- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 08-DHCPv6 configuration | 384.16 KB |
DHCPv6 address/prefix assignment
Rapid assignment involving two messages
Assignment involving four messages
Configuring the DHCPv6 relay agent
DHCPv6 relay agent operating process
DHCPv6 relay agent tasks at a glance
Enabling the DHCPv6 relay agent on an interface
Specifying DHCPv6 servers on the relay agent
Specifying DHCPv6 server IP addresses
Specifying DHCPv6 servers for a DHCPv6 relay address pool
Specifying a gateway address for DHCPv6 clients
Specifying the source IPv6 address for relayed DHCPv6 requests
Setting the DSCP value for DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 relay agent
Specifying a padding mode for the Interface-ID option
Enabling the DHCPv6 relay agent to advertise IPv6 prefixes
Configuring DHCPv6 relay security features
Enabling the DHCPv6 relay agent to record relay entries
Enabling IPv6 release notification
Enabling client offline detection
Specifying a DHCPv6 request processing method for roaming DHCPv6 clients
Display and maintenance commands for DHCPv6 relay agent
DHCPv6 relay agent configuration examples
Example: Configuring DHCPv6 relay agent
Restrictions and guidelines: DHCPv6 client configuration
DHCPv6 client tasks at a glance
Configuring the DHCPv6 client DUID
Configuring IPv6 address acquisition
Configuring IPv6 prefix acquisition
Configuring IPv6 address and prefix acquisition
Configuring acquisition of configuration parameters except IP addresses and prefixes
Setting the DSCP value for DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 client
Display and maintenance commands for DHCPv6 client
DHCPv6 client configuration examples
Example: Configuring IPv6 address acquisition
Example: Configuring IPv6 prefix acquisition
Example: Configuring IPv6 address and prefix acquisition
Example: Configuring stateless DHCPv6
DHCPv6 overview
DHCPv6 address/prefix assignment
An address/prefix assignment process involves two or four messages.
Rapid assignment involving two messages
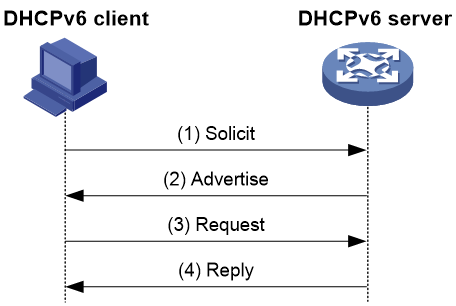
As shown in Figure 1, rapid assignment operates in the following steps:
1. The DHCPv6 client sends to the DHCPv6 server a Solicit message that contains a Rapid Commit option to prefer rapid assignment.
2. If the DHCPv6 server supports rapid assignment, it responds with a Reply message containing the assigned IPv6 address/prefix and other configuration parameters. If the DHCPv6 server does not support rapid assignment, Assignment involving four messages is performed.
Figure 1 Rapid assignment involving two messages
Assignment involving four messages
As shown in Figure 2, four-message assignment operates using the following steps:
1. The DHCPv6 client sends a Solicit message to request an IPv6 address/prefix and other configuration parameters.
2. The DHCPv6 server responds with an Advertise message that contains the assignable address/prefix and other configuration parameters if either of the following conditions exists:
¡ The Solicit message does not contain a Rapid Commit option.
¡ The DHCPv6 server does not support rapid assignment even though the Solicit message contains a Rapid Commit option.
3. The DHCPv6 client might receive multiple Advertise messages offered by different DHCPv6 servers. It selects an offer according to the receiving sequence and server priority, and sends a Request message to the selected server for confirmation.
4. The DHCPv6 server sends a Reply message to the client, confirming that the address/prefix and other configuration parameters are assigned to the client.
Figure 2 Assignment involving four messages
Address/prefix lease renewal
An IPv6 address/prefix assigned by a DHCPv6 server has a valid lifetime. After the valid lifetime expires, the DHCPv6 client cannot use the IPv6 address/prefix. To use the IPv6 address/prefix, the DHCPv6 client must renew the lease time.
Figure 3 Using the Renew message for address/prefix lease renewal
As shown in Figure 3, at T1, the DHCPv6 client sends a Renew message to the DHCPv6 server. The recommended value of T1 is half the preferred lifetime. The DHCPv6 server responds with a Reply message, informing the client whether the lease is renewed.
Figure 4 Using the Rebind message for address/prefix lease renewal
As shown in Figure 4:
· If the DHCPv6 client does not receive a response from the DHCPv6 server after sending a Renew message at T1, it multicasts a Rebind message to all DHCPv6 servers at T2. Typically, the value of T2 is 0.8 times the preferred lifetime.
· The DHCPv6 server responds with a Reply message, informing the client whether the lease is renewed.
· If the DHCPv6 client does not receive a response from any DHCPv6 server before the valid lifetime expires, the client stops using the address/prefix.
For more information about the valid lifetime and the preferred lifetime, see "Configuring basic IPv6 settings."
Stateless DHCPv6
Stateless DHCPv6 enables a device that has obtained an IPv6 address/prefix to get other configuration parameters from a DHCPv6 server.
The device performs stateless DHCPv6 if an RA message with the following flags is received from the router during stateless address autoconfiguration:
· The managed address configuration flag (M flag) is set to 0.
