- Table of Contents
-
- 01-Fundamentals Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-CLI configuration
- 02-RBAC configuration
- 03-Login management configuration
- 04-FTP and TFTP configuration
- 05-File system management configuration
- 06-Configuration file management configuration
- 07-Software upgrade configuration
- 08-ISSU configuration
- 09-Device management configuration
- 10-Tcl configuration
- 11-Python configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-Login management configuration | 216.00 KB |
Contents
Using the console port for the first device access
Restrictions and guidelines: CLI login configuration
Console login configuration tasks at a glance
Configuring console login authentication
Configuring common console login settings
Configuring the device as a Telnet server
Using the device to log in to a Telnet server
Configuring the device as an SSH server
Using the device to log in to an SSH server
Display and maintenance commands for CLI login
Web login configuration tasks at a glance
Configuring a Web login local user
Enabling Web operation logging
Display and maintenance commands for Web login
Web login configuration examples
Example: Configuring HTTP login
Accessing the device through SNMP
Configuring RESTful access over HTTP
Configuring RESTful access over HTTPS
Login overview
The device supports the following types of login methods:
· CLI login—At the CLI, you can enter text commands to configure and manage the device.
To log in to the CLI, you can use one of the following methods:
¡ Connect to the console port.
¡ Use Telnet.
¡ Use SSH.
· Web login—Through the Web interface, you can configure and manage the device visually.
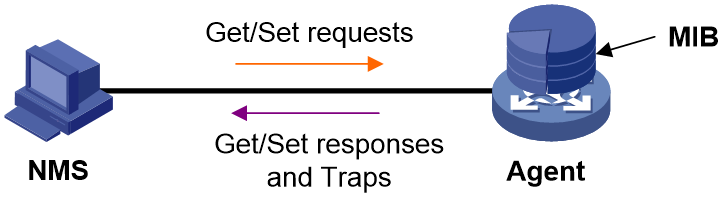
· SNMP access—You can run SNMP on an NMS to access the device MIB, and perform Get and Set operations to configure and manage the device.
· RESTful access—You can use RESTful API operations to configure and manage the device.
The first time you access the device, you can only log in to the CLI through the console port unless the device is automatically configured at startup. After login, you can change console login parameters or configure other access methods.
In login management related descriptions, it is assumed that the device does not enter the automatic configuration process at startup.
Using the console port for the first device access
About this task
Console login is the fundamental login method.
Prerequisites
To log in through the console port, prepare a terminal, for example, a PC. Make sure the terminal has a terminal emulation program, such as HyperTerminal or PuTTY. For information about how to use terminal emulation programs, see the programs' user guides.
Procedure
1. Turn off the PC.
The serial ports on PCs do not support hot swapping. Before connecting a cable to or disconnecting a cable from a serial port on a PC, you must turn off the PC.
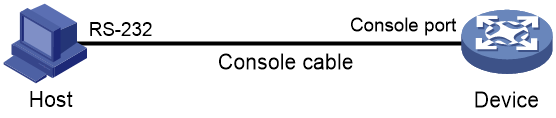
2. Find the console cable shipped with the device and connect the DB-9 female connector of the console cable to the serial port of the PC.
3. Identify the console port of the device carefully and connect the RJ-45 connector of the console cable to the console port.
|
IMPORTANT: To connect a PC to an operating device, first connect the PC end. To disconnect a PC from an operating device, first disconnect the device end. |
Figure 1 Connecting a terminal to the console port
4. Turn on the PC.
5. On the PC, launch the terminal emulation program, and create a connection that uses the serial port connected to the device. Set the port properties so the port properties match the following console port default settings:
¡ Bits per second—9600 bps.
¡ Flow control—None.
¡ Parity—None.
¡ Stop bits—1.
¡ Data bits—8.
6. Power on the device and press Enter as prompted.
The user view prompt appears. You can enter commands to configure or manage the device. To get help, enter a question mark (?).
Configuring CLI login
About CLI login
The device uses user lines (also called user interfaces) to manage CLI sessions and monitor user behavior. For a user line, you can configure access control settings, including the login authentication method and user roles.
