- Table of Contents
-
- 01-Fundamentals Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-CLI configuration
- 02-RBAC configuration
- 03-Login management configuration
- 04-FTP and TFTP configuration
- 05-File system management configuration
- 06-Configuration file management configuration
- 07-Software upgrade configuration
- 08-ISSU configuration
- 09-Device management configuration
- 10-Tcl configuration
- 11-Python configuration
- 12-License management
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-FTP and TFTP configuration | 140.12 KB |
Contents
Using the device as an FTP server
FTP server configuration tasks at a glance
Configuring client authentication and authorization
Configuring FTP server access control
Setting connection management parameters
Specifying an SSL server policy for SFTP connections
Setting the DSCP value for outgoing FTP packets
Manually releasing FTP connections
Display and maintenance commands for the FTP server
Example: Using the device as an FTP server
Using the device as an FTP client
FTP client configuration tasks at a glance
Establishing an FTP connection
Displaying command help information
Displaying directories and files on the FTP server
Managing directories on the FTP server
Managing directories on the FTP client
Working with files on the FTP server
Changing to another user account
Maintaining and troubleshooting the FTP connection
Terminating the FTP connection
Display and maintenance commands for the FTP client
Restrictions and guidelines: TFTP configuration
Configuring the device as a TFTP server
Configuring and using the IPv4 TFTP client
Configuring and using the IPv6 TFTP client
Configuring FTP
About FTP
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is an application layer protocol for transferring files from one host to another over an IP network. It uses TCP port 20 to transfer data and TCP port 21 to transfer control commands.
FTP is based on the client/server model. The device can act as the FTP server or FTP client.
FTP file transfer modes
FTP supports the following transfer modes:
· Binary mode—Used to non-text files, such as .app, .bin, and .btm files.
· ASCII mode—Used to transfer text files, such as .txt, .bat, and .cfg files.
When the device acts as the FTP client, you can set the transfer mode (binary by default). When the device acts as the FTP server, the transfer mode is determined by the FTP client.
FTP operation modes
FTP can operate in either of the following modes:
· Active mode (PORT)—The FTP server initiates the TCP connection. This mode is not suitable when the FTP client is behind a firewall, for example, when the FTP client resides in a private network.
· Passive mode (PASV)—The FTP client initiates the TCP connection. This mode is not suitable when the server does not allow the client to use a random unprivileged port greater than 1024.
FTP operation mode varies depending on the FTP client program.
Using the device as an FTP server
To use the device as an FTP server, you must enable the FTP server and configure authentication and authorization on the device. Other commands are optional.
FTP server configuration tasks at a glance
To use the device as an FTP server, perform the following tasks:
2. Configuring client authentication and authorization
3. (Optional.) Configuring FTP server access control
4. (Optional.) Setting connection management parameters
5. (Optional.) Specifying an SSL server policy for SFTP connections
6. (Optional.) Setting the DSCP value for outgoing FTP packets
7. (Optional.) Manually releasing FTP connections
Enabling the FTP server
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable the FTP server.
ftp server enable
By default, the FTP server is disabled.
Configuring client authentication and authorization
Perform this task on the FTP server to authenticate FTP clients and set the authorized directories that authenticated clients can access.
The following authentication modes are available:
· Local authentication—The device looks up the client's username and password in the local user account database. If a match is found, authentication succeeds.
· Remote authentication—The device sends the client's username and password to a remote authentication server for authentication. The user account is configured on the remote authentication server rather than the device.
The following authorization modes are available:
· Local authorization—The device assigns authorized directories to FTP clients based on the locally configured authorization attributes.
· Remote authorization—A remote authorization server assigns authorized directories on the device to FTP clients.
For more information about configuring authentication and authorization, see AAA in Security Configuration Guide.
Configuring FTP server access control
About this task
Use ACLs to prevent unauthorized access. If an applied ACL does not exist or does not have any rules, no user login restriction is applied. If the ACL exists and has rules, only FTP clients permitted by the ACL can access the device.
Restrictions and guidelines
When no ACL is applied, all FTP clients can access the FTP server. To control FTP access, specify an ACL that exists and has rules so only FTP clients permitted by the ACL can access the FTP server. If you specify an ACL that does not exist or does not have rules, no FTP clients can access the FTP server.
The ACL takes effect only for FTP connections to be established. It does not impact existing FTP connections.
For more information about ACL, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
If you configure FTP server access control multiple times, the most recent configuration takes effect.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. (Optional.) Use an ACL to control access to the FTP server.
