- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-Voice entity commands | 227.65 KB |
Voice entity commands
The following compatibility matrix shows the support of hardware platforms for voice entities:
|
Hardware |
Voice entity compatibility |
|
MSR810, MSR810-W, MSR810-W-DB, MSR810-LM, MSR810-W-LM, MSR810-10-PoE, MSR810-LM-HK, MSR810-W-LM-HK, MSR810-LMS-EA |
MSR810, MSR810-W, MSR810-W-DB, MSR810-LM, MSR810-W-LM, MSR810-10-PoE, MSR810-LM-HK, MSR810-W-LM-HK: Yes for only VoIP entities and IVR entities MSR810-LMS-EA: No |
|
MSR810-LMS, MSR810-LUS |
No |
|
MSR2600-6-X1 |
No |
|
MSR2600-10-X1 |
Yes |
|
MSR 2630 |
Yes |
|
MSR3600-28, MSR3600-51 |
Yes |
|
MSR3600-28-SI, MSR3600-51-SI |
No |
|
MSR3600-28-X1, MSR3600-28-X1-DP, MSR3600-51-X1, MSR3600-51-X1-DP |
No |
|
MSR3610-I-DP, MSR3610-IE-DP |
No |
|
MSR3610-X1, MSR3610-X1-DP, MSR3610-X1-DC, MSR3610-X1-DP-DC |
Yes |
|
MSR 3610, MSR 3620, MSR 3620-DP, MSR 3640, MSR 3660 |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-G, MSR3620-G |
No |
To support voice entities, some device models require the Voice Software License. For more information, see license management in Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
answer-address
Use answer-address to configure a calling number string for a voice entity to match incoming calls.
Use undo answer-address to restore the default.
Syntax
answer-address calling-number-string
undo answer-address
Default
No calling number string is configured for a voice entity to match incoming calls.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
calling-number-string: Specifies a calling number string of 1 to 31 characters that is in the format of [ + ] { regular-expression [ T ] [ $ ] | T }. The following describe the characters:
· Plus sign (+): If the plus sign (+) is at the beginning of the string, the string indicates an E.164 standard number. For example, +110022 indicates that 110022 is an E.164 standard number.
· Dollar sign ($): Can be used only at the end of the string. The number must exactly match the string before the dollar sign. If the string has no dollar sign, the number template matches all numbers starting with the string. For example, the answer-address 20 command matches all numbers starting with 20.
· T: Indicates the timer. The system waits for the subscriber to dial any number until one of the following events occurs:
¡ The number length threshold is exceeded.
¡ The subscriber enters the terminator.
¡ The timer expires.
· regular-expression: Specifies a matching pattern of characters. Table 1 lists the available characters.
Table 1 Description of the characters in a regular-expression
|
Character |
Description |
|
0-9 |
Digits 0 through 9. |
|
Pound sign (#) or asterisk (*) |
Indicates a valid digit. |
|
Dot (.) |
Wildcard, which can match any valid digit. For example, 555…. can match any 7-digit numbers beginning with 555. |
|
Exclamation point (!) |
Indicates that the preceding subexpression appears zero or one time. For example, 56!1234 can match 51234 and 561234. |
|
Plus sign (+) |
Indicates that the preceding subexpression appears one or more times. For example, 9876(54)+ can match 987654, 98765454, 9876545454, and so on. |
|
Percent sign (%) |
Indicates that the preceding subexpression appears zero or more times. For example, 9876(54)% can match 9876, 987654, 98765454, 9876545454, and so on. |
|
Hyphen (-) |
Connects two digits to indicate a range of numbers, for example, [1-9] indicates 1 to 9, inclusive. The hyphen (-) can appear only in brackets ([ ]). |
|
Brackets ([ ]) |
Indicates a range. Only numbers 0 through 9 are allowed in the range. For example, [1-36] matches 1, 2, 3, or 6. |
|
Parentheses (( )) |
Indicates a string of characters. For example, (123) indicates a character string of 123. It is usually used together with signs such as exclamation point (!), percent sign (%), and plus sign (+). For example, 408(12)+ can match the character string 40812 or 408121212, but not 408. In this pattern, 408 must be followed by one string of 12 at a minimum. |
|
|
NOTE: · An exclamation point (!), plus sign (+), or percent sign (%) must follow a valid digit or digit string. · To use brackets ([ ]) and parentheses (( )) together, use them in the form of "( [ ] )". The "( ( ) )", "[ [ ] ]", and "[ ( ) ]" forms are not allowed. |
Usage guidelines
If the calling number of an incoming call matches the calling number string for a voice entity, the voice entity becomes the incoming voice entity of the call.
Examples
# Configure the calling number string as 456 for VoIP entity 1 to match incoming calls.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 1 voip
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity1] answer-address 456
codec
Use codec to configure a codec for a voice entity.
Use undo codec to restore the default.