User lines
User line types
The device supports the following types of user lines, and different user lines require different login methods:
· Console line—Login through the console port.
· Virtual type terminal (VTY) line—Telnet or SSH login.
User line numbering
A user line has an absolute number and a relative number.
An absolute number uniquely identifies a user line among all user lines. The user lines are numbered starting from 0 and incrementing by 1, in the sequence of console and VTY lines. You can use the display line command without any parameters to view supported user lines and their absolute numbers.
A relative number uniquely identifies a user line among all user lines of the same type. The number format is user line type + number. All types of user lines are numbered starting from 0 and incrementing by 1.
User line assignment
The device assigns user lines to CLI login users depending on their login methods, as described in "User line types." When a user logs in, the device checks the idle user lines for the login method, and assigns the lowest numbered user line to the user. For example, if VTY 0 and VTY 3 are idle when a user Telnets to the device, the device assigns VTY 0 to the user.
Each user line can be assigned only to one user at a time. If no user line is available, a CLI login attempt will be rejected.
Login authentication modes
You can configure login authentication to prevent illegal access to the device CLI.
In non-FIPS mode, the device supports the following login authentication modes:
· None—Disables authentication. This mode allows access without authentication and is insecure.
· Password—Requires password authentication. A user must provide the correct password at login.
· Scheme—Uses the AAA module to provide local or remote login authentication. A user must provide the correct username and password at login.
Different login authentication modes require different user line configurations, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Configuration required for different login authentication modes
|
Authentication mode |
Configuration tasks |
|
|
None |
Set the authentication mode to none. |
|
|
Password |
1. Set the authentication mode to password. 2. Set a password. |
|
|
Scheme |
1. Set the authentication mode to scheme. 2. Configure login authentication methods in ISP domain view. For more information, see Security Configuration Guide. |
|
User roles
A user is assigned user roles at login. The user roles control the commands available for the user. For more information about user roles, see "Configuring RBAC."
The device assigns user roles based on the login authentication mode and user type.
· In none or password authentication mode, the device assigns the user roles specified for the user line.
· In scheme authentication mode, the device uses the following rules to assign user roles:
¡ For an SSH login user who uses publickey or password-publickey authentication, the device assigns the user roles specified for the local device management user with the same name.
¡ For other users, the device assigns user roles according to the user role configuration of the AAA module. If the AAA server does not assign any user roles and the default user role feature is disabled, a remote AAA authentication user cannot log in.
Restrictions and guidelines: CLI login configuration
For commands that are available in both user line view and user line class view, the following rules apply:
· A setting in user line view applies only to the user line. A setting in user line class view applies to all user lines of the class.
· A non-default setting in either view takes precedence over the default setting in the other view. A non-default setting in user line view takes precedence over the non-default setting in user line class view.
· A setting in user line class view takes effect only on users who log in after the setting is made. It does not affect users who are already online when the setting is made.
Configuring console login
About console login
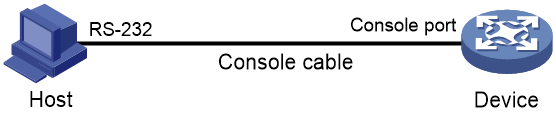
You can connect a terminal to the console port of the device to log in and manage the device, as shown in Figure 2. For information about the login procedure, see "Using the console port for the first device access."
Figure 2 Logging in through the console port
By default, console login is enabled and does not require authentication. The default user role is network-admin for a console user. To improve device security, configure password or scheme authentication for console login immediately after you log in to the device for the first time.
Restrictions and guidelines
A console login configuration change takes effect only on users who log in after the change is made. It does not affect users who are already online when the change is made.
Console login configuration tasks at a glance
To configure console login, perform the following tasks:
1. Configuring console login authentication
¡ Disabling authentication for console login
¡ Configuring password authentication for console login
¡ Configuring scheme authentication for console login
2. (Optional.) Configuring common console login settings
Configuring console login authentication
Disabling authentication for console login
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter console line view or class view.
