- Table of Contents
-
- 04-Layer 2 - LAN Switching Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-MAC address table configuration
- 02-Ethernet link aggregation configuration
- 03-Port isolation configuration
- 04-Spanning tree configuration
- 05-Loop detection configuration
- 06-VLAN configuration
- 07-MVRP configuration
- 08-QinQ configuration
- 09-VLAN mapping configuration
- 10-LLDP configuration
- 11-Service loopback group configuration
- 12-EPON configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 12-EPON configuration | 523.03 KB |
Contents
EPON port types and port numbering rules
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
Changing the type of a fiber interface
Setting the link type of an OLT port
Enabling compatibility with third-party ONUs
Enabling grant filtering on an OLT port
Enabling invalid MAC address check
Setting the LLID key update interval
Setting the maximum ONU-OLT RTT
Setting the timeout timer for extended OAM discovery
Configuring the management VLAN of an ONU
Configuring ONU serial interfaces
Setting the link type of an ONU port and assigning the port to VLANs
Enabling user network management features on an ONU
Configuring the loop protection action
Setting the multicast mode of an ONU
Configuring ONU bandwidth allocation and related parameters
Enabling UNI count-based PON port activation for an ONU
Enabling an ONU to send flush messages
Enabling event reporting for an ONU
Enabling downlink traffic encryption for an ONU
Bringing up a VoIP interface on an ONU
Configuring basic settings of UNIs
Setting the VLAN operation mode for a UNI
Enabling fast-leave processing for a UNI
Configuring UNI port isolation
Configuring port mirroring on a UNI
Testing the cable connected to a UNI
Displaying and maintaining EPON
Displaying and maintaining the OLT
Displaying and maintaining ONUs
Displaying and maintaining UNIs
Support for non-EPON features and configuration restrictions
OLT port features and restrictions
Commands unavailable in OLT port view
ONU port features and restrictions
Commands unavailable in ONU port view
Fiber backup configuration example
ONU binding configuration example
Multicast in IGMP snooping mode configuration example
Multicast in multicast control mode configuration example
ONU update configuration example
Configuring an OLT as a BCMP proxy
Configuring EPON
Overview
Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON) is a Passive Optical Network (PON) that carries Ethernet frames encapsulated in 802.3 standards. EPON is a combination of Ethernet technology and PON technology in compliance with the IEEE 802.3ah standards issued in June 2004.
EPON architecture
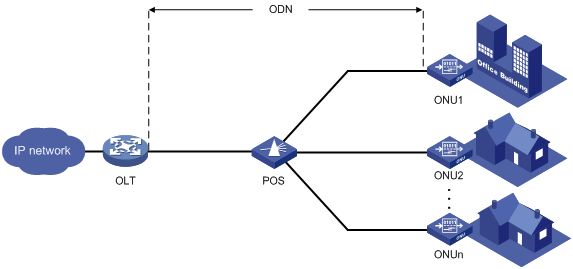
As shown in Figure 1, a typical EPON system contains optical line terminals (OLTs), optical network units (ONUs), and optical distribution networks (ODNs).
· OLT—The core device of an EPON system, located at the central office. The OLT manages ONUs in the EPON system and forwards traffic between the EPON system and the IP network.
· ONU—A device connected to customer premises equipment such as PCs, set-top boxes, and switches. Typically, ONUs are placed at customers' homes, corridors, or roadsides. ONUs forward uplink data sent by customer premises equipment (from ONU to OLT) and selectively forward downlink broadcasts sent by OLTs (from OLT to ONU).
· ODN—A network formed by optical fibers, one or multiple passive optical splitters (POSes), and other passive optical components. ODNs provide optical signal transmission paths between OLTs and ONUs. A POS can couple uplink data into a single piece of fiber and distribute downlink data to ONUs.
Figure 1 Typical EPON architecture
Working mechanisms
EPON uses the single-fiber wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology to implement single-fiber bidirectional transmission. WDM uses a downlink central wavelength of 1490 nm and an uplink central wavelength of 1310 nm. WDM can support a transmission distance of up to 20 km (12.43 miles).
An EPON system must complete ONU registration, extended OAM connection establishment, and bandwidth allocation before it can transmit data.
ONU registration
EPON uses the following types of Multipoint Control Protocol (MPCP) messages for ONU registration:
· GATE messages, including:
? Discovery GATE message, broadcasted by the OLT to discover ONUs.
? General GATE message, unicasted by the OLT to allocate bandwidth to ONUs.
· REGISTER_REQ message.
· REGISTER message.
· REGISTER_ACK message.
Each of these messages contains a timestamp field that records the local clock at the time of packet transmission.
An ONU is registered by using the following workflow:
1. An OLT broadcasts a discovery GATE message to notify the start time and length of the discovery timeslot to all ONUs.
2. An unregistered ONU receives the discovery GATE message and sets its local clock to be the same as the timestamp contained in the message. When the local clock reaches the start time, the ONU sends a REGISTER_REQ message to the OLT after a random delay. The REGISTER_REQ message contains the MAC address of the ONU and the local timestamp of the ONU when the message is sent.
3. The OLT receives the REGISTER_REQ message and obtains the MAC address of the ONU and ONU-OLT round trip time (RTT). The ONU-OLT RTT is mainly used for time synchronization between an OLT and ONUs.
4. The OLT parses the REGISTER_REQ message, and uses the MAC address in the message to unicast a REGISTER message to the ONU. The REGISTER message contains a logical link ID (LLID) assigned to the ONU as a unique identifier.
5. The OLT sends a general GATE message to the same ONU immediately after sending the REGISTER message.
6. The ONU receives the REGISTER message and general GATE message. Then, the ONU sends a REGISTER_ACK message in the timeslot assigned in the GATE message to notify the OLT that the REGISTER message is parsed successfully.
ONU registration is completed.
Extended OAM connection establishment
EPON supports Ethernet Operation, Administration and Maintenance (OAM) and extended OAM functions. Ethernet OAM is a network monitoring tool that operates at the data link layer. It reports link status by periodically exchanging OAMPDUs between devices for administrators to effectively manage the network. Extended OAM uses both basic OAMPDUs and extended OAMPDUs for OLTs and ONUs to establish connections and implement remote management.
An extended OAM connection is established by using the following workflow:
1. An OLT and an ONU establish a standard OAM connection.
2. The ONU reports the supported organizationally unique identifier (OUI) and extended OAM version number to the OLT.
3. The OLT identifies whether the OLT supports the reported OUI and extended OAM version number.
? If the OLT supports the reported OUI and extended OAM version, the extended OAM connection for the ONU is established successfully.
? If the reported OUI and extended OAM version are not supported, the extended OAM connection cannot be established.
Bandwidth allocation
After the extended OAM connection is established, downlink data transmission can begin. Uplink data transmission can begin only after uplink bandwidth is allocated.
An OLT allocates uplink bandwidth to an ONU by using the following workflow:
1. The OLT sends a general GATE message to assign a transmission timeslot to the ONU.
2. The ONU sends a REPORT message to report the local status information such as buffer usage to the OLT. The OLT assigns timeslots intelligently based on the local status information of ONUs.
3. The OLT receives the REPORT message, and sends a general GATE message to assign the ONU a data transmission timeslot based on the current bandwidth.
4. The ONU receives the GATE message and transmits data at the transmission start time contained in the message.
Data transmission
EPON transmits uplink data and downlink data differently.
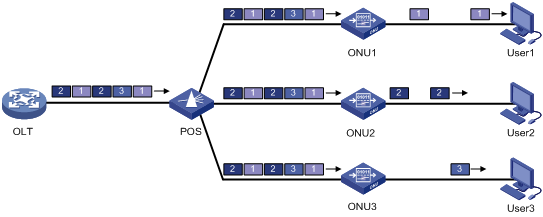
· Downlink data transmission—As shown in Figure 2, the OLT broadcasts downlink data to ONUs. Each ONU receives packets destined for it based on the LLID and drops the other packets.
Figure 2 Downlink data transmission in an EPON system
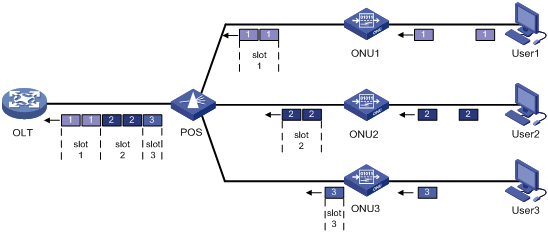
· Uplink data transmission—As shown in Figure 3, each ONU buffers the data frames received from users and sends the frames at the full wire-speed when the timeslot for the ONU arrives.
EPON uses the Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) technology to transmit uplink data. This technology ensures that one optical fiber between the OLT and the POS can transmit data signals from multiple ONUs to the OLT without signal interference.
Figure 3 Uplink data transmission in an EPON system
EPON port types and port numbering rules
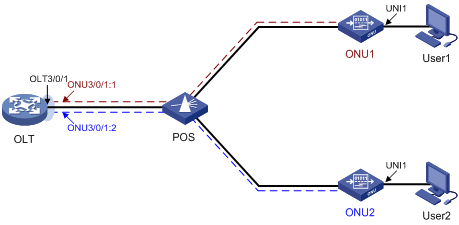
As shown in Figure 4, EPON defines the following port types:
· OLT port—A physical ONU-facing port on an OLT. Each OLT port on an EPON card acts as an independent OLT device.
OLT ports are numbered in the format of EPON card slot number/subcard slot number/OLT port number, for example, OLT 3/0/1.
· ONU port—A virtual port created on an OLT port. Each ONU port corresponds to a physical ONU. The configuration performed in ONU port view takes effect on the ONU bound to the ONU port. An ONU port can identify an ONU only after the port is bound to the ONU.
ONU ports are numbered in the format of EPON card slot number/subcard slot number/OLT port number:ONU port number, for example, ONU 3/0/1:1.
· UNI—User network interface, a physical user-facing port on an ONU.