· The other stateful configuration flag (O flag) is set to 1.
Figure 5 Stateless DHCPv6 operation
As shown in Figure 5, stateless DHCPv6 operates in the following steps:
1. The DHCPv6 client sends an Information-request message to the multicast address of all DHCPv6 servers and DHCPv6 relay agents. The Information-request message contains an Option Request option that specifies the requested configuration parameters.
2. The DHCPv6 server returns to the client a Reply message containing the requested configuration parameters.
3. The client checks the Reply message. If the obtained configuration parameters match those requested in the Information-request message, the client uses these parameters to complete configuration. If not, the client ignores the configuration parameters. If the client receives multiple replies with configuration parameters matching those requested in the Information-request message, it uses the first received reply.
DHCPv6 options
Option 18
Option 18, also called the interface-ID option, is used by the DHCPv6 relay agent to determine the interface to use to forward RELAY-REPLY message.
The DHCPv6 snooping device adds Option 18 to the received DHCPv6 request message before forwarding it to the DHCPv6 server. The server then assigns IP address to the client based on the client information in Option 18.
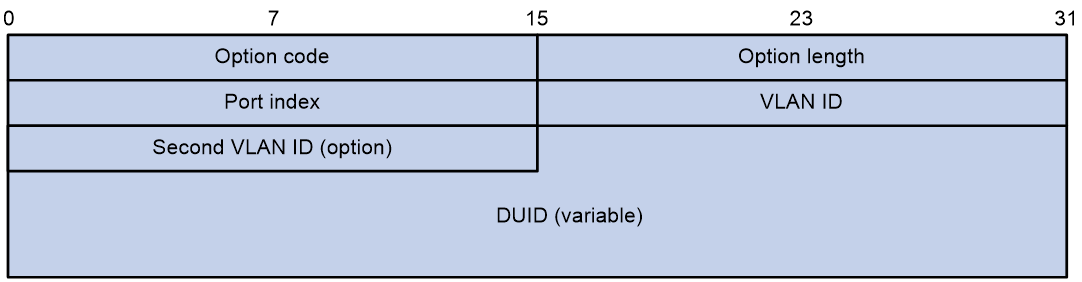
Figure 6 shows the Option 18 format, which includes the following fields:
· Option code—Option code. The value is 18.
· Option length—Size of the option data.
· Port index—Port that receives the DHCPv6 request from the client.
· VLAN ID—ID of the outer VLAN.
· Second VLAN ID—ID of the inner VLAN. This field is optional. If the received DHCPv6 request does not contain a second VLAN, Option 18 also does not contain it.
· DUID—DUID of the DHCPv6 client.
Option 37
Option 37, also called the remote-ID option, is used to identify the client.
The DHCPv6 snooping device adds Option 37 to the received DHCPv6 request message before forwarding it to the DHCPv6 server. This option provides client information about address allocation.
Figure 7 shows the Option 37 format, which includes the following fields:
· Option code—Option code. The value is 37.
· Option length—Size of the option data.
· Enterprise number—Enterprise number.
· Port index—Port that receives the DHCPv6 request from the client.
· VLAN ID—ID of the outer VLAN.
· Second VLAN ID—ID of the inner VLAN. This field is optional. If the received DHCPv6 request does not contain a second VLAN, Option 37 also does not contain it.
· DUID—DUID of the DHCPv6 client.
Protocols and standards
· RFC 3736, Stateless Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Service for IPv6
· RFC 3315, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6)
· RFC 2462, IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
· RFC 3633, IPv6 Prefix Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) version 6
Configuring the DHCPv6 relay agent
About DHCPv6 relay agent
Typical application
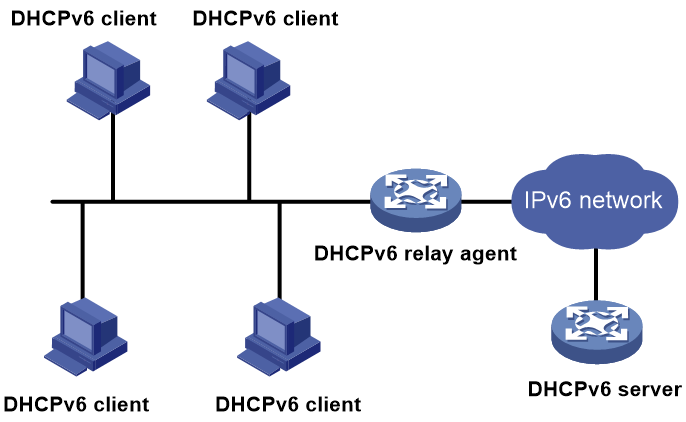
A DHCPv6 client usually uses a multicast address to contact the DHCPv6 server on the local link to obtain an IPv6 address and other configuration parameters. As shown in Figure 8, if the DHCPv6 server resides on another subnet, the DHCPv6 clients need a DHCPv6 relay agent to contact the server. The relay agent feature avoids deploying a DHCPv6 server on each subnet.
