- Table of Contents
-
- 04-DPI Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-DPI overview
- 02-DPI engine configuration
- 03-IPS configuration
- 04-URL filtering configuration
- 05-Data filtering configuration
- 06-File filtering configuration
- 07-Anti-virus configuration
- 08-Data analysis center configuration
- 09-Proxy policy configuration
- 10-WAF configuration
- 11-IP reputation configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-DPI engine configuration | 147.00 KB |
Contents
Configure a DPI application profile
Activating policy and rule settings for DPI service modules
Configuring action parameter profiles
Configuring a block source parameter profile
Configuring a capture parameter profile
Configuring a logging parameter profile
Configuring a redirect parameter profile
Configuring an email parameter profile
Enabling inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage
Configuring stream fixed length inspection
Setting the maximum data size for file decompression
Configuring MD5 hash-based virus inspection for all files
Enabling source port-based application identification
Specifying a proxy server for online DPI service signature update
Specifying the cloud query server for DPI services
Display and maintenance commands for DPI engine
Configuring DPI engine
About DPI engine
DPI engine is an inspection module shared by DPI service modules. DPI engine uses inspection rules to identify the application layer information, including the application layer protocol and behavior. DPI service modules process packets based on the inspection results.
DPI functions
DPI engine provides the following functions:
· Protocol parsing—Identifies the application layer protocols and analyzes the application layer information. Information analysis includes recognizing, normalizing, and uncompressing application layer fields.
· AC pattern matching—Matches packet payloads by the Aho-Corasick (AC) patterns in inspection rules. AC pattern matching is fast and it is the core function of the DPI engine.
· Option matching—Matches packet payloads by the options in the inspection rules whose AC patterns have been matched. Option matching is slower than AC pattern matching.
DPI engine inspection rules
DPI engine uses inspection rules to match packets. Inspection rules are transformed from the rules or signatures of the DPI service modules. The match criteria in an inspection rule can contain the following types:
· AC pattern—Criteria that identify packet signatures. An AC pattern is a character string that is three or more bytes long.
· Option—Criteria other than AC patterns. For example, an option can be the port number or protocol type.
An inspection rule can contain both AC patterns and options. A packet must match both the AC patterns and options to match the rule.
An inspection rule can also contain only options. A packet matches the rule if it matches the options in the rule.
DPI engine mechanism
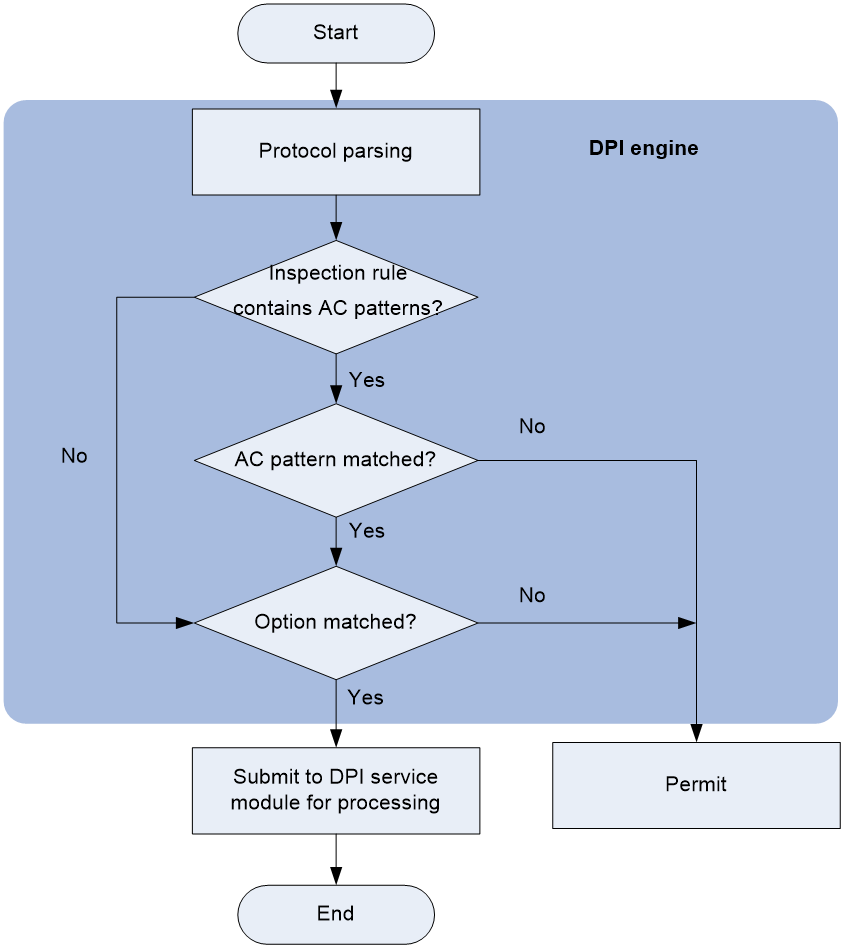
As shown in Figure 1, DPI engine works as follows:
1. The DPI engine performs protocol parsing for the packet and searches for applicable inspection rules according to the parsing results.
