- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-ARP attack protection configuration | 156.58 KB |
Contents
Configuring ARP attack protection
ARP attack protection tasks at a glance
Configuring unresolvable IP attack protection
About unresolvable IP attack protection
Configuring ARP source suppression
Configuring ARP blackhole routing
Display and maintenance commands for unresolvable IP attack protection
Configuring ARP packet rate limit
Configuring source MAC-based ARP attack detection
About source MAC-based ARP attack detection
Display and maintenance commands for source MAC-based ARP attack detection
Example: Configuring source MAC-based ARP attack detection
Configuring ARP packet source MAC consistency check
About ARP packet source MAC consistency check
Display and maintenance commands for ARP packet source MAC consistency check
Configuring ARP active acknowledgement
Configuring ARP scanning and fixed ARP
Enabling SNMP notifications for ARP
Configuring ARP attack protection
About ARP attack protection
The device can provide multiple features to detect and prevent ARP attacks and viruses in the LAN. An attacker can exploit ARP vulnerabilities to attack network devices in the following ways:
· Sends a large number of unresolvable IP packets to have the receiving device busy with resolving IP addresses until its CPU is overloaded. Unresolvable IP packets refer to IP packets for which ARP cannot find corresponding MAC addresses.
· Sends a large number of ARP packets to overload the CPU of the receiving device.
· Acts as a trusted user or gateway to send ARP packets so the receiving devices obtain incorrect ARP entries.
ARP attack protection tasks at a glance
All ARP attack protection tasks are optional.
· Preventing flood attacks
¡ Configuring unresolvable IP attack protection
¡ Configuring ARP packet rate limit
¡ Configuring source MAC-based ARP attack detection
· Preventing user and gateway spoofing attacks
¡ Configuring ARP packet source MAC consistency check
¡ Configuring ARP active acknowledgement
¡ Configuring ARP scanning and fixed ARP
¡ Enabling SNMP notifications for ARP
Configuring unresolvable IP attack protection
About unresolvable IP attack protection
Upon receiving unresolvable IP packets, the device generates ARP Miss messages which are sent to the CPU for processing. Such unresolvable IP packets are called ARP Miss packets. The device generates and issues temporary ARP entries based on the ARP Miss messages and sends ARP requests to the target subnets in the ARP Miss packets. The device generates a large number of ARP Miss messages if it receives a large number of unresolvable IP packets from a host, and the following situations can occur:
· The device sends a large number of ARP requests, overloading the target subnets in the ARP Miss packets.
· The device keeps trying to resolve the destination IP addresses and the CPU processes a large number of ARP Miss messages, overloading the CPU.
To protect the device from such IP attacks, you can configure the following features:
· ARP source suppression—Stops resolving packets from an IP address if the number of unresolvable IP packets from the IP address exceeds the upper limit within 5 seconds. The device continues ARP resolution when the interval elapses. This feature is applicable if the attack packets have the same source addresses.
· ARP blackhole routing—Creates a blackhole route destined for an unresolved IP address. The device drops all matching packets until the blackhole route is deleted. A blackhole route is deleted when its aging timer is reached or the route becomes reachable.
After a blackhole route is created for an unresolved IP address, the device immediately starts the first ARP blackhole route probe by sending an ARP request. If the resolution fails, the device continues probing according to the probe settings. If the IP address resolution succeeds in a probe, the device converts the blackhole route to a normal route. If an ARP blackhole route ages out before the device finishes all probes, the device deletes the blackhole route and does not perform the remaining probes.
This feature is applicable regardless of whether the attack packets have the same source addresses.
Configuring ARP source suppression
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable ARP source suppression.
arp source-suppression enable
By default, ARP source suppression is disabled.
3. Set the maximum number of unresolvable packets that the device can process per source IP address within 5 seconds.
arp source-suppression limit limit-value
By default, the maximum number is 10.
Configuring ARP blackhole routing
Restrictions and guidelines
Set the ARP blackhole route probe count to a big value, for example, 25. If the device fails to reach the destination IP address temporarily and the probe count is too small, all probes might finish before the problem is resolved. As a result, non-attack packets will be dropped. This setting can avoid such situation.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable ARP blackhole routing.
arp resolving-route enable
By default, ARP blackhole routing is enabled.
3. (Optional.) Set the number of ARP blackhole route probes for each unresolved IP address.
arp resolving-route probe-count count
The default setting is three probes.
4. (Optional.) Set the interval at which the device probes ARP blackhole routes.
arp resolving-route probe-interval interval
The default setting is 1 second.
Display and maintenance commands for unresolvable IP attack protection
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display ARP source suppression configuration information. |
display arp source-suppression |
Configuring ARP packet rate limit
About this task
The ARP packet rate limit feature allows you to limit the rate of ARP packets delivered to the CPU.
You can enable sending notifications to the SNMP module or enable logging for ARP packet rate limit.
· If notification sending is enabled, the device sends the highest threshold-crossed ARP packet rate within the sending interval in a notification to the SNMP module. You must use the snmp-agent target-host command to set the notification type and target host. For more information about notifications, see Network Management and Monitoring Command Reference.
· If logging for ARP packet rate limit is enabled, the device sends the highest threshold-crossed ARP packet rate within the sending interval in a log message to the information center. You can configure the information center module to set the log output rules. For more information about information center, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Restrictions and guidelines
As a best practice, configure this feature when is enabled, or when ARP flood attacks are detected.
If excessive notifications and log messages are sent for ARP packet rate limit, you can increase notification and log message sending interval.
If you enable notification sending and logging for ARP packet rate limit on an aggregate interface, the features apply to all aggregation member ports.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. (Optional.) Enable SNMP notifications for ARP packet rate limit.
snmp-agent trap enable arp [ rate-limit ]
By default, SNMP notifications for ARP packet rate limit are disabled.
3. (Optional.) Enable logging for ARP packet rate limit.
arp rate-limit log enable
By default, logging for ARP packet rate limit is disabled.
4. (Optional.) Set the notification and log message sending interval.
arp rate-limit log interval interval
By default, the device sends notifications and log messages every 60 seconds.
5. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
Supported interface types include Layer 3 Ethernet interface and Layer 3 aggregate interface.
6. Enable ARP packet rate limit.
arp rate-limit [ pps ]
By default, ARP packet rate limit is enabled.
Configuring source MAC-based ARP attack detection
About source MAC-based ARP attack detection
This feature checks the number of ARP packets delivered to the CPU. If the number of packets from the same MAC address within the check interval exceeds the threshold, the device generates an ARP attack entry for the MAC address. The device handles the attack by using either of the following methods before the ARP attack entry ages out:
· Monitor—Only generates log messages.
· Filter—Generates log messages and filters out subsequent ARP packets from the MAC address.
When an ARP attack entry ages out, if the number of ARP packets dropped within the aging time is greater than or equal to the threshold, the device resets the aging time of the entry. If the number is less than the threshold, the device deletes the entry and ARP packets sourced from the MAC address in the entry can be processed correctly.
Source MAC-based ARP attack detection checks the number of ARP packets delivered to the CPU on a per-slot basis. If the number of ARP packets received from the same MAC address within a check interval on a slot exceeds the threshold, the device determines that an attack has occurred.
Restrictions and guidelines
When you change the attack handling method from monitor to filter, the configuration takes effect immediately. When you change the attack handling method from filter to monitor, the device continues filtering packets that match existing attack entries.
You can exclude the MAC addresses of some gateways and servers from this detection. This feature does not inspect ARP packets from those devices even if they are attackers.
If attacks occur frequently in your network, set a short check interval so that source MAC-based ARP attacks can be detected in a timely manner. If attacks seldom occur, you can set a long check interval.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable source MAC-based ARP attack detection and specify the attack handling method.
arp source-mac { filter | monitor }
By default, this feature is disabled.
3. Set the check interval for source MAC-based ARP attack detection.
arp source-mac check-interval interval
By default, the check interval for source MAC-based ARP attack detection is 5 seconds.
4. Set the threshold.
arp source-mac threshold threshold-value
By default, the threshold is 30.
5. Set the aging timer for ARP attack entries.
arp source-mac aging-time time
By default, the lifetime is 300 seconds.
6. (Optional.) Exclude specific MAC addresses from this detection.
arp source-mac exclude-mac mac-address&<1-n>
By default, no MAC address is excluded.
