- Table of Contents
-
- 04-DPI Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-DPI overview
- 02-DPI engine configuration
- 03-IPS configuration
- 04-URL filtering configuration
- 05-Data filtering configuration
- 06-File filtering configuration
- 07-Anti-virus configuration
- 08-Data analysis center configuration
- 09-Proxy policy configuration
- 10-WAF configuration
- 11-IP reputation configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 10-WAF configuration | 238.32 KB |
Contents
WAF signature library management
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with WAF
Restrictions: Licensing requirements for WAF
Configuring WAF signature filtering criteria for a WAF policy
Configuring WAF actions for a WAF policy
Specifying a parameter profile for a WAF action
Applying a WAF policy to a DPI application profile
Activating WAF policy settings
Using the DPI application profile in a security policy rule
Using the DPI application profile in an object policy rule
Managing the WAF signature library
Scheduling automatic WAF signature library update
Triggering an immediate WAF signature update
Performing a WAF signature manual update
Rolling back the WAF signature library
Display and maintenance commands for WAF
Example: Using the default WAF policy in a security policy
Example: Using a user-defined WAF policy in a security policy
Example: Manually updating the WAF signature library
Example: Configuring automatic WAF signature library update
Example: Using the default WAF policy in an object policy
Example: Using a user-defined WAF policy in an object policy
Example: Manually updating the WAF signature library
Example: Configuring automatic WAF signature library update
Configuring WAF
About WAF
The Web application firewall (WAF) feature monitors HTTP and HTTPS traffic to and from Web applications for malicious activity and to proactively take prevention actions.
WAF policies
WAF is implemented based on WAF policies. A WAF policy contains a set of WAF signatures for matching packets and the actions for the packets.
WAF signatures
The device compares packets with WAF signatures to detect, classify, and prevent network attacks.
Each WAF signature contains various attributes, including attack category, action, protected target, severity level, and direction. You can filter the WAF signatures that a WAF policy uses based on the WAF signature attributes.
The device supports only the predefined WAF signatures. They are automatically generated by the device based on the local signature library. You cannot modify or delete a predefined WAF signature.
WAF actions
When the device detects a matching packet for a WAF signature, it takes the actions specified for the signature on the packet.
The device supports the following signature actions:
· Reset—Closes the TCP connections for matching packets by sending TCP reset messages.
· Redirect—Redirects matching packets to a webpage.
· Block-source—Drops matching packets and adds the packet sources to the IP blacklist. If the IP blacklist feature is enabled, the device blocks the packets from the blacklisted sources for a duration set by the block-period command. If the IP blacklist feature is not enabled, the device does not block the packets from the blacklisted sources.
To enable the IP blacklist feature, use the blacklist global enable command. For more information about the IP blacklist feature, see Security Configuration Guide.
For more information about the block-period command, see DPI Command Reference.
· Drop—Drops matching packets.
· Permit—Permits matching packets to pass.
· Capture—Captures matching packets.
· Logging—Logs matching packets.
WAF mechanism
WAF takes effect after you apply a WAF policy to a DPI application profile and use the DPI application profile in a security policy rule or object policy rule.
As shown in Figure 1, upon receiving a packet, the device performs the following operations:
1. The device identifies the packet application layer protocol and extracts the packet signatures.
2. The device determines the actions for the packet by comparing the extracted packet signatures with the WAF signatures in the WAF policy:
¡ If the packet does not match any WAF signatures, the device permits the packet to pass.
¡ If the packet matches only one WAF signature, the device takes the signature actions.
¡ If the packet matches multiple WAF signatures, the device uses the following rules to select the actions:
- If the matching WAF signatures have two or more actions, including redirect, drop, permit, and reset, the device takes the action of the highest priority. The actions in descending order of priority are reset, redirect, drop, and permit.
- The device executes the block-source, capture, and logging actions if they are in the matching WAF signatures.
WAF signature library management
The device uses WAF signatures to inspect Web application layer traffic for malicious threats and attacks.
You can update the device WAF signature library to the latest version or roll back the library to the previous or the factory default version.
Updating the WAF signature library
The following methods are available for updating the WAF signature library on the device:
· Automatic update.
The device automatically downloads the most up-to-date WAF signature file to update its local signature library periodically.
· Triggered update.
The device downloads the most up-to-date WAF signature file to update its local signature library immediately after you trigger the operation.
· Manual update.
Use this method when the device cannot obtain the WAF signature file automatically.
You must manually download the most up-to-date WAF signature file, and then use the file to update the signature library on the device.
Rolling back the WAF signature library
If filtering false alarms or filtering exceptions occur frequently, you can roll back the WAF signature library to the previous version or to the factory default version.
