- Table of Contents
-
- 06-Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Basic IP routing configuration
- 02-Static routing configuration
- 03-RIP configuration
- 04-OSPF configuration
- 05-IS-IS configuration
- 06-Basic BGP configuration
- 07-Advanced BGP configuration
- 08-Policy-based routing configuration
- 09-IPv6 static routing configuration
- 10-RIPng configuration
- 11-OSPFv3 configuration
- 12-IPv6 policy-based routing configuration
- 13-Routing policy configuration
- 14-DCN configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 12-IPv6 policy-based routing configuration | 161.35 KB |
Contents
IPv6 packet forwarding process
Restrictions and guidelines: IPv6 PBR configuration
Setting match criteria for an IPv6 node
Configuring actions for an IPv6 node
Specifying a policy for IPv6 PBR
Specifying an IPv6 policy for IPv6 local PBR
Specifying an IPv6 policy for IPv6 interface PBR
Enabling the IPv6 PBR logging feature
Verifying and maintaining IPv6 PBR
Verifying IPv6 PBR policy configuration
Displaying IPv6 PBR configuration and statistics
IPv6 PBR configuration examples
Configuring IPv6 PBR
About IPv6 PBR
IPv6 policy-based routing (PBR) uses user-defined policies to route IPv6 packets. A policy can specify parameters for packets that match specific criteria such as ACLs. The parameters include the next hop, output interface, default next hop, and default output interface.
IPv6 packet forwarding process
When the device receives an IPv6 packet, the device searches the IPv6 PBR policy for a matching node to forward that packet.
· If a matching node is found and its match mode is permit, the device performs the following operations:
a. Uses the output interfaces or next hops specified on the node to forward the packet.
b. Searches the routing table for a route (except the default route) to forward the packet if one of the following conditions exists:
- No output interfaces or next hops are specified on the node.
- Forwarding failed based on the output interfaces or next hops.
c. Uses the default next hops or default output interfaces specified on the node to forward the packet if one of the following conditions exists:
- No matching route was found in the routing table.
- The routing table-based forwarding failed.
d. Uses the default route to forward the packet if one of the following conditions exists:
- No default next hops or default output interfaces are specified on the node.
- The forwarding failed based on the default next hops or default output interfaces.
· The device performs routing table lookup to forward the packet in either of the following conditions:
¡ No matching node is found.
¡ A matching node is found, but its match mode is deny.
IPv6 PBR types
IPv6 PBR includes the following types:
· Local PBR—Guides the forwarding of locally generated packets, such as the ICMP packets generated by using the ping command.
· Interface PBR—Guides the forwarding of packets received on an interface only.
Policy
An IPv6 policy includes match criteria and actions to be taken on the matching packets. A policy can have one or multiple nodes as follows:
· Each node is identified by a node number. A smaller node number has a higher priority.
· A node contains if-match and apply clauses. An if-match clause specifies a match criterion, and an apply clause specifies an action.
· A node has a match mode of permit or deny.
An IPv6 policy compares packets with nodes in ascending order of node numbers. If a packet matches the criteria on a node, it is processed by the action on the node. Otherwise, it goes to the next node for a match. If the packet does not match the criteria on any node, the device performs a routing table lookup for the packet.
Relationship between if-match clauses
Only the if-match acl clause is supported. On a node, you can specify only one if-match acl clause.
Relationship between apply clauses
You can specify multiple apply clauses for a node, but some of them might not be executed. For more information about the relationship between the apply clauses, see "Configuring actions for an IPv6 node."
Relationship between the match mode and clauses on the node
|
Match mode |
||
|
In permit mode |
In deny mode |
|
|
Yes |
· If the node contains apply clauses, IPv6 PBR executes the apply clauses on the node. ¡ If IPv6 PBR-based forwarding succeeds, IPv6 PBR does not compare the packet with the next node. ¡ If IPv6 PBR-based forwarding fails, IPv6 PBR does not compare the packet with the next node. · If the node does not contain apply clauses, the device performs a routing table lookup for the packet. |
The device performs a routing table lookup for the packet. |
|
No |
IPv6 PBR compares the packet with the next node. |
IPv6 PBR compares the packet with the next node. |
|
|
NOTE: A node that has no if-match clauses matches any packet. |
IPv6 PBR and Track
IPv6 PBR can work with the Track feature to dynamically adapt the availability status of an apply clause to the link status of a tracked object. The tracked object can be a next hop, output interface, default next hop, or default output interface.
· When the track entry associated with an object changes to Negative, the apply clause is invalid.