IPv4:
ftp server acl { advanced-acl-number | basic-acl-number | mac mac-acl-number }
IPv6:
ftp server acl ipv6 { advanced-acl-number | basic-acl-number | mac mac-acl-number }
By default, no ACL is used for access control.
3. (Optional.) Enable logging for FTP login attempts that are denied by the FTP login control ACL.
ftp server acl-deny-log enable
By default, logging is disabled for FTP login attempts that are denied by the FTP login control ACL.
Setting connection management parameters
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the FTP connection idle-timeout timer.
ftp timeout minutes
By default, the FTP connection idle-timeout timer is 30 minutes.
If no data transfer occurs on an FTP connection before the idle-timeout timer expires, the FTP server closes the FTP connection.
3. Set the maximum number of concurrent FTP users.
aaa session-limit ftp max-sessions
By default, the maximum number of concurrent FTP users is 64.
Changing this setting does not affect users who are currently online. If the new limit is less than the number of online FTP users, no additional FTP users can log in until the number drops below the new limit.
For more information about this command, see Security Command Reference.
Specifying an SSL server policy for SFTP connections
About this task
After you associate an SSL server policy with the device, a client that supports SFTP will establish a secure connection to the device to ensure data security.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Associate an SSL server policy with the FTP server to ensure data security.
ftp server ssl-server-policy policy-name
By default, no SSL server policy is associated with the FTP server.
Setting the DSCP value for outgoing FTP packets
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the DSCP value for outgoing FTP packets.
IPv4:
ftp server dscp dscp-value
IPv6:
ftp server ipv6 dscp dscp-value
By default, the DSCP value is 0.
Manually releasing FTP connections
To manually release FTP connections, execute the following commands in user view:
· Release the FTP connection established by using a specific user account:
free ftp user username
· Release the FTP connection to a specific IP address:
free ftp user-ip [ ipv6 ] ip-address [ port port ]
Display and maintenance commands for the FTP server
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display FTP server configuration and status information. |
display ftp-server |
|
Display detailed information about online FTP users. |
display ftp-user |
Example: Using the device as an FTP server
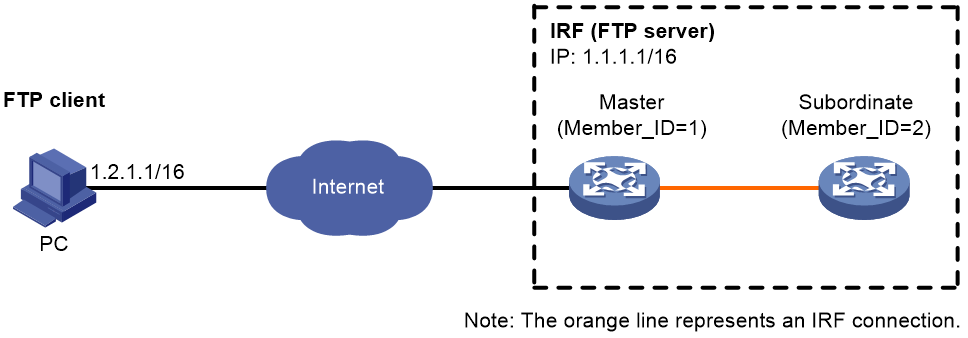
Network configuration
· Configure the IRF fabric as an FTP server.
· Create a local user account named abc on the FTP server. Set the password to 123456.
· Use the user account to log in to the FTP server from the FTP client.
· Upload the temp.bin file from the FTP client to the FTP server.
· Download configuration file config.cfg from the FTP server to the FTP client for backup.
Procedure
1. Configure IP addresses as shown in Figure 1. Make sure the IRF fabric and the PC can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the FTP server:
# Examine the storage space on the member devices. If the free space is insufficient, use the delete/unreserved file command to delete unused files. (Details not shown.)
# Create a local user named abc. Set the password to 123456.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] local-user abc class manage
[Sysname-luser-abc] password simple 123456
# Assign the network-admin user role to the user. Set the working directory to the root directory of the flash memory on the global active MPU. (To set the working directory to the root directory of the flash memory on a global standby MPU, you must include the chassis and slot numbers in the directory path.)
[Sysname-luser-abc] authorization-attribute user-role network-admin work-directory flash:/
# Assign the service type FTP to the user.
[Sysname-luser-abc] service-type ftp
[Sysname-luser-abc] quit
# Enable the FTP server.
[Sysname] ftp server enable
[Sysname] quit
3. Perform FTP operations from the FTP client:
# Log in to the FTP server at 1.1.1.1 using username abc and password 123456.
c:\> ftp 1.1.1.1
Connected to 1.1.1.1.
