. |
|
API server address |
Enter a WeChat Work API server address. With this address configured, the device interacts with the WeChat Work API server to obtain user information on receiving a message redirected from the WeChat Work server. Then, the device uses the obtained information for user authentication and authorization. |
|
Corp ID |
Enter the company ID, which uniquely identifies a company on the WeChat Work. |
|
App secret |
Enter an App secret key. Each App has an independent access key. For data security, make sure the App secret key is not leaked. |
|
AuthN request timeout |
Enter the timeout time of the authentication request sent from the SSL VPN gateway to the API server. A WeChat Work authentication fails if the SSL VPN gateway does not receive the response from the API server within the timeout time after sending an HTTP request. |
|
User ID field name |
Enter a user ID field name. The SSL VPN gateway uses this item to construct the parameter that carries user information in the access requests sent to the internal server. |
|
AuthZ policy group field name |
Enter an authorization policy group name. The SSL VPN gateway uses this item to obtain the authorization policy group name from the response of the WeChat Work API server. |
|
WeChat open platform URL |
Select a method to configure a WeChat open platform URL. Options include: · Predefined—The URL is https://open.weixin.qq.com by default, which cannot be edited. · User-defined—You can enter a URL as needed. After this item is configured, the client can access the WeChat open platform directly to complete the authentication when the internal server requires client authentication again. |
Configure URI ACLs
You can create multiple URI ACLs in an SSL VPN context.
A URI ACL is a set of rules that permit or deny access to resources. You can add multiple rules to a URI ACL. The device matches a packet against the rules in ascending order of the rule ID. The match process stops once a matching rule is found.
A URL ACL can be used for the following purposes:
· Filter resources under the URL specified in a URL item.
· Filter Web, TCP, and IP access requests in an SSL VPN resource group.
Procedure
1. On the URI ACL tab, click Create.
2. On the Add URI ACL page that opens, enter an ACL name.
3. In the URI ACL Resources section, click Create.
4. On the Add URI ACL Rule page that opens, create a URI ACL rule.
Table 3 Configuration items for a rule
|
Item |
Description |
|
Rule ID |
Enter a rule ID. |
|
Action |
Select the action for the matching packets. Options include Permit and Deny. |
|
URI pattern |
Enter a URI pattern in the format of protocol://host:port/path, where protocol and host are required. |
5. Click OK.
The rule is displayed on the Add URI ACL page.
6. Click OK.
The URI ACL is displayed on the URI ACL page.
7. Click Next.
Configure access services
You can configure access resources for the following access services: Web access service, TCP access service, and IP access service.
Configure the Web access service
On the Web access service configuration page, perform the following tasks:
1. Select the SSL client policy used by the SSL VPN gateway to access internal HTTPS servers.
By default, the SSL VPN gateway uses the default SSL client policy to access internal HTTPS servers. The default SSL client policy uses cipher suite rsa_rc4_128_md5.
2. Create a URL item for an internal Web resource:
a. Create a URL item.
b. Specify the URL of the Web resource for the URL item.
c. Select an existing URI ACL to filter the Web resources under the specified URL.
d. Select a mapping type for the resource URL. Options are Normal mapping (the default), Domain mapping, and Port mapping.
The SSL VPN gateway rewrites the resource URL before sending it to the client. The URL mapping type determines how the gateway rewrites the URL.
The following example describes how URL mapping works when the user accesses internal resource URL http://www.server.com:8080 behind SSL VPN gateway with name gw, domain name https://www.gateway.com:4430, and IP address 1.1.1.1.
¡ Normal mapping—The resource URL returned to the client will be rewritten to https://www.gateway.com:4430/_proxy2/http/8080/www.server.com. Normal mapping may cause problems such as missed URL rewriting and rewriting errors, resulting in SSL VPN clients not being able to access the internal resources. Use domain mapping or URL mapping as a best practice.
¡ Domain mapping—The Domain name item is displayed after Domain mapping is selected. The resource URL returned to the client will be rewritten to https://mapped domain name:4430, where mapped domain name is the domain name you entered for the Domain name item.
¡ Port mapping—The Gateway name and Virtual host items are displayed after Port mapping is selected. The virtual host name is optional.
- If you enter gw2 for the Gateway name item and do not enter the virtual host name, the resource URL will be rewritten to https://2.2.2.2:4430, where 2.2.2.2 and 4430 are the IP address and port number of SSL VPN gateway gw2.
