- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-IGMP Snooping Configuration | 331.69 KB |
Basic concepts in IGMP snooping
IGMP snooping configuration task list
Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions
Specifying the version of IGMP snooping
Configuring IGMP snooping port functions
Setting aging timers for dynamic ports
Configuring a port as a simulated member host
Enabling IGMP snooping fast-leave processing
Disabling a port from becoming a dynamic router port
Configuring IGMP snooping querier
Enabling IGMP snooping querier
Configuring parameters for IGMP queries and responses
Configuring source IP addresses for IGMP queries
Configuring IGMP snooping policies
Configuring a multicast group filter
Enabling dropping unknown multicast data
Enabling IGMP report suppression
Setting the maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join
Enabling multicast group replacement
Setting the 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages
Enabling the IGMP snooping host tracking function
Enabling the PIM hello proxy function
Displaying and maintaining IGMP snooping
IGMP snooping configuration examples
Group policy configuration example
Static port configuration example
Layer 2 multicast forwarding cannot function
Configured multicast group policy fails to take effect
The term "router" in this document refers to both routers and access points.
Overview
IGMP snooping is a multicast constraining mechanism that runs on Layer 2 devices to manage and control multicast groups.
By analyzing received IGMP messages, an IGMP snooping–enabled Layer 2 device establishes mappings between ports and multicast MAC addresses, and forwards multicast data based on these mappings.
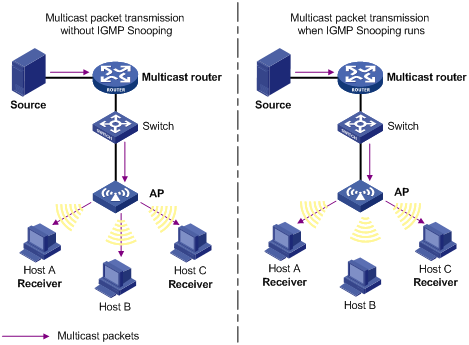
As shown in Figure 1, without IGMP snooping, the AP floods multicast packets out of all ports but the incoming port. IGMP snooping enables the AP to forward multicast packets destined for a known multicast group address out of only ports that have multicast receivers. This feature improves bandwidth efficiency, enhances multicast security, and helps per-host accounting for multicast users.
Figure 1 Before and after IGMP snooping is enabled on the Layer 2 device
Basic concepts in IGMP snooping
This section lists the basic concepts in IGMP snooping.
IGMP snooping related ports
As shown in Figure 2, the router connects to the multicast source, IGMP snooping runs on the switch and the AP, and Host A and Host B are receiver hosts as members of a multicast group.
Figure 2 IGMP snooping related ports
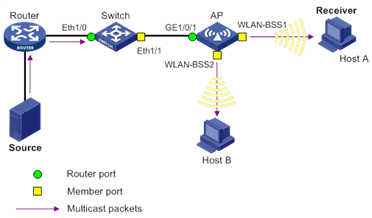
As shown in Figure 2, IGMP snooping divides the ports on Layer 2 switch into the following types:
· Router port—Layer 3 multicast device-side port. Layer 3 multicast devices include DRs and IGMP queriers. In the figure, Ethernet 1/0 of the switch and GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of the AP are router ports. The switch and the AP register all their local router ports in their router port lists.
Do not confuse the "router port" in IGMP snooping with the "routed interface" commonly known as the "Layer 3 interface." The router port in IGMP snooping is the Layer 2 interface.
· Member port—Multicast receiver-side port. In the figure, Ethernet 1/1 of the switch and WLAN-BSS 1 and WLAN-BSS 2 of the AP are member ports. The switch and the AP register all their local member ports in their IGMP snooping forwarding tables.
Unless otherwise specified, router ports and member ports in this document include both static and dynamic router ports and member ports.
Dynamic router ports include ports that receive IGMP general queries with the source IP address other than 0.0.0.0 and ports that receive PIM hello messages. For more information about PIM hello messages, see "Configuring PIM."
Aging timers for dynamic ports in IGMP snooping and related messages and actions
|
Timer |
Description |
Message before expiry |
Action after expiry |
|
Dynamic router port aging timer. |
For each dynamic router port, the AP starts an aging timer. When the timer expires, the dynamic router port ages out. |
IGMP general query of which the source address is not 0.0.0.0 or PIM hello message. |
The AP removes this port from its router port list. |
|
Dynamic member port aging timer. |
When a port dynamically joins a multicast group, the AP starts an aging timer for the port. When the timer expires, the dynamic member port ages out. |
IGMP membership report. |
The AP removes this port from the IGMP snooping forwarding table. |
|
|
NOTE: In IGMP snooping, only dynamic ports age out. Static ports never age out. |
How IGMP snooping works
An IGMP snooping–enabled AP performs different actions when it receives different IGMP messages.
