- Table of Contents
-
- 02-System Management Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Basic device management configuration
- 02-Device hardening configuration
- 03-Hardware resource management configuration
- 04-EAA configuration
- 05-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 06-Information center configuration
- 07-GOLD configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-Hardware resource management configuration | 233.10 KB |
Hardware resource management tasks at a glance
Configuring CPU usage tracking
Displaying CPU usage monitoring information
Setting memory alarm thresholds
Displaying memory usage monitoring information
Configuring the allocation mode for MDB resources
Displaying the MDB resources allocation mode
Configuring resource monitoring
Displaying resource monitoring information
Setting the temperature alarm thresholds
Displaying device temperature information
Configuring hardware failure detection and protection
Specifying the actions to be taken for hardware failures
Enabling hardware failure protection for aggregation groups
Power supply management tasks at a glance
Enabling power supply management
Specifying the number of redundant power supplies
Configuring the exception monitoring mode for power supplies
Setting the port status detection timer
Verifying and diagnosing transceiver modules
Diagnosing transceiver modules
Specifying an ITU channel number for a transceiver module
Managing 400-GE transceiver modules
Enabling lanes on 400-GE transceiver modules
Setting a power mode for 400-GE transceiver modules
Configuring pre-cursor, post-cursor, and amplitude
Displaying 400-GE transceiver module information
Resetting 400-GE transceiver modules
Enabling shutdown of service ports
Enabling power on/off management of cards
Configuring an asset profile for a physical component
Displaying and maintaining user asset information
Isolating switching fabric modules
Suppressing removal interrupt signals from switching fabric modules
About isolating a service card
Configuring consistency error logging for software and hardware forwarding entries
Configuring parity error and ECC error logging for entries on forwarding chips
Configuring uncorrectable parity error and ECC error logging for entries on forwarding chips
Displaying device hardware information
Displaying device hardware electronic label information
Displaying backplane electronic label information
Managing hardware resources
This chapter describes routine device hardware resource management tasks, including monitoring CPU and memory usage, displaying power supply and fan operating status, and configuring basic device operating parameters.
Hardware resource management tasks at a glance
All hardware resource management tasks are optional. You can perform any of the tasks in any order.
¡ Configuring CPU usage tracking
¡ Displaying CPU usage monitoring information
¡ Setting memory alarm thresholds
¡ Displaying memory usage monitoring information
¡ Configuring the allocation mode for MDB resources
¡ Displaying the MDB resources allocation mode
¡ Configuring resource monitoring
¡ Displaying resource monitoring information
· Monitoring device temperature
¡ Setting the temperature alarm thresholds
¡ Displaying device temperature information
· Configuring hardware failure detection and protection
¡ Specifying the actions to be taken for hardware failures
¡ Enabling hardware failure protection for aggregation groups
¡ Enabling power supply management
¡ Specifying the number of redundant power supplies
¡ Configuring the exception monitoring mode for power supplies
· Setting the port status detection timer
· Verifying and diagnosing transceiver modules
¡ Verifying transceiver modules
¡ Diagnosing transceiver modules
· Specifying an ITU channel number for a transceiver module
· Managing 400-GE transceiver modules
¡ Enabling lanes on 400-GE transceiver modules
¡ Setting a power mode for 400-GE transceiver modules
¡ Configuring pre-cursor, post-cursor, and amplitude
¡ Displaying 400-GE transceiver module information