Figure 4 EPON port types and port numbers
EPON system reliability
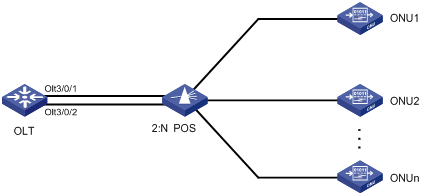
To ensure high reliability for the trunk fibers and OLTs in an EPON system, you can assign two OLT ports to a fiber backup group. The two OLT ports can reside on one EPON card or on two different EPON cards. The OLT port assigned first acts as the master port, and the other OLT port acts as the subordinate port. Only the master OLT port forwards traffic.
When a system fault occurs (for example, the trunk fiber of the master port is disconnected or the master port goes down), an automatic master/subordinate switchover is performed. Alternatively, you can perform a manual master/subordinate switchover. Figure 5 shows a fiber backup group, where the POS is a 2:N optical splitter.
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
ONU ports do not support ARP detection and MFF. For more information about ARP detection and MFF, see Security Configuration Guide.
For more information about commands not supported by OLT ports and ONU ports, see "Commands unavailable in OLT port view" and "Commands unavailable in ONU port view."
EPON configuration task list
The following table lists only EPON tasks. For non-EPON features supported by the device, see "Support for non-EPON features and configuration restrictions."
Configuring an OLT
This section introduces only EPON configuration tasks. For information about non-EPON features supported by OLT ports, see "OLT port features and restrictions."
Changing the type of a fiber interface
You can configure the EPON fiber interfaces on the LSQM1PT24TSSC0 interface card as OLT ports or GigabitEthernet interfaces.
The fiber interfaces on the LSQM1PT24TSSC0 interface card are grouped by port number in order, starting from 1. Each group contains four interfaces. To change the type of an interface in a group, you must change the type of all the four interfaces in the group. For the interface type change to take effect, reboot the interface card.
If you change the type of an interface, the system removes the original interface and then creates the target interface with the same number as the original interface.
When you use a GigabitEthernet interface that is changed from an OLT port, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· The interface does not support jumbo frames larger than 2043 bytes. As a best practice, set the permitted jumbo frame length of the interface to 2043 bytes or a smaller value by using the jumboframe enable command. For more information about this command, see Interface Command Reference.
· The interface does not support the following Ethernet interface commands in Interface Command Reference:
? duplex
? eee enable
? flow-control
? flow-control receive enable
? loopback
? mdix-mode
? port up-mode
? speed
· The interface does not support a 100-Mbps optical transceiver module.
· For the peer interface to come up, you must configure it to work in full duplex mode and set its speed to 1000 Mbps.
· The interface does not support IPv6 services.
· The interface does not support 802.1X or Ethernet OAM. For more information, see Security Configuration Guide and High Availability Configuration Guide.
To change the type of an interface:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter OLT port view: · Enter Layer 2/Layer 3 GigabitEthernet
interface view: |
N/A |
|
3. Change the type of the interface. |
· Change the OLT port to a GigabitEthernet interface: · Change the GigabitEthernet interface to an OLT
port: |
By default, the GigabitEthernet interface changed from an OLT port is in Layer 2 mode. |
Setting the link type of an OLT port
OLT ports support only the hybrid link type. For more information about port link types, see "Configuring VLANs."
To set the link type of an OLT port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter OLT port view. |
interface olt interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the link type of the OLT port to hybrid. |
port link-type hybrid |
By default, the link type of an OLT port is hybrid. |
|
4. Assign the OLT port to VLANs as a tagged or untagged member. |
port hybrid vlan vlan-id-list { tagged | untagged } |
By default, an OLT port is an untagged member of VLAN 1. Make sure the specified VLANs have been created. |
|
5. (Optional.) Set the PVID of the OLT port. |
port hybrid pvid vlan vlan-id |
By default, the PVID of an OLT port is VLAN 1. |
Configuring fiber backup
When you configure fiber backup, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· A fiber backup group contains a maximum of two OLT ports. An OLT port can be assigned to only one fiber backup group.
· Before you delete a fiber backup group, make sure all OLT ports have been removed from the group.
· To ensure correct traffic forwarding after switchovers, make sure the OLT ports in a fiber backup group have the same settings in OLT port view and ONU configuration.
You can assign an OLT port to a fiber backup group in fiber backup group view or OLT port view.
Assigning an OLT port to a fiber backup group in system view
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
N/A |
|
3. Create a fiber backup group and enter its view. |
fiber-backup group group-number |
By default, no fiber backup groups exist. |
|
4. Assign an OLT port to the fiber backup group. |
member olt interface-number |
By default, a fiber backup group does not contain any OLT ports. |
Assigning an OLT port to a fiber backup group in OLT port view
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
5. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
6. Enter OLT port view. |
interface olt interface-number |
N/A |
|
7. Assign the OLT port to a fiber backup group. |
port fiber-backup group group-number |
By default, a fiber backup group does not contain any OLT ports. Make sure the specified fiber backup group has been created. To create a fiber backup group, use the fiber-backup group command. |
Performing a manual master/subordinate switchover
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
N/A |
|
3. Enter fiber backup group view. |
fiber-backup group group-number |
Make sure the specified fiber backup group has been created and contains two OLT ports. To create a fiber backup group, use the fiber-backup group command. |
|
4. Perform a manual master/subordinate switchover. |
port switch-over |
For successful command execution, use this command when the subordinate OLT port is in Ready state. |
Enabling compatibility with third-party ONUs
To allow non-H3C ONUs to register with an OLT, enable compatibility with third-party ONUs. If this feature is disabled, only H3C ONUs can register with the OLT.
If you bind a non-H3C ONU to an ONU port before this feature is enabled, the ONU cannot register with the OLT even if you enable this feature. For successful registration, you must perform one of the following tasks:
· Use the deregister onu command to deregister the ONU.
· Use the shutdown command to shut down the ONU port and then use the undo shutdown command to bring it up.
To enable compatibility with third-party ONUs:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
N/A |
|
3. Enable compatibility with third-party ONUs. |
vendor-compatible slot slot-number |
By default, compatibility with third-party ONUs is enabled. |
Enabling grant filtering on an OLT port
If time synchronization of an EPON system is accurate, an OLT receives packets from an ONU only within the timeslot assigned to the ONU. If the clock of an ONU is inaccurate, the ONU might send packets to the OLT in another ONU's timeslot. For correct data transmission, enable grant filtering on the OLT port. The OLT port will drop the packets that are transmitted in an incorrect timeslot.
To enable grant filtering on an OLT port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter OLT port view. |
interface olt interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable grant filtering on the OLT port. |
grant-filtering enable |
By default, grant filtering is enabled on an OLT port. |
Enabling invalid MAC address check
An invalid MAC address is a MAC address whose seventh bit of the first byte is 1, for example, 02-10-94-00-00-02 (the first byte is 00000010). The OLT floods frames sourced from an invalid MAC address. If you enable invalid MAC address check, the OLT drops frames with an invalid source MAC address.
Invalid MAC address check is not supported on a GigabitEthernet interface that is changed from an EPON fiber interface.
To enable invalid MAC address check:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
N/A |
|
3. Enable invalid MAC address check. |
onu invalid-address check enable |
By default, invalid MAC address check is enabled. |
Setting the LLID key update interval
An OLT broadcasts downlink data to ONUs. To secure user data transmission, each LLID in an EPON system uses an independent key. The OLT periodically requests ONUs to update their LLID keys. Each ONU responds with a new LLID key after it receives the LLID key update request from the OLT.
To set the LLID key update interval:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
N/A |
|
3. Set the LLID key update interval. |
encryption slot slot-number update-time update-time |
By default, the LLID key update interval is 10 seconds. |
Setting the maximum ONU-OLT RTT
|
|
IMPORTANT: Make sure you are fully aware of the impact of this task when you perform it on a live network. |
You can adjust the scale of an EPON system by setting the maximum ONU-OLT RTT on the OLT. An ONU cannot be registered if its RTT is greater than the maximum ONU-OLT RTT set on the OLT.
An ONU distant from the OLT suffers high optical power attenuation. To prevent distant ONUs from registering with the EPON system, set a short maximum ONU-OLT RTT.
The maximum ONU-OLT RTT takes effect only on unregistered ONUs.
To set the maximum ONU-OLT RTT:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter OLT port view. |
interface olt interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the maximum ONU-OLT RTT. |
max-rtt value |
By default, the maximum ONU-OLT RTT is 14500 TQ. 1 time quantum (TQ) is equal to 16 ns, the time for transmitting two bytes of data at 1 Gbps. |
Setting the timeout timer for extended OAM discovery
The timeout timer for extended OAM discovery determines the timeout period for extended OAM messages during extended OAM discovery.
As a best practice, use the default setting for this timer. Increase this timer on the card that hosts an OLT port if an ONU connected to the OLT and bound to an ONU port remains down.
To set the timeout timer for extended OAM discovery:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
N/A |
|
3. Set the timeout timer for extended OAM discovery. |
oam-discovery-timeout slot slot-number value value |
The unit for the value argument is 100 milliseconds. By default, the timeout timer for extended OAM discovery is 3 seconds. |
Setting DBA parameters
|
|
CAUTION: Incorrect DBA settings might interrupt services. Make sure you are fully aware of the impact of this task when you perform it on a live network. |
An OLT uses dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) to adjust the uplink bandwidth of individual ONUs in real time based on the traffic status of the ONUs.
DBA is implemented through a request-response mechanism as follows:
1. An OLT obtains the traffic information of ONUs from the bandwidth requests (REPORT messages) received from ONUs.
2. The OLT uses a bandwidth allocation algorithm to calculate the bandwidth to be allocated for this cycle within the uplink bandwidth range for each ONU.
3. The OLT sends the bandwidth allocation results to the ONUs through bandwidth authorization (general GATE messages).
DBA ensures that uplink data sent by ONUs will not conflict with each other. For more information about uplink bandwidth allocation configuration, see "Configuring uplink bandwidth allocation."