2. If an applicable inspection rule contains AC patterns, DPI engine performs AC pattern matching first. If an applicable inspection rule does not contain AC patterns, DPI engine directly performs option matching. The packet matches the rule if it matches the options.
3. If the packet matches an AC pattern in an applicable inspection rule, the DPI engine further compares the packet against the options associated with the AC pattern. The packet matches the rule if it matches the both the AC pattern and its associated options. If the packet matches an AC pattern but does not match its associated options, the DPI engine permits the packet to pass.
4. If the packet matches an inspection rule, the DPI engine submits the packet to the corresponding DPI service module for processing. If the packet does not match any rule, the DPI engine permits the packet to pass.
DPI engine tasks at a glance
To configure the DPI engine, perform the following tasks:
1. Configure a DPI application profile
2. Activating policy and rule settings for DPI service modules
3. Configuring action parameter profiles
4. (Optional.) Optimizing the DPI engine
5. (Optional.) Enabling inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage
6. (Optional.) Configuring stream fixed length inspection
7. (Optional.) Setting the maximum data size for file decompression
8. (Optional.) Configuring MD5 hash-based virus inspection for all files
9. (Optional.) Enabling source port-based application identification
10. (Optional.) Specifying a proxy server for online DPI service signature update
11. (Optional.) Specifying the cloud query server for DPI services
12. (Optional.) Disabling the DPI engine
Configure a DPI application profile
About this task
A DPI application profile includes a set of DPI service policies, such as a URL filtering policy. It can be applied to an object policy rule or a security policy rule to specify the DPI service policy for packets that match the rule.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a DPI application profile and enter its view.
app-profile profile-name
3. Apply DPI service policies to the DPI application profile.
¡ Specify an IPS policy.
ips apply policy policy-name mode { protect | alert }
For more information about this command, see IPS commands in DPI Command Reference.
¡ Specify a URL filtering policy.
url-filter apply policy policy-name
For more information about this command, see URL filtering commands in DPI Command Reference.
¡ Specify a data filtering policy.
data-filter apply policy policyname
For more information about this command, see data filtering commands in DPI Command Reference.
¡ Specify a file filtering policy.
file-filter apply policy policyname
For more information about this command, see file filtering commands in DPI Command Reference.
¡ Specify an anti-virus policy.
anti-virus apply policy policyname mode { alert | protect }
For more information about this command, see anti-virus commands in DPI Command Reference.
¡ Specify a WAF policy.
waf apply policy policy-name mode { protect | alert }
By default, no DPI service policies are applied to a DPI application profile.
Activating policy and rule settings for DPI service modules
About this task
By default, when a configuration change to the policies and rules for DPI service modules (such as URL filtering module) occurs, the system detects whether another configuration change occurs at 20-second intervals.
· If no configuration change occurs during an interval, the system performs an activation operation at the end of the next interval.
· If another configuration change occurs during an interval, the system continues to detect configuration changes.
To immediately activate a configuration change, execute the inspect activate command.
Restrictions and guidelines
This task can cause temporary service outage. As a best practice, perform the task after the configuration of all DPI service policies and rules is complete.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Activate policy and rule settings for DPI service modules.
inspect activate
By default, configuration changes to DPI service policies and rules will be automatically activated.
Configuring action parameter profiles
Configuring a block source parameter profile
About this task
A block source parameter profile defines the block period for the block source action in DPI service modules.
Restrictions and guidelines
The block source action takes effect only after the blacklist feature is enabled.
With the blacklist feature is enabled, the device drops the matching packet and adds the packet's source IP address to the IP blacklist. Subsequent packets from the source IP address will be dropped directly during the block period.