Figure 8 Typical DHCPv6 relay agent application
DHCPv6 relay agent operating process
As shown in Figure 9, a DHCPv6 client obtains an IPv6 address and other network configuration parameters from a DHCPv6 server through a DHCPv6 relay agent. The following example uses rapid assignment to describe the process:
· The DHCPv6 client sends a Solicit message containing the Rapid Commit option to the multicast address FF02::1:2 of all the DHCPv6 servers and relay agents.
· After receiving the Solicit message, the DHCPv6 relay agent encapsulates the message into the Relay Message option of a Relay-forward message, and sends the message to the DHCPv6 server.
· After obtaining the Solicit message from the Relay-forward message, the DHCPv6 server performs the following tasks:
¡ Selects an IPv6 address and other required parameters.
¡ Adds them to a reply that is encapsulated within the Relay Message option of a Relay-reply message.
¡ Sends the Relay-reply message to the DHCPv6 relay agent.
· The DHCPv6 relay agent obtains the reply from the Relay-reply message and sends the reply to the DHCPv6 client.
· The DHCPv6 client uses the IPv6 address and other network parameters assigned by the DHCPv6 server to complete network configuration.
Figure 9 Operating process of a DHCPv6 relay agent
DHCPv6 relay agent tasks at a glance
To configure a DHCPv6 relay agent, perform the following tasks:
1. Enabling the DHCPv6 relay agent on an interface
2. Specifying DHCPv6 servers on the relay agent
3. (Optional.) Specifying a gateway address for DHCPv6 clients
4. (Optional.) Specifying the source IPv6 address for relayed DHCPv6 requests
5. (Optional.) Setting the DSCP value for DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 relay agent
6. (Optional.) Specifying a padding mode for the Interface-ID option
7. (Optional.) Enabling the DHCPv6 relay agent to advertise IPv6 prefixes
8. (Optional.) Configuring DHCPv6 relay security features
9. Specifying a DHCPv6 request processing method for roaming DHCPv6 clients
Enabling the DHCPv6 relay agent on an interface
Restrictions and guidelines
As a best practice, do not enable DHCPv6 relay agent and DHCPv6 client on the same interface.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable DHCPv6 relay agent on the interface.
ipv6 dhcp select relay
By default, the DHCPv6 relay agent is disabled on the interface.
Specifying DHCPv6 servers on the relay agent
Specifying DHCPv6 server IP addresses
Restrictions and guidelines
· You can use the ipv6 dhcp relay server-address command to specify a maximum of eight DHCPv6 servers on the DHCPv6 relay agent interface. The DHCPv6 relay agent forwards DHCP requests to all the specified DHCPv6 servers.
· If a DHCPv6 server address is a link-local address or multicast address, you must specify an outgoing interface by using the interface keyword in this command. Otherwise, DHCPv6 packets might fail to reach the DHCPv6 server.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Specify a DHCPv6 server.
ipv6 dhcp relay server-address ipv6-address [ interface interface-type interface-number ]
By default, no DHCPv6 server is specified.
Specifying DHCPv6 servers for a DHCPv6 relay address pool
About this task
This feature allows DHCPv6 clients of the same type to obtain IPv6 addresses, IPv6 prefixes, and other configuration parameters from the DHCPv6 servers in the matching DHCPv6 relay address pool.
It applies to scenarios where the DHCPv6 relay agent connects to clients of the same access type but classified into different types by their locations. In this case, the relay interface typically has no IPv6 address configured. You can use the gateway-list command to specify the gateway addresses for clients matching the same DHCPv6 relay address pool.
Upon receiving a DHCPv6 Solicit or Request from a client that matches a DHCPv6 relay address pool, the relay agent processes the packet as follows:
· Fills the link-address field of the packet with a specified gateway address.
· Forwards the packet to all DHCPv6 servers in the matching DHCPv6 relay address pool.
The DHCPv6 servers select an IPv6 address pool according to the gateway address.
Restrictions and guidelines
· You can specify a maximum of eight DHCPv6 servers for one DHCPv6 relay address pool for high availability. The relay agent forwards DHCPv6 Solicit and Request packets to all DHCPv6 servers in the DHCPv6 relay address pool.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a DHCPv6 relay address pool and enter its view.
ipv6 pool pool-name bas remote
3. Specify gateway addresses for the clients matching the DHCPv6 relay address pool.
gateway-list ipv6-address&<1-8>
By default, no gateway address is specified.
4. Specify DHCPv6 servers for the DHCPv6 relay address pool.
remote-server ipv6-address [ interface interface-type interface-number ]
By default, no DHCPv6 server is specified for the DHCPv6 relay address pool.
Specifying a gateway address for DHCPv6 clients
About this task
By default, the DHCPv6 relay agent fills the link-address field of DHCPv6 Solicit and Request packets with the first IPv6 address of the relay interface. This task is required if a relay interface connects to multiple subnets and you want the DHCP server to assign IPv6 addresses to clients in a specific subnet. When receiving DHCPv6 Solicit and Request packets from a client of this subnet, the DHCPv6 relay agent uses the specified gateway address to fill the link-address field of the packets.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Specify a gateway address for DHCPv6 clients.
ipv6 dhcp relay gateway ipv6-address
By default, the DHCPv6 relay agent uses the first IPv6 address of the relay interface as the clients' gateway address.