The ports in this section are dynamic ports. For information about how to configure and remove static ports, see "Configuring static ports."
When receiving a general query
The IGMP querier periodically sends IGMP general queries to all hosts and routers (224.0.0.1) on the local subnet to determine whether any active multicast group members exist on the subnet.
After receiving an IGMP general query, the AP forwards it to all ports in the VLAN, except the port that received the query. The AP also performs one of the following actions:
· If the receiving port is a dynamic router port in the router port list, restarts the aging timer for the port.
· If the receiving port is not in the router port list, adds it into the router port list as a dynamic router port and starts an aging timer for the port.
When receiving a membership report
A host sends an IGMP report to the IGMP querier for the following purposes:
· If the host has been a member of a multicast group, responds to an IGMP query.
· Applies for joining a multicast group.
After receiving an IGMP report, the AP forwards it through all the router ports in the VLAN, resolves the address of the reported multicast group, and performs the following judgment:
· If no forwarding entry matches the group address, the AP creates a forwarding entry for the group, adds the port that received the IGMP report as a dynamic member port to the forwarding entry, and starts an aging timer for the port.
· If a forwarding entry matches the group address, but the port that received the IGMP report is not in the forwarding entry for the group, the AP adds the port as a dynamic member port to the forwarding entry, and starts an aging timer for the port.
· If a forwarding entry matches the group address and the port that received the IGMP report is in the forwarding entry for the group, the AP restarts the aging timer for the port.
The AP does not forward an IGMP report through a non-router port. If the AP forwards a report message through a member port, the IGMP report suppression mechanism causes all attached hosts that monitor the reported multicast address to suppress their own reports. This makes the AP unable to know whether the reported multicast group still has active members attached to that port. For more information about the IGMP report suppression mechanism, see "Configuring IGMP."
When receiving a leave message
An IGMPv1 host silently leaves a multicast group and the AP is not notified of the leave. However, because the host stops sending IGMP reports as soon as it leaves the multicast group, the AP removes the port that connects to the host from the forwarding entry for the multicast group when the aging timer for the port expires.
An IGMPv2 or IGMPv3 host sends an IGMP leave message to the multicast router when leaving a multicast group.
When the AP receives an IGMP leave message on a dynamic member port, the AP first examines whether a forwarding entry matches the group address in the message, and, if a match is found, whether the forwarding entry for the group contains the dynamic member port.
· If no forwarding entry matches the group address, or if the forwarding entry does not contain the port, the AP directly discards the IGMP leave message.
· If a forwarding entry matches the group address and the forwarding entry contains the port, the AP forwards the leave message to all router ports in the VLAN. Because the AP does not know whether any other hosts attached to the port are still listening to that group address, the AP does not immediately remove the port from the forwarding entry for that group. Instead, it restarts the aging timer for the port.
After receiving the IGMP leave message, the IGMP querier resolves the multicast group address in the message and sends an IGMP group-specific query to the multicast group through the port that received the leave message. After receiving the IGMP group-specific query, the AP forwards it through all its router ports in the VLAN and all member ports of the multicast group. The AP also performs the following judgment for the port that received the IGMP leave message:
· If the port (assuming that it is a dynamic member port) receives an IGMP report in response to the group-specific query before its aging timer expires, it indicates that some host attached to the port is receiving or expecting to receive multicast data for the multicast group. The AP restarts the aging timer for the port.
· If the port receives no IGMP report in response to the group-specific query before its aging timer expires, it indicates that no hosts attached to the port are still listening to that group address. The AP removes the port from the forwarding entry for the multicast group when the aging timer expires.
Protocols and standards
RFC 4541, Considerations for Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) and Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) Snooping Switches
IGMP snooping configuration task list
For the configuration tasks in this section, the following rules apply:
· The configurations made in IGMP-snooping view are effective for all VLANs. The configurations made in VLAN view are effective for only the current VLAN. For a given VLAN, a configuration made in IGMP-snooping view is effective only if you do not make the same configuration in VLAN view.
· The configurations made in IGMP-snooping view are effective for all ports. The configurations made in Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view are effective for only the current port. The configurations made in port group view are effective for all ports in only the current port group. For a given port, a configuration made in IGMP-snooping view is effective only if you do not make the same configuration in Layer 2 Ethernet interface view, Layer 2 aggregate interface view, or port group view.
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
|
Required. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Setting the maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join |
Optional. |
|
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions
This section describes how to configure basic IGMP snooping functions.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure basic IGMP snooping functions, complete the following tasks:
· Configure the corresponding VLANs.
· Determine the version of IGMP snooping.
Enabling IGMP snooping
When you enable IGMP snooping, follow these guidelines:
· Enable IGMP snooping globally before you enable it for a VLAN.