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with WAF
|
Hardware |
WAF compatibility |
|
F5010, F5020, F5020-GM, F5030, F5030-6GW, F5040, F5060, F5080, F5000-AI-20, F5000-AI-40, F5000-V30, F5000-C, F5000-S, F5000-M, F5000-A |
Yes |
|
F1000-AI-20, F1000-AI-30, F1000-AI-50, F1000-AI-60, F1000-AI-70, F1000-AI-80, F1000-AI-90 |
Yes |
|
F1003-L, F1005-L, F1010-L |
No |
|
F1005, F1010 |
No |
|
F1020, F1020-GM, F1030, F1030-GM, F1050, F1060, F1070, F1070-GM, F1070-GM-L, F1080, F1090, F1000-V70 |
Yes |
|
F1000-AK1110, F1000-AK1120, F1000-AK1130, F1000-AK1140 |
No |
|
F1000-AK1212, F1000-AK1222, F1000-AK1232, F1000-AK1312, F1000-AK1322, F1000-AK1332 |
Yes |
|
F1000-AK1414, F1000-AK1424, F1000-AK1434, F1000-AK1514, F1000-AK1524, F1000-AK1534, F1000-AK1614 |
Yes |
|
F1000-AK108, F1000-AK109, F1000-AK110, F1000-AK115, F1000-AK120, F1000-AK125, F1000-AK710 |
No |
|
F1000-AK130, F1000-AK135, F1000-AK140, F1000-AK145, F1000-AK150, F1000-AK155, F1000-AK160, F1000-AK165, F1000-AK170, F1000-AK175, F1000-AK180, F1000-AK185, F1000-GM-AK370, F1000-GM-AK380, F1000-AK711 |
Yes |
|
LSU3FWCEA0, LSUM1FWCEAB0, LSX1FWCEA1 |
Yes |
|
LSXM1FWDF1, LSUM1FWDEC0, IM-NGFWX-IV, LSQM1FWDSC0, LSWM1FWD0, LSPM6FWD, LSQM2FWDSC0 |
Yes |
|
vFW1000, vFW2000 |
Yes |
Restrictions: Licensing requirements for WAF
The WAF module requires a license to run on the device. If the license expires, you can still use the WAF functions but you cannot upgrade the WAF signature library to the version released after the expiration time. For more information about licenses, see license management in Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
WAF tasks at a glance
To configure WAF, perform the following tasks:
2. Configuring WAF signature filtering criteria for a WAF policy
3. Configuring WAF actions for a WAF policy
4. Specifying a parameter profile for a WAF action
5. Applying a WAF policy to a DPI application profile
6. (Optional.) Activating WAF policy settings
7. Using the DPI application profile in a security policy rule
8. Using the DPI application profile in an object policy rule
9. Managing the WAF signature library
Creating a WAF policy
About this task
By default, a newly created WAF policy uses all enabled WAF signatures and applies to the packet matching a signature the default signature action. You can filter the WAF signatures used by the WAF policy and change the signature actions.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a WAF policy and enter its view.
waf policy policy-name
A default WAF policy named default exists. The default WAF policy uses all enabled WAF signatures on the device and cannot be modified or deleted.
Configuring WAF signature filtering criteria for a WAF policy
About this task
By default, a WAF policy uses all enabled WAF signatures on the device. You can set criteria to filter WAF signatures that a WAF policy uses based on the signature attributes.
A WAF policy uses a WAF signature only if the signature matches all the configured criteria.
For certain attribute-based criterion (such as the action, direction, or severity level criterion), you can specify multiple attribute values. A WAF signature matches the criterion if it matches any of the specified attribute values.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WAF policy view.
waf policy policy-name
3. Configure the WAF signature filtering criteria.
¡ Set a target criterion.
protected-target { target [ sub-target subtarget ]| all }
By default, the target attribute is not used for WAF signature filtering.
¡ Set an attack category criterion.
attack-category { sub-category subcategory ] | all }
By default, the attack category attribute is not used for WAF signature filtering.
¡ Set an action criterion.
action { block-source | drop | permit | reset } *
By default, the action attribute is not used for WAF signature filtering.
¡ Set a direction criterion.
object-dir { client | server } *
By default, the direction attribute is not used for WAF signature filtering.
¡ Set a severity level criterion.
severity-level { critical | high | low | medium } *
By default, the severity level attribute is not used for WAF signature filtering.
Configuring WAF actions for a WAF policy
About this task
By default, the system applies the default actions of a WAF signature to packets matching the signature.
You can also configure global actions for a WAF policy or change the actions for individual WAF signatures in the policy.
The system selects the actions for packets matching a WAF signature in the following order:
1. Actions configured for the WAF signature in the WAF policy.
2. Actions configured for the WAF policy.
3. Default actions of the WAF signature.
Restrictions and guidelines
The logging keyword enables the WAF module to log packet matching events and send log messages to the information center.
With the information center, you can set log message filtering and output rules, including output destinations.
