- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-Text | 410.45 KB |
|
|
|
Cloud-Managed AP Office Scenario Configuration Examples |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Contents
Features and precautions of cloud-managed APs
Connecting the device to the Internet
Specifying the time zone and the region code
Configuring the wireless service
Wireless optimization configuration
Wireless clients cannot detect wireless signals
Clients cannot connect to wireless services
Wireless service lags and occasionally disrupts
Some clients cannot detect the SSID
Some clients cannot detect the SSID (advanced issue)
Internet lag in a specific zone
Features and precautions of cloud-managed APs
Features
· Support quickly deploying a wireless network without an AC and support seamless expansion.
· Support Cloudnet-based configuration, management, and maintenance without needing to know commands.
· Optimize wireless-related features, such as low-speed packet suppression and proxy responses, 5G preferred, and roaming navigation.
· Provide comprehensive operational capabilities, including historical operations such as in-depth analysis, intelligent operations such as problem identification and automatic repair, visual operations for monitoring network health, and automated operations such as alarm notifications.
Restrictions and guidelines
· Cloud-managed APs cannot block or ensure services on their own. They rely on higher-level devices, such as ACG, to perform these functions.
· Cloud-managed APs must comply with relevant regulatory restrictions, such as those related to channels, bandwidth, power, and radar signal avoidance in specific countries or regions.
· For low-speed, stationary devices such as printers and projectors, as a best practice, use wired connections to save wireless resources.
· Plan AP locations reasonably. Place APs close to where clients frequently appear and where many clients gather. Avoid harsh environments (such as high temperature and humidity) and screened environments (such as environments requiring signal transmission through walls or metal boxes).
· Pay attention to whether a bandwidth bottleneck exists at the AP upstream port or the external network exit.
Planning
Model selection
1. Select the AP model based on the deployment location (such as ceiling or walljack mounting), usage scenario (such as high-density), number of users, and traffic volume.
2. Confirm channels supported by main clients. If the clients support different channels, pay special attention to channel-level coverage.
|
|
NOTE: In some countries such as Indonesia (ID) and Pakistan (PK), due to changes in regulations, some devices support only 5.2G and not 5.8G, and others support only 5.8G and not 5.2G. For this type of locations, select a tri-radio AP to provide services on both 5.2G and 5.8G simultaneously, avoiding blind spots in connecting to remote APs. |
3. For more information about model selection, see Wireless Office Scenario Deployment Guide.
Field engineering
For more information, see Wireless Office Scenario Deployment Guide.
Use the cloud engineering feature in Cloudnet for preliminary AP positioning planning.
Deployment
For more information, see Wireless Office Scenario Deployment Guide.
Preparation
Preparing a Cloudnet account
1. Access https://cloudnet.h3c.com/ and register an account.
2. Create a site.
Connecting the device to the Internet
Typically, cloud-managed APs access the Internet through a PoE switch or by directly connecting to the exit gateway.
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show common networking methods.
Figure 1 Cloud-managed AP accessing the Internet through a PoE switch
Figure 2 Cloud-managed AP directly connecting to the gateway to access the Internet
Follow the quick installation guide for each device to power on the device and connect the device to the network.
In most cases, a gateway exists in the network for accessing the Internet. DHCP-Client is enabled for cloud-managed APs by default. If the cloud-managed AP is connected to the gateway directly or through a PoE switch, the cloud-managed AP is able to access the Internet.
For most single-LED cloud-managed APs, if the LED is steady green or is flashing green, it indicates that the APs have been connected to the Internet successfully.
Adding the device to a site
1. Open the Cloudnet app or access https://cloudnet.h3c.com/ and log in to Cloudnet.
2. Click the target site.
3. Click Add Device.
4. Enter the device name and device serial number. When you use the Cloudnet app, you can also scan the bar code on the device to add the device.
Specifying the time zone and the region code
· Access the Network > Network > Sites page. Select the right site. Click the Time Zone tab, select the correct time zone, and then click OK.
· Access the Network > Settings > Cloud APs > WLAN Settings page. Select the right site. On the Region Code tab, select the correct region code, and then click OK.
Wireless configuration
Configuring the wireless service
1. Make sure you have added all cloud-managed APs to the site.
2. Open the Wi-Fi Settings page. Access the Network > Settings > Cloud APs > WLAN Settings page. Select the right site, and click the Wi-Fi Settings tab.
3. Delete unnecessary services. Some APs support up to 7 wireless services. Do not delete the service currently used to access Cloudnet.
