- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-SBFD Troubleshooting Guide | 89.62 KB |
Troubleshooting high availability
Troubleshooting SBFD
SBFD session establishment failure
Symptom
After executing the display sbfd session initiator command on the device, if you cannot view session information, or the Session state field value in the command output is not Up, the SBFD session cannot come up.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The upper-layer protocol has not issued an SBFD session creation command.
· The number of SBFD sessions has exceeded the device capacity.
· The SBFD local discriminator is not configured on the reflector.
· Route entry or related forwarding entry anomalies occur on the initiator and reflector of the SBFD session.
· The link detected by SBFD is faulty. As a result, SBFD packets cannot be exchanged correctly.
Analysis
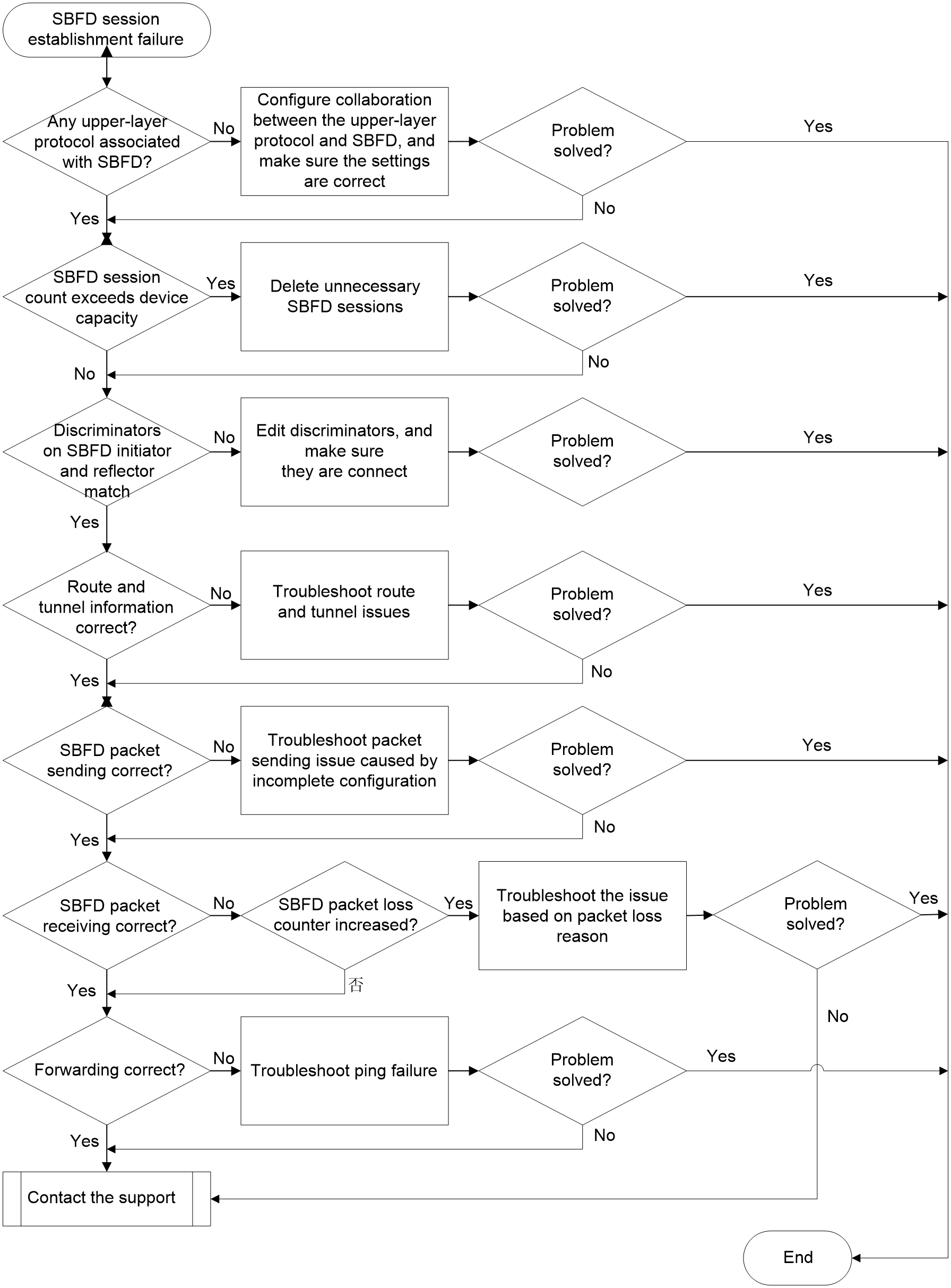
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting SBFD session establishment failure
Solution
To resolve the issue:
1. Executing the display sbfd session initiator command to verify that SBFD session information exists.
a. If no SBFD session information exists, proceed to step 2.
b. If SBFD session information exists, but the Session state field value is Down, proceed to step 4.
2. Verify that the configuration of collaboration between an upper-layer protocol and SBFD exists.
Execute the display current-configuration command to identify whether the configuration of collaboration between an upper-layer protocol and SBFD exists on the initiator.
For example, the configuration of collaboration between an SRv6 TE policy and SBFD is as follows:
segment-routing ipv6
traffic-engineering
policy 1
sbfd enable remote 1000
¡ If such a collaboration configuration exists, proceed to step 3.
¡ If no such collaboration exists, configure the settings for the collaboration between the upper-layer protocol and SBFD, and make sure the settings are correct.
3. Identify whether the number of SBFD sessions has exceeded the device capacity.
a. Execute the display system internal bfd capability command to view the maximum number of sessions supported by the device in the Max session count field.
b. Use the display sbfd session initiator command to view the number of SBFD sessions on the device. Use the display bfd session command to view the number of BFD sessions on the device.
c. Verify that the total number of SBFD and BFD sessions has reached the maximum number of sessions supported by the device.
