H3C SeerEngine-Campus Controller
05-08-2021Product Overview
H3C SeerEngine-Campus controller is a key component of H3C application-driven campus solutions that allow user access anytime anywhere in the new digital era of growing access mobility, heterogeneous wired/wireless networks, and rapid growth of IoE. Deployed on cloud native containerized platforms that provide hyper-converged architecture, SeerEngine-Campus provides GUI-based unified management, control, and analytics for application-driven campus networks. It is applicable to VXLAN-based campus networks of all sizes and provides automated device deployment, automated end-to-end service deployment, account-IP binding, unified wired and wireless management, optoelectronic integrated management, multi-campus management, security management, and SeerEngine Analyzer-based intelligent management and operation.
Features and Benefits
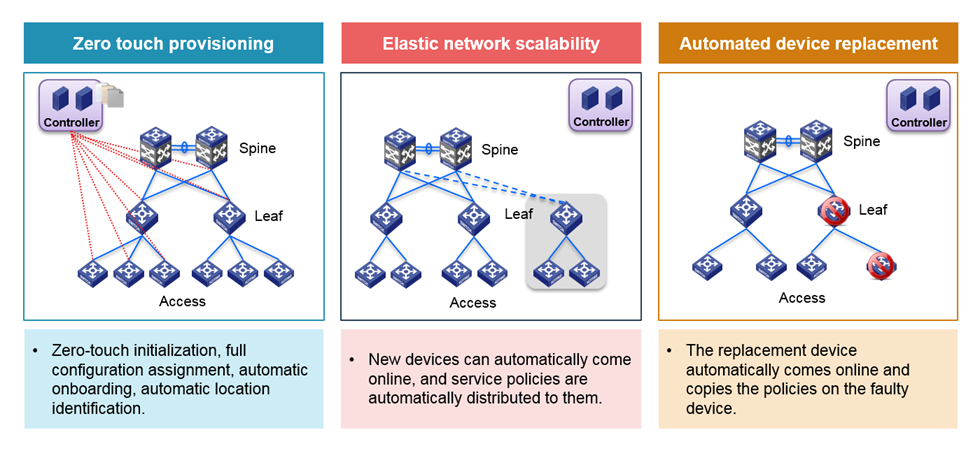
Automated campus network deployment
Simplified network configuration—Simplifies network configurations based on the spine-leaf-access layer network design to deploy the same configuration file on devices at the same layer. SeerEngine-Campus can guide you to complete configuration file generation for a layer without any command execution and can load the configuration file for the devices at this layer automatically.
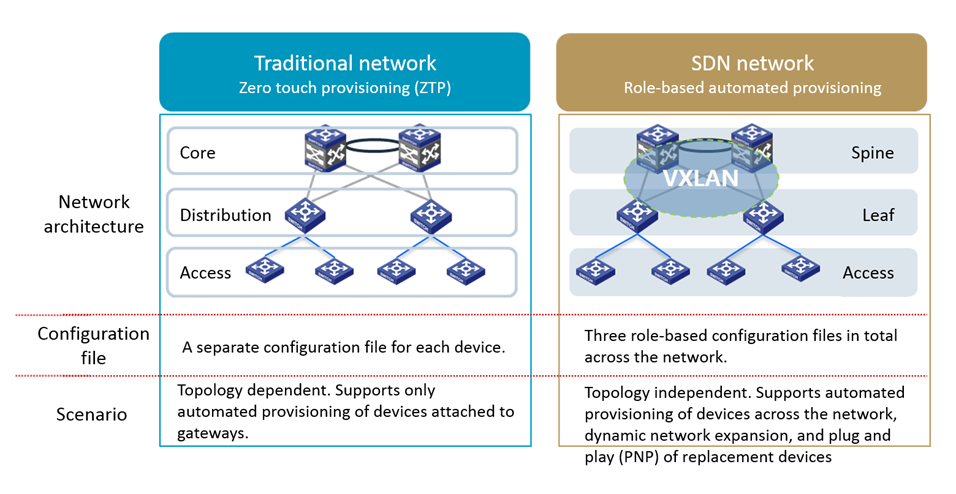
Location identifier import—Allows configuration of site information for all devices and automatically imports device location identifiers after the devices come online, allowing for fast device locating and troubleshooting.