¡ Enter console line view.
line console first-number [ last-number ]
¡ Enter console line class view.
line class console
3. Disable authentication.
authentication-mode none
By default, authentication is disabled for console login.
4. Assign a user role.
user-role role-name
By default, a console user is assigned the network-admin user role.
Configuring password authentication for console login
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter console line view or class view.
¡ Enter console line view.
line console first-number [ last-number ]
¡ Enter console class view.
line class console
3. Enable password authentication.
authentication-mode password
By default, authentication is disabled for console login.
4. Set a password.
set authentication password { hash | simple } password
By default, no password is set.
5. Assign a user role.
user-role role-name
By default, a console user is assigned the network-admin user role.
Configuring scheme authentication for console login
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter console line view or class view.
¡ Enter console line view.
line console first-number [ last-number ]
¡ Enter console line class view.
line class console
3. Enable scheme authentication.
authentication-mode scheme
By default, authentication is disabled for console login.
4. Configure user authentication parameters in ISP domain view.
To use local authentication, configure a local user and set the relevant attributes. To use remote authentication, configure a RADIUS, LDAP, or HWTACACS scheme. For more information, see AAA in Security Configuration Guide.
Configuring common console login settings
Restrictions and guidelines
Some common console login settings take effect immediately and can interrupt the current session. Use a login method different from console login to log in to the device before you change console login settings.
After you change console login settings, adjust the settings on the configuration terminal accordingly for a successful login.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter console line view or class view.
¡ Enter console line view.
line console first-number [ last-number ]
¡ Enter console line class view.
line class console
3. Configure transmission parameters.
¡ Set the transmission rate.
speed speed-value
By default, the transmission rate is 9600 bps.
This command is not available in user line class view.
¡ Specify the parity mode.
parity { even | mark | none | odd | space }
By default, a user line does not use parity.
This command is not available in user line class view.
¡ Configure flow control.
flow-control { hardware | none | software }
By default, the device does not perform flow control.
This command is not available in user line class view.
¡ Specify the number of data bits for a character.
databits { 7 | 8 }
The default is 8.
This command is not available in user line class view.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
7 |
Uses standard ASCII characters. |
|
8 |
Uses extended ASCII characters. |
¡ Specify the number of stop bits for a character.
stopbits { 1 | 1.5 | 2 }
The default is 1.
Stop bits indicate the end of a character. The more the stop bits, the slower the transmission.
This command is not available in user line class view.
4. Configure terminal attributes.
¡ Enable the terminal service.
shell
Be default, the terminal service is enabled on all user lines.
The undo shell command is not available in console line view.
¡ Specify the terminal display type.
terminal type { ansi | vt100 }
By default, the terminal display type is ANSI.
The device supports ANSI and VT100 terminal display types. As a best practice, specify VT100 type on both the device and the configuration terminal. You can also specify the ANSI type for both sides, but a display problem might occur if a command line has more than 80 characters.
¡ Set the maximum number of lines of command output to send to the terminal at a time.
screen-length screen-length
By default, the device sends a maximum of 24 lines to the terminal at a time.
To disable pausing between screens of output, set the value to 0.
¡ Set the size for the command history buffer.
history-command max-size value
By default, the buffer size is 10. The buffer for a user line can save a maximum of 10 history commands.
¡ Set the CLI connection idle-timeout timer.
idle-timeout minutes [ seconds ]
By default, the CLI connection idle-timeout timer is 10 minutes.
If no interaction occurs between the device and the user within the idle-timeout interval, the system automatically terminates the user connection on the user line.
If you set the timeout timer to 0, the connection will not be aged out.
5. Specify the command to be automatically executed for login users on the lines.
auto-execute command command
By default, no command is specified for auto execution.
The device will automatically execute the specified command when a user logs in through the user line, and close the user connection after the command is executed.
This command is not available in console line view or console line class view.
6. Configure shortcut keys.
¡ Specify the terminal session activation key.
activation-key character
By default, pressing Enter starts the terminal session.
¡ Specify the escape key.
escape-key { character | default }
By default, pressing Ctrl+C terminates a command.
¡ Set the user line locking key.
lock-key key-string
By default, no user line locking key is set.
