- Table of Contents
-
- 05-Objects
- 01-Health monitoring
- 02-User management
- 03-Authentication
- 04-Portal
- 05-WAF
- 06-IPS
- 07-Anti-virus
- 08-Data filtering
- 09-URL filtering
- 10-File filtering
- 11-APT defense
- 12-APR
- 13-Terminal identification
- 14-Security action
- 15-Advanced settings
- 16-Intelligences from the threat management platform
- 17-Object group
- 18-ACL
- 19-SSL
- 20-Public key management
- 21-PKI
- 22-Attack defense
- 23-Trusted access controllers
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 06-IPS | 115.24 KB |
IPS
This help contains the following topics:
¡ Import or delete Snort signatures
¡ Create and delete user-defined IPS signatures
¡ Export all signatures in the signature library
¡ Specify the number of captured packets to be cached
Introduction
The intrusion prevention system (IPS) feature enables devices to monitor network traffic for malicious activity and to proactively take prevention actions.
IPS functions
IPS provides the following functions:
· In-depth protection—IPS inspects the application layer data of packets, performs protocol analysis and reassembly on network traffic flows, and takes actions according to the analysis results.
· Real-time protection—IPS monitors network traffic in real-time and can take actions on detected attacks.
· All-around protection—IPS can detect and prevent the following types of attacks:
¡ Malicious software such as worms, viruses, Trojan, bots, spyware, adware, scanners, and backdoors.
¡ Malicious attacks such as common gateway interface (CGI) attacks, cross-site scripting attacks, injection attacks, directory traversal attacks, information leakage attacks, remote file inclusion attacks, buffer overflow attacks, code execution attacks, and DoS attacks.
· Bidirectional protection—IPS monitors both incoming and outgoing traffic to prevent attacks arising from the internal and external networks.
IPS profiles
IPS is implemented based on IPS profiles. An IPS profiles contains a set of IPS signatures to match packets and the actions for the matching packets.
IPS signatures
The device compares packets with IPS signatures to detect, classify, and prevent network attacks.
Each IPS signature contains various attributes, including attack category, action, protected target, severity level, and direction. By default, an IPS profile uses all enabled IPS signatures on the device. You can set criteria to filter IPS signatures that an IPS profile uses based on the signature attributes.
The device supports the following types of IPS signatures:
· Predefined IPS signatures—Automatically generated by the device based on the local signature library. You cannot add, modify, or delete a predefined IPS signature.
· User-defined IPS signatures—For attacks that cannot be detected by predefined signatures, you can create user-defined IPS signatures. You can also modify and delete user-defined signatures.
· Snort signatures—Imported from a Snort file. You can import and delete Snort signatures.
Predefined, user-defined, and Snort IPS signatures have default signature actions and enabling status.
To change the action for an IPS signature in an IPS profile, select the IPS signature and customize the settings for the IPS signature. The action customized for an IPS signature takes precedence over the default signature action in the IPS profile. For more information about IPS actions, see "IPS actions." You can also add an inactive IPS signature to an IPS profile. For more information about adding an inactive IPS signature, see "Configure an IPS profile."
IPS actions
When the device detects a packet matching an IPS signature, it takes the actions specified for the signature on the packet.
The device supports the following IPS actions:
· Blacklist—Drops matching packets and adds the sources of the packets to the IP blacklist. If the IP blacklist feature is enabled, packets from the blacklisted sources will be blocked for the blacklist period. If the IP blacklist feature is not enabled, packets from the blacklisted sources are not blocked.
For more information about the IP blacklist feature, see attack defense online help.
· Drop—Drops matching packets.
· Permit—Permits matching packets to pass.
· Reset—Closes the TCP or UDP connections for matching packets by sending TCP reset messages or ICMP port unreachable messages.
· Redirect—Redirects matching packets to a webpage.
· Predefined action—Uses the predefined signature action in the signature library.
