- Released At: 15-04-2021
- Page Views:
- Downloads:
- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
About the H3C access controller configuration guides
|
Configuration guide |
Content |
|
License Management Configuration Guide |
Describes license types and how to apply for, install, uninstall, and transfer a license. This guide includes: · License management · AP license synchronization · License client |
|
Fundamentals Configuration Guide |
Describes how to log in to and set up the device. This guide includes: · CLI (CLI overview and advanced CLI configuration) · FTP and TFTP · Python · RBAC · Tcl · File system management · Login management (CLI login and user configuration and management) · Automatic configuration · Software upgrade · Configuration file management |
|
System Management Configuration Guide |
Describes how to manage the device and logs by using device management, information center, and NTP features. This guide includes: · NTP · Information center · Device management |
|
Interface Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure Ethernet interfaces, PoE, loopback interfaces, null interfaces, inloopback interfaces, and bulk interface settings. This guide includes: · Loopback, null, and inloopback interface · PoE · Ethernet interface · Bulk interface configuration |
|
Network Connectivity Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure network connectivity-related Layer 2 and Layer 3 features. This guide includes: · About the network connectivity configuration guide · MAC address table · Ethernet link aggregation · VLAN · Loop detection · Spanning tree · LLDP · Layer 2 forwarding · VLAN termination · Port isolation · PPP · L2TP · ARP · IP addressing · DHCP · DHCPv6 · DNS · NAT · IP performance optimization · IPv6 basics · Policy routing · IPv6 policy routing · GRE · Tunneling · IP routing basics · IP forwarding basics · Static routing · IPv6 static routing · RIP · RIPng · Multicast overview · IGMP snooping · MLD snooping |
|
WLAN Access Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure WLAN access. This guide includes: WLAN access |
|
AP and WT Management Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure centralized management of fit APs and WTs in an AC+fit AP network. This guide includes: · AP management · WT |
|
WLAN Security Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure WLAN security, WAPI, PMM, DPI, and WIPS features, and reporting user application and URL session information to the server. This guide includes: · WLAN security · WIPS · WAPI · WLAN DRS · PMM |
|
Radio Resources Management Configuration Guide |
Describes how to manage radio channel, power, rate, and load balancing, and measure link quality and WLAN performance. This guide includes: · Radio management · WLAN radio load balancing · WLAN load balancing · WLAN radio resource measurement · Band navigation · WLAN RRM · Channel scanning · Spectrum management |
|
WLAN Roaming Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure wireless client roaming and fast roaming. This guide includes: · WLAN roaming · WLAN roaming center · 802.11r |
|
WLAN Traffic Optimization Configuration Guide |
Describes how to optimize WLAN traffic by using multicast optimization and user isolation. This guide includes: · WLAN multicast optimization · User isolation |
|
WLAN Advanced Features Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure advanced WLAN features, WLAN mesh, AC hierarchy, optimization, and management features. This guide includes: · WLAN optimization · Hotspot 2.0 · WLAN probe · WSA · Wireless location · WLAN fast forwarding · WLAN process maintenance · Bonjour gateway · WLAN mesh · AC hierarchy |
|
User Access and Authentication Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure wired and wireless access and authentication. This guide includes: · WLAN authentication · WLAN IP snooping · AAA · 802.1X · 802.1X client · MAC authentication · Port security · Portal · User identification |
|
Oasis Connection Configuration Guide |
Describes how to manage devices from the Oasis platform. This guide includes: Cloud connection |
|
High Availability Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure wired and wireless high availability features and track. This guide includes: · WLAN high availability (dual-link backup, AP load balancing and backup, and client backup) · IRF · Track · Load balancing · Interface backup |
|
Security Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure identity authentication (PKI), secure management (password control, public key management, IPsec, and SSH), and security protection (IP source guard and ARP attack protection). This guide includes: · ACL · Time range · User profile · Password control · Public key management · PKI · IPsec · SSH · SSL · Session management · Connection limit · Attack detection and prevention · IP source guard · ARP attack protection · ND attack protection · ASPF · Protocol packet rate limit · Crypto engine · ARP · URL filtering · Bandwidth management · DPI engine |
|
QoS Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure wired and wireless QoS. This guide includes: · WLAN QoS (WMM, SVP, bandwidth guaranteeing, and client rate limit) · QoS (priority mapping, traffic policing, traffic filtering, and priority marking) |
|
Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide |
Describes how to manage networks, display system information, control network traffic, sample packets, analyze network performance, and debug network connectivity. This guide includes: · System maintenance and debugging (ping, tracert, and system debugging) · NQA · SNMP · RMON · NETCONF · EAA · Process monitoring and maintenance · Flow log · Packet capture · Mirroring · Fast log output |
|
Internet of Things Configuration Guide |
Describes how to configure and manage IoT modules. This guide includes: IoT AP |
|
Acronyms |
Lists the significant acronyms in the configuration guides. |
Product overview
H3C ACs include the WX series ACs and access controller modules.