¡ Resetting 400-GE transceiver modules
· Enabling shutdown of service ports
· Enabling power on/off management of cards
· Isolating switching fabric modules
· Suppressing removal interrupt signals from switching fabric modules
· Configuring consistency error logging for software and hardware forwarding entries
· Configuring parity error and ECC error logging for entries on forwarding chips
· Configuring uncorrectable parity error and ECC error logging for entries on forwarding chips
· Displaying device hardware information
· Displaying device hardware electronic label information
· Displaying backplane electronic label information
· Displaying device hardware alarm information
Monitoring CPU usage
Configuring CPU usage alarm
About this task
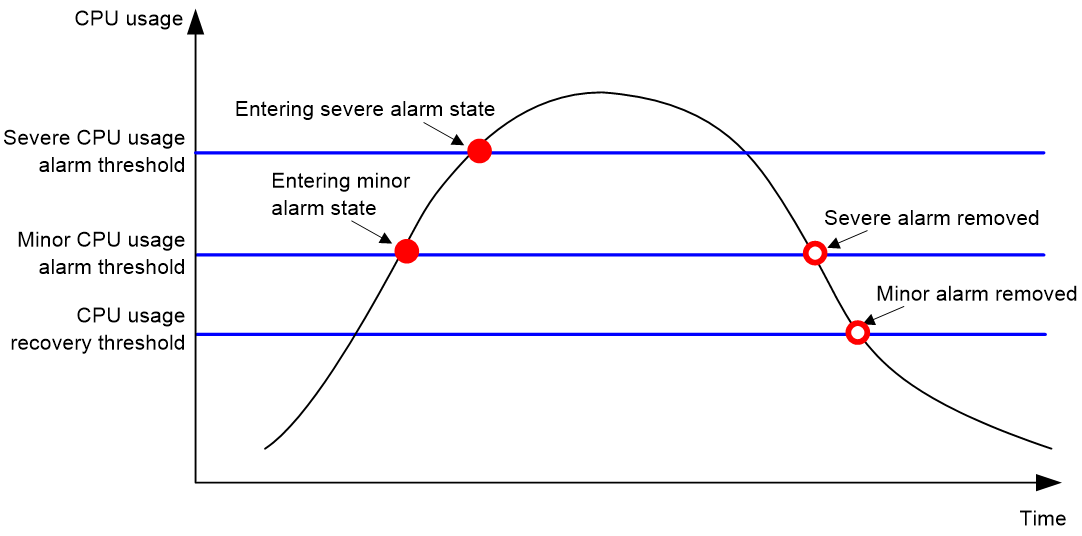
The device samples CPU usage at 1-minute intervals, and compares the samples with CPU usage thresholds to identify the CPU usage status and send alarms or notifications accordingly.
The device supports the following CPU usage thresholds:
· Minor threshold—If the CPU usage increases to or above the minor threshold but is less than the severe threshold, the CPU usage enters minor alarm state. The device sends minor alarms periodically until the CPU usage increases above the severe threshold or the minor alarm is removed.
· Severe threshold—If the CPU usage increases above the severe threshold, the CPU usage enters severe alarm state. The device sends severe alarms periodically until the severe alarm is removed.
· Recovery threshold—If the CPU usage decreases below the recovery threshold, the CPU usage enters recovered state. The device sends a recovery notification.
CPU usage alarms and notifications can be sent to NETCONF, SNMP, and the information center to be encapsulated as NETCONF events, SNMP traps and informs, and log messages. For more information about NETCONF and SNMP, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide. For more information about information center, see "Configuring the information center."
Figure 1 CPU alarms and alarm-removed notifications
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the CPU usage alarm thresholds.
monitor cpu-usage threshold severe-threshold [ minor-threshold minor-threshold recovery-threshold recovery-threshold ] [ slot slot-number [ cpu cpu-number ] ]
By default, the CPU usage alarm threshold is 99%.
|
CAUTION: If you set the severe CPU usage alarm threshold to a too low value, the device will reach the threshold easily. Normal service processing will be affected. |
Configuring CPU usage tracking
About this task
After you enable CPU usage tracking, the system samples CPU usage at intervals and saves the samples to a buffer. You can use the display cpu-usage history command to view the recent CPU usage.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the sampling interval for CPU usage tracking.
monitor cpu-usage interval interval [ slot slot-number [ cpu cpu-number ] ]
By default, the sampling interval for CPU usage tracking is 1 minute.
3. Enable CPU usage tracking.
monitor cpu-usage enable [ slot slot-number [ cpu cpu-number ] ]
By default, CPU usage tracking is enabled.
Displaying CPU usage monitoring information
Perform display tasks in any view.
· Display CPU usage monitoring settings.
display cpu-usage configuration [ slot slot-number [ cpu cpu-number ] ]
· Display the current CPU usage statistics.
display cpu-usage [ summary ] [ slot slot-number [ cpu cpu-number ] ]
· Display the historical CPU usage statistics in a coordinate system.
display cpu-usage history [ job job-id ] [ slot slot-number [ cpu cpu-number ] ]
Monitoring memory usage
Setting memory alarm thresholds
About this task
To ensure correct operation and improve memory efficiency, the system monitors the amount of free memory space in real time. If the amount of free memory space reaches the minor, severe, or critical alarm threshold, the system issues an alarm to affected service modules and processes.
You can use the display memory command to display memory usage information.