The information center can output WAF logs to any destinations except the console and the monitor terminal. If you configure the console or monitor terminal as an output destination, the output destination setting will not take effect.
To view WAF logs stored on the device, use the display logbuffer command. Make sure you do not disable log output to the log buffer, which is enabled by default.
For more information about configuring the information center, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter the view of a WAF policy.
waf policy policy-name
3. Specify the global packet processing actions for the WAF policy.
signature override all { { block-source | drop | permit | redirect | reset } | capture | logging } *
By default, no actions are specified for a WAF policy and the default actions of WAF signatures are applied to matching packets.
4. (Optional.) Change the status or actions for a WAF signature.
signature override pre-defined signature-id { disable | enable } [ { block-source | drop | permit | redirect | reset } | capture | logging ] *
By default, the predefined WAF signatures use the actions and statuses defined by the system.
Specifying a parameter profile for a WAF action
About this task
You can specify parameter profiles for WAF signature actions. A parameter profile is a set of parameters that determine how an action is executed. If you do not specify a parameter profile for an action, or if the specified profile does not exist, the default action parameter settings are used. For information about configuring parameter profiles, see "Configuring DPI engine."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify a parameter profile for a WAF action.
waf { block-source | capture | logging | redirect } parameter-profile parameter-name
By default, no parameter profile is specified for a WAF action.
Applying a WAF policy to a DPI application profile
About this task
A WAF policy must be applied to a DPI application profile to take effect.
Restrictions and guidelines
A DPI application profile can use only one WAF policy. If you apply different WAF policies to the same DPI application profile, only the most recent configuration takes effect.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter DPI application profile view.
app-profile profile-name
For more information about this command, see DPI engine commands in DPI Command Reference.
3. Apply a WAF policy to the DPI application profile.
waf apply policy policy-name mode { protect | alert }
By default, no WAF policy is applied to the DPI application profile.
Activating WAF policy settings
About this task
After detecting WAF policy changes, the system starts a timer to check for new changes 20 seconds later.
· If no further changes are detected when the timer expires, the system determines that the changes are final and activate the changes at the expiration of the next check interval.
· If new changes are detected, the system resets the check interval timer and continue the periodic check until it determines that the changes are final and activates the changes.
You can also use this function to manually activate WAF policy changes.
Restrictions and guidelines
This task can cause temporary outage for all DPI services. As a best practice, perform the task after all DPI service policy and rule settings are complete.
For more information about activating DPI service module configuration, see "Configuring DPI engine."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Activate WAF policy settings.
inspect activate
By default, changes to WAF policy settings take effect after the system automatically activates the changes during the periodic check.
Using the DPI application profile in a security policy rule
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter security policy view.
security-policy { ip | ipv6 }
3. Enter security policy rule view.
rule { rule-id | name name } *
4. Set the rule action to pass.
action pass
The default rule action is drop.
5. Use a DPI application profile in the rule.
profile app-profile-name
By default, no DPI application profile is used in a security policy rule.
Using the DPI application profile in an object policy rule
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter object policy view.
object-policy { ip | ipv6 } object-policy-name
3. Use a DPI application profile in an object policy rule.
rule [ rule-id ] inspect app-profile-name
By default, no DPI application profile is used in an object policy rule.
4. Return to system view.
quit
5. Create a zone pair and enter zone pair view.
zone-pair security source source-zone-name destination destination-zone-name
For more information about zone pairs, see security zone configuration in Security Configuration Guide.
6. Apply the object policy to the zone pair.
object-policy apply { ip | ipv6 } object-policy-name
By default, no object policy is applied to a zone pair.
Managing the WAF signature library
You can update or roll back the version of the WAF signature library on the device.
Restrictions and guidelines
· Do not delete the /dpi/ folder in the root directory of the storage medium.
· Do not perform WAF signature update or rollback when the device's free memory is below the normal state threshold. For more information about device memory thresholds, see device management in Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
· For successful automatic and immediate signature update, make sure the device can resolve the domain name of the official website into an IP address through DNS. For more information about DNS, see DNS configuration in Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
· Update only one signature library at a time. Do not perform signature library update until the existing signature library update is completed.
Scheduling automatic WAF signature library update
About this task
You can schedule automatic WAF signature library update if the device can access the signature database services on the official website. The device periodically obtains the latest signature file from the official website to update its local signature library according to the update schedule.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable automatic WAF signature library update and enter automatic WAF signature library update configuration view.
waf signature auto-update
By default, automatic WAF signature library update is disabled.
3. Schedule the update time.
update schedule { daily | weekly { fri | mon | sat | sun | thu | tue | wed } } start-time time tingle minutes
By default, the device updates the WAF signature library at a random time between 01:00:00 and 03:00:00 every day.
4. (Optional.) Configure the device to overwrite the current WAF signature library without backing up the library during an automatic signature library update.
override-current
By default, the device backs up the current WAF signature library as the previous version before performing an automatic WAF signature library update.