Table 1 H3C AC models
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Product code |
|
WX1800H series |
WX1804H |
EWP-WX1804H-PWR-CN |
|
WX2500H series |
WX2508H-PWR-LTE WX2510H WX2510H-F WX2540H WX2540H-F WX2560H |
EWP-WX2508H-PWR-LTE EWP-WX2510H-PWR EWP-WX2510H-F-PWR EWP-WX2540H EWP-WX2540H-F EWP-WX2560H |
|
WX3000H series |
WX3010H WX3010H-X WX3010H-L WX3024H WX3024H-L WX3024H-F |
EWP-WX3010H EWP-WX3010H-X-PWR EWP-WX3010H-L-PWR EWP-WX3024H EWP-WX3024H-L-PWR EWP-WX3024H-F |
|
WX3500H series |
WX3508H WX3510H WX3520H WX3520H-F WX3540H |
EWP-WX3508H EWP-WX3510H EWP-WX3520H EWP-WX3520H-F EWP-WX3540H |
|
WX5500E series |
WX5510E WX5540E |
EWP-WX5510E EWP-WX5540E |
|
WX5500H series |
WX5540H WX5560H WX5580H |
EWP-WX5540H EWP-WX5560H EWP-WX5580H |
|
Access controller modules |
LSUM1WCME0 EWPXM1WCME0 LSQM1WCMX20 LSUM1WCMX20RT LSQM1WCMX40 LSUM1WCMX40RT EWPXM2WCMD0F EWPXM1MAC0F |
LSUM1WCME0 EWPXM1WCME0 LSQM1WCMX20 LSUM1WCMX20RT LSQM1WCMX40 LSUM1WCMX40RT EWPXM2WCMD0F EWPXM1MAC0F |
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Product code |
|
WX1800H series |
WX1804H WX1810H WX1820H WX1840H |
EWP-WX1804H-PWR EWP-WX1810H-PWR EWP-WX1820H EWP-WX1840H-GL |
|
WX3800H series |
WX3820H WX3840H |
EWP-WX3820H-GL EWP-WX3840H-GL |
|
WX5800H series |
WX5860H |
EWP-WX5860H-GL |
Typical application scenarios
This section describes the typical application scenarios of H3C ACs.
Gateway mode
About gateway mode
The WX2500H access controller provides both AC and gateway functionality and can be connected to an ISP network through a Layer 2 or Layer 3 switch, a router, or a modem. Ethernet ports on the AC can operate in WAN mode or LAN mode. You can deploy the AC as the gateway and configure the AC to provide wireless services at the same time.
To use the AC as a gateway, configure one or more ports on the AC to operate in WAN mode based on the number of links at the network egress. Configure the other ports to operate in LAN mode.
To ensure network connectivity, configure PPPoE on the AC's WAN ports.
Applicable scenarios
This deployment mode enables the AC to connect to the ISP network and LANs as a network gateway to provide cost-effective wired and wireless services. It is applicable to small- and medium-sized networks.
Bypass mode
About bypass mode
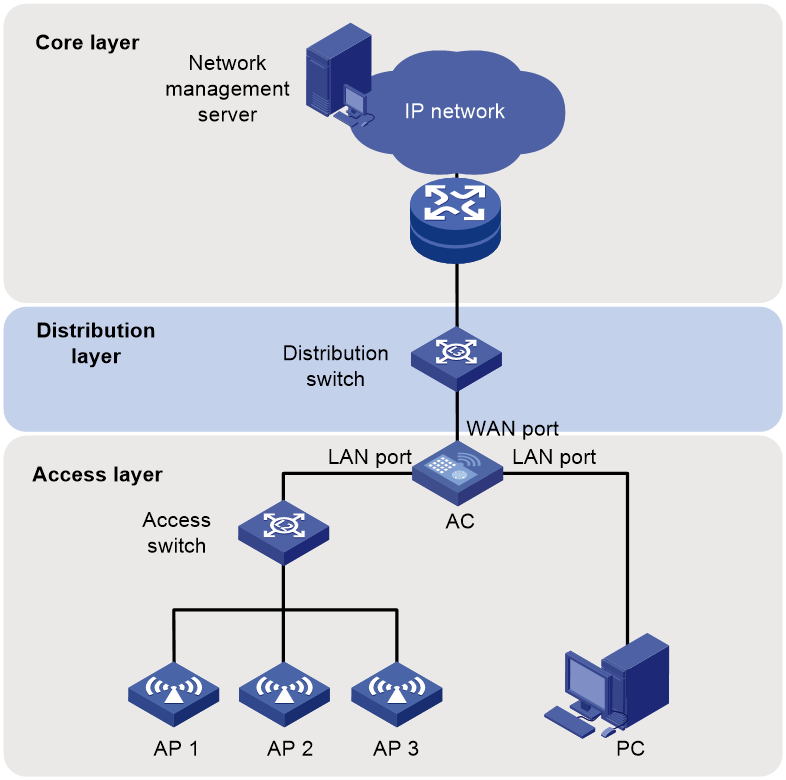
In bypass mode, an AC is attached to an access, distribution, or core switch to manage all the fit APs connected to the switch. The AC obtains its IP address from the DHCP server and APs discover the AC through DHCP, DNS, or broadcast. VLANs can be configured for clients accessing different SSIDs to isolate client traffic.
In this mode, data traffic can be forwarded by the AC (centralized forwarding) or by APs (local forwarding).
Centralized forwarding
As shown in Figure 2, in centralized forwarding mode, the APs send 802.11 traffic to the AC and the AC converts 802.11 traffic to 802.3 traffic for forwarding. This mode is applicable to networks requiring centralized control of data traffic.
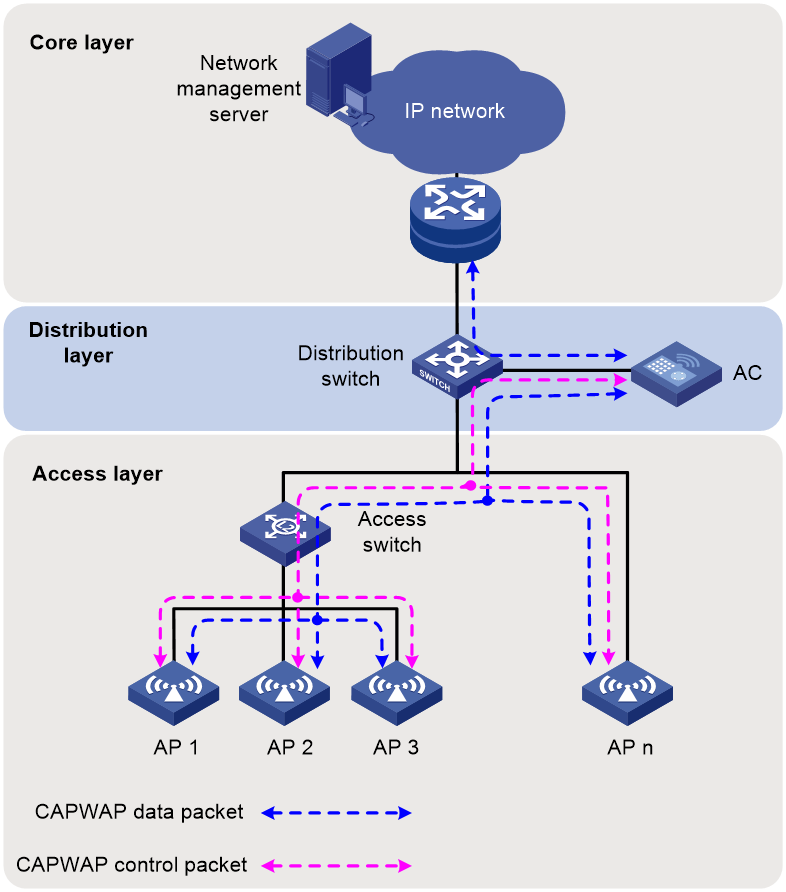
Local forwarding
As shown in Figure 3, data traffic is forwarded directly by the APs through the distribution switch. In this mode, the APs convert 802.11 packets to 802.3 packets. This mode reduces the burden on the AC. It also enables security settings configured for the wired network to take effect on traffic from WLANs because the traffic is transmitted over wired connections in 802.3 format from the APs.
Applicable scenarios
This mode enables wireless services in an existing wired network without reconstructing the network and is applicable to networks with scattered APs.
Direct connection mode
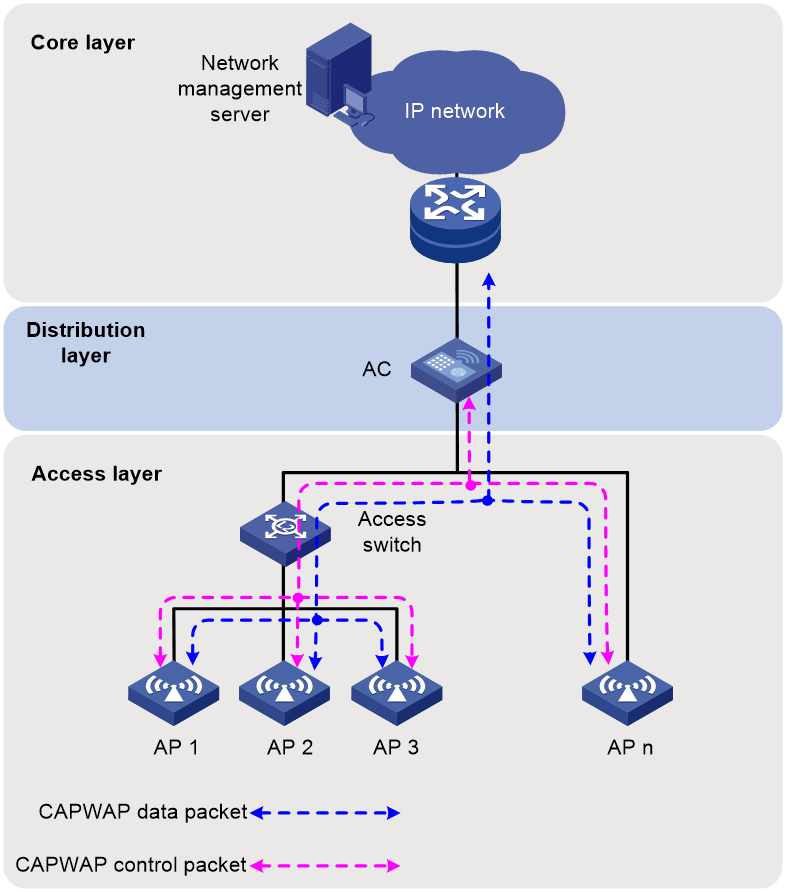
About direct connection mode
As shown in Figure 4, APs access the IP network through direct connections with the AC. The AC assign IP addresses to APs as a DHCP server and APs discover the AC through DHCP, DNS, or broadcast.
Both centralized forwarding and local forwarding are available in this network. In centralized forwarding mode, control traffic and data traffic are transmitted to the AC over the CAPWAP tunnel. In local forwarding mode, only control traffic is transmitted to the AC over the CAPWAP tunnel. As a best practice, use local forwarding to reduce AC's workload.
In this network, a minimum of three VLANs are required on the AC to isolate the following traffic:
· Traffic between the AC and the NMS.
· Control traffic between the AC and APs.
· Client data traffic.
On the uplink switch of the AC, configure the VLAN for AC-NMS traffic and add the inbound interface to the client VLAN to permit data traffic.
Figure 4 Network diagram (local forwarding)
Applicable scenarios
This deployment mode is applicable to small- and medium-sized WLANs with centralized wireless coverage requirements.
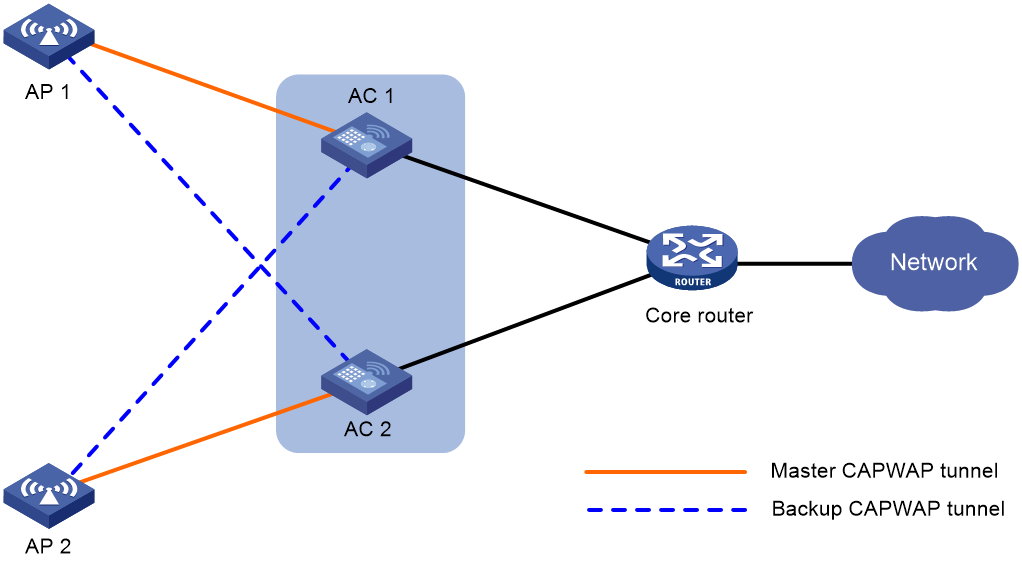
AC high availability
Dual-link backup
Dual-link backup enables two ACs to back up each other to reduce risks of service interruption caused by single-AC failures.
With dual-link backup enabled, an AP establishes a master CAPWAP tunnel and a backup CAPWAP tunnel with the master AC and the backup AC, respectively. When the master AC fails, the backup AC takes over to forward traffic. When the failed master AC recovers, the master CAPWAP tunnel preemption feature determines the master CAPWAP tunnel based on the AP connection priority.
When the backup AC takes over traffic forwarding upon a master AC failure, temporary communication interruption occurs. Therefore, dual-link backup mode applies to scenarios where service continuity
Figure 5 Dual-link backup network
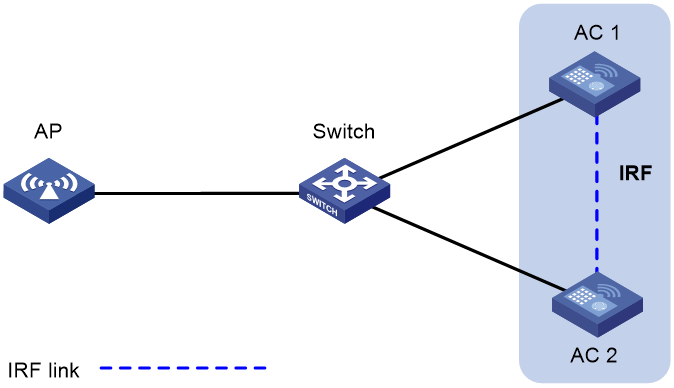
Star-topology IRF
Star-topology IRF enables two ACs to be connected in star topology through a Layer 2 network to form a virtual AC (IRF fabric). The IRF fabric provides the following benefits:
· Easy connection—Member devices can communicate with one another as long as they have Layer 2 connectivity. You do not need to use dedicated physical links to connect IRF member devices.