As shown in Table 1, the system supports the following free-memory thresholds:
· Sufficient-memory threshold.
· Early-warning threshold.
· Normal state threshold.
· Minor alarm threshold.
· Severe alarm threshold.
· Critical alarm threshold.
Table 1 Memory alarm notifications and memory alarm-removed notifications
|
Notification |
Triggering condition |
Remarks |
|
Early-warning notification |
The amount of free memory space decreases below the early-warning threshold. |
After generating and sending an early-warning notification, the system does not generate and send any additional early-warning notifications until the early warning is removed. |
|
Minor alarm notification |
The amount of free memory space decreases to or below the minor alarm threshold. |
After generating and sending a minor alarm notification, the system does not generate and send any additional minor alarm notifications until the minor alarm is removed. |
|
Severe alarm notification |
The amount of free memory space decreases to or below the severe alarm threshold. |
After generating and sending a severe alarm notification, the system does not generate and send any additional severe alarm notifications until the severe alarm is removed. |
|
Critical alarm notification |
The amount of free memory space decreases to or below the critical alarm threshold. |
After generating and sending a critical alarm notification, the system does not generate and send any additional critical alarm notifications until the critical alarm is removed. |
|
Critical alarm-removed notification |
The amount of free memory space increases above the severe alarm threshold. |
N/A |
|
Severe alarm-removed notification |
The amount of free memory space increases above the minor alarm threshold. |
N/A |
|
Minor alarm-removed notification |
The amount of free memory space increases above the normal state threshold. |
N/A |
|
Early-warning-removed notification |
The amount of free memory space increases above the sufficient-memory threshold. |
N/A |
Figure 2 Memory alarm notifications and alarm-removed notifications
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the memory usage threshold.
memory-threshold [ slot slot-number [ cpu cpu-number ] ] usage memory-threshold
By default, the memory usage threshold is 100%.
3. Set the free-memory thresholds.
memory-threshold [ slot slot-number [ cpu cpu-number ] ] [ ratio ] minor minor-value severe severe-value critical critical-value normal normal-value
The default settings are as follows:
¡ Minor alarm threshold—256 MB.
¡ Severe alarm threshold—192 MB.
¡ Critical alarm threshold—128 MB.
¡ Normal state threshold—320 MB.
¡ Early-warning threshold—384 MB.
¡ Sufficient-memory threshold—448 MB.
Displaying memory usage monitoring information
Perform display tasks in any view.
· Display memory usage information.
display memory [ summary ] [ slot slot-number [ cpu cpu-number ] ]
· Display memory alarm thresholds and statistics.
display memory-threshold [ slot slot-number [ cpu cpu-number ] ]
Monitoring MDB resources
Configuring the allocation mode for MDB resources
About this task
You can configure the routing or normal allocation mode for MDB resources. The MAC address table, ARP table, and routing table capacities vary by the resource allocation mode.
Restrictions and guidelines
For this configuration to take effect, you must reboot the device.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the allocation mode for MDB resources.
hardware-resource mdb { normal | routing }
By default, the routing allocation mode is used for MDB resources.
Displaying the MDB resources allocation mode
To display the MDB resources allocation mode, execute the following command in any view:
display hardware-resource [ mdb ]
Monitoring resource usage
Configuring resource monitoring
About this task
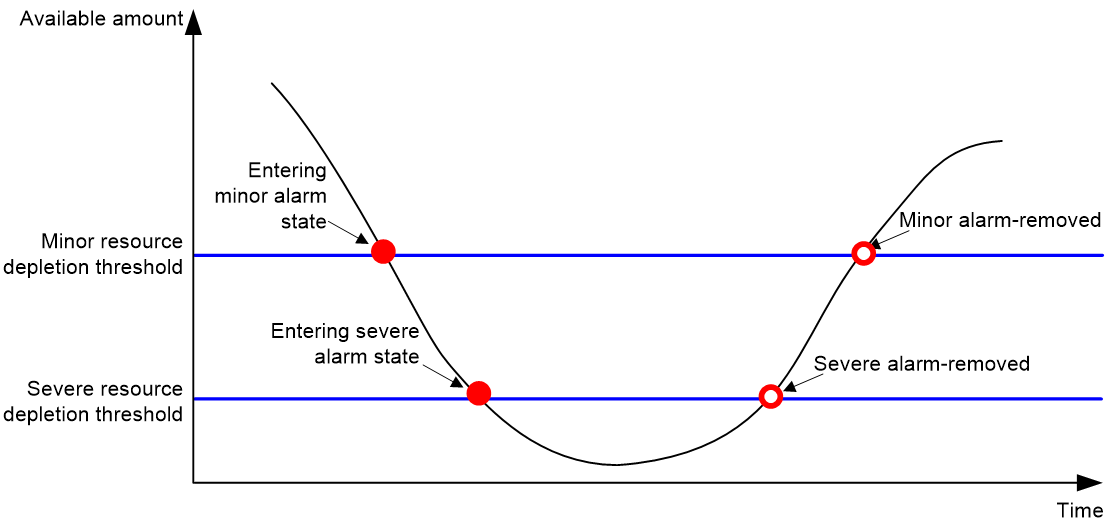
The resource monitoring feature enables the device to monitor the available amounts of types of resources, for example, the space for ARP entries. The device samples the available amounts periodically and compares the samples with resource depletion thresholds to identify the resource depletion status.