Automatic expansion and replacement—Automatically identifies newly added devices and replaced devices, assigns configuration to the newly added, and restores configuration on the replaced.
Automatic end-to-end service deployment
SeerEngine-Campus can automatically identify devices and port roles in the network and issue specific configuration to devices and ports based on their roles. This can greatly reduce service deployment time and improve efficiency.
As shown in the following table, to deploy 4 spine devices, 40 leaf devices, and 500 access devices in a school network with 10000 access users, a total of 133 hours are required for deploying the configurations listed in the table, with 10 minutes for each device. However, with SeerEngine-Campus, deployment can be finished within one hour.
Item | Time required with traditional deployment | Time required with SeerEngine-Campus | |
VRF instance creation | VRF instance creation for the spine device group | 4 × 10 = 40 minutes | < 1 minute |
VRF instance creation for the leaf device group | 40 × 10 = 400 minutes | < 1 minute | |
VXLAN configuration | VSI and VSI interface creation for the spine device group | 4 × 10 = 40 minutes | < 1 minute |
VSI and VSI interface creation for the leaf device group | 40 × 10 = 400 minutes | < 1 minute | |
AC creation and AC-VXLAN association for leaf device downlink interfaces | 40 × 10 = 400 minutes | < 2 minutes | |
VLAN creation for the access device group | 500 × 10 = 5000 minutes | 500 × 0.05 = 25 minutes | |
VLAN creation for the leaf device group | 40 × 10 = 400 minutes | < 2 minutes | |
VLAN creation for the spine device group | 4 × 10 = 40 minutes | < 1 minute | |
Security group configuration | DHCP network segment and Option 28 configuration | 20 minutes | < 1 minute |
DHCP relay configuration on the VSI interfaces of the leaf device group | 40 × 10 = 400 minutes | < 2 minutes | |
VRF instance and VSI binding for the spine device group | 4 × 10 = 40 minutes | < 1 minute | |
VRF instance and VSI binding for the leaf device group | 40 × 10 = 400 minutes | < 2 minutes | |
Inter-group policy creation | ACL configuration on the source security groups' VSI interface for the spine device group | 4 × 10 = 40 minutes | < 1 minute |
ACL configuration on the source security groups' VSI interface for the leaf device group | 40 × 10 = 400 minutes | < 2 minutes | |
Total | N/A | 8020/60 = 133 hours | < 1 hour |
Comprehensive resource management
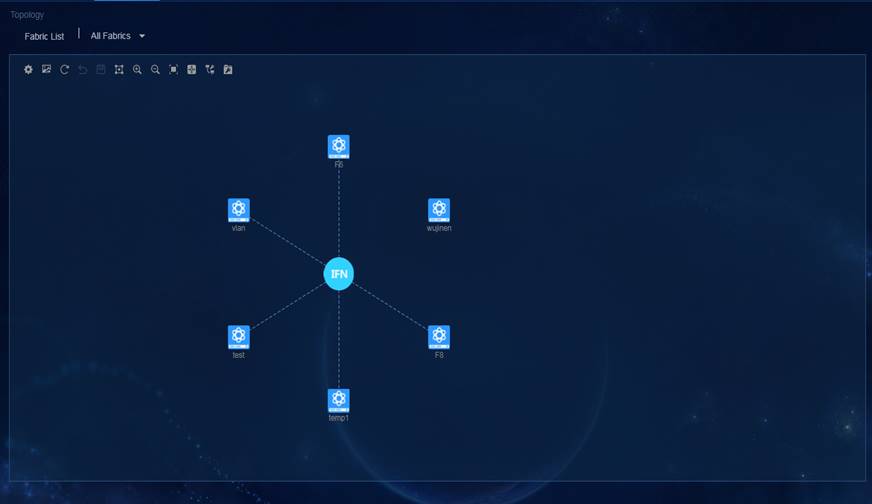
Topology management—Provides multiple topology views for multi-dimensional network management and allows you to view topologies of all fabrics and the topologies of all devices in a specific fabric.