· IGMP snooping for a VLAN works on only the ports within that VLAN.
To enable IGMP snooping:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable IGMP snooping globally and enter IGMP-snooping view. |
igmp-snooping |
Disabled by default. |
|
3. Return to system view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
4. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
5. Enable IGMP snooping in the VLAN. |
igmp-snooping enable |
Disabled by default. |
Specifying the version of IGMP snooping
Different versions of IGMP snooping can process different versions of IGMP messages:
· IGMPv2 snooping can process IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 messages, but flood IGMPv3 messages in the VLAN instead of processing them.
· IGMPv3 snooping can process IGMPv1, IGMPv2, and IGMPv3 messages.
If you change IGMPv3 snooping to IGMPv2 snooping, the system does the following:
· Clears all IGMP snooping forwarding entries that are dynamically added.
· Keeps static IGMPv3 snooping forwarding entries (*, G).
· Clears static IGMPv3 snooping forwarding entries (S, G), which will be restored when IGMP snooping is switched back to IGMPv3 snooping.
For more information about static joins, see "Configuring static ports."
To specify the version of IGMP snooping:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
3. Specify the version of IGMP snooping. |
igmp-snooping version version-number |
IGMPv2 snooping by default. |
Configuring IGMP snooping port functions
This section describes how to configure IGMP snooping port functions.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure IGMP snooping port functions, complete the following tasks:
· Enable IGMP snooping in the VLAN.
· Configure the corresponding port groups.
· Determine the aging timer for dynamic router ports.
· Determine the aging timer for dynamic member ports.
· Determine the multicast group and multicast source addresses.
Setting aging timers for dynamic ports
If the AP does not receive IGMP general queries or PIM hello messages on a dynamic router port when the aging timer of the port expires, the AP removes the port from the router port list.
If the AP receives no IGMP reports for a multicast group on a dynamic member port when the aging timer of the port expires, the AP removes the port from the multicast forwarding entry for that multicast group.
If the memberships of multicast groups change frequently, you can set a relatively small value for the aging timer of the dynamic member ports. If the memberships of multicast groups change rarely, you can set a relatively large value.
Setting aging timers for dynamic ports globally
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter IGMP-snooping view. |
igmp-snooping |
N/A |
|
3. Set the global aging timer for dynamic router ports. |
router-aging-time interval |
105 seconds by default. |
|
4. Set the global aging timer for dynamic member ports. |
host-aging-time interval |
260 seconds by default. |
Setting aging timers for the dynamic ports in a VLAN
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
3. Set the aging timer for dynamic router ports in the VLAN. |
igmp-snooping router-aging-time interval |
105 seconds by default. |
|
4. Set the aging timer for dynamic member ports in the VLAN. |
igmp-snooping host-aging-time interval |
260 seconds by default. |
Configuring static ports
If all hosts attached to a port are interested in the multicast data addressed to a particular multicast group or the multicast data that a particular multicast source sends to a particular group, you can configure the port as a static member port for the specified multicast group or the specified multicast source and group.
Configuration guidelines
· A static member port does not respond to queries from the IGMP querier. When you configure a port as a static member port or cancel this configuration on the port, the port does not unsolicitedly send any IGMP report or an IGMP leave message.
· Static member ports never age out. To remove such a port, use the corresponding undo command.
Configuration procedure
To configure static ports:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view, Layer 2 aggregate interface view, or port group view. |
·
Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer
2 aggregate interface view: ·
Enter port group view: |
Use either command. |
|
3. Configure the port as a static member port. |
igmp-snooping static-group group-address [ source-ip source-address ] vlan vlan-id |
No static member ports exist by default. |
Configuring a port as a simulated member host
Generally, a host that runs IGMP can respond to IGMP queries. If a host fails to respond, the multicast router might deem that no member of this multicast group exists on the subnet, and removes the corresponding forwarding path.
To avoid this situation, you can configure the port as a simulated member host for a multicast group. When the simulated member host receives an IGMP query, it gives a response. Therefore, the AP can continue receiving multicast data.
A simulated host is equivalent to an independent host in the following ways:
· When a port is configured as a simulated member host, the AP sends an unsolicited IGMP report through the port, and can respond to IGMP general queries with IGMP reports through the port.
· When you disable the simulated joining function on the port, the AP sends an IGMP leave message through the port.
To configure a port as a simulated member host:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view, Layer 2 aggregate interface view, or port group view. |
·
Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer
2 aggregate interface view: ·
Enter port group view: |
Use either command. |
|
3. Configure the port as a simulated member host. |
igmp-snooping host-join group-address [ source-ip source-address ] vlan vlan-id |
Not configured by default. |
|
|
NOTE: Unlike a static member port, a port configured as a simulated member host ages out like a dynamic member port. |
Enabling IGMP snooping fast-leave processing
On a port that has only one host attached, you can enable fast-leave processing to save bandwidth and resources. However, on a port that has multiple hosts attached, you should not enable fast-leave processing if you have enabled dropping unknown multicast data globally or for the port. Otherwise, if a host on the port leaves a multicast group, the other hosts attached to the port in the same multicast group cannot receive the multicast data for the group.
Enabling IGMP snooping fast-leave processing globally
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter IGMP-snooping view. |
igmp-snooping |
N/A |
|
3. Enable IGMP snooping fast-leave processing. |
fast-leave [ vlan vlan-list ] |
Disabled by default. |
Enabling IGMP snooping fast-leave processing for a port
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view, Layer 2 aggregate interface view, or port group view. |
·
Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer
2 aggregate interface view: ·
Enter port group view: |
Use either command. |
|
3. Enable IGMP snooping fast-leave processing for the port. |
igmp-snooping fast-leave [ vlan vlan-list ] |
Disabled by default. |
Disabling a port from becoming a dynamic router port
The following problems might exist in a multicast access network:
· After receiving an IGMP general query or a PIM hello message from a connected host, a router port becomes a dynamic router port. Before its timer expires, this dynamic router port receives all multicast packets within the VLAN where the port belongs, and forwards them to the host, affecting normal multicast reception of the host.
· In addition, the IGMP general query or PIM hello message that the host sends affects the multicast routing protocol state on Layer 3 devices, such as the IGMP querier or DR election, and might further cause network interruption.
To solve these problems, disable that router port from becoming a dynamic router port after the port receives an IGMP general query or a PIM hello message, so as to improve network security and the control over multicast users.
To disable a port from becoming a dynamic router port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view, Layer 2 aggregate interface view, or port group view. |
·
Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer
2 aggregate interface view: ·
Enter port group view: |
Use either command. |
|
3. Disable the port from becoming a dynamic router port. |
igmp-snooping router-port-deny [ vlan vlan-list ] |
By default, a port can become a dynamic router port. This configuration does not affect the static router port configuration. |
Configuring IGMP snooping querier
This section describes how to configure IGMP snooping querier.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure IGMP snooping querier, complete the following tasks:
· Enable IGMP snooping in the VLAN.
· Determine the interval for sending IGMP general queries.
· Determine the IGMP last-member query interval.
· Determine the maximum response delay for IGMP general queries.
· Determine the source address of IGMP general queries.
· Determine the source address of IGMP group-specific queries.
Enabling IGMP snooping querier
However, a Layer 2 multicast switch does not support IGMP, and therefore cannot send general queries by default. When you configure an IGMP snooping querier on a Layer 2 switch in a VLAN where multicast traffic is switched only at Layer 2 and no multicast routers are present, the Layer 2 switch sends IGMP queries, so that multicast forwarding entries can be established and maintained at the data link layer.
It is meaningless to configure an IGMP snooping querier in a multicast network that runs IGMP. Although an IGMP snooping querier does not take part in IGMP querier elections, it might affect IGMP querier elections because it sends IGMP general queries with a low source IP address.
To enable IGMP snooping querier in a VLAN:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
3. Enable IGMP snooping querier. |
igmp-snooping querier |
Disabled by default. |
Configuring parameters for IGMP queries and responses
|
|
CAUTION: Make sure the interval for sending IGMP general queries is larger than the maximum response delay for IGMP general queries. Otherwise, multicast group members might be deleted by mistake. |
You can modify the IGMP general query interval based on actual condition of the network.
A multicast listening host starts a timer for each multicast group that it has joined when it receives an IGMP query (general query or group-specific query). This timer is initialized to a random value in the range of 0 to the maximum response delay advertised in the IGMP query message. When the timer value decreases to 0, the host sends an IGMP report to the multicast group.
To speed up the response of hosts to IGMP queries and avoid simultaneous timer expirations causing IGMP report traffic bursts, you must properly set the maximum response delay.
· The maximum response delay for IGMP general queries is set by the max-response-time command.
· The maximum response delay for IGMP group-specific queries equals the IGMP last-member query interval.