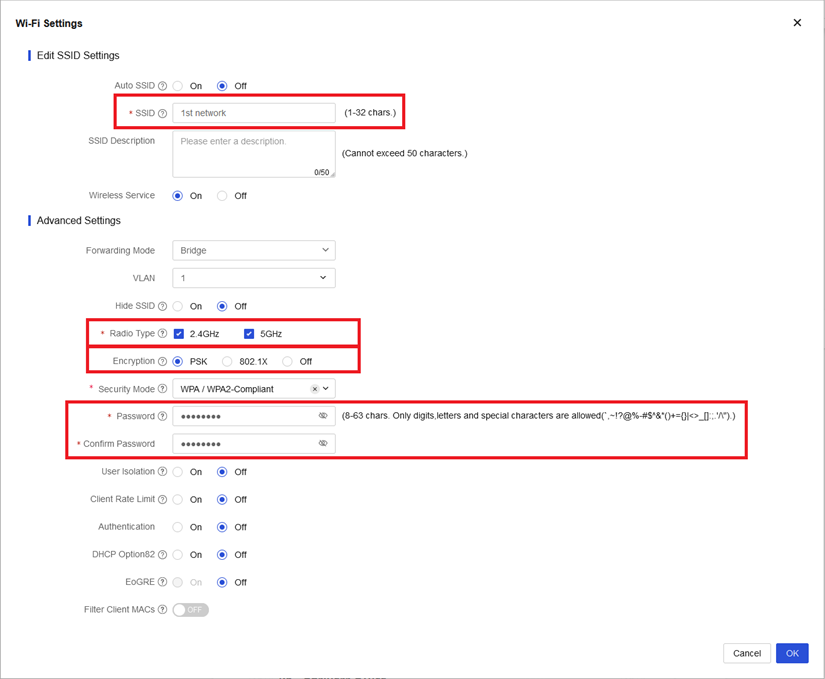
4. Create a wireless service. Click Add. In the dialog box that opens, enter the SSID, select both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radio types, select PSK encryption, specify the password, and retain the default settings in the other fields. See Figure 3.
5. To limit the uplink or downlink rate of each client, enable client rate limit.
Wireless optimization configuration
Radio configuration
1. Open the Radio Configuration page. Access the Network > Settings > Cloud APs > WLAN Settings page. Select the right site, and click the Radio Configuration tab.
2. In the Scenario Configuration section, select Office and click OK.
Network optimization
1. Open the Network Optimization page. Access the Network > Settings > Cloud APs > WLAN Settings page. Select the right site, and click the Network Optimization tab.
2. Retain the default settings. If the site was created a long time ago or had operational errors, make sure the following features are enabled:
¡ 5GHz-Preferred.
¡ Broadcast Optimization.
¡ Distributed RRM.
3. Click OK.
FAQs
Wireless clients cannot detect wireless signals
Symptom
You cannot detect the SSID with a phone or laptop.
Analysis
Possible reasons include:
· The cloud-managed AP is running abnormally.
· The AP configuration contains errors.
Solution
1. Check the operating state of the cloud-managed AP.
|
Possible reasons |
Criteria for judgment |
Solution |
|
Failure of a single cloud-managed AP |
Examine the LED of the cloud-managed AP. The AP is operating correctly if the LED is in either state: · Steady green—The AP is connected to the cloud and no client is online. · Flashing green—The AP is connected to the cloud and wireless clients are online. |
Examine the external network link. Replace the AP and try again. |
2. Examine the configuration of the AP.
|
Possible reasons |
Criteria for judgment |
Solution |
|
The client does not support the current channel of the AP |
Some other clients (phones, tablets, or laptops) at the site can detect the SSID. |
1. Change the radio channel. 2. Note that the channels supported by different clients might differ in specific country or region (such as Indonesia and Pakistan). In this case, as a best practice, use tri-radio APs to complete the coverage. |
|
The wireless service is either not enabled or configured to be hidden |
Examine the Cloudnet configuration. |
Verify that the wireless service is enabled and the SSID is not hidden. |
|
Other client compatibility issues |
Some other clients (phones, tablets, or laptops) at the site can detect the SSID. |
1. Verify if the SSID has compatibility issues due to special characters. 2. Whether known compatibility issues exist. For example, some Intel Wi-Fi 5 wireless network cards cannot list Wi-Fi 6 services. |
Clients cannot connect to wireless services
Symptom
You cannot connect a mobile phone or laptop to the Wi-Fi.
Analysis
Possible reasons include:
· Incorrect cloud-managed AP configuration.
