- Table of Contents
-
- 07-Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-ARP configuration
- 02-IP addressing configuration
- 03-DHCP configuration
- 04-DNS configuration
- 05-HTTP configuration
- 06-IP forwarding basics configuration
- 07-Fast forwarding configuration
- 08-Adjacency table configuration
- 09-IRDP configuration
- 10-IP performance optimization configuration
- 11-UDP helper configuration
- 12-IPv6 basics configuration
- 13-IPv6 neighbor discovery configuration
- 14-DHCPv6 configuration
- 15-IPv6 fast forwarding configuration
- 16-WAAS configuration
- 17-HTTP redirect configuration
- 18-Web caching configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-DNS configuration | 713.33 KB |
Contents
DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution
DNS server group-based dynamic domain name resolution
About domain name resolution on the DNS client
Configuring static domain name resolution
Configuring DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution
Configuring DNS server group-based dynamic domain name resolution
Enabling DNS server health check
Specifying DNS server addresses
Configuring a DNS server group
Configuring the DNS transparent proxy
Configuring the DNS trusted interface
Configuring network mode tracking for an output interface
Specifying the source interface for DNS packets
Setting the DSCP value for outgoing DNS packets
Verifying DNS configuration and running status
IPv4 DNS configuration examples
Example: Configuring static domain name resolution
Example: Configuring DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution
Example: Configuring DNS server group-based dynamic domain name resolution
Example: Configuring DNS proxy
IPv6 DNS configuration examples
Example: Configuring static domain name resolution
Example: Configuring DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution
Example: Configuring DNS server group-based domain name resolution
Example: Configuring DNS proxy
Troubleshooting DNS configuration
Failure to resolve IPv4 addresses
Failure to resolve IPv6 addresses
Restrictions and guidelines: DDNS configuration
Applying the DDNS policy to an interface
Setting the DSCP value for outgoing DDNS packets
Verifying and maintaining DDNS
Example: Configuring DDNS with www.3322.org
Example: Configuring DDNS with PeanutHull server
Configuring DNS
About DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) is a distributed database used by TCP/IP applications to translate domain names into IP addresses. The domain name-to-IP address mapping is called a DNS entry.
Types of DNS services
DNS services can be static or dynamic. After a user specifies a name, the device checks the static name resolution table for an IP address. If no IP address is available, it contacts the DNS server or DNS server group for dynamic name resolution, which takes more time than static name resolution. To improve efficiency, you can put frequently queried name-to-IP address mappings in the local static name resolution table.
Static domain name resolution
Static domain name resolution means manually creating mappings between domain names and IP addresses. For example, you can create a static DNS mapping for a device so that you can Telnet to the device by using the domain name.
DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution
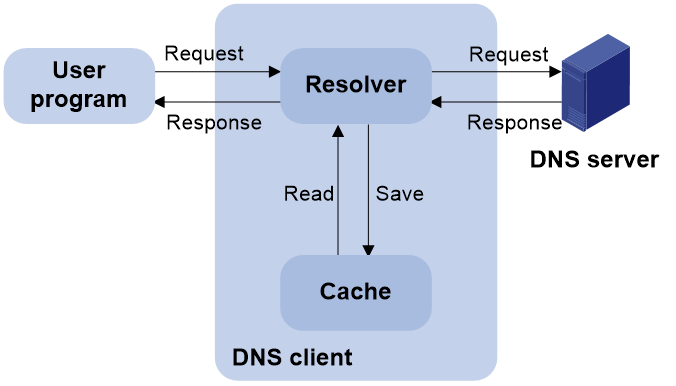
Architecture
Figure 1 shows the relationship between the user program, DNS client, and DNS server. The DNS client includes the resolver and cache. The user program and DNS client can run on the same device or different devices. The DNS server and the DNS client usually run on different devices.
Figure 1 Dynamic domain name resolution
The device can function as a DNS client, but not a DNS server.
If an alias is configured for a domain name on the DNS server, the device can resolve the alias into the IP address of the host.
Resolution process
The DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution process is as follows:
1. A user program sends a name query to the resolver of the DNS client.
2. The DNS resolver looks up the local domain name cache for a match. If the resolver finds a match, it sends the corresponding IP address back. If not, it sends a query to the DNS server.
3. The DNS server looks up the corresponding IP address of the domain name in its DNS database. If no match is found, the server sends a query to other DNS servers. This process continues until a result, whether successful or not, is returned.
4. After receiving a response from the DNS server, the DNS client returns the resolution result to the user program.
Caching
DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution allows the DNS client to store latest DNS entries in the DNS cache. The DNS client does not need to send a request to the DNS server for a repeated query within the aging time. To make sure the entries from the DNS server are up to date, a DNS entry is removed when its aging timer expires. The DNS server determines how long a mapping is valid, and the DNS client obtains the aging information from DNS responses.
DNS suffixes
You can configure a domain name suffix list so that the resolver can use the list to supply the missing part of an incomplete name.
For example, you can configure com as the suffix for example.com. The user only needs to enter example to obtain the IP address of example.com. The resolver adds the suffix and delimiter before passing the name to the DNS server.
The name resolver handles the queries based on the domain names that the user enters:
· If the user enters a domain name without a dot (.) (for example, example), the resolver considers the domain name to be a host name. It adds a DNS suffix to the host name before performing the query operation. If no match is found for any host name and suffix combination, the resolver uses the user-entered domain name (for example, example) for the IP address query.
· If the user enters a domain name with a dot (.) among the letters (for example, www.example), the resolver directly uses this domain name for the query operation. If the query fails, the resolver adds a DNS suffix for another query operation.
· If the user enters a domain name with a dot (.) at the end (for example, example.com.), the resolver considers the domain name an FQDN and returns the successful or failed query result. The dot at the end of the domain name is considered a terminating symbol.
DNS server group-based dynamic domain name resolution
This feature allows the device (DNS client or proxy) to search for a matching domain name rule and send queries to servers in the DNS server group bound to the rule.
When the device receives a user query and fails to find a local matching DNS entry, the device determines whether a matching domain name rule exists in the same VPN instance or on the public network as the user. If a matching rule exists, the device forwards the query to DNS servers in the DNS server group bound to the rule. If no matching rule exists, the device does not forward the query to DNS servers in DNS server groups.
A domain name rule can be matched by using one of the following methods:
· Exact match—The match succeeds only when the domain name in the query is exactly the same as a domain name in the rule.
· Fuzzy match—The match succeeds if the domain name in the query contains a subdomain name.
The device looks for a matching domain name rule in ascending order of rule IDs and compares the domain name in the query with domain names and subdomain names one by one. The domain name match order is the same as the order displayed in the display this command for the rule.
· If the domain name in the query matches a domain name or subdomain name in a rule, the device sends the query to DNS servers in the DNS server group bound to the rule.
¡ After receiving the reply, the device sends the reply to the user and stores the DNS mapping in its local DNS cache.
¡ If no reply is received, the device turns to the next domain name rule.
· If the domain name in the query does not match any domain names or subdomain names in all rules, the domain name resolution fails.
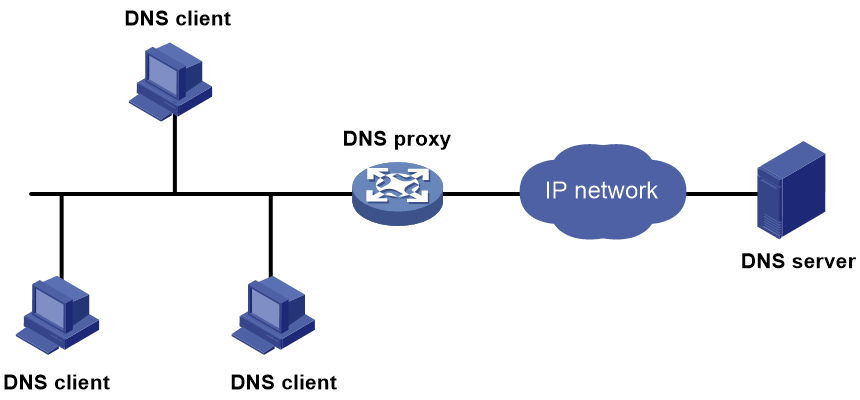
DNS proxy
The DNS proxy performs the following functions:
· Forwards the request from the DNS client to the designated DNS server.
· Conveys the reply from the DNS server to the client.
The DNS proxy simplifies network management. When the DNS server address is changed, you can change the configuration only on the DNS proxy instead of on each DNS client.
Figure 2 shows the typical DNS proxy application.
Figure 2 DNS proxy application
A DNS proxy operates as follows:
1. A DNS client considers the DNS proxy as the DNS server, and sends a DNS request to the DNS proxy. The destination address of the request is the IP address of the DNS proxy.
2. The DNS proxy searches the local static domain name resolution table and dynamic domain name resolution cache after receiving the request. If the requested information is found, the DNS proxy returns a DNS reply to the client.