· Capture—Captures matching packets.
· Logging—Logs matching packets.
IPS mechanism
As shown in Figure 1, upon receiving a packet, the device performs the following operations:
1. The device compares the packet with the security policies.
If the packet matches a security policy that is associated with an IPS profile, the device identifies the packet application layer protocol and extracts the packet signatures.
2. The device determines the actions for the packet by comparing the extracted packet signatures with the IPS signatures in the IPS profile:
¡ If the packet does not match any IPS signatures, the device permits the packet to pass.
¡ If the packet matches only one IPS signature, the device takes the signature actions.
¡ If the packet matches multiple IPS signatures, the device uses the following rules to select the actions:
- If the matching IPS signatures have two or more actions, including redirect, drop, permit, and reset, the device takes the action of the highest priority. The actions in descending order of priority are reset, redirect, drop, and permit.
- The device will execute the blacklist, capture, and logging actions if they are in the matching IPS signatures.
Restrictions and guidelines
· The Submit operation can cause temporary outage for DPI services. Services based on the DPI services might also be interrupted. For example, security policies cannot control access to applications.
· After you click Submit, the interface prompts a success message, but the configuration might not have been activated completely. The device cannot recognize packets that pass through before the configuration takes effect.
· To use IPS functions, you must purchase and install a license. If the license expires, you can still use the existing IPS signature library but you can no longer upgrade the IPS signature library on the device. For more information about licenses, see license online help.
· When configuring a whitelist entry, you must enter a threat ID, URL, or IP address, or two or all of them.
Configure IPS
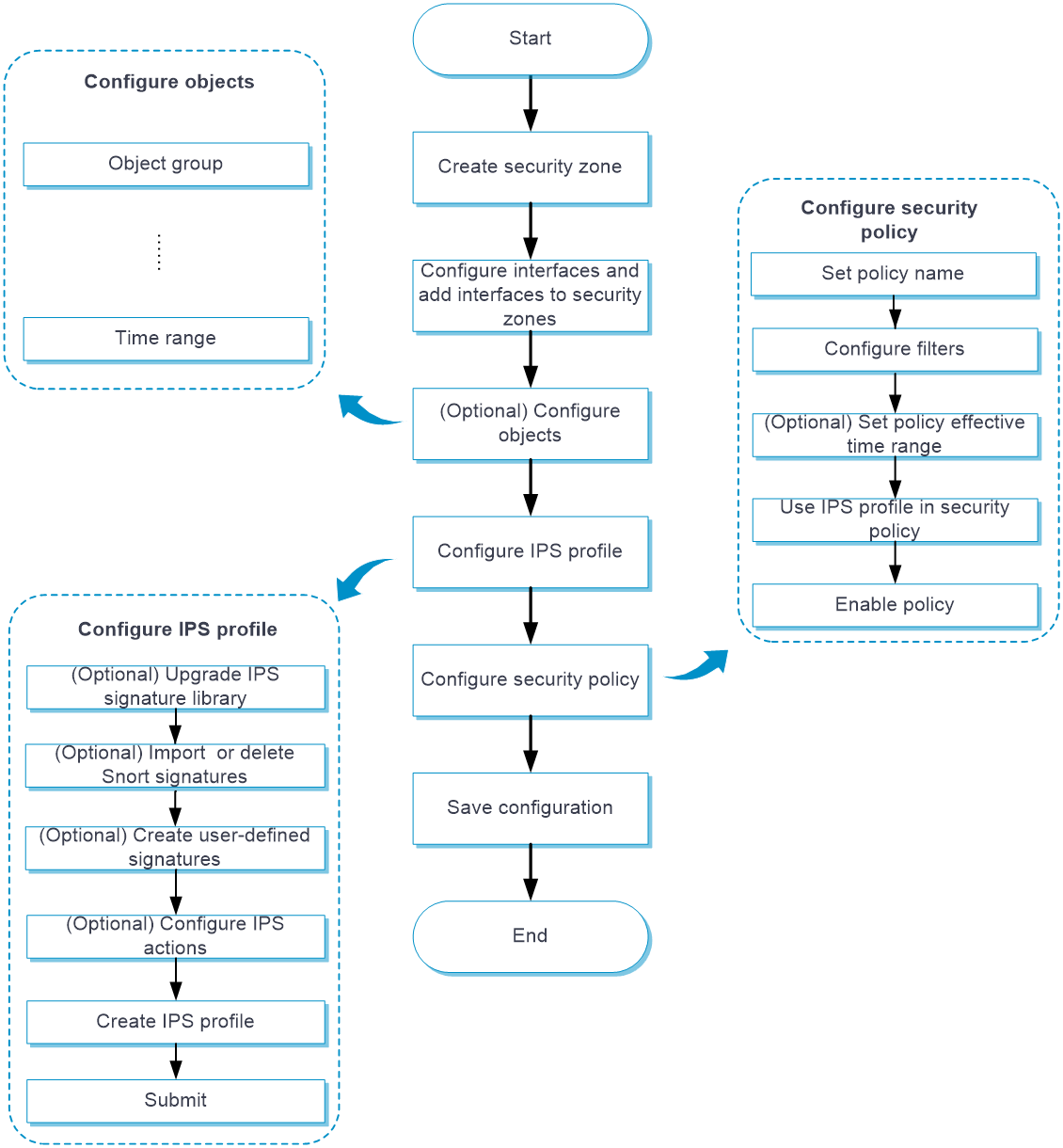
Configure IPS as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 IPS configuration procedure
Configure an IPS profile
The device provides a predefined IPS profile named default. The default IPS profile uses all enabled IPS signatures on the device and cannot be modified or deleted.
You can also create IPS profiles on the device. By default, a newly created IPS profile uses all enabled IPS signatures and applies to the packet matching a signature the default signature action. You can filter the IPS signatures used by the IPS profile and change the signature actions.