Configuring Telnet login
About Telnet login
The device can act as a Telnet server to allow Telnet login, or as a Telnet client to Telnet to other devices.
Restrictions and guidelines
A Telnet login configuration change takes effect only on users who log in after the change is made. It does not affect users who are already online when the change is made.
Configuring the device as a Telnet server
Telnet server configuration tasks at a glance
To configure the device as a Telnet server, perform the following tasks:
2. Configuring Telnet login authentication
¡ Disabling authentication for Telnet login
¡ Configuring password authentication for Telnet login
¡ Configuring scheme authentication for Telnet login
3. (Optional.) Configuring common Telnet server settings
4. (Optional.) Configuring common VTY line settings
Enabling the Telnet server
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable the Telnet server.
telnet server enable
By default, the Telnet server is disabled.
Disabling authentication for Telnet login
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VTY line view or class view.
¡ Enter VTY line view.
line vty first-number [ last-number ]
¡ Enter VTY line class view.
line class vty
3. Disable authentication.
authentication-mode none
By default, password authentication is enabled for Telnet login.
In VTY line view, this command is associated with the protocol inbound command. If one command has a non-default setting in VTY line view, the other command uses its setting in VTY line view, regardless of its setting in VTY line class view.
4. (Optional.) Assign a user role.
user-role role-name
By default, a Telnet user is assigned the network-operator user role.
Configuring password authentication for Telnet login
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VTY line view or class view.
¡ Enter VTY line view.
line vty first-number [ last-number ]
¡ Enter VTY line class view.
line class vty
3. Enable password authentication.
authentication-mode password
By default, password authentication is enabled for Telnet login.
In VTY line view, this command is associated with the protocol inbound command. If one command has a non-default setting in VTY line view, the other command uses its setting in VTY line view, regardless of its setting in VTY line class view.
4. Set a password.
set authentication password { hash | simple } password
By default, no password is set.
5. (Optional.) Assign a user role.
user-role role-name
By default, a Telnet user is assigned the network-operator user role.
Configuring scheme authentication for Telnet login
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VTY line view or class view.
¡ Enter VTY line view.
line vty first-number [ last-number ]
¡ Enter VTY line class view.
line class vty
3. Enable scheme authentication.
authentication-mode scheme
By default, password authentication is enabled for Telnet login.
In VTY line view, this command is associated with the protocol inbound command. If one command has a non-default setting in VTY line view, the other command uses its setting in VTY line view, regardless of its setting in VTY line class view.
4. Configure user authentication parameters in ISP domain view.
To use local authentication, configure a local user and set the relevant attributes.
To use remote authentication, configure a RADIUS, LDAP, or HWTACACS scheme. For more information, see AAA configuration in Security Configuration Guide.
Configuring common Telnet server settings
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the DSCP value for outgoing Telnet packets.
IPv4:
telnet server dscp dscp-value
IPv6:
telnet server ipv6 dscp dscp-value
By default, the DSCP value is 48.
3. Specify the Telnet service port number.
IPv4:
telnet server port port-number
IPv6:
telnet server ipv6 port port-number
By default, the Telnet service port number is 23.
4. Set the maximum number of concurrent Telnet users.
aaa session-limit telnet max-sessions
By default, the maximum number of concurrent Telnet users is 32.
Changing this setting does not affect users who are currently online. If the new limit is less than the number of online Telnet users, no additional users can Telnet in until the number drops below the new limit.
For more information about this command, see Security Command Reference.
Configuring common VTY line settings
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VTY line view or class view.
¡ Enter VTY line view.
line vty first-number [ last-number ]
¡ Enter VTY line class view.
line class vty
3. Configure VTY terminal attributes.
¡ Enable the terminal service.
shell
By default, the terminal service is enabled on all user lines.
¡ Specify the terminal display type.
terminal type { ansi | vt100 }
By default, the terminal display type is ANSI.
¡ Set the maximum number of lines of command output to send to the terminal at a time.
screen-length screen-length
By default, the device sends a maximum of 24 lines to the terminal at a time.
