- Table of Contents
-
- 05-Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Basic IP routing configuration
- 02-Static routing configuration
- 03-RIP configuration
- 04-OSPF configuration
- 05-Policy-based routing configuration
- 06-IPv6 static routing configuration
- 07-RIPng configuration
- 08-OSPFv3 configuration
- 09-IPv6 policy-based routing configuration
- 10-Routing policy configuration
- 11-DCN configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 11-DCN configuration | 139.84 KB |
Contents
Configuring the NE ID and NE IP
Enabling the automatic report feature
Configuring the source MAC address of LLDP frames
Advertising the LLDP management address
Enabling the device to generate ARP entries for received management address LLDP TLVs
Display and maintenance commands for DCN
Configuring DCN
About DCN
Data communication network (DCN) is built for the network management system (NMS) to implement operation, administration, and maintenance (OAM) on the network elements (NEs).
On large-scaled networks with DCN configured, the NMS remotely manages and controls all NEs through the gateway network element (GNE), which reduces operation and maintenance costs.
On the DCN network, all NEs must operate in Area 0 of OSPF process 65535.
Basic concepts
NE
A network device managed by the NMS on the DCN network.
GNE
The NE that is directly connected to the NMS. The NSM communicates with the GNE at the network layer or application layer and manages the NEs through the GNE.
NE table
Stores the NE ID-to-NE IP mappings for each NE in the DCN domain. After DCN is enabled, an NE encapsulates its NE ID and NE IP in a Type-10 Opaque LSA. It floods the LSA to synchronize the mappings with other NEs in the DCN domain.
The NE IP in the Type-10 Opaque LSA might be inconsistent with the NE's router ID when DCN is enabled on an OSPF network. Devices from other vendors will fail to identify the NE. To avoid this problem, make sure the following requirements are met:
· Change the router ID by modifying the NE IP. Do not change the default IP address of the DCN's loopback interface.
· Do not associate other loopback interfaces with the DCN VPN instance.
GNE
The GNE allows the NMS to access NEs on the DCN network. The GNE provides the NE ID-to-NE IP mappings of all NEs for the Telnet users to access the target NE remotely.
NE search
The NE search feature allows the NMS to search for all NEs that are connected to the GNE. With this feature, the GNE can report information about all NEs in its NE table and the GNE itself to the NMS.
Automatic report
The automatic report feature enables the GNE to automatically report online or offline events of NEs to the NMS.
DCN tasks at a glance
To configure DCN, perform the following tasks:
1. Enabling DCN
2. (Optional.) Configuring the NE ID and NE IP
4. (Optional.) Enabling the automatic report feature
5. Configuring the LLDP features
a. (Optional.) Configuring the source MAC address of LLDP frames
b. Advertising the LLDP management address
c. Enabling the device to generate ARP entries for received management address LLDP TLVs
Enabling DCN
About this task
After DCN is enabled, the device assigns an NE IP to the loopback interface with the largest interface number and uses the interface for communication. The NE IP is specified as the management address and advertised in an LLDP frame. For more information about LLDP, see LLDP configuration in Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable DCN and enter DCN view.
dcn
By default, DCN is disabled.
Configuring the NE ID and NE IP
About this task
Typically an NE automatically generates an NE IP according to its NE ID. The automatically generated NE IP changes when the NE ID changes. When you replan your network or an NE ID conflict occurs, you can manually configure the NE ID and NE IP. The manually configured NE IP does not change when the NE ID changes.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter DCN view.
dcn
3. Configure the NE ID.
ne-id id-number
By default, the NE ID is automatically generated by using the 24 low-order bits of the bridge MAC address.
4. Configure the NE IP.
ne-ip ip-address { mask-length | mask }
By default, the NE IP is automatically generated by using 129 as the eight high-order bits and the NE ID as the rest 16 bits. The mask length is 32.
Configuring DCN VPN
About this task
Perform this task to ensure the independence of DCN services. For more information about VPN instances, see MCE configuration in MCE Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a VPN instance and enter its view, or enter the view of an existing VPN instance.
ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
For more information about this command, see MCE configuration in MCE Configuration Guide.
3. Quit VPN instance view.
quit
4. Create a loopback interface and enter its view, or enter the view of an existing loopback interface.
interface loopback interface-number
5. Associate the loopback interface with a VPN instance.
ip binding vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
By default, the loopback interface is not associated with a VPN instance.