· Client configuration or compatibility issue.
· Weak Wi-Fi signals or high interference.
· Failure of the client to obtain an IP address or a correct IP address.
Procedure
1. Examine the configuration of the AP.
|
Possible reasons |
Criteria for judgment |
Solution |
|
The client does not support certain AP configuration |
The AP is configured with parameters unsupported by the client, such as WEP encryption, TKIP encryption, or 802.11b-only mode. |
Change to commonly used settings, such as WPA/WPA2 compatibility and 802.11ax operation mode. |
|
The cloud-managed AP is configured with a denylist or allowlist |
Examine if MAC address-based client filtering is enabled on the Wi-Fi Settings page. |
Disable MAC address-based client filtering or configure the corresponding MAC to allow user devices access individually on the Wi-Fi Settings page. |
2. Examine the state of the client.
|
Possible reasons |
Criteria for judgment |
Solution |
|
Client model-specific issue |
Clients of another brand or model can access the wireless network correctly. |
For compatibility issues, contact Technical Support. |
|
Incorrect password |
The client remembers the password but the password is modified for the AP. |
Change the password remembered by the client, or delete the remembered SSID on the client. |
|
Static IP address configured for the client network card |
The client cannot access the wireless network even with the correct password. |
Configure the client network card to automatically obtain an IP address. |
|
Anomaly inside the client network card |
All of the above potential causes have been eliminated. |
Disable and then re-enable the client network card, or restart the client device. |
3. Examine the Wi-Fi signal strength of the AP and nearby interference.
|
Possible reasons |
Criteria for judgment |
Solution |
|
Weak Wi-Fi signal |
Use the inSSIDer software to scan the environment and the SSID signal is detected to be weak. |
1. Examine the Cloudnet configuration and verify if the transmit power was reduced manually. 2. Scan near the cloud-managed AP. If the signal is still weak, consider replacing the AP. 3. Optimize the AP deployment location. As a best practice, deploy the AP in an open area free from obstructions and away from heat sources. Do not place the AP around metal, and do not place it in a power distribution box. 4. Optimize the AP deployment orientation. For APs with built-in antennas, the device LOGO generally indicates the direction of signal emission. 5. If a weak signal is caused by a long reach or walls, add APs as a best practice. |
|
Strong inter-AP interference around the cloud-managed AP |
Use the inSSIDer software to scan the environment and strong inter-AP interference is detected. |
1. If the interference is from your own network, see "Radio resource optimization." 2. If the interference is from an external network, evaluate whether the interference source can be streamlined or replaced. 3. If the interference is from non-WiFi signals, such as a microwave, consider adjusting the location. |
4. Failure of the client to obtain an IP address or a correct IP address.
|
Possible reasons |
Criteria for judgment |
Solution |
|
The network is not configured with a DHCP server. |
The client gets stuck at IP address obtaining when connecting to the wireless network. |
For public VLAN networking, use the DHCP server for AP management. For a network with different management and service VLANs, verify if the service VLAN is enabled with the DHCP server feature. |
|
Multiple DHCP servers are configured in the network, or the same wireless service corresponds to different DHCP servers |
When a client connects multiple times or connects from different locations, it might obtain IP addresses from different network segments. |
1. Verify if the network contains multiple DHCP servers, including unauthorized user-initiated DHCP servers. 2. Do not enable auto SSID and the NAT mode at the same time. |
|
Incorrect device VLAN configuration |
The network is configured with different management and service VLANs, but the cloud-managed AP lacks VLAN-related settings. |
1. Enable the corresponding VID on the VLAN Settings page. 2. Add the wired uplink port to the specified VLAN on the Port Settings page. |
Wireless service lags and occasionally disrupts
Symptom
When you use the wireless network to watch videos or browse the Internet, lags or intermittent disruptions occur.
Analysis
Possible reasons include:
· Wired uplink issues.
· Client model-specific issues.
· Weak Wi-Fi signals or high interference.
