- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-Web configuration examples | 958.06 KB |
Contents
Wireless features configuration examples
Wireless service configuration examples
Shared key authentication configuration example
PSK authentication and bypass authentication configuration example
PSK authentication and MAC authentication configuration example
Wireless QoS configuration examples
Client rate limiting configuration example
Bandwidth guarantee configuration example
Radio management configuration example
Radio management configuration example
Band navigation configuration example
Wireless security configuration examples
WIPS device classification and countermeasures configuration example
WIPS malformed packet and flood attack detection configuration example
Signature-based attack detection configuration example
Application configuration examples
WLAN mesh configuration example
Multicast optimization configuration example
Network feature configuration examples
Interface configuration examples
Layer 2 static aggregation configuration example
Layer 2 dynamic aggregation configuration example
PPPoE client configuration example
MAC address configuration example
Routing configuration examples
IPv4 static route configuration example
IPv6 static route configuration example
Outbound dynamic NAT configuration example
Outbound static NAT configuration example
Proxy ARP configuration example
IPv4 static DNS configuration example
IPv4 dynamic DNS configuration example
IPv4 DNS proxy configuration example
Static IPv6 address configuration example
IPv6 static DNS configuration example
IPv6 dynamic DNS configuration example
IPv6 DNS proxy configuration example
Management protocol configuration examples
DHCP server configuration example
DHCP relay agent configuration example
Network security configuration examples
Access control configuration examples
ACL-based packet filter configuration example
Access authentication configuration examples
802.1X RADIUS authentication configuration example
802.1X local authentication configuration example
802.1X AKM configuration example
Direct IPv4 portal authentication configuration example
System feature configuration examples
Device management configuration examples
Administrators configuration example
Local SSH server configuration example
Wireless features configuration examples
Wireless service configuration examples
Shared key authentication configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 1, the client is in the WLAN coverage. Configure shared key authentication to enable the client to access the network by using the WEP key 12345.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure a wireless service:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
- Create a wireless service named service1.
- Set the SSID to service.
- Enable the wireless service.
2. Click Apply and Configure Advanced Settings, and then click the Authentication tab.
3. Configure static WEP authentication:
¡ Set the security type to static WEP.
¡ Set the key type to Passphrase.
¡ Select the WEP40 cipher suite.
¡ Set the key to plain text string 12345.
4. Apply the wireless service.
5. Bind the wireless service service1 to the radio:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Click the Edit icon in the Actions column for service1.
c. Click the Binding tab.
d. Select the 5 GHz radio of the AP and then click Apply.
Verifying the configuration
View details about the wireless service service1 to verify that the configuration is correct.
PSK authentication and bypass authentication configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2, the client is in the WLAN coverage.
· Configure open system authentication and bypass authentication.
· Configure the client to use the preshared key 12345678 to access the network.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure a wireless service:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Add a wireless service:
- Create a wireless service named service1.
- Set the SSID to service.
- Enable the wireless service.
2. Click Apply and Configure Advanced Settings, and then click the Authentication tab.
3. Configure static PSK authentication:
¡ Set the security type to static PSK.
¡ Set the security mode to WPA.
¡ Select the CCMP cipher suite.
¡ Set the key type to Passphrase and the key to 12345678.
4. Apply the wireless service.
5. Bind the wireless service service1 to the radio:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Click the Edit icon in the Actions column for service1.
c. Click the Binding tab.
d. Select the 5 GHz radio of the AP and then click Apply.
Verifying the configuration
View details about the wireless service service1 to verify that the configuration is correct.
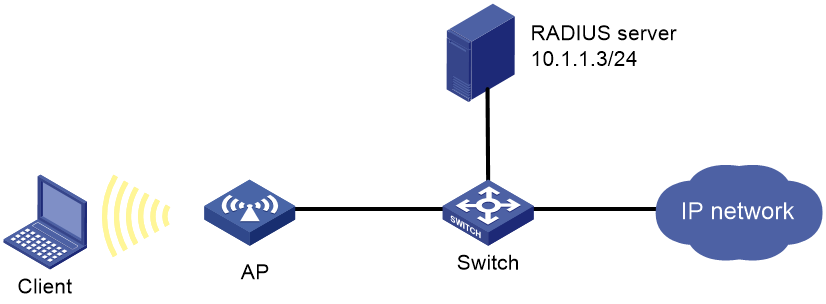
PSK authentication and MAC authentication configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 3, the client is in the WLAN coverage.
· Configure open system authentication and MAC authentication for clients.
· Configure the client to use the preshared key 12345678 to access the network.
Configuration procedure
1. On the RADIUS server, configure the client's MAC address as the username and password used for authentication. The MAC address cannot contain hyphens and upper case letters.
2. Configure the RADIUS server correctly to provide authentication, authorization, and accounting functions.
3. Configure RADIUS and an authentication domain.
4. Configure a wireless service:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Add a wireless service:
- Create a wireless service named service1.
- Set the SSID to service.
- Enable the wireless service.
5. Click Apply and Configure Advanced Settings, and then click the Authentication tab.
6. Configure static PSK authentication and MAC authentication:
¡ Set the security type to static PSK and select MAC authentication.
¡ Set the security mode to WPA.
¡ Select the CCMP cipher suite.
¡ Set the key type to Passphrase and the key to 12345678.
¡ Set the domain name to dom1.
7. Apply the wireless service.
8. Bind the wireless service service1 to the radio:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Click the Edit icon in the Actions column for service 1.
c. Click the Binding tab.
d. Select the 5 GHz radio of the AP and then click Apply.
Verifying the configuration
View details about the wireless service service1 to verify that the configuration is correct.
Wireless QoS configuration examples
Client rate limiting configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 4, Perform the following tasks on the AP:
· Configure static mode client rate limiting to limit the rate of incoming client traffic.
· Configure dynamic mode client rate limiting to limit the rate of outgoing client traffic.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure a wireless service:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Add a wireless service:
- Create a wireless service named service.
- Set the SSID to service.
- Enable the wireless service.
2. Bind the service to the radio:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > AP Management > Bind WLAN Service. Bind service service to radio 1 of the AP.
3. Configure client rate limiting:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless QoS > Client Rate Limit.
b. Click the More icon in the service based configuration area.
c. Select the service name service, and click the edit icon for the wireless service service.
d. On the edit page, perform the following tasks:
- Set the limit mode to static mode for inbound traffic.
- Set the per-client limit rate to 8000 for inbound traffic.
