- Table of Contents
-
- 10-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA configuration
- 02-802.1X configuration
- 03-MAC authentication configuration
- 04-Portal configuration
- 05-Port security configuration
- 06-Password control configuration
- 07-Keychain configuration
- 08-Public key management
- 09-PKI configuration
- 10-IPsec configuration
- 11-SSH configuration
- 12-SSL configuration
- 13-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 14-TCP attack prevention configuration
- 15-IP source guard configuration
- 16-ARP attack protection configuration
- 17-ND attack defense configuration
- 18-uRPF configuration
- 19-MFF configuration
- 20-FIPS configuration
- 21-MACsec configuration
- 22-802.1X client configuration
- 23-Web authentication configuration
- 24-Triple authentication configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 22-802.1X client configuration | 66.02 KB |
802.1X client configuration task list
Enabling the 802.1X client feature
Configuring an 802.1X client username and password
Configuring an 802.1X client MAC address
Specifying an 802.1X client EAP authentication method
Configuring an 802.1X client anonymous identifier
Specifying an SSL client policy
Displaying and maintaining 802.1X client
Configuring 802.1X client
As shown in Figure 1, the 802.1X client feature allows the access device to act as the supplicant in the 802.1X architecture. For information about the 802.1X architecture, see "802.1X overview."
Figure 1 802.1X client network diagram
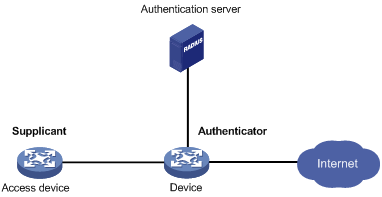
802.1X client configuration task list
|
Tasks at a glance |
|
(Required.) Enabling the 802.1X client feature |
|
(Required.) Configuring an 802.1X client username and password |
|
(Optional.) Configuring an 802.1X client MAC address |
|
(Required.) Specifying an 802.1X client EAP authentication method |
|
(Optional.) Configuring an 802.1X client anonymous identifier |
|
(Optional.) Specifying an SSL client policy |
Enabling the 802.1X client feature
Before enabling the 802.1X client feature, make sure you have configured 802.1X authentication on the authenticator. For information about 802.1X configuration, see "Configuring 802.1X."
To enable the 802.1X client feature on an interface:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Ethernet interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable the 802.1X client feature. |
dot1x supplicant enable |
By default, the 802.1X client feature is disabled. |
Configuring an 802.1X client username and password
An 802.1X client-enabled device uses the configured username and password for 802.1X authentication.
Make sure the username and password configured on the device is consistent with the username and password configured on the authentication server. If any inconsistency occurs, the device cannot pass 802.1X authentication to access the network.
To configure an 802.1X client username and password on an interface:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Ethernet interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure an 802.1X client username. |
dot1x supplicant username username |
By default, no 802.1X client username exists. |
|
4. Set an 802.1X client password. |
dot1x supplicant password { cipher | simple } string |
By default, no 802.1X client password exists. |
Configuring an 802.1X client MAC address
The authenticator adds the MAC address of an authenticated 802.1X client to the MAC address table and then assigns access rights to the client.
If the device acting as an 802.1X client has multiple Ethernet interfaces to seek MACsec protection, configure a unique MAC address for each interface to ensure successful 802.1X client authentication. For information about MACsec, see "Configuring MACsec."
You can use either of the following methods to configure a unique MAC address for each interface:
· Execute the mac-address command in Ethernet interface view. For information about this command, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference.
· Configure an 802.1X client MAC address.
To configure an 802.1X client MAC address on an interface:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Ethernet interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure an 802.1X client MAC address. |
dot1x supplicant mac-address mac-address |
By default, an Ethernet interface uses the interface's MAC address for 802.1X client authentication. If the interface's MAC address is unavailable, the interface uses the device's MAC address for 802.1X client authentication. |
Specifying an 802.1X client EAP authentication method
An 802.1X client-enabled device supports the following EAP authentication methods:
· MD5-Challenge.
· PEAP-MSCHAPv2.
· PEAP-GTC.
· TTLS-MSCHAPv2.
· TTLS-GTC.
An 802.1X authenticator supports both the EAP relay and EAP termination modes. Support of the EAP authentication methods for the two modes varies.
· The MD5-Challenge EAP authentication supports both modes.
· Other EAP authentication methods support only the EAP relay mode.
For information about EAP relay and EAP termination, see "Configuring 802.1X."
To specify an 802.1X client EAP authentication method on an interface:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Ethernet interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Specify an 802.1X client EAP authentication method. |
dot1x supplicant eap-method { md5 | peap-gtc | peap-mschapv2 | ttls-gtc | ttls-mschapv2 } |
By default, an 802.1X client-enabled interface uses the MD5-Challenge EAP authentication. Make sure the specified 802.1X client EAP authentication method is supported by the authentication server. |
Configuring an 802.1X client anonymous identifier
At the first authentication phase, packets sent to the authenticator are not encrypted. The use of an 802.1X client anonymous identifier prevents the 802.1X client username from being disclosed at the first phase. The 802.1X client-enabled device sends the anonymous identifier to the authenticator instead of the 802.1X client username. The 802.1X client username will be sent to the authenticator in encrypted packets at the second phase.
If no 802.1X client anonymous identifier is configured, the device sends the 802.1X client username at the first authentication phase.
The configured 802.1X client anonymous identifier takes effect only if one of the following EAP authentication methods is used:
· PEAP-MSCHAPv2.
· PEAP-GTC.
· TTLS-MSCHAPv2.
· TTLS-GTC.
If the MD5-Challenge EAP authentication is used, the configured 802.1X client anonymous identifier does not take effect. The device uses the 802.1X client username at the first authentication phase.
Do not configure the 802.1X client anonymous identifier if the vendor-specific authentication server cannot identify anonymous identifiers.
To configure an 802.1X client anonymous identifier on an interface:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Ethernet interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure an 802.1X client anonymous identifier. |
dot1x supplicant anonymous identify identifier |
By default, no 802.1X client anonymous identifier exists. |
Specifying an SSL client policy
If the PEAP-MSCHAPv2, PEAP-GTC, TTLS-MSCHAPv2, or TTLS-GTC authentication is used, the 802.1X client authentication process is as follows:
· The first phase—The device acts as an SSL client to negotiate with the SSL server.
The SSL client uses the SSL parameters defined in the specified SSL client policy to establish a connection with the SSL server for negotiation. The SSL parameters include a PKI domain, supported cipher suites, and the SSL version. For information about SSL client policy configuration, see "Configuring SSL."
· The second phase—The device uses the negotiated result to encrypt and transmit the interchanged authentication packets.
If the MD5-Challenge authentication is used, the device does not use an SSL client policy during the authentication process.
To specify an SSL client policy on an interface:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Ethernet interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Specify an SSL client policy. |
dot1x supplicant ssl-client-policy policy-name |
By default, an 802.1X client-enabled interface uses the default SSL client policy. |
Displaying and maintaining 802.1X client
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display 802.1X client information. |
display dot1x supplicant [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |

