- Table of Contents
-
- 08-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA configuration
- 02-802.1X configuration
- 03-MAC authentication configuration
- 04-Portal configuration
- 05-Web authentication configuration
- 06-Triple authentication configuration
- 07-Port security configuration
- 08-User profile configuration
- 09-Password control configuration
- 10-Keychain configuration
- 11-Public key management
- 12-PKI configuration
- 13-IPsec configuration
- 14-SSH configuration
- 15-SSL configuration
- 16-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 17-IP source guard configuration
- 18-ARP attack protection configuration
- 19-ND attack defense configuration
- 20-uRPF configuration
- 21-SAVI configuration
- 22-MFF configuration
- 23-Crypto engine configuration
- 24-FIPS configuration
- 25-802.1X client configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 21-SAVI configuration | 94.92 KB |
Configuring ND snooping and ND attack detection
Setting the entry deletion delay
Example: Configuring DHCPv6-only SAVI
Example: Configuring SLAAC-only SAVI
Example: Configuring DHCPv6+SLAAC SAVI
Configuring SAVI
About SAVI
Source Address Validation Improvement (SAVI) checks the validity of the source addresses of DHCPv6 messages, ND messages, and IPv6 data packets. It implements the validity check by using the ND snooping, DHCPv6 snooping, and IP source guard features. SAVI checks only global unicast addresses and forwards the packets that pass the validity check. Packets sourced from an invalid address are dropped.
SAVI application scenarios
DHCPv6-only
The hosts connected to the SAVI-enabled device obtain addresses only through DHCPv6. In this scenario, SAVI drops all RA and RR messages. DHCPv6 messages, ND messages (RA and RR messages excluded), and IPv6 data packets are checked.
SLAAC-only
The hosts connected to the SAVI-enabled device obtain addresses only through Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC). In this scenario, SAVI drops all DHCPv6 messages. Only ND messages and IPv6 data packets are checked.
DHCPv6+SLAAC
The hosts connected to the SAVI-enabled device obtain addresses through DHCPv6 and SLAAC. In this scenario, SAVI checks all DHCPv6 messages, ND messages, and IPv6 data packets.
SAVI tasks at a glance
|
Tasks at a glance |
|
(Required.) Enabling SAVI |
|
(Required.) Configuring IP source guard |
|
(Required.) Configuring DHCPv6 snooping |
|
(Required.) Configuring ND snooping and ND attack detection |
|
(Optional.) Setting the entry deletion delay |
Enabling SAVI
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable SAVI. |
ipv6 savi strict |
By default, SAVI is disabled. |
Configuring IP source guard
|
Step |
Command |
|
1. Enable IPv6 source guard on an interface. |
See "Configuring IP source guard." |
|
2. (Optional.) Configure static IPv6SG bindings. |
Configuring DHCPv6 snooping
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enable DHCPv6 snooping. |
See DHCPv6 configuration in Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide. |
Perform only this step for the SLAAC-only scenario. |
|
2. Specify DHCPv6 snooping trusted ports. |
N/A |
|
|
3. Enable recording client information in DHCPv6 snooping entries. |
N/A |
Configuring ND snooping and ND attack detection
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enable ND snooping for global unicast addresses. |
See IPv6 basics in Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide. |
N/A |
|
2. Enable ND attack detection. |
See "Configuring ND attack defense." |
Perform only this step for the DHCPv6-only scenario. |
|
3. Specify ND trusted ports. |
N/A |
Setting the entry deletion delay
The entry deletion delay is the period of time that the device waits before deleting the DHCPv6 snooping entries and ND snooping entries for a down port.
To set the entry deletion delay:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Set the entry deletion delay. |
ipv6 savi down-delay delay-time |
By default, the entry deletion delay is 30 seconds. |
SAVI configuration examples
Example: Configuring DHCPv6-only SAVI
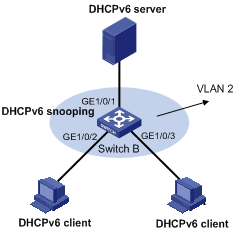
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, configure SAVI on Switch B to meet the following requirements:
· Clients obtain IPv6 addresses only through DHCPv6.