The device supports a minor resource depletion threshold and a severe resource depletion threshold for each supported resource type.
· If the available amount is equal to or less than the minor resource depletion threshold but greater than the severe resource depletion threshold, the resource type is in minor alarm state.
· If the available amount is equal to or less than the severe resource depletion threshold, the resource type is in severe alarm state.
· If the available amount increases above the minor resource depletion threshold, the resource type is in recovered state.
When a resource type enters severe alarm state, the device issues a severe alarm. If the resource type stays in severe alarm state, the device resends severe alarms periodically.
When a resource type enters minor alarm state, the device issues a minor alarm. If the resource type stays in minor alarm state or changes from severe alarm state to minor alarm state, the device identifies whether resending of minor resource depletion alarms is enabled. If the feature is disabled, the device does not issue additional minor alarms. If the feature is enabled, the device resends minor alarms periodically.
Resource depletion alarms can be sent to NETCONF, SNMP, and the information center to be encapsulated as NETCONF events, SNMP traps and informs, and log messages. For more information about NETCONF and SNMP, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide. For more information about information center, see "Configuring the information center."
Figure 3 Resource depletion alarms and alarm-removed notifications
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set resource depletion thresholds.
resource-monitor resource resource-name slot slot-number cpu cpu-number { by-absolute | by-percent } minor-threshold minor-threshold severe-threshold severe-threshold
The default settings vary by resource type. Use the display resource-monitor command to display the resource depletion thresholds.
3. Specify destinations for resource depletion alarms.
resource-monitor output { netconf-event | snmp-notification | syslog } *
By default, resource depletion alarms are sent to NETCONF, SNMP, and the information center.
4. Enable resending of minor resource depletion alarms.
resource-monitor minor resend enable
By default, resending of minor resource depletion alarms is enabled.
Displaying resource monitoring information
To display resource monitoring information, execute the following command in any view:
display resource-monitor [ resource resource-name ] [ slot slot-number [ cpu cpu-number ] ]
Monitoring device temperature
Setting the temperature alarm thresholds
About this task
The device monitors its temperature based on the following thresholds:
· Low-temperature threshold.
· High-temperature warning threshold.
· High-temperature alarming threshold.
When the device temperature drops below the low-temperature threshold or reaches the high-temperature warning or alarming threshold, the device performs the following operations:
· Sends log messages and traps.
· Sets LEDs on the device panel.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the temperature alarm thresholds.
temperature-limit slot slot-number hotspot sensor-number lowlimit warninglimit [ alarmlimit ]
The defaults vary by temperature sensor model. To view the defaults, execute the undo temperature-limit and display environment commands in turn.
The high-temperature alarming threshold must be higher than the high-temperature warning threshold, and the high-temperature warning threshold must be higher than the low-temperature threshold.
Displaying device temperature information
To display device temperature information, execute the following command in any view:
display environment [ slot slot-number ]
Configuring hardware failure detection and protection
The device can automatically detect hardware failures on components, cards, and the forwarding plane, and take actions in response.
Specifying the actions to be taken for hardware failures
About this task
The device can take the following actions in response to hardware failures:
· isolate—Performs the following tasks as appropriate to reduce impact from the failures:
¡ Shuts down the relevant ports.
¡ Prohibits loading software for the relevant cards.
¡ Isolates the relevant cards.
¡ Powers off the relevant cards.
· reset—Restarts the relevant components or cards to recover from failures.