- Set the limit mode to dynamic mode for outbound traffic.
- Set the per-client limit rate to 4000 for outbound traffic.
4. Enable radio 1 for the AP:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Radio Management > Radio Configuration.
b. Enable radio 1 of the AP.
Verifying the configuration
Verify that the download rate and upload rate of each client do not exceed 8 Mbps and 4 Mbps, respectively.
Bandwidth guarantee configuration example
Network requirements
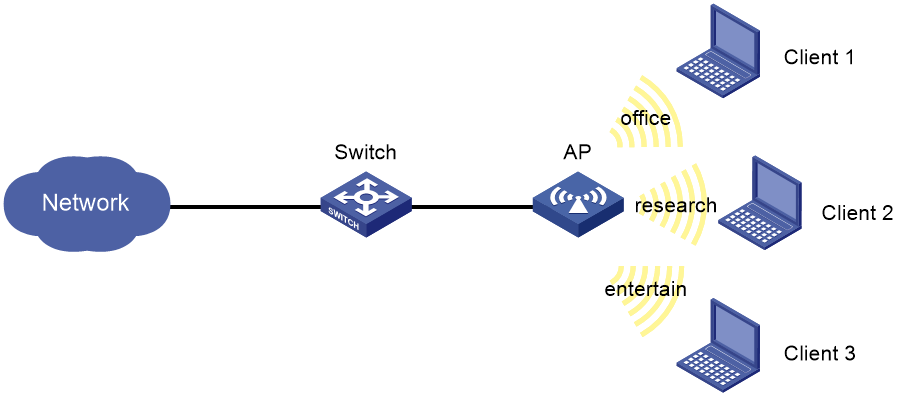
As shown in Figure 5, Clients 1, 2, and 3 access the network through the SSIDs research, office, and entertain, respectively.
For the network to operate correctly, guarantee 20% of the bandwidth for the SSID office, 80% for research, and none for entertain.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure wireless services:
a. From the navigation tree, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Add wireless services:
- Create wireless services named office, research, and entertain.
- Set their SSID to office, research, and entertain, respectively.
- Enable the wireless services.
2. Bind services to the radio:
a. From the navigation tree, select Wireless Configuration > AP Management > Bind WLAN Service. Bind services office, research, and entertain to radio 1 of the AP.
3. Configure bandwidth guaranteeing:
a. From the navigation tree, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless QoS > Bandwidth Guarantee.
b. Click the more icon in the AP configuration area.
- Enable bandwidth guaranteeing.
- Set the guaranteed bandwidth percentage to 20% for the wireless service office.
- Set the guaranteed bandwidth percentage to 80% for the wireless service research.
4. Enable radio 1 for the AP:
a. From the navigation tree, select Wireless Configuration > Radio Management > Radio Configuration.
b. Enable radio 1 of the AP.
Verifying the configuration
# View details about AP configuration to verify that the effective bandwidth percentage for each SSID is not greater than the guaranteed bandwidth percentage.
Radio management configuration example
Radio management configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 6, the client connects to the AP through WLAN. Perform the following tasks to configure the 5 GHz radio of the AP:
· Set the radio type, working channel, and maximum transmit power to 802.11ac, 153, and 18 dBm, respectively for radio 1.
· Set the radio type, working channel, and maximum transmit power to 802.11ac, 48, and 19 dBm, respectively for radio 2.
· Set the maximum mandatory NSS, maximum supported NSS, multicast NSS, and multicast VHT-MCS index to 2, 3, 2, and 5, respectively.
· Enable the A-MSDU and A-MPDU aggregation methods to improve network throughput.
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Radio Management > Radio Configuration.
2. Click the Edit icon in the Actions column for the 5 GHz radio of the AP. You are placed on the Basic tab. Perform the following tasks to configure radio 1 and radio 2:
In the basic settings area:
a. Set the radio type to 802.11ac (5GHz) for both radio 1 and radio 2.
b. Set the channel to 153 and 48 for radio 1 and radio 2, respectively.
c. Set the maximum transmit power to 18 dBm and 19 dBm for radio 1 and radio 2, respectively.
In the rates configuration area:
a. Set the maximum mandatory NSS to 2.
b. Set the maximum supported NSS to 3.
c. Set the multicast NSS to 2.
d. Set the VHT-MCS index to 5.
In the 802.11n/802.11ac/802.11ax settings area:
a. Enable the A-MSDU aggregation method.
b. Enable the A-MPDU aggregation method.
3. Apply the configuration.
Verifying the configuration
1. Access the Wireless Configuration > Radio Management > Radio Configuration page.
2. Click the Edit icon in the Actions column for the 5 GHz radio
3. Verify that the configuration is correct.
Band navigation configuration example
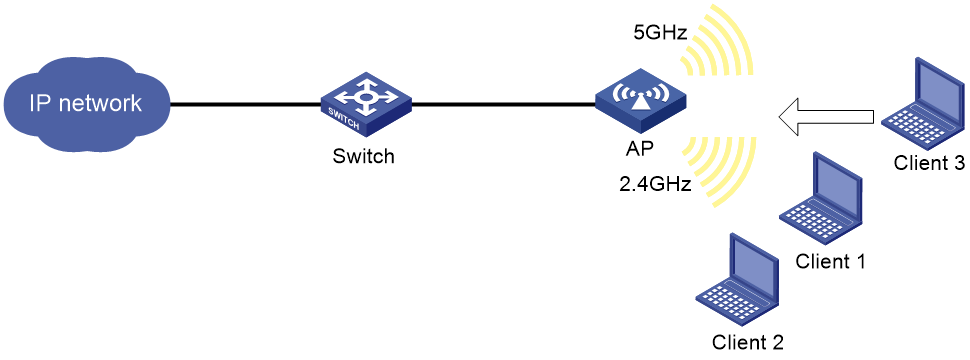
Network requirements
Both the 5 GHz radio and the 2.4 GHz radio are enabled on the AP. Configure band navigation for band navigation to load balance the radios.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure a wireless service:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Access the page for adding a wireless network to perform the following tasks:
- Set the name of the wireless service to service.
- Set its SSID to band-navigation.
- Disable fast association.
- Enable the wireless service.
2. Bind the service to the AP:
a. Access the Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration page and click Edit for service service to access the Binding page.
b. Bind service service to both the 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz radios of the AP.
3. Configure band navigation:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Radio Management > Band Navigation.
b. Access the details page for global configuration to perform the following tasks:
- Enable band navigation globally.