For more information about this command, see MCE configuration in MCE Configuration Guide.
Enabling the automatic report feature
Restrictions and guidelines
Perform this task only on GNE to enable it to automatically report online or offline events of NEs to the NMS.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter DCN view.
dcn
3. Enable the automatic report feature.
auto-report
By default, the automatic report feature is disabled.
Configuring the LLDP features
Configuring the source MAC address of LLDP frames
About this task
Perform this task to configure the MAC address of the as the source MAC address of LLDP frames. For more information about LLDP, see LLDP configuration in Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Configure the MAC address of the Dot1q termination-enabled VLAN interface as the source MAC address of LLDP frames.
lldp source-mac vlan vlan-id
By default, the MAC address of the current Ethernet interface is specified as the source MAC address of LLDP frames.
For more information about this command, see LLDP commands in Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference.
Advertising the LLDP management address
About this task
An NE on the DCN network learns the MAC address of its neighbor through LLDP. Perform this task to enable an NE to advertise the IP address of the specified loopback interface (management address) for ARP entry learning. For more information about LLDP, see LLDP configuration in Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Advertise the LLDP management address.
lldp tlv-enable basic-tlv management-address-tlv [ ip-address | interface loopback interface-number ]
By default, the LLDP management address is not advertised.
For more information about this command, see LLDP commands in Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference.
Enabling the device to generate ARP entries for received management address LLDP TLVs
About this task
This feature enables the device to generate an ARP entry for a received LLDP frame that meets the following requirements:
· The LLDP frame carries a management address TLV.
· The management address TLV contains an IPv4 address.
The generated ARP entry contains the management address and the source MAC address of the frame. For more information about LLDP, see LLDP configuration in Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable the device to generate an ARP entry when receiving a management address LLDP TLV.
lldp management-address arp-learning vlan vlan-id
By default, the device does not generate an ARP entry when receiving a management address LLDP TLV.
The vlan-id argument specifies the VLAN ID of a VLAN interface.
For more information about this command, see LLDP commands in Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
Display and maintenance commands for DCN
Execute the display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the brief DCN information. |
display dcn |
|
Display information about all online NEs on the DCN network. |
display dcn ne-info |
DCN configuration examples
Example: Configuring DCN
Network configuration
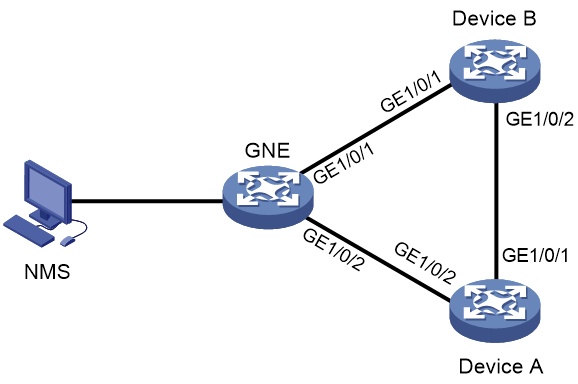
As shown in Figure 1, the GNE, Device A, and Device B run DCN in the same VPN instance. The NMS uses SNMP to manage the GNE, and the GNE automatically sends notifications to the NMS to report online or offline events of NEs.
Procedure
1. Configure the GNE:
# Enable SNMP on the GNE. (Details not shown. For more information, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.)
# Enable DCN, configure the NE ID as 100001 and NE IP as 11.1.1.1/32, and enable the automatic report feature.
<GNE> system-view
[GNE] dcn
[GNE-dcn] ne-id 100001
[GNE-dcn] ne-ip 11.1.1.1 32
[GNE-dcn] auto-report
[GNE-dcn] quit
# Create a VPN instance named dcn_vpn.
[GNE] ip vpn-instance dcn_vpn
[GNE-vpn-instance-dcn_vpn] quit
# Create interface Loopback 1023, and associate it with VPN instance dcn_vpn.
[GNE] interface loopback 1023
[GNE-LoopBack1023] ip binding vpn-instance dcn_vpn
[GNE-LoopBack1023] quit
# Enable LLDP globally.
[GNE] lldp global enable
# Enable the nearest bridge agents on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to advertise basic LLDP TLVs and management address TLVs. The IP address of interface Loopback 1023 is specified as the management address.