To set DBA parameters:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter OLT port view. |
interface olt interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set ONU discovery parameters. |
dba-parameters { discovery-frequency frequency | discovery-length length } * |
By default, an OLT port initiates ONU discovery at an interval of 500 milliseconds, and each ONU discovery process lasts for 307.6 milliseconds. The unit for the frequency and length argument is 0.1 millisecond. |
|
4. Return to system view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
5. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
6. Set the number of queue sets that ONU REPORT messages support. |
dba-report queue-set-number queue-set-number |
By default, ONU REPORT messages support two queue sets. |
|
7. Configure the threshold for a queue. |
dba-report queue-set-id queue-set-id queue-id queue-id { active | inactive } threshold threshold-value |
The default thresholds are as follows: · 0 for queues 1 through 3, and the threshold is activated. · 65535 for queues 4 and 5, and the threshold is activated. · 0 for queues 6 through 8, and the threshold is not activated. |
Configuring CDR
The Call Detail Record (CDR) feature enables the OLT to record basic access information of users, including:
· IGMP query type (report or leave).
· IGMP request time.
· User identification.
· Requested channels.
· Leave mode (passive or active).
· CDR record generation time.
The information is saved in the CDR buffer. You can use one of the following methods to send CDR records to the information center module:
· Set the upper limit for the CDR buffer.
· Set the CDR sending interval.
· Manually send CDR records.
The CDR records sent to the information center are deleted from the CDR buffer. You can set CDR record output rules, including output destinations. For more information about using the information center, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
To configure CDR:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
N/A |
|
3. Enable CDR. |
multicast call-detail-record enable |
By default, CDR is disabled. CDR takes effect only on ONUs in multicast control mode. |
|
4. Set the upper limit for the CDR buffer. |
multicast call-detail-record cache-limit number |
By default, the CDR buffer can save a maximum of 32 records. |
|
5. Set the CDR generation delay. |
multicast call-detail-record record-delay delay-time |
By default, the CDR generation delay is 30 seconds. After CDR is enabled, the OLT periodically checks the online duration of users. If the online duration of a user is longer than the CDR generation delay, the OLT generates a CDR record and saves it to the CDR buffer. |
|
6. Set the CDR sending interval. |
multicast call-detail-record report-interval interval |
By default, the CDR sending interval is 30 seconds. |
|
7. Manually send CDR records. |
multicast call-detail-record send |
N/A |
Remotely managing ONUs
|
|
NOTE: Support for ONU features depends on the ONU model. |
This section introduces only EPON configuration tasks. For information about non-EPON features supported by ONU ports, see "ONU port features and restrictions."
Creating ONU ports
|
Command |
Remarks |
|
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter OLT port view. |
interface olt interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Create ONU ports. |
using onu onu-number-list |
By default, no ONU ports exist. |
Configuring ONU bindings
An OLT authenticates ONUs based on the ONU MAC addresses and denies illegal ONU access to the system. For an ONU to pass authentication and be registered, you must bind the ONU to an ONU port. After the ONU passes authentication, the bound ONU port comes up, and the ONU comes online.
If the EPON system contains a small number of ONUs, you can manually bind ONUs to ONU ports. If the EPON system contains a large number of ONUs, use batch ONU binding or automatic ONU binding to ease your workload.
An OLT port can register a maximum of 63 ONUs.
Binding an ONU to an ONU port
If fiber backup is not configured, you can create only one-to-one bindings between ONUs and ONU ports. For a fiber backup group, you can bind an ONU to two ONU ports that are on different member OLT ports.
To bind an ONU to an ONU port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Bind an ONU to the ONU port. |
bind onu-id mac-address |
By default, no ONU is bound to an ONU port. |
Performing batch ONU binding
If an ONU is not bound to any ONU port, the ONU cannot be registered. Such an ONU is called a silent ONU. Batch ONU binding automatically binds existing silent ONUs to ONU ports at a time. The ONUs that join the system after batch ONU binding is performed will not be bound.
Batch ONU binding applies to a newly established EPON system that contains only legal ONUs. You can use the bind onu-id command to manually bind new ONUs after batch ONU binding is performed.
To perform batch ONU binding:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
N/A |
|
3. Perform batch ONU binding. |
onu bind batch [ slot slot-number ] |
By default, batch ONU binding is not performed. |
Enabling automatic ONU binding
Automatic ONU binding automatically binds ONU ports to existing silent ONUs and ONUs that join the system after this feature is enabled.
Automatic ONU binding applies to an EPON system where ONUs attached to the OLT are completely trustworthy. To unbind an ONU, first use the undo onu bind auto command to disable automatic ONU binding.
To enable automatic ONU binding:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
N/A |
|
3. Enable automatic ONU binding. |
onu bind auto [ slot slot-number ] |
By default, automatic ONU binding is disabled. |
Configuring the management VLAN of an ONU
To manage an ONU through Telnet, you must assign an IP address to the management VLAN interface of the ONU. This task allows you to specify the management VLAN of an ONU.
The management VLAN interface of an ONU can obtain an IP address by using the following methods:
· Manual IP address configuration.
· DHCP (with the ONU as a DHCP client).
A new IP address overwrites the old IP address if both methods are used.
To configure the management VLAN of an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the management VLAN of the ONU. |
management-vlan vlan-id |
By default, the management VLAN of an ONU is VLAN 1. If the management VLAN is changed, the IP address of the original management VLAN interface is deleted. |
|
4. Bring up the management VLAN interface. |
undo shutdown management-vlan-interface |
By default, a management VLAN interface is down. |
|
5. Assign an IP address to the management VLAN interface. |
· Manual configuration: · Automatic allocation: |
By default, the management VLAN interface of an H3C ONU uses the IP address 192.168.0.240 and subnet mask 255.255.255.0. |
Configuring ONU serial interfaces
Perform this task to set serial interface parameters and establish sessions on serial interfaces of an ONU.
Configure ONU serial interfaces:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the number of data bits for a serial interface. |
serial interface-number databit { 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 } |
By default, the number of data bits is 8 for an ONU serial interface. |
|
4. Set the parity type for a serial interface. |
serial interface-number parity { even | mark | none | odd | space } |
By default, the parity type of an ONU serial interface is none, which indicates that no parity is used. |
|
5. Set the baud rate for a serial interface. |
serial interface-number speed { 300 | 600 | 1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 57600 | 115200 } |
By default, the baud rate of an ONU serial interface is 9600 bps. |
|
6. Set the number of stop bits for a serial interface. |
serial interface-number stopbit { 1 | 1.5 | 2 } |
By default, the number of stop bits is 1 for an ONU serial interface. |
|
7. Establish a session on a serial interface. |
· Establish a TCP session with the ONU as the client: · Establish a TCP session with the ONU as the server: · Establish a UDP session with the ONU as
both the server and client: |
By default, no session is established on an ONU serial interface. |
Setting the link type of an ONU port and assigning the port to VLANs
Configure an ONU port as an access port or trunk port by using the following guidelines:
· If a PC is directly connected to the ONU, configure the ONU port as an access port. The ONU port will receive and transmit only untagged packets.
· If a home gateway or Layer 2 switch is connected to the ONU, configure the ONU port as a trunk port.
Table 1 shows how access and trunk ONU ports process traffic.
Table 1 ONU port link types and packet processing
|
Port link type |
Traffic direction |
Packet processing |
|
Access |
Uplink |
Permits only untagged packets and tags these packets with the PVID. |
|
Downlink |
Permits only PVID-tagged packets and untags these packets. |
|
|
Trunk |
Uplink |
· Tags untagged packets with the PVID. · Forwards tagged packets with their tags intact. |
|
Downlink |
Permits only tagged packets of the VLANs that the port belongs to. |
Table 1 does not describe how packets are processed by an access port in VLAN 1 (the default VLAN setting of an ONU port). An ONU port using the default VLAN setting processes packets as follows:
· Permits untagged uplink packets, and tags these packets with VLAN ID 1.
· Permits downlink packets tagged with VLAN ID 1, and processes the tag based on the link types of the other ONU ports on the same OLT port.
? Removes the VLAN tag if the other ONU ports are access ports.
? Keeps the VLAN tag if the other ONU ports are trunk ports.
Configuring an ONU port as an access port and assigning the port to a VLAN
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the link type to access. |
port link-type access |
By default, the link type of an ONU port is access. |
|
4. Assign the ONU port to a VLAN. |
port access vlan vlan-id |
By default, all ONU ports belong to VLAN 1. |
Configuring an ONU port as a trunk port and assigning the port to VLANs
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the link type to trunk. |
port link-type trunk |
By default, the link type of an ONU port is access. |
|
4. Assign the port to all VLANs. |
port trunk permit vlan all |
By default, a trunk port permits only VLAN 1. You must assign the trunk port to all VLANs. Do not use the undo port trunk permit vlan command. |
|
5. Set the PVID of the port. |
port trunk pvid vlan vlan-id |
By default, the PVID of a trunk port is VLAN 1. |
Enabling user network management features on an ONU
You can use an OLT to remotely enable RSTP, DHCP snooping, DHCP snooping Option82, and PPPoE+ on an ONU through extended OAM packets.
RSTP
RSTP enables an ONU to eliminate the loops in the user networks by blocking redundant links.
For more information about RSTP, see "Configuring spanning tree protocols."
Loop detection
Loop detection enables an ONU to detect loops in the user networks. If a loop is detected, loop detection generates a log message and takes the loop protection action on the looped port. Log messages are maintained in the information center. For more information about the information center and loop detection, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide and "Configuring loop detection."
DHCP snooping
DHCP snooping enables an ONU to generate a DHCP snooping table. The table records the IP address that each connected DHCP client obtains from the DHCP server and client MAC address information.
For more information about DHCP snooping, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
DHCP snooping Option82
DHCP snooping Option82 allows a DHCP server to record the location of DHCP clients. If DHCP snooping Option82 is enabled on an ONU, the ONU adds the Option82 field to the DHCP requests sent by DHCP clients before broadcasting the requests. The Option82 field contains the ONU MAC address, the number of the UNI connected to the DHCP client, and the VLAN to which the UNI belongs.
PPPoE+
PPPoE+, also called PPPoE Intermediate Agent, implements user port identification by adding user port information into PPPoE packets.
After you enable PPPoE+ on an ONU, the ONU processes the request packet sent by a PPPoE client as follows:
· If the request packet does not carry a PPPoE tag, the ONU adds the tag (which contains the UNI information) to the packet and forwards it to the OLT.