Configuring the global parameters for IGMP queries and responses
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter IGMP-snooping view. |
igmp-snooping |
N/A |
|
3. Set the maximum response delay for IGMP general queries. |
max-response-time interval |
10 seconds by default. |
|
4. Set the IGMP last-member query interval. |
last-member-query-interval interval |
1 second by default. |
Configuring the parameters for IGMP queries and responses in a VLAN
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
3. Set the interval for sending IGMP general queries. |
igmp-snooping query-interval interval |
60 seconds by default. |
|
4. Set the maximum response delay for IGMP general queries. |
igmp-snooping max-response-time interval |
10 seconds by default. |
|
5. Set the IGMP last-member query interval. |
igmp-snooping last-member-query-interval interval |
1 second by default. |
Configuring source IP addresses for IGMP queries
After the AP receives an IGMP query whose source IP address is 0.0.0.0 on a port, it does not enlist that port as a dynamic router port. This might prevent multicast forwarding entries from being correctly created at the data link layer and eventually cause multicast traffic forwarding to fail. To avoid this problem, when the AP acts as the IGMP snooping querier, H3C recommends that you configure a non-all-zero IP address as the source IP address of IGMP queries.
Changing the source address of IGMP queries might affect the IGMP querier election within the subnet.
To configure source IP addresses for IGMP queries in a VLAN:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the source IP address for IGMP general queries. |
igmp-snooping general-query source-ip { ip-address | current-interface } |
0.0.0.0 by default. |
|
4. Configure the source IP address for IGMP group-specific queries. |
igmp-snooping special-query source-ip { ip-address | current-interface } |
0.0.0.0 by default. |
Configuring IGMP snooping policies
This section describes how to configure IGMP snooping policies.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure IGMP snooping policies, complete the following tasks:
· Enable IGMP snooping for the VLAN.
· Determine the ACL rule for multicast group filtering.
· Determine the maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join.
· Determine the 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages.
Configuring a multicast group filter
On an IGMP snooping–enabled AP, you can configure a multicast group filter to limit multicast programs available to users.
In an application, when a user requests a multicast program, the user's host initiates an IGMP report. After receiving this report message, the AP resolves the multicast group address in the report and looks up the ACL. If a match is found to permit the port that received the report to join the multicast group, the AP creates an IGMP snooping forwarding entry for the multicast group and adds the port to the forwarding entry. Otherwise, the AP drops this report message. In this case, the multicast data for the multicast group is not sent to this port, and the user cannot retrieve the program.
Configuring a multicast group filter globally
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter IGMP-snooping view. |
igmp-snooping |
N/A |
|
3. Configure a multicast group filter globally. |
group-policy acl-number [ vlan vlan-list ] |
By default, no group filter is globally configured. A host can join any valid multicast group. |
Configuring a multicast group filter for a port
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view, Layer 2 aggregate interface view, or port group view. |
·
Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer
2 aggregate interface view: ·
Enter port group view: |
Use either command. |
|
3. Configure a multicast group filter. |
igmp-snooping group-policy acl-number [ vlan vlan-list ] |
By default, no group filter is configured on the current port. The hosts on this port can join any valid multicast group. |
Enabling dropping unknown multicast data
Unknown multicast data refers to multicast data for which no forwarding entries exist in the IGMP snooping forwarding table. When the AP receives such multicast traffic, one of the following occurs:
· When the function of dropping unknown multicast data is disabled, the AP floods unknown multicast data in the VLAN that the unknown multicast data belongs to.
· When the function of dropping unknown multicast data is enabled, the AP drops all received unknown multicast data.
If you enable this function in IGMP-snooping view, you should not enable or disable it in VLAN view, or vice versa.
Enabling dropping unknown multicast data globally
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter IGMP-snooping view. |
igmp-snooping |
N/A |
|
3. Enable dropping unknown multicast data globally. |
drop-unknown |
Disabled by default. |
Enabling dropping unknown multicast data in a VLAN
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
3. Enable dropping unknown multicast data. |
igmp-snooping drop-unknown |
Disabled by default. |
Enabling IGMP report suppression
Upon receiving an IGMP report from a multicast group member, the AP forwards the message to the Layer 3 device that directly connects to the Layer 2 switch. When multiple members of a multicast group are attached to the AP, the Layer 3 device might receive duplicate IGMP reports for the multicast group from these members.
With the IGMP report suppression function enabled, within each query interval, the AP forwards only the first IGMP report for the multicast group to the Layer 3 device. It does not forward the subsequent IGMP reports for the same multicast group. This helps reduce the number of packets being transmitted over the network.
To enable IGMP report suppression:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter IGMP-snooping view. |
igmp-snooping |
N/A |
|
3. Enable IGMP report suppression. |
report-aggregation |
Enabled by default. |
Setting the maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join
You can set the maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join to regulate traffic on the port.
When you configure this maximum number, if the number of multicast groups the port has joined exceeds the configured maximum value, the system deletes all the forwarding entries for the port from the IGMP snooping forwarding table, and the hosts on this port join multicast groups again until the number of multicast groups that the port joins reaches the maximum value. When the port joins a multicast group, if the port has been configured as a static member port, the system applies the configurations to the port again. If you have configured simulated joining on the port, the system establishes corresponding forwarding entry for the port after receiving a report from the simulated member host.