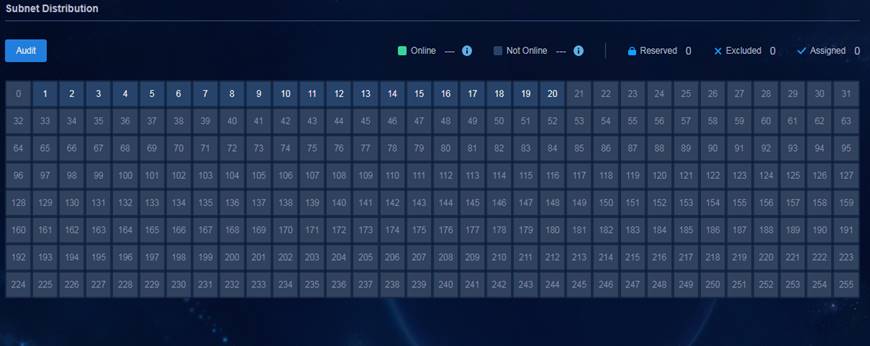
DHCP, DNS, and IP (DDI) management—Assigns IP addresses automatically to devices and users that come online and allows administrators to view and control IP address allocation on the entire network by displaying the usage of IP address pool, reserved IPs, excluded IPs, and other detailed information from a cinema seating plan-like panel.
Underlay management—Manages device configuration files and image files with the following features:
Baseline configuration—Allows for setting a configuration file baseline to track configuration changes.
Software upgrade history—Records software upgrade history and provides fast rollback to a previous version.
Configuration template and software file libraries—Allows you to upload software files, and create configuration templates or use pre-set templates. This implements configuration template and software file reuse and reduces maintenance complexity.
Overlay management—Provides VLAN-VXLAN mapping and other VXLAN management functions.
Application-driven service orchestration