Syntax
codec { g711alaw | g711ulaw | g723r53 | g723r63 | g726r16 | g726r24 | g726r32 | g726r40 | g729a | g729br8 | g729r8 } [ bytes payload-size ]
undo codec
Default
No codec is configured for a voice entity.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
IVR entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
g711alaw: Specifies the G.711 A-law codec at 64 kbps (without compression), which is typically used in Europe.
g711ulaw: Specifies the G.711 μ-law codec at 64 kbps (without compression), which is typically used in North America and Japan.
g723r53: Specifies the G.723.1 Annex A codec at 5.3 kbps.
g723r63: Specifies the G.723.1 Annex A codec at 6.3 kbps.
g726r16: Specifies the G.726 Annex A codec at 16 kbps. Support for this keyword depends on the line card.
g726r24: Specifies the G.726 Annex A codec at 24 kbps. Support for this keyword depends on the line card.
g726r32: Specifies the G.726 Annex A codec at 32 kbps. Support for this keyword depends on the line card.
g726r40: Specifies the G.726 Annex A codec at 40 kbps. Support for this keyword depends on the line card.
g729a: Specifies the G.729 Annex A codec (a simplified version of G.729) at 8 kbps.
g729br8: Specifies the G.729 Annex B codec at 8 kbps.
g729r8: Specifies the G.729 codec at 8 kbps.
bytes payload-size: Specifies the number of bytes sent per second.
Table 2 Value range and default of payload-size for codecs
|
Codec |
Value range (in bytes) |
Default (in bytes) |
|
g711alaw g711ulaw |
16 to 80 in multiples of 8, 80 to 240 in multiples of 80 |
160 |
|
g723r53 |
20 to 120 in multiples of 20 |
20 |
|
g723r63 |
24 to 144 in multiples of 24 |
24 |
|
g726r16 |
20 to 220 in multiples of 20 |
60 |
|
g726r24 |
30 to 210 in multiples of 30 |
90 |
|
g726r32 |
40 to 200 in multiples of 40 |
120 |
|
g726r40 |
50 to 200 in multiples of 50 |
150 |
|
g729a g729br8 g729r8 |
10 to 180 in multiples of 10 |
30 |
Usage guidelines
A call can be established only when the calling party and the called party use the same codec.
You can use this command to directly configure a codec for a voice entity, or use the voice-class codec command to bind a codec template to a voice entity.
The g711alaw and g711ulaw codecs provide high-quality voice transmission but consume high bandwidth.
The g723r53 and g723r63 codecs provide silence suppression technology and comfortable noise as follows:
· The relatively high speed output is based on multipulse multiquantitative level technology and provides relatively high voice quality.
· The relatively low speed output is based on the Algebraic-Code-Excited Linear-Prediction technology and provides greater flexibility for applications.
The g729r8 and g729a codecs provide a voice quality (nearly toll quality) similar to the 32-kbps adaptive differential pulse code modulation (ADPCM). These two codecs feature low bandwidth, short delay, and medium processing complexity.
Table 3 Voice quality for codecs
|
Codec |
Voice quality |
|
g711alaw g711ulaw |
Excellent |
|
g726r16 g726r24 g726r32 g726r40 |
Good |
|
g729a g729br8 g729r8 |
Good |
|
g723r53 g723r63 |
Average |
If you execute this command multiple times, the most recent configuration takes effect.
Examples
# Configure the codec as g711alaw for VoIP entity 10.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 voip
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] codec g711alaw
codec preference
Use codec preference to assign a priority to a codec in a codec template.
Use undo codec preference to delete the priority for a codec.
Syntax
codec preference priority { g711alaw | g711ulaw | g723r53 | g723r63 | g726r16 | g726r24 | g726r32 | g726r40 | g729a | g729br8 | g729r8 } [ bytes payload-size ]
undo codec preference priority
Default
No codecs exist in a codec template.
Views
Codec template view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
priority: Specifies the priority of a codec, in the range of 1 to 4. The smaller the value, the higher the priority.
g711alaw: Specifies the G.711 A-law codec at 64 kbps (without compression), which is typically used in Europe.
g711ulaw: Specifies the G.711 μ-law codec at 64 kbps (without compression), which is typically used in North America and Japan.
g723r53: Specifies the G.723.1 Annex A codec at 5.3 kbps.
g723r63: Specifies the G.723.1 Annex A codec at 6.3 kbps.
g726r16: Specifies the G.726 Annex A codec at 16 kbps. Support for this keyword depends on the line card.
g726r24: Specifies the G.726 Annex A codec at 24 kbps. Support for this keyword depends on the line card.
g726r32: Specifies the G.726 Annex A codec at 32 kbps. Support for this keyword depends on the line card.
g726r40: Specifies the G.726 Annex A codec at 40 kbps. Support for this keyword depends on the line card.
g729a: Specifies the G.729 Annex A codec (a simplified version of G.729) at 8 kbps.
g729br8: Specifies the G.729 Annex B codec at 8 kbps.
g729r8: Specifies the G.729 codec at 8 kbps.
bytes payload-size: Specifies the number of bytes sent per second.
Table 4 Value range and default of payload-size for codecs
|
Codec |
Value range (in bytes) |
Default (in bytes) |
|
g711alaw g711ulaw |
16 to 80 in multiples of 8, 80 to 240 in multiples of 80 |
160 |
|
g723r53 |
20 to 120 in multiples of 20 |
20 |
|
g723r63 |
24 to 144 in multiples of 24 |
24 |
|
g726r16 |
20 to 220 in multiples of 20 |
60 |
|
g726r24 |
30 to 210 in multiples of 30 |
90 |
|
g726r32 |
40 to 200 in multiples of 40 |
120 |
|
g726r40 |
50 to 200 in multiples of 50 |
150 |
|
g729a g729br8 g729r8 |
10 to 180 in multiples of 10 |
30 |
Usage guidelines
For information about the codecs, see the codec command.