Triggering an immediate WAF signature update
About this task
Anytime you find a release of new signature version on the official website, you can trigger the device to immediately update the local signature library.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Trigger an immediate WAF signature library update.
waf signature auto-update-now
Performing a WAF signature manual update
About this task
If the device cannot access the signature database services on the official website, use one of the following methods to manually update the WAF signature library on the device:
· Local update—Updates the WAF signature library by using a locally stored update WAF signature file.
Store the update file on the master device for successful signature library update.
· FTP/TFTP update—Updates the WAF signature library by using the file stored on the FTP or TFTP server.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Manually update the WAF signature library on the device.
waf signature update [ override-current ] file-path
Rolling back the WAF signature library
About this task
If a WAF signature library update causes exceptions or a high false alarm rate, you can roll back the WAF signature library.
Before rolling back the WAF signature library, the device backs up the current signature library as the previous version. For example, the previous library version is V1 and the current library version is V2. If you perform a rollback to the previous version, library version V1 becomes the current version and library version V2 becomes the previous version. If you perform a rollback to the previous version again, the library rolls back to library version V2.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Roll back the WAF signature library to the previous version or to the factory default version.
waf signature rollback { factory | last }
Display and maintenance commands for WAF
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display WAF policy information. |
display waf policy policy-name |
|
Display WAF signature library information. |
display waf signature library |
|
Display WAF signature information. |
display waf signature [ pre-defined ] [ direction { any | to-client | to-server } ] [ category category-name | fidelity { high | low | medium } | severity { critical | high | low | medium } ] * |
|
Display detailed information about a predefined WAF signature. |
display waf signature pre-defined signature-id |
WAF configuration examples
Example: Using the default WAF policy in a security policy
Network configuration
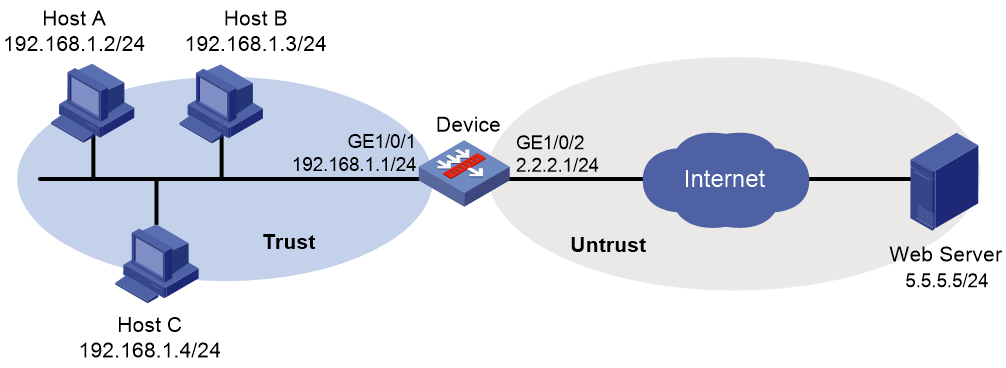
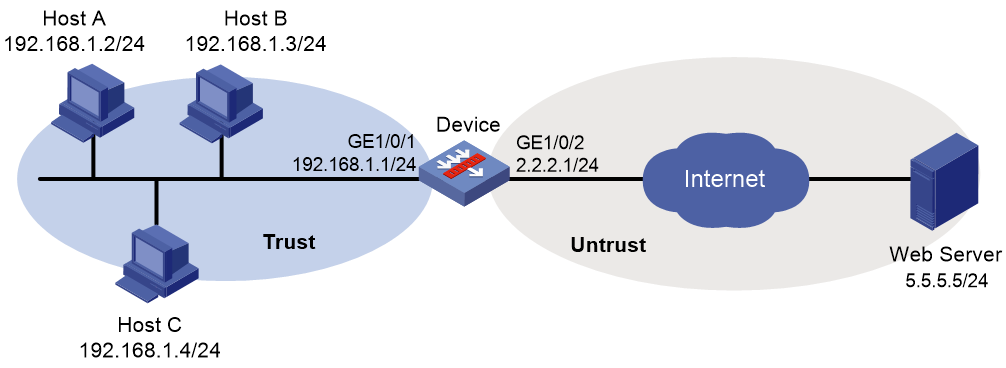
As shown in Figure 2, the device connects to the LAN and Internet through security zones Trust and Untrust, respectively.
Configure the device to use the default WAF policy for attack detection and prevention.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces:
# Assign an IP address to interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure settings for routing.
This example configures a static route with next hop address 2.2.2.2.
[Device] ip route-static 5.5.5.0 24 2.2.2.2
3. Add interfaces to security zones.
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
4. Apply the default WAF policy to a DPI application profile and activate the WAF policy settings:
# Create a DPI application profile named sec and enter its view. Apply the default WAF policy to the DPI application profile and set the policy mode to protect.