To set the maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view, Layer 2 aggregate interface view, or port group view. |
·
Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer
2 aggregate interface view: ·
Enter port group view: |
Use either command. |
|
3. Set the maximum number of multicast groups that the port can join. |
igmp-snooping group-limit limit [ vlan vlan-list ] |
The default depends on the product model. |
Enabling multicast group replacement
For various reasons, the number of multicast groups that the AP or a port joins might exceed the upper limit. In addition, in some specific applications, a multicast group that the AP newly joins must replace an existing multicast group automatically. A typical example is channel switching. To view a new channel, a user switches from the current multicast group to the new one.
To realize such requirements, you can enable the multicast group replacement function on the AP or on a certain port. When the number of multicast groups that the AP or on the port has joined reaches the limit, one of the following occurs:
· If the multicast group replacement feature is disabled, new IGMP reports are automatically discarded.
· If the multicast group replacement feature is enabled, the multicast group that the AP or the port newly joins automatically replaces an existing multicast group that has the lowest address.
|
|
IMPORTANT: Be sure to configure the maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join to a value other than the default one (see "Setting the maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join") before enabling multicast group replacement. Otherwise, the multicast group replacement functionality will not take effect. |
Enabling multicast group replacement globally
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter IGMP-snooping view. |
igmp-snooping |
N/A |
|
3. Enable multicast group replacement. |
overflow-replace [ vlan vlan-list ] |
Disabled by default. |
Enabling multicast group replacement on a port
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view, Layer 2 aggregate interface view, or port group view. |
·
Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer
2 aggregate interface view: ·
Enter port group view: |
Use either command. |
|
3. Enable multicast group replacement. |
igmp-snooping overflow-replace [ vlan vlan-list ] |
Disabled by default. |
Setting the 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages
You can change the 802.1p precedence of IGMP messages so that they can be assigned higher forwarding priority when congestion occurs on their outgoing ports.
Setting the 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages globally
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter IGMP-snooping view. |
igmp-snooping |
N/A |
|
3. Set the 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages. |
dot1p-priority priority-number |
The default 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages is 0. The global configuration takes effect for all VLANs. |
Setting the 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages in a VLAN
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
3. Set the 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages in the VLAN. |
igmp-snooping dot1p-priority priority-number |
The default 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages is 0. |
Enabling the IGMP snooping host tracking function
With the IGMP snooping host tracking function, the AP can record the information of the member hosts that are receiving multicast traffic, including the host IP address, running duration, and timeout time. You can monitor and manage the member hosts according to the recorded information.
Enabling the IGMP snooping host tracking function globally
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter IGMP-snooping view. |
igmp-snooping |
N/A |
|
3. Enable the IGMP snooping host tracking function globally. |
host-tracking |
Disabled by default. |
Enabling the IGMP snooping host tracking function in a VLAN
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
3. Enable the IGMP snooping host tracking function in the VLAN. |
igmp-snooping host-tracking |
Disabled by default. |
Enabling the PIM hello proxy function
This function is typically used in subway WLAN mesh deployment. It enables a train mesh point (MP) to forward the recorded PIM hello message through the new active mesh link after a mesh link switchover. Upon receiving the PIM hello message, the upstream device forwards subsequent multicast traffic to receivers through the new active mesh link.
To enable the PIM hello proxy function:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
3. Enable the PIM hello proxy function. |
igmp-snooping pim-hello-proxy enable |
Disabled by default. |
Displaying and maintaining IGMP snooping
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display IGMP snooping group information. |
display igmp-snooping group [ vlan vlan-id ] [ verbose ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display information about the hosts tracked by IGMP snooping. |
display igmp-snooping host vlan vlan-id group group-address [ source source-address ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display statistics for the IGMP messages learned through IGMP snooping. |
display igmp-snooping statistics [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Remove all the dynamic group entries of a specified IGMP snooping group or all IGMP snooping groups. |
reset igmp-snooping group { group-address | all } [ vlan vlan-id ] |
Available in user view. |
|
Clear statistics for the IGMP messages learned through IGMP snooping. |
reset igmp-snooping statistics |
Available in user view. |
IGMP snooping configuration examples
This section provides examples of configuring IGMP snooping.
Group policy configuration example
Network requirements
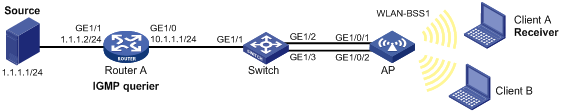
As shown in Figure 3:
· Link aggregation is configured on the switch and the AP.
· Router A runs IGMPv2 and acts as the IGMP querier. The switch and the AP run IGMPv2 snooping.
· Client A joins the multicast group 224.1.1.1 through a multicast client application (VLC media player).