You can configure global action for an IPS profile or change the action for individual IPS signatures in the profile.
The system selects the actions for packets matching an IPS signature in the following order:
1. Actions configured for the IPS signature as a signature exception in the IPS profile.
2. Global action configured for the IPS profile.
3. Default action of the IPS signature.
Procedure
1. Click the Objects tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select APP Security > IPS > Profiles.
The IPS Profiles page opens.
3. Click Create.
The Create IPS Profile page opens.
4. Configure basic settings for the IPS profile.
Table 1 Basic configuration items for IPS profile
|
Item |
Description |
|
Name |
Specify an IPS profile name. As a best practice, do not enter the following special characters for the name of an IPS profile: < > \ / | * ? " : , ; If you export an IPS profile with the name containing these special characters, these special characters in the IPS profile name will be replaced with underscores (_). |
|
Action |
Select the global action for the IPS profile. Options are Predefined action, Blacklist, Drop, Permit, Reset, and Redirect. The global action applies to all packets matching the signatures in the IPS profile. |
5. Configure the criteria to filter the IPS signatures in the IPS profile.
If you do not configure any filtering criteria, all IPS signatures in Enabled default status are added to the IPS profile.
Table 2 Configuration items for IPS signature filtering
|
Item |
Description |
|
Protected |
Select the protected targets for the protected target criterion. |
|
Attack |
Select the attack categories for the attack category criterion. |
|
Direction |
Select the traffic directions for the direction criterion. Options are: · To-server—Client to server direction. · To-client—Server to client direction. |
|
Predefined action |
Select the actions for the predefined IPS signature action criterion. Options are Drop, Permit, Reset, and Blacklist. |
|
Severity level |
Select the severity levels for the severity level criterion. Options are Critical, High, Medium, and Low. |
|
Predefined status |
Select the predefined states for the default IPS signature status criterion. Options are Enabled and Disabled. |
6. Click Search. View the IPS signatures in the Viewing matching signatures section.
¡ To view the IPS signatures used in the IPS profile, click the Active Signatures tab.