SeerEngine-Campus can dynamically orchestrate network resources to achieve on-demand service allocation. It abstracts the complexity of network resources to simplify network infrastructure and provides easy but highly efficient management. By defining virtualized network resources as virtual objects, SeerEngine-Campus allows you to use an easy drag-and-drop process to orchestrate them.
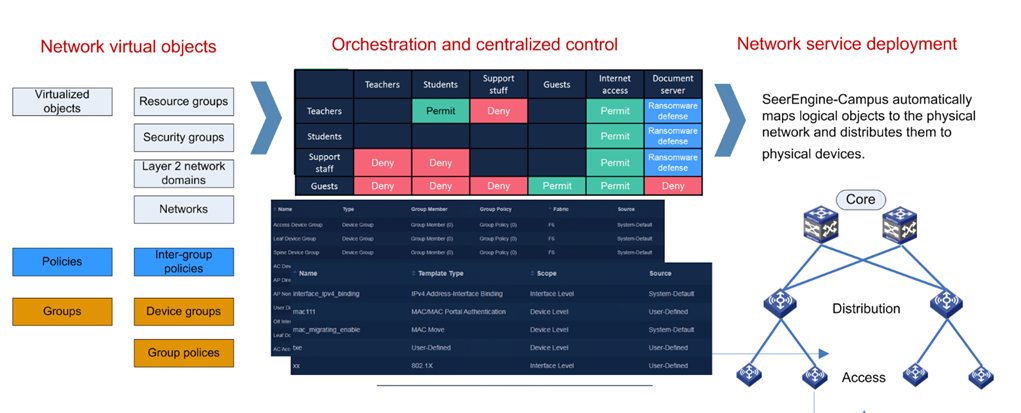
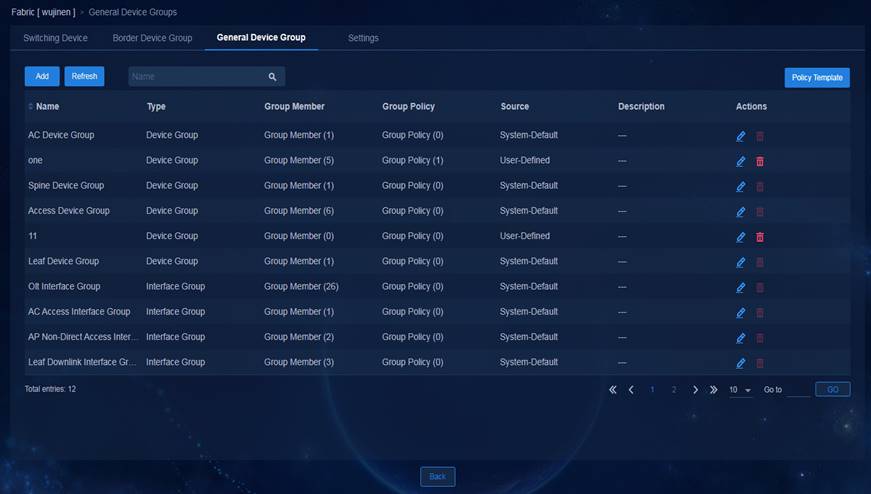
General device group—Allows you to place devices or interfaces at the same layer in one group. SeerEngine-Campus has created device groups and interface groups based on device roles and their relationships in the spine-leaf-access structure. You can adjust the groups as needed.
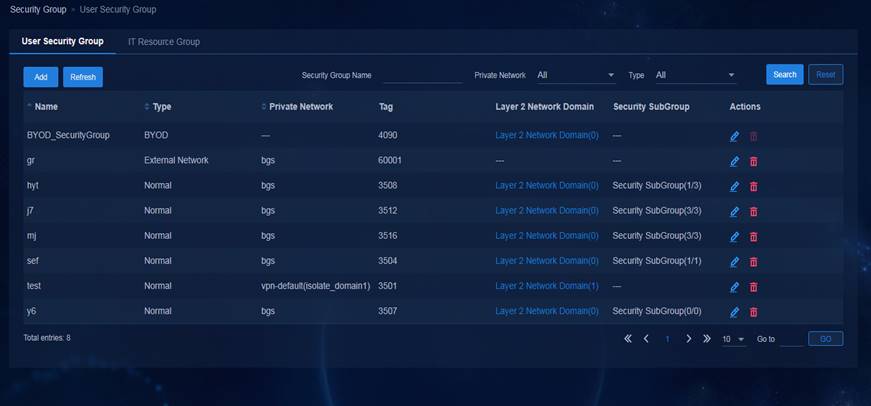
Security group—Restricts user privileges by security groups instead of legacy VLAN and ACL combinations. It allows you to define security groups, resource groups, and inter-group policies and orchestrate user privileges to implement flexible and coherent user access anywhere.
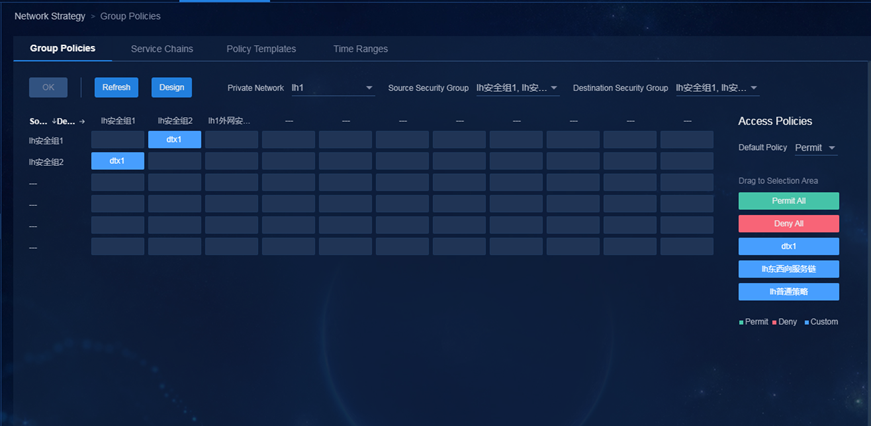
Inter-group policies—Controls east-west traffic between users and between users and servers within the campus network.