To disable pausing between screens of output, set the value to 0.
¡ Set the size for the command history buffer.
history-command max-size value
By default, the buffer size is 10. The buffer for a user line can save a maximum of 10 history commands.
¡ Set the CLI connection idle-timeout timer.
idle-timeout minutes [ seconds ]
By default, the CLI connection idle-timeout timer is 10 minutes.
If no interaction occurs between the device and the user within the idle-timeout interval, the system automatically terminates the user connection on the user line.
If you set the timeout timer to 0, the connection will not be aged out.
4. Specify the supported protocols.
protocol inbound { all | ssh | telnet }
By default, Telnet and SSH are supported.
A protocol change takes effect only on users who log in after the setting is made. It does not affect users who are already online when the setting is made.
In VTY line view, this command is associated with the authentication-mode command. If one command has a non-default setting in VTY line view, the other command uses its setting in VTY line view, regardless of its setting in VTY line class view.
5. Specify the command to be automatically executed for login users on the user lines.
auto-execute command command
By default, no command is specified for auto execution.
|
IMPORTANT: Before you execute this command and save the configuration, make sure you can access the CLI to modify the configuration through other VTY lines. |
For a VTY line, you can specify a command that is to be automatically executed when a user logs in. After executing the specified command, the system automatically disconnects the Telnet session.
6. Configure shortcut keys.
¡ Specify the shortcut key for terminating a task.
escape-key { character | default }
The default setting is Ctrl+C.
¡ Set the user line locking key.
lock-key key-string
By default, no user line locking key is set.
Using the device to log in to a Telnet server
About this task
You can use the device as a Telnet client to log in to a Telnet server.
Figure 3 Telnetting from the device to a Telnet server
Prerequisites
Assign an IP address to the device and obtain the IP address of the Telnet server. If the device resides on a different subnet than the Telnet server, make sure the device and the Telnet server can reach each other.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. (Optional.) Specify the source IPv4 address or source interface for outgoing Telnet packets.
telnet client source { interface interface-type interface-number | ip ip-address }
By default, no source IPv4 address or source interface is specified. The device uses the primary IPv4 address of the output interface as the source address for outgoing Telnet packets.
3. Return to user view.
quit
4. Use the device to log in to a Telnet server.
IPv4:
telnet remote-host [ service-port ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ source { interface interface-type interface-number | ip ip-address } | dscp dscp-value ] *
IPv6:
telnet ipv6 remote-host [ -i interface-type interface-number ] [ port-number ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ source { interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6 ipv6-address } | dscp dscp-value ] *
Configuring SSH login
About SSH login
SSH offers a secure remote login method. By providing encryption and strong authentication, it protects devices against attacks such as IP spoofing and plaintext password interception. For more information, see Security Configuration Guide.
The device can act as an SSH server to allow Telnet login, or as an SSH client to log in to an SSH server.
Configuring the device as an SSH server
About this task
This section provides the SSH server configuration procedure used when the SSH client authentication method is password. For more information about SSH and publickey authentication configuration, see Security Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create local key pairs.
public-key local create { dsa | ecdsa [ secp192r1 | secp256r1 | secp384r1 | secp521r1 ] | rsa } [ name key-name ]
3. Enable the SSH server.
ssh server enable
By default, the SSH server is disabled.
4. (Optional.) Create an SSH user and specify the authentication mode.
ssh user username service-type stelnet authentication-type password
5. Enter VTY line view or class view.
¡ Enter VTY line view.
line vty first-number [ last-number ]
¡ Enter VTY line class view.
line class vty
6. Enable scheme authentication.
authentication-mode scheme
By default, password authentication is enabled for VTY lines.
In VTY line view, this command is associated with the protocol inbound command. If one command has a non-default setting in VTY line view, the other command uses its setting in VTY line view, regardless of its setting in VTY line class view.
7. (Optional.) Specify the protocols for the user lines to support.
In non-FIPS mode:
protocol inbound { all | ssh | telnet }
By default, Telnet and SSH are supported.
A protocol change takes effect only on users who log in after the setting is made. It does not affect users who are already online when the setting is made.