[GNE] interface Gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[GNE-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port access vlan 3001
[GNE-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] lldp source-mac vlan 3001
[GNE-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] lldp tlv-enable basic-tlv management-address-tlv interface loopback 1023
# Configure the system to issue the generated ARP entry to the Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface associated with VLAN 4094 in Dot1q termination after GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 receives an LLDP frame.
[GNE-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] lldp management-address arp-learning vlan 3001
[GNE-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Enable the nearest bridge agents on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to advertise basic LLDP TLVs and management address TLVs. The IP address of interface Loopback 1023 is specified as the management address.
[GNE] interface Gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[GNE-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port access vlan 3002
[GNE-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] lldp source-mac vlan 3002
[GNE-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] lldp tlv-enable basic-tlv management-address-tlv interface loopback 1023
# Configure the system to issue the generated ARP entry to the Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface associated with VLAN 4094 in Dot1q termination after GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 receives an LLDP frame.
[GNE-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] lldp management-address arp-learning vlan 3002
[GNE-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 3001 that borrows the IP address of Loopback 1023.
[GNE] interface Vlan-interface 3001
[GNE-Vlan-interface3001] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1023
[GNE-Vlan-interface3001] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 3002 that borrows the IP address of Loopback 1023.
[GNE] interface Vlan-interface 3002
[GNE-Vlan-interface3002] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1023
[GNE-Vlan-interface3002] quit
# Enable OSPF process 65535 and create area 0.
[GNE] ospf 65535 vpn-instance dcn_vpn
[GNE-ospf-65535] area 0
[GNE-ospf-65535-area-0.0.0.0] network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255
[GNE-ospf-65535-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[GNE-ospf-65535] quit
# Set the OSPF network type for VLAN-interface 3001 to P2P.
[GNE] interface Vlan-interface 3001
[GNE-Vlan-interface3001] ospf network-type p2p
[GNE-Vlan-interface3001] quit
# Set the OSPF network type for VLAN-interface 3002 to P2P.
[GNE] interface Vlan-interface 3002
[GNE-Vlan-interface3002] ospf network-type p2p
[GNE-Vlan-interface3002] quit
2. Configure Device A:
# Enable DCN, configure the NE ID as 200002 and NE IP as 22.2.2.2/32.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] dcn
[DeviceA-dcn] ne-id 200002
[DeviceA-dcn] ne-ip 22.2.2.2 32
[DeviceA-dcn] quit
# Create a VPN instance named dcn_vpn.
[DeviceA] ip vpn-instance dcn_vpn
[DeviceA-vpn-instance-dcn_vpn] quit
# Create interface Loopback 1023, and associate it with VPN instance dcn_vpn.
[DeviceA] interface loopback 1023
[DeviceA-LoopBack1023] ip binding vpn-instance dcn_vpn
[DeviceA-LoopBack1023] quit
# Enable LLDP globally.
[DeviceA] lldp global enable
# Enable the nearest bridge agents on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to advertise basic LLDP TLVs and management address TLVs. The IP address of interface Loopback 1023 is specified as the management address.
[DeviceA] interface Gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port access vlan 3002
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] lldp source-mac vlan 3002
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] lldp tlv-enable basic-tlv management-address-tlv interface loopback 1023
# Configure the system to issue the generated ARP entry to the Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface associated with VLAN 3002 in Dot1q termination after GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 receives an LLDP frame.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] lldp management-address arp-learning vlan 3002
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Enable the nearest bridge agents on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to advertise basic LLDP TLVs and management address TLVs. The IP address of interface Loopback 1023 is specified as the management address.
[DeviceA] interface Gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port access vlan 3003
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] lldp source-mac vlan 3003
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] lldp tlv-enable basic-tlv management-address-tlv interface loopback 1023
# Configure the system to issue the generated ARP entry to the Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface associated with VLAN 3003 in Dot1q termination after GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 receives an LLDP frame.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] lldp management-address arp-learning vlan 3003
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 3002 that borrows the IP address of Loopback 1023.
[DeviceA] interface Vlan-interface 3002
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface3002] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1023
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface3002] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 3003 that borrows the IP address of Loopback 1023.