Display and maintenance commands for source MAC-based ARP attack detection
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the configuration for source MAC-based ARP attack detection. |
display arp source-mac configuration [ slot slot-number ] |
|
Display ARP attack entries detected by source MAC-based ARP attack detection. |
display arp source-mac interface interface-type interface-number [ slot slot-number ] [ verbose ] display arp source-mac { mac mac-address slot slot-number [ verbose ] display arp source-mac slot slot-number [ count | verbose ] |
|
Display statistics for packets dropped by source MAC-based ARP attack detection. |
display arp source-mac statistics slot slot-number |
|
Delete source MAC-based ARP attack entries. |
reset arp source-mac [ interface interface-type interface-number | mac mac-address ] [ slot slot-number ] |
|
Clear statistics of packets dropped by source MAC-based ARP attack detection. |
reset arp source-mac statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number | mac mac-address ] [ slot slot-number ] |
Example: Configuring source MAC-based ARP attack detection
Network configuration
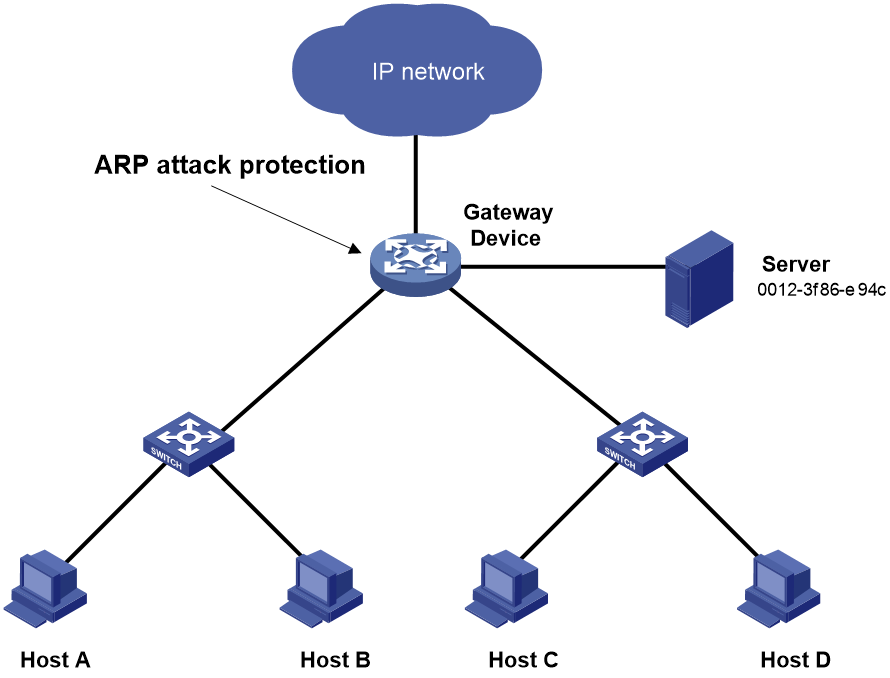
As shown in Figure 1, the hosts access the Internet through a gateway (Device). If malicious users send a large number of ARP requests to the gateway, the gateway might crash and cannot process requests from the clients. To solve this problem, configure source MAC-based ARP attack detection on the gateway. Set the check interval to 10 seconds, the threshold to 30, and the lifetime for ARP attack entries to 60 seconds. Exclude the MAC address 0012-3f86-e94c from source MAC-based ARP attack detection.
Procedure
# Enable source MAC-based ARP attack detection, and specify the handling method as filter.
<Device> system-view
[Device] arp source-mac filter
# Set the check interval for source MAC-based ARP attack detection to 10 seconds.
[Device] arp source-mac check-interval 10
# Set the threshold to 30.
[Device] arp source-mac threshold 30
# Set the lifetime for ARP attack entries to 60 seconds.
[Device] arp source-mac aging-time 60
# Exclude MAC address 0012-3f86-e94c from this detection.
[Device] arp source-mac exclude-mac 0012-3f86-e94c
Configuring ARP packet source MAC consistency check
About ARP packet source MAC consistency check
This feature enables a gateway to filter out ARP packets whose source MAC address in the Ethernet header is different from the sender MAC address in the message body. This feature allows the gateway to learn correct ARP entries.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable ARP packet source MAC address consistency check.
arp valid-check enable
By default, ARP packet source MAC address consistency check is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for ARP packet source MAC consistency check
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display statistics for packets dropped by ARP packet source MAC consistency check. |
display arp valid-check statistics slot slot-number |
|
Clear statistics for packets dropped by ARP packet source MAC consistency check. |
reset arp valid-check statistics { all | slot slot-number } |
Configuring ARP active acknowledgement
About this task
Use the ARP active acknowledgement feature on gateways to prevent user spoofing.
This feature enables the device to perform active acknowledgement before creating an ARP entry.
· Upon receiving an ARP request that requests the MAC address of the device, the device sends an ARP reply. Then, it sends an ARP request for the sender IP address in the received ARP request to determine whether to create an ARP entry for the sender IP address.
¡ If the device receives an ARP reply within the probe interval, it creates the ARP entry.
¡ If the device does not receive an ARP reply within the probe interval, it does not create the ARP entry.
· Upon receiving an ARP reply, the device examines whether it was the reply to the request that the device has sent.
¡ If it was, the device creates an ARP entry for the sender IP address in the ARP reply.
¡ If it was not, the device sends an ARP request for the sender IP address to determine whether to create an ARP entry for the sender IP address.
- If the device receives an ARP reply within the probe interval, it creates the ARP entry.