Egress policies—Manages firewall/IPS, bandwidth, and NAT settings and control north-south traffic for granular access control and security protection of external and Internet access.
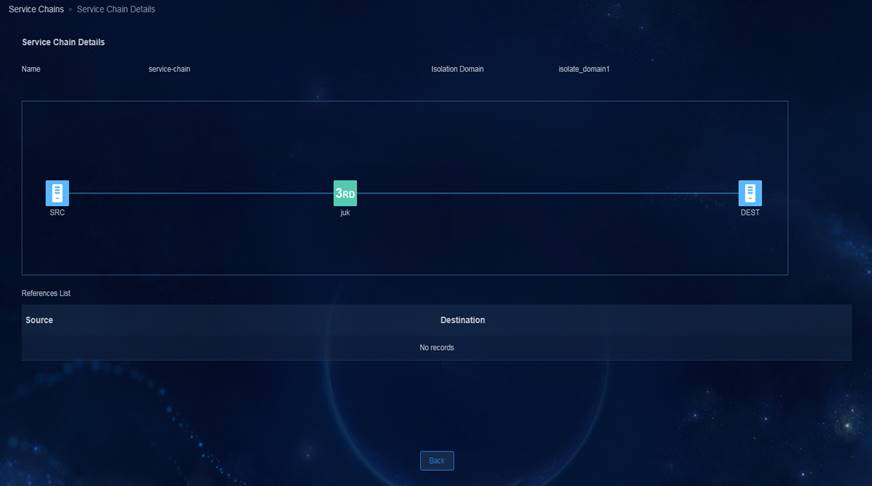
Service chains—Allows flexible configuration and application of inter-group policies and egress policies based on service chains to meet policy orchestration requirements on campus networks.
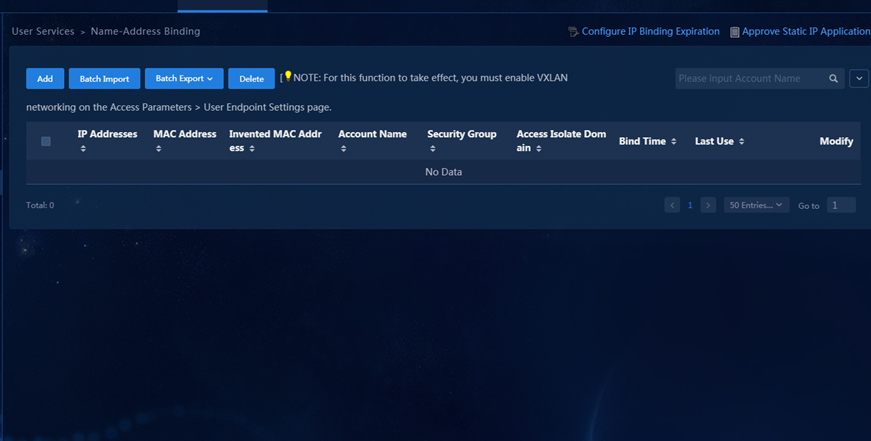
Account-IP Binding—Allows users to access the network from anywhere, anytime, and any endpoint with the IP address and access rights unchanged.
Uniform policy enforcement across the network—Network policies move along with users. For a user to access the network after the office location changes, you only need to change the access scenario for the user on SeerEngine-Campus.
Comprehensive O&M monitoring
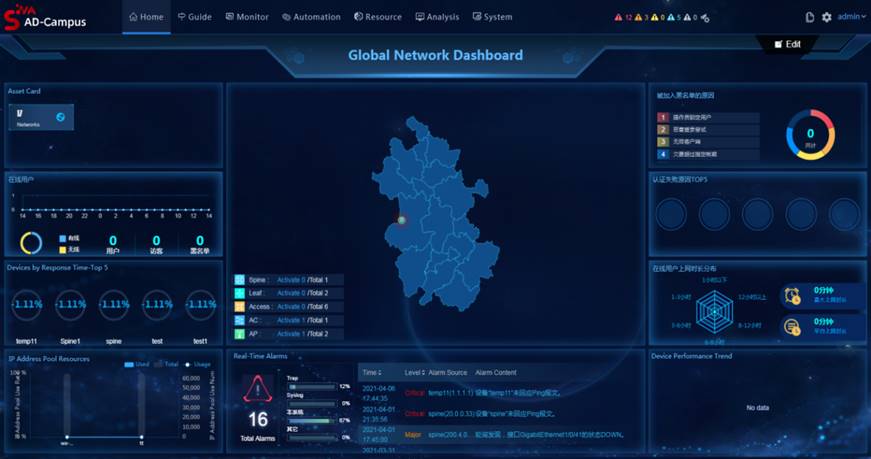
Dashboard—Displays network resource statistics as well as statistics about endpoints, online users, IP address pool usage, real-time alarms, application health, network health, and user health.
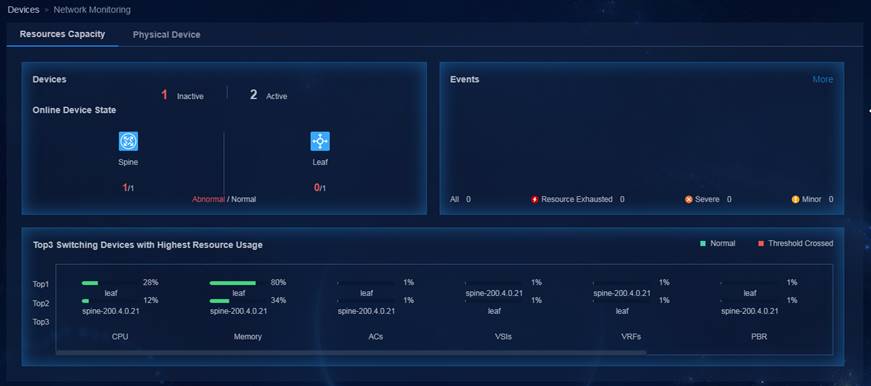
Resources capacity management—Provides resources usage status for devices across the network for you to understand the overall running status of the devices. Multi-level alarm thresholds for resources and automatic rollback from oversized configurations enable real-time adjustment for network resources configuration.
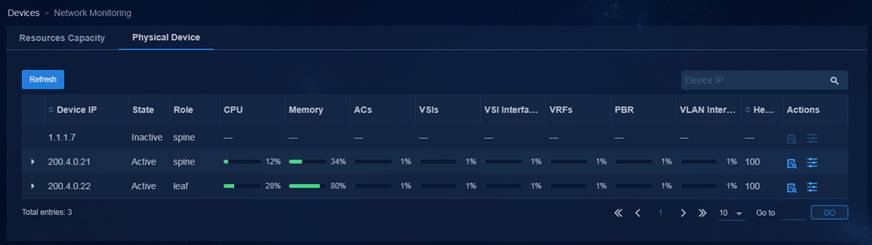
Log management—Allows you to query, filter, export, and delete operation logs, system logs, and running logs, so that you can quickly find, locate, and resolve faults.
