- Table of Contents
-
- 01-Fundamentals Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-CLI configuration
- 02-RBAC configuration
- 03-Login management configuration
- 04-FTP and TFTP configuration
- 05-File system management configuration
- 06-Configuration file management configuration
- 07-Software upgrade configuration
- 08-ISSU configuration
- 09-Emergency shell configuration
- 10-Device management configuration
- 11-Tcl configuration
- 12-Python configuration
- 13-License management
- 14-Preprovisioning feature configuration
- 15-Automatic configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 07-Software upgrade configuration | 102.97 KB |
Contents
Software file naming conventions
Comware image redundancy and loading procedure
Upgrade restrictions and guidelines
Preloading the BootWare image to BootWare
Specifying startup images and completing the upgrade
Upgrading PEXs from the parent fabric
Upgrading software
Overview
Software upgrade enables you to add new features and fix bugs. This chapter describes types of software and methods to upgrade software from the CLI without using ISSU. For a comparison of all software upgrade methods, see "Upgrade methods."
Software types
The following software types are available:
· BootWare image—This image is a .bin file that contains a basic segment and an extended segment. The basic segment is the minimum code that bootstraps the system. The extended segment enables hardware initialization and provides system management menus. You can use these menus to load software and the startup configuration file or manage files when the device cannot start up correctly.
· Comware image—Includes the following image subcategories:
¡ Boot image—A .bin file that contains the Linux operating system kernel. It provides process management, memory management, file system management, and the emergency shell.
¡ System image—A .bin file that contains the Comware kernel and standard features, including device management, interface management, configuration management, and routing.
¡ Feature image—A .bin file that contains advanced software features. Users purchase feature images as needed.
¡ Patch image—A .bin file irregularly released for fixing bugs without rebooting the device. A patch image does not add new features or functions.
Comware images that have been loaded are called current software images. Comware images specified to load at the next startup are called startup software images.
BootWare image, boot image, and system image are required for the system to operate. These images might be released separately or as a whole in one .ipe package file. If an .ipe file is used, the system decompresses the file automatically, loads the .bin images and sets them as startup software images. Typically, the BootWare and startup software images for the device are released in an .ipe file named main.ipe.
