- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-WAPI configuration | 249.66 KB |
Contents
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with WAPI
Restrictions and guidelines: WAPI configuration
Specifying an authentication mode for WAPI
Configuring certificate authentication
Certificate authentication tasks at a glance
Specifying a PKI domain and a certificate
Configuring PSK authentication
Specifying an IPS domain for WAPI users
Display and maintenance commands for WAPI
Example: Configuring PSK authentication
Example: Configuring standard certificate authentication
Example: Configuring standard certificate authentication for accounting
Configuring WAPI
About WAPI
WLAN Authentication and Privacy Infrastructure (WAPI) is developed by the China Broadband Wireless Internet Protocol Standard Group based on 802.11 wireless protocols.
WAPI uses digital certificates and preshared keys (PSKs) to authenticate clients, and it protects the traffic between clients and AC through the USK negotiation and MSK advertisement mechanisms.
WAPI components
WAPI includes the following components:
· WLAN Authentication Infrastructure—WAI provides identity authentication and key management for WLANs.
· WLAN Privacy Infrastructure—WPI provides a security solution for data transmission in WLANs, including data encryption, data decryption, and anti-replay.
Basic concepts
AS
As an important part of WAI, an authentication server (AS) authenticates users and certificates based on the public key technology.
BK
A base key (BK) is used for USK derivation. A BK can be obtained through certificate authentication negotiation or derived from a PSK.
MSK
A multicast session key (MSK) is a random value used to protect multicast MPDUs. An MSK contains a multicast encryption key and a multicast integrity check key.
PSK
A PSK is a static key advertised to clients.
USK
A unicast session key (USK) is a random value derived from a BK by using a pseudo random function. A USK contains a unicast encryption key, unicast integrity check key, key encryption key, and message authentication key.
WAPI authentication
WAPI supports certificate authentication and PSK authentication.
Certificate authentication
For more information about certificate authentication, see PKI configuration in Security Configuration Guide.
WAI uses UDP to encapsulate packets exchanged between AC and AS.
Figure 1 Certificate authentication
As shown in Figure 1, certificate authentication proceeds as follows:
1. After 802.11 link negotiation, the AC sends an authentication activation message that contains the certificate of the AC to the client.
2. After receiving the authentication activation message, the client sends an access authentication request to the AC.
The access authentication request contains the certificate of the client and the digital signature of the client in the access authentication request.
3. After receiving the access authentication request, the AC obtains the public key from the certificate of the client and verifies the signature of the client.
¡ If the signature is correct, the AC sends a certificate authentication request that contains the certificates of the AC and client to the AS.
¡ If the signature is incorrect, the AC discards the access authentication request.
4. After receiving the certificate authentication request, the AS verifies the certificates of the AC and client and then sends a certificate authentication response to the AC.
The certificate authentication response contains the certificate verification result and the digital signature of the AS.
5. After receiving the certificate authentication response, the AC sends an access authentication response to the client.
The access authentication response contains the access authentication result, certificate verification result, digital signature of the AS, and the AC's digital signature in the access authentication response.
6. After receiving the access authentication response, the client checks the certificate verification result.
¡ If the certificate of the AC is incorrect, the client disconnects from the AC.
¡ If the certificate of the AC is correct, the client continues to check the access authentication result.
- If the access authentication has succeeded, the client continues to perform USK negotiation and MSK advertisement with the AC.
- If the access authentication has failed, the client disconnects from the AC.
PSK authentication
PSK authentication is implemented between wireless client and AC. WAPI uses the PSK configured on the AC and client to generate a BK, which will be used for USK negotiation and MSK advertisement.
WAPI key management
USK negotiation
WAPI performs a USK negotiation when a certificate authentication completes, a PSK authentication is performed, or a USK update occurs.