For more information about the blacklist feature, see attack detection and prevention configuration in the Security Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a block source parameter profile and enter its view.
inspect block-source parameter-profile parameter-name
3. Set the block period during which a source IP address is blocked.
block-period period
The default setting is 1800 seconds.
Configuring a capture parameter profile
About this task
A capture parameter profile defines the following parameters for the capture action in DPI service modules:
· Maximum number of bytes that can be cached.
· Daily export time for cached packets.
· URL to which cached packets are exported.
The device caches captured packets locally and exports the cached packets to the designated URL at the daily export time or when the number of cached bytes reaches the limit. After the export, the device clears the local cache and starts to capture new packets.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a capture parameter profile and enter its view.
inspect capture parameter-profile parameter-name
3. Set the maximum volume of captured packets that can be cached.
capture-limit kilobytes
By default, the device can cache a maximum of 512 Kilobytes of captured packets.
4. Set the daily export time for cached captured packets.
export repeating-at time
By default, the cached captured packets are exported at 1:00 a.m. every day.
5. Specify the URL to which cached captured packets are exported
export url url-string
By default, no URL is specified for exporting the cached captured packets.
Configuring a logging parameter profile
About this task
A logging parameter profile defines the log output method and log output language for the logging action in DPI service modules.
Restrictions and guidelines
After setting the IPS log language to Chinese, only the attack name field of the IPS logs supports displaying in Chinese.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a logging parameter profile and enter its view.
inspect logging parameter-profile parameter-name
3. Specify the log export method.
log { email | syslog }
By default, logs are exported to the information center.
4. Set the language for IPS log output to Chinese.
log language chinese
By default, IPS logs are output in English.
Configuring a redirect parameter profile
About this task
A redirect parameter profile defines the URL to which packets are redirected for the redirect action in DPI service modules.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a redirect parameter profile and enter its view.
inspect redirect parameter-profile parameter-name
3. Specify the URL to which packets are redirected.
redirect-url url-string
By default, no URL is specified for packet redirecting.
Configuring an email parameter profile
About this task
An email parameter profile defines the following parameters for the email action in DPI service modules:
· Email server.
· Email sender and receiver.
· Username and password for logging in to the email server.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create an email parameter profile and enter its view.
inspect email parameter-profile parameter-name
3. Specify the email server.
email-server addr-string
By default, no email server is specified.
4. Specify the DNS server address.
dns-server ip-address
By default, no DNS server is specified.
5. Specify the email sender address.
sender addr-string
By default, no email sender address is specified.
6. Specify the email receiver address.
receiver addr-string
By default, no email receiver address is specified.
7. (Optional.) Configure email client authentication.
a. Enable email client authentication.
authentication enable
By default, email client authentication is enabled.
b. Specify the username for logging in to the email server.
username name-string
By default, no username is specified for logging in to the email server.
c. Specify the password for logging in to the email server.
password { cipher | simple } string
By default, no password is specified for logging in to the email server.
d. Enable the secure password transmission feature.
secure-authentication enable
By default, the secure password transmission feature is disabled.
Optimizing the DPI engine
About this task
The DPI engine includes a series of optimization features. For example, you can enable the DPI engine to uncompress or decode the compressed or encoded packets to identify the application information of the packets. The optimization features improve inspection and accuracy of the DPI engine, but consume more system resources.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the maximum number of payload-carrying packets to be inspected per data flow.
inspect packet maximum max-number
By default, the DPI engine can inspect a maximum of 32 payload-carrying packets per data flow.
3. Set the maximum number of options to be cached per TCP or UDP data flow.
inspect cache-option maximum max-number
By default, the DPI engine can cache a maximum of 32 options per TCP or UDP data flow.
4. Configure the TCP segment reassembly feature.
¡ Enable TCP segment reassembly.
inspect tcp-reassemble enable
By default, the TCP segment reassembly feature is disabled.
¡ Set the maximum number of TCP segments that can be cached for reassembly per TCP flow.
inspect tcp-reassemble max-segment max-number
By default, a maximum of 10 TCP segments can be cached for reassembly per TCP flow.
5. (Optional.) Disable a DPI engine optimization feature.
inspect optimization [ chunk | no-acsignature | raw | uncompress | url-normalization ] disable
By default, all DPI engine optimization features are enabled.
You can disable DPI engine optimization features to improve the device performance as needed.
Enabling inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage
About this task
Packet inspection of the DPI engine is a complex and resource-consuming process.
Inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage works as follows:
· When the device's CPU usage rises to or above the CPU usage threshold, the DPI engine suspends packet inspection to guarantee the device performance.