¡ To view the IPS signatures that are not used by the IPS profile, click the Inactive Signatures tab.
7. To change the status or action for an active or inactive IPS signature:
a. Select the IPS signature on the Active Signatures or Inactive Signatures tab.
b. Click Custom.
c. In the dialog box that opens, configure the settings as needed, and then click OK.
8. To add an inactive IPS signature to the IPS profile:
a. Select the IPS signature on the Inactive Signatures tab, and click Custom.
b. In the dialog box that opens, select Enable for the Status field, and then click OK.
The IPS signature will be displayed on the Active Signatures tab.
9. To remove an IPS signature from the IPS profile:
a. Select the IPS signature on the Active Signatures tab, and click Custom.
b. In the dialog box that opens, select Disable for the Status field, and then click OK.
The IPS signature will be displayed on the Inactive Signatures tab.
10. Click Advanced settings.
11. In the dialog box that opens, configure the advanced settings for the IPS profile.
Table 3 Advanced configuration items for IPS profile
|
Item |
Description |
|
Count policy matches |
Select whether to enable match counting for the IPS profile. |
|
Log settings |
Select the method to configure the logging settings. Options are: · Global—View or edit the global settings on the Log Settings > Threat Log Settings > IPS Logs page in the System tab. · User-defined—Continue with logging settings on this page. |
|
Log output |
This field is only available after you select User-defined for the Log settings field. Options are Output system logs and Output through email. You can select both options at the same time. |
|
Email server |
After you select Output through email for the Log output field, an email server must be configured. You can configure a new email server or select an existing email server. To view or edit the existing email servers, go to the Log Settings > Email Server page in the System tab. |
|
Sig. library baseline version |
Select a signature library baseline version to enable IPS to use the signatures in the baseline version in addition to the signatures in the current active signature library to match packets. With a signature library baseline version selected, all the signatures whose version is higher than the baseline version are in inactive state and cannot be used to match packets. To change the status of those signatures, perform the following tasks: 1. If the current version with newly added signatures is higher than the baseline version, configure the current version number as the baseline version number. 2. If the current version with newly added signatures is lower than the baseline version, select the signatures and click Custom to enable the signatures. |
|
Email output condition |
Configure the filtering criteria of the matching IPS signatures for log output via email. |
|
Min. signature severity level |
Specify the lowest severity level of the matching IPS signatures for log output via email. The system outputs logs via email only when the severity levels of the matching signatures are not lower than specified severity level. |
12. Click OK.
The IPS profile is displayed on the IPS Profiles page.
13. Use the IPS profile in a security policy. For more information about security policies, see security policy online help.
14. To have the configuration take effect, click Submit.
This operation can cause temporary DPI service outage. As a best practice, perform the operation after all DPI service configurations are complete.
15. To export the IPS signatures used in the IPS profile, click the ![]() icon in
the Export signatures column for the IPS profile entry in IPS Profiles page.
icon in
the Export signatures column for the IPS profile entry in IPS Profiles page.
All IPS signatures in the signature library will be exported to a .csv file, but the IPS signatures used in this IPS profile will be marked Y in the Active column of the export file.
Import or delete Snort signatures
Import Snort signatures
To add Snort signatures, create an IPS signature file in the Snort format and import the signatures from the file to the device.
Make sure the IPS signature file contains all user-defined signatures that you want to use. All existing Snort signatures on the device will be overwritten by the imported Snort signatures.
For a signature defined by a Snort rule to be imported correctly from the IPS signature file, make sure Snort rule is valid.
To import Snort signatures:
1. Click the Objects tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select APP Security > IPS > Signatures.
The IPS Signatures page displays all IPS signatures on the device.