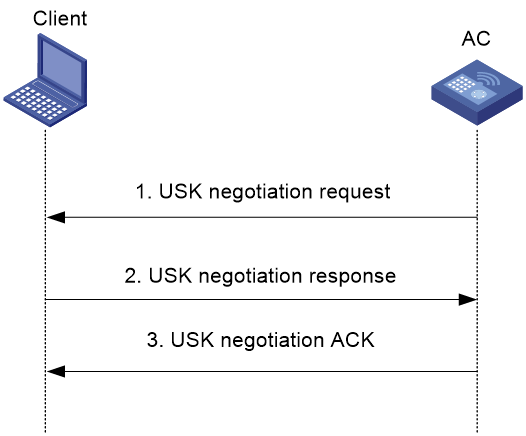
As shown in Figure 2, USK negotiation proceeds as follows:
1. The AC sends a USK negotiation request that contains the Challenge value of the AC to the client.
2. After receiving the USK negotiation request, the client performs the following tasks:
¡ If the USK negotiation is triggered during an association process, the client sends a USK negotiation response to the AC.
¡ If the USK negotiation is triggered during a USK update process, the client matches the Challenge value of the AC carried in the USK negotiation request against that saved on the client.
- If the Challenge values are the same, the client sends a USK negotiation response to the AC.
- If the Challenge values are different, the client discards the USK negotiation request.
The USK negotiation response contains the Challenge value of the client, the Challenge value of the AC, and the message authentication code.
3. After receiving the USK negotiation response, the AC verifies the Challenge value of the AC and the message authentication code carried in the response.
¡ If the verification succeeds, the AC sends a USK negotiation acknowledgement that contains the Challenge value of the client and the message authentication code to the client.
¡ If the verification fails, the AC discards the USK negotiation response.
4. After receiving the USK negotiation acknowledgement, the client verifies the Challenge value of the client and the message authentication code carried in the acknowledgement.
¡ If the verification succeeds, the USK negotiation succeeds.
¡ If the verification fails, the client discards the acknowledgement, and the USK negotiation fails.
MSK advertisement
After a USK negotiation completes, WAPI uses the negotiated key to advertise an MSK. An MSK is a 16-byte random value generated by the AC. The AC uses the MSK to encrypt its broadcast and multicast packets. The client uses the MSK advertised by the AC to decrypt the broadcast and multicast packets received from the AC.
WAPI advertises an MSK when a USK negotiation completes or a MSK update occurs.
As shown in Figure 3, MSK advertisement proceeds as follows:
1. The AC sends an MSK advertisement that contains the key data and key advertisement ID to the client.
2. After receiving the MSK advertisement, the client decrypts the key data to obtain the notification master key and then sends an MSK response that contains the key advertisement ID to the AC.
3. After receiving the MSK response, the AC verifies the key advertisement ID.
¡ If the key advertisement ID is correct, the MSK advertisement succeeds.
¡ If the key advertisement ID is incorrect, the AC discards the MSK response, and the MSK advertisement fails.
Protocols and standards
· GB 15629.11-2003/XG1-2006, Information technology-Telecommunications and information exchange between systems-Local and metropolitan area networks--Specific requirements-Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control(MAC) and Physical Layer(PHY) specifications
· RFC 4492, Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) Cipher Suites for Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with WAPI
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Product code |
WAPI compatibility |
|
WX1800H series |
WX1804H-PWR |
EWP-WX1804H-PWR-CN |
Yes |
|
WX2500H series |
WX2508H-PWR-LTE WX2510H-PWR WX2510H-F-PWR WX2540H WX2540H-F WX2560H |
EWP-WX2508H-PWR-LTE EWP-WX2510H-PWR EWP-WX2510H-F-PWR EWP-WX2540H EWP-WX2540H-F EWP-WX2560H |
Yes |
|
MAK series |
MAK204 MAK206 |
EWP-MAK204 EWP-MAK206 |
Yes |
|
WX3000H series |
WX3010H WX3010H-X-PWR WX3010H-L-PWR WX3024H WX3024H-L-PWR WX3024H-F |
EWP-WX3010H EWP-WX3010H-X-PWR EWP-WX3010H-L-PWR EWP-WX3024H EWP-WX3024H-L-PWR EWP-WX3024H-F |
Yes |
|
WX3500H series |
WX3508H WX3508H WX3510H WX3510H WX3520H WX3520H-F WX3540H WX3540H |