- Set the session threshold to 5.
- Set the session gap threshold to 2.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that clients supporting both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz prefer to access the 5 GHz radio. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that the system rejects client access requests to the 5 GHz radio when the following conditions are met:
· The number of online clients on the 5 GHz radio reaches 5.
· The client quantity gap between the 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz radios reach 2. (Details not shown.)
# On the Monitoring > Clients > Client Info page, verify that the 5 GHz radio and the 2.4 GHz radio of AP 1 are load balanced.
Wireless security configuration examples
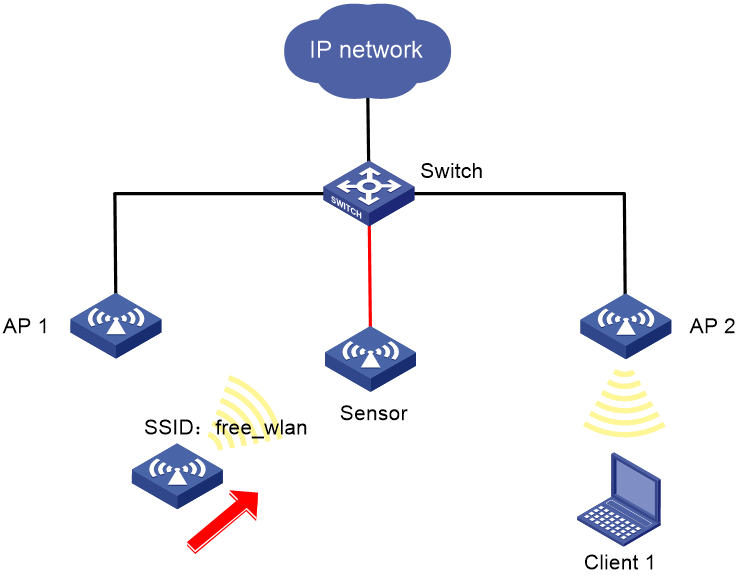
WIPS device classification and countermeasures configuration example
Network requirements
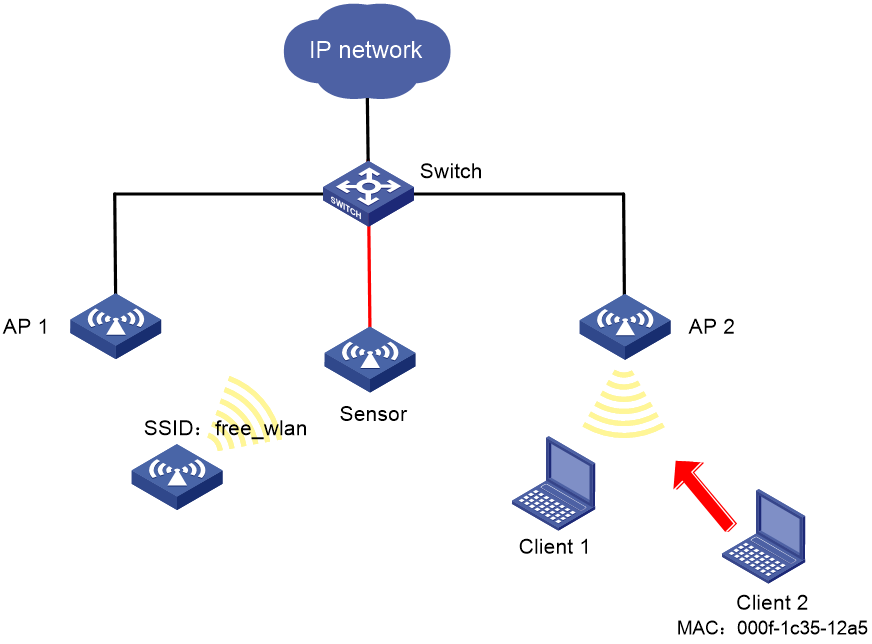
As shown in Figure 8, AP 1 and AP 2 provide wireless services to clients through the SSID abc. Perform the following tasks:
· Enable WIPS for the sensor.
· Configure wireless device classification to add the MAC address 000f-1c35-12a5 to the static prohibited device list and the SSID abc to the trusted SSID list.
· Configure countermeasures to enable WIPS to take countermeasures against potential-external APs and unauthorized clients.
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Security > WIPS.
2. Click the VSD tab, and then create VSD VSD_1.
3. Click the WIPS Enable tab, click Edit for the target AP, and specify a radio list and VSD name VSD_1.
4. Click the Classification tab, perform the following tasks:
¡ Create the classification policy class1.
¡ Add the MAC address of Client 2 to the prohibited device list.
¡ Add the SSID abc to the trusted SSID list.
5. Click the Countermeasure tab, perform the following tasks:
¡ Create the countermeasure policy protect.
¡ Configure WIPS to take countermeasures against unauthorized clients and potential-external APs.
6. Access the modifying VSD page for the VSD VSD_1 to perform the following tasks:
¡ Apply the classification policy class1 to the VSD VSD_1.
¡ Apply the countermeasure policy protect to the VSD VSD_1.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the AP with the MAC address 000f-e223-1616 is classified as a potential-external AP and the client with the MAC address 000f-1c35-12a5 is classified as an unauthorized client.
# Verify that WIPS has taken countermeasures against the unauthorized client with the MAC address 000f-1c35-12a5 and the potential-external AP with the MAC address 000f-e223-1616.
WIPS malformed packet and flood attack detection configuration example
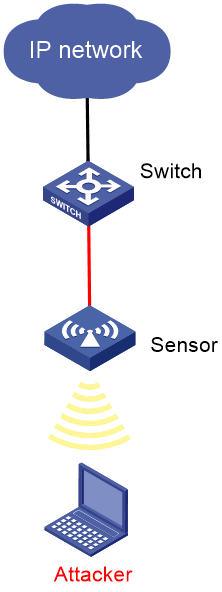
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 9, configure the AP as a sensor. Add the sensor to the VSD VSD_1. Configure malformed packet detection and flood attack detection to enable WIPS to trigger an alarm when it detects beacon flood attacks or malformed packets with duplicated IE.
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Security > WIPS.
2. Click the VSD tab, and then create VSD VSD_1.
3. Click the WIPS Enable tab, click Edit for the target AP, and specify a radio list and VSD name VSD_1.
4. Click the Detection tab, perform the following tasks:
¡ Create an attack detection policy.