3. If the requested information is not found, the DNS proxy forwards the request as follows:
a. If a matching domain name rule exists, the proxy forwards the request to DNS servers in the DNS server group bound to the rule.
b. If no matching DNS server group exists but a DNS server is specified, the DNS proxy sends the request to the DNS server for domain name resolution.
4. After receiving a reply from the DNS server, the DNS proxy records the IP address-to-domain name mapping and forwards the reply to the DNS client.
If no DNS server is designated or no route is available to the designated DNS server, the DNS proxy does not forward DNS requests.
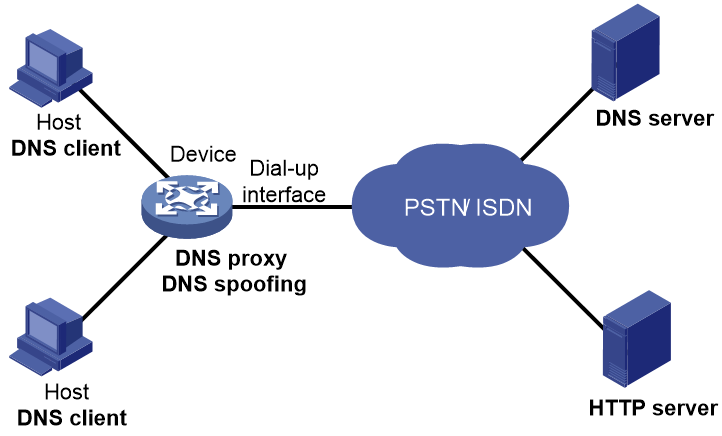
DNS spoofing
As shown in Figure 3, DNS spoofing is applied to the dial-up network.
· The device connects to a PSTN/ISDN network through a dial-up interface. The device triggers the establishment of a dial-up connection only when packets are to be forwarded through the dial-up interface.
· The device acts as a DNS proxy and is specified as a DNS server on the hosts. After the dial-up connection is established, the device dynamically obtains the DNS server address through DHCP or another autoconfiguration mechanism.
Figure 3 DNS spoofing application
The DNS proxy does not have the DNS server address or cannot reach the DNS server after startup. A host accesses the HTTP server in the following steps:
1. The host sends a DNS request to the device to resolve the domain name of the HTTP server into an IP address.
2. Upon receiving the request, the device searches the local static and dynamic DNS entries for a match. Because no match is found, the device spoofs the host by replying a configured IP address. The device must have a route to the IP address with the dial-up interface as the output interface.
The IP address configured for DNS spoofing is not the actual IP address of the requested domain name. Therefore, the TTL field is set to 0 in the DNS reply. When the DNS client receives the reply, it creates a DNS entry and ages it out immediately.
3. Upon receiving the reply, the host sends an HTTP request to the replied IP address.
4. When forwarding the HTTP request through the dial-up interface, the device performs the following operations:
¡ Establishes a dial-up connection with the network.
¡ Dynamically obtains the DNS server address through DHCP or another autoconfiguration mechanism.
5. Because the DNS entry ages out immediately upon creation, the host sends another DNS request to the device to resolve the HTTP server domain name.
6. The device operates the same as a DNS proxy. For more information, see "DNS server group-based dynamic domain name resolution."
7. After obtaining the IP address of the HTTP server, the host can access the HTTP server.
Without DNS spoofing, the device forwards the DNS requests from the host to the DNS server if it cannot find a matching local DNS entry. However, the device cannot obtain the DNS server address, because no dial-up connection is established. Therefore, the device cannot forward or answer the requests from the client. DNS resolution fails, and the client cannot access the HTTP server.
DNS tasks at a glance
To configure DNS, perform the following tasks:
To establish domain name-IP mappings, choose the following tasks as needed:
¡ Configuring static domain name resolution
¡ Configuring DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution
¡ Configuring DNS server group-based dynamic domain name resolution
¡ Enabling DNS server health check
2. (Optional.) Configuring the DNS proxy features.
¡ Configuring the DNS transparent proxy
3. (Optional.) Configuring DNS spoofing
This feature is applied to the dial-up network.
4. (Optional.) Configuring DNS redirection
5. (Optional.) Configuring DNS security features
¡ Configuring the DNS trusted interface
6. (Optional.) Configuring DNS packet parameters
¡ Specifying the source interface for DNS packets
¡ Setting the DSCP value for outgoing DNS packets
Configuring the DNS client
About domain name resolution on the DNS client
You can create domain name-to-address mappings on the DNS client by using the following methods:
· Configure static domain name resolution—Use this method when you use domain names to access a small number of devices or when the network does not have available DNS servers. The network administrator must configure or maintain the domain name-to-address mappings manually.
· Configure dynamic domain name resolution—Use this method when you use domain names to access a large number of devices and the network has an available DNS server. Dynamic domain name resolution includes DNS server-based domain name resolution and DNS server group-based domain name resolution.
A DNS client resolves a domain name in the following order:
1. Static domain name resolution.
2. Locally saved DNS mappings that have been resolved.
3. DNS server group-based domain name resolution.
4. DNS server-based domain name resolution.
The resolution fails if domain name cannot be resolved after all these methods are used.
Configuring static domain name resolution
Restrictions and guidelines
For the public network or a VPN instance, each host name maps to only one IPv4 address and one IPv6 address.
A maximum of 2048 DNS entries can be configured for the public network or each VPN instance. You can configure DNS entries for both public network and VPN instances.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure a host name-to-address mapping.
IPv4:
ip host host-name ip-address [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
IPv6:
ipv6 host host-name ipv6-address [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
Configuring DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution
Restrictions and guidelines
· The limit on the number of DNS servers on the device is as follows:
¡ In system view, you can specify a maximum of six DNS server IPv4 addresses for the public network or each VPN instance. You can specify DNS server IPv4 addresses for both public network and VPN instances.
¡ In system view, you can specify a maximum of six DNS server IPv6 addresses for the public network or each VPN instance. You can specify DNS server IPv6 addresses for both public network and VPN instances.
¡ In interface view, you can specify a maximum of six DNS server IPv4 addresses for the public network or each VPN instance. You can specify DNS server IPv4 addresses for both public network and VPN instances.
· A DNS server address is required so that DNS queries can be sent to a correct server for resolution. If you specify both an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address, the device performs the following operations:
¡ Sends an IPv4 DNS query first to the DNS server IPv4 addresses. If the query fails, the device turns to the DNS server IPv6 addresses.
¡ Sends an IPv6 DNS query first to the DNS server IPv6 addresses. If the query fails, the device turns to the DNS server IPv4 addresses.
· A DNS server address specified in system view takes priority over a DNS server address specified in interface view. A DNS server address specified earlier has a higher priority. A DNS server address manually specified takes priority over a DNS server address dynamically obtained, for example, through DHCP. The device first sends a DNS query to the DNS server address of the highest priority. If the first query fails, it sends the DNS query to the DNS server address of the second highest priority, and so on.
· You can configure a DNS suffix that the system automatically adds to the incomplete domain name that a user enters.
¡ You can configure a maximum of 16 DNS suffixes for the public network or each VPN instance. You can configure DNS suffixes for both public network and VPN instances.
¡ A DNS suffix manually configured takes priority over a DNS suffix dynamically obtained, for example, through DHCP. A DNS suffix configured earlier has a higher priority. The device first uses the suffix that has the highest priority. If the query fails, the device uses the suffix that has the second highest priority, and so on.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. (Optional.) Configure a DNS suffix.
dns domain domain-name [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no DNS suffix is configured and only the domain name that a user enters is resolved.
3. Specify a DNS server address.
¡ Specify a DNS server address in system view.
IPv4:
dns server ip-address [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
IPv6:
ipv6 dns server ipv6-address [ interface-type interface-number ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to specify a DNS server IPv4 address in interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
dns server ip-address [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no DNS server address is specified.
4. (Optional.) Set the aging time for the specified domain name.
dns host host-name [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] aging-time { time-value | infinite }
By default, the DNS server determines how long a mapping is valid, and the DNS client obtains the aging information from DNS responses.
Configuring DNS server group-based dynamic domain name resolution
Restrictions and guidelines
The device supports a maximum of 16 DNS server groups. Each DNS server group can contain a maximum of six IPv4 DNS server addresses and a maximum of six IPv6 DNS server addresses.
The device supports a maximum of 16 domain name rules. Each rule can contain a maximum of eight domain names and subdomain names, and can be bound with only one DNS server group.
You can add both IPv4 and IPv6 DNS server addresses to a DNS server group. The user query can only match a domain name rule that is in the same VPN instance or on the public network as the user. The device forwards the query to DNS servers of the DNS server group bound to the matching rule in the order that is same as the one displayed in the display this command for the group. If the query is an IPv4 packet, the device forwards the query first to IPv4 DNS servers. If the query is an IPv6 packet, the device forwards the query first to IPv6 DNS servers.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a DNS server group.
dns server-group group-id [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no DNS server groups exist.