Examples
# Configure the g711alaw codec to have the highest priority 1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] voice class codec 1
[Sysname-voice-class-codec1] codec preference 1 g711alaw
description
Use description to configure a description for a voice entity.
Use undo description to restore the default.
Syntax
description text
undo description
Default
No description is configured for a voice entity.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
IVR entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
text: Specifies a description, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 80 characters.
Examples
# Configure the description as room10 for POTS entity 10.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 pots
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] description room10
display voice call
Use display voice call to display control information for voice calls in progress.
Syntax
display voice call
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
Examples
# As shown in Figure 1, after Telephone 2222 (the calling party) establishes a call with Telephone 1111, display control information for voice calls in progress.
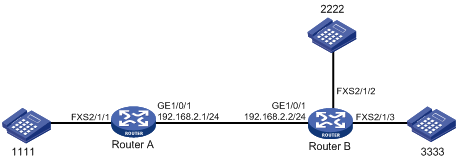
<RouterB> display voice call
Voice call information:
Call1
CallID : 6
Calling number : 2222
Called number : 1111
Call info-table index : 0
Total call-legs : 2
Leg 1
LegID : 10
Leg type : Call-Leg
Status : Connected
Call reference ID : 3
Signal protocol : LGS
Voice line : 2/1/2
Leg 2
LegID : 11
Leg type : Call-Leg
Status : Connected
Call reference ID : 4
Signal protocol : SIP
Target SIP address : 192.168.2.1:5060
# As shown in Figure 1, after Telephone 1111 (the calling party) establishes a call with Telephone 2222 and then Telephone 2222 presses hookflash to place the call on hold, display control information for voice calls in progress.
<RouterB> display voice call
Voice call information:
Call1
CallID : 7
Calling number : 1111
Called number : 2222
Call info-table index : 0
Total call-legs : 2
Leg 1
LegID : 17
Leg type : Call-Leg
Status : Connected
Call reference ID : 7
Signal protocol : SIP
Target SIP address : 192.168.2.1:5060
Leg 2
LegID : 18
Leg type : Call-Leg
Status : Connected
Call reference ID : 14
Signal protocol : LGS
Voice line : 2/1/2
Number of services : 1
Service name : CH
Table 5 Command output
|
Field |
Description |
|
CallID |
A call ID in the range of 0 to 999 uniquely identifies a call. |
|
Total call-legs |
Total number of call legs, in the range of 0 to 3. |
|
LegID |
A leg ID in the range of 0 to 2999 uniquely identifies a leg. |
|
Leg type |
Leg type: · Call Leg—Call leg. A voice call has two call legs: an inbound call leg and an outbound call leg. · Temp Leg—Temporary leg. This leg type exists on a device operating as a SIP trunk device. · MOH Leg—Music on hold leg. |
|
Status |
Leg status: · Call leg status: ¡ Finding-route—The leg is waiting for a route lookup response. ¡ Incoming_ACK—The leg received a call. ¡ Outgoing_ACK—The leg sent out a call. ¡ Connected—A call was connected. · MOH leg status: ¡ Waiting-music-response—The leg is waiting for a response from the MOH server. ¡ MOH_connected—The leg established a connection with the MOH server. This field displays -NA- for temporary legs, because temporary legs have no status. |
|
Call reference ID |
Control block ID for the leg. |
|
Signal protocol |
Signaling type for the leg: · SIP. · LGS. · R2. · E&M. · IVA. |
|
Voice line |
Voice interface used by the leg. |
|
Number of services |
Number of services on the leg. |
|
Service name |
Service name: · CH—Call hold. · CW—Call waiting. · MCH—Multiparty call hold. · MOH—Music on hold. · CT—Call transfer for SIP-to-SIP calls. · CF—Call forwarding for SIP-to-SIP calls. · CB—Call backup. · CFO—Call forwarding originator. · CTO—Call transfer originator. · CTR—Call transfer recipient. · CTT—Call transfer target. · Conference—Three-party conference. |
display voice call-info
Use display voice call-info to display information about calls in progress.
Syntax
display voice call-info { tag | all }
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
Parameters
tag: Specifies a call in progress by its number in the range of 0 to 2147483647.
all: Specifies all calls in progress.
Examples
# Display information about all calls in progress.
<Sysname> display voice call-info all
Call tag 0
Caller number : 5000
Called number : 1000
Call direction : From packet switch
Voice interface index : 0x00000000
Voice entity currently used : 1
Voice entities offered : 1
Table 6 Command output
|
Field |
Description |
|
Call direction |
· From packet switch—The call is initiated from the IP side. · From circuit switch—The call is initiated from the PSTN side. |
|
Voice interface index |
Index of the voice interface that initiates the call. |
|
Voice entities offered |
Number of voice entities that can be used for the call. |
display voice entity
Use display voice entity to display the configuration of voice entities.
Syntax
display voice entity { entity-tag | all | ivr | pots | voip }
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
Parameters
entity-tag: Specifies a voice entity by its number in the range of 1 to 2147483647.
all: Specifies all voice entities.
ivr: Specifies IVR entities.
pots: Specifies POTS entities.
voip: Specifies VoIP entities.