¡ Enable detection on malformed packets with duplicated IE, and set the quiet time to 50 seconds.
¡ Enable beacon flood attack detection, and set the statistics interval, threshold, and quiet time to 100 seconds, 200, and 50 seconds, respectively.
5. Access the modifying page for the VSD VSD_1 to apply the attack detection policy to the VSD VSD_1.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that no malformed packets or flood attack messages exist when WIPS does not detect any attacks in the WLAN.
# Verify that the number of malformed packets or flood attack messages is not zero when WIPS detects beacon flood attacks and malformed packets with duplicated IE.
Signature-based attack detection configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 10, AP 1 and AP 2 provide wireless services for clients through the SSID abc. Enable WIPS for the sensor, and configure a signature to enable WIPS to trigger an alarm when it detects beacon frames whose SSIDs are not abc.
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Security > WIPS.
2. Click the VSD tab, and then create VSD VSD_1.
3. Click the WIPS Enable tab, select an interface to enable WIPS and add the interface to the VSD VSD_1.
4. Click the Signature rule tab, perform the following tasks:
¡ Create signature 1.
¡ Configure a subsignature to match beacon frames.
¡ Configure a subsignature to match frames whose SSIDs are not abc.
5. Click the Signature tab, perform the following tasks:
¡ Create a signature policy named sig1.
¡ Bind signature 1 to the signature policy sig1.
¡ Set the detection interval, quiet time, and alarm threshold to 5 seconds, 60 seconds, and 60, respectively.
6. Access the modifying page for the VSD VSD_1 to apply the signature policy sig1 to the VSD VSD_1.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that an alarm is triggered when the sensor detects the wireless service with the SSID free_wlan.
# Verify that the number of detected messages for packets that match the signature is not zero.
Application configuration examples
WLAN mesh configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 11, configure the MPP, MAP 1, and MAP 2 to use channel 149 and 5 GHz radios in 802.11n mode to establish mesh links for the client to access network resources.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure a wireless service (for an MAP only):
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Create a wireless service named service.
c. Set the SSID to mesh-network.
d. Enable the wireless service.
2. Bind the service to the radio (for an MAP only):
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > AP Management > Bind WLAN Service. Bind service service to radio 1 of the AP.
3. Configure a mesh profile:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Applications > Mesh Services.
b. Click the Add icon + in the Mesh Profile area.
c. Set the profile number to 1.
d. Enable the mesh profile.
e. Set the mesh ID to 1.
f. Set the authentication and key management mode to SAE and specify the key to 12345678.
g. Retain the default settings for the other fields.
4. Bind the mesh profile to radios:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Applications > Mesh Services.
b. Click the More icon in the Binding Info area.
c. Select the 5 GHz radio and bind mesh profile 1 to the radio.
5. Configure the peer whitelist ( for an MAP only):
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Applications > Mesh Services.
b. Click the More icon in the Mesh Peer Whitelist area.
c. Click Edit for the 5 GHz radio. Configure the peer MAC address to add MPP to the whitelist of MAP 1 and MAP 2 for the MAPs to establish mesh links only with the MPP to avoid loops.
6. Configure the radio mode and channel:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Radio Management > Radio Configuration.
b. Configure the 5 GHz radio as follows:
- Set the radio mode to 802.11n (5 GHz).
- Set the channel to 149.
- Enable the radio.
Verifying the configuration
Verify that the client can access the network and you can view mesh link packet statistics from the Web interface.
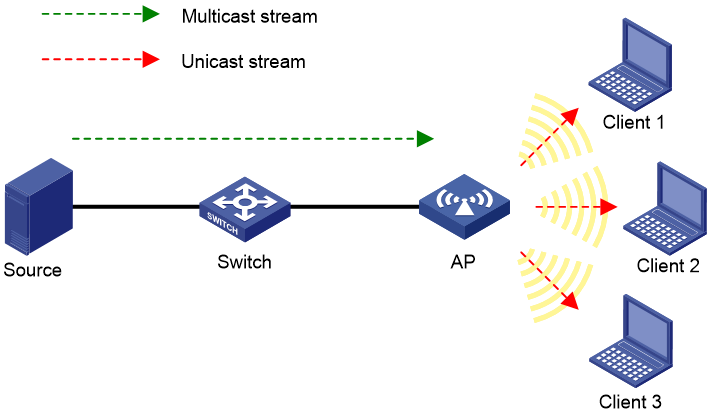
Multicast optimization configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 12, the AP connects to the switch. Configure IPv4 multicast optimization to manage multicast packet forwarding.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure a wireless service:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Create a wireless service named service1.
c. Set the SSID to service.
d. Enable the wireless service.
2. Bind the service to the radio:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Select service service1 and click Bind to Radio to access the Bind to Radio page.
c. Select the 5 GHz radio of the AP and click Bind.
3. Configure multicast optimization:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Applications > Multicast Optimization.
b. Click the More icon for IPv4 multicast optimization.
c. Enable multicast optimization for wireless service service1.
d. Click the Advanced Configuration tab and then perform the following tasks:
- Set the entry aging time to 300 seconds.
- Set the entry limit to 1024 and set the entry limit per client to 256.
- Set the client limit per group to 2 and set the action to drop multicast packets.
- Configure the device to learn a maximum of 100 IGMP packets every 60 seconds.
Verifying the configuration
# Connect Client 1, Client 2, and Client 3 to the WLAN service with SSID service.
# Send IGMP reports from Client 1 and Client 2 to join the IPv4 multicast group that the source uses to forward IPv4 multicast data. Both Client 1 and Client 2 can receive the IPv4 multicast data.
# Send an IGMP report from Client 3 to join the IPv4 multicast group. None of the clients can receive the IPv4 multicast data.
Network feature configuration examples
Interface configuration examples
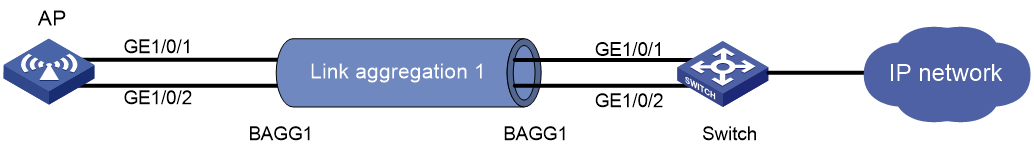
Layer 2 static aggregation configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 13, configure a Layer 2 static aggregation group on both the AP and the switch to improve the link reliability. This section takes the configuration for the AP as an example.