· If the request packet carries a PPPoE tag, the ONU directly forwards the packet to the OLT.
Configuration procedure
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable a user network management feature. |
onu protocol { dhcp-snooping | dhcp-snooping information | loopback-detection | pppoe | stp } enable |
By default, RSTP is enabled, and DHCP snooping, DHCP snooping Option82, loop detection, and PPPoE+ are disabled on an ONU. If the spanning tree feature is enabled globally on the OLT, you must enable RSTP on all ONUs. To avoid forwarding failures in the EPON system, make sure the ONUs are not selected as root bridges. |
Configuring the loop protection action
The loop protection action determines how an ONU deals with a looped port. Loop protection actions include the following:
· No-learning—Disables MAC address learning and generates a log.
· Semi-block—Disables MAC address learning, generates a log, and blocks inbound traffic.
· Shutdown—Shuts down the port and generates a log. The device automatically sets the port to the forwarding state after the interval set by using the shutdown-interval command (see Fundamentals Command Reference).
To configure the loop protection action:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the loop protection action. |
onu protocol loopback-detection action { no-learning | semi-block | shutdown } |
By default, the loop protection action of an ONU port is semi-block. |
Setting the multicast mode of an ONU
You can configure the multicast mode of an ONU as IGMP snooping mode or multicast control mode.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure the multicast mode of an ONU, first map its multicast IP addresses to a multicast VLAN.
When receiving an IGMP report message, the OLT verifies whether the multicast IP address in the message belongs to the multicast VLAN.
· If the address belongs to the multicast VLAN, the OLT generates a multicast forwarding entry for the multicast VLAN.
· If the address does not belong to the multicast VLAN, the OLT drops the message.
To complete prerequisites for multicast mode configuration:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
N/A |
|
3. Map multicast IP addresses to a multicast VLAN. |
multicast vlan-id vlan-id ip ip-address-list |
By default, no multicast IP addresses are mapped to a multicast VLAN. A multicast IP address can be mapped to only one multicast VLAN. |
|
4. Return to system view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
5. Enable IGMP snooping globally. |
igmp-snooping |
By default, IGMP snooping is disabled globally. |
|
6. Return to system view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
7. Enter the view of the multicast VLAN. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
8. Enable IGMP snooping in the multicast VLAN. |
igmp-snooping enable |
By default, IGMP snooping is disabled in a VLAN. |
|
9. Enable IGMP snooping querier. |
igmp-snooping querier |
By default, IGMP snooping querier is disabled. If a network does not contain Layer 3 multicast devices, you must enable IGMP snooping querier on Layer 2 devices for them to generate and maintain multicast forwarding entries at the data link layer. |
|
10. (Optional.) Enable dropping unknown multicast traffic. |
igmp-snooping drop-unknown |
N/A |
Configuring multicast in IGMP snooping mode
In IGMP snooping mode, the OLT and ONUs mainly use IGMP report, leave, and query messages to manage dynamic multicast group membership. The OLT can implement simple user multicast access control through the multicast VLAN configuration on UNIs of ONUs.
When an ONU receives an IGMP membership report from a multicast group member, the ONU forwards the message to the OLT. When multiple members of a multicast group are attached to the ONU, the OLT will receive duplicate IGMP reports from these members. To reduce IGMP reports, enable IGMP report suppression. Within each query cycle, the ONU forwards only the first IGMP report of a multicast group to the OLT. Subsequent IGMP reports from the same multicast group are not forwarded.
On the OLT, you can configure the router port aging timer, the multicast group member port aging timer, and the query response timer for an ONU.
· Router port aging timer—The router port is the port that connects the ONU to the router. The ONU receives IGMP general query messages from the router through this port. If no IGMP general query message is received through the router port when the router port aging timer expires, the ONU determines that the port is not a router port. The router port aging timer must be a value about 2.5 times of the general query interval. For more information about the general query interval, see IGMP in IP Multicast Configuration Guide.
· Multicast group member port aging timer—This timer determines how often multicast group members are refreshed. If the ONU does not receive an IGMP report from a multicast group member port when this timer expires, the ONU deletes the port. In a network where multicast group members change frequently, set this timer to a small value.
· Query response timer—This timer sets the response timeout time for group-specific queries. If the ONU does not receive a response before the query response timer expires for the first time, it re-sends group-specific queries and re-starts the query response timer. If the ONU still does not receive a response when the timer expires, the multicast group on the ONU is deleted.
To configure multicast in IGMP snooping mode:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the multicast mode to IGMP snooping. |
multicast mode igmp-snooping |
By default, the multicast mode of an ONU is IGMP snooping. |
|
4. Assign a UNI to multicast VLANs. |
uni uni-number multicast vlan vlan-id-list |
By default, a UNI is not assigned to any multicast VLANs. |
|
5. Configure the number of multicast channels that users can access at the same time on a UNI. |
uni uni-number multicast-group-number number |
By default, the users on a UNI can access 64 multicast channels at the same time. |
|
6. Configure a UNI to remove the VLAN tag of downlink multicast flows. |
uni uni-number multicast-strip-tag enable |
By default, a UNI does not remove the VLAN tag of downlink multicast flows. |
|
7. Set IGMP snooping timers. |
onu protocol igmp-snooping timer { host-aging-time host-aging-time | max-response-time max-response-time | router-aging-time router-aging-time } |
This command is available on the ET704 ONU. The default values of IGMP snooping timers are as follows: · The multicast group member port aging timer is 260 seconds. · The query response timer is 1 second. · The router port aging timer is 105 seconds. |
|
8. Enable IGMP membership report suppression or IGMP leave suppression. |
onu protocol igmp-snooping suppression { leave | report } |
This command is available on the ET704 ONU. By default, IGMP leave suppression is enabled, and IGMP membership report suppression is disabled. |
Configuring multicast in multicast control mode
In multicast control mode, the OLT performs the following operations:
· The OLT maintains an access control table for user multicast services to centrally manage user multicast service access rights.
· The OLT identifies users based on the user LLID and the VLAN tag (same as the UNI number) carried in uplink IGMP report messages. The OLT also determines whether a user has the right to access the requested multicast service and determines the related parameters.
· The OLT uses extended multicast control OAM packets to send the ONU a user's access right to a multicast channel. This allows the ONU to forward or shut off the multicast traffic for the user. The network management system on the OLT centrally manages multicast access control. Multicast right management is governed by the OLT and executed by ONUs. The OLT also supports the cooperation between IGMP proxy and upper-layer multicast routers to dynamically request and deliver multicast traffic.
In multicast control mode, an ONU performs the following operations:
· The ONU maintains a table for multicast address filtering and multicast forwarding. The ONU performs flow control only for the current multicast service on the ONU.
· The ONU adds VLAN tags to untagged IGMP report and leave messages to identify users and transparently sends the messages to the OLT. The VLAN tag ID is the same as the UNI number. For example, the packets received on UNI 1 are tagged with VLAN ID 1. The ONU adds or deletes the group address filtering and multicast forwarding entries on the ONU based on the multicast control OAM packets delivered by the OLT. The multicast control OAM packets contain a series of multicast control entries. Based on the action taken on the entries, the ONU forwards or shuts off multicast traffic.
To configure multicast in multicast control mode:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the multicast mode to multicast control. |
multicast mode multicast-control |
By default, the multicast mode of an ONU is IGMP snooping. |
|
4. Set the multicast group member port aging timer. |
multicast-control host-aging-time host-aging-time |
By default, the multicast group member port aging timer is 260 seconds. |
|
5. Configure the access to multicast channels on a UNI. |
uni uni-number multicast-control multicast-address multicast-address-list [ source-ip ip-address [ to ip-address ] ] rule { deny | permit [ channel-limit channel-number ] | preview time-slice preview-time [ preview-interval interval-time | preview-times preview-times [ reset-interval reset-interval-time ] ]* } |
By default, the access to multicast channels is not configured on a UNI. |
|
6. Configure a UNI to remove the VLAN tag of downlink multicast flows. |
uni uni-number multicast-strip-tag enable |
By default, a UNI does not remove the VLAN tag of downlink multicast flows. |
Configuring ONU bandwidth allocation and related parameters
Perform this task to allocate uplink and downlink bandwidth based on different terminal service requirements to realize efficient bandwidth utilization.
Configuring downlink bandwidth allocation
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable the downlink bandwidth allocation policy. |
bandwidth-downstream policy enable |
By default, the downlink bandwidth allocation policy is disabled on an ONU port. Downlink bandwidth limits take effect only when the downlink bandwidth allocation policy is enabled. |
|
4. Configure the downlink bandwidth limits. |
bandwidth-downstream { max-bandwidth value1 | max-burstsize value2 } * |
By default, the maximum downlink bandwidth is 999994 Kbps, and the maximum downlink burst buffer is 4194240 bytes. The downlink bandwidth limits take effect only on known unicast packets. |
Configuring uplink bandwidth allocation
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the uplink bandwidth limits. |
upstream-sla { fixed-bandwidth fixed-value | maximum-bandwidth max-value | minimum-bandwidth min-value } * |
By default, the fixed uplink bandwidth is 0 kbps, the maximum uplink bandwidth is 23552 kbps, and the minimum uplink bandwidth is 2048 kbps. Make sure the sum of the minimum uplink bandwidth and the fixed uplink bandwidth is not greater than the maximum uplink bandwidth. Make sure the total minimum uplink bandwidth of ONUs does not exceed 972800 kbps on an OLT port. |
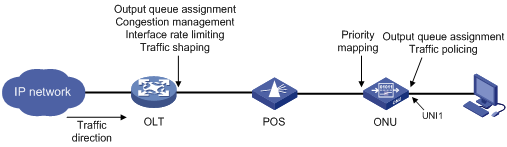
Configuring QoS for an ONU
Figure 6 shows how QoS operates when an EPON system receives downlink traffic.
This section provides QoS feature configuration for an ONU. For information about QoS features on an OLT, see "OLT port features and restrictions."
Configuring CoS-to-local priority mappings
When an ONU receives downlink traffic from an ONU port, the ONU assigns the traffic to different output queues based on CoS-to-local priority mappings.