3. Add DNS servers to the DNS server group.
IPv4:
dns server ip-address
IPv6:
ipv6 dns server ipv6-address [ interface-type interface-number ]
By default, no DNS servers exist in the DNS server group.
4. (Optional.) Configure a description for the DNS server group.
description text
By default, no description is configured for the DNS server group.
5. Return to system view.
quit
6. Configure a domain name rule.
dns domain-rule rule-id { domain-name domain-name | subdomain-name subdomain-name } [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] server-group group-id
By default, no domain name rule is configured.
Enabling DNS server health check
About this task
This feature enables the device to detect the availability of DNS servers in a DNS server group, which prevents the device from forwarding packets to unavailable DNS servers.
When the device enabled with DNS redirection receives a DNS request that matches a domain name rule, the device forwards the request to a DNS server. The DNS server is selected according to the server order displayed in the display this command.
If the device does not receive a DNS reply from the DNS server within two seconds, it reselects a DNS server. To prevent the device from selecting an unavailable DNS server, execute the health-check enable command to detect the availability of DNS servers. After you execute the command on the device, it works as follows:
1. The device periodically sends a DNS request to each DNS server in the DNS server group.
2. If the device receives a DNS reply from a DNS server, it regards the DNS server available.
3. If the device does not receive any DNS reply from a DNS server after it sends a DNS request to the DNS server for three consecutive times, it regards the DNS server unavailable.
4. Upon receiving a DNS request that matches a domain name rule, the device ignores the unavailable DNS servers automatically and selects a DNS server according to the lexicographical order.
Restrictions and guidelines
In a scenario disabled with DNS redirection, as a best practice to prevent the device from periodically sending DNS requests, disable DNS server health check.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a DNS server group and enter its view.
dns server-group group-id [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
3. Enable DNS server health check.
health-check enable
By default, DNS server health check is disabled.
Configuring the DNS proxy
Enabling DNS proxy
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable DNS proxy.
dns proxy enable
By default, DNS proxy is disabled.
Specifying DNS server addresses
Restrictions and guidelines
You can specify multiple DNS servers. The DNS proxy forwards a request to the DNS server that has the highest priority. If having not received a reply, it forwards the request to a DNS server that has the second highest priority, and so on.
You can specify both an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address.
· A DNS proxy forwards an IPv4 name query first to IPv4 DNS servers. If no reply is received, it forwards the request to IPv6 DNS servers.
· A DNS proxy forwards an IPv6 name query first to IPv6 DNS servers. If no reply is received, it forwards the request to IPv4 DNS servers.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify a DNS server address.
¡ Specify a DNS server address in system view.
IPv4:
dns server ip-address [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
IPv6:
ipv6 dns server ipv6-address [ interface-type interface-number ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to specify a DNS server IPv4 address in interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
dns server ip-address [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no DNS server address is specified.
Configuring a DNS server group
For more information, see "Configuring DNS server group-based dynamic domain name resolution."
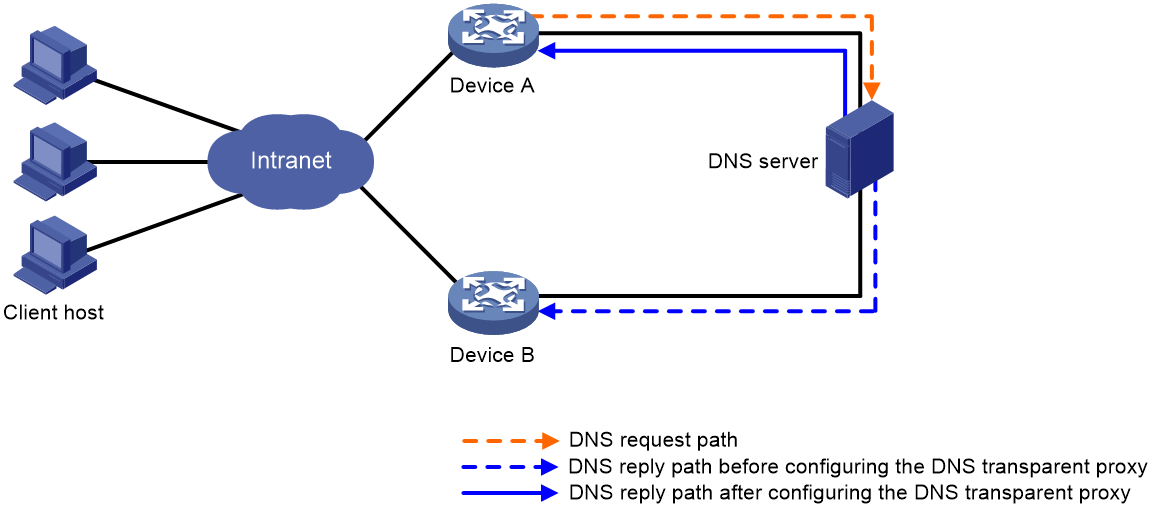
Configuring the DNS transparent proxy
About this task
DNS transparent proxy modifies the source address in DNS requests so that the DNS client seems to receive a DNS reply directly from the DNS server. This feature is applicable to domain name-based policies, such as security policies and bandwidth policies.
The DNS client does not configure the DNS server address as the DNS transparent proxy address, which simplifies the DNS client configuration. As a best practice, enable DNS transparent proxy in some load balancing scenarios.
The device enabled with DNS transparent proxy monitors received DNS requests and replies and records DNS mappings as follows:
1. The device monitors all received DNS packets. Upon receiving a DNS request, the device specifies a local IP address that can reach the DNS server as the source IP address for the request.
2. Upon receiving the DNS reply, the device records the DNS mapping and forwards the reply to the DNS client.
3. The device searches the local entries after receiving another request. If a match is found, the device returns a DNS reply to the client. If no match is found, the device forwards the query to the DNS server for domain name resolution.
As shown in Figure 4, a DNS transparency proxy operates as follows:
1. Device A is enabled with DNS transparency proxy. Upon receiving a DNS request, Device A changes the source address in the request to its own address and forwards the query to the DNS server.
2. Upon receiving the DNS reply, Device A records the domain name-to-IP address mapping and forwards the reply to the DNS client.
Restrictions and guidelines
Do not configure the DNS transparent proxy feature and the following features on the same device:
· DNS caching.
· DNS fast-reply.
· DNS redirection.
· DNS snooping.
The DNS transparent proxy feature cannot be used across VPNs. Make sure the input and output interfaces of DNS packets on the device belong to the same VPN.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable DNS transparent proxy.
dns transparent-proxy enable
By default, DNS transparent proxy is disabled.
Configuring DNS spoofing
Restrictions and guidelines
· You can configure DNS spoofing for both public network and VPN instances.
· After DNS spoofing takes effect, the device spoofs a DNS request even though a matching static DNS entry exists.
Prerequisites
The DNS proxy is enabled on the device.
No DNS server or route to any DNS server is specified on the device.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable DNS proxy.
dns proxy enable
By default, DNS proxy is disabled.
3. Enable DNS spoofing and specify the IP address used to spoof DNS requests. Choose one option as needed:
IPv4:
dns spoofing ip-address [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
IPv6:
ipv6 dns spoofing ipv6-address [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, DNS spoofing is disabled.
Configuring DNS fast-reply
About this task
With this feature enabled, the device monitors the received DNS requests (only UDP packets are supported in the current software version). Then, it resolves the domain names in the requests, and searches for a match in the local static domain name resolution table, DNS cache, and dynamic domain name resolution cache.
· If a match is found, the device sends a DNS reply to the DNS client.
· If no match is found, the device forwards the query to the DNS server.
As DNS fast-reply can process a large number of DNS requests per second, use this feature in scenarios that require high DNS packet processing performance.
Restrictions and guidelines
This command does not take effect on labeled DNS packets.
The dns fast-reply enable and dns transparent-proxy enable commands are mutually exclusive. After one command is executed, the other command cannot be executed.
Hardware and feature compatibility
Support for this feature depends on the device model. For more information about the support of the devices for this feature, see the command reference.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable DNS fast-reply.
dns fast-reply enable
By default, DNS fast-reply is disabled.
3. (Optional.) Enable DNS fast-reply to ignore client VPN information in DNS requests.
dns fast-reply ignore-client-vpn
By default, the client VPN information and the VPN information in the DNS cache must match.
Configuring DNS redirection
About this task
DNS redirection applies to the scenarios that require DNS request distribution. For example, to reduce the transmission pressure on the core network, enable DNS redirection on the edge UPF device. For more information about UPF configurations, see Mobile Communication Configuration Guide.
With DNS redirection enabled, the device monitors the received DNS requests (only UDP packets are supported in the current software version) and resolves the source IP addresses, source port numbers, and domain names. Then the device searches for a matching domain name rule and redirects the request to the DNS server in the rule.