EWP-WX3508H EWP-WX3508H-F EWP-WX3510H EWP-WX3510H-F EWP-WX3520H EWP-WX3520H-F EWP-WX3540H EWP-WX3540H-F |
Yes |
|
WX5500E series |
WX5510E WX5540E |
EWP-WX5510E EWP-WX5540E |
Yes |
|
WX5500H series |
WX5540H WX5560H WX5580H |
EWP-WX5540H EWP-WX5560H EWP-WX5580H |
Yes |
|
Access controller modules |
LSUM1WCME0 EWPXM1WCME0 LSQM1WCMX20 LSUM1WCMX20RT LSQM1WCMX40 LSUM1WCMX40RT EWPXM2WCMD0F EWPXM1MAC0F |
LSUM1WCME0 EWPXM1WCME0 LSQM1WCMX20 LSUM1WCMX20RT LSQM1WCMX40 LSUM1WCMX40RT EWPXM2WCMD0F EWPXM1MAC0F |
Yes |
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Product code |
WAPI compatibility |
|
WX1800H series |
WX1804H-PWR WX1810H-PWR WX1820H WX1840H |
EWP-WX1804H-PWR EWP-WX1810H-PWR EWP-WX1820H EWP-WX1840H-GL |
No |
|
WX3800H series |
WX3820H WX3840H |
EWP-WX3820H-GL EWP-WX3840H-GL |
No |
|
WX5800H series |
WX5860H |
EWP-WX5860H-GL |
No |
Restrictions and guidelines: WAPI configuration
Before configuring WAPI, disable A-MSDU by using the a-msdu disable command. For more information about A-MSDU, see radio management configuration in Radio Resources Management Configuration Guide.
The signature algorithm used in certificate authentication must be Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA). For more information about ECDSA, see public key management configuration in Security Configuration Guide.
WAPI supports centralized data forwarding and local data forwarding.
As a best practice, do not configure WAPI in 802.11ac mode.
WAPI tasks at a glance
To configure WAPI, perform the following tasks:
1. Specifying an authentication mode for WAPI.
2. Configuring certificate authentication.
This task is required if you select the certificate authentication mode.
3. Configuring PSK authentication.
This task is required if you select the certificate authentication mode.
4. Enabling WAPI.
5. Specifying an IPS domain for WAPI users.
This task is required if the WAPI users need to be charged.
Specifying an authentication mode for WAPI
8. Enter system view.
system-view
9. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
10. Specify an authentication mode for WAPI.
wapi authentication-method { certificate | certificate-or-psk | psk }
By default, WAPI uses the certificate authentication mode.
Configuring certificate authentication
Certificate authentication tasks at a glance
To configure certificate authentication, perform the following tasks:
1. Specifying an AS.
2. Specifying a PKI domain and a certificate.
3. (Optional.) Configuring BK update.
Specifying an AS
Restrictions and guidelines
You can specify only one AS for a service template.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Specify an AS by its IP address.
wapi authentication-server ip ip-address
By default, no AS is specified.
Specifying a PKI domain and a certificate
Restrictions and guidelines
You can specify only one PKI domain and one certificate for a service template.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Specify a PKI domain by its name and a certificate by its serial number.
wapi certificate domain domain-name serial serial-number
By default, no PKI domain or certificate is specified.
Configuring BK update
About this task
Perform this task to enable BK update and specify a BK lifetime. WAPI updates the BK after the BK expires.
Restrictions and guidelines
WAPI can update the BK only when you enable BK update.
When both BK update and USK update are enabled, WAPI updates the USK every time the BK is updated, regardless of whether the USK has expired or not. The BK lifetime timer is reset after the USK is updated.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Enable BK update.
wapi bk-rekey enable
By default, BK update is enabled.
4. Set the BK lifetime.
wapi bk lifetime time
By default, the BK lifetime is 43200 seconds.