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Network Interfaces > Link Aggregation.
2. Configure a Layer 2 aggregation group:
¡ Add Layer 2 aggregation group 1.
¡ Configure the aggregation mode as Static.
¡ Assign ports GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to the aggregation group.
Verifying the configuration
Access the link aggregation page, and verify that ports GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 have been assigned to link aggregation group 1.
Layer 2 dynamic aggregation configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 14, configure a dynamic Layer 2 aggregation group on the AP and the switch to improve the link reliability. This section takes the configuration for the AP as an example.
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Network Interfaces > Link Aggregation.
2. Configure a Layer 2 aggregation group:
¡ Add Layer 2 aggregation group 1.
¡ Configure the aggregation mode as Dynamic.
¡ Assign ports GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to the aggregation group.
Verifying the configuration
Access the link aggregation page, and verify that ports GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 have been assigned to link aggregation group 1.
PPPoE client configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 15, connect the Fat AP to the Internet as a PPPoE client through Layer 3 Ethernet interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, and make sure the PC can telnet to the Web interface through VLAN interface Vlan-interface10.
Configuration procedure
# Configure the PPPoE server to assign a username and password to the device. (Details not shown.)
# Configure the PPPoE client:
1. From the navigation tree, select Network Configuration > Network Interfaces > PPPoE.
3. Select VLAN interface Vlan-interface 10.
4. Enter the username and password, and select an online mode.
5. Select Open the NAT function, and then click Apply.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the AP and the PPPoE server can reach other.
Link configuration examples
MAC address configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 16, the MAC addresses of Host A and the client are 000f-e235-dc71 and 000f-e235-abcd, respectively. Host A connects to the AP through interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1. Both Host A and the client belong to VLAN 1. Configure MAC address settings on the AP to meet the following requirements:
· Allow packets to forward correctly to Host A by adding a static MAC address entry.
· Forbid the client to receive any packets from the network by adding a blackhole MAC address entry.
· The aging timer for dynamic MAC address entries is 500 seconds.
Configuration procedure
From the left navigation pane, select Network Configuration > VLAN > MAC. Perform the following tasks:
· Add a static MAC address entry:
¡ Specify the MAC address 000f-e235-dc71.
¡ Specify outbound interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1.
¡ Specify VLAN 1.
· Add a blackhole MAC address entry:
¡ Specify the MAC address 000f-e235-abcd.
¡ Specify VLAN 1.
· Click Advanced settings, configure the aging timer for dynamic MAC address entries as 500 seconds.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the static and blackhole MAC address entries are created in the list successfully. Host A cannot ping the client.
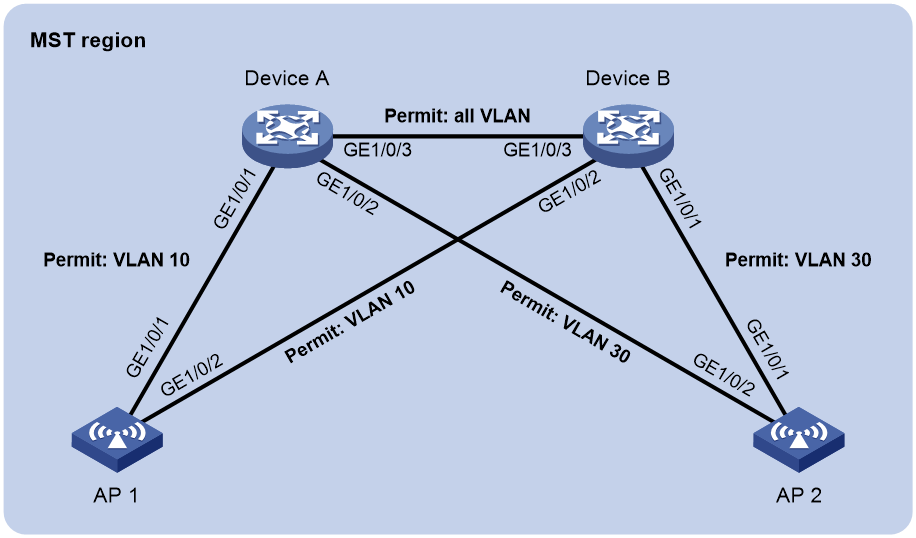
MSTP configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 17, all devices belong to the MST region. Device A and Device B are in the aggregation layer and AP 1 and AP 2 are in the access layer. Configure MSTP to enable packets in VLAN 10 to be forwarded along MSTI 1 and packets in VLAN 30 to be forwarded along MSTI 2.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure VLANs. From the left navigation pane, select Network Configuration > VLAN. Perform the following tasks:
¡ Configure VLANs on device A:
- Created VLAN 10 and VLAN 30.
- Access the VLAN 10 details page and add interfaces GigabitEthernet1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet1/0/3 to the tagged port list of VLAN 10.
- Access the VLAN 30 details page and add interfaces GigabitEthernet1/0/2 and GigabitEthernet1/0/3 to the tagged port list of VLAN 30.
¡ Configure VLANs on device B:
- Created VLAN 10 and VLAN 30.
- Access the VLAN 10 details page, add interfaces GigabitEthernet1/0/2 and GigabitEthernet1/0/3 to the tagged port list of VLAN 10.
- Access the VLAN 30 details page, add interfaces GigabitEthernet1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet1/0/3 to the tagged port list of VLAN 30.
¡ Configure VLANs on AP 1:
- Created VLAN 10.
- Access the VLAN 10 details page, add interfaces GigabitEthernet1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet1/0/2 to the tagged port list of VLAN 10.
¡ Configure VLANs on AP 2:
- Created VLAN 30.
- Access the VLAN 30 details page, add interfaces GigabitEthernet1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet1/0/2 to the tagged port list of VLAN 30.
2. Configure MSTP. From the left navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Network Links > STP. Perform the following tasks:
¡ Enable STP globally.
¡ Set the operation mode to MSTP for Device A, Device B, AP 1, and AP 2.
¡ On the MST region page for Device A, Device B, AP 1, and AP 2, configure the region name as Web, map VLAN 10 and VLAN 30 to MSTI 1 and MSTI 2, respectively and configure the MSTP revision level as 0.
Verifying the configuration
# Check the port roles and port states from the spanning tree status.
Routing configuration examples
IPv4 static route configuration example
Network requirements
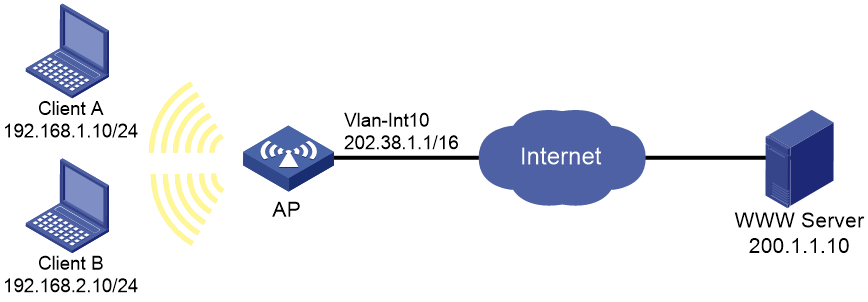
As shown in Figure 18, configure IPv4 static routes on the AP for the client to communicate with the WWW server.
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Network Routing > Static Routing.
2. Click IPv4 static routing.
3. Configure the default route:
¡ Set the destination IP address to 0.0.0.0.
¡ Set the mask length to 0.
¡ Set the next hop address to 192.168.2.2.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the client can access the WWW server.
IPv6 static route configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 19, configure IPv6 static routes on the AP for the client to communicate with the WWW server.
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Network Routing > Static Routing.
2. Click IPv6 static routing.
3. Configure the IPv6 default route:
¡ Set the destination IP address to ::.
¡ Set the mask length to 0.
¡ Set the next hop address to 4::2.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the client can access the WWW server.
IP configuration examples
Outbound dynamic NAT configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 20, a company has a private address 192.168.0.0/16 and two public IP addresses 202.38.1.2 and 202.38.1.3. Configure outbound dynamic NAT to allow only internal users on subnet 192.168.1.0/24 to access the Internet.
Configuration procedures
1. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > IP > NAT.
2. Click the add icon.
3. On the New Dynamic NAT Rule page, perform the following tasks:
a. Add ACL 2000 to permit packets only from subnet 192.168.1.0/24 to pass through.
b. Add address group 0, and add an address range from 202.38.1.2 to 202.38.1.3 to the group.
4. Apply the dynamic NAT rule to Vlan-interface 10.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that Client A can access the WWW server, but Client B cannot. (Details not shown.)
Outbound static NAT configuration example
Network requirements
Configure static NAT to enable the client to access the WWW server on the external network.
Figure 21 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation tree, select Network Configuration > IP > NAT.
2. Click Static NAT.
3. Click the Rules tab.
5. Select the Host to host translation mode.
6. Enter 192.168.1.10 in the private address field and 202.38.1.100 in the public address field.
7. Click Apply.
8. Click the Apply tab.
9. Select interface Vlan-interface 10.
10. Click Apply.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the client can access the WWW server on the external network.
Proxy ARP configuration example
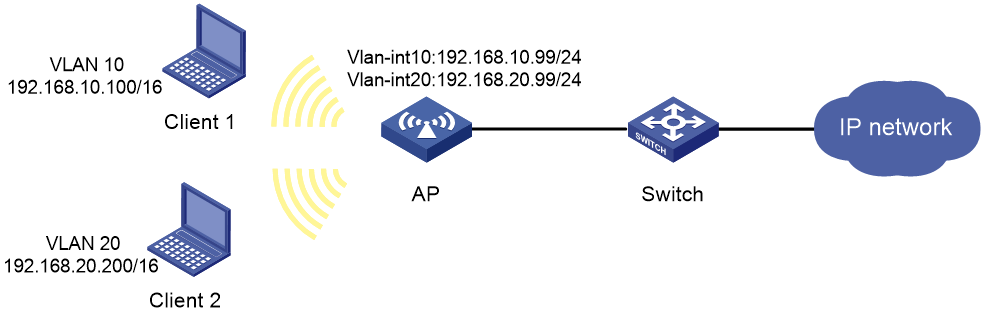
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 22, Client 1 and Client 2 have the same IP prefix and mask, but they are located on different subnets separated by the AP. Client 1 belongs to VLAN 10, and Client 2 belongs to VLAN 20. No default gateway is configured on Client 1 and Client 2.
Configure proxy ARP on the AP to enable communication between the two clients.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure VLAN 10 and VLAN 20, and assign IP addresses to VLAN-interface 10 and VLAN-interface 20:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Network Links > VLAN.
b. Create VLAN 10, and assign IP address 192.168.10.99/24 to VLAN-interface 10.
c. Create VLAN 20, and assign IP address 192.168.20.99/24 to VLAN-interface 20.
2. Enable proxy ARP on VLAN-interface 10 and VLAN-interface 20.
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > IP > ARP.
b. Access the advanced settings page to configure proxy ARP.
- Enable proxy ARP on VLAN-interface 10.
- Enable proxy ARP on VLAN-interface 20.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that Client 1 and Client 2 can ping each other successfully.
IPv4 static DNS configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 23, configure a static DNS entry on the AP, so the AP can use the domain name host.com to access the host at 10.1.1.2.
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > IP > IPv4 DNS.
2. On the Manual tab, create a static DNS entry:
¡ Configure the host name as host.com.
¡ Configure the IPv4 address as 10.1.1.2.
Verifying the configuration
Use the ping host.com command on the AP to verify the following items:
· The ping operation succeeds.
· The AP can use static domain name resolution to resolve the domain name host.com into the IPv4 address 10.1.1.2.
IPv4 dynamic DNS configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 24, the DNS server at 2.1.1.2/16 has a com domain that stores the mapping between the domain name host and the IPv4 address 3.1.1.1/16.
Configure dynamic DNS and the DNS suffix com on the AP that acts as a DNS client. The AP can use the domain name host to access the host whose domain name is host.com and IPv4 address is 3.1.1.1/16.
Configuration procedure
1. Map the domain name host.com to the IPv4 address 3.1.1.1 on the DNS server. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure static routes or dynamic routing protocols on the devices to make sure the devices can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure DNS client on the AP:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > IP > IPv4 DNS.
b. Specify the DNS server address 2.1.1.2.
c. Access the advanced settings page and add the domain name suffix com.
Verifying the configuration
Use the ping host command on the AP to verify the following items:
· The ping operation succeeds.
· The AP can resolve the domain name host.com into the IPv4 address 3.1.1.1 through the DNS server.
IPv4 DNS proxy configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 25, the LAN has a large number of devices deployed. The devices access the DNS server for domain name resolution. If the DNS server's IP address changes, the administrator must modify the DNS server address on each device, which takes a lot of time.
To simplify the configuration, configure the AP as the DNS proxy. Specify the real DNS server address on the AP. Specify the DNS proxy address as the DNS server address on the other devices. If the DNS server address changes, the administrator only needs to modify the DNS server address on the DNS proxy.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure static routes or dynamic routing protocols on the devices to make sure the devices can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the DNS server. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure DNS proxy on the AP:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > IP > IPv4 DNS.
b. Specify the DNS server address 4.1.1.1.
c. On the advanced settings page, enable DNS proxy.
4. Configure DNS clients.
Specify the DNS proxy address 2.1.1.2 as the DNS server address on the other devices that act as DNS clients.
Verifying the configuration
Use the ping host.com command on a DNS client to verify the following items:
· The ping operation succeeds.
· The client can resolve the domain name host.com into the IPv4 address 3.1.1.1 through the DNS server.
IPv6 configuration examples
Static IPv6 address configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 26, the client generates an IPv6 address through stateless address autoconfiguration.
Assign a global unicast IPv6 address to VLAN-interface 1 of the AP.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure wireless service and AP settings. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure an IPv6 address for VLAN-interface 1:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > IPv6 > IPv6.
b. Access the details page for VLAN-interface 1 to perform the following tasks:
- Configure the IPv6 address of the interface as 2001::1.
- Set the prefix length to 64.
3. Configure VLAN-interface 1 to advertise RA messages.
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > IPv6 > ND.
b. Access the advanced settings page to configure the RA settings.
c. Configure VLAN-interface 1 to advertise RA messages.
4. Install IPv6 on the client. The client automatically generates an IPv6 address based on the address prefix information contained in the RA message.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the client and the AP can ping each other successfully.
IPv6 static DNS configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 27, configure a static DNS entry on the AP, so the AP can use the domain name host.com to access the host at 1::2.
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > IPv6 > IPv6 DNS.
2. Create a static DNS entry:
¡ Configure the host name as host.com.
¡ Configure the IPv6 address as 1::2.
Verifying the configuration
Use the ping ipv6 host.com command on the AP to verify the following items:
· The ping operation succeeds.
· The AP can use static domain name resolution to resolve the domain name host.com into the IPv6 address 1::2.
IPv6 dynamic DNS configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 28, the DNS server at 2::2/64 has a com domain that stores the mapping between the domain name host and the IPv6 address 1::1/64.
Configure dynamic DNS and the DNS suffix com on the AP that acts as a DNS client. The AP can use the domain name host to access the host whose domain name is host.com and IPv6 address is 1::1/64.
Configuration procedure
1. Map the domain name host.com to the IPv6 address 1::1 on the DNS server. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure static routes or dynamic routing protocols on the devices to make sure the devices can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure DNS client on the AP:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > IPv6 > IPv6 DNS.
b. Specify the DNS server address 2::2.
c. Access the advanced settings page and add the domain name suffix com.
Verifying the configuration
Use the ping ipv6 host command on the AP to verify the following items:
· The ping operation succeeds.
· The AP can resolve the domain name host.com into the IPv6 address 1::1 through the DNS server.
IPv6 DNS proxy configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 29, the LAN has a large number of devices deployed. The devices access the DNS server for domain name resolution. If the DNS server's IPv6 address changes, the administrator must modify the DNS server address on each device, which takes a lot of time.
To simplify the configuration, configure the AP as the DNS proxy. Specify the real DNS server address on the AP. Specify the DNS proxy address as the DNS server address on the other devices. If the DNS server address changes, the administrator only needs to modify the DNS server address on the DNS proxy.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure static routes or dynamic routing protocols on the devices to make sure the devices can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the DNS server. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure DNS proxy on the AP:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > IPv6 > IPv6 DNS.
b. Specify the DNS server address 4000::1.
c. On the advanced settings page, enable DNS proxy.
4. Configure DNS clients.
Specify the DNS proxy address 2000::2 as the DNS server address on the other devices that act as DNS clients.
Verifying the configuration
Use the ping ipv6 host.com command on a DNS client to verify the following items:
· The ping operation succeeds.
· The client can resolve the domain name host.com into the IPv6 address 3000::1 through the DNS server.
Management protocol configuration examples
DHCP server configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 30, the DHCP server (AP) assigns IP addresses to the switch and DHCP client on subnet 10.1.1.0/24, which is subnetted into 10.1.1.0/25 and 10.1.1.128/25. The AP is connected to the client and the switch through two VLAN interfaces: VLAN-interface 10 at 10.1.1.1/25 and VLAN-interface 20 at 10.1.1.129/25.
Configure DHCP server on the AP to assign an IP address on subnet 10.1.1.0/25 to the switch and IP addresses on subnet 10.1.1.128/25 to the DHCP client.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure VLANs and VLAN interfaces:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Network Links > VLAN.
b. Create VLANs and VLAN interfaces:
- Create VLAN 10 and VLAN-interface 10.
- Create VLAN 20 and VLAN-interface 20.
c. Access Network Configuration > Network Interfaces > Interfaces, click Edit for the target interface and click IP address/Mask:
- Assign IP address 10.1.1.1/25 to VLAN-interface 10.
- Assign IP address 10.1.1.129/25 to VLAN-interface 20.
2. Configure the DHCP server:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Management Protocols > DHCP.
b. Enable DHCP.
c. Specify VLAN-interface 10 and VLAN-interface 20 as DHCP servers.
d. Click the address pool link and perform the following tasks:
- Create the address pool pool1, specify 10.1.1.0/25 as the subnet for dynamic assignment, and specify 10.1.1.1 as the gateway.
- Create the address pool pool2, specify 10.1.1.128/25 as the subnet for dynamic assignment, and specify 10.1.1.129 as the gateway.
e. Access the advanced settings page to perform the following tasks:
- Set the maximum number of ping packets to 1.
- Set the ping response timeout time to 500 milliseconds.
3. Configure a wireless service:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Add a wireless service:
- Create a wireless service named service.
- Set the SSID to office.
- Specify the default VLAN 20.
- Enable the wireless service.
4. Configure the AP:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Bind service service to the 5 GHz radio of the AP.
5. Configure the AP radio:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Radio Management > Radio Configuration.
b. Set the status of the 5 GHz radio of the AP to On.