The device enabled with DNS redirection works as follows:
1. The device searches for a matching domain name rule.
¡ If a match is found, it replaces the destination IP address in the request with the IP address of the first reachable DNS server in the server group bound to the rule. Then the device forwards the request to the DNS server.
¡ If no match is found, the device does not redirect the DNS request.
2. The device records the replacement, including the source IP address, source port number, and requested server address in the DNS request, and the replaced server address.
3. Upon receiving the DNS reply, the device replaces the source IP address in the reply with the original server address in the request.
Restrictions and guidelines
This command does not take effect on labeled DNS packets.
The dns redirect enable and dns transparent-proxy enable commands are mutually exclusive. After one command is executed, the other command cannot be executed.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable DNS redirection.
dns redirect enable
By default, DNS redirection is disabled.
Configuring DNS snooping
About this task
DNS snooping is applicable to scenarios where user traffic is filtered based on domain names.
Other modules (for example, the address object group module) can obtain the IP addresses corresponding to domain names through DNS snooping only after they send domain name subscription requests to the DNS module. If the domain name in a DNS request matches a subscribed domain name, the device records the DNS mapping after receiving the DNS reply, and reports the mapping to the corresponding module for traffic filtering.
If the domain name in a DNS request does not match any subscribed domain name, the device does not record the DNS mapping.
When the domain names subscribed to by other modules age out, the DNS module notifies the modules of deleting the corresponding DNS mappings to ensure accuracy.
Restrictions and guidelines
DNS snooping works only between the DNS client and DNS server, or the DNS client and DNS proxy.
The DNS snooping and DNS transparent proxy features cannot be both configured.
The DNS snooping feature cannot be used across VPNs. Make sure the input and output interfaces of DNS packets on the device belong to the same VPN.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable DNS snooping.
dns snooping enable
By default, DNS snooping is disabled.
Configuring the DNS trusted interface
About this task
This task enables the device to use only the DNS suffix and domain name server information obtained through the trusted interface. The device can then obtain the correct resolved IP address. This feature protects the device against attackers that act as the DHCP server to assign incorrect DNS suffix and domain name server address.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can configure a maximum of 128 DNS trusted interfaces.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify the DNS trusted interface.
dns trust-interface interface-type interface-number
By default, no DNS trusted interface is specified.
Configuring network mode tracking for an output interface
About this task
This feature tracks the network mode of an output interface and spoofs DNS requests if the network mode is 2G. This feature takes effect on the cellular interface when the interface acts as the output interface to reach the DNS server. Spoofing DNS requests avoids DNS packet loss that might be caused by limited 2G network bandwidth.
Hardware and feature compatibility
Support for this feature depends on the device model. For more information about the support of the devices for this feature, see the command reference.
Restrictions and guidelines
As a best practice, specify a private address on the device as the address used to spoof DNS requests if the network mode is 2G.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the device to track the network mode of an output interface.
dns spoofing track controller interface-type interface-number
By default, the device does not track the network mode of an output interface.
Specifying the source interface for DNS packets
About this task
This task enables the device to always use the primary IP address of the specified source interface as the source IP address of outgoing DNS packets. This feature applies to scenarios in which the DNS server responds only to DNS requests sourced from a specific IP address. If no IP address is configured on the source interface, no DNS packets can be sent out.
Restrictions and guidelines
When sending an IPv6 DNS request, the device follows the method defined in RFC 3484 to select an IPv6 address of the source interface.
You can configure only one source interface on the public network or a VPN instance. You can configure source interfaces for both public network and VPN instances.
Make sure the source interface belongs to the specified VPN instance if you specify the vpn-instance vpn-instance-name option.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify the source interface for DNS packets.
dns source-interface interface-type interface-number [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no source interface for DNS packets is specified.
Setting the DSCP value for outgoing DNS packets
About this task
The DSCP value of a packet specifies the priority level of the packet and affects the transmission priority of the packet. A bigger DSCP value represents a higher priority.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the DSCP value for DNS packets sent by a DNS client or a DNS proxy.
IPv4:
dns dscp dscp-value
By default, the DSCP value is 0 in IPv4 DNS packets sent by a DNS client or a DNS proxy.
IPv6:
ipv6 dns dscp dscp-value
By default, the DSCP value is 0 in IPv6 DNS packets sent by a DNS client or a DNS proxy.
Verifying and maintaining DNS
Verifying DNS configuration and running status
Perform display tasks in any view.
display dns domain [ dynamic ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
· Display domain name rules.
display dns domain-rule { dynamic [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] | static }
· Display the domain name resolution table.
display dns host [ ip | ipv6 ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
· Display IPv4 DNS server information.
display dns server [ dynamic ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
· Display health status of DNS servers.
display dns server health status
· Display manually configured DNS server groups.
display dns server-group
· Display IPv6 DNS server information.
display ipv6 dns server [ dynamic ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
· Display dynamic entries for domain name-to-IP address mappings recorded by DNS transparent proxy.
display dns transparent host [ ip | ipv6 ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
Clearing dynamic DNS entries
To clear dynamic DNS entries, execute the following command in user view:
reset dns host [ cache ] [ ip | ipv6 ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
IPv4 DNS configuration examples
Example: Configuring static domain name resolution
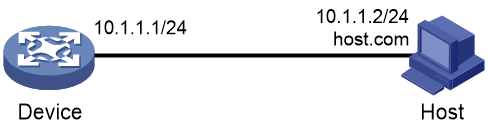
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 5, the host at 10.1.1.2 is named host.com. Configure static IPv4 DNS on the device so that the device can use the easy-to-remember domain name rather than the IP address to access the host.
Procedure
# Configure a mapping between host name host.com and IP address 10.1.1.2.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip host host.com 10.1.1.2
# Verify that the device can use static domain name resolution to resolve domain name host.com into IP address 10.1.1.2.
[Sysname] ping host.com
Ping host.com (10.1.1.2): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for host.com ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms
Example: Configuring DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution
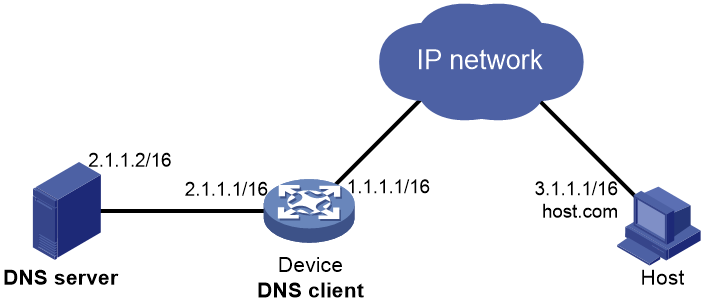
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 6, configure the DNS server to store the mapping between the host's domain name host and IPv4 address 3.1.1.1/16 in the com domain. Configure dynamic IPv4 DNS and DNS suffix com on the device so that the device can use domain name host to access the host.
Prerequisites
Before you configure dynamic domain name configuration, make sure the following requirements are met:
· The device and the host can reach each other.
· The IP addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown in Figure 6.
The configuration might vary by DNS server. The following configuration is performed on a PC running Windows Server 2008 R2.
Procedure
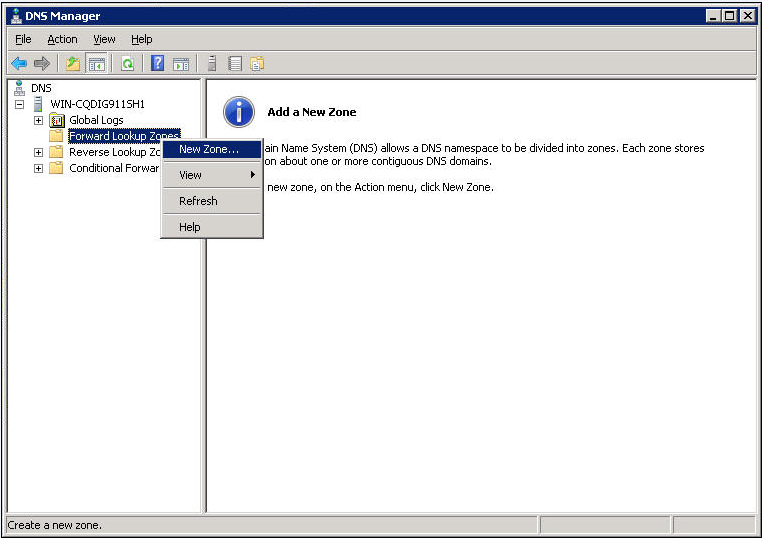
1. Configure the DNS server:
a. Select Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > DNS.
