- Table of Contents
-
- 11-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA Configuration
- 02-802.1X_Configuration
- 03-MAC Authentication Configuration
- 04-Portal Configuration
- 05-Password Control Configuration
- 06-Public Key Configuration
- 07-IPsec Configuration
- 08-SSH Configuration
- 09-Blacklist Configuration
- 10-TCP and ICMP Attack Protection Configuration
- 11-IP Source Guard Configuration
- 12-ARP Attack Protection Configuration
- 13-ND Attack Defense Configuration
- 14-URPF Configuration
- 15-PKI Configuration
- 16-SSL Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 14-URPF Configuration | 122.72 KB |
Contents
URPF overview
What is URPF
Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (URPF) protects a network against source address spoofing attacks, such as denial of service (DoS) and distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks.
Attackers send packets with forged source addresses to access a system that uses IP-address-based authentication in the name of authorized users, or even the administrator. Even if the attackers cannot receive any response packets, the attacks are still disruptive to the attacked target.
Figure 1 Attack based on source address spoofing
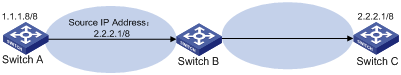
As shown in Figure 1, Switch A sends the server (Switch B) requests with a forged source IP address 2.2.2.1 at a high rate, and Switch B sends packets to IP address 2.2.2.1 (Switch C) in response to the request. Consequently, both Switch B and Switch C are attacked.
URPF can prevent this source address spoofing attack by checking the source addresses of packets and filtering out invalid packets.
URPF check modes
URPF provides two check modes: strict and loose. The switch supports the strict mode only.
Strict URPF
To pass strict URPF check, the source address and receiving interface of a packet must match the destination address and output interface of a forwarding information base (FIB) entry.
In some scenarios such as asymmetrical routing, strict URPF may discard valid packets.
Strict URPF is often deployed between an internet service provider (ISP) and the connected users.
Loose URPF
To pass loose URPF check, the source address of a packet must match the destination address of a FIB entry. Loose URPF can avoid discarding valid packets, but may let go attack packets.
Loose URPF is often deployed between ISPs, especially in asymmetrical routing.
URPF advantages
Strict URPF check can perform link layer check on a packet. It uses the next hop address in the matching FIB entry to look up the ARP table for a matching entry. If the source MAC address of the packet matches the MAC address in the matching ARP entry, the packet passes strict URPF check.
Link layer check is applicable to the scenario where a Layer 3 Ethernet interface connects to a large number of users.
How URPF works
|
|
NOTE: URPF does not check multicast packets. |
URPF works as follows:
1. If the source IP address of an incoming packet is found in the FIB table:
URPF does a reverse route lookup for routes to the source address of the packet. If at least one outgoing interface of such a route matches the receiving interface, the packet passes the check. Otherwise, the packet is discarded. The reverse route lookup refers to searching the outgoing interface whose destination IP address is the source IP address of the packet.
2. If the packet has its source IP address found in the FIB table and passes the check, URPF starts the link layer check:
¡ If the link-check keyword is not configured, the packet passes the check and is forwarded normally.
¡ If the link-check keyword is configured, URPF compares the MAC address of the next hop in the FIB entry with the source MAC address of the packet. If they are the same, the packet passes the check; otherwise, the packet is rejected.
Configuring URPF
To configure URPF:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable URPF check. |
ip urpf strict [ link-check ] |
URPF check is disabled by default. |
|
|
NOTE: · URPF check can be configured only on the VLAN interfaces of an Ethernet interface card. · URPF only checks packets arriving at the interface. · When the system works in standard mode, you cannot configure URPF on the VLAN interface that is bound to a VPN instance configured with no reserved VLAN. For more information about system working mode, see Fundamentals Configuration Guide. For more information about the reserved VLAN, see MPLS Configuration Guide. |
URPF configuration example
|
|
NOTE: By default, the Ethernet, VLAN, and aggregate interfaces are down. Before configuring them, bring them up with the undo shutdown command. |
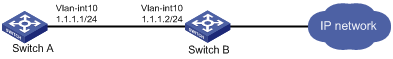
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2, a client (Switch A) directly connects to the ISP switch (Switch B). Enable strict URPF check on VLAN-interface 10 of Switch B to allow packets whose source addresses match ACL 2010 to pass. Enable strict URPF check on VLAN-interface 10 of Switch A to allow use of the default route for URPF check.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure Switch B
# Create VLAN 10.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] vlan 10
[SwitchB-vlan10] quit
# Specify the IP address of VLAN-interface 10.
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface10] ip address 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
# Enable strict URPF check on VLAN-interface 10.
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface10] ip urpf strict
2. Configure Switch A
# Create VLAN 10.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] vlan 10
[SwitchA-vlan10] quit
# Specify the IP address of VLAN-interface 10.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# Enable strict URPF check on VLAN-interface 10.
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] ip urpf strict