[Device] app-profile sec
[Device-app-profile-sec] waf apply policy default mode protect
[Device-app-profile-sec] quit
# Activate the WAF policy settings.
[Device] inspect activate
5. Configure a security policy:
# Enter IPv4 security policy view. Create a security policy rule named trust-untrust so the device can apply the WAF policy to traffic between the internal users and the Internet.
[Device] security-policy ip
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name trust-untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] source-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] source-ip-subnet 192.168.1.0 24
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] destination-zone untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] profile sec
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] quit
# Activate rule matching acceleration.
[Device-security-policy-ip] accelerate enhance enable
[Device-security-policy-ip] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the device can use the default WAF policy to detect and prevent known network attacks. (Details not shown.)
For example, if an incoming attack packet matches predefined WAF signature GNU_Bash_Remote_Code_Execution_Vulnerability(CVE-2014-6271), the device automatically applies the signature actions (reset and logging) to the packet.
Example: Using a user-defined WAF policy in a security policy
Network configuration
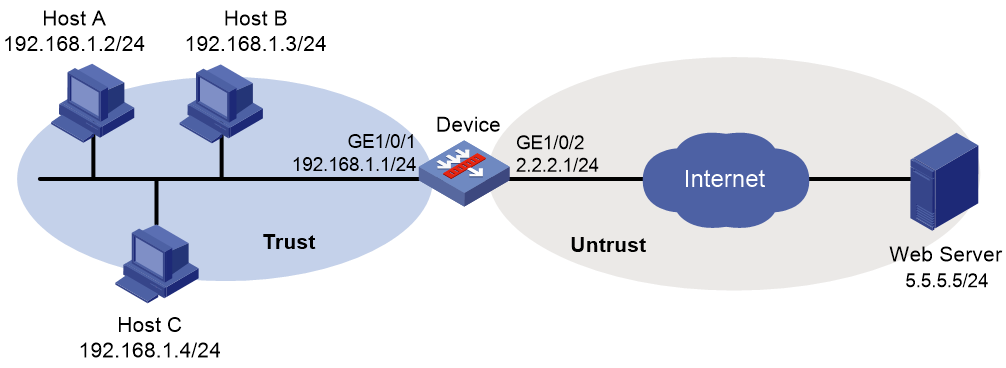
As shown in Figure 3, the device connects to the LAN and Internet through security zones Trust and Untrust, respectively.
Perform the following tasks:
1. Configure the device to use a WAF policy for attack detection and prevention.
2. Enable predefined WAF signature 2 and specify actions drop and logging for the signature.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces:
# Assign an IP address to interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure settings for routing.
This example configures a static route with next hop address 2.2.2.2.
[Device] ip route-static 5.5.5.0 24 2.2.2.2
3. Add interfaces to security zones.
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
4. Create a WAF policy named waf1, and then configure the following settings in the policy:
a. Configure the server to client direction as signature filtering criterion.
b. Enable predefined WAF signature 2 and specify actions drop and logging for the signature.
[Device] waf policy waf1
[Device-waf-policy-waf1] object-dir client
[Device-waf-policy-waf1] signature override pre-defined 2 enable drop logging
[Device-waf-policy-waf1] quit
5. Apply WAF policy waf1 to a DPI application profile and activate the WAF policy settings:
# Create a DPI application profile named sec. Apply WAF policy waf1 to the DPI application profile and set the policy mode to protect.
[Device] app-profile sec
[Device-app-profile-sec] waf apply policy waf1 mode protect
[Device-app-profile-sec] quit
# Activate the WAF policy settings.
[Device] inspect activate
6. Configure a security policy:
# Enter IPv4 security policy view. Create a security policy rule named trust-untrust so the device can apply the WAF policy to traffic between the internal users and the Internet.
[Device] security-policy ip
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name trust-untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] source-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] source-ip-subnet 192.168.1.0 24
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] destination-zone untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] profile sec
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] quit
# Activate rule matching acceleration.
[Device-security-policy-ip] accelerate enhanced enable
[Device-security-policy-ip] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the device can use the default WAF policy to detect and prevent known network attacks. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that when a packet matches predefined WAF signature 2, the device executes the drop and logging actions.