220 FTP service ready.
User(1.1.1.1:(none)):abc
331 Password required for abc.
Password:
230 User logged in.
# Use the ASCII mode to download configuration file config.cfg from the server to the client for backup.
ftp> ascii
200 TYPE is now ASCII
ftp> get config.cfg back-config.cfg
# Use the binary mode to upload the temp.bin file to the root directory of the flash memory on the global active MPU.
ftp> binary
200 TYPE is now 8-bit binary
ftp> put temp.bin
# Exit FTP.
ftp> bye
Using the device as an FTP client
FTP client configuration tasks at a glance
To use the device as an FTP server, perform the following tasks:
1. Establishing an FTP connection
2. (Optional.) Displaying command help information
3. (Optional.) Displaying directories and files on the FTP server
4. (Optional.) Managing directories on the FTP server
5. (Optional.) Working with files on the FTP server
6. (Optional.) Changing to another user account
7. (Optional.) Maintaining and troubleshooting the FTP connection
8. (Optional.) Terminating the FTP connection
Establishing an FTP connection
FTP connection establishment task list
To establish an FTP connection, perform the following tasks:
1. (Optional.) Specifying a source IP address for outgoing FTP packets
2. Establishing an FTP connection
3. Setting the FTP file transfer mode and operation mode
Restrictions and guidelines
The source IP address specified in the ftp command takes precedence over the one set by the ftp client source command.
The source IP address specified in the ftp ipv6 command takes precedence over the one set by the ftp client ipv6 source command.
Specifying a source IP address for outgoing FTP packets
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify a source IP address for outgoing FTP packets.
IPv4:
ftp client source { interface interface-type interface-number | ip source-ip-address }
By default, no source IP address is specified. The device uses the primary IP address of the output interface as the source IP address.
IPv6:
ftp client ipv6 source { interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6 source-ipv6-address }
By default, no source IPv6 address is specified. The source address is automatically selected as defined in RFC 3484.
Establishing an FTP connection
· Log in to the FTP server from user view.
IPv4:
ftp [ ftp-server [ service-port ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ dscp dscp-value | source { interface interface-type interface-number | ip source-ip-address } ] ] *
IPv6:
ftp ipv6 [ ftp-server [ service-port ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ dscp dscp-value | source { ipv6 source-ipv6-address | interface interface-type interface-number } ] * [ -i interface-type interface-number ] ]
· Log in to the FTP server from FTP client view.
a. Enter FTP client view.
ftp [ ipv6 ]
b. Log in to the FTP server.
open server-address [ service-port ]
Setting the FTP file transfer mode and operation mode
1. Enter FTP client view from user view.
ftp
2. Set the file transfer mode.
¡ Set the file transfer mode to ASCII.
ascii
¡ Set the file transfer mode to binary.
binary
The default file transfer mode is binary.
3. Change the FTP operation mode.
passive
The default FTP operation mode is passive.
Displaying command help information
1. Enter FTP client view from user view.
ftp
2. Display command help information.
¡ help [ command-name ]
¡ ? [ command-name ]
Displaying directories and files on the FTP server
1. Enter FTP client view from user view.
ftp
2. Display directories and files on the FTP server.
¡ dir [ remotefile [ localfile ] ]
¡ ls [ remotefile [ localfile ] ]
Managing directories on the FTP server
Prerequisites
Use the dir or ls command to display the directories and files on the FTP server.
Procedure
1. Enter FTP client view from user view.
ftp
2. Manage directories on the FTP server.
¡ Display the working directory that is being accessed on the FTP server.
pwd
¡ Change the working directory on the FTP server.
cd { directory | .. | / }
¡ Return to the upper level directory on the FTP server.
cdup
¡ Create a directory on the FTP server.
mkdir directory
¡ Delete a directory from the remote FTP server.
rmdir directory
Managing directories on the FTP client
1. Enter FTP client view from user view.
ftp
2. Display or change the local working directory of the FTP client.
lcd [ directory | / ]
To upload a file, use this command to change to the directory where the file resides. Downloaded files are saved in the working directory.
Working with files on the FTP server
Prerequisites
Use the dir or ls command to display the directories and files on the FTP server.
Procedure
1. Enter FTP client view from user view.
ftp
2. Work with files on the FTP server.
¡ Delete a file from the FTP server permanently.
delete remotefile
This command requires that you have the delete right.