Specifying the source IPv6 address for relayed DHCPv6 requests
About this task
This task is required if multiple relay interfaces share the same IPv6 address or if a relay interface does not have routes to DHCPv6 servers. You can use this command to specify the IPv6 address of another interface (typically a loopback interface) on the DHCPv6 relay agent as the source IPv6 address for relayed DHCP requests.
Restrictions and guidelines
Specify the gateway keyword if the DHCPv6 relay agent has a reachable route to the DHCPv6 address from the address filled in the Link-address field.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter DHCPv6 relay address pool view.
ipv6 pool pool-name bas remote
3. Specify the source IPv6 address of the DHCPv6 requests that the DHCPv6 relay agent forwards to the DHCPv6 server.
dhcpv6-relay source-address { ipv6-address | gateway | interface interface-type interface-number }
By default, the source IPv6 address for replayed DHCPv6 requests is the IPv6 address of the output interface through which the DHCPv6 relay agent reaches the DHCPv6 server.
Setting the DSCP value for DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 relay agent
About this task
The DSCP value of a packet specifies the priority level of the packet and affects the transmission priority of the packet.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the DSCP value for DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 relay agent.
ipv6 dhcp dscp dscp-value
The default DSCP value is 56.
Specifying a padding mode for the Interface-ID option
About this task
This feature enables the relay agent to fill the Interface-ID option in the specified mode. When receiving a DHCPv6 packet from a client, the relay agent fills the Interface-ID option in the mode and then forwards the packet to the DHCPv6 server.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Specify a padding mode for the Interface-ID option.
ipv6 dhcp relay interface-id { bas | cn-telecom | interface | tr-101 }
By default, the relay agent fills the Interface-ID option with the index of the interface.
Enabling the DHCPv6 relay agent to advertise IPv6 prefixes
About this task
A DHCPv6 client can obtain an IPv6 prefix through DHCPv6 and use this IPv6 prefix to assign IPv6 address to clients in a downstream network. If the IPv6 prefix is in a different subnet than the IPv6 address of the DHCPv6 client's upstream interface, the clients in the downstream network cannot access the external network. You can enable the DHCPv6 relay agent that is on the same link as the DHCPv6 client to advertise the IPv6 prefix.
This feature enables the DHCPv6 relay agent to generate a routing entry for the IPv6 prefix when it receives a reply message with the IPv6 prefix. The DHCPv6 relay agent advertises this entry to the dynamic routing protocol. After the DHCPv6 client learns this route through the dynamic routing protocol, clients in the downstream network can access the external network.
Prerequisites
Before you perform this task, make sure the DHCPv6 relay agent is enabled to record DHCPv6 relay entries.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable the DHCPv6 relay agent to advertise IPv6 prefixes.
ipv6 dhcp advertise pd-route
By default, the DHCPv6 relay agent does not advertise IPv6 prefixes.
Configuring DHCPv6 relay security features
Enabling the DHCPv6 relay agent to record relay entries
About this task
This feature enables the DHCPv6 relay agent to automatically record DHCPv6 relay entries after DHCPv6 clients obtain IPv6 addresses or prefixes through DHCPv6. A DHCPv6 relay entry contains the binding between a client's hardware address and IPv6 address or prefix.
Restrictions and guidelines
The DHCP relay agent does not record IP-to-MAC bindings for DHCP clients that use WAN access methods.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable the recording of DHCPv6 relay entries.
ipv6 dhcp relay client-information record
By default, the DHCPv6 relay agent does not record relay entries.
Enabling IPv6 release notification
About this task
This feature enables the DHCPv6 relay agent to send a Release message to the DHCPv6 server after it deletes a DHCPv6 relay entry. After the DHCPv6 server receives the message, it reclaims the IPv6 address or prefix and marks the lease as expired.
If you do not enable this feature, the DHCPv6 relay agent will not send a Release message after it deletes a relay entry.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable IPv6 release notification.
ipv6 dhcp relay release-agent
By default, IPv6 release notification is disabled.
Enabling client offline detection
About this task
This feature enables the DHCPv6 relay agent to detect the status of ND entries. After an ND entry ages out, the DHCPv6 relay agent considers the client offline and deletes the relay entry for the client. For more information about ND, see "Configuring basic IPv6 settings."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable client offline detection.
ipv6 dhcp client-detect
By default, client offline detection is disabled.
Specifying a DHCPv6 request processing method for roaming DHCPv6 clients
About this task
When a DHCPv6 client (for example, a wireless client) roams in a network, the client sends an offline request to the DHCP relay agent before request a new address or prefix. If the DHCP relay agent does not receive the offline request, it will discard the DHCP client's address or prefix request because it determines that the request is an attack packet.
This feature allows the DHCP relay agent to process address or prefix requests as follows upon receiving them from roaming DHCP clients:
· The fast-renew method enables the relay agent to inform the DHCP server to release existing address or prefix leases of roaming clients and forward the requests to the DHCP server.
· The roam method enables the relay agent to forward the address or prefix requests to the DHCP server. The clients can use the original IP addresses or prefixes to access the network without another authentication.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Specify a method for the DHCPv6 relay agent to process address or prefix requests of roaming clients.
ipv6 dhcp session-mismatch action { fast-renew | roam }
By default, the DHCPv6 relay agent discards DHCPv6 address or prefix requests sent from roaming DHCPv6 clients.