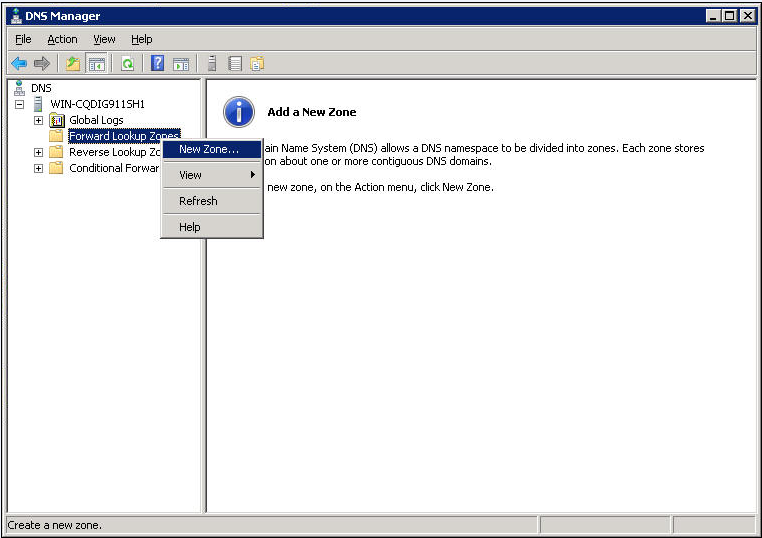
The DNS server configuration page opens, as shown in Figure 7.
b. Right-click Forward Lookup Zones, select New Zone, and then follow the wizard to create a new zone named com.
Figure 7 Creating a zone
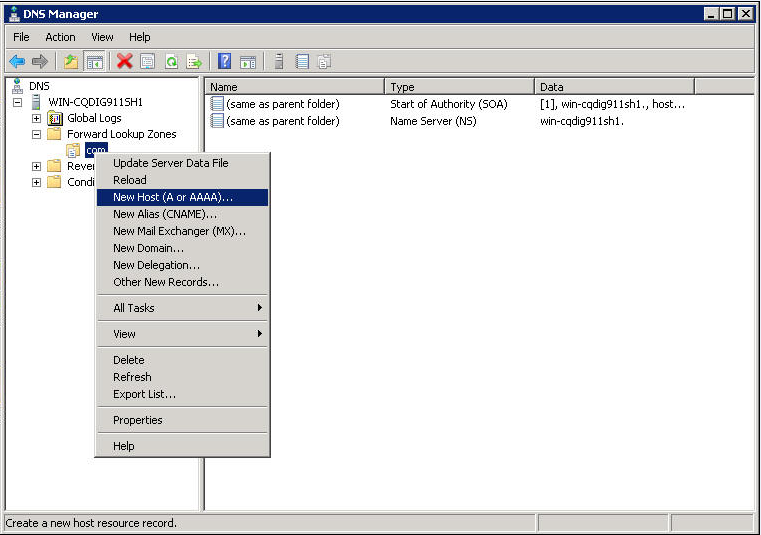
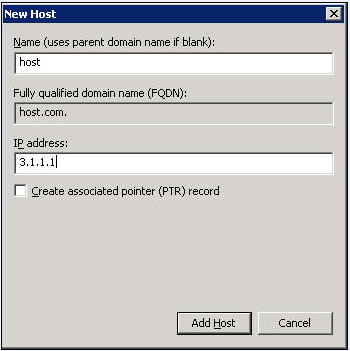
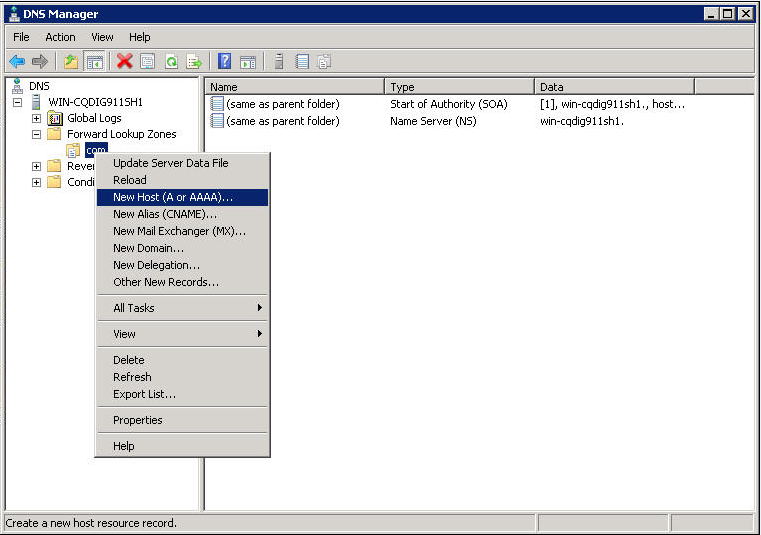
c. On the DNS server configuration page, right-click zone com and select New Host.
d. On the page that opens, enter host name host and IP address 3.1.1.1.
e. Click Add Host.
The mapping between the IP address and host name is created.
Figure 9 Adding a mapping between domain name and IP address
2. Configure the DNS client:
# Specify the DNS server 2.1.1.2.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] dns server 2.1.1.2
# Specify com as the name suffix.
[Sysname] dns domain com
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the device can use the dynamic domain name resolution to resolve domain name host.com into IP address 3.1.1.1.
[Sysname] ping host
Ping host.com (3.1.1.1): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for host ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms
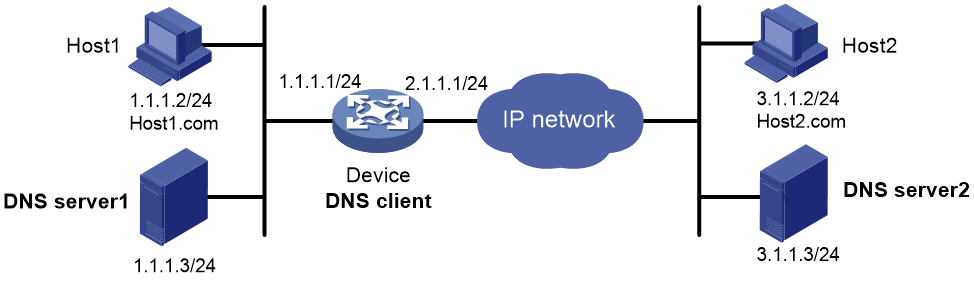
Example: Configuring DNS server group-based dynamic domain name resolution
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 10, the device acts as the DNS client and needs to access Host 1 and Host 2. The DNS mappings for Host 1 and Host 2 are saved on DNS server 1 and DNS server 2, respectively.
On the DNS client, configure DNS server groups and domain name rules for dynamic domain name resolution.
· Add DNS server 1 to DNS server group 1, and bind domain name host1.com to DNS server group 1 in domain name rule 1.
· Add DNS server 2 to DNS server group 2, and bind domain name host2.com to DNS server group 2 in domain name rule 2.
Procedure
Before performing the following configuration, make sure that:
· Routes are reachable between the device and DNS servers, and between the device and the hosts.
· The IP addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown in Figure 10.
1. Configure DNS server 1 and DNS server 2. The configuration methods might vary by DNS server. For more information about configuring DNS servers on PCs running Windows Server 2008 R2, see "Example: Configuring DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution."
2. Configure the DNS client:
# Create DNS server group 1 and add DNS server 1.1.1.3 to the group.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] dns server-group 1
[Sysname-dns-server-group-1] dns server 1.1.1.3
[Sysname-dns-server-group-1] quit
# Create DNS server group 2 and add DNS server 3.1.1.3 to the group.
[Sysname] dns server-group 2
[Sysname-dns-server-group-2] dns server 3.1.1.3
[Sysname-dns-server-group-2] quit
# Create domain name rule 1, and bind domain name host1.com to DNS server group 1.
[Sysname] dns domain-rule 1 domain-name host1.com server-group 1
# Create domain name rule 2, and bind domain name host2.com to DNS server group 2.
[Sysname] dns domain-rule 2 domain-name host2.com server-group 2
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the ping host1.com command on the device to verify that the device can successfully ping host 1 and resolve domain name host1.com into IP address 1.1.1.2.
[Sysname] ping host1.com
Ping host1.com (1.1.1.2): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 1.1.1.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1.1.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1.1.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1.1.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1.1.1.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for host ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms
# Execute the ping host2.com command on the device to verify that the device can successfully ping host 2 and resolve domain name host2.com into IP address 3.1.1.2.