· When the device's CPU usage drops to or below the CPU usage recovery threshold, the DPI engine resumes packet inspection.
For information about configuring the CPU usage thresholds, see device management in Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Restrictions and guidelines
Do not disable inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage if the device's CPU usage is high.
When the device's CPU usage is low, you can disable this feature to improve inspection accuracy.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage.
undo inspect cpu-threshold disable
By default, inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage is enabled.
Configuring stream fixed length inspection
About this task
This feature enables the DPI engine to inspect only a fixed length of data for a stream instead of the whole packet data in a stream.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable stream fixed length inspection.
undo inspect stream-fixed-length disable
By default, stream fixed length inspection is enabled.
3. Set the fixed data inspection length for application protocols.
inspect stream-fixed-length { email | ftp | http | nfs | smb } * length
The default length is 32 Kilobytes for FTP, HTTP, NFS, SMB, and email protocols.
The longer the inspection data length, the lower the device throughput, and the higher the packet inspection accuracy.
Setting the maximum data size for file decompression
About this task
The device can decompress .zip files for file data inspection. Perform this task to set the maximum data size that can be decompressed in a file. The remaining file data will be ignored.
Set an appropriate maximum data size for file decompression. A large data size might make the device get stuck in decompressing large files and the device forwarding performance might be affected. A small data size will affect the accuracy of the file inspection results for DPI services (such as anti-virus and data filtering).
Restrictions and guidelines
The device can decompress only .zip files.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the maximum data size that can be decompressed in a .zip file.
inspect file-uncompr-len max-size
By default, the device can decompress a maximum of 100 MB data in a .zip file.
Configuring MD5 hash-based virus inspection for all files
About this task
This feature enables the DPI engine to generate MD5 hashes for all files and to compare the generated MD5 hashes with the MD5 rules in the signature library. If the MD5 hash generated for a file matches an MD5 rule in the signature library, the file is considered to contain viruses. For more information about virus inspection, see "Configuring anti-virus."
This feature might degrade the processing performance of other services. Enable it only when necessary.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable MD5 hash-based virus inspection for all files.
inspect md5-verify all-files
By default, the DPI engine performs MD5 hash-based virus inspection only for executable files, office files, and compressed files.
Enabling source port-based application identification
About this task
You can use this feature to identify traffic of applications that use fixed source ports when the following conditions are true:
· The types of traffic transmitted over networks are relatively unvaried and use fixed source ports.
· Destination port-based application identification or signature-based traffic content identification is not supported.
The application identification results produced by this feature might not be accurate. Configure this feature according to your live network as a best practice.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable source port-based application identification.
inspect source-port-identify enable
By default, source port-based application identification is disabled.
Specifying a proxy server for online DPI service signature update
About this task
The device must access the company's website for online signature update of DPI services (such as URL filtering). If direct connectivity is not available, the device can access the company's website through the specified proxy server. For more information about online signature update, see "Configuring URL filtering" and "Configuring anti-virus."
Restrictions and guidelines
If you specify a proxy server by domain name instead of IP address, make sure the device can resolve the domain name into an IP address through DNS. For more information about DNS, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify a proxy server for online DPI service signature update
inspect signature auto-update proxy { domain domain-name | ip ip-address } [ port port-number ] [ user user-name password { cipher | simple } string ]
By default, the proxy server used by DPI services for online signature update is not specified.
Specifying the cloud query server for DPI services
About this task
You can specify the server used for cloud query by DPI services.
Currently, the cloud query server supports URL filtering cloud query and anti-virus MD5 value cloud query.
Restrictions and guidelines
For successful cloud query, make sure the device can resolve the host name of the cloud query server into an IP address through DNS. For more information about DNS, see DNS configuration in Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify the cloud query server for DPI services.
inspect cloud-server host-name
By default, DPI services use the cloud query server with host name sec.h3c.com.
Disabling the DPI engine
About this task
Packet inspection in the DPI engine is a complex and resource-consuming process. When the CPU usage is too high, you can disable the DPI engine to guarantee the device performance. After you disable the DPI engine, packets will not be processed by DPI.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Disable the DPI engine.
inspect bypass
By default, the DPI engine is enabled.
Display and maintenance commands for DPI engine
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the status of the DPI engine. |
display inspect status |
|
Display information about the MD5 hash-based virus inspection for all files feature. |
display inspect md5-verify configuration |