Display and maintenance commands for DHCPv6 relay agent
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the DUID of the local device. |
display ipv6 dhcp duid |
|
Display DHCPv6 relay entries that record clients' IPv6 address information. |
display ipv6 dhcp relay client-information address [ interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6 ipv6-address ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] |
|
Display DHCPv6 relay entries that record clients' IPv6 prefix information. |
display ipv6 dhcp relay client-information pd [ interface interface-type interface-number | prefix prefix/prefix-len ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] |
|
Display DHCPv6 server addresses specified on the DHCPv6 relay agent. |
display ipv6 dhcp relay server-address [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
|
Display packet statistics on the DHCPv6 relay agent. |
display ipv6 dhcp relay statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
|
Clear DHCPv6 relay entries that record clients' IPv6 address information. |
reset ipv6 dhcp relay client-information address [ interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6 ipv6-address ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] |
|
Clear DHCPv6 relay entries that record clients' IPv6 prefix information. |
reset ipv6 dhcp relay client-information pd [ interface interface-type interface-number | prefix prefix/prefix-len ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] |
|
Clear packets statistics on the DHCPv6 relay agent. |
reset ipv6 dhcp relay statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
DHCPv6 relay agent configuration examples
Example: Configuring DHCPv6 relay agent
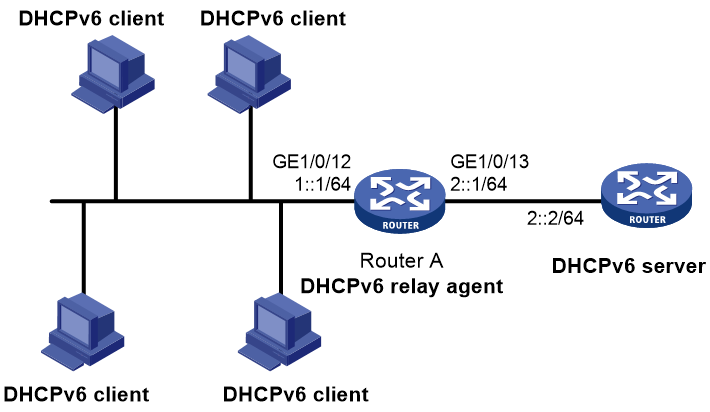
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 10, configure the DHCPv6 relay agent on Router A to relay DHCPv6 packets between DHCPv6 clients and the DHCPv6 server.
Router A acts as the gateway of network 1::/64. It sends RA messages to notify the hosts to obtain IPv6 addresses and other configuration parameters through DHCPv6. For more information about RA messages, see "Configuring basic IPv6 settings."
Procedure
# Specify IPv6 addresses for GigabitEthernet 1/0/12 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/13.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/13
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/13] ipv6 address 2::1 64
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/13] quit
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/12
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 address 1::1 64
# Disable RA message suppression on GigabitEthernet 1/0/12.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] undo ipv6 nd ra halt
# Set the M flag to 1 in RA advertisements to be sent on GigabitEthernet 1/0/12. Hosts that receive the RA messages will obtain IPv6 addresses through DHCPv6.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 nd autoconfig managed-address-flag
# Set the O flag to 1 in RA advertisements to be sent on GigabitEthernet 1/0/12. Hosts that receive the RA messages will obtain information other than IPv6 address through DHCPv6.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 nd autoconfig other-flag
# Enable the DHCPv6 relay agent on GigabitEthernet 1/0/12 and specify the DHCPv6 server on the relay agent.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 dhcp select relay
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 dhcp relay server-address 2::2
Verifying the configuration
# Display DHCPv6 server address information on Router A.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] display ipv6 dhcp relay server-address
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
Server address Outgoing Interface
2::2
# Display packet statistics on the DHCPv6 relay agent.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] display ipv6 dhcp relay statistics
Packets dropped : 0
Packets received : 14
Solicit : 0
Request : 0
Confirm : 0
Renew : 0
Rebind : 0
Release : 0
Decline : 0
Information-request : 7
Relay-forward : 0
Relay-reply : 7
Packets sent : 14
Advertise : 0
Reconfigure : 0
Reply : 7
Relay-forward : 7
Relay-reply : 0
Configuring the DHCPv6 client
About the DHCPv6 client
With DHCPv6 client configured, an interface can obtain configuration parameters from the DHCPv6 server.
A DHCPv6 client can use DHCPv6 to complete the following functions:
· Obtain an IPv6 address, an IPv6 prefix, or both, and obtain other configuration parameters. If DHCPv6 server is enabled on the device, the client can automatically save the obtained parameters to a DHCPv6 option group. With the obtained IPv6 prefix, the client can generate its global unicast address.
· Support stateless DHCPv6 to obtain configuration parameters except IPv6 address and IPv6 prefix. The client obtains an IPv6 address through stateless IPv6 address autoconfiguration. If the client receives an RA message with the M flag set to 0 and the O flag set to 1 during address acquisition, stateless DHCPv6 starts.
Restrictions and guidelines: DHCPv6 client configuration
Do not configure the DHCPv6 client on the same interface as the DHCPv6 server or the DHCPv6 relay agent.
DHCPv6 client tasks at a glance
To configure a DHCPv6 client, perform the following tasks:
1. (Optional.) Configuring the DHCPv6 client DUID
2. Configuring the DHCPv6 client to obtain IPv6 addresses, IPv6 prefixes and other network parameters
Choose the following tasks as needed:
¡ Configuring IPv6 address acquisition
¡ Configuring IPv6 prefix acquisition
¡ Configuring IPv6 address and prefix acquisition
¡ Configuring acquisition of configuration parameters except IP addresses and prefixes
3. (Optional.) Setting the DSCP value for DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 client
Configuring the DHCPv6 client DUID
About this task
The DUID of a DHCPv6 client is the globally unique identifier of the client. The client pads its DUID into Option 1 of the DHCPv6 packet that it sends to the DHCPv6 server. The DHCPv6 server can assign specific IPv6 addresses or prefixes to DHCPv6 clients with specific DUIDs.
Restrictions and guidelines
Make sure the DUID that you configure is unique.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Configure the DHCPv6 client DUID.
ipv6 dhcp client duid { ascii string | hex string | mac interface-type interface-number }
By default, the interface uses the device bridge MAC address to generate its DHCPv6 client DUID.
Configuring IPv6 address acquisition
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Configure the interface to use DHCPv6 to obtain an IPv6 address and other configuration parameters.
ipv6 address dhcp-alloc [ option-group group-number | rapid-commit ] *
By default, the interface does not use DHCPv6 for IPv6 address acquisition.
Configuring IPv6 prefix acquisition
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Configure the interface to use DHCPv6 to obtain an IPv6 prefix and other configuration parameters.
ipv6 dhcp client pd prefix-number [ option-group group-number | rapid-commit ] *
By default, the interface does not use DHCPv6 for IPv6 prefix acquisition.
Configuring IPv6 address and prefix acquisition
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Configure the interface to use DHCPv6 to obtain an IPv6 address, an IPv6 prefix, and other configuration parameters.
ipv6 dhcp client stateful prefix prefix-number [ option-group option-group-number | rapid-commit ] *
By default, the interface does not use DHCPv6 for IPv6 address and prefix acquisition.
Configuring acquisition of configuration parameters except IP addresses and prefixes
About this task
When a DHCPv6 client has obtained an IPv6 address and prefix, you can configure the following methods for the client to obtain other network configuration parameters:
· Execute the ipv6 address auto command to enable an interface to automatically generate an IPv6 global unicast address and a link-local address. Then stateless DHCPv6 will be triggered when the M flag is set to 0 and the O flag is set to 1 in a received RA message. For more information about the commands, see Layer 3—IP services Command Reference.
· Executing the ipv6 dhcp client stateless enable command on an interface to enable the interface to act as a DHCPv6 client to obtain configuration parameters from a DHCPv6 server.
If you execute both the ip address auto and ipv6 dhcp client stateless enable commands, the interface acts as follows:
· Generate a global unicast address and a link-local address.
· Obtain other configuration parameters from a DHCPv6 server.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Configure the interface to support stateless DHCPv6. Choose the options to configure as needed:
¡ Enable stateless IPv6 address autoconfiguration:
ipv6 address auto
¡ Configure the client to obtain network parameters from DHCPv6 servers:
ipv6 dhcp client stateless enable
By default, the interface does not support stateless DHCPv6.
Setting the DSCP value for DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 client
About this task
The DSCP value of a packet specifies the priority level of the packet and affects the transmission priority of the packet.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the DSCP value for DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 client.
ipv6 dhcp client dscp dscp-value
By default, the DSCP value in DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 client is 56.
Display and maintenance commands for DHCPv6 client
Execute the display commands in any view, and execute the reset command in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the DHCPv6 client information. |
display ipv6 dhcp client [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
|
Display the DHCPv6 client statistics. |
display ipv6 dhcp client statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
|
Clear the DHCPv6 client statistics. |
reset ipv6 dhcp client statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
DHCPv6 client configuration examples
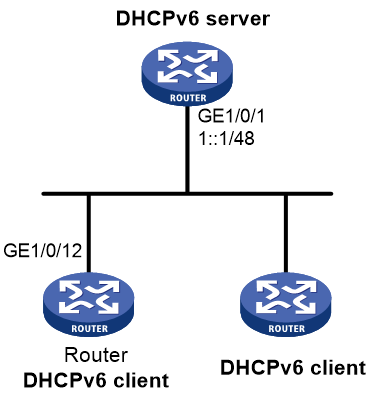
Example: Configuring IPv6 address acquisition
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 11, configure the router to use DHCPv6 to obtain configuration parameters from the DHCPv6 server. The parameters include IPv6 address, DNS server address, domain name suffix, SIP server address, and SIP server domain name.
Prerequisites
Configure the DHCPv6 server before configuring the DHCPv6 client.
Procedure
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/12 as a DHCPv6 client for IPv6 address acquisition. Configure the DHCPv6 client to support DHCPv6 rapid address assignment. Configure the DHCPv6 client to create a dynamic DHCPv6 option group for saving configuration parameters.
<Router> system-view
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/12
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 address dhcp-alloc rapid-commit option-group 1
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the DHCPv6 client has obtained configuration parameters from the server.