Configuring PSK authentication
5. Enter system view.
system-view
6. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
7. Specify a PSK.
wapi psk { cipher | simple } { hex | string } key
By default, no PSK is specified.
Enabling WAPI
Restrictions and guidelines
Before enabling WAPI for a service template, disable the service template.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Enable WAPI for the service template.
wapi enable
By default, WAPI is disabled for a service template.
Specifying an IPS domain for WAPI users
About this task
Perform this task to charge WAPI users by using the accounting method of the specified ISP domain.
Restrictions and guidelines
Make sure the ISP domain specified for WAPI users has been created using the domain command. For more information about the domain command, see AAA commands in User Access and Authentication Command Reference.
In the current software version, the authentication and authorization methods of an ISP domain do not take effect on WAPI users.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Specify an ISP domain to charge WAPI users.
wapi domain domain-name
By default, no IPS domain is specified, and the system does not charge WAPI users.
Configuring USK update
About this task
Perform this task to enable USK update and specify a USK lifetime. WAPI updates the USK after the USK expires.
Restrictions and guidelines
WAPI can update the USK only when you enable USK update.
When both BK update and USK update are enabled, WAPI updates the USK every time the BK is updated, regardless of whether the USK has expired or not.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Enable USK update.
wapi usk-rekey enable
By default, USK update is enabled.
4. Set the USK lifetime.
wapi usk lifetime time
By default, the USK lifetime is 86400 seconds.
Configuring MSK update
About this task
Perform this task to enable MSK update and configure the MSK update mode. WAPI supports the following MSK update modes:
· Packet-based—WAPI updates the MSK based on the number of packets.
· Time-based—WAPI updates the MSK at the specified interval.
You can also enable WAPI to update the MSK every time a client goes offline.
Restrictions and guidelines
WAPI can update the MSK only when you enable MSK update.
Packet-based MSK update and time-based MSK update are mutually exclusive.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Enable MSK update.
wapi msk-rekey enable
By default, MSK update is enabled.
4. Configure WAPI to update the MSK every time a client goes offline.
wapi msk-rekey client-offline enable
By default, WAPI does not update the MSK when a client goes offline.
5. Configure the MSK update mode.
wapi msk-rekey method { packet-based [ packet ] | time-based [ interval ] }
By default, WAPI uses the time-based MSK update mode.
Display and maintenance commands for WAPI
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display WAPI statistics. |
display wapi statistics [ ap ap-name [ radio radio-id ] ] |
|
Display WAPI user information. |
display wapi user [ ap ap-name [ radio radio-id ] | user-mac mac-address ] |
|
Clear WAPI statistics. |
reset wapi statistics [ ap ap-name [ radio radio-id ] ] |
WAPI configuration examples
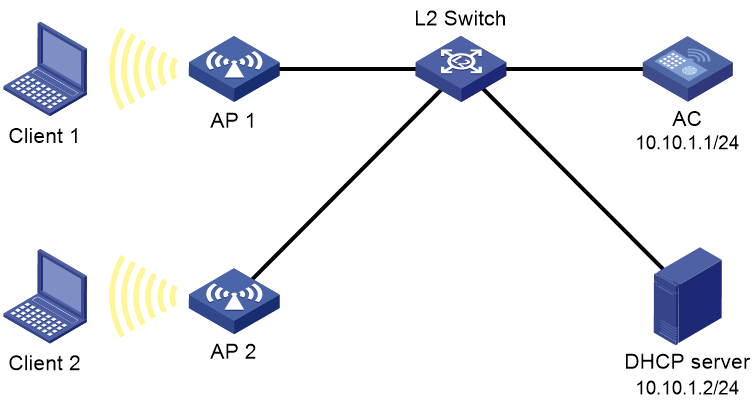
Example: Configuring PSK authentication
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 4, configure PSK authentication to authenticate clients associated with AP 1 and AP 2.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the AC.