Configure a multicast group policy on the AP so that Client A can receive multicast data only for the multicast group 224.1.1.1.
Configuration procedure
1. Assign an IP address and subnet mask to each interface according to Figure 3. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure Router A:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] multicast routing-enable
# Enable IGMP and PIM-DM on GigabitEthernet 1/0.
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0] igmp enable
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0] pim dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0] quit
# Enable PIM-DM on GigabitEthernet 1/1.
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/1] pim dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/1] quit
3. Configure the switch:
# Enable IGMP snooping globally.
<Switch> system-view
[Switch] igmp-snooping
[Switch-igmp-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100, and assign GigabitEthernet 1/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/3 to the VLAN.
[Switch] vlan 100
[Switch-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/1 to GigabitEthernet 1/3
# Enable IGMP snooping for VLAN 100.
[Switch-vlan100] igmp-snooping enable
[Switch-vlan100] quit
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 1.
[Switch] interface Bridge-Aggregation 1
[Switch-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/2 and GigabitEthernet 1/3 to link aggregation group 1.
[Switch] interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/2] port link-aggregation group 1
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/2] quit
[Switch] interface GigabitEthernet 1/3
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/3] port link-aggregation group 1
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/3] quit
# Configure Bridge-Aggregation 1 as a trunk port, and assign the port to VLAN 100.
[Switch] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[Switch-Bridge-Aggregation1] port link-type trunk
[Switch-Bridge-Aggregation1] port trunk permit vlan 100
# Configure Bridge-Aggregation 1 as a static router port of VLAN 100.
[Switch-Bridge-Aggregation1] igmp-snooping static-router-port vlan 100
[Switch-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
4. Configure the AP:
# Enable IGMP snooping globally.
<AP> system-view
[AP] igmp-snooping
[AP-igmp-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100, and assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, and WLAN-BSS 1 to the VLAN.
[AP] vlan 100
[AP-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[AP-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/0/2
[AP-vlan100] port WLAN-BSS1
# Enable IGMP snooping and dropping unknown multicast data for VLAN 100.
[AP-vlan100] igmp-snooping enable
[AP-vlan100] igmp-snooping drop-unknown
[AP-vlan100] quit
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 1.
[AP] interface Bridge-Aggregation 1
[AP-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to link aggregate group 1.
[AP] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[AP-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1
[AP-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[AP] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2
[AP-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1
[AP-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Configure Bridge-Aggregation 1 as a trunk port, and assign the port to VLAN 100.
[AP] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[AP-Bridge-Aggregation1] port link-type trunk
[AP-Bridge-Aggregation1] port trunk permit vlan 100
# Configure a multicast group filter for VLAN 100 so that hosts in the VLAN can join only the multicast group 224.1.1.1.
[AP] acl number 2001
[AP-acl-basic-2001] rule permit source 224.1.1.1 0
[AP-acl-basic-2001] quit
[AP] igmp-snooping
[AP-igmp-snooping] group-policy 2001 vlan 100
[AP-igmp-snooping] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Start the multicast client application on Client A to join the multicast group 224.1.1.1. (Details not shown.)
# Display detailed information about IGMP multicast groups for VLAN 100 on the AP.
[AP] display igmp-snooping group vlan 100 verbose
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Port flags: D-Dynamic port, S-Static port, C-Copy port
Vlan(id):100.
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Router port(s):total 1 port(s).
BAGG1 (D) ( 00:01:31 )
IP group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group.
IP group address:224.1.1.1
(0.0.0.0, 224.1.1.1):
Attribute: Host Port
Host port(s):total 2 port(s).
WLAN-BSS1 (D) ( 00:04:07 )
MAC group(s):
MAC group address:0100-5e01-0101
Host port(s):total 2 port(s).
WLAN-BSS1
The output shows that WLAN-BSS 1 on the AP has joined the multicast group 224.1.1.1 and VLAN 100 has only the entry of the multicast group 224.1.1.1.
Static port configuration example
Network requirements
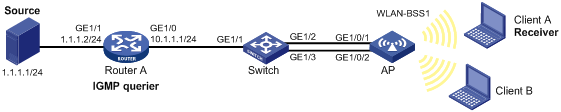
As shown in Figure 4:
· Link aggregation is configured on the switch and the AP.
· Router A runs IGMPv2 and acts as the IGMP querier. The switch and the AP run IGMPv2 snooping.
Configure a static member port on the AP so that client A can receive multicast data for the group 224.1.1.1 without a multicast client application.