· When the track entry changes to Positive or NotReady, the apply clause is valid.
For more information about Track-IPv6 PBR collaboration, see High Availability Configuration Guide.
Restrictions and guidelines: IPv6 PBR configuration
If a packet destined for the local device matches an IPv6 PBR policy, IPv6 PBR will execute the apply clauses in the policy, including the clause for forwarding. When you configure an IPv6 PBR policy, be careful to avoid this situation.
IPv6 PBR tasks at a glance
To configure IPv6 PBR, perform the following tasks:
b. Setting match criteria for an IPv6 node
c. Configuring actions for an IPv6 node
3. Specifying a policy for IPv6 PBR
Choose the following tasks as needed:
¡ Specifying an IPv6 policy for IPv6 local PBR
¡ Specifying an IPv6 policy for IPv6 interface PBR
4. (Optional.) Enabling the IPv6 PBR logging feature
Configuring an IPv6 policy
Creating an IPv6 node
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create an IPv6 policy or policy node and enter its view.
ipv6 policy-based-route policy-name [ deny | permit ] node node-number
3. (Optional.) Configure a description for the IPv6 policy node.
description text
By default, no description is configured for an IPv6 policy node.
Setting match criteria for an IPv6 node
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter IPv6 policy node view.
ipv6 policy-based-route policy-name [ deny | permit ] node node-number
3. Set match criteria.
¡ Set an ACL match criterion.
if-match acl { ipv6-acl-number | name ipv6-acl-name }
By default, no ACL match criterion is set.
IPv6 PBR supports both basic and advanced ACLs.
When using the ACL to match packets, IPv6 PBR ignores the action (permit or deny) and time range settings in the ACL.
Configuring actions for an IPv6 node
About this task
The apply clauses allow you to specify actions to take on matching packets on a node.
The following apply clauses determine the packet forwarding paths in a descending order:
· apply next-hop
· apply output-interface
· apply default-next-hop
· apply default-output-interface
IPv6 PBR supports the apply clauses in Table 1.
Table 1 Apply clauses supported in IPv6 PBR
|
Clause |
Meaning |
Remarks |
|
apply precedence |
Sets an IP precedence. |
This clause is always executed. |
|
apply output-interface and apply next-hop |
Sets output interfaces and next hops. |
If both clauses are configured, only the apply next-hop clause is executed. |
|
apply default-next-hop and apply default-output-interface |
Sets default next hops and default output interface |
If both clauses are configured, only the apply default-next-hop clause is executed. The clauses take effect only in the following cases: · No output interfaces or next hops are set or the output interfaces and next hops are invalid. · The packet does not match any route in the routing table. |
|
apply statistics |
Counts successful matches and matching bytes on the IPv6 policy node. |
To include the number of successful matches and matching bytes on an IPv6 policy node in the statistics displayed by a display command, execute this command. This clause is always executed for matching packets. |
Restrictions and guidelines for action configuration
IPv6 PBR periodically performs a lookup in the FIB table to determine the availability of a next hop or default next hop specified in an IPv6 PBR policy. If a route change occurs to the next hop, IPv6 PBR might not update the route immediately. This results in a temporary communication interruption.
Setting an IP preference
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter IPv6 policy node view.
ipv6 policy-based-route policy-name [ deny | permit ] node node-number
3. Set an IP precedence.
apply precedence { type | value }
By default, no IP precedence is specified.
Configuring actions for a node
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter IPv6 policy node view.
ipv6 policy-based-route policy-name [ deny | permit ] node node-number
3. Configure actions for a node.
¡ Set next hops for permitted IPv6 packets.
apply next-hop [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] { ipv6-address [ direct ] [ track track-entry-number ] } &<1-2>
By default, no next hops are specified.
You can specify multiple next hops for backup in one command line or by executing this command multiple times. You can specify a maximum of two next hops for a node.
¡ Set output interfaces.
apply output-interface { interface-type interface-number [ track track-entry-number ] }
By default, no output interfaces are specified.
As a best practice, do not specify the interface of a VXLAN tunnel automatically created by EVPN for this command.
¡ Set default next hops.
apply default-next-hop [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | inbound-vpn ] { ipv6-address [ direct ] [ track track-entry-number ] } &<1-2>
By default, no default next hops are specified.
You can specify multiple default next hops for backup in one command line or by executing this command multiple times. You can specify a maximum of two default next hops for a node.
¡ Set default output interfaces.
apply default-output-interface { interface-type interface-number [ track track-entry-number ] }
By default, no default output interfaces are specified.
As a best practice, do not specify the interface of a VXLAN tunnel automatically created by EVPN for this command.