Ping host2.com (3.1.1.2): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 3.1.1.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for host ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms
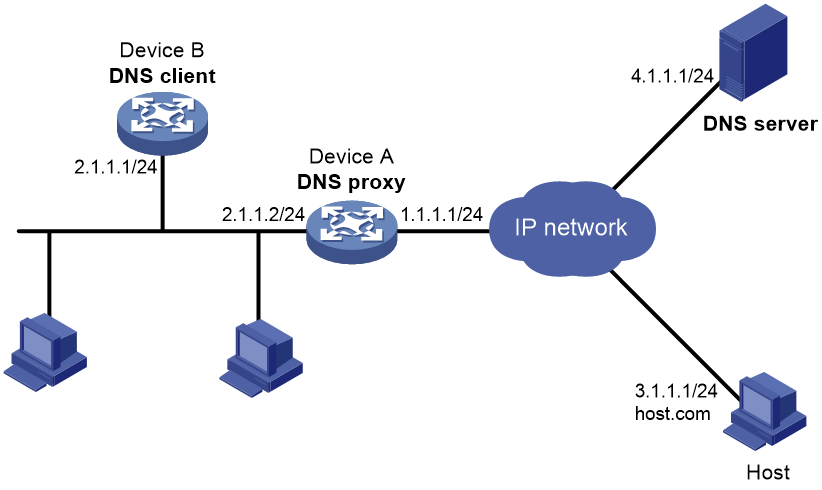
Example: Configuring DNS proxy
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 11, configure Device A as the DNS proxy to forward DNS packets between the DNS client (Device B) and the DNS server at 4.1.1.1.
Prerequisites
Before you configure DNS proxy, make sure the following requirements are met:
· Device A, the DNS server, and the host can reach each other.
· The IP addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown in Figure 11.
Procedure
1. Configure the DNS server:
The configuration might vary by DNS server. When a PC running Windows Server 2008 R2 acts as the DNS server, see "Example: Configuring DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution" for configuration information.
2. Configure the DNS proxy:
# Specify the DNS server 4.1.1.1.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] dns server 4.1.1.1
# Enable DNS proxy.
[DeviceA] dns proxy enable
3. Configure the DNS client:
<DeviceB> system-view
# Specify the DNS server 2.1.1.2.
[DeviceB] dns server 2.1.1.2
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that DNS proxy on Device A functions.
[DeviceB] ping host.com
Ping host.com (3.1.1.1): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for host.com ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms
IPv6 DNS configuration examples
Example: Configuring static domain name resolution
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 12, the host at 1::2 is named host.com. Configure static IPv6 DNS on the device so that the device can use the easy-to-remember domain name rather than the IPv6 address to access the host.
Procedure
# Configure a mapping between host name host.com and IPv6 address 1::2.
<Device> system-view
[Device] ipv6 host host.com 1::2
# Verify that the device can use static domain name resolution to resolve domain name host.com into IPv6 address 1::2.
[Sysname] ping ipv6 host.com
Ping6(56 data bytes) 1::1 --> 1::2, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=0 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=1 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=2 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=3 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=4 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms
--- Ping6 statistics for host.com ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 0.000/0.600/1.000/0.490 ms
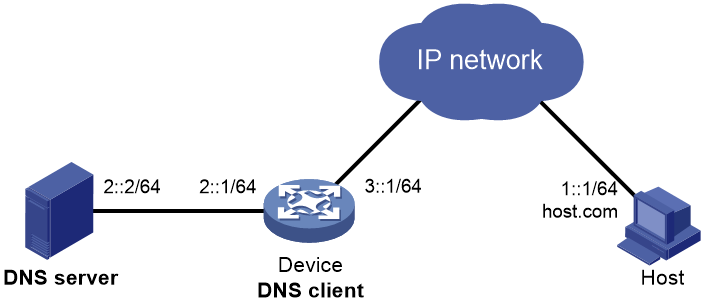
Example: Configuring DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 13, configure the DNS server to store the mapping between the host's domain name host and IPv6 address 1::1/64 in the com domain. Configure dynamic IPv6 DNS and DNS suffix com on the device so that the device can use domain name host to access the host.
Prerequisites
Before you configure dynamic domain name configuration, make sure the following requirements are met:
· The device and the host can reach each other.
· The IPv6 addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown in Figure 13.
The configuration might vary by DNS server. The following configuration is performed on a PC running Windows Server 2008 R2. Make sure the DNS server supports IPv6 DNS so that the server can process IPv6 DNS packets and its interfaces can forward IPv6 packets.
Procedure
1. Configure the DNS server:
a. Select Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > DNS.
The DNS server configuration page opens, as shown in Figure 14.
b. Right-click Forward Lookup Zones, select New Zone, and then follow the wizard to create a new zone named com.
c. On the DNS server configuration page, right-click zone com and select New Host.
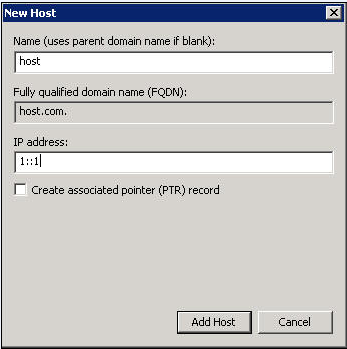
d. On the page that opens, enter host name host and IPv6 address 1::1.
e. Click Add Host.
The mapping between the IPv6 address and host name is created.
Figure 16 Adding a mapping between domain name and IPv6 address
2. Configure the DNS client:
# Specify the DNS server 2::2.
<Device> system-view
[Device] ipv6 dns server 2::2
# Configure com as the DNS suffix.
[Device] dns domain com
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the device can use the dynamic domain name resolution to resolve the domain name host.com into the IP address 1::1.
[Device] ping ipv6 host
Ping6(56 data bytes) 3::1 --> 1::1, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 1::1, icmp_seq=0 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::1, icmp_seq=1 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::1, icmp_seq=2 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::1, icmp_seq=3 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::1, icmp_seq=4 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms
--- Ping6 statistics for host ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 0.000/0.600/1.000/0.490 ms
Example: Configuring DNS server group-based domain name resolution
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 17, the device acts as the DNS client and needs to access Host 1 and Host 2. The DNS mappings for Host 1 and Host 2 are saved on DNS server 1 and DNS server 2, respectively.
On the DNS client, configure DNS server groups and domain name rules for dynamic domain name resolution.
· Add DNS server 1 to DNS server group 1, and bind domain name host1.com to DNS server group 1 in domain name rule 1.
· Add DNS server 2 to DNS server group 2, and bind domain name host2.com to DNS server group 2 in domain name rule 2.
Procedure
Before performing the following configuration, make sure that:
· Routes are reachable between the device and DNS servers, and between the device and the hosts.
· The IPv6 addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown in Figure 17.
1. Configure DNS server 1 and DNS server 2. The configuration methods might vary by DNS server. For more information about configuring DNS servers on PCs running Windows Server 2008 R2, see "Example: Configuring DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution."
2. Configure the DNS client:
# Create DNS server group 1 and add DNS server 1::3 to the group.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] dns server-group 1
[Sysname-dns-server-group-1] ipv6 dns server 1::3
[Sysname-dns-server-group-1] quit
# Create DNS server group 2 and add DNS server 3::3 to the group.
[Sysname] dns server-group 2
[Sysname-dns-server-group-2] ipv6 dns server 3::3
[Sysname-dns-server-group-2] quit
# Create domain name rule 1, and bind domain name host1.com to DNS server group 1.
[Sysname] dns domain-rule 1 domain-name host1.com server-group 1
# Create domain name rule 2, and bind domain name host2.com to DNS server group 2.
[Sysname] dns domain-rule 2 domain-name host2.com server-group 2
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the ping ipv6 host1.com command on the device to verify that the device can successfully ping host 1 and resolve domain name host1.com into IPv6 address 1::2.
[Sysname] ping ipv6 host1.com
Ping6(56 data bytes) 1::1 --> 1::2, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=0 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=1 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=2 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=3 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=4 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms
--- Ping6 statistics for host ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 0.000/0.600/1.000/0.490 ms
# Execute the ping ipv6 host2.com command on the device to verify that the device can successfully ping host 2 and resolve domain name host2.com into IPv6 address 3::2.
[Sysname] ping ipv6 host2.com
Ping6(56 data bytes) 2::1 --> 3::2, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=0 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=1 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=2 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=3 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=4 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms
--- Ping6 statistics for host ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 0.000/0.600/1.000/0.490 ms
Example: Configuring DNS proxy
Network configuration
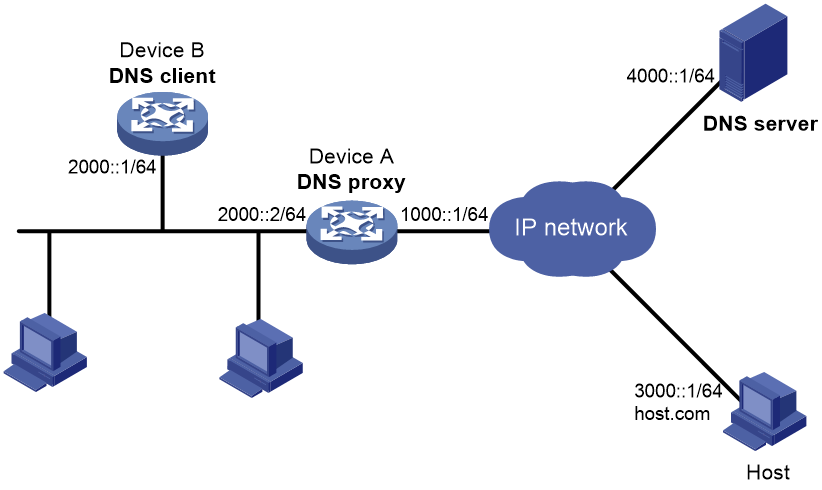
As shown in Figure 18, configure Device A as the DNS proxy to forward DNS packets between the DNS client (Device B) and the DNS server at 4000::1.