Example: Manually updating the WAF signature library
Network configuration
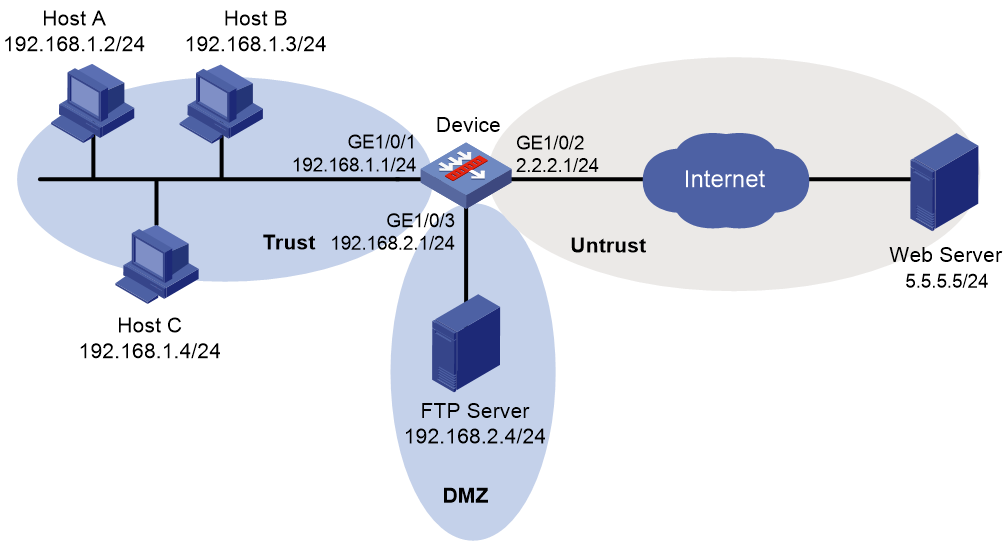
As shown in Figure 4, LAN users in security zone Trust can access the following resources:
· Internet resources in security zone Untrust.
· The FTP server at 192.168.2.4/24 in security zone DMZ. The FTP login username and password are waf and 123, respectively.
Manually update the WAF signature library by using the latest WAF signature file stored on the FTP server.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces:
# Assign an IP address to interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure settings for routing.
This example configures a static route with next hop address 2.2.2.2.
[Device] ip route-static 5.5.5.0 24 2.2.2.2
3. Add interfaces to security zones.
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
[Device] security-zone name dmz
[Device-security-zone-DMZ] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[Device-security-zone-DMZ] quit
4. Configure a security policy:
# Configure a security policy rule to permit the traffic between the Trust and Untrust security zones so internal users can access external resources.
[Device] security-policy ip
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name trust-untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] source-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] source-ip-subnet 192.168.1.0 24
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] destination-zone untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] quit
# Configure a security policy rule to permit the traffic between the Trust and DMZ security zones so internal users can access the FTP server in the DMZ security zone.
[Device] security-policy ip
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name trust-dmz
[Device-security-policy-ip-11-trust-dmz] source-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-11-trust-dmz] source-ip-subnet 192.168.1.0 24
[Device-security-policy-ip-11-trust-dmz] destination-zone dmz
[Device-security-policy-ip-11-trust-dmz] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-11-trust-dmz] quit
# Configure a security policy rule to permit the traffic between the FTP server and the device so the device can access the FTP server to obtain the signature library file.
[Device] security-policy ip
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name downloadlocalout
[Device-security-policy-ip-12-downloadlocalout] source-zone local
[Device-security-policy-ip-12-downloadlocalout] destination-zone dmz
[Device-security-policy-ip-12-downloadlocalout] destination-ip-subnet 192.168.2.0 24
[Device-security-policy-ip-12-downloadlocalout] application ftp
[Device-security-policy-ip-12-downloadlocalout] application ftp-data
[Device-security-policy-ip-12-downloadlocalout] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-12-downloadlocalout] quit
# Activate rule matching acceleration.
[Device-security-policy-ip] accelerate enhanced enable
[Device-security-policy-ip] quit
5. Update the WAF signature library on the device by using WAF signature file waf-1.0.8-encrypt.dat on the FTP server.
[Device] waf signature update ftp://waf:[email protected]/waf-1.0.8-encrypt.dat
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the device WAF signature library is updated.
<Device> display waf signature library
Example: Configuring automatic WAF signature library update
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 5, LAN users in security zone Trust can access Internet resources in security zone Untrust.
Configure the device to start automatically updating the local WAF signature library at a random time between 08:30 a.m. and 09:30 a.m. every Saturday.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces:
# Assign an IP address to interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure settings for routing.
This example configures a static route with next hop address 2.2.2.2.
[Device] ip route-static 5.5.5.0 24 2.2.2.2
3. Add interfaces to security zones.
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
4. Configure DNS for the device to resolve the domain name of the official website into the correct IP address.
[Device] dns server 10.72.66.36
5. Configure a security policy:
# Configure a security policy rule to permit the traffic between the Trust and Untrust security zones so internal users can access external resources.
[Device] security-policy ip
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name trust-untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] source-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] source-ip-subnet 192.168.1.0 24
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] destination-zone untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-10-trust-untrust] quit
# Configure a security policy rule to permit the traffic between the Local and Untrust security zones so the device can access the official website to obtain the signature library file.
