- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-WLAN IDS Configuration | 102.62 KB |
Table of Contents
Configuring IDS Attack Detection
Configuring IDS Attack Detection
Displaying and Maintaining WLAN IDS
Configuring WIDS-Frame Filtering
Configuring Static White and Black Lists
Configuring Dynamic Blacklist Feature
Displaying and Maintaining WLAN IDS Frame Filtering
WLAN IDS Frame Filtering Configuration Example
l The models listed in this document are not applicable to all regions. Please consult your local sales office for the models applicable to your region.
l Support of the H3C WA series WLAN access points (APs) for features may vary by AP model. For more information, see Feature Matrix.
l The interface types and the number of interfaces vary by AP model.
l The radio types supported by the H3C WA series WLAN access points vary by AP model.
l The term AP in this document refers to common APs, wireless bridges, or mesh APs.
This chapter includes these sections:
l Configuring IDS Attack Detection
l Displaying and Maintaining WLAN IDS
l Configuring WIDS-Frame Filtering
l Displaying and Maintaining WLAN IDS Frame Filtering
l WLAN IDS Frame Filtering Configuration Example
WLAN IDS Overview
802.11 networks are susceptible to a wide array of threats such as unauthorized access points and clients, ad-hoc networks, Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. Rogue devices are a serious threat to enterprise security. WLAN intrusion detection system (IDS) is used for the early detection of malicious attacks and intrusions on a wireless network. WLAN IPS helps to protect enterprise networks and users from unauthorized wireless access.
Terminology
l WLAN intrusion detection system: WLAN IDS is designed to be deployed in an area that an existing wireless network covers. It aids in the early detection of malicious outsider attacks and intrusions via the wireless network.
l Rogue AP: An unauthorized or malicious access point on the network, such as an employee setup AP, misconfigured AP, neighbor AP or an attacker operated AP. As it is not authorized, if there is any vulnerability in the AP, the hacker will have chance to compromise your network security.
l Rogue STA: An unauthorized or malicious station on the network.
l Ad-hoc mode: A station in ad-hoc mode can directly communicate with other stations without support from any other device.
WLAN IDS IPS
WLAN IDS IPS is a sub-feature of WLAN IDS. WLAN IDS IPS supports detection of the following attacks:
l Flood attack
l Weak IV attack
l Spoofing attack
WLAN IDS IPS detects intrusions or attacks on the WLAN system, and DoS attacks.
Flood attack detection
When a device tries to flood a network, it sends large volumes of frames of the same kind within a short span of time. When this occurs, the Access Controller (AC) and the Access Points (APs) are overwhelmed with frames from this device and consequently, frames from authorized stations get dropped.
WLAN IDS IPS counters this flood attack by constantly keeping track of the density of traffic generated by each device. When this density exceeds the tolerance limit, the device is reported to be flooding the network and will be blocked. Subsequent frames from this device will not be processed. If the dynamic blacklist feature is enabled, the detected device is added to the dynamic blacklist. WLAN IDS IPS detects flood attacks for the following types of frames: authentication requests, deauthentication requests, association requests, disassociation requests, reassociation requests, probe requests, null data frames, and action frames.
When an AP supports multiple BSSIDs, stations send probe request frames to the individual BSSIDs. Therefore, to track the density of probe request frames, both the source and destination addresses are considered. For other frame types, only the source address is considered.
Weak IV detection
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a protocol used for encrypting frames in a WLAN. WEP is based on a shared secret key and a pseudo-randomly generated 3-byte sequence called Initialization Vector (IV). When a WEP frame is sent, the IV used in encrypting the frame is also sent as part of the frame header.
However, sending some classes of IVs can ultimately reveal the shared secret key to any potential attackers. When the shared secret key is compromised, the attacker can access network resources.
WLAN IDS IPS counters this attack by verifying the IVs in WEP frames. Whenever a frame with a weak IV is detected, the attack is immediately logged.
Spoofing attack detection
In this kind of attack, a potential attacker can send a frame in the air on behalf of another device. For instance, a spoofed deauthentication frame can cause a station to get deauthenticated from the network.
WLAN IDS IPS counters this attack by detecting broadcast deauthentication and disassociation frames. When such a frame is received, this is identified as a spoofed frame, and the attack is immediately logged.
Configuring IDS Attack Detection
Configuring IDS Attack Detection
Follow these steps to configure IDS attack detection:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter IDS view |
wlan ids |
— |
|
Enable IDS attack detection |
attack-detection enable { all | flood | weak-iv | spoof } |
Required Disabled by default. |
Displaying and Maintaining WLAN IDS
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display the history of attacks detected in the WLAN system |
display wlan ids history |
Available in any view |
|
Display the statistics of attacks detected in the WLAN system |
display wlan ids statistics |
Available in any view |
|
Clear the history of attacks detected in the WLAN system |
reset wlan ids history |
Available in user view |
|
Clear the statistics of attacks detected in the WLAN system |
reset wlan ids statistics |
Available in user view |
Frame Filtering
Frame filtering is a feature of 802.11 MAC and a sub-feature of WLAN IDS.