- If you enter gw for the Gateway name item and vhosta for the Virtual host item, the resource URL will be rewritten to https://vhosta:4430.
3. Create a URL list and assign URL items to the URL list.
The URL lists can be assigned to resource groups. After the AAA server authorizes a user to use a resource group, the user can access the Web resources provided by the URL list in the resource group.
To configure the Web access service:
4. On the Access services tab, select Web access, and then click Next.
5. In the Web access resources section, click Create in the URL Items area.
6. On the page that opens, configure a URL item, and then click OK.
Table 4 Configuration items for a URL item
|
Item |
Description |
|
URL item name |
Enter a URL item name. |
|
URL |
Enter a URL in the URL item. |
|
URI ACL |
Select a URI ACL as a filtering criterion. |
|
Mapping type |
Select a mapping type. Options include Normal mapping, Domain mapping, and Port mapping. |
|
Enable URL masking |
Select whether to enable the masking for the specified URL. When this feature is enabled, the user will not be able to see the real address of the visited internal server. |
|
Single sign-on |
Select whether to enable SSO login. When this feature is enabled, a user can use one set of login credentials to access multiple trusted systems. |
|
SSO mode |
Select an SSO login mode. Options include: · Basic access request—Requires configuring login parameters. · Auto-build access request—Requires configuring the request method, encoding mode, request parameters, and encryption file uploading. |
|
Login parameters |
This item is available only after you select Basic access request for the SSO mode field. Select a method to obtain login parameters. Options include: · Use SSL VPN login username and password—Uses SSL VPN login username and password for SSO login. · Use custom username and password—Uses a custom username and password for SSO login. The custom username and password are configured on the SSL VPN Web interface. |
|
Request method |
This item is available only after you select Auto-build access request for the SSO mode field. Select a request method. Options include GET and POST. |
|
Encoding mode |
This item is available only after you select Auto-build access request for the SSO mode field. Select an encoding method. Options include GB18030 and UTF-8. |
|
Request parameters |
This item is available only after you select Auto-build access request for the SSO mode field. To add a request parameter (attribute name and value), click Add in this field, and configure the following items in the dialog box that opens: · Parameter name—Enter a parameter name. The parameter name is the attribute name used for SSO login requests. · Type—Select a parameter type. The parameter value used for SSO login is the actual value abstracted according to the parameter type. Options include: ¡ Login name—Uses the SSL VPN login username as the value of the SSO request parameter. ¡ Login password—Uses the SSL VPN login password as the value of the SSO request parameter. ¡ Certificate subject—Uses the certificate title as the value of the SSO request parameter. ¡ Certificate serial number—Uses the certificate serial number as the value of the SSO request parameter. ¡ Certificate fingerprint—Uses the certificate fingerprint as the value of the SSO request parameter. ¡ Phone number—Uses the mobile phone number as the value of the SSO request parameter. ¡ User group—Uses the user group name as the value of the SSO request parameter. ¡ Custom name—Uses the customized username as the value of the SSO request parameter. ¡ Custom password—Uses the customized password as the value of the SSO request parameter. ¡ Custom—Specifies an actual parameter value of the SSO request parameter in the Parameter value field. · Encrypt parameter value—Select whether to enable parameter value encryption. |
|
Set encryption file |
This item is available only after you select Auto-build access request for the SSO mode field. Upload an encryption file for parameter value encryption. The encryption file must be a .js file, and cannot exceed 200 KB. To upload an encryption file, click Select file to select a .js file, and then click Upload. To cancel the use of the current encryption file, click Cancel encryption. |
|
Current encryption file |
Display the current encryption file. |
7. Click Create in the URL List area.
8. On the page that opens, configure a URL list, and then click OK.
Table 5 Configuration items for a URL list
|
Item |
Description |
|
URL list name |
Enter a URL list name. |
|
Heading |
Enter a URL list heading. |
|
URL entry list |
Select the URL items to add to the URL list. |
Configure the TCP access service
On the TCP access service configuration page, perform the following tasks:
1. Create a port forwarding item.
A port forwarding item maps a TCP service (such as Telnet, SSH, and POP3) provided on an internal server to a local address and port number on the SSL VPN client. Remote users can access the TCP service though the local address and port number.
For example, you can configure a port forwarding item to allow a client to access HTTP service provided on port 80 of server 192.168.0.213 through IP address 127.0.0.1 and port 80.
Configure a port forwarding item as follows:
a. Specify a name for the port forwarding item.
b. Specify the client host address, client port number, server address, and server port number.
c. Configure a description for the port forwarding item.
d. Specify the resource link for the port forwarding item as needed.