Examples
# Display the configuration of all voice entities.
<Sysname> display voice entity all
POTS 9999
Current state: Up
Description: entity9999
Priority level: 0
Match template: 9999
Voice line: 2/2/1
Dial prefix: Not configured
Send number: All
Max connections: 50
Codec: g723r53; bytes: 80; vad: Disabled
Caller permit: 1
Caller group: permit group 1
Substitute called: 9999
Substitute calling: 9999
DTMF relay: Outband-NTE
RTP payload-type for NTE: 113
Playout mode: adaptive
Playout initial delay: 30 ms
Playout minimum delay: 10 ms
Playout maximum delay: 160 ms
IP media DSCP: ef
IP signaling DSCP: ef
Register number: Enabled
Call-forwarding no-reply number: 5555
Call-forwarding on-busy number: 6666
Call-forwarding unavailable number: 7777
Call-forwarding unconditional number: 8888
Authentication info:
Username: 1000
Password: ******
Realm: abc.com
VoIP 8888
Current state: Up
Description: Not configured
Priority level: 0
Match template: 8888
Target SIP address: 1.1.1.1
Max connections: 10
Caller permit: 1
Caller group: permit group 1
Substitute called: 9999
Substitute calling: 9999
DTMF relay: Outband-SIP
Playout mode: adaptive
Playout initial delay: 30 ms
Playout minimum delay: 10 ms
Playout maximum delay: 160 ms
IP media DSCP: ef
Codec transparent: Disabled
Media flow-around: Enabled
Voice class SIP early-offer forced: Disabled
Voice class SIP URI scheme: Global
Voice class SIP bind media source-interface: GigabitEthernet2/1/1
Voice class SIP bind control source-interface: GigabitEthernet2/1/1
Voice class SIP keepalive state: Available
Voice class SIP keepalive up-interval: 60 s
Voice class SIP keepalive down-interval: 30 s
Voice class SIP keepalive retry: 5
Fax protocol: standard-t38; ls-redundancy: 0; hs-redundancy: 0
Fax cng-switch: Disabled
Fax level: -15
Fax local-train threshold: 10
Fax nsf: 0x000000
Fax rate: Voice
Fax train-mode: PPP
Fax ecm: Disabled
Table 7 Command output
|
Field |
Description |
|
VoIP entity-number |
Voice entity type and number. The voice entity type can be VoIP, POTS, or IVR. |
|
Match template |
Number template of the voice entity. |
|
Target SIP address |
Call destination IP address of the voice entity. |
|
Voice line |
Voice interface bound to the voice entity. |
|
Send number |
Number sending mode: · All—Sends all digits of a called number. · Truncate—Sends a truncated called number. · number—Number of digits (that are extracted from the end of a number) to be sent. |
|
bytes: 80 |
Number of bytes sent per second. |
|
Caller permit |
Calling number permitted to originate calls to the voice entity. |
|
Caller group |
Subscriber group bound to the voice entity. |
|
Substitute called |
Number substitution rule list bound to the voice entity and applied to the called number. |
|
Substitute calling |
Number substitution rule list bound to the voice entity and applied to the calling number. |
|
DTMF relay |
· Outband-SIP—DTMF tones are transmitted in SIP packets. · Outband-NTE—DTMF tones are transmitted in RTP packets compliant with RFC 2833. · Inband-voice—DTMF tones are transmitted in RTP packets. |
|
Playout mode |
Playout delay mode: · adaptive. · fixed. |
|
Playout initial delay |
Initial playout delay time. |
|
Playout minimum delay |
Minimum playout delay time. |
|
Playout maximum delay |
Maximum playout delay time. |
|
IP media DSCP |
DSCP value of IP packets carrying streaming media. |
|
Codec transparent |
State of transparent transmission of codecs: Enabled or Disabled. |
|
Media flow-around |
State of the media flow-around feature: Enabled or Disabled. |
|
Voice class SIP early-offer forced |
State of DO-EO conversion: Enabled or Disabled. |
|
Voice class SIP URI scheme |
URL scheme used for SIP calls: · Global—The SIP scheme is used globally. · SIP—The voice entity uses the SIP scheme. · SIPS—The voice entity uses the SIPS scheme. |
|
Voice class SIP bind media |
Source interface of outgoing media streams. |
|
Voice class SIP bind control |
Source interface of outgoing SIP messages. |
|
Voice class codec |
Codec template bound to the voice entity. |
|
Call-forwarding no-reply number |
Destination number to which incoming calls will be forwarded when the voice interface is not answered within a period of time. |
|
Call-forwarding on-busy number |
Destination number to which incoming calls will be forwarded when the voice interface is busy. |
|
Call-forwarding unavailable number |
Destination number to which incoming calls will be forwarded when the voice interface is shut down by executing the shutdown command. |
|
Call-forwarding unconditional number |
Destination number to which incoming calls will be forwarded, whether or not the voice interface is available. |
|
Voice class SIP keepalive state |
Status of the VoIP entity: · Available. · Unavailable. |
|
Voice class SIP keepalive up-interval |
Interval for the local end to send OPTIONS messages before marking the voice entity unavailable. |
|
Voice class SIP keepalive down-interval |
Interval for the local end to send OPTIONS messages before marking the voice entity available. |
|
Voice class SIP keepalive retry |
Number of keepalives sent before the status of the voice entity is changed. |
|
Fax cng-switch |
CNG fax switchover status: · Enabled. · Disabled. |
|
Fax level |
Transmit energy level. |
|
Fax local-train threshold |
Threshold percentage of local training. |
|
Fax nsf |
NSF code for nonstandard capabilities negotiation. |
|
Fax rate |
Maximum fax rate for rate training. |
|
Fax train-mode |
Rate training mode: · Local—Local training. · PPP—Point-to-point training. |
|
Fax ecm |
Error Correction Mode status: Enabled or Disabled. |
dsp-image
Use dsp-image to set the type of the DSP image.