3. Click Import Snort signatures in the upper-left corner of the page.
The Import Snort Signatures window opens.
4. Select the IPS signature file to import.
5. Click Import signatures.
Delete all Snort signatures
1. Click the Objects tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select APP Security > IPS > Signatures.
The IPS Signatures page opens.
3. Click Delete signatures and then select Delete all Snort signatures in the upper-left corner of the page.
4. Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box that opens.
Create and delete user-defined IPS signatures
You can create user-defined signatures that do not exist in the current signature library.
A user-defined IPS signature contains basic settings and rules.
A user-defined signature can contain multiple rules. The logical operators between rules are as follows:
· Logical AND—A packet matches an IPS signature only when the packet matches all rules in the signature.
· Logical OR—A packet matches an IPS signature when the packet matches any rule in the signature.
In a user-defined signature rule, you can configure the match criteria of source IPv4 address, destination IPv4 address, source port, destination port, and request method, the detection items, and the detection trigger conditions.
A user-defined signature can be one of the following types:
· Keyword—A keyword type requires configuring one or multiple detection items and only one detection trigger condition. The device continues to compare a packet with detection items only after the packet matches the detection trigger condition. A packet matches a rule only when the packet matches all detection items in the rule.
· Number—A number type requires configuring only one detection item. A packet matches a rule only when the packet matches the detection item in the rule.
Create a user-defined IPS signature
1. Click the Objects tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select APP Security > IPS > Signatures.
The IPS Signatures page displays all IPS signatures on the device.
3. Click Create user-defined signature.
4. On the page that opens, configure basic settings for a user-defined IPS signature.
Table 4 Basic configuration items for an IPS signature
|
Item |
Description |
|
Name |
Enter an IPS signature name. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for easy identification. |
|
Severity level |
Select the severity level of the risk impacts that the matching packets might bring to the network. Options are Critical, High, Medium, and Low. |
|
Direction |
Select the traffic direction for the direction criterion. Options are: · To-server—Client to server direction. · To-client—Server to client direction. · To-server, To-client—Both client-to-server and server-to-client directions. |
|
Action |
Select the action for packets matching the IPS signature. Options are Blacklist, Drop, Permit, and Reset. |
|
Logging |
Select whether to enable logging for matching packets. Options are Enable and Disable. |
|
Capture |
Select whether to enable capture matching packets. Options are Enable and Disable. The capture action enables the device to capture packets and export the captured packets to the specified URL at the scheduled export time. For more information about configuring the capture action, see security actions online help. |
5. In the Rules area, select a logical operator before you configure rules for the signature.
6. Click Create.
7. On the page that opens, configure basic settings for the rule.
Table 5 Basic configuration items for a rule
|
Item |
Description |
|
ID |
Enter a rule ID. |
|
Match pattern type |
Select a signature match pattern type. Options are Keyword and Number. |
|
Application layer protocol |
Select an application layer protocol as a filtering criterion. |
|
Transport layer protocol |
Select a transport layer protocol as a filtering criterion. |
|
Request method |
Select an HTTP request method, such as GET and POST. |
|
Source IPv4 address |
Enter a source IPv4 addresses as a filtering criterion. |
|
Source port range |
Specify a source port range as filtering criteria. |
|
Destination IPv4 address |
Enter a destination IPv4 addresses as a filtering criterion. |
|
Destination port range |
Specify a range of destination ports as filtering criteria. |
8. In the Detection trigger conditions area, click Create.
This area is available only when Keyword has been selected as the match pattern type.
9. Create a detection trigger condition.
Table 6 Detection trigger condition configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
Protocol field |
Select a protocol field to inspect. |
|
Match pattern type |
Select the type of the match pattern. Options are Text and Hex. |
|
Match pattern |
Enter the content of the match pattern. |
|
Depth |
Specify the number of bytes to be inspected |
|
Offset |
Enter an offset in bytes after which the inspection starts. The offset is counted from the beginning of the protocol field. |
10. Click OK.
The detection trigger condition is displayed on the Detection trigger conditions list.