If you configure a resource link for a port forwarding item, the port forwarding item name will be displayed as a link on the SSL VPN Web page. You can click the link to access the resource directly.
2. Create a port forwarding list.
a. Specify a name for the port forwarding list.
b. Add the port forwarding items to the port forwarding list.
The port forwarding lists can be assigned to resource groups. After the AAA server authorizes a user to use a resource group, the user can access the TCP services provided by the port forwarding list in the resource group.
To configure the TCP access service:
3. On the Access services tab, select TCP access, and then click Next.
4. In the TCP access resources section, click Create in the Port Forwarding Item area.
5. On the page that opens, configure a port forwarding item, and then click OK.
Table 6 Configuration items for a port forwarding item
|
Item |
Description |
|
Name |
Enter a port forwarding item name. |
|
Client host |
Specify the local address or host name of the SSL VPN client to which a TCP service on an internal server is mapped. |
|
Client port |
Specify the local port of the SSL VPN client to which a TCP service on an internal server is mapped. |
|
Server address |
Specify the IP address or FQDN of the internal server that provides the TCP service. |
|
Server port |
Specify the port of the internal server that provides the TCP service. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for the port forwarding item. |
|
Resource link |
Specify the resource link for the port forwarding item. SSL VPN users can click the resource link on the SSL VPN Web interface to access the resource. |
6. Click Create in the Port Forwarding List area.
7. On the page that opens, configure a port forwarding list, and then click OK.
Table 7 Configuration items for a port forwarding list
|
Item |
Description |
|
Port forwarding list |
Enter a port forwarding list name. |
|
Port forwarding items |
Specify the port forwarding items to add to the port forwarding list. |
Configure the IP access service
On the IP access service configuration page, perform the following tasks:
1. Specify an SSL VPN AC interface for IP access.
2. Specify an IP access address pool.
After a user passes the authentication, the SSL VPN gateway allocates an IP address to the VNIC of the user from the specified address pool.
3. Configure route lists.
A route list contains the routing entries to be issued to SSL VPN clients.
You can configure the following types of routing entries in a route list:
¡ Included route—Client packets matching an included routing entry will be forwarded to the SSL VPN gateway through the VNIC of the client host.
¡ Excluded route—Client packets matching an excluded routing entry will not be forwarded to the SSL VPN gateway.
The route lists can be assigned to resource groups. After the AAA server authorizes a user to use a resource group, the SSL VPN gateway will issue the routing entries in the route list of the resource group to the user. The user can then access the IP resources provided by the route list in the resource group.
4. To enable automatic startup of the IP access client after Web login, select Start IP access client. After a user logs in to the SSL VPN gateway through a Web browser, the IP access client on the user host will automatically connect to the gateway. If the IP access client software is not installed, the user will be prompted to install the software. For the IP access client to connect the SSL VPN gateway correctly, make sure the IP access resources are configured on the SSL VPN gateway.
5. To enable automatic pushing of accessible resources to IP access users, select Push Web resources. After a user logs in to the SSL VPN gateway through the IP access client, the SSL VPN gateway automatically pushes accessible SSL VPN resources to the user through the Web page. For successful push of SSL VPN resources through the Web page, make sure SSL VPN resources are configured on the SSL VPN gateway.
6. Configure the rate limits for upstream traffic and downstream traffic. IP access packets will be dropped if the rate limit is exceeded.
7. Create the user-to-IP address bindings.
Bind IP addresses to an SSL VPN user in one of the following methods:
¡ Bind a range of IP addresses to the user.
¡ Enable the SSL VPN gateway to automatically bind the specified number of free addresses in the IP access address pool to the user.
When the user accesses the SSL VPN gateway in IP access mode, the SSL VPN gateway assigns a bound IP address to the user. If an IP address in the specified IP address range has been assigned to another user, the SSL VPN gateway terminates the connection for that user and releases the IP address.