Prerequisites
Before you configure DNS proxy, make sure the following requirements are met:
· Device A, the DNS server, and the host are reachable to each other.
· The IPv6 addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown in Figure 18.
Procedure
1. Configure the DNS server:
This configuration might vary by DNS server. When a PC running Windows Server 2008 R2 acts as the DNS server, see "Example: Configuring DNS server-based dynamic domain name resolution" for configuration information.
2. Configure the DNS proxy:
# Specify the DNS server 4000::1.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] ipv6 dns server 4000::1
# Enable DNS proxy.
[DeviceA] dns proxy enable
3. Configure the DNS client:
# Specify the DNS server 2000::2.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] ipv6 dns server 2000::2
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that DNS proxy on Device A functions.
[DeviceB] ping host.com
Ping6(56 data bytes) 2000::1 --> 3000::1, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 3000::1, icmp_seq=0 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3000::1, icmp_seq=1 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms
56 bytes from 3000::1, icmp_seq=2 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3000::1, icmp_seq=3 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 3000::1, icmp_seq=4 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms
--- Ping6 statistics for host.com ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 0.000/0.600/1.000/0.490 ms
Troubleshooting DNS configuration
Failure to resolve IPv4 addresses
Symptom
After enabling dynamic domain name resolution, the user cannot get the correct IP address.
Solution
To resolve the problem:
1. Use the display dns host ip command to verify that the specified domain name is in the cache.
2. If the specified domain name does not exist, check that the DNS client can communicate with the DNS server.
3. If the specified domain name is in the cache, but the IP address is incorrect, check that the DNS client has the correct IP address of the DNS server.
4. Verify that the mapping between the domain name and IP address is correct on the DNS server.
Failure to resolve IPv6 addresses
Symptom
After enabling dynamic domain name resolution, the user cannot get the correct IPv6 address.
Solution
To resolve the problem:
1. Use the display dns host ipv6 command to verify that the specified domain name is in the cache.
2. If the specified domain name does not exist, check that dynamic domain name resolution is enabled, and that the DNS client can communicate with the DNS server.
3. If the specified domain name is in the cache, but the IPv6 address is incorrect, check that the DNS client has the correct IPv6 address of the DNS server.
4. Verify that the mapping between the domain name and IPv6 address is correct on the DNS server.
Configuring DDNS
About DDNS
DNS provides only the static mappings between domain names and IP addresses. When the IP address of a node changes, your access to the node fails.
Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) can dynamically update the mappings between domain names and IP addresses for DNS servers.
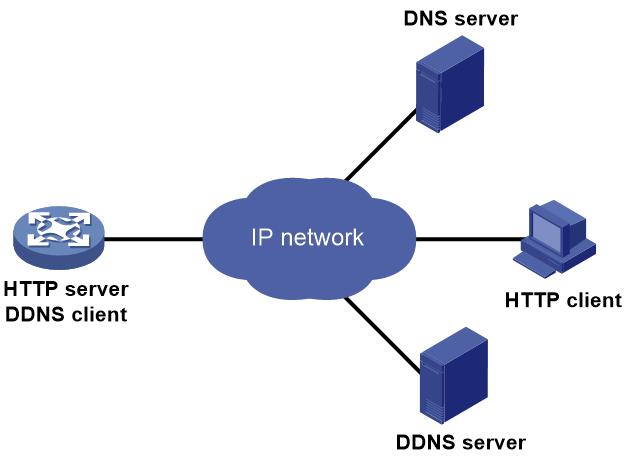
Figure 19 shows the typical DDNS application.
DDNS works on the client-server model.
· DDNS client—A device that needs to update the mapping between its domain name and IP address dynamically on the DNS server when its IP address changes. An Internet user typically accesses an application layer server such as an HTTP server or an FTP server by using the server's domain name. When its IP address changes, the application layer server runs as a DDNS client. It sends a request to the DDNS server for updating the mapping between its domain name and its IP address.
· DDNS server—Informs the DNS server of latest mappings. When receiving the mapping update request from a DDNS client, the DDNS server tells the DNS server to re-map the domain name and the IP address of the DDNS client. Therefore, the Internet users can use the same domain name to access the DDNS client even if the IP address of the DDNS client has changed.
The device can function as a DDNS client to update the domain name-IP address mappings on the DNS servers through DDNS servers such as www.3322.org and PeanutHull.
|
|
NOTE: The DDNS update process does not have a unified standard but varies by DDNS server that the DDNS client contacts. |
Restrictions and guidelines: DDNS configuration
DDNS is supported by only IPv4 DNS. It is used to update the mappings between domain names and IPv4 addresses.
DDNS client tasks at a glance
To configure a DDNS client, perform the following tasks:
2. Applying the DDNS policy to an interface
3. (Optional.) Setting the DSCP value for outgoing DDNS packets
Configuring a DDNS policy
About this task
A DDNS policy contains the DDNS server address, port number, login ID, password, time interval, associated SSL client policy, and update time interval. After creating a DDNS policy, you can apply it to multiple interfaces to simplify DDNS configuration.
Restrictions and guidelines
The URL address for update requests varies by DDNS server.
Table 1 Common URL addresses
|
DDNS server |
URL address for DDNS update requests |
|
www.3322.org |
http://members.3322.org/dyndns/update?system=dyndns&hostname=<h>&myip=<a> |
|
DYNDNS |
http://members.dyndns.org/nic/update?system=dyndns&hostname=<h>&myip=<a> |
|
DYNS |
http://www.dyns.cx/postscript.php?host=<h>&ip=<a> |
|
ZONEEDIT |
http://dynamic.zoneedit.com/auth/dynamic.html?host=<h>&dnsto=<a> |
|
TZO |
http://cgi.tzo.com/webclient/signedon.html?TZOName=<h>IPAddress=<a> |
|
EASYDNS |
http://members.easydns.com/dyn/ez-ipupdate.php?action=edit&myip=<a>&host_id=<h> |
|
HEIPV6TB |
http://dyn.dns.he.net/nic/update?hostname=<h>&myip=<a> |
|
CHANGE-IP |
http://nic.changeip.com/nic/update?hostname=<h>&offline=1 |
|
NO-IP |
http://dynupdate.no-ip.com/nic/update?hostname=<h>&myip=<a> |
|
DHS |
http://members.dhs.org/nic/hosts?domain=dyn.dhs.org&hostname=<h>&hostscmd=edit&hostscmdstage=2&type=1&ip=<a> |
|
HP |
https://server-name/nic/update?group=group-name&myip=<a> |
|
ODS |
ods://update.ods.org |
|
GNUDIP |
gnudip://server-name |
|
PeanutHull |
Select the URL according to your network situation: · oray://phddns60.oray.net · oray://phservice2.oray.net |
Identify the DDNS server type in your network and follow the following restrictions and guidelines to set an appropriate URL address:
· The URL address for an update request can start with:
¡ http://—The HTTP-based DDNS server.
¡ https://—The HTTPS-based DDNS server.
¡ ods://—The TCP-based ODS server.
¡ gnudip://—The TCP-based GNUDIP server.
¡ oray://—The TCP-based PeanutHull DDNS server.
· HP and GNUDIP are common DDNS update protocols. The server-name argument is the domain name or IP address of the service provider's server using one of the update protocols.
· The port number in the URL address is optional. If no port is specified, the system uses the default port numbers: port 80 for HTTP, port 443 for HTTPS, and port 6060 for PeanutHull DDNS server.
· The <h> value can be automatically filled with an FQDN if it is specified in the command for applying a DDNS policy to an interface. The <a> value is automatically filled with the primary IP address of the interface to which the DDNS policy is applied. For more information about applying DDNS policies, see "Applying the DDNS policy to an interface."
· You can also manually specify an FQDN and an IP address for the <h> and <a> fields. In this case, the FQDN specified at the CLI does not take effect. As a best practice, do not manually change the <h> and <a> because your configuration might be incorrect.
· No FQDN or IP address can be specified in the URL address for update requests sent to the PeanutHull DDNS server. You can specify the FQDN when applying the DDNS policy to an interface. The IP address is the primary IP address of the interface to which the DDNS policy is applied.
Prerequisites
Visit the website of a DDNS service provider, register an account, and apply for a domain name for the DDNS client. When the DDNS client updates the mapping between the domain name and the IP address through the DDNS server, the DDNS server checks the following:
· Whether the account information is correct.