- If the device does not receive an ARP reply within the probe interval, it does not create the ARP entry.
To improve validity and reliability of ARP entries, you can enable ARP active acknowledgement in strict mode. In this mode, the device creates ARP entries only for the IP addresses that the device actively initiates the ARP resolution.
After you enable ARP active acknowledgement notifications, the device sends a notification to the SNMP module when it does not establish an ARP entry because of the ARP active acknowledgement feature. The notification includes the sender IP and MAC addresses in the received ARP request. For ARP active acknowledgement event notifications to be sent correctly, you must also configure SNMP on the device. For more information about SNMP configuration, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. (Optional.) Enable SNMP notifications for ARP.
snmp-agent trap enable arp [ active-ack ]
By default, SNMP notifications for ARP are disabled.
If you do not specify any keywords, this command enables all SNMP notifications for ARP. If you specify only the active-ack keyword, this command enables only ARP active acknowledgement notifications.
3. Enable ARP active acknowledgement.
arp active-ack [ strict ] enable
By default, this feature is disabled.
For ARP active acknowledgement to take effect in strict mode, make sure ARP blackhole routing is enabled.
Configuring authorized ARP
About authorized ARP
Authorized ARP entries are generated based on the DHCP clients' address leases on the DHCP server or dynamic client entries on the DHCP relay agent.
Use this feature to prevent user spoofing and to allow only authorized clients to access network resources.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable authorized ARP on the interface.
arp authorized enable
By default, authorized ARP is disabled.
Configuring ARP scanning and fixed ARP
About this task
ARP scanning is typically used together with the fixed ARP feature in small-scale and stable networks.
ARP scanning automatically creates ARP entries for devices in an address range. The device performs ARP scanning in the following steps:
1. Sends ARP requests for each IP address in the address range.
2. Obtains their MAC addresses through received ARP replies.
3. Creates dynamic ARP entries.
Fixed ARP converts existing dynamic ARP entries (including those generated through ARP scanning) to static ARP entries. These static ARP entries are of the same attributes as the ARP entries that are manually configured. This feature prevents ARP entries from being modified by attackers.
Restrictions and guidelines
IP addresses in existing ARP entries are not scanned.
Due to the limit on the total number of static ARP entries, some dynamic ARP entries might fail the conversion.
The arp fixup command is a one-time operation. You can use this command again to convert the dynamic ARP entries learned later to static.
To delete a static ARP entry converted from a dynamic one, use the undo arp ip-address [ vpn-instance-name ] command. You can also use the reset arp all command to delete all ARP entries or the reset arp static command to delete all static ARP entries.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Trigger an ARP scanning.
arp scan [ start-ip-address to end-ip-address ]
|
|
CAUTION: ARP scanning will take some time. To stop an ongoing scan, press Ctrl + C. Dynamic ARP entries are created based on ARP replies received before the scan is terminated. |
4. Return to system view.
quit
5. Convert existing dynamic ARP entries to static ARP entries.
arp fixup
Enabling SNMP notifications for ARP
About this task
Enable SNMP notifications for ARP as required.
· If you enable ARP active acknowledgement notifications, the device sends a notification to the SNMP module when it does not establish an ARP entry due to active acknowledgement. The notification includes the sender IP and MAC addresses in the received ARP request.
· If you enable rate limit notifications for sending ARP Miss messages or ARP packets, the device sends the highest threshold-crossed rate as a notification to the SNMP module.
· If you enable ARP entry limit notifications, the device sends the current number of ARP entries as a notification to the SNMP module when the number of global ARP entries exceeds the alarm threshold.
· If you enable endpoint and local device conflict notifications, the device sends a notification to the SNMP module when an endpoint and local device conflict occurs. The notification includes the sender IP address, sender MAC address, target IP address, and target MAC address in the conflicting ARP packet.
· If you enable rate limit notifications for receiving ARP packets, the device sends the highest threshold-crossed rate as a notification to the SNMP module.
· If you enable user IP address conflict notifications, the device sends a notification to the SNMP module when a user IP address conflict occurs. The notification includes the sender IP and MAC addresses in the conflicting ARP packet, and MAC address in the corresponding local ARP entry.
· If you enable user port migration notifications, the device sends a notification to the SNMP module when a user port changes. The notification includes the IP address, MAC address, port before migration, and port after migration of the user.
For ARP event notifications to be sent correctly, you must also configure SNMP on the device. For more information about SNMP configuration, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable SNMP notifications for ARP.
snmp-agent trap enable arp [ active-ack | arp-miss | entry-limit | local-conflict | rate-limit | user-ip-conflict | user-move ] *
By default, SNMP notifications for ARP are disabled.
If you do not specify any keywords, this command enables all SNMP notifications for ARP.