To configure the IP access service:
1. On the Access services tab, select IP access, and then click Next.
2. On the IP access page, configure basic settings for the IP access service.
Table 8 Basic configuration items for the IP access service
|
Item |
Description |
|
SSL VPN AC interface |
Select an SSL VPN AC interface for IP access. |
|
IP access address pool |
Select the address pool from which the SSL VPN gateway assigns an IP address to a client. |
|
Mask length |
Specify the mask length for the address pool. |
|
Primary DNS server |
Specify the IP address of the internal primary DNS server. |
|
Secondary DNS server |
Specify the IP address of the internal secondary DNS server. |
|
Primary WINS server |
Specify the IP address of the internal primary WINS server. Only IPv4 addresses are supported. |
|
Secondary WINS server |
Specify the IP address of the internal secondary WINS server. Only IPv4 addresses are supported. |
|
Keepalive interval |
Specify the keepalive interval. A client sends keepalive messages to the SSL VPN gateway to maintain sessions between them. |
|
Start IP access client |
Select this item to enable automatic startup of the IP access client after Web login. After a user logs in to the SSL VPN gateway through a Web browser, the IP access client on the user host will automatically start and connect to the gateway. |
|
Push Web resources |
Select this item to enable automatic pushing of accessible resources to a user through Web after the user logs in to the SSL VPN gateway through the IP access client. |
|
Rate limit |
Specify the rate limits for upstream traffic and downstream traffic. Upstream traffic refers to the traffic sent from the user to the server. Downstream traffic refers to the traffic sent from the server to the user. |
|
Packet drop logging |
Select this item to enable logging for IP access packet drop events. The SSL VPN gateway generates logs when packets for SSL VPN IP access users are dropped. |
|
IP connt close logging |
Select this item to enable logging for IP access connection close events. The SSL VPN gateway generates logs when the connections established for SSL VPN IP access users are closed. |
|
IP addr asgmt and release logging |
Select this item to enable logging for IP address assignment and release events. The SSL VPN gateway generates logs when it assigns or releases an IP address to or from the VNIC of the SSL VPN client. |
3. In the IP access resources section, you can configure IPv4 access resources, IPv6 access resources, and user management.
4. Click Create in the IPv4 Access Resources area.
5. On the page that opens, enter a route list name.
6. In the Route entries section, click Create.
7. On the page that opens, configure a route entry.
Table 9 Configuration items for a route entry
|
Item |
Description |
|
Type |
Select a route entry type. Options include: · Included route—Add the route entry to the route list as an included route. · Excluded route—Add the route entry to the route list as an excluded route. The SSL VPN gateway issues the route list to a login client. The client adds the routes to the local routing table. Traffic that matches the included routes is sent to the SSL VPN gateway. Traffic that matches the excluded routes is not sent to the SSL VPN gateway. |
|
Subnet address |
Specify the destination address of the route entry. To configure an included route, the destination network of the route entry must be the network where the internal server locates. |
|
Mask length |
Specify the subnet mask length. |
8. Click OK.
The route entry is displayed on the Route entries section.
9. Click OK.
The route list is displayed on the IPv4 Access Resources area.
10. Click Create in the IPv6 Access Resources area.
11. On the page that opens, enter an IPv6 route list name.
12. In the IPv6 route items section, click Create.
13. On the page that opens, configure an IPv6 route entry.
Table 10 Configuration items for an IPv6 route entry
|
Item |
Description |
|
Type |
Select a route entry type. Options include: · Included route—Add the route entry to the route list as an included route. · Excluded route—Add the route entry to the route list as an excluded route. The SSL VPN gateway issues the route list to a login client. The client adds the routes to the local routing table. Traffic that matches the included routes is sent to the SSL VPN gateway. Traffic that matches the excluded routes is not sent to the SSL VPN gateway. |
|
Subnet address |
Specify the destination address of the route entry. To configure an included route, the destination network of the route entry must be the network where the internal server locates. |
|
Prefix length |
Specify the prefix length for the destination address. |
14. Click OK.
The route entry is displayed on the IPv6 route items section.
15. Click OK.
The route list is displayed on the IPv6 Access Resources area.
16. In the User Management area, click Create.
17. On the page that opens, bind a user to IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Table 11 Configuration items for user management
|
Item |
Description |
|
Username |
Enter an SSL VPN username. |
|
Auto binding |
Select this item to enable automatic user-to-IP address binding and specify the number of IP addresses to bind. This feature enables the SSL VPN gateway to automatically bind the specified number of free IPv4 or IPv6 addresses in the IP access address pool to the user. |
|
IPv4 addresses to be bound |
Specify comma-separated IPv4 address items. Each item specifies an IPv4 address or specifies a range of IPv4 addresses in the form of start address-end address. The end address must be higher than the start IP address. For example, 10.1.1.5,10.1.1.10-10.1.1.20. Multicast, broadcast, and loopback addresses are not supported. |
|
IPv6 addresses to be bound |
Specify comma-separated IPv6 address items. Each item specifies an IPv6 address or specifies a range of IPv6 addresses in the form of start address-end address. The end address must be higher than the start IP address. For example, 1234::10,1234::100-1234::200. Only unicast and anycast addresses are supported. Unspecified, multicast, and loopback addresses are not supported. |
Configure the BYOD access service
1. On the Access services tab, select BYOD access, and then click Next.
2. On the BYOD access page, configure the following items:
¡ Address and port number of the EMO server.