· warning—Sends traps to report the failures.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify the action to be taken in response to a type of hardware failures.
hardware-failure-detection { board | chip | forwarding } { off | isolate | reset | warning }
By default, the system takes the action of warning in response to hardware failures.
Enabling hardware failure protection for aggregation groups
About this task
Hardware failure protection for aggregation groups uses the following rules upon detecting a hardware failure on an aggregation group member interface:
· Does not shut down the interface if the member interface is the only member in up state in the group.
· Shuts down the interface if the member interface is not the only member in up state in the group.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the action to be taken in response to failures on the forwarding plane to isolate.
hardware-failure-detection forwarding isolate
By default, the system takes the action of warning in response to forwarding-plane failures.
3. Enable hardware failure protection for aggregation groups.
hardware-failure-protection aggregation
By default, hardware failure protection is disabled for aggregation groups.
Enabling chip reset
About this task
This task enables the system to reset a chip when an alarm indicating that the chip is faulty is generated.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable chip reset.
monitor chipblock reset [ logging ]
By default, chip reset is enabled.
Managing power supply
About power supply management
Power supplies might have problems such as overload overcurrent, overvoltage, overtemperature, and short circuit. Some power supplies use a hardware protection measure, for example, powering off the device, to protect the entire device from being damaged. The hardware protection measure helps protect the device but causes service outage. The power supply management feature can minimize service outage while protecting the device against overload problems.
The power supply management feature constantly monitors the available power and the system loads. If a potential power supply problem is found, this feature takes protective measures immediately to remove requirements for power supply hardware protection. Examples of protective measures include sending a notification, starting redundant power supplies, and powering off certain interface cards.
Power supply management tasks at a glance
To manage power supply, perform the following tasks:
1. Enabling power supply management
2. (Optional.) Specifying the number of redundant power supplies
To avoid overload problems, you can install redundant power supplies.
Enabling power supply management
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable power supply management.
power-supply policy enable
By default, power supply management is enabled.
Specifying the number of redundant power supplies
About this task
To avoid overload problems, you can install redundant power supplies. For example, if the device requires a minimum of N power supplies to operate correctly, you can install M power supplies (M > N). The M power supplies operate in load balance mode. When a power supply fails, the load is rebalanced among the other power supplies.
After you specify the number of redundant power supplies, the device compares the maximum power consumption of a newly added card with the remaining power.
· If the remaining power is sufficient for the card, the device powers on the card.
· If the power is insufficient, the device does not power on the card. You can add power supplies or scale the number of redundant power supplies down.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature takes effect only if power supply management is enabled.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify the number of redundant power supplies.
power-supply policy redundant module-count
By default, the number of redundant power supplies is 0.
Configuring the exception monitoring mode for power supplies
Restrictions and guidelines
The enhanced exception monitoring mode for the power supplies occupies lots of system resources.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the exception monitoring mode for the power supplies.
power-exception-monitor { normal | enhanced }
By default, the normal exception monitoring mode applies to the power supplies.
Verifying power supply
Displaying power supply information
To display power supply information, execute the following command in any view:
display power [ power-id | verbose ]
Displaying power supply management information
To display power supply management information, execute the following command in any view:
display power-supply [ verbose ]
Displaying electronic label information for a power supply
To display electronic label information for a power supply, execute the following command in any view:
display device manuinfo power power-id
Displaying electronic label information for a power monitoring module
To display electronic label information for a power monitoring module, execute the following command in any view:
display device manuinfo power-monitor pm-id
Monitoring fans
Displaying fan information
Perform display tasks in any view.
· Display fan tray operating status information.
display fan [ fan-id ] [ verbose ]
· Display electronic label information for a fan tray.
display device manuinfo fan fan-id
Setting the port status detection timer
About this task
The device starts a port status detection timer when a port is shut down by a protocol. Once the timer expires, the device brings up the port so the port status reflects the port's physical status.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the port status detection timer.
shutdown-interval time
The default setting is 30 seconds.
Verifying and diagnosing transceiver modules
Verifying transceiver modules
About this task
You can use one of the following methods to verify the genuineness of a transceiver module:
· Display the key parameters of a transceiver module, including its transceiver type, connector type, central wavelength of the transmit laser, transfer distance, and vendor name.
· Display its electronic label. The electronic label is a profile of the transceiver module and contains the permanent configuration, including the serial number, manufacturing date, and vendor name. The data was written to the transceiver module or the device's storage component during debugging or testing of the transceiver module or device.