A fat AP maintains a white list (Entries in the list will be permitted and can be configured through CLI), static black list (Entries in the list will be denied and can be configured through CLI) and dynamic black list (Entries in the list will be denied and are added when WLAN IDS detects flood attacks).
Overview
Blacklist and white list
You can configure the blacklist and white list functions to filter frames from WLAN clients and thereby implement client access control.
WLAN client access control is accomplished through the following three types of lists.
l White list: Contains the MAC addresses of all clients allowed to access the WLAN. If the white list is used, only permitted clients can access the WLAN, and all frames from other clients will be discarded.
l Static blacklist: Contains the MAC addresses of clients forbidden to access the WLAN. This list is manually configured.
l Dynamic blacklist: Contains the MAC addresses of clients forbidden to access the WLAN. A client is dynamically added to the list if it is considered sending attacking frames until the timer of the entry expires.
When an AP receives an 802.11 frame, it checks the source MAC address of the frame and processes the frame as follows:
1) If the source MAC address does not match any entry in the white list, the frame is dropped. If there is a match, the frame is considered valid and will be further processed.
2) If no white list entries exist, the static and dynamic blacklists are searched.
3) If the source MAC address matches an entry in any of the two lists, the frame is dropped.
4) If there is no match, or no blacklist entries exist, the frame is considered valid and will be further processed.
Figure 1-1 Frame filtering
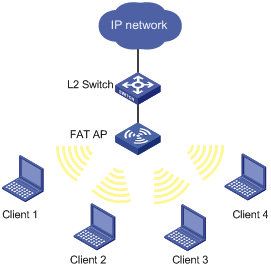
If client 1 is present in the backlist, it cannot associate with the fat AP; if it is only in the white list, it can get associated with the fat AP.
Configuring WIDS-Frame Filtering
WLAN IDS frame filtering configuration involves white list, black list configuration and dynamic black list feature configuration.
l In WLAN IDS view, you can configure the static black list, white list, enable dynamic blacklist feature and configure the lifetime for dynamic entries.
l Only entries present in the white list will be permitted. You can add entries into or delete entries from the list.
l Entries present in the static blacklist will be denied.
l Whenever WLAN IDS detects a flood attack, the attacking device is added into the dynamic blacklist. You can set a lifetime in seconds for dynamic blacklist entries. After the lifetime of an entry expires, the device entry will be removed from the dynamic list.
Configuring Static White and Black Lists
Follow these steps to configure static white and black lists:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN IDS view |
wlan ids |
— |
|
Add an entry into the white list |
whitelist mac-address mac-address |
Optional |
|
Add an entry into the static black list |
static-blacklist mac-address mac-address |
Optional |
Configuring Dynamic Blacklist Feature
Follow these steps to configure dynamic blacklist feature:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN IDS view |
wlan ids |
— |
|
Enable the dynamic black list feature |
dynamic-blacklist enable |
Optional By default, the dynamic blacklist feature is disabled. |
|
Configure the lifetime for dynamic blacklist entries |
dynamic-blacklist lifetime lifetime |
Optional By default, the lifetime is 300 seconds. |
Displaying and Maintaining WLAN IDS Frame Filtering
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display static or dynamic blacklist entries |
display wlan blacklist { static | dynamic } |
Available in any view |
|
Display white list entries |
display wlan whitelist |
Available in any view |
|
Clear dynamic black list entries |
reset wlan dynamic-blacklist { mac-address mac-address | all } |
Available in user view |
WLAN IDS Frame Filtering Configuration Example
Network requirements
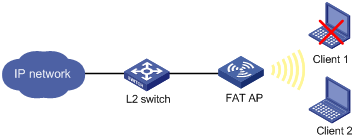
l As shown in Figure 1-2, a fat AP is connected to a Layer 2 switch. Client 1 (0000-000f-1211) is a rogue client. To ensure WLAN security, add the MAC address of the client into the blacklist on the fat AP to disable it from accessing the wireless network through any AP.
Figure 1-2 WLAN IDS frame filtering configuration
Configuration procedure
# Add MAC address 0000-000f-1211 of Client 1 into the blacklist.
<AP> system-view
[AP] wlan ids
[AP-wlan-ids] static-blacklist mac-address 0000-000f-1211
After the above configuration, Client 1 cannot access the AP, and other clients can access the network.