Configuration procedure
1. Assign an IP address and subnet mask to each interface according to Figure 4. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure Router A:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] multicast routing-enable
# Enable IGMP and PIM-DM on GigabitEthernet 1/0.
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0] igmp enable
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0] pim dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0] quit
# Enable PIM-DM on GigabitEthernet 1/1.
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/1] pim dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/1] quit
3. Configure the switch:
# Enable IGMP snooping globally.
<Switch> system-view
[Switch] igmp-snooping
[Switch-igmp-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100, and assign GigabitEthernet 1/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/3 to the VLAN.
[Switch] vlan 100
[Switch-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/1 to GigabitEthernet 1/3
# Enable IGMP snooping for VLAN 100.
[Switch-vlan100] igmp-snooping enable
[Switch-vlan100] quit
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 1.
[Switch] interface Bridge-Aggregation 1
[Switch-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/2 and GigabitEthernet 1/3 to link aggregate group 1.
[Switch] interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/2] port link-aggregation group 1
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/2] quit
[Switch] interface GigabitEthernet 1/3
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/3] port link-aggregation group 1
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/3] quit
# Configure Bridge-Aggregation 1 as a trunk port, and assign the port to VLAN 100.
[Switch] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[Switch-Bridge-Aggregation1] port link-type trunk
[Switch-Bridge-Aggregation1] port trunk permit vlan 100
# Configure Bridge-Aggregation 1 as a static router port of VLAN 100.
[Switch-Bridge-Aggregation1] igmp-snooping static-router-port vlan 100
[Switch-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
4. Configure the AP:
# Enable IGMP snooping globally.
<AP> system-view
[AP] igmp-snooping
[AP-igmp-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100, and assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, and WLAN-BSS 1 to VLAN 100.
[AP] vlan 100
[AP-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[AP-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/0/2
[AP-vlan100] port WLAN-BSS1
# Enable IGMP snoop and dropping unknown multicast data for VLAN 100.
[AP-vlan100] igmp-snooping enable
[AP-vlan100] igmp-snooping drop-unknown
[AP-vlan100] quit
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 1.
[AP] interface Bridge-Aggregation 1
[AP-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to link aggregation group 1.
[AP] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[AP-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1
[AP-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[AP] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2
[AP-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1
[AP-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Configure Bridge-aggregation 1 as a trunk port, and assign the port to VLAN 100.
[AP] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[AP-Bridge-Aggregation1] port link-type trunk
[AP-Bridge-Aggregation1] port trunk permit vlan 100
# Configure Bridge-Aggregation 1 as a static member port of VLAN 100.
[AP-Bridge-Aggregation1] igmp-snooping static-group 224.1.1.1 vlan 100
[AP-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display detailed information about IGMP multicast groups for VLAN 100 on the AP.
[AP] display igmp-snooping group vlan 100 verbose
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Port flags: D-Dynamic port, S-Static port, C-Copy port, P-PIM port
Vlan(id):100.
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
IP group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group.
IP group address:224.1.1.1
(0.0.0.0, 224.1.1.1):
Attribute: Host Port
Host port(s):total 1 port(s).
BAGG1 (S)
MAC group(s):
MAC group address:0100-5e01-0101
Host port(s):total 1 port(s).
BAGG1 (S)
The output shows that Bridge-Aggregation 1 has statically joined the multicast group 224.1.1.1 and VLAN 100 has only the entry of the multicast group 224.1.1.1.
Troubleshooting IGMP snooping
This section describes common IGMP snooping problems and how to troubleshoot them.
Layer 2 multicast forwarding cannot function
Symptom
Layer 2 multicast forwarding cannot function.
Analysis
IGMP snooping is not enabled.
Solution
1. Use the display current-configuration command to view the running status of IGMP snooping.
2. If IGMP snooping is not enabled, use the igmp-snooping command in system view to enable IGMP snooping globally, and then use the igmp-snooping enable command in VLAN view to enable IGMP snooping for the VLAN.
3. If IGMP snooping is enabled globally but not enabled for the VLAN, use the igmp-snooping enable command in VLAN view to enable IGMP snooping for the VLAN.
Configured multicast group policy fails to take effect
Symptom
Although a multicast group policy has been configured to allow hosts to join specific multicast groups, the hosts can still receive multicast data addressed to other multicast groups.
Analysis
· The ACL rule is incorrectly configured.
· The multicast group policy is not correctly applied.
· The function of dropping unknown multicast data is not enabled, so unknown multicast data is flooded.
Solution
1. Use the display acl command to check the configured ACL rule. Make sure the ACL rule conforms to the multicast group policy to be implemented.
2. Use the display this command in IGMP-snooping view or in the corresponding interface view to verify that the correct multicast group policy has been applied. If not, use the group-policy or igmp-snooping group-policy command to apply the correct multicast group policy.
3. Use the display current-configuration command to verify that the function of dropping unknown multicast data is enabled. If not, use the drop-unknown or igmp-snooping drop-unknown command to enable the function of dropping unknown multicast data.