[Device] security-policy ip
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name downloadlocalout
[Device-security-policy-ip-11-downloadlocalout] source-zone local
[Device-security-policy-ip-11-downloadlocalout] destination-zone untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-11-downloadlocalout] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-11-downloadlocalout] quit
# Activate rule matching acceleration.
[Device-security-policy-ip] accelerate enhanced enable
[Device-security-policy-ip] quit
6. Configure automatic WAF signature library update:
Enable automatic WAF signature library update. Configure the device to perform automatic update at a random time between 08:30 a.m. and 09:30 a.m. every Saturday.
<Device> system-view
[Device] waf signature auto-update
[Device-waf-autoupdate]
[Device-waf-autoupdate] update schedule weekly sat start-time 9:00:00 tingle 60
[Device-waf-autoupdate] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the device WAF signature library is updated as scheduled.
<Device> display waf signature library
Example: Using the default WAF policy in an object policy
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 6, the device connects to the LAN and Internet through security zones Trust and Untrust, respectively.
Configure the device to use the default WAF policy for attack detection and prevention.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces, as shown in Figure 6. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the security zones:
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to security zone Trust.
<Device> system-view
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to security zone Untrust.
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
3. Create an IP address object group named waffilter and configure an IP address object with subnet 192.168.1.0/24.
[Device] object-group ip address waffilter
[Device-obj-grp-ip-waffilter] network subnet 192.168.1.0 24
[Device-obj-grp-ip-waffilter] quit
4. Apply the default WAF policy to a DPI application profile:
# Create a DPI application profile named sec and enter its view.
[Device] app-profile sec
# Apply the default WAF policy to the DPI application profile and set the policy mode to protect.
[Device-app-profile-sec] waf apply policy default mode protect
[Device-app-profile-sec] quit
5. Activate the WAF policy settings.
[Device] inspect activate
6. Configure an object policy:
# Create an IPv4 object policy named waffilter and enter its view.
[Device] object-policy ip waffilter
# Configure an object policy rule to apply DPI application profile sec to packets with source IP addresses contained in IP address object group waffilter.
[Device-object-policy-ip-waffilter] rule inspect sec source-ip waffilter destination-ip any
[Device-object-policy-ip-waffilter] quit
7. Create a zone pair between source security zone Trust and destination security zone Untrust, and apply object policy waffilter to the zone pair.
[Device] zone-pair security source trust destination untrust
[Device-zone-pair-security-Trust-Untrust] object-policy apply ip waffilter
[Device-zone-pair-security-Trust-Untrust] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the device can use the default WAF policy to detect and prevent known network attacks. (Details not shown.)
For example, if an incoming attack packet matches predefined WAF signature GNU_Bash_Remote_Code_Execution_Vulnerability(CVE-2014-6271), the device automatically applies the signature actions (reset and logging) to the packet.
Example: Using a user-defined WAF policy in an object policy
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 7, the device connects to the LAN and Internet through security zones Trust and Untrust, respectively.
Perform the following tasks:
1. Configure the device to use a WAF policy for attack detection and prevention.
2. Enable predefined WAF signature 2 and specify actions drop and logging for the signature.
3. Apply WAF policy waf1 to zone pair between source security zone Trust and destination security zone Untrust.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces, as shown in Figure 7. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the security zones:
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to security zone Trust.
<Device> system-view
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to security zone Untrust.
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
3. Create an IP address object group named waffilter and configure an IP address object with subnet 192.168.1.0/24.
[Device] object-group ip address waffilter
[Device-obj-grp-ip-waffilter] network subnet 192.168.1.0 24
[Device-obj-grp-ip-waffilter] quit
4. Configure a WAF policy:
# Create a WAF policy named waf1 and enter its view.
[Device] waf policy waf1
# Configure the server to client direction as signature filtering criteria in the WAF policy.
[Device-waf-policy-waf1] object-dir client
# Enable predefined WAF signature 2 and specify actions drop and logging for the signature.
[Device-waf-policy-waf1] signature override pre-defined 2 enable drop logging
5. Apply WAF policy waf1 to a DPI application profile:
# Create a DPI application profile named sec.
[Device] app-profile sec
# Apply WAF policy waf1 to the DPI application profile and set the policy mode to protect.
[Device-app-profile-sec] waf apply policy waf1 mode protect
[Device-app-profile-sec] quit
6. Activate the WAF policy settings.
[Device] inspect activate
7. Configure an object policy:
# Create an IPv4 object policy named waffilter and enter its view.
[Device] object-policy ip waffilter
# Configure an object policy rule to apply DPI application profile sec to packets with source IP addresses contained in IP address object group waffilter.
[Device-object-policy-ip-waffilter] rule inspect sec source-ip waffilter destination-ip any
[Device-object-policy-ip-waffilter] quit
8. Create a zone pair between source security zone Trust and destination security zone Untrust, and apply object policy waffilter to the zone pair.
[Device] zone-pair security source trust destination untrust
[Device-zone-pair-security-Trust-Untrust] object-policy apply ip waffilter
[Device-zone-pair-security-Trust-Untrust] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the device can use the default WAF policy to detect and prevent known network attacks. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that when a packet matches predefined WAF signature 2, the device executes the drop and logging actions.
Example: Manually updating the WAF signature library
Network configuration
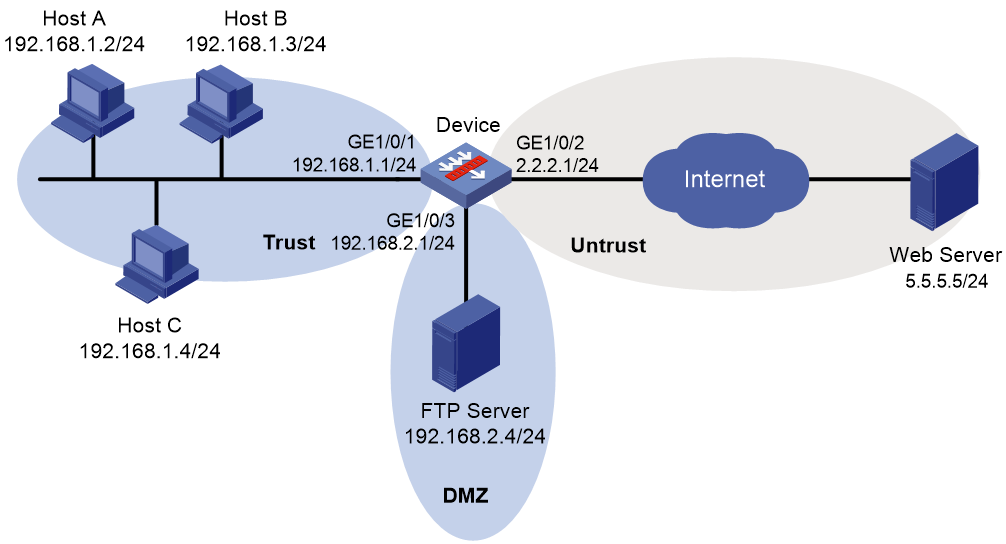
As shown in Figure 8, LAN users in security zone Trust can access the following resources:
· Internet resources in security zone Untrust.
· The FTP server at 192.168.2.1/24 in security zone DMZ. The FTP login username and password are waf and 123, respectively.
Perform the following tasks:
· Manually update the WAF signature library by using the latest WAF signature file stored on the FTP server.
· Configure the device to use the default WAF policy to detect and prevent known attacks on the network.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces, as shown in Figure 8. (Details not shown.)
2. Enable the device to communicate with the FTP server:
# Configure ACL 2001 to permit all traffic.
<Device> system-view
[Device] acl basic 2001
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2001] rule permit
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2001] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to zone DMZ.
[Device] security-zone name dmz
[Device-security-zone-DMZ] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[Device-security-zone-DMZ] quit
# Create a zone pair between source security zone Local and destination security zone DMZ, and then apply ACL 2001 to the zone pair.
[Device] zone-pair security source local destination dmz
[Device-zone-pair-security-Local-DMZ] packet-filter 2001
[Device-zone-pair-security-Local-DMZ] quit
# Create a zone pair between source security zone DMZ and destination security zone Local, and the apply ACL 2001 to the zone pair.
[Device] zone-pair security source dmz destination local
[Device-zone-pair-security-DMZ-Local] packet-filter 2001
[Device-zone-pair-security-DMZ-Local] quit
3. Update the device WAF signature library by using WAF signature file waf-1.0.8-encrypt.dat on the FTP server.
[Device] waf signature update ftp://waf:[email protected]/waf-1.0.8-encrypt.dat
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the device WAF signature library is updated.
<Device> display waf signature library
Example: Configuring automatic WAF signature library update
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 9, LAN users in security zone Trust can access Internet resources in security zone Untrust.
Configure the device to automatically update the local WAF signature library at a random time between 08:30 a.m. and 09:30 a.m. every Saturday.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces, as shown in Figure 9. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure DNS for the device to resolve the domain name of the official website into the IP address. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure an object policy to allow LAN users in security zone Trust to access Internet resources in security zone Untrust. (Details not shown.)
4. Configure automatic WAF signature library update:
# Enable automatic WAF signature library update.
<Device> system-view
[Device] waf signature auto-update
[Device-waf-autoupdate]
# Configure the device to perform automatic update at a random time between 08:30 a.m. and 09:30 a.m. every Saturday.
[Device-waf-autoupdate] update schedule weekly sat start-time 9:00:00 tingle 60
[Device-waf-autoupdate] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the device WAF signature library is updated as scheduled.
<Device> display waf signature library