Software file naming conventions
Software image file names use the chassis-comware version-image type-release format. This document uses boot.bin and system.bin as boot and system image file names.
Comware image redundancy and loading procedure
You can specify two lists of Comware software images: one main and one backup.
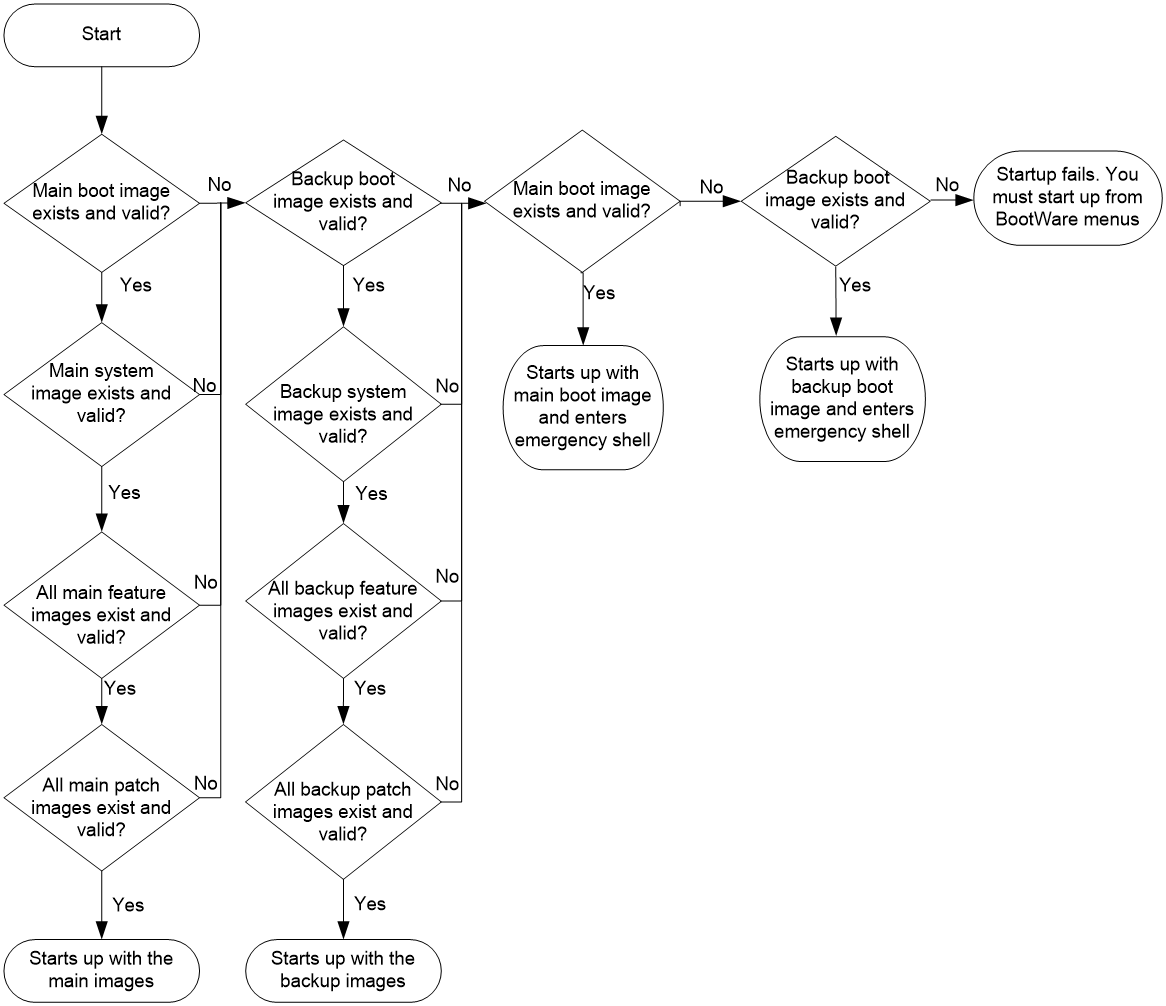
The system always attempts to start up with the main images. If any main image does not exist or is invalid, the system tries the backup images. Figure 1 shows the entire Comware image loading procedure.
In this procedure, both the main and backup image lists have feature and patch images. If an image list does not have feature or patch images, the system starts up with the boot and system images after they pass verification.
If both the main and backup boot images are nonexistent or invalid, access the BootWare menu during the system startup to upgrade software.
After accessing the emergency shell, connect to the console port and load a system image so you can access the Comware system. For more information about using the emergency shell, see "Using the emergency shell."
Figure 1 Comware image loading procedure
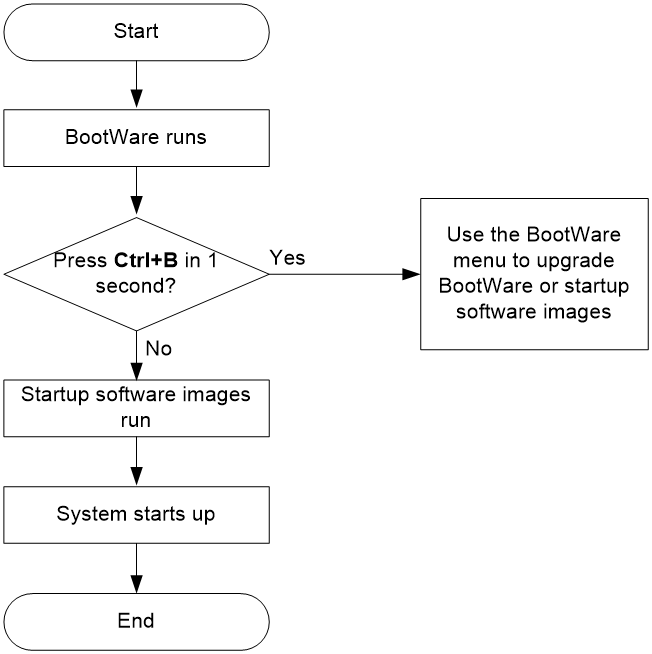
System startup process
Upon power-on, the BootWare image runs to initialize hardware, and then the startup software images run to start up the entire system, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 System startup process
Upgrade methods
|
Upgrading method |
Software types |
Remarks |
|
Upgrading from the CLI without using ISSU |
· BootWare image · Comware images (excluding patches) |
This method is disruptive. You must reboot the entire device to complete the upgrade. |
|
Performing an ISSU |
Comware images |
The ISSU method enables a software upgrade without service interruption. Use this method for a multichassis IRF fabric. For more information about ISSU, see "Performing an ISSU." |
|
Upgrading from the BootWare menu |
· BootWare image · Comware software images |
Use this method when the device cannot start up correctly. To use this method, first connect to the console port and power cycle the device. Then press Ctrl+B at prompt to access the BootWare menu. For more information about upgrading software from the BootWare menu, see the release notes for the software version. Upgrade a multichassis IRF fabric from the CLI instead of the BootWare menu, if possible. The BootWare menu method increases the service downtime, because it requires that you upgrade the member devices one by one. |
This chapter only covers upgrading software from the CLI without using ISSU.
