- Table of Contents
-
- 18-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Ping and tracert configuration
- 02-System debugging configuration
- 03-NQA configuration
- 04-SNMP configuration
- 05-RMON configuration
- 06-NETCONF configuration
- 07-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 08-Mirroring configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 08-Mirroring configuration | 88.68 KB |
Contents
Configuring local port mirroring (SPAN)
Restrictions and guidelines for local port mirroring configuration
Local port mirroring tasks at a glance
Creating a local mirroring group
Configuring local port mirroring group with multiple monitoring devices
Verifying and maintaining port mirroring
Configuring port mirroring
About port mirroring
Port mirroring copies the packets passing through a port to a port that connects to a data monitoring device for packet analysis.
Terminology
The following terms are used in port mirroring configuration.
Mirroring source
The mirroring sources can be one or more monitored ports (called source ports).
Packets passing through mirroring sources are copied to a port connecting to a data monitoring device for packet analysis. The copies are called mirrored packets.
Source device
The device where the mirroring sources reside is called a source device.
Mirroring destination
The mirroring destination connects to a data monitoring device and is the destination port (also known as the monitor port) of mirrored packets. Mirrored packets are sent out of the monitor port to the data monitoring device.
A monitor port might receive multiple copies of a packet when it monitors multiple mirroring sources. For example, two copies of a packet are received on Port A when the following conditions exist:
· Port A is monitoring bidirectional traffic of Port B and Port C on the same device.
· The packet travels from Port B to Port C.
Destination device
The device where the monitor port resides is called the destination device.
Mirroring direction
The mirroring direction specifies the direction of the traffic that is copied on a mirroring source.
· Inbound—Copies packets received.
· Outbound—Copies packets sent.
· Bidirectional—Copies packets received and sent.
Mirroring group
Port mirroring is implemented through mirroring groups.
Local port mirroring (SPAN)
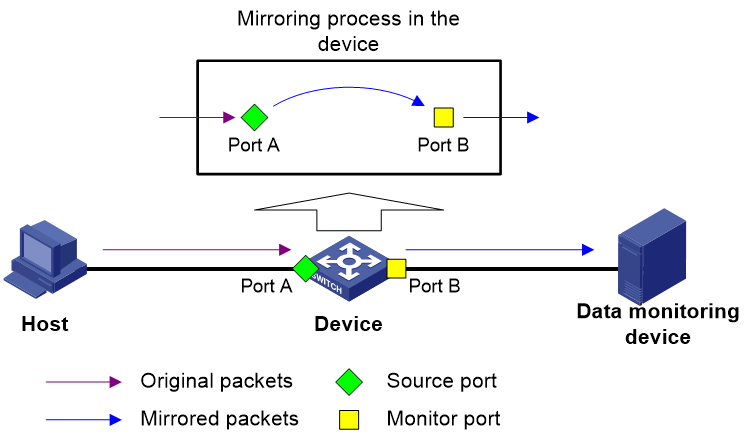
Figure 1 Local port mirroring implementation
As shown in Figure 1, the source port (Port A) and the monitor port (Port B) reside on the same device. Packets received on Port A are copied to Port B. Port B then forwards the packets to the data monitoring device for analysis.
Configuring local port mirroring (SPAN)
Restrictions and guidelines for local port mirroring configuration
A local mirroring group takes effect only after it is configured with the monitor port and mirroring sources.
Local port mirroring tasks at a glance
To configure local port mirroring, perform the following tasks:
1. Configuring mirroring sources
2. Configuring the monitor port
Creating a local mirroring group
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a local mirroring group.
mirroring-group group-id local
Configuring mirroring sources
Restrictions and guidelines for mirroring source configuration
When you configure source ports for a local mirroring group, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· A mirroring group can contain multiple source ports.
· A port can act as a source port for only one mirroring group.
· A source port cannot be configured as a monitor port.
Configuring source ports
· Configure source ports in system view:
a. Enter system view.
system-view
b. Configure source ports for a local mirroring group.
mirroring-group group-id mirroring-port interface-list { both | inbound | outbound }
By default, no source port is configured for a local mirroring group.