¡ Address and port number of the message server.
3. Click Next.
Configure a shortcut list
To provide quick access to frequently accessed internal resources on the SSL VPN Web page, configure shortcuts for these resources and add the shortcuts to a shortcut list.
You can create multiple shortcut lists in an SSL VPN context.
When you configure a resource group, you can assign a shortcut list to the group. The shortcuts on the shortcut list will be displayed on the SSL VPN Web page for the user authorized to use the resource group. The user can click a shortcut to access the associated resource directly.
Procedure
1. On the Shortcuts tab, click Create in the Shortcut area.
2. On the page that opens, configure a shortcut, and then click OK.
Table 12 Configuration items for a shortcut
|
Item |
Description |
|
Shortcut name |
Enter a name for the shortcut. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for the shortcut. |
|
Resource address |
Specify the resource address for the shortcut. SSL VPN users can click the link on the SSL VPN Web interface to access the resource. You can configure a resource address in one of the following methods: · Enter a resource link in the format of url('url-value'). The url-value argument specifies the corresponding resource. The complete format for url-value is protocol://hostname or address:port number/resource path. · Enter an application path in the format of app('app-value'). The app-value argument specifies the corresponding resource. The complete format for app-value can be an absolute path or environment variable, for example, c:\windows\system32\notepad++.exe. · Enter an executable JavaScript for a resource to provide access to the resource. |
3. In the Shortcut List area, click Create.
4. On the page that opens, configure a shortcut list, and then click OK.
Table 13 Configuration items for a shortcut list
|
Item |
Description |
|
List name |
Enter a shortcut list name. |
|
Select shortcuts |
Select shortcuts to add them to the shortcut list. |
5. Click Next.
Configure a resource group
A resource group defines the Web resources, TCP resources, and IP resources that SSL VPN users can access. You can also use ACLs in resource groups to control user access more specifically.
Procedure
1. On the Resource groups tab, click Create in the Resource groups section.
2. On the page that opens, configure basic settings for the resource group.
Table 14 Configuration items for basic resource group settings
|
Item |
Description |
|
Resource group name |
Enter a name for the resource group. |
|
Instant access resource after login |
Select the resource opened for users immediately after they log in to the SSL VPN gateway. Users do not need to select the resource on the SSL VPN resource page to access the resource. |
|
Shortcut list |
Select a shortcut list for the resource group. |
3. In the Web access section, configure accessible Web resources.
a. Select the one or more URL lists.
b. Specify an IPv4 ACL to filter IPv4 Web access requests.
c. Specify an IPv6 ACL to filter IPv6 Web access requests.
d. Specify a URI ACL to filter Web access requests.
4. In the TCP access section, configure accessible TCP resources.
a. Select a TCP port forwarding list.
b. Specify an IPv4 ACL to filter IPv4 TCP access requests.
c. Specify an IPv6 ACL to filter IPv6 TCP access requests.
d. Specify a URI ACL to filter TCP access requests.