[DeviceA] interface Vlan-interface 3003
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface3003] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1023
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface3003] quit
# Enable OSPF process 65535 and create area 0.
[DeviceA] ospf 65535 vpn-instance dcn_vpn
[DeviceA-ospf-65535] area 0
[DeviceA-ospf-65535-area-0.0.0.0] network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255
[DeviceA-ospf-65535-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceA-ospf-65535] quit
# Set the OSPF network type for VLAN-interface 3002 to P2P.
[DeviceA] interface Vlan-interface 3002
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface3002] ospf network-type p2p
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface3002] quit
# Set the OSPF network type for VLAN-interface 3003 to P2P.
[DeviceA] interface Vlan-interface 3003
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface3003] ospf network-type p2p
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface3003] quit
3. Configure Device B:
# Enable DCN, configure the NE ID as 300003 and NE IP as 33.3.3.3/32.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] dcn
[DeviceB-dcn] ne-id 300003
[DeviceB-dcn] ne-ip 33.3.3.3 32
[DeviceB-dcn] quit
# Create a VPN instance named dcn_vpn.
[DeviceB] ip vpn-instance dcn_vpn
[DeviceB-vpn-instance-dcn_vpn] quit
# Create interface Loopback 1023, and associate it with VPN instance dcn_vpn.
[DeviceB] interface loopback 1023
[DeviceB-LoopBack1023] ip binding vpn-instance dcn_vpn
[DeviceB-LoopBack1023] quit
# Enable LLDP globally.
[DeviceB] lldp global enable
# Enable the nearest bridge agents on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to advertise basic LLDP TLVs and management address TLVs. The IP address of interface Loopback 1023 is specified as the management address.
[DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port access vlan 3001
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] lldp source-mac vlan 3001
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] lldp tlv-enable basic-tlv management-address-tlv interface loopback 1023
# Configure the system to issue the generated ARP entry to the Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface associated with VLAN 3001 in Dot1q termination after GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 receives an LLDP frame.
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] lldp management-address arp-learning vlan 3001
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Enable the nearest bridge agents on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to advertise basic LLDP TLVs and management address TLVs. The IP address of interface Loopback 1023 is specified as the management address.
[DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port access vlan 3003
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] lldp source-mac vlan 3003
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] lldp tlv-enable basic-tlv management-address-tlv interface loopback 1023
# Configure the system to issue the generated ARP entry to the Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface associated with VLAN 3003 in Dot1q termination after GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 receives an LLDP frame.
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] lldp management-address arp-learning vlan 3003
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 3001 that borrows the IP address of Loopback 1023.
[DeviceB] interface Vlan-interface 3001
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface3001] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1023
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface3001] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 3003 that borrows the IP address of Loopback 1023.
[DeviceB] interface Vlan-interface 3003
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface3003] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1023
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface3003] quit
# Enable OSPF process 65535 and create area 0.
[DeviceB] ospf 65535 vpn-instance dcn_vpn
[DeviceB-ospf-65535] area 0
[DeviceB-ospf-65535-area-0.0.0.0] network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255
[DeviceB-ospf-65535-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceB-ospf-65535] quit
# Set the OSPF network type for VLAN-interface 3001 to P2P.
[DeviceB] interface Vlan-interface 3001
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface3001] ospf network-type p2p
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface3001] quit
# Set the OSPF network type for VLAN-interface 3003 to P2P.
[DeviceB] interface Vlan-interface 3003
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface3003] ospf network-type p2p
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface3003] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display brief DCN information on the GNE.
[GNE] display dcn
DCN Brief Information
NE ID : 0x100001
NE IP : 11.1.1.1
Mask : 255.255.255.255
DCN interface: LoopBack1023
Auto report : Enabled
# Display all DCN NE information on the GNE.
[GNE] display dcn ne-info
DCN Network Elements Information
NE ID NE IP Metric Device Type
0x100001 11.1.1.1 0 H3C S5136S-8FP4XS-EI-Q
0x200002 22.2.2.2 1 H3C S5136S-8FP4XS-EI-Q
0x300003 33.3.3.3 1 H3C S5136S-8FP4XS-EI-Q
Total number: 3
The output shows that GNE, Device A, and Device B are online. The GNE notifies the NMS of the online event. You can successfully ping the NE IP addresses of Device A and Device B from the GNE.
# Remove Device B from the DCN network and display all DCN NE information for the GNE.
[GNE] display dcn ne-info
DCN Network Elements Information
NE ID NE IP Metric Device Type
0x100001 11.1.1.1 0 H3C S5136S-8FP4XS-EI-Q
0x200002 22.2.2.2 1 H3C S5136S-8FP4XS-EI-Q
Total number: 2
The output shows that GNE and Device A are online. The GNE notifies the NMS of the offline event of Device B. You can still successfully ping the NE IP address of Device A from the GNE.