The device regularly checks transceiver modules for their vendor names. If a transceiver module does not have a vendor name or the vendor name is not H3C, the device repeatedly outputs traps and log messages. For information about logging rules, see "Configuring the information center."
Procedure
To verify transceiver modules, execute the following commands in any view:
· Display the key parameters of transceiver modules.
display transceiver interface [ interface-type interface-number ]
· Display the electrical label information of transceiver modules.
display transceiver manuinfo interface [ interface-type interface-number ]
Diagnosing transceiver modules
About this task
The device provides the alarm and digital diagnosis functions for transceiver modules. When a transceiver module fails or is not operating correctly, you can perform the following tasks:
· Check the alarms that exist on the transceiver module to identify the fault source.
· Examine the key parameters monitored by the digital diagnosis function, including the temperature, voltage, laser bias current, TX power, and RX power.
Procedure
To diagnose transceiver modules, execute the following commands in any view:
· Display transceiver alarms.
display transceiver alarm interface [ interface-type interface-number ]
· Display the current values of the digital diagnosis parameters on transceiver modules.
display transceiver diagnosis interface [ interface-type interface-number ]
· Display key optical parameters for transceiver modules.
display transceiver optics interface [ interface-type interface-number ]
Specifying an ITU channel number for a transceiver module
About ITU channel numbers
ITU numbers identify fiber signals by wavelength and frequency. A transceiver module sends signals of a specific wavelength and frequency based on the specified ITU channel number.
This feature is required in dense wavelength division multiplexing scenarios.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature is supported only on the SFP-XG-LH80-Tunable transceiver module.
The device saves the ITU number setting in the transceiver module's register, not in the configuration file.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Ethernet interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Specify an ITU channel number.
itu-channel channel-number
By default, the ITU channel number is 1.
Display and maintenance
To display ITU number information for a transceiver module, execute the following command in any view:
display transceiver itu-channel interface [ interface-type interface-number [ supported-channel ] ]
Managing 400-GE transceiver modules
Enabling lanes on 400-GE transceiver modules
About this task
Use this task only to verify that a transceiver module is normal.
Restrictions and guidelines
Disabling a lane on a transceiver module will stop signal transmission on the lane.
The lane enablement setting is saved in a register on the transceiver module. It is not saved to the configuration file.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter 400-GE Ethernet interface view and its breakout interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable a lane on the transceiver module.
transceiver lane channel-number enable
By default, the lanes on the transceiver module are enabled.
Setting a power mode for 400-GE transceiver modules
About this task
A transceiver module generally operates in high power mode. If the transceiver module does not work for a long time, you can switch the transceiver module to low power mode to reduce power consumption. In low power mode, the transceiver module does not transmit signals unless you switch the transceiver to high power mode.
Restrictions and guidelines
The power mode setting is saved in a register on the transceiver module. It is not saved to the configuration file.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter 400-GE Ethernet interface view and its breakout interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Set a power mode for the transceiver module.
transceiver power-mode { high | low }
The default settings vary by modem model.
Configuring pre-cursor, post-cursor, and amplitude
About this task
Use this task for debugging and testing on high speed signals to achieve optimal link status. The default settings are generally applied. To change the default settings, contact professional engineers to avoid transceiver module exceptions.
Restrictions and guidelines
As a best practice, do not perform this task when the interface is transmitting traffic. This command enables the device to automatically disable and then enable the transceiver module, which affects traffic transmission.
The configuration is saved in a register on the transceiver module. It is not saved to the configuration file.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter 400-GE Ethernet interface view and its breakout interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Configure the pre-cursor and post-cursor equalizers, and amplitude for the transceiver module.
transceiver lane [ lane-number ] equalization { precursor precursor-value | postcursor postcursor-value | amplitude amplitude-value }
The default settings vary by modem model.
Displaying 400-GE transceiver module information
Perform all display tasks in in any view.
· Display the active control information of 400-GE transceiver modules.
display transceiver active-control interface [ interface-type interface-number ]
· Display the advertising information of 400-GE transceiver modules.
display transceiver advertising interface [ interface-type interface-number ]
· Display application related information for 400-GE transceiver modules.
display transceiver application interface [ interface-type interface-number ]
· Display 400-GE transceiver module status information.
display transceiver status interface [ interface-type interface-number ]
Resetting 400-GE transceiver modules
About this task
Use this feature only when you cannot troubleshoot transceiver modules by using other methods.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature will restart transceiver modules.