5. In the IP access section, configure accessible IP resources.
Table 15 Configuration items for IP access
|
Item |
Description |
|
Force all IPv4 traffic to SSL VPN |
Select this item to force all IPv4 traffic of a client to be sent to the SSL VPN gateway. The SSL VPN gateway will issue a default IPv4 route to the SSL VPN client. The default IPv4 route uses the VNIC as the output interface and has the highest priority among all default IPv4 routes on the client. Packets for destinations not in the IPv4 routing table are sent to the SSL VPN gateway through the VNIC. The SSL VPN gateway monitors the SSL VPN client in real time. It does not allow the client to delete the default IPv4 route or add a default IPv4 route with a higher priority. |
|
Issue specified IPv4 routes to client |
Select an IPv4 route list to issue the routes in the list to the client, or select Host IPv4 address and configure an IPv4 route to issue to the client. |
|
IPv4 access address pool |
Specify the IPv4 address pool from which the SSL VPN gateway assigns IPv4 addresses to IP access users authorized to use the resource group. If no IPv4 access address pool is specified for the authorized resource group, the SSL VPN gateway will assign IPv4 addresses in the IPv4 address pool specified for the SSL VPN context to IP access users. If no addresses are available in the IPv4 address pool for a user, the IP access request of the user will be rejected. |
|
Force all IPv6 traffic to SSL VPN |
Select this item to force all IPv6 traffic of a client to be sent to the SSL VPN gateway. The SSL VPN gateway issues a default IPv6 route to the SSL VPN client. The default IPv6 route uses the VNIC as the output interface and has the highest priority among all default IPv6 routes on the client. Packets for destinations not in the IPv6 routing table are sent to the SSL VPN gateway through the VNIC. The SSL VPN gateway monitors the SSL VPN client in real time. It does not allow the client to delete the default IPv6 route or add a default IPv6 route with a higher priority. |
|
Issue specified IPv6 routes to client |
Select an IPv6 route list to issue the routes in the list to the client, or select Host IPv6 address and configure an IPv6 route to issue to the client. |
|
IPv6 access address pool |
Specify the IPv6 address pool from which the SSL VPN gateway assigns IPv6 addresses to IP access users authorized to use the resource group. If no IPv6 access address pool is specified for the authorized resource group, the SSL VPN gateway will assign IPv6 addresses in the IPv6 address pool specified for the SSL VPN context to IP access users. If no addresses are available in the IPv6 address pool for a user, the IP access request of the user will be rejected. |
|
IPv4 ACL |
Specify an IPv4 ACL to filter IPv4 TCP access requests. |
|
IPv6 ACL |
Specify an IPv6 ACL to filter IPv6 TCP access requests. |
|
URI ACL |
Specify a URI ACL to filter TCP access requests. |
6. Click OK.
The newly created resource group is displayed on the Resource groups page.
7. Click Finish.
FAQ
After I change resource authorization settings in SSL VPN, the settings do not take effect immediately. Why?
The SSL VPN gateway does not support dynamic authorization. Table 16 describes how and when changed resource authorization settings in SSL VPN will take effect.
Table 16 How and when changed authorization settings take effect
|
Changed item |
How and when the changes take effect |
|
Authorization to a remote server |
The changes take effect only on new users. Users already logged in are not affected. |
|
ACL or ACL rules in a resource group |
For IP, TCP, and Web access users, the changes take effect immediately. |
|
Accessible Web resources |
The changes take effect after the user refreshes the SSL VPN Web page. |
|
Accessible TCP resources |
The changes take effect after the user restarts the TCP access client software. |
|
Routing entries, DNS server address, and WINS server address configured for the IP access service |
The changes take effect immediately. |
Do SSL VPN users need to pass certificate authentication to log in to an SSL VPN gateway?
Whether users need to pass certificate authentication to log in to an SSL VPN gateway depends on the following settings:
· Whether certificate authentication is enabled in the SSL VPN context associated with the SSL VPN gateway.
· Type of certificate authentication method configured in the SSL server policy used by the SSL VPN gateway.
Table 17 describes the possible certificate authentication methods that users might encounter when connecting the SSL VPN gateway.
Table 17 Certificate authentication methods
|
Authentication method |
Description |
|
Certificate authentication disabled |
The user will not be asked to select a certificate for authentication when connecting the SSL VPN gateway through the Web browser. |
|
Mandatory certificate authentication enabled |
The user will be asked to select a certificate for authentication when connecting the SSL VPN gateway through the Web browser. The connection request will be rejected if the user does not have a certificate. |
|
Optional certificate authentication enabled |
The user will be asked to select a certificate for authentication when accessing the SSL VPN gateway through the Web browser. A connection to the SSL VPN gateway will be established in either of the following situations: · The user selects a certificate and passes the identity authentication. · The user chooses not to select a certificate and proceed with the connection request. |
If you want users to pass certificate authentication to log in to an SSL VPN gateway, make sure the following requirements are met:
· Certificate authentication is enabled in the SSL VPN context associated with the SSL VPN gateway.
· Mandatory or optional SSL client authentication is enabled in the SSL server policy used by the SSL VPN gateway.
After receiving the client certificate, the SSL VPN gateway will extract the username from the CN field of the certificate, and then sends the username to the AAA server. The user passes the authentication only when extracted username exists on the local AAA server.
Mandatory certificate authentication is supported only for Web users and IP access users. For TCP access users and mobile client users to access the SSL VPN gateway successfully, you need to enable the optional SSL client authentication.