- If the total number of SBFD and BFD sessions has reached the maximum number of sessions supported by the device, new SBFD sessions cannot be created. To resolve this issue, you can delete unnecessary SBFD or BFD sessions. For example, if an unnecessary BFD session for OSPF exists, delete this session by using undo ospf bfd enable command.
- If the total number of SBFD and BFD sessions has not reached the maximum number of sessions supported by the device, proceed to step 4.
4. Identify whether the discriminators on SBFD initiator and reflector match.
Execute the display sbfd session initiator command on the SBFD session initiator to view the value for the Remote discr field. Then, execute the display current-configuration command on the SBFD session reflector to view the value of the local discriminator.
¡ If the remote discriminator of the SBFD session initiator matches the local discriminator of the SBFD session reflector, proceed to step 5.
¡ If the remote discriminator of the SBFD session initiator does not match the local discriminator of the SBFD session reflector, take relevant actions based on the actual situation.
- If the SBFD session initiator does not have a remote discriminator specified, specify a remote discriminator by using the command for SBFD collaboration with the upper-layer protocol, or by using the sbfd destination ipv4 or sbfd destination ipv6 command.
- If the SBFD session reflector does not have a local discriminator specified, or the local discriminator does not match the remote discriminator specified for the initiator, execute the sbfd local-discriminator command to configure a local discriminator or edit the local discriminator value.
5. Verify that the SBFD route and tunnel information are normal.
When the SBFD initiator or reflector forwards SBFD packets through the IP path, take the following steps to examine the route information:
a. Execute the display sbfd session initiator command on the SBFD session initiator to view the IPv4 or IPv6 address in the Destination IP field.
b. Execute the display ip routing-table or display ipv6 routing-table command on the SBFD session initiator to identify whether a route is available to the destination address indicated by the Destination IP field.
c. If no such a route exists, troubleshoot the route issue. For more information, see the Layer 3—IP routing troubleshooting guide.
If such a route exists, but the BFD session cannot come up, proceed to step 6.
When the SBFD initiator or reflector forwards SBFD packets through the LSP, PW, VXLAN, MPLS TE, SRLSP, or SRv6 TE policy tunnel, verify the tunnel status. For more information, see troubleshooting guide for the associated modules. If the tunnel status is abnormal, troubleshoot the tunnel failure. If the tunnel status is normal, but the SBFD session cannot come up, proceed to step 6.
6. Verify that the SBFD packets are sent correctly.
Repeatedly execute the display sbfd session initiator verbose command to view the changes in the value for the Tx count field. The Tx Count value represents the number of packets transmitted. If the value for this field is fixed at 0 or does not change, SBFD packet sending is abnormal. Follow these steps to examine the SBFD packet transmission status:
a. Execute the display interface interface-type interface-number command to view the interface running status. If the value for the Current state or Line protocol state field is not UP, troubleshoot the interface failure. If the interface is running correctly, proceed to step b.
b. Execute the debugging bfd error command to identify the packet sending failure reason based on the debugging information, and troubleshoot the failure according to the failure reason. For example:
<Sysname> debugging bfd error
*Feb 22 11:27:58:715 2023 Sysname BFD/7/DEBUG: Encap link head return:0x40010001
The information above indicates a link-layer header encapsulation failure for SBFD packets. If you cannot troubleshoot the failure, proceed to step 9.
c. After the previous operations, if SBFD can send packets correctly, but the SBFD session cannot come up or the SBFD session flaps, proceed to step 7. After the previous operations, if SBFD packet transmission anomalies still persist, proceed to step 8.
7. Verify that the SBFD packets are received correctly.
Repeatedly execute the display sbfd session initiator verbose command on the SBFD initiator to view the value for the Rx Count field. The Rx Count value represents the number of packets received.
a. If the value for this field is fixed at 0 or does not change, SBFD packet receiving is abnormal. Execute the display system internal bfd packet statistics command in probe check for packet loss count in The detailed discarded packet statistics field. If packet loss occurs, troubleshoot the fault according to the packet loss reason.
- If you cannot troubleshoot the fault, proceed to step 8.
- If no packet loss occurs, proceed to step 9.
b. If the value for the Rx Count field keeps increasing, but the SBFD session flaps, proceed to step 8.
8. Verify that the SBFD packets are forwarded correctly.
Use the ping tool to identify whether the link associated with the SBFD session can forward packets correctly. The ping tool used varies by link type. For more information, see Table 1.
Table 1 Link types and the associated ping tools
|
Link type |
Ping tool |
|
IP link |
IP ping tool. Execute ping ip or ping ipv6 command to verify the reachability of the specified IPv4 address or IPv6 address. |
|
LSP tunnel |
MPLS ping tool. Execute the ping mpls ipv4 command to verify the LSP tunnel connectivity. |
|
MPLS TE tunnel |
MPLS ping tool. Execute the ping mpls te command to verify the MPLS TE tunnel connectivity. |
|
PW |
MPLS ping tool. Execute the ping mpls pw command to verify the PW tunnel connectivity. |
|
SRv6 TE policy tunnel |
SRv6 TE policy ping tool. Execute the ping srv6-te policy command to verify the SRv6 forwarding path connectivity. |
¡ If the ping operation fails, troubleshoot the link failure. For more information, see the ping, MPLS, and segment routing troubleshooting guides.
¡ If the ping operation succeeds, proceed to step 9.
9. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
Module name: HH3C-BFD-STD-MIB
· hh3cBfdSessNumberLimit (1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.72.1.1.4)
Log messages
· BFD_REACHED_UPPER_LIMIT