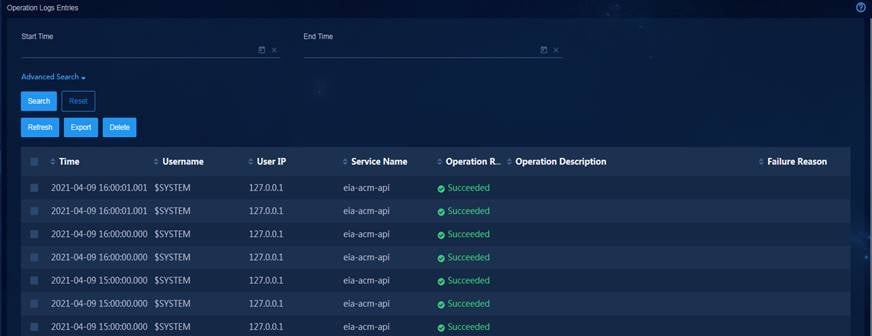
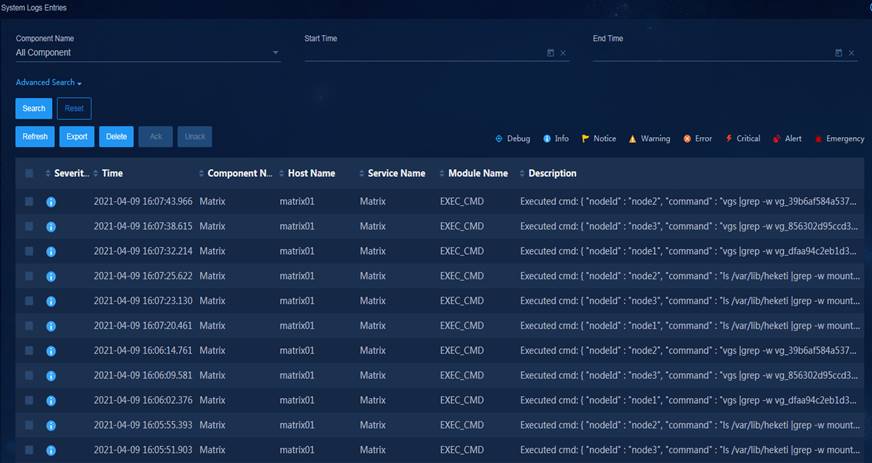
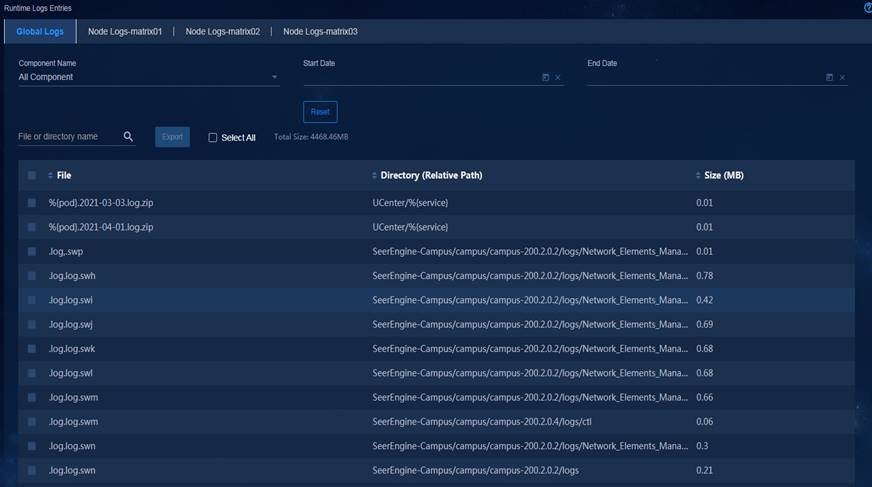
Configuration requirements
Server configuration requirements (for cluster deployment)
Role | Minimum requirements |
Master in cluster (3 in total) | CPU: 16 cores, 2.0 GHz main frequency Memory: 96 GB System disk: 2 TB in RAID ETCD disk: 50 GB in RAID NIC: 2*1 Gbps ports, support for NIC bonding |
Technical specifications
Feature | Description | |
Dashboard | Dashboard | Displays statistics about overall network performance, status, and alarms. |
Fabric | Fabric Management | Manages multiple fabrics. |
Automation | Device Automation | Configures settings to enable automated onboarding of devices in a fabric. |
Topology | Physical Topology | Displays the topology and connection state of fabric networks. |
Resource Management | Wired & Wireless | Allows wired & wireless resources management. |
DHCP and IP | Allows DHCP and IP resources management | |
Capacity Management | Supports configuration of resources alarms and automatic rollback from oversized configurations | |
Policy | Operation Policy | Allows management of interface groups, device groups, user policy (access authority configuration), network policy (domains and groups configuration) |
QoS | Allows QoS configuration for traffic with specific characteristics. | |
Security Policy | Allows configuration of firewall-based security policies, service chain-based service orchestration | |
User | Access Groups | Allows configuration and management of access groups, access policies, access scenarios, LDAP server synchronization, and other functions. |
