- Table of Contents
-
- 13-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-System maintenance and debugging configuration
- 02-NQA configuration
- 03-NTP configuration
- 04-SNMP configuration
- 05-RMON configuration
- 06-Event MIB configuration
- 07-NETCONF configuration
- 08-CWMP configuration
- 09-EAA configuration
- 10-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 11-Sampler configuration
- 12-Mirroring configuration
- 13-NetStream configuration
- 14-IPv6 NetStream configuration
- 15-sFlow configuration
- 16-Fast log output configuration
- 17-Flow log configuration
- 18-Information center configuration
- 19-GOLD configuration
- 20-Packet capture configuration
- 21-VNF connection configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 20-Packet capture configuration | 100.11 KB |
Restrictions and guidelines: Packet capture configuration
Packet capture tasks at a glance
Configuring packet capture settings
Display and maintenance commands for packet capture
Packet capture configuration examples
Example: Configuring packet capture
Configuring packet capture
About packet capture
The packet capture feature captures incoming and outgoing packets, generates packet capture records, and saves the records to a .cap file. The file can reside on the device or a remote file server. You can use a packet analyzer such as Wireshark to view the file for traffic analysis.
The minimum packet capture unit is a packet. The packet capture process is as follows:
1. The device captures a specific number of bytes from a packet and generates a packet capture record, ignoring the remaining part of the packet (if any).
2. The device saves the packet capture record in memory.
3. When the maximum number of packet capture records for a file is reached, the device saves the records to a file and clears the records in memory.
Restrictions and guidelines: Packet capture configuration
Start packet capture only when necessary. Packet capture affects device performance.
Only one packet capture process can run on the device.
You can configure packet capture parameters only when packet capture is not started.
If packet capture saves .cap files on the device, back up the .cap files on the device as required after you finish packet capture. Starting packet capture again deletes the existing .cap files.
Packet capture tasks at a glance
To configure packet capture, perform the following tasks:
1. Configuring packet capture settings
Configuring packet capture settings
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the maximum packet size for a packet capture record.
packet-capture max-bytes bytes
By default, the maximum packet size is 1600 bytes for a packet capture record.
To capture all bytes of packets, make sure the maximum packet size for a packet capture record is equal to or greater than the interface MTU.
3. Set the maximum number of packet capture records for a file.
packet-capture max-file-packets number
By default, the maximum number of packet capture records is 100 for a file.
4. Specify the storage directory for the .cap files.
packet-capture storage { local [ limit limit-space ] | remote serverpath [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ user username [ password { cipher | simple } string ] ] }
The default storage directory is the pcap directory of the default file system.
The default storage directory is the pcap directory of the default file system on the master. (In IRF mode.)
Starting packet capture
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Start packet capture.
packet-capture start [ acl { acl-number | ipv6 acl-number } | interface interface-type interface-number ] *
By default, the system does not capture packets.
Stopping packet capture
About stopping packet capture
Saving packet capture records to a file takes time. The packet-capture stop command without the immediately keyword saves all packet capture records to a file before stopping packet capture. If you do not want to use the packet capture records in memory, execute the packet-capture stop immediately command.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Stop packet capture.
packet-capture stop [ immediately ]
Display and maintenance commands for packet capture
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Command |
|
|
Display packet capture settings and status information. |
display packet-capture status |
Packet capture configuration examples
Example: Configuring packet capture
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 1, capture packets on GigabitEthernet 1/0. Set the maximum packet size for a packet capture record to 3000 bytes. Use a remote file server to save the .cap files.
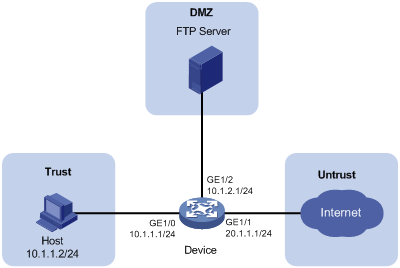
Configuration procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces and configure routes, security zones, zone pairs, and interzone policies. Make sure the network connections are available. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure packet capture:
# Set the storage directory for the .cap files to ftp://ftp.remote.com/pcap/. Specify the username and password for accessing the FTP server.
<Device> system-view
[Device] packet-capture storage remote ftp://ftp.remote.com/pcap/ user zhangsan password simple 123
# Set the maximum packet size for a packet capture record to 3000 bytes.
[Device] packet-capture max-bytes 3000
# Start packet capture on GigabitEthernet 1/0.
[Device] packet-capture start interface gigabitethernet 1/0
Verifying the configuration
# Display packet capture settings and status information.
[Device] display packet-capture status
Capture status: Started
Filter: Interface GigabitEthernet1/0
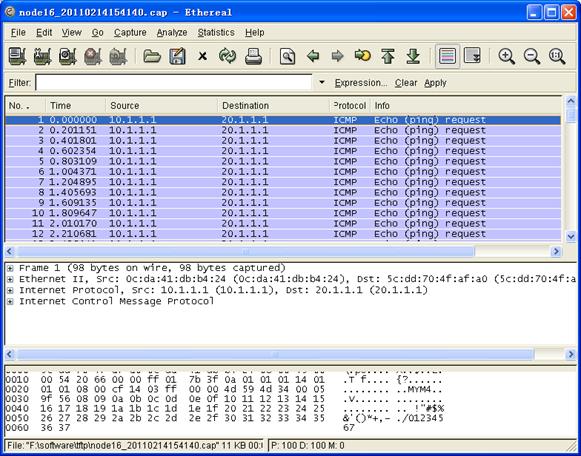
# Use a packet analyzer to display captured packets. In this example, Ethereal is used.
Figure 2 Displaying the captured packets on Ethereal