To configure CoS-to-local priority mappings:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure CoS-to-local priority mappings. |
qos cos-local-precedence-map cos0 cos1 cos2 cos3 cos4 cos5 cos6 cos7 |
Table 2 shows default CoS-to-local priority mappings. |
Table 2 Default CoS-to-local priority mappings
|
CoS priority |
Local precedence |
|
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
|
2 |
1 |
|
3 |
1 |
|
4 |
2 |
|
5 |
2 |
|
6 |
3 |
|
7 |
3 |
Configuring priority marking on a UNI
Priority marking enables an ONU to perform the following operations on packets received from a UNI:
1. Classifies packets received from a UNI into multiple classes based on information of the packets, such as MAC addresses and IP addresses.
2. Applies different priority mapping policies to packets of different classes.
To configure priority marking on a UNI:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure priority marking on a UNI. |
uni uni-number classification-marking index index queue qid priority priority { selector operator matched-value } & <1-4> uni uni-number classification-marking index index queue qid priority priority { always-match | never-match } |
By default, priority marking is not configured on a UNI. Do not use the uni classification-marking commands together with the qos trust dscp command. For more information about the qos trust dscp command, see ACL and QoS Command Reference. |
Configuring traffic policing on a UNI
Traffic policing allows ONUs to evaluate traffic and limit the traffic rate. Traffic evaluation is implemented through the token bucket mechanism.
The token bucket mechanism evaluates traffic by checking the number of tokens in the bucket.
· If the number of tokens in the bucket is enough for forwarding the packets, the traffic conforms to the specification (called conforming traffic).
· If the number of tokens is not enough, the traffic does not conform to the specification (called excess traffic).
A token bucket has the following parameters:
· Committed information rate (CIR)—Rate at which tokens are put into the bucket, or the permitted average rate of traffic.
· Committed burst size (CBS)—Burst size or the capacity of the token bucket. It is the maximum traffic size permitted in each burst. The burst size must be greater than the maximum packet size.
· Excess Burst Size (EBS). For more information, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
· Peak Information Rate (PIR). For more information, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
To configure traffic policing on a UNI:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure uplink traffic policing on a UNI. |
uni uni-number port-policy inbound { bucket-depth bucket-depth-value | cir cir-value | extra-burst-size extra-burst-size-value } * |
The bucket-depth bucket-depth-value option sets the CBS, and the extra-burst-size extra-burst-size-value option sets the EBS. By default, the CBS is 1522 bytes, the CIR is not configured, and the EBS is 0 bytes. |
|
4. Configure downlink traffic policing on a UNI. |
uni uni-number port-policy outbound cir cir-value [ pir pir-value ] |
By default, downlink traffic policing is not configured. |
Enabling FEC for an ONU
Forward Error Correction (FEC) can implement downlink error correction on the OLT and uplink error correction on the ONU. This feature reduces the bit error rate and extends the optical transmission distance. Because error correction codes are added to packets, the actual uplink bandwidth of an ONU cannot reach the configured uplink bandwidth.
To enable FEC:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable FEC. |
forward-error-correction enable |
By default, FEC is disabled on an ONU port. |
Enabling UNI count-based PON port activation for an ONU
This feature is supported by ET824-E ONUs.
After this feature is enabled, the ONU activates the PON port that has more online UNIs if two PON ports are online.
To enable UNI count-based PON port activation for an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable UNI count-based PON port activation for the ONU. |
onu protocol smart-link uni-bind enable |
By default, UNI count-based PON port activation is disabled for an ONU. |
Enabling an ONU to send flush messages
|
Step |
Command |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
|
3. Enable the ONU to send flush messages. |
onu protocol smart-link flush enable [ control-vlan vlan-id ] |
Enabling event reporting for an ONU
Perform this task for an ONU to inform the OLT of events such as configuration changes, failures, and debugging events.
If an OLT manages a large number of ONUs, event report traffic from the ONUs might cause congestion. As a best practice, enable reporting only for critical events.
To enable event reporting for an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable event reporting for the ONU. |
onu event { debug | log | trap } enable level severity |
By default, event reporting is disabled for an ONU. |
Enabling downlink traffic encryption for an ONU
To protect user information against illegal access, enable encryption for the downlink traffic transmitted from the OLT to ONUs.
To enable downlink traffic encryption for an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable downlink traffic encryption for the ONU. |
encryption enable |
By default, downlink traffic encryption is enabled for an ONU. |
Bringing up a VoIP interface on an ONU
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Bring up a VoIP interface. |
undo voip-port port-number shutdown |
By default, a VoIP interface is down. |
Deregistering an ONU
After you deregister an ONU, the ONU will be re-registered.
To deregister an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
|
3. Deregister the ONU. |
deregister onu |
Updating ONUs
Table 3 shows the methods for updating ONUs. You can use one or multiple of the methods based on the network requirements.
Table 3 Remote ONU update methods
|
Method |
Description |
|
Update the ONUs of a specific type. You can perform this take multiple times to update different types of ONUs. |
|
|
Update the ONU bound to an ONU port. |
|
|
Update all ONUs attached to an OLT port. |
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
Before you perform an upgrade, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· You must upload the ONU update files to the active MPU of the OLT.
· To ensure successful update for ONUs that come online after an active/standby switchover, you must upload the update files to both the active and standby MPUs.
· If ONUs and update files do not match, the update for the ONUs will fail. For example, if you specify the update file for ET704-A ONUs in OLT port view, other types of ONUs attached to the OLT port cannot be updated.
· Update commands in interface view take precedence over the update commands in FTTH view. For example, the ONU bound to ONU 3/0/1:1 is the A type. If you specify the update file 1.app for ONUs of the A type in FTTH view and specify the update file 2.app in the view of ONU 3/0/1:1, the ONU uses 2.app for update. If you cancel the update configuration in the view of ONU 3/0/1:1, the OLT does not immediately update the ONU by using 1.app. The ONU will be updated after it is reregistered and its ONU port comes up.
During an upgrade, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· ONUs automatically reboot to update after they obtain update files from the OLT. To avoid update failures, do not power off the ONUs during an update.
· The update commands are automatically saved to the configuration file of the OLT after execution. If you only want to update online ONUs, use the undo form of the update commands after the update is completed on online ONUs.
· If an ONU is not online or its ONU port is down during an update, the OLT updates the ONU after the ONU is registered and its ONU port comes up.
Batch updating ONUs by type
This feature enables the OLT to automatically update ONUs that match the specified ONU type and do not have an update file. If a matching ONU is online, the ONU is updated. If a matching ONU is not online, the ONU is updated when it is online.
You can update a maximum of 64 types of ONUs at the same time.
|
Step |
Command |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
|
3. Update the ONUs of the specified type. |
update onu type onu-type filename filename |
Updating a single ONU
|
Step |
Command |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
|
3. Update the ONU. |
update onu filename filename |
Batch updating ONUs by OLT port
After you perform this task, whether the OLT updates a matching ONU that newly comes online depends on the creation time of the corresponding ONU port.
· If the ONU port is created before you perform this task, the ONU will be updated.
· If the ONU port is created after you perform this task, the ONU will not be updated.
To batch update ONUs by OLT port:
Rebooting an ONU
|
Step |
Command |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
|
3. Reboot the ONU. |
reboot onu |
Configuring basic settings of UNIs
Basic settings of a UNI include the following:
· Duplex mode—When a UNI is operating in full duplex mode, it can send and receive packets simultaneously. When a UNI is operating in half duplex mode, it can either send or receive packets at a given time. When a UNI is operating in autonegotiation mode, the UNI and its peer port determine the duplex mode of the UNI through negotiation.
· Autonegotiation—The UNI and its peer port determine the duplex mode, cable type, and port rate of the UNI through negotiation.
· Flow control—If flow control is enabled for a UNI and its peer, the UNI will send messages to notify the peer to stop sending packets temporarily when congestion occurs on the UNI. This mechanism avoids packet loss.
· MDIX mode—You can use both crossover and straight-through Ethernet cables to connect UNIs to user terminals. To accommodate these types of cables, set the MDIX mode of a UNI by following these guidelines:
? As a best practice, set the MDIX mode to AutoMDIX. Set the MDIX mode to MDI or MDIX only when the device cannot determine the cable type.
? When a straight-through cable is used, configure the UNI to operate in an MDIX mode different than its peer.
? When a crossover cable is used, perform one of the following tasks:
- Configure the UNI to operate in the same MDIX mode as its peer.
- Configure either end to operate in AutoMDIX mode.
· Port rate—The port rate of a UNI can be manually set or autonegotiated by the UNI and its peer port.
On a UNI, do not enable autonegotiation and manually set the duplex mode, MDIX mode, or port rate at the same time.
To configure basic settings of UNIs:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable autonegotiation on a UNI. |
uni uni-number auto-negotiation |
By default, autonegotiation is enabled on a UNI. |
|
4. Configure the description for a UNI. |
uni uni-number description text |
By default, a UNI does not have a description. |
|
5. Set the duplex mode of a UNI. |
uni uni-number duplex { auto | full | half } |
By default, a UNI is operating in full-duplex mode. |
|
6. Enable flow control for a UNI. |
uni uni-number flow-control |
By default, flow control is disabled for a UNI. |
|
7. Set the MDIX mode for a UNI. |
uni uni-number mdix-mode { automdix | mdi | mdix } |
By default, the MDIX mode of a UNI is automdix. ET254 ONUs do not support this command. |
|
8. Shut down a UNI. |
uni uni-number shutdown |
By default, a UNI is up. |
|
9. Set the rate of a UNI. |
uni uni-number speed { 10 | 100 | 1000 | auto } |
By default, the rate of a UNI is 100 Mbps. |
|
10. Force a UNI to restart autonegotiation. |
uni uni-number restart auto-negotiation |
This command can be used only when autonegotiation is enabled. |
Setting the VLAN operation mode for a UNI
The VLAN operation mode of a UNI can be transparent, tag, translation, or QinQ.
· Transparent mode—Applicable when the service provider provides and manages the user-end family gateway or switch. In this scenario, the VLAN tags generated by the family gateway or switch are trusted. In transparent mode, an ONU transparently forwards the received uplink Ethernet packets (whether the Ethernet packets are VLAN-tagged or not) to the OLT without changing them. Downlink Ethernet packets are also forwarded transparently.