User Management | Allows granular management of access users, online users, guests and perception-free users | |
User Behavior Auditing | Allows user auditing of online behaviors. | |
Asset List | Allows management of desktop assets, peripherals, and software deployment. | |
O&M | O&M Management | Displays event statistics, system alarms, system logs, operation logs, and running logs. |
System management | Operation Management | Allows management of operators and controller parameters |
HA Management | Allows management of the controller cluster & backup restoration. | |
Typical networking
Standard networking
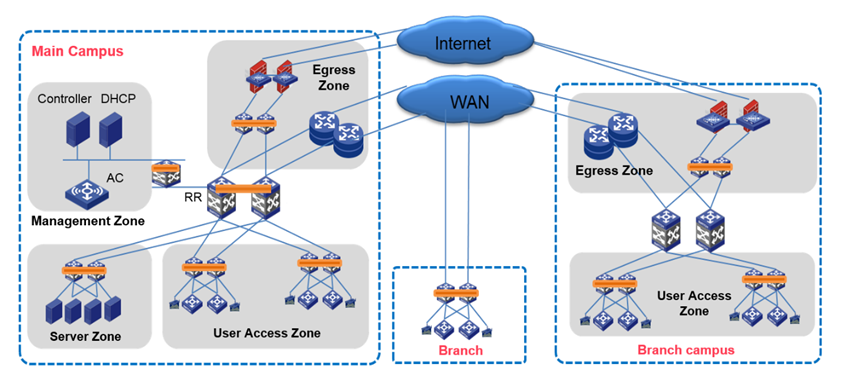
In a standard networking scenario as shown in the following figure, the network egress zone is separated from the spine layer, and multiple campus networks are connected in a hybrid way. The route reflector (RR) in the main campus synchronizes route entries across the whole network.
VTEPs are deployed at the spine layer and access layer and multiple campus networks are connected in a hybrid way. The main and branch campuses are each deployed with a RR. The RRs synchronize route entries with each other.
Lightweight networking
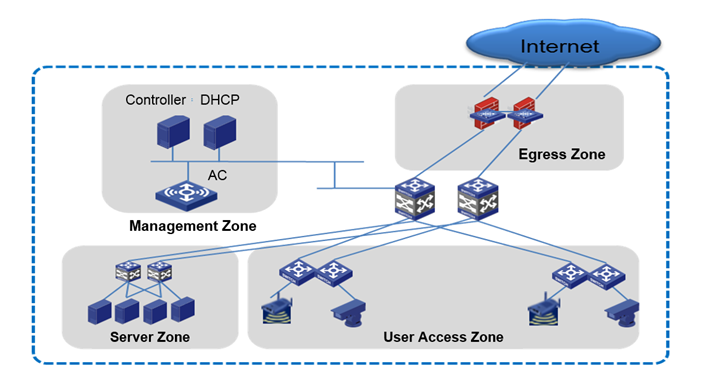
Lightweight networking as shown in the following figure is applicable to small Layer 2 campus networks.
Ordering information
Item | Description |
LIS-SeerEngine-Campus-BAS1 | H3C SeerEngine Campus, 1 server node license |
LIS-SeerEngine-Campus-PSW-VAR | H3C SeerEngine Campus, 1 physical switch license |
LIS-SeerEngine-Campus-PON-VAR | H3C SeerEngine Campus, 1 PON device license |
LIS-SeerEngine-Campus-SC-VAR | H3C SeerEngine Campus, 1 service chain node license |