Collecting statistics
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter IPv6 policy node view.
ipv6 policy-based-route policy-name [ deny | permit ] node node-number
3. Count successful matches and matching bytes on the IPv6 policy node.
apply statistics
Match counting is disabled on an IPv6 policy node.
After configuring this command, you cannot specify the share-mode keyword when applying the IPv6 policy to an interface for IPv6 interface PBR.
Specifying a policy for IPv6 PBR
Specifying an IPv6 policy for IPv6 local PBR
About this task
Perform this task to specify an IPv6 policy for IPv6 local PBR to guide the forwarding of locally generated packets.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can specify only one policy for IPv6 local PBR and must make sure the specified policy already exists. Before you apply a new policy, you must first remove the current policy.
IPv6 local PBR might affect local services, such as ping and Telnet. When you use IPv6 local PBR, make sure you fully understand its impact on local services of the device.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify an IPv6 policy for IPv6 local PBR.
ipv6 local policy-based-route policy-name
By default, IPv6 local PBR is not enabled.
Specifying an IPv6 policy for IPv6 interface PBR
About this task
Perform this task to apply an IPv6 policy to an interface to guide the forwarding of packets received on the interface only.
To apply an IPv6 policy to multiple VLAN interfaces at the same time, you can use the ipv6 policy-based-route apply command. Using this command simplifies configuration and saves device resources.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can apply only one policy to an interface and must make sure the specified policy already exists. Before you apply a new policy, you must first remove the current policy from the interface.
You can apply a policy to multiple interfaces.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Specify an IPv6 policy for IPv6 interface PBR.
ipv6 policy-based-route policy-name [ share-mode ]
By default, no IPv6 policy is applied to the interface.
You cannot specify the share-mode keyword for the command if you have configured the apply statistics command for the IPv6 policy.
Enabling the IPv6 PBR logging feature
About this task
The IPv6 PBR logging feature helps the administrator locate and fix faults. The feature logs IPv6 PBR events and sends the logs to the information center. The information center processes the logs according to output rules. For more information about the information center, see System Management Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable the IPv6 PBR logging feature.
ipv6 policy-based-route-log enable
By default, the IPv6 PBR logging feature is disabled.
Verifying and maintaining IPv6 PBR
Verifying IPv6 PBR policy configuration
To display IPv6 PBR policy information, execute the following command in any view:
display ipv6 policy-based-route [ policy policy-name ]
Displaying IPv6 PBR configuration and statistics
Perform display tasks in any view.
· Display IPv6 PBR configuration.
display ipv6 policy-based-route setup
· Display IPv6 local PBR configuration and statistics.
display ipv6 policy-based-route local [ slot slot-number ]
· Display IPv6 interface PBR configuration and statistics.
display ipv6 policy-based-route interface interface-type interface-number [ slot slot-number ]
Clearing IPv6 PBR statistics
To clear IPv6 PBR statistics, execute the following command in user view:
reset ipv6 policy-based-route statistics [ policy policy-name ]
IPv6 PBR configuration examples
Example: Configuring packet type-based IPv6 local PBR
Network configuration
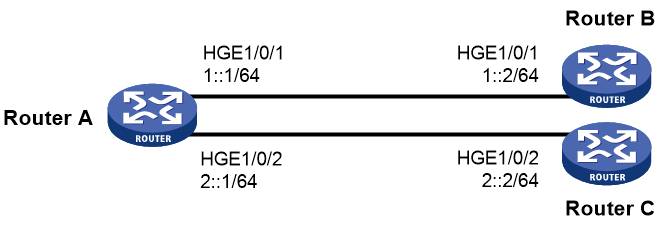
As shown in Figure 1, Router B and Router C are connected through Router A. Router B and Router C do not have a route to reach each other.
Configure IPv6 PBR on Router A to forward all TCP packets to the next hop 1::2 (Router B).
Procedure
|
IMPORTANT: By default, interfaces on the devices are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface. |
1. Configure Router A:
# Configure the IPv6 addresses of HundredGigE 1/0/1 and HundredGigE 1/0/2.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1] ipv6 address 1::1 64
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
[RouterA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/2] ipv6 address 2::1 64
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Configure ACL 3001 to match TCP packets.