11. In the Detection items area, click Create.
12. Create a detection item.
Table 7 Detection item configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
ID |
Enter a detection item ID. |
|
Protocol field |
Select a protocol field. |
|
Operator |
Select an operator to define the match operation in the detection item. Options vary by the match pattern type selected in the Create Rule page: · If Keyword has been selected, the options are Contain and Not contain. · If Number has been selected, the options are Greater than, Equal to, Not equal to, Less than, Greater than or equal to, and Less than or equal to. |
|
Match pattern type |
Select the type of the match pattern. Options are Text, Regular expression, and Hex. |
|
Match pattern |
Enter the content of the match pattern. |
|
Depth |
Specify the number of bytes to be inspected. |
|
Offset |
Enter an offset in bytes after which the inspection starts. The offset is counted from the beginning of the protocol field. |
|
Relative depth |
Specify the number of bytes to be inspected. |
|
Relative offset |
Enter an offset after which the inspection starts. The offset is counted from the end of the previous detection item. |
13. Click OK.
The detection item is displayed on the Detection items list.
14. Click OK.
The rule is displayed on the Rules list.
15. Click OK.
The signature is displayed on the IPS Signatures page.
16. To have the configuration take effect, click Submit.
Delete user-defined IPS signatures
1. Click the Objects tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select APP Security > IPS > Signatures.
The IPS Signatures page opens.
3. Select the user-defined signatures that you want to delete.
4. Click Delete signatures and then select Delete user-defined signatures.
5. Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box that opens.
Export all signatures in the signature library
1. Click the Objects tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select APP Security > IPS > Signatures.
The IPS Signatures page opens.
3. Click Export all signatures.
All IPS signatures in the signature library will be exported to a .csv file.
Configure IPS whitelist
If false alarms exist in threat logs, you can enable the whitelist feature, and add the detected threat IDs (the IPS signature IDs), URLs, and IP addresses to the whitelist. The device permits packets matching the IPS signatures or URLs on the whitelist to pass through, reducing false alarms.
After the whitelist is enabled, the device will record the hit count for each whitelist entry. You can view the statistics on the Whitelist page.
Procedure
1. Click the Objects tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select APP Security > IPS > Whitelist.
The Whitelist page displays all whitelist entries on the device.
3. Create a whitelist entry.
Table 8 Whitelist entry configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
Entry ID |
Enter a whitelist entry ID. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for the whitelist entry. |
|
Threat ID |
Enter a threat ID. You can obtain the threat ID from threat logs. |
|
URL |
Enter a URL. You can obtain the URL from threat logs. A URL contains packet header fields and packet first line, for example 111.15.93.166/wnm/get.j. After you create, edit, or delete URLs, you must click Activate to have the configuration take effect. |
|
Match type |
Select a match type. Options are: · Exact match—Deems a match if the detected URL in the packet is exactly the same as the configured URL. · Substring match—Deems a match if the detected URL in the packet contains the configured URL. |
|
IP type |
Select the type of IP addresses that can be obtained from threat logs. Options are IPv4 and IPv6. |
|
IP address |
Enter an IP address. You can obtain the IP address from threat logs. |
4. Click OK.
5. Click Enable whitelist.
Specify the number of captured packets to be cached
The device can cache the specified number of captured packets for threat analysis, including the hit packet matching the IPS profile and the packets captured before and after the hit packet. When the specified number of captured packets is cached, the device writes all cached packets into the capture file. With hard disks or USB disks installed, you can click Download of a log to obtain the capture file on the Threat Logs page for threat analysis.
To specify the number of captured packets to be cached:
1. Click the Objects tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select APP Security > IPS > Profiles.
The IPS Profiles page opens.
3. Click Advanced settings.
4. Set the number of captured packets to be cached as needed.
5. Click OK.