Upgrade restrictions and guidelines
The device can start up from the built-in flash memory or the USB disk. As a best practice, store the startup images in the built-in flash memory. If you store the startup images on the USB disk, do not remove the USB disk during the startup process.
If the CPLD is also upgraded, it will take a long time to complete the upgrade. For the device to start up successfully, do not power off the device during the upgrade process.
Preparing for the upgrade
1. Use the display version command to verify the current BootWare image version and startup software version.
2. Use the release notes for the upgrade software version to evaluate the upgrade impact on your network and verify the following items:
¡ Software and hardware compatibility.
¡ Version and size of the upgrade software.
¡ Compatibility of the upgrade software with the current BootWare image and startup software image.
3. Use the release notes to verify whether the software images require a license. If licenses are required, register and activate licenses for each license-based software image. For more information about licensing, see "Managing licenses."
4. Use the dir command to verify that all IRF member devices have sufficient storage space for the upgrade images. If the storage space is not sufficient, delete unused files by using the delete command. For more information, see "Managing file systems."
5. Use FTP or TFTP to transfer the upgrade image file to the root directory of any file system. For more information about FTP and TFTP, see "Configuring FTP" or "Configuring TFTP." For more information about file systems, see "Managing file systems."
Upgrade task list
|
Tasks at a glance |
Remarks |
|
(Optional.) Preloading the BootWare image to BootWare |
If a BootWare upgrade is required, you can perform this task to shorten the subsequent upgrade time. This task helps avoid upgrade problems caused by unexpected electricity failure. If you skip this task, the device upgrades the BootWare automatically when it upgrades the startup software images. The BootWare image preloaded into the BootWare takes effect only after you reboot the device. |
|
(Required.) Specifying startup images and completing the upgrade |
N/A |
Preloading the BootWare image to BootWare
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Load the upgrade BootWare image to the Normal area of BootWare. |
bootrom update file file slot slot-number-list [ subslot subslot-number-list ] |
Specify the downloaded software image file for the file argument. The new BootWare image takes effect at a reboot. |
Specifying startup images and completing the upgrade
Perform this task in user view.
To specify the startup image file and complete the upgrade:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Specify main or backup startup images for the master device. |
· Use an .ipe file for upgrade: · Use .bin files for upgrade: |
Upgrade files must be saved in the root directory of a file system. |
|
2. Specify main startup images for each subordinate device. |
· Method 1: ¡ Use an .ipe file for upgrade: ¡ Use .bin files for upgrade: · Method 2: |
Skip this step if you have only one device. When you use the boot-loader update command, make sure you understand the following requirements and upgrade results: · If an ISSU or patch installation has been performed, use the install commit command to update the main startup images on the master device before software synchronization. The command ensures startup image consistency among IRF member devices. · The boot-loader update command uses the main or backup startup image list for synchronization, instead of the current software images list. ¡ The main images list is used if the master device started up with the main startup images. ¡ The backup image list is used if the master device started up with the backup startup images. · Startup image synchronization will fail if any software image being synchronized is corrupted or is not available. |
|
3. Save the running configuration. |
save |
This step ensures that any configuration you have made can survive a reboot. |
|
4. Reboot the IRF fabric. |
reboot |
At startup, each device reads the preloaded BootWare image to RAM, and loads the startup images. |
|
5. (Optional.) Verify the software image settings. |
display boot-loader [ slot slot-number ] |
Verify that the current software images are the same as the startup software images. |
Upgrading PEXs from the parent fabric
About PEX upgrade
Perform this task to upgrade PEXs from the parent fabric in an IRF 3.1 system. You can also upgrade a PEX by logging in to the PEX through the console port. Upgrading PEXs from the parent fabric has the following benefits:
· It is easy to ensure compatibility between the startup images of PEXs and the startup images of the parent fabric.