Syntax
dsp-image { ms | general }
Default
The DSP image is a general version.
Views
Voice view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
ms: Specifies a Microsoft-verified version. This version can meet the voice quality requirements of Microsoft but does not support the G.723 codec.
general: Specifies a general version.
Usage guidelines
After you execute this command, you must reboot the device to apply the new configuration.
When the device interoperates with Microsoft Lync Server, you must use the Microsoft-verified version. In other situations, use the general version.
Examples
# Configure the DSP image as a Microsoft-verified version.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dsp-image ms
entity
Use entity to create a voice entity and enter its view, or enter the view of an existing voice entity.
Use undo entity to delete voice entities.
Syntax
entity entity-number [ ivr | pots | voip ]
undo entity { entity-number | all | ivr | pots | voip }
Default
No voice entities exist.
Views
Voice dial program view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
entity-number: Specifies the number of a voice entity, in the range of 1 to 2147483647.
all: Specifies all voice entities.
ivr: Specifies an IVR entity.
pots: Specifies a POTS entity.
voip: Specifies a VoIP entity.
Usage guidelines
If you create a new voice entity, you must specify the voice entity type. If you enter the view of an existing voice entity, you can optionally specify the voice entity type.
You can create a maximum of 1000 voice entities.
Examples
# Create POTS entity 10 and enter its view.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 pots
incoming called-number
Use incoming called-number to configure a called number string for a voice entity to match incoming calls.
Use undo incoming called-number to restore the default.
Syntax
incoming called-number called-number-string
undo incoming called-number
Default
No called number string is configured for a voice entity to match incoming calls.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
called-number-string: Specifies a called number string of 1 to 31 characters that is in the format of [ + ] { regular-expression [ T ] [ $ ] | T }. The following describe the characters:
· Plus sign (+): If the plus sign (+) is at the beginning of the string, the string indicates an E.164 standard number. For example, +110022 indicates that 110022 is an E.164 standard number.
· Dollar sign ($): Can be used only at the end of the string. The number must exactly match the string before the dollar sign. If the string has no dollar sign, the number template matches all numbers starting with the string. For example, the incoming called-number 20 command matches all numbers starting with 20.
· T: Indicates the timer. The system waits for the subscriber to dial any number until one of the following events occurs:
¡ The number length threshold is exceeded.
¡ The subscriber enters the terminator.
¡ The timer expires.
· regular-expression: Specifies a matching pattern of characters. Table 8 lists the available characters.
Table 8 Description of the characters in a regular-expression
|
Character |
Description |
|
0-9 |
Digits 0 through 9. |
|
Pound sign (#) or asterisk (*) |
Indicates a valid digit. |
|
Dot (.) |
Wildcard, which can match any valid digit. For example, 555…. can match any 7-digit numbers beginning with 555. |
|
Exclamation point (!) |
Indicates that the preceding subexpression appears zero or one time. For example, 56!1234 can match 51234 and 561234. |
|
Plus sign (+) |
Indicates that the preceding subexpression appears one or more times. For example, 9876(54)+ can match 987654, 98765454, 9876545454, and so on. |
|
Percent sign (%) |
Indicates that the preceding subexpression appears zero or more times. For example, 9876(54)% can match 9876, 987654, 98765454, 9876545454, and so on. |
|
Hyphen (-) |
Connects two digits to indicate a range of numbers, for example, [1-9] indicates 1 to 9, inclusive. The hyphen (-) can appear only in brackets ([ ]). |
|
Brackets ([ ]) |
Indicates a range. Only numbers 0 through 9 are allowed in the range. For example, [1-36] matches 1, 2, 3, or 6. |
|
Parentheses (( )) |
Indicates a string of characters. For example, (123) indicates a character string of 123. It is usually used together with signs such as exclamation point (!), percent sign (%), and plus sign (+). For example, 408(12)+ can match the character string 40812 or 408121212, but not 408. In this pattern, 408 must be followed by one string of 12 at a minimum. |
|
|
NOTE: · An exclamation point (!), plus sign (+), or percent sign (%) must follow a valid digit or digit string. · To use brackets ([ ]) and parentheses (( )) together, use them in the form of "( [ ] )". The "( ( ) )", "[ [ ] ]", and "[ ( ) ]" forms are not allowed. |
Usage guidelines
If the called number of an incoming call matches the called number string for a voice entity, the voice entity becomes the incoming voice entity of the call.
Examples
# Configure the called number string as 456 for VoIP entity 1 to match incoming calls.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 1 voip
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity1] incoming called-number 456
ip qos dscp
Use ip qos dscp to set the DSCP value for IP packets carrying media streams.
Use undo ip qos dscp to restore the default.
Syntax
ip qos dscp { dscp-value | dscp-value-set } media
undo ip qos dscp { dscp-value | dscp-value-set } media
Default
The DSCP value for IP packets is ef (101110), the global default value.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
IVR entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
dscp-value: Specifies a DSCP value in the range of 0 to 63.
dscp-value-set: DSCP value, which can be the keyword af11, af12, af13, af21, af22, af23, af31, af32, af33, af41, af42, af43, cs1, cs2, cs3, cs4, cs5, cs6, cs7, or ef.