Procedure
To reset 400-GE transceiver modules, execute the following command in user view:
reset transceiver interface [ interface-type interface-number]
Locating devices
About device locating
The device provides LEDs for device locating. The locator blink blink-time command flashes the LEDs quickly for a specified period of time unless you execute the locator blink stop command.
Starting LED flashing
To start LED flashing, execute one of the following commands in user view:
locator blink blink-time
Stopping LED flashing
To stop LED flashing, execute one of the following commands in user view:
locator blink stop
Enabling shutdown of service ports
About this task
This task is typically used in active/standby dual host scenarios (such as VRRP). After the task is executed, the system will shut down all service ports on the active device when the connection between the MPU and the service modules on the active device times out, or no fabric modules are detected. As a consequence, all services will be switched to the standby device rapidly.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable shutdown of all service ports.
monitor { handshake-timeout | fab-absent } disable-port
By default, shutdown of all service ports is enabled.
Enabling power on/off management of cards
About this task
After the power-monitor enable command is executed, the system performs the following operations:
· Check the total system power and the power distribution on the cards to determine whether to power on cards.
· Check the card temperature and fan tray conditions to determine whether to power off cards.
If power on/off management of cards is disabled, the device will not manage the power-on and -off of the cards, and all cards are powered on by default.
Restrictions and guidelines
Disabling power on/off management of cards might result in unpredictable risks. Perform this task with caution.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable power on/off management of cards.
power-monitor enable
By default, power on/off management of cards is enabled.
Managing user assets
Configuring an asset profile for a physical component
About this task
For easy asset management, you can use this task to configure asset profiles for physical components, including the chassis, cards, fan trays, and power supplies.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure an asset profile for a physical component
set asset-info { chassis | fan fan-id | power power-id | slot slot-number } { csn csn-number | custom name value | department department | description description | location location | service-date date | state state }
Displaying and maintaining user asset information
To display the asset profile for a component, execute the following command in any view:
display asset-info { chassis | fan fan-id | power power-id | slot slot-number } [ csn | custom| department | description | location | service-date | state ]
To clear the asset profile for a physical component, execute the following command in any view:
reset asset-info { chassis | fan fan-id | power power-id | slot slot-number } [ csn | custom | department | description | location | service-date | state ]
Isolating switching fabric modules
About this task
Isolating a switching fabric module isolates the module from the data plane. An isolated switching fabric module continues to communicate with the MPU, and can forward traffic immediately after the isolation is canceled. The isolation does not affect protocol packet parsing and protocol calculation on the control plane.
Restrictions and guidelines
|
CAUTION: Do not reboot the device when a switching fabric module is isolated. |
To use an isolated switching fabric module or channel, use the undo switch-fabric isolate command to cancel the isolation.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Isolate a switching fabric module or channel.
switch-fabric isolate slot slot-number [ channel channel-number ]
By default, a switching fabric module is not isolated and can forward traffic.
|
CAUTION: · Do not isolate the only switching fabric module of the device. · Isolate a switching fabric module only if required. If the device has multiple switching fabric modules, isolating a switching fabric module or channel decreases the forwarding bandwidth and reduces the forwarding performance. |
Suppressing removal interrupt signals from switching fabric modules
About this task
Typically, removing a switching fabric module triggers one removal interrupt signal. Upon receiving the signal, the system switches traffic on the switching fabric module to other switching fabric modules to ensure service continuity. Upon hardware failure or signal interference, however, removal interrupt signals might be frequently triggered. To prevent the interrupt signals from affecting system operation, use this feature to suppress the interrupt signals.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature is supported only on the default MDC.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Suppress removal interrupt signals from switching fabric modules.
switch-fabric removal-signal-suppression
By default, removal interrupt signals from switching fabric modules are not suppressed.
|
CAUTION: Suppressing removal interrupt signals from switching fabric modules might result in packet loss and service outage. |
Isolating a service card
About isolating a service card
To decrease the impact of service card failures on device performance, use this command to isolate failed service cards before troubleshooting the issue. An isolated service card does not forward packets.
Restrictions and guidelines
To view the operating status of service cards, execute the display device command. The status field for an isolated service card displays Offline. Rebooting an isolated service card cancels the isolation.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Isolate a service card.
switch-linecard isolate chassis slot slot-number
Configuring consistency error logging for software and hardware forwarding entries
About consistency error logging for software and hardware forwarding entries
To forward packets, the device generates hardware forwarding entries in forwarding chips and software forwarding entries in memory at the same time. The device automatically detects whether the hardware forwarding entries and the software forwarding entries are consistent.
The consistency error logging for software and hardware forwarding entries enables the device to collect statistics for consistency errors periodically. If the number of consistency errors reaches or exceeds the logging threshold, the device generates a log message.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the statistics period for consistency errors between software and hardware forwarding entries.
parity-error consistency-check period value
The default statistics period is 3600 seconds.
3. Set the logging threshold for consistency errors between software and hardware forwarding entries.
parity-error consistency-check threshold value
The default logging threshold is 10.
4. Enable consistency error logging for software and hardware forwarding entries.
parity-error consistency-check log enable
By default, consistency error logging is disabled for software and hardware forwarding entries.
Configuring parity error and ECC error logging for entries on forwarding chips
About parity error and ECC error logging for entries on forwarding chips
The device automatically detects parity errors and ECC errors in entries in forwarding chips. The parity error and ECC error logging feature collects parity errors and ECC error statistics periodically, and generates a log message if the number of parity errors and ECC errors reaches or exceeds the logging threshold.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the parity error and ECC error statistics period for entries on forwarding chips.
parity-error monitor period value
The default statistics period is 60 seconds.
3. Set the parity error and ECC error logging threshold for entries on forwarding chips.
parity-error monitor threshold value
The default logging threshold is 5000.
4. Enable parity error and ECC error logging for entries on forwarding chips.
parity-error monitor log enable
By default, parity error and ECC error logging is disabled for entries on forwarding chips.
Configuring uncorrectable parity error and ECC error logging for entries on forwarding chips
About configuring uncorrectable parity error and ECC error logging for entries on forwarding chips
The device automatically detects parity errors and ECC errors in entries in forwarding chips and tries to correct the error when an error is detected. The uncorrectable parity error and ECC error logging feature enables the device to collect statistics for uncorrectable parity errors and ECC errors periodically. If the number of uncorrectable parity errors and ECC errors reaches or exceeds the logging threshold, the device generates a log message.
Uncorrectable parity errors and ECC errors in entries on forwarding chips might affect system services. To remove the errors from the entries on forwarding chips, you can enable automatic system reboot upon generation of an uncorrectable parity error and ECC error log.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the statistics period for uncorrectable parity error and ECC errors for entries on forwarding chips.
parity-error unrecoverable period value
The default statistics period is 60 seconds.
3. Set the logging threshold for uncorrectable parity errors and ECC errors for entries on forwarding chips.
parity-error unrecoverable threshold value
The default logging threshold is 1.
4. Enable uncorrectable parity error and ECC error logging for entries on forwarding chips.
parity-error unrecoverable log enable
By default, uncorrectable parity error and ECC error logging is enabled for entries on forwarding chips.
5. (Optional.) Enable automatic system reboot upon generation of an uncorrectable parity error and ECC error log.
parity-error unrecoverable reboot
By default, the device reboots upon generation of an uncorrectable parity error and ECC error log.
Displaying device hardware information
To display device hardware information, execute the following command in any view:
display device [ flash | usb ] [ slot slot-number [ subslot subslot-number ] | verbose ]
Displaying device hardware electronic label information
To display hardware electronic label information for the device, execute the following command in any view:
display device manuinfo [ slot slot-number [ subslot subslot-number ] ]
Displaying backplane electronic label information
To display electronic label information for the backplane, execute the following command in any view:
display device manuinfo chassis-only
Displaying device hardware alarm information
To display device hardware alarm information, execute the following command in any view:
display alarm [ slot slot-number ]
Displaying diagnostic information
About this task
When you perform routine maintenance or the system fails, you might need to view the operational information of each feature module to locate failures. Typically, you need to run all the related display commands one by one. To display or collect operational statistics of multiple feature modules of the device, you can use the display diagnostic-information command in any view.
Restrictions and guidelines
For correct collection of operational statistics of the device, do not configure the device during the execution of this task.
Procedure
To display or save the operational statistics of multiple feature modules of the device, execute the following command in any view:
display diagnostic-information [ hardware | infrastructure | l2 | l3 | service ] [ key-info ] [ filename ]