· Whether the domain name to be updated belongs to the account.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a DDNS policy and enter its view.
ddns policy policy-name
3. Specify a URL address for DDNS update requests.
url request-url
By default, no URL address is specified for DDNS update requests.
The URL address cannot contain a username or password. To configure them, use the username command and the password command.
4. Specify the username for logging in to the DDNS server.
username username
By default, no username is specified.
5. Specify the password for logging in to the DDNS server.
password { cipher | simple } string
By default, no password is specified.
6. (Optional.) Specify the parameter transmission method for sending DDNS update requests to HTTP/HTTPS-based DDNS servers.
method { http-get | http-post }
By default, the http-get method is used.
This step is effective for communicating with HTTP/HTTPS-based DDNS servers.
Specify the http-post keyword for DDNS update with a DHS server.
7. (Optional.) Associate an SSL client policy with the DDNS policy.
ssl-client-policy policy-name
By default, no SSL client policy is associated with the DDNS policy.
This step is only effective and a must for HTTP-based DDNS update requests. For SSL client policy configuration, see Security Configuration Guide.
8. (Optional.) Specify the interval for sending update requests.
interval days [ hours [ minutes ] ]
By default, the time interval is one hour.
Applying the DDNS policy to an interface
About this task
After you apply the DDNS policy to an interface and specify the FQDN for update, the DDNS client can send requests to the DDNS server. The requests are to update the mapping between the domain name and the primary IP address of the interface.
Restrictions and guidelines
· The fqdn domain-name option is a must for all DDNS servers except the PeanutHull DDNS server.
· The fqdn domain-name option is optional for PeanutHull DDNS server. If no FQDN is specified, the DDNS server updates all domain names for the DDNS client account. If an FQDN is specified, the DDNS server updates only the mapping between the specified FQDN and the primary IP address.
Prerequisites
Before you apply a DDNS policy to an interface, complete the following tasks:
· Specify the primary IP address of the interface and make sure the DDNS server and the interface can reach each other.
· Configure static or dynamic domain name resolution to translate the domain name of the DDNS server into the IPv4 address. For more information, see "Configuring the DNS client."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Apply the DDNS policy to the interface to update the mapping between the specified FQDN and the primary IP address of the interface, and enable DDNS update.
ddns apply policy policy-name [ fqdn domain-name ]
By default, no DDNS policy is applied to the interface, no FQDN is specified for update, and DDNS update is disabled.
An FQDN, including a host name and a domain name, is the only identifier for a network node and can be resolved as an IP address.
Setting the DSCP value for outgoing DDNS packets
About this task
The DSCP value of a packet specifies the priority level of the packet and affects the transmission priority of the packet. A bigger DSCP value represents a higher priority.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the DSCP value for outgoing DDNS packets.
ddns dscp dscp-value
By default, the DSCP value for outgoing DDNS packets is 0.
Verifying and maintaining DDNS
To display DDNS policy information, execute the following command in any view:
display ddns policy [ policy-name ]
DDNS configuration examples
Example: Configuring DDNS with www.3322.org
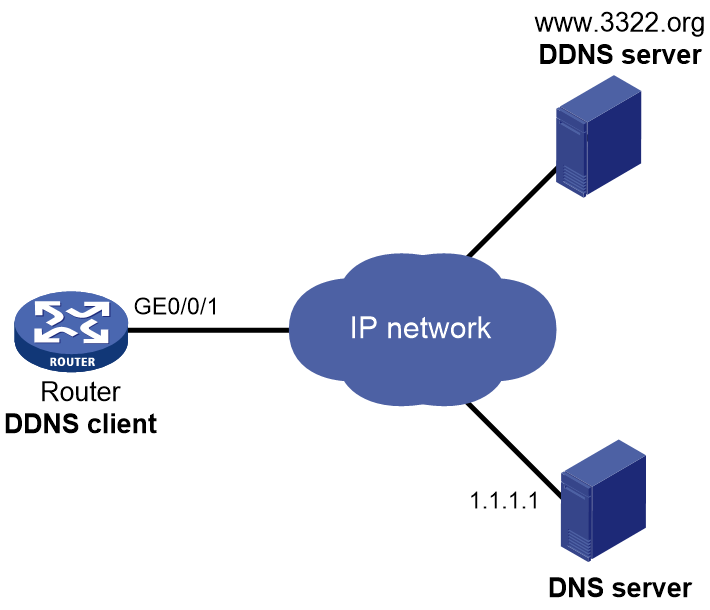
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 20, the router is a Web server with domain name example.3322.org and uses an IP address dynamically obtained through DHCP. To make sure the router can always provide Web services at example.3322.org when its IP address changes, perform the following tasks on the router:
· Configure a DDNS policy to update the router's domain name-to-IP address mapping on the DDNS server. The DDNS server then updates the mapping on the DNS server.
· Specify the IP address of the DNS server so that the router can access the DDNS server through domain name.
Prerequisites
Before configuring DDNS on the router, perform the following tasks:
· Register with username steven and password nevets at http://www.3322.org/.
· Configure a DDNS policy to update the mapping between the router's FQDN and IP address.
· Make sure the devices can reach each other.
Procedure
# Create a DDNS policy named 3322.org, and enter its view.
<Router> system-view
[Router] ddns policy 3322.org
# Specify the URL address, username, and password for DDNS update requests.
[Router-ddns-policy-3322.org] url http://members.3322.org/dyndns/update?system=dyndns&hostname=<h>&myip=<a>
[Router-ddns-policy-3322.org] username steven
[Router-ddns-policy-3322.org] password simple nevets
# Set the interval to 15 minutes for sending DDNS update requests.
[Router-ddns-policy-3322.org] interval 0 0 15
[Router-ddns-policy-3322.org] quit
# Specify the IP address of the DNS server as 1.1.1.1.
[Router] dns server 1.1.1.1
# Apply DDNS policy 3322.org to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 to enable DDNS update. The mapping between domain name example.3322.org and the primary IP address of the interface will be dynamically updated.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ddns apply policy 3322.org fqdn example.3322.org
Verifying the configuration
Verify that the router can update its domain name-IP mapping through the DDNS provider www.3322.org when its IP address changes. The Internet users can resolve the correct IP address through the domain name example.3322.org to access the Web service.
Example: Configuring DDNS with PeanutHull server
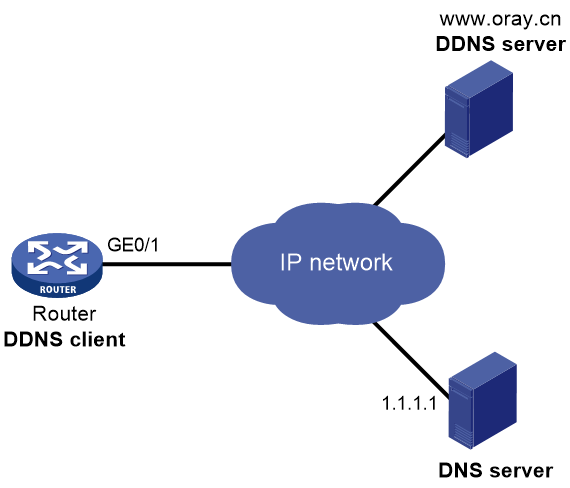
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 21, the router is a Web server with domain name example.gicp.cn and uses an IP address dynamically obtained through DHCP. To make sure the router can always provide Web services at example.gicp.cn when its IP address changes, perform the following tasks on the router:
· Configure a DDNS policy to update the router's domain name-to-IP address mapping on the DDNS server. The DDNS server then updates the mapping on the DNS server.
· Specify the IP address of the DNS server so that the router can access the DDNS server through domain name.
Prerequisites
Before configuring DDNS on the router, perform the following tasks:
· Register with username steven and password nevets at http://www.oray.cn/.
· Configure a DDNS policy to update the mapping between the router's FQDN and IP address.
· Make sure the devices can reach each other.
Procedure
# Create a DDNS policy named oray.cn and enter its view.
<Router> system-view
[Router] ddns policy oray.cn
# Specify the URL address, username, and password for DDNS update requests.
[Router-ddns-policy-oray.cn] url oray://phddns60.oray.net
[Router-ddns-policy-oray.cn] username steven
[Router-ddns-policy-oray.cn] password simple nevets
# Set the DDNS update request interval to 12 minutes.
[Router-ddns-policy-oray.cn] interval 0 0 12
[Router-ddns-policy-oray.cn] quit
# Specify the IP address of the DNS server as 1.1.1.1.
[Router] dns server 1.1.1.1
# Apply DDNS policy oray.cn to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 to enable DDNS update. The mapping between domain name example.gicp.cn and the primary IP address of the interface will be dynamically updated.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ddns apply policy oray.cn fqdn example.gicp.cn
Verifying the configuration
Verify that the router can update its domain name-IP mapping through the Peanuthull DDNS provider when its IP address changes. The Internet users can resolve the correct IP address through the domain name example.gicp.cn to access the Web service.