· RA and RR messages are dropped on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 in VLAN 2.
· SAVI checks the source addresses of DHCPv6 messages, ND messages (RA and RR messages excluded), and IPv6 data packets on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3.
Procedure
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ipv6 savi strict
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 2.
[SwitchB] vlan 2
[SwitchB-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 gigabitethernet 1/0/2 gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-vlan2] quit
# Enable DHCPv6 snooping.
[SwitchB] ipv6 dhcp snooping enable
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 as a DHCPv6 snooping trusted port.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipv6 dhcp snooping trust
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Enable recording DHCPv6 snooping entries on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ipv6 dhcp snooping binding record
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ipv6 dhcp snooping binding record
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Enable ND attack detection.
[SwitchB] vlan 2
[SwitchB-vlan2] ipv6 nd detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan2] quit
# Enable IPv6 source guard on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ipv6 verify source ip-address mac-address
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ipv6 verify source ip-address mac-address
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
Example: Configuring SLAAC-only SAVI
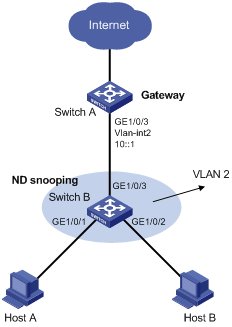
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, configure SAVI on Switch B to meet the following requirements:
· Hosts obtain IPv6 addresses only through SLAAC.
· DHCPv6 messages are dropped on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 in VLAN 2.
· SAVI checks the source addresses of ND messages and IPv6 data packets on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
Procedure
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ipv6 savi strict
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 2.
[SwitchB] vlan 2
[SwitchB-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 gigabitethernet 1/0/2 gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-vlan2] quit
# Enable ND snooping for global unicast addresses in VLAN 2.
[SwitchB] vlan 2
[SwitchB-vlan2] ipv6 nd snooping enable global
# Enable ND attack detection for VLAN 2.
[SwitchB-vlan2] ipv6 nd detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan2] quit
# Enable DHCPv6 snooping.
[SwitchB] ipv6 dhcp snooping enable
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 as an ND trusted port.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ipv6 nd detection trust
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Enable IPv6 source guard on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip verify source ip-address mac-address
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ip verify source ip-address mac-address
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
Example: Configuring DHCPv6+SLAAC SAVI
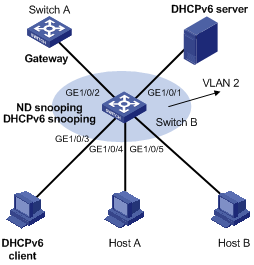
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, configure SAVI on Switch B to meet the following requirements:
· Hosts obtain IP addresses through DHCPv6 or SLAAC.
· SAVI checks the source addresses of DHCPv6 messages, ND messages, and IPv6 data packets on GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/5.
Procedure
# Enable SAVI.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ipv6 savi strict
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/5 to VLAN 2.
[SwitchB] vlan 2
[SwitchB-vlan2] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 gigabitethernet 1/0/2 gigabitethernet 1/0/3 gigabitethernet 1/0/4 gigabitethernet 1/0/5
# Enable DHCPv6 snooping.
[SwitchB] ipv6 dhcp snooping enable
# Enable recording DHCPv6 snooping entries on GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/5.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ipv6 dhcp snooping binding record
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] ipv6 dhcp snooping binding record
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] ipv6 dhcp snooping binding record
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 as a DHCPv6 snooping trusted port.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipv6 dhcp snooping trust
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Enable ND snooping for global unicast addresses in VLAN 2.
[SwitchB] vlan 2
[SwitchB-vlan2] ipv6 nd snooping enable global
# Enable ND attack detection for VLAN 2.
[SwitchB-vlan2] ipv6 nd detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan2] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 as an ND trusted port.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ipv6 nd detection trust
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Enable IPv6 source guard on GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/5.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ip verify source ipv6 ip-address mac-address
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] ip verify source ipv6 ip-address mac-address
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] ip verify source ipv6 ip-address mac-address