In VTY line view, this command is associated with the authentication-mode command. If one command has a non-default setting in VTY line view, the other command uses its setting in VTY line view, regardless of its setting in VTY line class view.
8. (Optional.) Set the maximum number of concurrent SSH users.
aaa session-limit ssh max-sessions
By default, the maximum number of concurrent SSH users is 32.
Changing this setting does not affect users who are currently online. If the new limit is less than the number of online SSH users, no additional SSH users can log in until the number drops below the new limit.
For more information about this command, see Security Command Reference.
9. (Optional.) Configure common settings for VTY lines:
a. Return to system view.
quit
b. Configure common settings for VTY lines.
See "Configuring common VTY line settings."
Using the device to log in to an SSH server
About this task
You can use the device as an SSH client to log in to an SSH server.
Figure 4 Logging in to an SSH server from the device
Prerequisites
Assign an IP address to the device and obtain the IP address of the SSH server. If the device resides on a different subnet than the SSH server, make sure the device and the SSH server can reach each other.
Procedure
To use the device to log in to an SSH server, execute one of the following commands in user view:
IPv4:
ssh2 server
IPv6:
ssh2 ipv6 server
To work with the SSH server, you might need to specify a set of parameters. For more information, see Security Configuration Guide.
Display and maintenance commands for CLI login
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display user line information. |
display line [ num1 | { console | vty } num2 ] [ summary ] |
N/A |
|
Display the packet source setting for the Telnet client. |
display telnet client |
N/A |
|
Display online CLI users. |
display users [ all ] |
N/A |
|
Release a user line. |
free line { num1 | { console | vty } num2 } |
Multiple users can log in to the device to simultaneously configure the device. When necessary, you can execute this command to release some connections. You cannot use this command to release the connection you are using or a redirected Telnet connection. This command is available in user view. |
|
Lock the current user line and set the password for unlocking the line. |
lock |
By default, the system does not lock any user lines. This command is not supported in FIPS mode. This command is available in user view. |
|
Lock the current user line and enable unlocking authentication. |
lock reauthentication |
By default, the system does not lock any user lines or initiate reauthentication. To unlock the locked user line, you must press Enter and provide the login password to pass reauthentication. This command is available in any view. |
|
Send messages to user lines. |
send { all | num1 | { console | vty } num2 } |
This command is available in user view. |
Configuring Web login
About Web login
The device provides a built-in Web server that supports HTTP 1.0 and HTTP 1.1. You can use a Web browser to log in to and configure the device.
Web login configuration tasks at a glance
To configure Web login, perform the following tasks:
1. Configuring Web login
2. Configuring a Web login local user
4. Enabling Web operation logging
Prerequisites for Web login
Before logging in to the Web interface of the device, log in to the device by using any other method and assign an IP address to the device. Make sure the configuration terminal and the device can communicate over the IP network.
Configuring HTTP login
1. (Optional.) Specify a fixed verification code for Web login.
web captcha verification-code
By default, no fixed verification code is specified. A Web user must enter the verification code displayed on the login page at login.
Execute this command in user view.
2. Enter system view.
system-view
3. Enable the HTTP service.
ip http enable
By default, the HTTP service is disabled.
4. (Optional.) Specify the HTTP service port number.
ip http port port-number
The default HTTP service port number is 80.
5. (Optional.) Specify the HTTP methods to be added to the reply to an OPTIONS request.
http method { delete | get | head | options | post | put } *
By default, no HTTP methods are specified.
6. (Optional.) Enable the HTTP preflight request feature.
ip http preflight enable
By default, the HTTP preflight request feature is disabled.
Configuring a Web login local user
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a local user and enter local user view.
local-user user-name [ class manage ]
3. (Optional.) Configure a password for the local user.
password [ { hash | simple } password ]
By default, no password is configured for a local user. The local user can pass authentication after entering the correct username and passing attribute checks.
4. Configure user attributes.
¡ Assign a user role to the local user.
authorization-attribute user-role user-role
The default user role is network-operator for a Web user.
¡ Specify the service type for the local user.
service-type { http | https }
By default, no service type is specified for a local user.