Table 9 DSCP values
|
Keyword |
DSCP value in binary |
DSCP value in decimal |
|
af11 |
001010 |
10 |
|
af12 |
001100 |
12 |
|
af13 |
001110 |
14 |
|
af21 |
010010 |
18 |
|
af22 |
010100 |
20 |
|
af23 |
010110 |
22 |
|
af31 |
011010 |
26 |
|
af32 |
011100 |
28 |
|
af33 |
011110 |
30 |
|
af41 |
100010 |
34 |
|
af42 |
100100 |
36 |
|
af43 |
100110 |
38 |
|
cs1 |
001000 |
8 |
|
cs2 |
010000 |
16 |
|
cs3 |
011000 |
24 |
|
cs4 |
100000 |
32 |
|
cs5 |
101000 |
40 |
|
cs6 |
110000 |
48 |
|
cs7 |
111000 |
56 |
|
ef |
101110 |
46 |
Usage guidelines
You can set the DSCP value for IP packets carrying media streams both globally (in SIP view) and for a specific voice entity (in POTS/VoIP entity view). The configuration in POTS/VoIP entity view takes precedence over the global configuration. A voice entity uses the global configuration only when the ip qos dscp command is not configured in POTS/VoIP entity view.
Examples
# Configure DSCP value af41 for IP packets carrying media streams.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 pots
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] ip qos dscp af41 media
Related commands
ip qos dscp (SIP view)
line
Use line to bind a voice interface to a POTS entity.
Use undo line to restore the default.
Syntax
line line-number
undo line
Default
No voice interface is bound to a POTS entity.
Views
POTS entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
line-number: Specifies a voice interface by its number.
Examples
# Bind voice interface 1/0 to POTS entity 10.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 pots
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] line 1/0
match-template
Use match-template to configure a number template for a voice entity.
Use undo match-template to restore the default.
Syntax
match-template match-string
undo match-template
Default
No number template exists.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
IVR entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
match-string: Specifies a number template, a string of 1 to 31 characters that is in the format of [ + ] { string [ T ] [ $ ] | T }. The following describe the characters:
· Plus sign (+): If the plus sign (+) is at the beginning of the string, the string indicates an E.164 standard number. For example, +110022 indicates that 110022 is an E.164 standard number.
If a number starts with the plus sign (+), note the following when you use it on a trunk:
¡ The E&M, R2, and LGS signaling methods use DTMF transmission. Because the plus sign (+) does not have a DTMF tone, the number cannot be transmitted to the called side successfully.
¡ Because the DSS1 signaling uses ISDN transmission, this problem does not exist.
¡ You should avoid using a number that cannot be identified by the signaling itself. Otherwise, the call will fail.
· Dollar sign ($): Can be only at the end of the string. The number must exactly match the string before the dollar sign. If the string has no dollar sign, the number template matches all numbers starting with the string. For example, the match-template 20 command matches all numbers starting with 20.
· T: Indicates the timer. The system waits for the subscriber to dial any number until one of the following conditions occurs:
¡ The number length threshold is exceeded.
¡ The subscriber enters the terminator.
¡ The timer expires.
· string: Specifies a matching pattern of characters. Table 10 lists the available characters.
Table 10 Description of the characters in a string
|
Character |
Description |
|
0-9 |
Digits 0 through 9. |
|
Pound sign (#) or asterisk (*) |
Indicates a valid digit. |
|
Dot (.) |
Wildcard, which can match any valid digit. For example, 555…. can match any 7-digit numbers beginning with 555. |
|
Exclamation point (!) |
Indicates that the preceding subexpression appears zero or one time. For example, 56!1234 can match 51234 and 561234. |
|
Plus sign (+) |
Indicates that the preceding subexpression appears one or more times. For example, 9876(54)+ can match 987654, 98765454, 9876545454, and so on. |
|
Percent sign (%) |
Indicates that the preceding subexpression appears zero or more times. For example, 9876(54)% can match 9876, 987654, 98765454, 9876545454, and so on. |
|
Hyphen (-) |
Connects two digits to indicate a range of numbers, for example, [1-9] indicates 1 to 9, inclusive. The hyphen (-) can appear only in brackets ([ ]). |
|
Brackets ([ ]) |
Indicates a range. Only numbers 0 through 9 are allowed in the range. For example, [1-36] matches 1, 2, 3, or 6. |
|
Parentheses (( )) |
Indicates a string of characters. For example, (123) indicates a character string of 123. It is usually used together with signs such as exclamation point (!), percent sign (%), and plus sign (+). For example, 408(12)+ can match the character string 40812 or 408121212, but not 408. In this pattern, 408 must be followed by one string of 12 at a minimum. |
|
|
NOTE: · An exclamation point (!), plus sign (+), or percent sign (%) must follow a valid digit or digit string. · To use brackets ([ ]) and parentheses (( )) together, use them in the form of "( [ ] )". The "( ( ) )", "[ [ ] ]", and "[ ( ) ]" forms are not allowed. |
Usage guidelines
For a local POTS entity, this command defines a local number template to be bound to the local voice interface.
For a trunk POTS entity or a VoIP entity, this command defines a called number template.
Examples
# Configure the number template as 1000 for POTS entity 1000.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 1000 pots
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity1000] match-template 1000
# Configure the number template as 2000 for VoIP entity 2000.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 2000 voip
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity2000] match-template 2000
outband nte
Use outband nte to enable NTE mode for out-of-band DTMF signaling.
Use undo outband to restore the default.