[RouterA] acl ipv6 advanced 3001
[RouterA-acl-ipv6-adv-3001] rule permit tcp
[RouterA-acl-ipv6-adv-3001] quit
# Configure Node 5 for policy aaa to forward TCP packets to next hop 1::2.
[RouterA] ipv6 policy-based-route aaa permit node 5
[RouterA-pbr6-aaa-5] if-match acl 3001
[RouterA-pbr6-aaa-5] apply next-hop 1::2
[RouterA-pbr6-aaa-5] quit
# Configure IPv6 local PBR by applying policy aaa to Router A.
[RouterA] ipv6 local policy-based-route aaa
2. On Router B, configure the IPv6 address of HundredGigE 1/0/1.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[RouterB-HundredGigE1/0/1] ipv6 address 1::2 64
3. On Router C, configure the IPv6 address of HundredGigE 1/0/2.
<RouterC> system-view
[RouterC] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[RouterC-HundredGigE1/0/2] ipv6 address 2::2 64
Verifying the configuration
1. Perform telnet operations to verify that IPv6 local PBR on Router A operates as configured to forward the matching TCP packets to the next hop 1::2 (Router B), as follows:
# Verify that you can telnet to Router B from Router A successfully. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that you cannot telnet to Router C from Router A. (Details not shown.)
2. Verify that Router A forwards packets other than TCP packets through HundredGigE 1/0/2. For example, verify that you can ping Router C from Router A. (Details not shown.)
Example: Configuring packet type-based IPv6 interface PBR
Network configuration
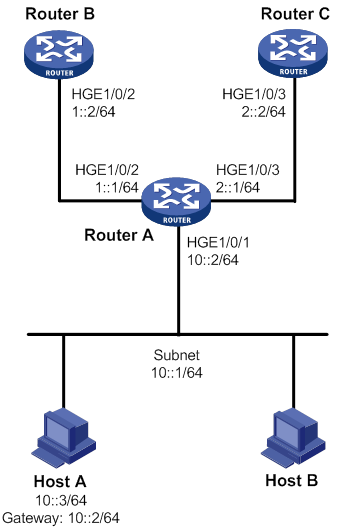
As shown in Figure 2, Router B and Router C do not have a route to reach each other.
Configure IPv6 PBR on Router A to forward all TCP packets received on HundredGigE 1/0/1 to the next hop 1::2 (Router B).
Procedure
|
IMPORTANT: By default, interfaces on the devices are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface. |
1. Configure Router A:
# Configure RIPng.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] ripng 1
[RouterA-ripng-1] quit
[RouterA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/2] ipv6 address 1::1 64
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/2] ripng 1 enable
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
[RouterA] interface hundredgige 1/0/3
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/3] ipv6 address 2::1 64
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/3] ripng 1 enable
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/3] quit
# Configure ACL 3001 to match TCP packets.
[RouterA] acl ipv6 advanced 3001
[RouterA-acl-ipv6-adv-3001] rule permit tcp
[RouterA-acl-ipv6-adv-3001] quit
# Configure Node 5 for policy aaa to forward TCP packets to next hop 1::2.
[RouterA] ipv6 policy-based-route aaa permit node 5
[RouterA-pbr6-aaa-5] if-match acl 3001
[RouterA-pbr6-aaa-5] apply next-hop 1::2
[RouterA-pbr6-aaa-5] quit
# Configure IPv6 interface PBR by applying policy aaa to HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[RouterA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1] ipv6 address 10::2 64
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo ipv6 nd ra halt
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1] ripng 1 enable
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1] ipv6 policy-based-route aaa
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
2. Configure RIPng on Router B.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] ripng 1
[RouterB-ripng-1] quit
[RouterB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[RouterB-HundredGigE1/0/2] ipv6 address 1::2 64
[RouterB-HundredGigE1/0/2] ripng 1 enable
[RouterB-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
3. Configure RIPng on Router C.
<RouterC> system-view
[RouterC] ripng 1
[RouterC-ripng-1] quit
[RouterC] interface hundredgige 1/0/3
[RouterC-HundredGigE1/0/3] ipv6 address 2::2 64
[RouterC-HundredGigE1/0/3] ripng 1 enable
[RouterC-HundredGigE1/0/3] quit
Verifying the configuration
1. Enable IPv6 and configure the IPv6 address 10::3 for Host A.
C:\>ipv6 install
Installing...
Succeeded.
C:\>ipv6 adu 4/10::3
2. Perform telnet operations to verify that IPv6 interface PBR on Router A operates as configured to forward the matching TCP packets to the next hop 1::2 (Router B), as follows:
# Verify that you can telnet to Router B from Host A successfully. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that you cannot telnet to Router C from Host A. (Details not shown.)
3. Verify that Router A forwards packets other than TCP packets through HundredGigE 1/0/3. For example, verify that you can ping Router C from Host A. (Details not shown.)