· Tag mode—Applicable when the VLAN tags generated by the user-end family gateway or switch are not trusted. For packet processing in tag mode, see Table 4.
· Translation mode—In translation mode, an ONU translates the CVLAN tag into a unique SVLAN tag. Translation mode ensures correct traffic forwarding if two users in an EPON system use the same VLAN ID. For packet processing in translation mode, see Table 4.
· QinQ mode—In QinQ mode, an ONU adds an SVLAN tag to packets that have a CVLAN tag. Then, the service provider can centrally manage and control the VLANs of the packets.
You can enable transparent transmission for VLANs used for special purposes when the QinQ mode is used. For example, a VLAN dedicated to a corporation or a management VLAN. When receiving packets tagged with the VLAN ID, the ONU does not add the SVLAN tag to the packets before forwarding them to the service provider network.
How an ONU in QinQ mode processes packets depends on the ONU model.
Table 4 Packet processing for VLAN operation modes
|
VLAN operation mode |
Traffic direction |
Tagging status of packets |
Packet processing |
|
Transparent mode |
Uplink |
Tagged |
The UNI forwards the packet without any changes. |
|
Untagged |
|||
|
Downlink |
Tagged |
||
|
Untagged |
|||
|
Tag mode |
Uplink |
Tagged |
The UNI drops the packet. |
|
Untagged |
The UNI tags the packet with the PVID and forwards it. |
||
|
Downlink |
Tagged |
The ONU forwards the packet to the outgoing UNI based on the VLAN tag and removes the VLAN tag before sending the packet. |
|
|
Untagged |
The UNI drops the packet. |
||
|
Translation mode |
Uplink |
Tagged |
· If the VLAN tag is the PVID of the UNI, the UNI drops the packet. · If the VLAN tag matches a VLAN translation entry for the UNI, the UNI replaces the VLAN tag and forwards the packet. If no matching entry is found, the UNI drops the packet. |
|
Untagged |
The UNI tags the packet with the PVID and forwards the packet. |
||
|
Downlink |
Tagged |
· If the VLAN tag is the PVID of the UNI, the UNI removes the VLAN tag and forwards the packet. · If the VLAN tag matches a VLAN translation entry for the UNI, the UNI replaces the VLAN tag and forwards the packet. If no matching entry is found, the UNI drops the packet. |
|
|
Untagged |
The UNI drops the packet. |
To set the VLAN operation mode for a UNI:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the VLAN operation mode for a UNI. |
· Transparent mode: · Tag mode: · Translation mode: · QinQ mode: ? Enable QinQ mode: ? (Optional.) Specify the SVLAN tag for
packets with the specified CVLAN tags: ? (Optional.) Enable transparent transmission for the specified CVLANs: |
By default, the VLAN operation mode of a UNI is transparent. If the link type of all ONU ports on an OLT port is access, you must set the transparent mode for UNIs of the ONUs. This setting ensures that the ONU ports and users receive only untagged packets. |
Enabling fast-leave processing for a UNI
This feature immediately removes a UNI from the outgoing port list of the forwarding table when the UNI receives an IGMP leave message for a multicast group. Then, when the ONU receives IGMP group-specific queries for that multicast group, the ONU does not forward them to that UNI.
If only one host is attached to a UNI, fast-leave processing helps improve bandwidth and resource usage. If multiple hosts in the same multicast group are attached to a UNI, when one host leaves the multicast group, the other hosts cannot receive multicast data.
Before you enable fast-leave processing, make sure the ONU is operating in IGMP snooping mode. This feature takes effect only for IGMPv2 or IGMPv3 clients.
To enable fast-leave processing for a UNI:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. (Optional.) Set the multicast mode to IGMP snooping. |
multicast mode igmp-snooping |
By default, the multicast mode of an ONU is IGMP snooping. |
|
4. Enable fast-leave processing for UNIs. |
· Enable fast-leave processing for all UNIs: · Enable fast-leave processing for a UNI: |
You cannot use both commands. By default, fast-leave processing is disabled for a UNI. |
Configuring UNI port isolation
UNI port isolation improves security and allows flexible networking schemes by isolating UNIs at Layer 2. UNIs in an isolation group cannot communicate with each other.
An ONU supports only one isolation group. The number of UNIs in the isolation group is not limited.
To configure UNI port isolation:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure UNI port isolation. |
· Assign all UNIs on the ONU to the
isolation group: · Assign a UNI to the isolation group: |
You cannot use both commands. By default, a UNI is not in the isolation group. |
Configuring port mirroring on a UNI
Port mirroring copies the packets passing through a port to another port that connects to a data monitoring device for packet analysis. The monitored port is the mirroring source port. The port connected to the data monitoring device is the mirroring destination port.
A UNI cannot be both a mirroring source port and destination port.
To configure port mirroring on a UNI:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure a UNI as a mirroring source port. |
uni uni-number mirroring-port { both | inbound | outbound } |
By default, a UNI is not a mirroring source port. |
|
4. Configure a UNI as a mirroring destination port. |
uni uni-number monitor-port |
By default, a UNI is not a mirroring destination port. |
Testing the cable connected to a UNI
Perform this task to test the cable connected to a UNI and display the test result.
To test the cable connected to a UNI:
|
Step |
Command |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
|
2. Enter ONU port view. |
interface onu interface-number |
|
3. Test the cable connected to a UNI. |
uni uni-number virtual-cable-test |
Configuring EPON alarms
To report critical EPON events, enable alarms for EPON. For EPON event alarms to be sent correctly, you must also configure SNMP on the device. For more information about SNMP configuration, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Enabling alarm monitoring
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view. |
ftth |
N/A |
|
3. Enable alarm monitoring. |
monitor enable |
By default, alarm monitoring is enabled. |
|
4. (Optional.) Set the alarm monitoring interval. |
timer monitor seconds |
By default, the alarm monitoring interval is 80 seconds. |
Enabling alarms on OLT ports
If you enable alarms in OLT port view, the configuration takes effect only on the OLT port. If you enable alarms in FTTH view, the configuration takes effect on all OLT ports.
If you configure alarms in both OLT port view and FTTH view, the most recent configuration takes effect on the OLT port.
To view alarm settings, use the display this command in FTTH view or OLT port view.
To enable alarms on OLT ports:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter FTTH view or OLT port view. |
· Enter FTTH view: · Enter OLT port view: |
N/A |
|
3. Enable the device fatal error alarm. |
alarm device-fatal-error enable |
By default, the device fatal error alarm is enabled. This alarm is sent if an error that causes system unavailability occurs, such as memory leak and high memory usage. |
|
4. Enable the critical event alarm. |
alarm oam critical-event enable |
By default, the critical event alarm is enabled. This alarm is sent if the local link fault or dying gasp alarm is sent. |
|
5. Enable the dying gasp alarm. |
alarm oam dying-gasp enable |
By default, the dying gasp alarm is enabled. This alarm is sent if an irrecoverable error occurs, such as a system error and a data loading error. |
|
6. Enable the local link fault alarm. |
alarm oam local-link-fault enable |
By default, the local link fault alarm is enabled. This alarm is sent if a fault occurs in the inbound direction on the OLT. |
|
7. Enable the ONU laser always on alarm. |
alarm onu-laser always-on enable |
By default, the ONU laser always on alarm is enabled. This alarm is sent if an ONU keeps sending optical signals for a long period of time. |
|
8. Enable the ONU over limit alarm. |
alarm onu-over-limit enable |
By default, the ONU over limit alarm is enabled. This alarm is sent if the number of ONUs connected to the OLT reaches the upper limit. |
|
9. Enable the registration error alarm. |
alarm registration-error enable |
By default, the registration error alarm is enabled. This alarm is sent if an error occur during ONU registration. |
Displaying and maintaining EPON
Displaying and maintaining the OLT
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display information about fiber backup groups. |
display epon fiber-backup group { group-number | all } |
|
Display OAM information for an ONU port. |
display epon oam interface interface-type interface-number |
|
Display ONU registration and deregistration records for an ONU port. |
display epon onu-event interface interface-type interface-number |
|
Display optical parameters for an OLT port. |
display epon optics-parameters interface interface-type interface-number |
|
Display EPON system parameters. |
display epon parameter slot slot-number |
|
Display packet error rates on an ONU port. |
display epon statistics interface interface-type interface-number |
|
Display version information for an OLT or ONU port. |
display epon version interface interface-type interface-number |
|
Display the operating mode of an OLT or ONU port. |
display epon workmode interface interface-type interface-number |
Displaying and maintaining ONUs
|
Task |
Command |
View |
|
Display IP address assignment information for an ONU that acts as a DHCP client. |
display dhcp-client |
ONU port view |
|
Display multicast information for an ONU port in multicast control mode. |
display epon multicast |
ONU port view |
|
Display ONU information. |
display onu [ silent ] { interface interface-type interface-number | slot slot-number } |
Any view |
|
Display information about a legal ONU. |
display onu mac-address mac-address |
Any view |
|
Display information about protocols supported by an ONU. |
display onu protocol { dhcp-snooping information | igmp-snooping | loopback-detection | pppoe | smart-link | stp } |
ONU port view |
|
Display information about UNI count-based PON port activation for an ONU. |
display onu protocol smart-link uni-bind information |
ONU port view |
|
Display information about a serial interface on an ONU. |
display serial-information interface-number |
ONU port view |
|
Display information about a UNI on an ONU. |
display uni uni-number |
ONU port view |
|
Display detailed information about an ONU. |
display vendor-specific information |
ONU port view |
|
Clear packet statistics on a serial interface on an ONU. |
reset counters serial serial-port-id |
ONU port view |
|
Clear packet statistics on UNIs. |
reset counters uni [ uni-number ] |
ONU port view |
Displaying and maintaining UNIs
Execute display and reset commands in ONU port view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display information of a UNI. |
display uni uni-number |
|
Clear packet statistics on UNIs. |
reset counters uni [ uni-number ] |
Support for non-EPON features and configuration restrictions
|
|
NOTE: Support for the non-EPON features depends on the ONU model and software version. |
OLT port features and restrictions
Table 5 shows the features supported by an OLT port.
