- Table of Contents
-
- 04-Network Connectivity
- 00-Preface
- 01-About the network connectivity configuration guide
- 02-MAC address table configuration
- 03-Ethernet link aggregation configuration
- 04-Port isolation configuration
- 05-VLAN configuration
- 06-Loop detection configuration
- 07-Spanning tree configuration
- 08-LLDP configuration
- 09-Layer 2 forwarding configuration
- 10-ARP configuration
- 11-IP addressing configuration
- 12-DHCP configuration
- 13-DHCPv6 configuration
- 14-DNS configuration
- 15-IP performance optimization configuration
- 16-IPv6 basics configuration
- 17-Basic IP routing configuration
- 18-Static routing configuration
- 19-IPv6 static routing configuration
- 20-Multicast overview
- 21-IGMP snooping configuration
- 22-MLD snooping configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 18-Static routing configuration | 86.07 KB |
Configuring a static route group
Restrictions and guidelines for static route FRR
Configuring static route FRR by specifying a backup next hop
Configuring static route FRR to automatically select a backup next hop
Display and maintenance commands for static routing
Configuring static routing
About static routes
Static routes are manually configured. If a network's topology is simple, you only need to configure static routes for the network to work correctly.
Static routes cannot adapt to network topology changes. If a fault or a topological change occurs in the network, the network administrator must modify the static routes manually.
Configuring a static route
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure a static route.
ip route-static dest-address { mask-length | mask } { interface-type interface-number [ next-hop-address ] | next-hop-address } [ permanent | track track-entry-number ] [ preference preference ] [ tag tag-value ] [ description text ]
By default, no static route is configured.
You can associate Track with a static route to monitor the reachability of the next hops. For more information about Track, see High Availability Configuration Guide.
3. (Optional.) Configure the default preference for static routes.
ip route-static default-preference default-preference
The default setting is 60.
Configuring a static route group
About this task
This task allows you to batch create static routes with different prefixes but the same output interface and next hop.
You can create a static route group, and specify the static group in the ip route-static command. All prefixes in the static route group will be assigned the next hop and output interface specified in the ip route-static command.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a static route group and enter its view.
ip route-static-group group-name
By default, no static route group is configured.
3. Add a static route prefix to the static route group.
prefix dest-address { mask-length | mask }
By default, no static route prefix is added to the static route group.
4. Return to system view.
quit
5. Configure a static route.
ip route-static group group-name { interface-type interface-number [ next-hop-address ] | next-hop-address } [ permanent | track track-entry-number ] [ preference preference ] [ tag tag-value ] [ description text ]
By default, no static route is configured.
Deleting static routes
About this task
To delete a static route, use the undo ip route-static command. To delete all static routes including the default route, use the delete static-routes all command.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Delete all static routes.
delete static-routes all
Configuring static route FRR
About static route FRR
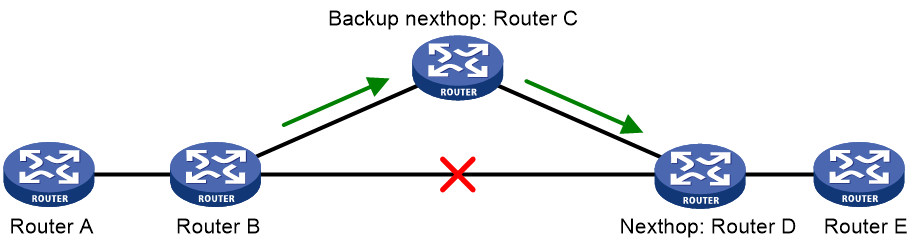
A link or router failure on a path can cause packet loss and even routing loop. Static route fast reroute (FRR) enables fast rerouting to minimize the impact of link or node failures.
As shown in Figure 1, upon a link failure, packets are directed to the backup next hop to avoid traffic interruption. You can either specify a backup next hop for FRR or enable FRR to automatically select a backup next hop (which must be configured in advance).
Restrictions and guidelines for static route FRR
Besides the configured static route for FRR, the device must have another route to reach the destination. When the state of the primary link (with Layer 3 interfaces staying up) changes from bidirectional to unidirectional or down, static route FRR quickly redirects traffic to the backup next hop. When the Layer 3 interfaces of the primary link are down, static route FRR temporarily redirects traffic to the backup next hop. In addition, the device searches for another route to reach the destination and redirects traffic to the new path if a route is found. If no route is found, traffic interruption occurs.
Configuring static route FRR by specifying a backup next hop
Restrictions and guidelines
A static route does not take effect when the backup output interface is unavailable.
To change the backup output interface or next hop, you must first remove the current setting. The backup output interface and next hop must be different from the primary output interface and next hop.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure static route FRR.
ip route-static dest-address { mask-length | mask } interface-type interface-number [ next-hop-address ] [ backup-interface interface-type interface-number [ backup-nexthop backup-nexthop-address ] ] ] [ permanent ] [ preference preference ] [ tag tag-value ] [ description text ]
By default, static route FRR is disabled.
Configuring static route FRR to automatically select a backup next hop
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure static route FRR to automatically select a backup next hop.
ip route-static fast-reroute auto
By default, static route FRR is disabled from automatically selecting a backup next hop.
Display and maintenance commands for static routing
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display static route information. |
display ip routing-table protocol static [ inactive | verbose ] |
|
Display static route next hop information. |
display route-static nib [ nib-id ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display static routing table information. |
display route-static routing-table [ ip-address { mask-length | mask } ] |
For more information about the display ip routing-table protocol static [ inactive | verbose ] command, see basic IP routing in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
Configuring a default route
A default route is used to forward packets that do not match any specific routing entry in the routing table. Without a default route, packets that do not match any routing entries are discarded and an ICMP destination-unreachable packet is sent to the source.
A default route can be configured in either of the following ways:
· The network administrator can configure a default route with both destination and mask being 0.0.0.0. For more information, see "Configuring static routing."
· Some dynamic routing protocols (such as OSPF, IS-IS, and RIP) can generate a default route. For example, an upstream router running OSPF can generate a default route and advertise it to other routers. These routers install the default route with the next hop being the upstream router. For more information, see the respective chapters on these routing protocols in this configuration guide.