Managing Web connections
Setting the Web connection idle-timeout timer
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the Web connection idle-timeout timer.
web idle-timeout minutes
By default, the Web connection idle-timeout timer is 10 minutes.
Specifying the maximum number of online HTTP or HTTPS users
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify the maximum number of online HTTP or HTTPS users.
aaa session-limit { http | https } max-sessions
By default, the device supports a maximum number of 32 online users.
Changing this setting does not affect users who are currently online. If the new setting is less than the number of online HTTP or HTTPS users, no additional HTTP or HTTPS users can log in until the number drops below the new limit. For more information about this command, see Security Command Reference.
Logging off Web users
To log off Web users, execute the following command in user view:
free web users { all | user-id user-id | user-name user-name }
Enabling Web operation logging
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable Web operation logging.
webui log enable
By default, Web operation logging is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for Web login
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display HTTP service configuration and status information. |
display ip http |
|
Display Web interface navigation tree information. |
display web menu [ chinese ] |
|
Display online Web users. |
display web users |
Web login configuration examples
Example: Configuring HTTP login
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 5, the PC and the device can communicate over the IP network.
Configure the device to allow the PC to log in by using HTTP.
Procedure
# Create a local user named admin. Set the password to admin, the service type to HTTP, and the user role to network-admin.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] local-user admin
[Sysname-luser-manage-admin] service-type http
[Sysname-luser-manage-admin] authorization-attribute user-role network-admin
[Sysname-luser-manage-admin] password simple admin
[Sysname-luser-manage-admin] quit
# Enable HTTP.
[Sysname] ip http enable
Verifying the configuration
1. On the PC, run a Web browser and enter the IP address of the device in the address bar.
2. On the login page, enter the username, password, and verification code. Select English and click Login.
After you pass authentication, the homepage appears and you can configure the device.
Accessing the device through SNMP
You can run SNMP on an NMS to access the device MIB and perform Get and Set operations to configure and manage the device.
For more information about SNMP, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Configuring RESTful access
About RESTful access
The device provides the Representational State Transfer application programming interface (RESTful API). Based on this API, you can use programming languages such as Python, Ruby, or Java to write programs to perform the following tasks:
· Send RESTful requests to the device to pass authentication.
· Use RESTful API operations to configure and manage the device. RESTful API operations include Get, Put, Post, and Delete.
The device supports using HTTP or HTTPS to transfer RESTful packets.
Configuring RESTful access over HTTP
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. (Optional.) Specify the service port number for RESTful access over HTTP.
restful http port port-number
By default, the service port number for RESTful access over HTTP is 80.
3. Enable RESTful access over HTTP.
restful http enable
By default, RESTful access over HTTP is disabled.
4. Create a local user and enter local user view.
local-user user-name [ class manage ]
5. Configure a password for the local user.
password [ { hash | simple } password ]
6. (Optional.) Assign a user role to the local user.
authorization-attribute user-role user-role
The default user role is network-operator for a RESTful access user.
7. Specify the HTTP service for the local user.
service-type http
By default, no service type is specified for a local user.
8. (Optional.) Use an ACL to control TCP connections from RESTful clients.
IPv4:
http acl { advanced-acl-number | basic-acl-number }
IPv6:
http ipv6 acl { advanced-acl-number | basic-acl-number }
By default, all RESTful clients can establish TCP connections to the device.
Configuring RESTful access over HTTPS
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. (Optional.) Specify the service port number for RESTful access over HTTPS.
restful https port port-number
By default, the service port number for RESTful access over HTTPS is 443.
3. Enable RESTful access over HTTPS.
restful https enable
By default, RESTful access over HTTPS is disabled.
4. Create a local user and enter local user view.
local-user user-name [ class manage ]
5. Configure a password for the local user.
In non-FIPS mode:
password [ { hash | simple } password ]
In FIPS mode:
password
6. (Optional.) Assign a user role to the local user.
authorization-attribute user-role user-role
The default user role is network-operator for a RESTful access user.
7. Specify the HTTPS service for the local user.
service-type https