Syntax
outband nte
undo outband
Default
Inband DTMF signaling is used.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
IVR entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
As a best practice to avoid DTMF tone transmission failure, configure the outband nte command and the same payload type value on the originating and terminating devices.
Examples
# Enable NTE mode for out-of-band DTMF signaling.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 voip
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] outband nte
rtp payload-type nte
playout delay
Use playout delay to set the playout delay time for voice packets.
Use undo playout delay to restore the default.
Syntax
playout-delay { initial milliseconds | maximum milliseconds | minimum milliseconds }
undo playout-delay { initial | maximum | minimum }
Default
The initial playout delay time for voice packets is 30 milliseconds. The maximum playout delay time is 160 milliseconds. The minimum playout delay time is 10 milliseconds.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
initial milliseconds: Specifies the initial playout delay time in adaptive mode or the fixed playout delay time in fixed mode. The value range for milliseconds is 5 to 300 milliseconds.
maximum milliseconds: (Adaptive mode only) Specifies the maximum playout delay time for voice packets. The value range is 60 to 300 milliseconds.
minimum milliseconds: (Adaptive mode only) Specifies the minimum playout delay time for voice packets. The value range is 0 to 40 milliseconds.
Examples
# Configure the playout delay mode as adaptive, and set the minimum playout delay time to 30 milliseconds.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 voip
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] playout-delay mode adaptive
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] playout-delay minimum 30
playout delay mode
Use playout delay mode to configure the playout delay mode for voice packets.
Use undo playout delay mode to restore the default.
Syntax
playout-delay mode { adaptive | fixed }
undo playout-delay mode
Default
The playout delay mode for voice packets is fixed.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
adaptive: Specifies the playout delay mode as adaptive. In adaptive mode, the buffer size is automatically adjusted based on network conditions.
fixed: Specifies the playout delay mode as fixed. In fixed mode, the buffer size is fixed.
Usage guidelines
In an ideal voice network environment, the delay of each voice packet (time for each voice packet to travel from the sender to the receiver) is fixed. That is, the jitter is 0. In an actual voice network, the delay might vary from packet to packet.
To smoothly play out voice packets received with different delay times, the receiver can buffer the voice packets for a period of time (playout delay time). By configuring playout delay, you can prevent delay variation (jitter) from affecting voice quality.
Examples
# Configure the playout delay mode as adaptive.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 voip
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] playout-delay mode adaptive
rtp payload-type nte
Use rtp payload-type nte to set the NTE payload type value in RTP packets.
Use undo rtp payload-type nte to restore the default.
Syntax
rtp payload-type nte value
undo rtp payload-type nte
Default
The NTE payload type value in RTP packets is 101.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
IVR entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
value: Specifies the value of the NTE payload type in RTP packets, in the range of 96 to 127. The value 98 is reserved for identifying nonstandard T38 fax packets.
Usage guidelines
|
|
CAUTION: To avoid negotiation failure, do not set the payload type field to a value forbidden by an interconnected device from another vendor. |
As a best practice to avoid DTMF tone transmission failure, configure the outband nte command and the same payload type value on the originating and terminating devices.
Examples
# Set the NTE payload value of RTP packets to 102 for VoIP entity 10.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 voip
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] outband nte
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] rtp payload-type nte 102
Related commands
outband nte
rtp-detect timeout
Use rtp-detect timeout to set the RTP timeout period.
Use undo rtp-detect timeout to restore the default.
Syntax
rtp-detect timeout value
undo rtp-detect timeout
Default
The RTP timeout period is 120 seconds.
Views
Voice view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
value: Specifies the RTP timeout period in the range of 2 to 300 seconds.
Usage guidelines
This command enables the device to disconnect a call if it does not receive RTP traffic during the set timeout period.
Examples
# Set the RTP timeout period to 60 seconds.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] rtp-detect timeout 60
send-ring
Use send-ring to configure the originating side to play ringback tones.
Use undo send-ring to restore the default.
Syntax
send-ring
undo send-ring
Default
The originating side cannot play ringback tones.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
If the terminating side of a call cannot play ringback tones, configure the POTS or VoIP entity on the originating side to play ringback tones.
This feature does not take effect on a POTS entity if the POTS entity is bound to an FXS or FXO interface.
Examples
# Configure the originating side to play ringback tones.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 1 voip
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity1] send-ring
shutdown
Use shutdown to shut down a voice entity.
Use undo shutdown to bring up a voice entity.
Syntax
shutdown
undo shutdown
Default
A voice entity is up.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
IVR entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Examples
# Shut down POTS entity 10.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 pots
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] shutdown
sip log enable
Use sip log enable to enable SIP logging.
Use undo sip log enable to disable SIP logging.
Syntax
sip log enable
undo sip log enable
Default
SIP logging is disabled.
Views
Voice view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Usage guidelines
SIP logging enables the device to log SIP call events and send the log messages to the information center. With the information center, you can set log message filtering and output rules, including output destinations. For more information about using the information center, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Examples
# Enable SIP logging.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] sip log enable
vad-on
Use vad-on to enable VAD.
Use undo vad-on to disable VAD.