|
Feature |
Tasks/commands and restrictions |
Related chapter/book |
|
Transceiver module management |
· Display transceiver alarms (display transceiver alarm). · Display the current values of the digital diagnosis parameters on transceiver modules (display transceiver diagnosis). · Display the key parameters of transceiver modules (display transceiver interface). · Display electronic label information for transceiver modules (display transceiver manuinfo). |
Fundamentals Command Reference |
|
Basic port parameters |
· Restore the default settings for an OLT port (default). · Configure a description for an OLT port (description). · Display OLT port information (display interface). · Bring up or shut down an OLT port (shutdown). · Clear packet statistics on an OLT port (reset counters interface). · Enable broadcast storm suppression (broadcast-suppression). · Enable multicast storm suppression (multicast-suppression). · Enable unknown unicast storm suppression (unicast-suppression). |
Interface Command Reference |
|
Configure port isolation for OLT ports (port-isolate enable). |
Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference |
|
|
QinQ and VLAN mapping |
· Configure user-side QinQ or VLAN mapping. · Configure network-side VLAN mapping. |
"Configuring QinQ" "Configuring VLAN mapping" |
|
IGMP snooping |
Configure IPv4 multicast source port filtering (igmp-snooping source-deny). |
IP Multicast Command Reference |
|
MPLS L2VPN/VPLS |
Configure Ethernet service instances on an OLT port. Transparent transmission of 802.1X, IGMP, MLD, and BCMP protocol packets is not supported. The Ethernet service instances on an OLT port support only the VLAN access mode. |
MPLS Configuration Guide |
|
QoS |
· Apply QoS policies on OLT ports (qos apply policy). · Display QoS policy information for OLT ports (display qos policy interface). · Configure priority mapping: ? Configure the priority trust mode for an OLT port (qos trust). ? Display the priority trust mode and port priorities of an OLT port (display qos trust interface). · Set GTS parameters (qos gts). · Display the GTS information for OLT ports (display qos gts interface). · Configure rate limiting on an OLT port (qos lr). · Display the rate limit information for OLT ports (display qos lr). · Configure hardware congestion management: ? Enable SP queuing on an OLT port (qos sp). ? Display the SP queuing configuration of an OLT port (display qos queue sp interface). ? Enable WRR queuing on an OLT port (qos wrr). ? Display the WRR queuing configuration of an OLT port (display qos queue wrr interface). |
ACL and QoS Command Reference |
|
MAC authentication |
· Enable MAC authentication (mac-authentication). · Display MAC authentication information for OLT ports (display mac-authentication). · Clear MAC authentication statistics (reset mac-authentication statistics). |
Security Command Reference |
|
IP source guard |
Configure IP source guard on OLT ports. |
Security Configuration Guide |
|
Smart Link |
Enable receiving of flush messages (smart-link flush enable). |
High Availability Command Reference |
|
Monitor Link |
Configure OLT ports as members of a monitor link group (port monitor-link group). |
High Availability Command Reference |
|
Port mirroring |
· Configure an OLT port as a source port for a mirroring group (mirroring-group mirroring-port). |
Network Management and Monitoring Command Reference |
|
SNMP notifications |
Enable link state notifications for OLT ports (enable snmp trap updown). |
Network Management and Monitoring Command Reference |
Commands unavailable in OLT port view
Table 6 Commands unavailable in OLT port view
|
Chapter |
Unavailable commands |
|
Interface Command Reference |
flow-control |
|
Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference |
qinq ethernet-type |
|
IP Multicast Command Reference |
mld-snooping source-deny |
|
ACL and QoS Command Reference |
qos priority |
|
Security Command Reference |
All 802.1X commands |
|
Network Management and Monitoring Command Reference |
mirroring-group monitor-port |
ONU port features and restrictions
Table 7 ONU port features
|
Feature |
Tasks/commands and restrictions |
Related chapter/book |
|
Basic port parameters |
· Restore the default settings for an ONU port (default). · Configure a description for an ONU port (description). · Display ONU port information (display interface). · Bring up or shut down an ONU port (shutdown). · Clear packet statistics on an ONU port (reset counters interface). · Enable broadcast suppression on an ONU port (broadcast-suppression). · Enable multicast storm suppression on an ONU port (multicast-suppression). · Enable unknown unicast storm suppression on an
ONU port (unicast-suppression). |
Interface Command Reference |
|
MAC address table |
· Display MAC address entries (display mac-address). · Display the global MAC address learning status and the MAC learning status of ONU ports (display mac-address mac-learning). · Add or modify a MAC address entry (mac-address). · Set the MAC learning limit on an OLT port (mac-address max-mac-count). |
Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference |
|
IGMP snooping |
· Enable fast-leave processing on an ONU port (igmp-snooping fast-leave). · Set the maximum number of multicast groups that an ONU port can join (igmp-snooping group-limit). · Configure a multicast group policy on an ONU port to control the multicast groups that hosts attached to the port can join (igmp-snooping group-policy). · Configure an ONU port as a simulated member host for a multicast group (igmp-snooping host-join). · Enable multicast group replacement on an ONU port (igmp-snooping overflow-replace). · Configure a port as a static member port of a multicast group (igmp-snooping static-group). · Configure a port as a static router port (igmp-snooping static-router-port). |
IP Multicast Command Reference |
|
QoS |
· Apply QoS policies on ONU ports (qos apply policy). · Display QoS policy information for ONU ports (display qos policy interface). · Configure priority mapping: ? Configure the port priority for an ONU port (qos priority). ? Configure the priority trust mode for an ONU port (qos trust). ? Display the priority trust mode and port priorities of an ONU port (display qos trust interface). · Configure hardware congestion management: ? Enable SP queuing on an ONU port (qos sp). ? Display the SP queuing configuration of an ONU port (display qos queue sp interface). ? Configure WFQ queuing on an ONU port (qos wfq). ? Display the WFQ configuration of an ONU port (display qos queue wfq interface). |
ACL and QoS Command Reference |
|
802.1X |
Configure 802.1X authentication on ONU ports. ONU ports do not support MAC-based authentication. If you execute the dot1x command on an ONU port, the dot1x port-method portbased command is automatically configured. If you execute the undo dot1x command on the ONU port, the access control method of the ONU port is restored to the default (macbased). |
Security Configuration Guide |
|
Monitor Link |
Configure ONU ports as members of a monitor link group (port monitor-link group). |
High Availability Command Reference |
|
SNMP notifications |
Enable link state notifications for ONU ports (enable snmp trap updown). |
Network Management and Monitoring Command Reference |
Table 8 QoS configuration restrictions
|
Feature |
Restrictions |
|
ACL rule action |
When an ACL rule is used in a traffic class of a QoS policy, the action defined in the ACL rule (deny or permit) does not take effect. Instead, the traffic behavior associated with the traffic class determines the actions on the packets that match the ACL rule. |
|
Packet filtering |
· ONU ports only support packet filtering based on the following criteria: ? Source MAC address. ? Destination MAC address. ? Ethernet type. ? VLAN ID. ? Source IP address. ? Destination IP address. ? Source TCP port. ? Source UDP port. · Source MAC address-based packet filtering on an ONU port works only on the uplink direction and supports a maximum of 32 ACL rules. · Destination MAC address-based packet filtering on an ONU port works on both uplink and downlink directions at the same time and supports a maximum of 32 ACL rules. |
|
ACL rule limit |
· The number of ACL rules supported by Ethernet type-based packet filtering on an ONU port depends on the direction: ? Supports a maximum of 30 ACL rules if configured only in one direction. ? Supports a maximum of 16 ACL rules for each direction if configured in both directions. · The number of ACL rules supported by VLAN ID-based packet filtering on an ONU port depends on the direction: ? Supports a maximum of 6 ACL rules for the uplink direction. ? Supports a maximum 8 ACL rules for the downlink direction. · The number of ACL rules supported by source or destination IP address-based packet filtering on an ONU port depends on the direction: ? Supports a maximum of 24 ACL rules if configured only in one direction. ? Supports a maximum of 16 ACL rules for each direction if configured in both directions. · The number of ACL rules supported by source TCP/UDP port-based packet filtering on an ONU port depends on the direction: ? Supports a maximum of 24 ACL rules if configured only in one direction. ? Supports a maximum of 32 ACL rules if configured in both directions. |
Commands unavailable in ONU port view
Table 9 Commands unavailable in ONU port view
|
Chapter |
Unavailable commands |
|
Interface Command Reference |
· link-delay · loopback |
|
Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference |
· undo mac-address max-mac-count enable-forwarding · All loop detection commands |
|
Security Command Reference |
· arp rate-limit · dot1x unicast-trigger |
|
Layer 3—IP Services Command Reference |
dhcp snooping rate-limit |
|
IP Multicast Command Reference |
All MLD snooping commands |
|
Network Management and Monitoring Command Reference |
· mirroring-group mirroring-port · mirroring-group monitor-port |
EPON configuration examples
Fiber backup configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 7, configure fiber backup for the two OLT ports to back up each other.
Configuration procedure
# Create fiber backup group 1.
<OLT> system-view
[OLT] ftth
[OLT-ftth] fiber-backup group 1
# Assign OLT 3/0/1 and OLT 3/0/2 to the fiber backup group in sequence. OLT 3/0/1 is the master port, and OLT 3/0/2 is the subordinate port.
[OLT-fiber-group1] member olt3/0/1
[OLT-fiber-group1] member olt3/0/2
[OLT-fiber-group1] display epon fiber-backup group 1
Fiber backup group 1 information:
Member Role State
OLT3/0/1 Master Active
OLT3/0/2 Standby Ready
Verifying the configuration
# Perform a master/subordinate switchover, and verify that OLT 3/0/2 becomes the master port.
[OLT-fiber-group1] port switch-over
[OLT-fiber-group1] display epon fiber-backup group 1
Fiber backup group 1 information:
Member Role State
OLT3/0/2 Master Active
OLT3/0/1 Standby Ready
# Shut down OLT 3/0/2, and verify that OLT 3/0/1 becomes the master port.
[OLT-fiber-group1] quit
[OLT] interface olt3/0/2
[OLT-Olt3/0/2] shutdown
[OLT-Olt3/0/2] display epon fiber-backup group 1
Fiber backup group 1 information:
Member Role State
OLT3/0/1 Master Active
OLT3/0/2 Standby Down
ONU binding configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 8, bind ONU1 (000f-e200-0031) and ONU2 (000f-e200-3749) to ONU ports ONU 3/0/1:1 and ONU 3/0/1:2, respectively.