Solution
1. Examine the network environment and the configuration of the cloud AP.
|
Possible reasons |
Criteria for judgment |
Solution |
|
Insufficient network bandwidth or network congestion during peak Internet usage periods |
The wired port speed is below standard, or specific periods have a high fault rate while the network functions normally during other periods. |
Increase the network bandwidth. |
|
High latency on some nodes in the link |
Use the client to ping the service network segment address, gateway address, and DNS address of the AP simultaneously to identify which node causes the latency. |
Identify the source of the latency and address it specifically. |
|
Video or website-specific issues |
No latency issues occur when you watch other videos or visit other websites. |
1. Verify if the service provider has any issues. 2. If any suspected compatibility issues exist, contact Technical Support. |
|
Distributed RRM is not enabled |
The interference between APs is significant. |
Enable distributed RRM on the Network Optimization page. See "Network optimization." |
2. Examine the client state.
|
Possible reasons |
Criteria for judgment |
Solution |
|
Insufficient client performance |
The client rate cannot approach the maximum value even when the client makes a close-range connection. |
Replace the client and try again. |
|
STA compatibility issues |
This issue occurs only on specific clients. |
For compatibility issues, contact Technical Support. |
3. Examine the Wi-Fi signal strength of the ONT and nearby interference. For more information, see "Clients cannot connect to wireless services."
4. Failure of the client to obtain an IP address or a correct IP address. For more information, see "Clients cannot connect to wireless services."
5. Examine the Wi-Fi signal strength of the ONT and nearby interference. For more information, see "Clients cannot connect to wireless services."
Classic cases
Some clients cannot detect the SSID
Symptom
Some smart speakers cannot detect the SSID, but other devices can.
Analysis
1. Check the cloud-managed AP's working channel and find it on channel 13. After the channel is changed to 1, the smart speaker can connect normally.
2. Query local regulations and find that the local Wi-Fi standard in the country or region supports channels 1-13, but smart speakers purchased by the user comply with North American specifications, which only support channels 1-11.
Solution
For devices requiring special configuration in specific zones, manually configure the channel.
Some clients cannot detect the SSID (advanced issue)
Symptom
Some wireless clients can detect the SSID under certain APs, but cannot detect the SSID under the other APs.
Analysis
1. Clients in group A can detect only the SSID provided by APs in group A, and clients in group B can detect only the SSID provided by APs in group B. Only a few clients in group C can detect the SSID provided by any AP.
2. The regulations in that country/region have changed, causing a delay in client compliance, which resulted in clients being divided into two groups: one supports only 5.2GHz channels, while the other supports only 5.8GHz channels. When users deploy dual-radio APs, a single AP can provide services to only clients in one group.
Solution
For countries/regions undergoing regulatory transition (currently known: Indonesia and Pakistan), use three-radio APs as a best practice.
Insufficient Wi-Fi coverage
Symptom
The AP signal is weak.
Analysis
1. Investigate the customer's installation environment on-site and find that the AP is installed inside a metal power distribution box. See Figure 4.
Figure 4 AP installed inside a metal power distribution box
2. Some APs also have poor coverage, such as APs installed on ceilings that are too high and APs installed facing upwards (installed upside down).
Solution
Move the cloud-managed APs to an open area, away from heat sources and obstructions, and as close as possible to the places users frequently visit. Aim the signal transmission orientation towards the users.
Internet lag in a specific zone
Symptom
The Internet connection stutters in specific zones, despite strong signal strength.
Analysis
1. Some 5G-capable clients remain stuck on a 2.4G radio. Enabling 5G-preferred alleviates the problem.
2. In some zones, the channels of some APs overlap with each other, resulting in high channel usage. Enabling distributed RRM alleviates the problem.
Solution
See the analysis.
Common precautions
1. As a best practice, upgrade 6500A APs used in Singapore to version R2595P30 or later to support 5G high and low frequencies.
2. For countries/regions undergoing regulatory transition (currently known: Indonesia and Pakistan), use three-radio APs as a best practice.
3. To configure the mobility group feature for the 65A and Wi-Fi7 series, make sure the number of APs in one site does not exceed 31.
4. Do not deploy Wi-Fi6 and Wi-Fi7 APs in the same site.
Appendices and references
· Reference 1: WLAN Enterprise Office Scenario Deployment Guide-6W100 (https://www.h3c.com/en/Support/Resource_Center/EN/Home/Public/00-Public/Technical_Documents/Plan___Design/Plan___Design_Guides/WLAN_Enterprise_Office_Scenario_De-21675/?CHID=1069399)
· Reference 2: Access point installation guide for each AP model (for example, H3C WA6520 Access Point Installation Guide for the WA6520 at https://www.h3c.com/en/Support/Resource_Center/EN/Wireless/Catalog/802.11ax/WA6520/Technical_Documents/Install___Upgrade/Installation_Guides/H3C_WA6520_AP_IG/?CHID=737365)
· Reference 3: Systems Using Intel® Wireless Adapters Supporting 802.11ac Not Displaying Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) Networks in Scan List of Available Networks (https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/support/articles/000054799/wireless.html)