· You do not need to log in to PEXs.
After you configure this task, the parent fabric performs the following operations:
1. Enables the file transfer service (FTP), and configures all file transfer settings.
2. Transfers the .ipe file to PEXs one by one.
3. Deletes the file transfer settings and disables the file transfer service.
After the file transfer process is completed, PEXs that successfully received the .ipe file automatically reboot to complete the upgrade. PEXs that failed to receive the .ipe file do not reboot and are not upgraded.
Hardware compatibility
S5560-EI PEXs do not support this feature. To upgrade the PEXs, you must log in to each of them through their respective console ports.
Preparing for the upgrade
1. Use the display version command to identify the current BootWare and Comware image versions on each PEX to be upgraded.
2. Use the release notes for the upgrade software version to identify the upgrade impact on your network and verify the following items:
¡ Versions and sizes of the upgrade software images.
¡ Compatibility of the upgrade software images with the current BootWare and Comware images.
¡ Software compatibility between the PEX and the parent fabric.
3. Use FTP or TFTP to transfer the upgrade image file to the root directory of a file system on the parent fabric.
For more information about FTP configuration and TFTP configuration, see "Configuring FTP" and "Configuring TFTP."
Procedure
To upgrade PEXs from the parent fabric:
|
Task |
Command |
|
Upgrade PEXs from the parent fabric. |
boot-loader pex file ipe ipe-filename transfer-service ftp { all | slot slot-list } |
Displaying and maintaining software image settings
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display current software images and startup software images. |
display boot-loader [ slot slot-number ] |
Software upgrade example
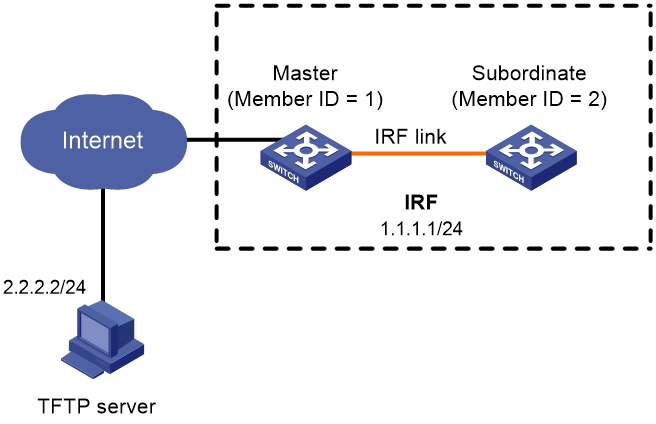
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 3, use the file startup-a2105.ipe to upgrade software images for the IRF fabric.
Configuration procedure
# Configure IP addresses and routes. Make sure the device and the TFTP server can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
# Configure TFTP settings on both the device and the TFTP server. (Details not shown.)
# Display information about the current software images.
<Sysname> display version
# Back up the current software images.
<Sysname> copy boot.bin boot_backup.bin
<Sysname> copy system.bin system_backup.bin
# Specify boot_backup.bin and system_backup.bin as the backup startup image files for both IRF member devices.
<Sysname> boot-loader file boot flash:/boot_backup.bin system flash:/system_backup.bin slot 1 backup
<Sysname> boot-loader file boot flash:/boot_backup.bin system flash:/system_backup.bin slot 2 backup
# Use TFTP to download the image file startup-a2105.ipe from the TFTP server to the root directory of the flash memory on the master device.
<Sysname> tftp 2.2.2.2 get startup-a2105.ipe
# Specify startup-a2105.ipe as the main startup image file for all IRF member devices.
<Sysname> boot-loader file flash:/startup-a2105.ipe slot 1 main
<Sysname> boot-loader file flash:/startup-a2105.ipe slot 2 main
# Verify the startup image settings.
<Sysname> display boot-loader
# Reboot the device to complete the upgrade.
<Sysname> reboot
# Verify that the device is running the correct software.
<Sysname> display version