Syntax
vad-on [ g711 | g723r53 | g723r63 | g729a | g729r8 ] *
undo vad-on [ g711 | g723r53 | g723r63 | g729a | g729r8 ] *
Default
VAD is disabled.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
IVR entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
g711: Enables VAD for the G.711 codec. The G.711 codec is supported only on the following interface modules: HMIM-1VE1, HMIM-1VT1, HMIM-2VE1, HMIM-2VT1, SIC-1BSV, SIC-1VE1T1, SIC-2BSV, SIC-2FXS1FXO. The G.711 codec is supported only if the DSP image is configured as the Microsoft-verified version.
g723r53: Enables VAD for the G.723.1 Annex A codec at 5.3 kbps.
g723r63: Enables VAD for the G.723.1 Annex A codec at 6.3 kbps.
g729a: Enables VAD for the G.729 Annex A codec at 8 kbps.
g729r8: Enables VAD for the G.729 codec at 8 kbps.
Usage guidelines
If you execute the vad-on or undo vad-on command without specifying a codec, VAD is enabled or disabled for all codecs.
The G.726 codec does not support VAD. The G.729br8 codec always supports VAD.
Examples
# Enable VAD for the g723r53 codec on POTS entity 10.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 pots
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] vad-on g723r53
voice class codec
Use voice class codec to create a codec template and enter its view, or enter the view of an existing codec template.
Use undo voice class codec to delete a codec template.
Syntax
voice class codec tag
undo voice class codec tag
Default
No codec templates exist.
Views
Voice view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
tag: Specifies the number of the codec template, in the range of 1 to 2147483647.
Usage guidelines
You can create a maximum of 16 codec templates.
Examples
# Create codec template 1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] voice class codec 1
[Sysname-voice-class-codec1]
voice-class codec
Use voice-class codec to bind a codec template to a voice entity.
Use undo voice-class codec to restore the default.
Syntax
voice-class codec tag
undo voice-class codec
Default
No codec template is bound to a voice entity.
Views
POTS entity view
VoIP entity view
IVR entity view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
tag: Specifies a codec template by its number in the range of 1 to 2147483647.
Usage guidelines
You can bind a nonexistent codec template to a voice entity. The codec template takes effect only after you assign priorities to the codecs in the template by using the codec preference command.
A call can be established only when the calling party and the called party use the same codec.
Only one codec template can be bound to a voice entity. If you configure the voice-class codec command multiple times, the most recent configuration takes effect.
You can use this command to bind a codec template to a voice entity, or use the codec command to directly configure a codec for a voice entity.
Examples
# Bind codec template 1 to VoIP entity 10.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] dial-program
[Sysname-voice-dial] entity 10 voip
[Sysname-voice-dial-entity10] voice-class codec 1
Related commands
codec preference
voice class codec
voice-setup
Use voice-setup to enter voice view and enable voice services.
Use undo voice-setup to disable voice services, delete all voice settings, and exit voice view.
Syntax
voice-setup
undo voice-setup
Default
Voice services are disabled.
Views
System view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Examples
# Enter voice view and enable voice services.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
vqa dsp-buffer maximum-time
|
|
NOTE: This command takes effect only on E&M interface modules. |
Use vqa dsp-buffer maximum-time to set the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data.
Use undo vqa dsp-buffer maximum-time to restore the default.
Syntax
vqa dsp-buffer maximum-time time
undo vqa dsp-buffer maximum-time
The following compatibility matrix shows the support of hardware platforms for this command:
|
Hardware |
Command compatibility |
|
MSR810, MSR810-W, MSR810-W-DB, MSR810-LM, MSR810-W-LM, MSR810-10-PoE, MSR810-LM-HK, MSR810-W-LM-HK, MSR810-LMS-EA |
No |
|
MSR810-LMS, MSR810-LUS |
No |
|
MSR2600-6-X1, MSR2600-10-X1 |
No |
|
MSR 2630 |
No |
|
MSR3600-28, MSR3600-51 |
No |
|
MSR3600-28-SI, MSR3600-51-SI |
No |
|
MSR3600-28-X1, MSR3600-28-X1-DP, MSR3600-51-X1, MSR3600-51-X1-DP |
No |
|
MSR3610-I-DP, MSR3610-IE-DP |
No |
|
MSR3610-X1, MSR3610-X1-DP, MSR3610-X1-DC, MSR3610-X1-DP-DC |
No |
|
MSR 3610, MSR 3620, MSR 3620-DP, MSR 3640, MSR 3660 |
Yes |
|
MSR3610-G, MSR3620-G |
No |
Default
The maximum duration of DSP-buffered data is 270 milliseconds.
Views
Voice view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
time: Specifies the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data, in milliseconds. The value range for this argument is 0 and 10 to 480. If you set the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data to 0 milliseconds, the device does not clear the DSP buffer.
Usage guidelines
VoIP voice data is buffered in the DSP buffer if a network latency or jitter exists. When the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data is reached, the device clears the DSP buffer to improve the quality of VoIP calls. You can use this command to adjust the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data.
When PCM pass-through is enabled, the set maximum duration of DSP-buffered data takes effect.
When PCM pass-through is disabled, one of the following rules applies:
· If the set maximum duration of DSP-buffered data is in the range of 10 to 179 milliseconds, the default value (270 milliseconds) takes effect.
· If the set maximum duration of DSP-buffered data is 0 or in the range of 180 to 480 milliseconds, the set value takes effect.
For more information about PCM pass-through, see voice interface configuration in Voice Configuration Guide.
Examples
# Set the maximum duration of DSP-buffered data to 300 milliseconds.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] voice-setup
[Sysname-voice] vqa dsp-buffer maximum-time 300
Related commands
pcm-passthrough