· Configure source ports in interface view:
a. Enter system view.
system-view
b. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
c. Configure the port as a source port for a local mirroring group.
mirroring-group group-id mirroring-port { both | inbound | outbound }
By default, a port does not act as a source port for any local mirroring groups.
Configuring the monitor port
Restrictions and guidelines
Do not enable the spanning tree feature on the monitor port.
Only one monitor port can be specified for a local mirroring group.
Use a monitor port only for port mirroring, so the data monitoring device receives only the mirrored traffic.
Procedure
· Configure the monitor port in system view:
a. Enter system view.
system-view
b. Configure the monitor port for a local mirroring group.
mirroring-group group-id monitor-port interface-type interface-number
By default, no monitor port is configured for a local mirroring group.
· Configure the monitor port in interface view:
a. Enter system view.
system-view
b. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
c. Configure the port as the monitor port for a mirroring group.
mirroring-group group-id monitor-port
By default, a port does not act as the monitor port for any local mirroring groups.
Configuring local port mirroring group with multiple monitoring devices
About this task
To monitor interested traffic passing through a device on multiple directly connected data monitoring devices, configure local port mirroring with a remote probe VLAN as follows:
1. Configure a remote source group on the device.
2. Configure mirroring sources and a reflector port for the remote source group.
3. Specify a VLAN as the remote probe VLAN and assign the ports connecting to the data monitoring devices to the VLAN.
This configuration enables the device to copy packets received on the mirroring sources to the reflector port, which broadcasts the packets in the remote probe VLAN. The packets are then sent out of the member ports of the remote probe VLAN to the data monitoring devices.
Restrictions and guidelines
The reflector port must be a port not in use. Do not connect a network cable to the reflector port.
When a port is configured as a reflector port, all the other settings on the port are cleared. You cannot configure other features on the reflector port.
Do not assign a source port of a mirroring group to the remote probe VLAN of the mirroring group.
A VLAN can act as the remote probe VLAN for only one remote source group. As a best practice, use the VLAN for port mirroring exclusively. Do not create a VLAN interface for the VLAN or configure other features for the VLAN.
The remote probe VLAN must be a static VLAN.
To delete a VLAN that has been configured as the remote probe VLAN for a mirroring group, remove the remote probe VLAN from the mirroring group first.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a remote source group.
mirroring-group group-id remote-source
3. Configure mirroring sources for the remote source group. Choose one of the following tasks:
¡ Configure mirroring ports in system view:
mirroring-group group-id mirroring-port interface-list { both | inbound | outbound }
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter interface view, and then configure the interface as a source port.
interface interface-type interface-number
mirroring-group group-id mirroring-port { both | inbound | outbound }
quit
4. Configure the reflector port for the remote source group.
mirroring-group group-id reflector-port reflector-port
By default, no reflector port is configured for a remote source group.
5. Create a VLAN and enter VLAN view.
vlan vlan-id
6. Assign the ports that connect to the data monitoring devices to the VLAN.
port interface-list
By default, a VLAN does not contain any ports.
7. Return to system view.
quit
8. Specify the VLAN as the remote probe VLAN for the remote source group.
mirroring-group group-id remote-probe vlan vlan-id
By default, no remote probe VLAN is configured for a remote source group
Verifying and maintaining port mirroring
To display mirroring group information, execute the following command in any view:
display mirroring-group { group-id | all | local }
Port mirroring configuration examples
Example: Configuring local port mirroring
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, configure local port mirroring to enable the server to monitor the bidirectional traffic of the marketing and technical departments.
Procedure
# Create local mirroring group 1.
[AC] mirroring-group 1 local
# Configure the source port and the monitor port in local mirroring group 1.
[AC] mirroring-group 1 mirroring-port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 both
[AC] mirroring-group 1 monitor-port gigabitethernet 1/0/2
Verifying the configuration
# Verify the mirroring group configuration.
[AC] display mirroring-group 1
Mirroring group 1:
Type: Local
Status: Active
Mirroring port: GigabitEthernet1/0/1 both
Monitor port: GigabitEthernet1/0/2