¡ Rename a file.
rename [ oldfilename [ newfilename ] ]
¡ Upload a file to the FTP server.
put localfile [ remotefile ]
¡ Download a file from the FTP server.
get remotefile [ localfile ]
¡ Add the content of a file on the FTP client to a file on the FTP server.
append localfile [ remotefile ]
¡ Specify the retransmit marker.
restart marker
Use this command together with the put, get, or append command.
¡ Update a local file.
newer remotefile
¡ Get the missing part of a file.
reget remotefile [ localfile ]
Changing to another user account
About this task
After you log in to the FTP server, you can initiate an FTP authentication to change to a new account. By changing to a new account, you can get a different privilege without re-establishing the FTP connection.
Restrictions and guidelines
For successful account change, you must enter the new username and password correctly. A wrong username or password can cause the FTP connection to be disconnected.
Procedure
1. Enter FTP client view from user view.
ftp
2. Initiate an FTP authentication on the current FTP connection.
user username [ password ]
Maintaining and troubleshooting the FTP connection
About this task
After you use the device to establish an FTP connection to the FTP server, use the commands in this section to locate and troubleshoot problems about the FTP connection.
Procedure
1. Enter FTP client view from user view.
ftp
2. Maintain and troubleshoot the FTP connection.
¡ Display FTP commands supported by the FTP server.
rhelp
¡ Display help information about an FTP command that is supported by the FTP server.
rhelp protocol-command
¡ Display FTP server status.
rstatus
¡ Display detailed information about a directory or file on the FTP server.
rstatus remotefile
¡ Display FTP connection status.
status
¡ Display the system information of the FTP server.
system
¡ Enable or disable FTP operation information display.
verbose
By default, this function is enabled.
¡ Enable FTP client debugging.
debug
By default, FTP client debugging is disabled.
¡ Clear the reply information in the buffer.
reset
Terminating the FTP connection
1. Enter FTP client view from user view.
ftp
2. Terminate the connection.
¡ Terminate the connection to the FTP server without exiting FTP client view.
disconnect
close
¡ Terminate the connection to the FTP server and return to user view.
bye
quit
Display and maintenance commands for the FTP client
Execute the display command in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display source IP address information on the FTP client. |
display ftp client source |
Configuring TFTP
About TFTP
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is a simplified version of FTP for file transfer over secure reliable networks. TFTP uses UDP port 69 for data transmission. In contrast to TCP-based FTP, TFTP does not require authentication or complex message exchanges, and is easier to deploy. TFTP is suited for reliable network environments.
The device can act as the TFTP server or TFTP client.
Restrictions and guidelines: TFTP configuration
You can upload a file from a TFTP client to the TFTP server or download a file from the TFTP server to a TFTP client. As a best practice, specify a file name that has not been used in the destination directory. If the destination file name has been used in the destination directory, the device deletes the existing file before saving the new file.
Configuring the device as a TFTP server
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable the TFTP server.
tftp server enable
By default, the TFTP server is disabled.
The device can act as the TFTP server on both IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
3. Set the TFTP server working directory.
tftp server work-directory directory
By default, the TFTP server working directory is the root directory of the default file system.
Configuring and using the IPv4 TFTP client
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. (Optional.) Use an ACL to control the client's access to TFTP servers.
tftp-server acl acl-number
By default, no ACL is used for access control.
3. Specify the source IP address for TFTP packets sent by the TFTP client.
tftp client source { interface interface-type interface-number | ip source-ip-address }
By default, no source IP address is specified. The device uses the primary IP address of the output interface as the source IP address.
4. Return to user view.
quit
5. Download or upload a file in an IPv4 network.
tftp tftp-server { get | put | sget } source-filename [ destination-filename ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ dscp dscp-value | source { interface interface-type interface-number | ip source-ip-address } ] *
The source IP address specified in this command takes precedence over the source IP address set by using the tftp client source command.
Configuring and using the IPv6 TFTP client
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. (Optional.) Use an ACL to control the client's access to TFTP servers.
tftp-server ipv6 acl ipv6-acl-number
By default, no ACL is used for access control.
3. Specify the source IPv6 address for TFTP packets sent by the TFTP client.
tftp client ipv6 source { interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6 source-ipv6-address }
By default, no source IPv6 address is specified. The source address is automatically selected as defined in RFC 3484.
4. Return to user view.
quit
5. Download or upload a file in an IPv6 network.
tftp ipv6 tftp-server [ -i interface-type interface-number ] { get | put | sget } source-filename [ destination-filename ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ dscp dscp-value | source { interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6 source-ipv6-address } ] *
The source IP address specified in this command takes precedence over the one set by the tftp client ipv6 source command.