# Create service template 1 and configure its SSID as wapi1.
[AC] wlan service-template 1
[AC-wlan-st-1] ssid wapi1
# Enable WAPI.
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi enable
# Configure WAPI to use the PSK authentication mode.
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi authentication-method psk
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi psk simple string 12345678
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi msk-rekey method time-based 20000
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi usk lifetime 20000
[AC-wlan-st-1] service-template enable
# Create AP ap1, and specify its model and serial number.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A2KF819CE0002T
# Create and bind radio 1 to WLAN service template 1, and then enable the radio.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
# Create AP ap2 and specify its model and serial number.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2] serial-id 219801A2KF819CE00021
# Create and bind radio 1 to WLAN service template 1, and then enable the radio.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-1] service-template 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display WAPI user information on all interfaces of the AC.
Total number of users: 2
AP name : ap1
Radio ID : 1
SSID : wapi1
BSSID : 487a-da52-d4f0
MAC address : 000b-c002-5e39
VLAN : 1
Authentication method : PSK
Current state : Online
Authentication state : Idle
Unicast key negotiation state : Established
Multicast key negotiation state : Established
Authorization state : Idle
Accounting state : Idle
Uptime : 00:02:26
AP name : ap1
Radio ID : 1
SSID : wapi1
BSSID : 487a-da52-d4f0
MAC address : 000b-c002-5e2f
VLAN : 1
Authentication method : PSK
Current state : Online
Authentication state : Idle
Unicast key negotiation state : Established
Multicast key negotiation state : Established
Authorization state : Idle
Accounting state : Idle
Uptime : 00:02:40
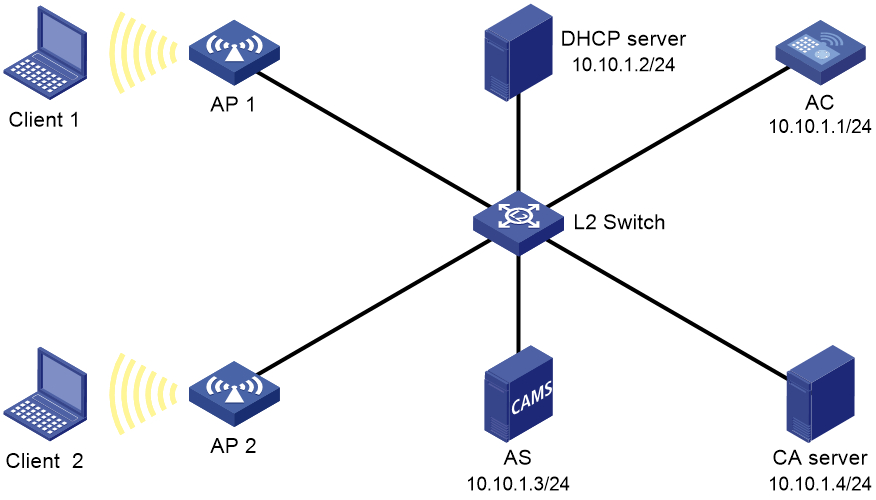
Example: Configuring standard certificate authentication
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 5, configure standard certificate authentication to authenticate clients associated with AP 1 and AP 2.
Procedure
1. Import the CA and AS certificates to the AS, and install the asue and AS certificates on the WAPI client.
An AS server and a CA server can be installed on the same physical device. In this case, the AS certificate and CA certificate are the same.