· High expansibility—The capabilities of the IRF fabric can be expanded simply by adding member devices. The total number of APs or clients the IRF fabric can manage is the sum of the manageable APs or clients of all member devices in the IRF fabric.
· Simple configuration—Configurations on the master device can be synchronized to all the devices in the IRF fabric.
· 1+1 redundancy—In an IRF fabric, one member acts as the master to manage and control the entire IRF fabric and the other member processes services while backing up the master. When the master fails, all the other member devices elect a new master from among them to take over without interrupting services.
· License sharing—Licenses installed on one member device can be used by other member devices.
Figure 6 Star-topology IRF
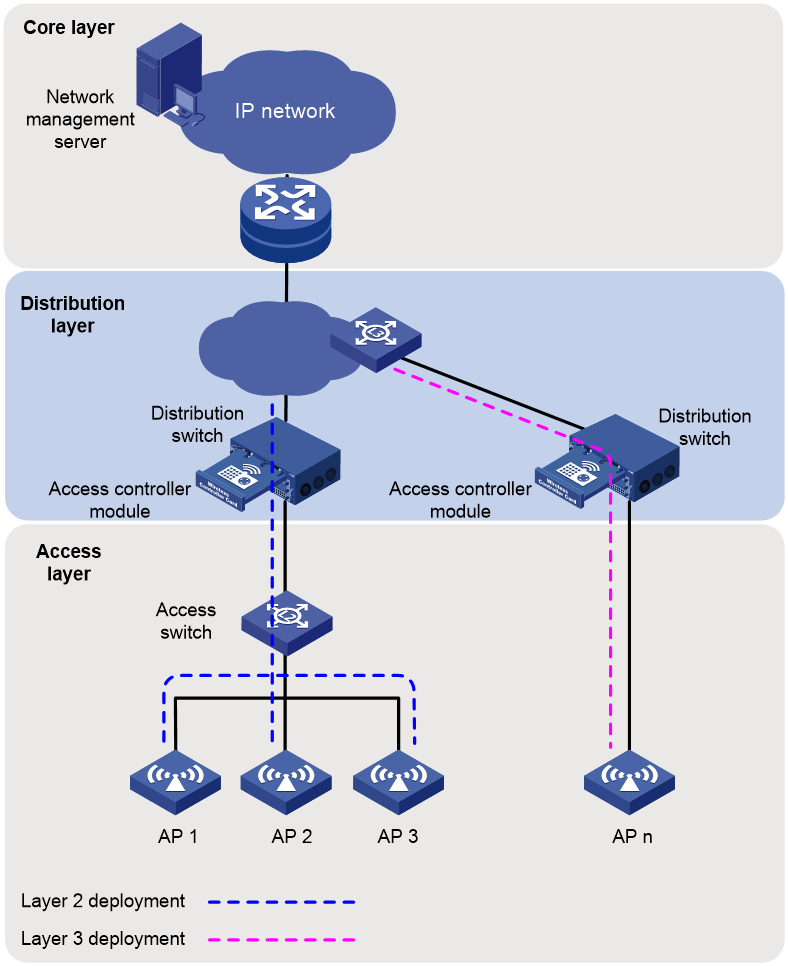
An access controller module acting as an AC
About the access control module deployment modes
An access controller module is installed in a service module slot on a chassis switch for centralized AP management and client access control.
· Layer 2 deployment—The access controller module directly connects to APs or connects to APs through an access switch at Layer 2.
· Layer 3 deployment—The access controller module connects to APs at Layer 3.
Figure 7 Network diagram
Applicable scenarios
Layer 2 deployment is applicable to small- and medium-sized WLANs.
Layer 3 deployment is applicable to large-sized WLANs. As a best practice, install the access controller module on a dedicated chassis switch to enable WLAN expansion by adding access controller modules.