[Router] display ipv6 dhcp client
GigabitEthernet1/0/12:
Type: Stateful client requesting address
State: OPEN
Client DUID: 00030001d07e28db74fb
Preferred server:
Reachable via address: FE80::2E0:1FF:FE00:19
Server DUID: 00030001000fe20a0a00
IA_NA: IAID 0x00000a02, T1 50 sec, T2 80 sec
Address: 1:2::2/128
Preferred lifetime 100 sec, valid lifetime 200 sec
Will expire on Mar 27 2014 at 15:35:55 (196 seconds left)
DNS server addresses:
2000::FF
Domain name:
example.com
SIP server addresses:
2:2::4
SIP server domain names:
bbb.com
# After DHCPv6 server is enabled on the device, verify that configuration parameters are saved in a dynamic DHCPv6 option group.
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] display ipv6 dhcp option-group 1
DHCPv6 option group: 1
DNS server addresses:
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 address allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
2000::FF
Domain name:
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 address allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
example.com
SIP server addresses:
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 address allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
2:2::4
SIP server domain names:
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 address allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
bbb.com
# Verify that the DHCPv6 client has obtained an IPv6 address.
[Router] display ipv6 interface brief
*down: administratively down
(s): spoofing
Interface Physical Protocol IPv6 Address
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 up up 1:1::2
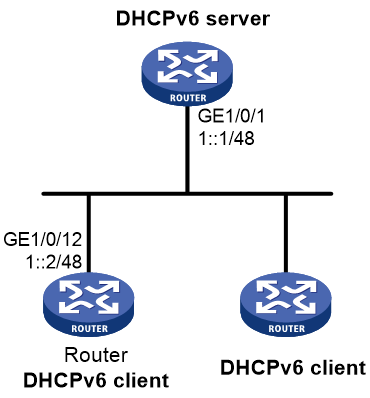
Example: Configuring IPv6 prefix acquisition
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 12, configure the router to use DHCPv6 to obtain configuration parameters from the DHCPv6 server. The parameters include IPv6 prefix, DNS server address, domain name suffix, SIP server address, and SIP server domain name.
Figure 12 Network diagram
Prerequisites
Configure the DHCPv6 server before configuring the DHCPv6 client. For information about configuring the DHCPv6 server, see "
."
Procedure
# Configure an IPv6 address for GigabitEthernet 1/0/12 that is connected to the DHCPv6 server.
<Router> system-view
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/12
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 address 1::2/48
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/12 as a DHCPv6 client for IPv6 prefix acquisition. Configure the DHCPv6 client to support DHCPv6 rapid prefix assignment. Configure the DHCPv6 client to assign an ID to the obtained IPv6 prefix and create a dynamic DHCPv6 option group for saving configuration parameters.
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 dhcp client pd 1 rapid-commit option-group 1
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the DHCPv6 client has obtained an IPv6 prefix and other configuration parameters from the DHCPv6 server.
[Router] display ipv6 dhcp client
GigabitEthernet1/0/12:
Type: Stateful client requesting prefix
State: OPEN
Client DUID: 00030001d07e28db74fb
Preferred server:
Reachable via address: FE80::2E0:1FF:FE00:19
Server DUID: 0003000100e001000000
IA_PD: IAID 0x00000a02, T1 50 sec, T2 80 sec
Prefix: 12:34::/48
Preferred lifetime 100 sec, valid lifetime 200 sec
Will expire on Feb 4 2014 at 15:37:20(80 seconds left)
DNS server addresses:
2000::FF
Domain name:
example.com
SIP server addresses:
2:2::4
SIP server domain names:
bbb.com
# Verify that the client has obtained an IPv6 prefix.
[Router] display ipv6 prefix 1
Number: 1
Type : Dynamic
Prefix: 12:34::/48
Preferred lifetime 100 sec, valid lifetime 200 sec
# After DHCPv6 server is enabled on the device, verify that configuration parameters are saved in a dynamic DHCPv6 option group.
[Router] display ipv6 dhcp option-group 1
DHCPv6 option group: 1
DNS server addresses
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 prefix allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
2000::FF
Domain name:
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 prefix allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
example.com
SIP server addresses:
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 prefix allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
2:2::4
SIP server domain names:
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 prefix allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
bbb.com
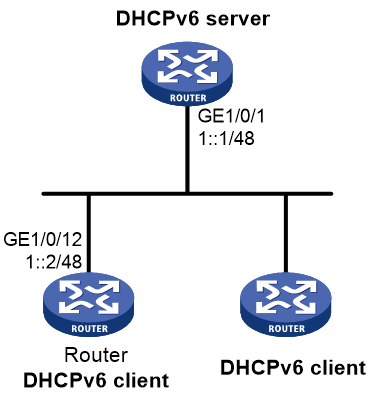
Example: Configuring IPv6 address and prefix acquisition
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 13, configure the router to use DHCPv6 to obtain configuration parameters from the DHCPv6 server. The parameters include IPv6 address, IPv6 prefix, DNS server address, domain name suffix, SIP server address, and SIP server domain name.
Prerequisites
Configure the DHCPv6 server before configuring the DHCPv6 client. For information about configuring the DHCPv6 server, see "
."