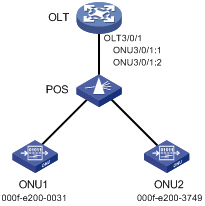
Configuration procedure
# Create ONU ports ONU 3/0/1:1 and ONU 3/0/1:2.
<OLT> system-view
[OLT] interface olt 3/0/1
[OLT-Olt3/0/1] using onu 1 to 2
[OLT-Olt3/0/1] quit
# Bind ONU1 to ONU 3/0/1:1.
[OLT] interface onu 3/0/1:1
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] bind onu-id 000f-e200-0031
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] quit
# Bind ONU2 to ONU 3/0/1:2.
[OLT] interface onu 3/0/1:2
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:2] bind onu-id 000f-e200-3749
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Power on ONU1 and ONU2, and verify that the ONUs have been bound to their respective ONU port.
<OLT> display onu interface olt 3/0/1
MAC LLID Dist(M) Port Model/Version Sft/Epm State Aging
000f-e200-0031 1 1 Onu3/0/1:1 ET724/A 105/100 Up N/A
000f-e200-3749 2 1 Onu3/0/1:2 ET302/A 103/100 Up N/A
--- 2 entries found ---
Multicast in IGMP snooping mode configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 9, the ONU has been bound to ONU 3/0/1:1.
Configure multicast in IGMP snooping mode on the ONU for User 1 to access channels 225.1.2.1 through 225.1.2.255 and User 2 to access channels 225.1.3.1 through 225.1.3.255.
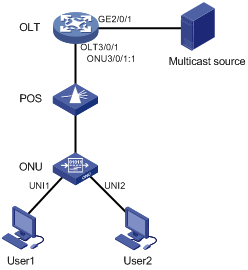
Configuration procedure
# Map the multicast IP addresses to multicast VLANs.
<OLT> system-view
[OLT] ftth
[OLT-ftth] multicast vlan-id 1002 ip 225.1.2.1 to 225.1.2.255
[OLT-ftth] multicast vlan-id 1003 ip 225.1.3.1 to 225.1.3.255
[OLT-ftth] quit
# Enable IGMP snooping globally.
[OLT] igmp-snooping
[OLT-igmp-snooping] quit
# Enable IGMP snooping and IGMP snooping querier in VLAN 1002 and VLAN 1003.
[OLT] vlan 1002
[OLT-vlan1002] igmp-snooping enable
[OLT-vlan1002] igmp-snooping querier
[OLT-vlan1002] quit
[OLT] vlan 1003
[OLT-vlan1003] igmp-snooping enable
[OLT-vlan1003] igmp-snooping querier
[OLT-vlan1003] quit
# Set the multicast mode to IGMP snooping on ONU 3/0/1:1.
[OLT] interface onu 3/0/1:1
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] multicast mode igmp-snooping
# Assign UNI 1 and UNI 2 of the ONU to multicast VLANs 1002 and 1003, respectively.
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] uni 1 multicast vlan 1002
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] uni 2 multicast vlan 1003
# Configure ONU 3/0/1:1 as a trunk port that permits all VLANs.
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] port link-type trunk
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] port trunk permit vlan all
# Configure UNI 1 and UNI 2 to remove the VLAN tag of downlink multicast flows.
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] uni 1 multicast-strip-tag enable
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] uni 2 multicast-strip-tag enable
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] quit
# Configure OLT 3/0/1 as a hybrid port, and assign it to VLAN 1002 and VLAN 1003 as a tagged member.
[OLT] interface olt 3/0/1
[OLT-Olt3/0/1] port link-type hybrid
[OLT-Olt3/0/1] port hybrid vlan 1002 1003 tagged
[OLT-Olt3/0/1] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 as a trunk port that permits VLAN 1002 and VLAN 1003.
[OLT] interface gigabitethernet2/0/1
[OLT-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] port link-type trunk
[OLT-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1002 1003
[OLT-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
Multicast in multicast control mode configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 10, the ONU has been bound to ONU 3/0/1:1.
Configure multicast in multicast control mode to provide different access rights for User 1 and User 2.
· User 1 has full access to Channel 1(225.1.1.1) and 60-second preview access to Channel 2 (225.1.2.1)
· User 2 only has access to Channel 2.

Configuration procedure
# Map the multicast IP addresses to multicast VLANs.
<OLT> system-view
[OLT] ftth
[OLT-ftth] multicast vlan-id 1002 ip 225.1.1.1
[OLT-ftth] multicast vlan-id 1003 ip 225.1.2.1
[OLT-ftth] quit
# Enable IGMP snooping globally.
[OLT] igmp-snooping
[OLT-igmp-snooping] quit
# Enable IGMP snooping in VLAN 1002 and VLAN 1003.
[OLT] vlan 1002
[OLT-vlan1002] igmp-snooping enable
[OLT-vlan1002] vlan 1003
[OLT-vlan1003] igmp-snooping enable
[OLT-vlan1003] quit
# Set the multicast mode to multicast control on ONU 3/0/1:1.
[OLT] interface onu 3/0/1:1
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] multicast mode multicast-control
# Configure UNI 1 to allow User 1 to access Channel 1 and to preview Channel 2 for only 60 seconds.
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] uni 1 multicast-control multicast-address 225.1.1.1 rule permit
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] uni 1 multicast-control multicast-address 225.1.2.1 rule preview time-slice 1
# Configure UNI 1 to remove the VLAN tags from downlink multicast packets.
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] uni 1 multicast-strip-tag enable
# Configure UNI 2 to allow User 2 to access Channel 2 only.
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] uni 2 multicast-control multicast-address 225.1.1.1 rule deny
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] uni 2 multicast-control multicast-address 225.1.2.1 rule permit
# Configure UNI 2 to remove the VLAN tags from downlink multicast packets.
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] uni 2 multicast-strip-tag enable
# Configure ONU 3/0/1:1 as a trunk port that permits all VLANs.
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] port link-type trunk
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] port trunk permit vlan all
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] quit
# Configure OLT 3/0/1 as a hybrid port, and assign it to VLAN 1002 and VLAN 1003 as a tagged member.
[OLT] interface olt 3/0/1
[OLT-Olt3/0/1] port link-type hybrid
[OLT-Olt3/0/1] port hybrid vlan 1002 1003 tagged
[OLT-Olt3/0/1] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 as a trunk port that permits VLAN 1002 and VLAN 1003.
[OLT] interface GigabitEthernet2/0/1
[OLT-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] port link-type trunk
[OLT-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1002 1003
[OLT-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
ONU update configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 11, update the type-A ONU bound to ONU 3/0/1:1 at Site A with the enhanced software version 110.
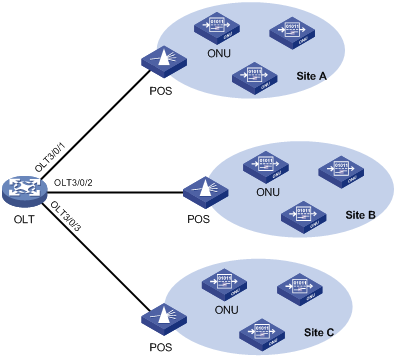
Configuration procedure
# Upload the file a110.app to the active and standby MPUs of the OLT. (Details not shown.)
# Update the type-A ONU bound to ONU 3/0/1:1 with the file a110.app.
<OLT> system-view
[OLT] interface onu 3/0/1:1
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] update onu filename a110.app
Update flash:/ a110.app?[Y/N]:y
Info: Download file to onu may take a long time, please wait...
Please wait while the firmware is being burnt, and check the software version after re-registration!
[OLT-Onu3/0/1:1] quit
Configuring BCMP
Overview
Broadband-access-network Cluster Management Protocol (BCMP) uses a BCMP server to centrally manage an EPON system as a management domain.
BCMP architecture
As shown in Figure 12, a BCMP system contains the following components:
· BCMP proxy—Proxy management server in a BCMP system. The BCMP proxy forwards member registration information and configuration between the BCMP server and BCMP clients.
· BCMP client—Member network elements in a BCMP system. BCMP clients are high-performance (HS) switches connected to ONUs or ONUs integrated with HS. The BCMP server centrally manages the BCMP clients through the BCMP proxy.
Figure 12 BCMP system architecture
Working mechanism
The BCMP server registers and configures a BCMP client by using the following procedure:
1. The BCMP client sends a registration request that contains its MAC address to the BCMP server.
2. The ONU connected to the BCMP client adds the UNI number of the client to the request, and forwards the request to the BCMP proxy (OLT).
3. The OLT performs the following operations:
a. Extracts the client MAC address and UNI number from the request.
b. Adds the ONU MAC address when re-encapsulating the request.
c. Sends the request to the BCMP server.
4. The BCMP server performs the following operations:
a. Extracts information from the request.
b. Creates a physical status entry for the BCMP client.
c. Sends the BCMP proxy the configuration for the client, including the management VLAN, management IP address, default gateway, and SNMP settings.
5. The BCMP proxy forwards the configuration to the BCMP client.
Configuring an OLT as a BCMP proxy
For a BCMP proxy to communicate with a BCMP server, you must specify the IP address of the server on the BCMP proxy.
To configure an OLT as a BCMP proxy:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable the BCMP proxy feature. |
bcmp-proxy enable |
By default, the BCMP proxy feature is disabled. |
|
3. (Optional.) Specify the BCMP VLAN. |
bcmp-proxy vlan vlan-id |
By default, the BCMP VLAN is 4041. |
|
4. Specify the IP address of the BCMP server. |
bcmp-proxy server address ip-address |
By default, the IP address of the BCMP server is not specified. |
|
5. (Optional.) Specify the port number of the BCMP server. |
bcmp-proxy server port port-number |
By default, the port number of the BCMP server is 5000. |