2. Assign IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure the AC.
# Create PKI domain pki1, and disable CRL checking for the domain so that certificate revocation is not verified.
[AC] pki domain pki1
[AC-pki-domain-pki1] undo crl check enable
[AC-pki-domain-pki1] quit
# Import certificate files ca.cer, ap.cer, and as.cer.
[AC] pki import domain pki1 pem ca filename ca.cer
[AC] pki import domain pki1 pem local filename ap.cer
[AC] pki import domain pki1 pem peer filename as.cer
# Create service template 1 and configure its SSID as wapi1.
[AC] wlan service-template 1
[AC-wlan-st-1] ssid wapi1
# Enable WAPI.
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi enable
# Configure WAPI to use the certificate authentication mode.
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi authentication-method certificate
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi authentication-server ip 10.10.1.3
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi certificate domain pki1 serial 29
[AC-wlan-st-1] undo wapi bk-rekey enable
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi msk-rekey method time-based 20000
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi usk lifetime 20000
[AC-wlan-st-1] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-1] quit
# Create AP ap1, and specify its model and serial number.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A2KF819CE0002T
# Create and bind radio 1 to WLAN service template 1, and then enable the radio.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
# Create AP ap2 and specify its model and serial number.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2] serial-id 219801A2KF819CE00021
# Create and bind radio 1 to WLAN service template 1, and then enable the radio.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-1] service-template 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display WAPI user information on all interfaces of the AC.
[AC] display wapi user
Total number of users: 2
AP name : ap1
Radio ID : 1
SSID : wapi1
BSSID : 487a-da52-d4f0
MAC address : 000b-c002-5e39
VLAN : 1
Authentication method : Certificate
Current state : Online
Authentication state : Authenticated
Unicast key negotiation state : Established
Multicast key negotiation state : Established
Authorization state : Idle
Accounting state : Idle
Uptime : 00:02:26
AP name : ap1
Radio ID : 1
SSID : wapi1
BSSID : 487a-da52-d4f0
MAC address : 000b-c002-5e2f
VLAN : 1
Authentication method : Certificate
Current state : Online
Authentication state : Authenticated
Unicast key negotiation state : Established
Multicast key negotiation state : Established
Authorization state : Idle
Accounting state : Idle
Uptime : 00:02:30
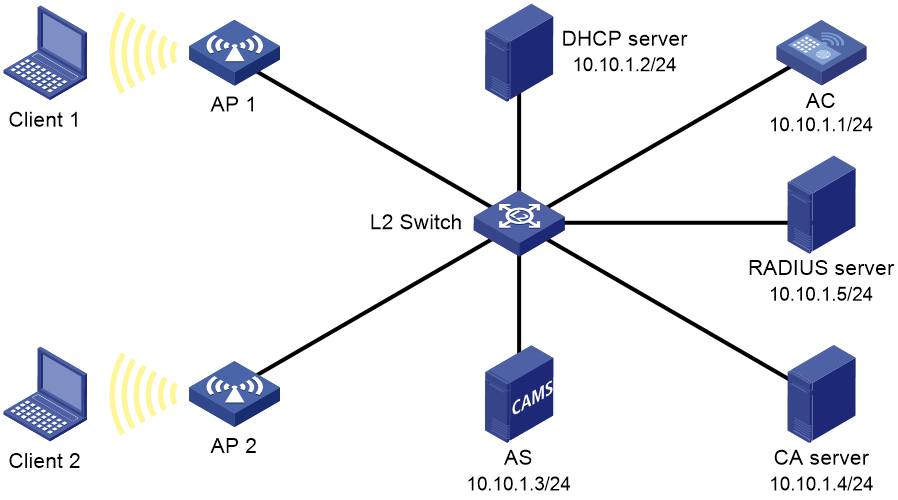
Example: Configuring standard certificate authentication for accounting
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 6, configure standard certificate authentication for accounting to authenticate and charge clients associated with AP 1 and AP 2.
Procedure
1. Import the CA and AS certificates to the AS, and install the asue and AS certificates on the WAPI client.
An AS server and a CA server can be installed on the same physical device. In this case, the AS certificate and CA certificate are the same.
2. Assign IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure the AC.
# Create PKI domain pki1, and disable CRL checking for the domain so that certificate revocation is not verified.
[AC] pki domain pki1
[AC-pki-domain-pki1] undo crl check enable
[AC-pki-domain-pki1] quit
# Import certificate files ca.cer, ap.cer, and as.cer.
[AC] pki import domain pki1 pem ca filename ca.cer
[AC] pki import domain pki1 pem local filename ap.cer
[AC] pki import domain pki1 pem peer filename as.cer
# Create RADIUS scheme radius1, specify IP addresses for the primary authentication and accounting servers, and specify a shared key for secure authentication and accounting communication.
[AC-radius-radius1] primary authentication 10.10.1.5
[AC-radius-radius1] primary accounting 10.10.1.5
[AC-radius-radius1] key authentication simple 12345678
[AC-radius-radius1] key accounting simple 12345678
[AC-radius-radius1] quit
# Create ISP domain domain1, and specify the default authentication, authorization, and accounting methods.
[AC-isp-domain1] authentication default none
[AC-isp-domain1] authorization default none
[AC-isp-domain1] accounting default radius-scheme radius1
[AC-isp-domain1] quit
[AC] domain default enable domain1
# Create service template 1 and configure its SSID as wapi1.
[AC] wlan service-template 1
[AC-wlan-st-1] ssid wapi1
# Enable WAPI.
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi enable
# Configure WAPI to use the certificate authentication mode.
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi authentication-method certificate
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi authentication-server ip 10.10.1.3
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi certificate domain pki1 serial 29
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi domain domain1
[AC-wlan-st-1] undo wapi bk-rekey enable
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi msk-rekey method time-based 20000
[AC-wlan-st-1] wapi usk lifetime 20000
[AC-wlan-st-1] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-1] quit
# Create AP ap1, and specify its model and serial number.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A2KF819CE0002T
# Create and bind radio 1 to WLAN service template 1, and then enable the radio.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
# Create AP ap2 and specify its model and serial number.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2] serial-id 219801A2KF819CE00021
# Create and bind radio 1 to WLAN service template 1, and then enable the radio.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-1] service-template 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display WAPI user information on all interfaces of the AC.
Total number of users: 2
AP name : ap1
Radio ID : 1
SSID : wapi1
BSSID : 487a-da52-d4f0
MAC address : 000b-c002-5e39
VLAN : 1
Authentication method : Certificate
Current state : Online
Authentication state : Authenticated
Unicast key negotiation state : Established
Multicast key negotiation state : Established
Authorization state : Idle
Accounting state : Success
Uptime : 00:02:26
AP name : ap1
Radio ID : 1
SSID : wapi1
BSSID : 487a-da52-d4f0
MAC address : 000b-c002-5e2f
VLAN : 1
Authentication method : Certificate
Current state : Online
Authentication state : Authenticated
Unicast key negotiation state : Established
Multicast key negotiation state : Established
Authorization state : Idle
Accounting state : Success
Uptime : 00:02:30
Troubleshooting WAPI
Client association failure
Symptom
A client cannot associate with an AP.
Solution
To resolve the issue:
1. Verify that the AP has associated with the AC. Execute the display wlan ap all command to verify the state of the AP is Run.
2. Verify the following settings on the AP and client:
¡ For PSK authentication, execute the display current-configuration command on the AC to verify that the PSKs on the client and AP are consistent.
- If the key type on the client is ASCII, the key on the AP must be a character string.
- If the key type on the client is HEX, the key on the AP must be in hexadecimal format.
¡ For standard certificate authentication, execute the display pki certificate command on the AC to verify that the certificates of the CA, AC, and AS are correct.
If the signature algorithm of the PKI domain is not ECDSA, you must delete all the certificates of this domain, and configure the signature algorithm as ECDSA and re-install all the certificates for the domain.
3. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
Accounting failure
Symptom
An accounting failure has occurred.
Solution
To resolve the issue:
1. Verify the following settings on the AC:
¡ The accounting scheme is none or RADIUS when WAPI uses the standard certificate authentication mode.
¡ IMC is not used as the accounting server.
¡ The ISP domain is specified for WAPI authentication by using the wapi domain command.
2. Verify that the accounting server is reachable.
3. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
Ping failure from an online client
Symptom
A client fails to ping the AC or other devices after coming online.
Solution
To resolve the issue:
1. Verify that the memory of AC is greater than 1 GB. If the memory of the AC is less than 1 GB, expand the memory of the AC or deploy another AC with memory more than 1 GB.
2. Execute the wmm disable command in radio view.
3. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.