Procedure
# Configure an IPv6 address for GigabitEthernet 1/0/12 that is connected to the DHCPv6 server.
<Router> system-view
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/12
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 address 1::2/48
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/12 as a DHCPv6 client for IPv6 address and prefix acquisition. Specify IDs for the dynamic IPv6 prefix and dynamic DHCPv6 option group, and configure the client to support rapid address and prefix assignment.
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 dhcp client stateful prefix 1 rapid-commit option-group 1
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display DHCPv6 client information. The output shows that the DHCPv6 client has obtained an IPv6 address, an IPv6 prefix, and other configuration parameters from the DHCPv6 server.
[Router] display ipv6 dhcp client
GigabitEthernet1/0/12:
Type: Stateful client requesting address and prefix
State: OPEN
Client DUID: 00030001d07e28db74fb
Preferred server:
Reachable via address: FE80::2E0:1FF:FE00:19
Server DUID: 0003000100e001000000
IA_NA: IAID 0x00000a02, T1 50 sec, T2 80 sec
Address: 1:1::2/128
Preferred lifetime 100 sec, valid lifetime 200 sec
Will expire on Mar 27 2014 at 15:29:34 (198 seconds left)
IA_PD: IAID 0x00000a02, T1 50 sec, T2 80 sec
Prefix: 12:34::/48
Preferred lifetime 100 sec, valid lifetime 200 sec
Will expire on Mar 27 2014 at 15:29:34 (198 seconds left)
DNS server addresses:
2000::FF
Domain name:
example.com
SIP server addresses:
2:2::4
SIP server domain names:
bbb.com
# Display brief IPv6 information for all interfaces on the device. The output shows that the DHCPv6 client has obtained an IPv6 address.
[Router] display ipv6 interface brief
*down: administratively down
(s): spoofing
Interface Physical Protocol IPv6 Address
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 up up 1:1::2
# Display information about the dynamic IPv6 prefix. The output shows that the client has obtained an IPv6 prefix.
[Router] display ipv6 prefix 1
Number: 1
Type : Dynamic
Prefix: 12:34::/48
Preferred lifetime 100 sec, valid lifetime 200 sec
# After DHCPv6 server is enabled on the device, display information about the dynamic DHCPv6 option group. The output shows that a dynamic DHCPv6 option group exists for saving configuration parameters.
[Router] display ipv6 dhcp option-group 1
DHCPv6 option group: 1
DNS server addresses:
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 address and prefix allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
2000::FF
Domain name:
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 address and prefix allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
example.com
SIP server addresses:
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 address and prefix allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
2:2::4
SIP server domain names:
Type: Dynamic (DHCPv6 address and prefix allocation)
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/12
bbb.com
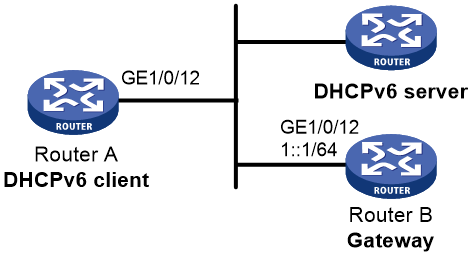
Example: Configuring stateless DHCPv6
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 14, configure Router A to use stateless DHCPv6 to obtain configuration parameters except IPv6 address and IPv6 prefix. Router B acts as the gateway and advertises RA messages periodically.
Prerequisites
Configure the DHCPv6 server before configuring the DHCPv6 client. For information about configuring the DHCPv6 server, see "
."
Procedure
1. Configure the gateway Router B:
# Configure an IPv6 address for GigabitEthernet 1/0/12.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/12
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 address 1::1 64
# Set the O flag to 1 in RA advertisements to be sent on GigabitEthernet 1/0/12. Hosts that receive the RA advertisements will obtain information other than IPv6 address through DHCPv6.
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 nd autoconfig other-flag
# Disable RA message suppression on GigabitEthernet 1/0/12.
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] undo ipv6 nd ra halt
2. Configure the DHCPv6 client on Router A:
# Enable stateless IPv6 address autoconfiguration on GigabitEthernet 1/0/12.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/12
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] ipv6 address auto
With stateless IPv6 address autoconfiguration enabled, but no IPv6 address configured for GigabitEthernet 1/0/12, Router A generates a link-local address. It sends an RS message to Router B to request configuration information for IPv6 address generation. Upon receiving the RS message, Router B sends back an RA message. After receiving an RA message with the M flag set to 0 and the O flag set to 1, Router A performs stateless DHCPv6 to get other configuration parameters.
Verifying the configuration
# Display the DHCPv6 client information.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] display ipv6 dhcp client interface gigabitethernet 1/0/12
GigabitEthernet1/0/12:
Type: Stateless client
State: OPEN
Client DUID: 00030001000fe2ff0000
Preferred server:
Reachable via address: FE80::213:7FFF:FEF6:C818
Server DUID: 0003000100137ff6c818
DNS server addresses:
1:2:4::5
1:2:4::7
Domain name:
abc.com
# Display the DHCPv6 client statistics.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] display ipv6 dhcp client statistics
Interface : GigabitEthernet1/0/12
Packets received : 1
Reply : 1
Advertise : 0
Reconfigure : 0
Invalid : 0
Packets sent : 5
Solicit : 0
Request : 0
Renew : 0
Rebind : 0
Information-request : 5
Release : 0
Decline : 0