Verifying the configuration
1. Verify that the switch can obtain an IP address on subnet 10.1.1.0/25 and the gateway address from the DHCP server.
2. Verify that the DHCP client can obtain IP addresses on subnet 10.1.1.128/25 and the gateway address from the DHCP server.
DHCP relay agent configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 31, the DHCP client and the DHCP server are in different subnets. The DHCP client resides in subnet 10.10.1.0/24 and the DHCP server is at 10.1.1.1/24. An AP is deployed between the DHCP clients and the DHCP server. The AP is connected to the network in which the DHCP client resides through VLAN-interface 10 at 10.10.1.1/24. The AP is connected to the DHCP server through VLAN-interface 20 at 10.1.1.2/24.
Configure the DHCP relay agent on the AP, so the DHCP client can obtain an IP address and other configuration parameters from the DHCP server.
Configuration procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the DHCP server. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure basic settings on the AP. (Details not shown.)
4. Configure the DHCP relay agent:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Management Protocols > DHCP.
b. Perform the following tasks:
- Enable DHCP.
- Specify VLAN-interface 10 as the DHCP relay agent.
- Specify the DHCP server address 10.1.1.1.
Verifying the configuration
Verify that the DHCP client can obtain an IP address and other configuration parameters from the DHCP server through the DHCP relay agent.
NTP configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 32:
· Configure the local clock of AP 1 as a reference source, with the stratum level 2.
· Set AP 2 to client mode and use AP 1 as the NTP server for AP 2.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure AP 1 (NTP server):
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Management Protocols > NTP.
b. Enable the NTP service.
c. Specify the IP address of the local clock as 127.127.1.0.
d. Configure the stratum level of the local clock as 2.
2. Configure AP 2:
a. From the navigation pane, select System > Management > Settings.
b. Select automatic time synchronization with a trusted time source, and then select NTP as the time protocol.
c. Specify the IP address of Device A as 1.0.1.11, and configure Device B to operate in server mode.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that AP 2 has synchronized to AP 1, and the clock stratum level is 3 on AP 2 and 2 on AP 1.
LLDP configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 33, configure LLDP on the AP and the switch to meet the following requirements:
· The AP can discover the switch and can obtain the system and configuration information of the switch.
· The switch cannot discover the AP.
Configuration procedure
1. From the left navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Management Protocols > LLDP.
2. Configure LLDP settings on the AP:
¡ Enable LLDP globally on the AP.
¡ Access the interface status page, enable LLDP on interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1.
¡ Access the interface settings page, enable nearest bridge agent on interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 and set the interface operation mode to Rx. This enables the AP to only receive LLDP packets and discover neighbors.
3. Configure LLDP settings on the switch:
¡ Enable LLDP globally on the switch.
¡ Access the interface status page, enable LLDP on interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2.
¡ Access the interface settings page, enable nearest bridge agent on interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 and set the interface operation mode to Tx. This enables the switch to only send LLDP packets and disables the switch to discover neighbors.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that you can see the switch information on the LLDP neighbors page of the AP, which indicates that the neighbor relationship is established, and you cannot see any neighbor information on the LLDP neighbors page of the switch.
Network security configuration examples
Access control configuration examples
ACL-based packet filter configuration example
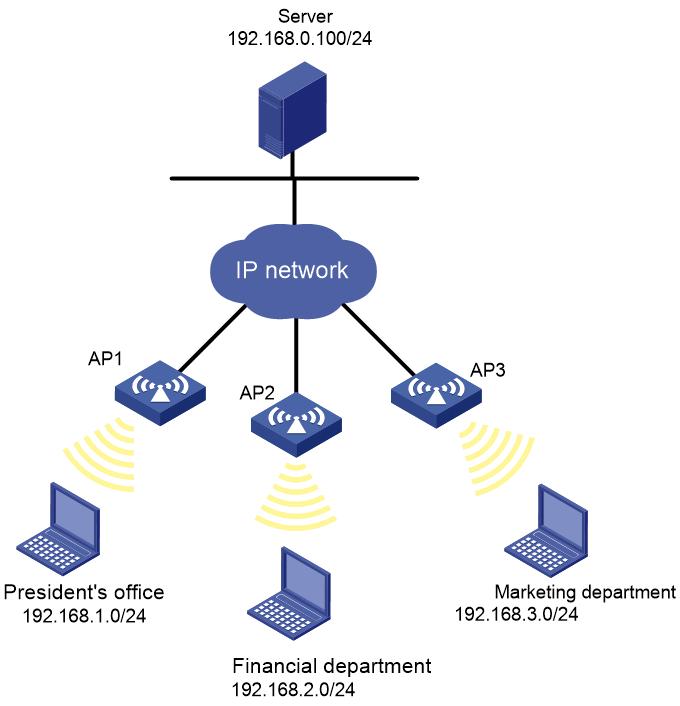
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 34, a company interconnects its departments through the APs. Configure the packet filter on the APs to meet the following requirements:
· Permit access from the President's office at any time to the financial database server.
· Permit access from the Financial Department to the financial database server only during working hours (from 8:00 to 18:00) on working days.
· Deny access from any other department to the financial database server.
Configuration procedure
1. From the navigation pane, select Network Security > Traffic Policy > Packet Filter.
2. Create a packet filter policy:
a. Select the uplink Ethernet interface GE1/0/1.
b. Select the outbound application direction.
c. Select the IPv4 ACL type for packet filter.
3. Create an advanced IPv4 ACL and configure the following rules in the order they are described:
|
Action |
Protocol type |
IP/wildcard mask |
Time range |
|
Permit |
256 |
Source: 192.168.1.0/0.0.0.255 Destination: 192.168.0.100/0 |
N/A |
|
Permit |
256 |
Source: 192.168.2.0/0.0.0.255 Destination: 192.168.0.100/0 |
Create a time range named work: · Specify the start time as 08:00. · Specify the end time as 18:00. · Select Monday through Friday. |
|
Deny |
256 |
Destination: 192.168.0.100/0 |
N/A |
4. Enable rule match counting for the ACL.
Verifying the configuration
1. Ping the database server from different departments to verify the following items:
¡ You can access the server from the President's office at any time.
¡ You can access the server from the Financial Department during the working hours on working days.
¡ You cannot access the server from the Marketing Department at any time.
2. Access the ACL rule Web interface, verify that the ACL rules are active and the number of matching packets is displayed.
Access authentication configuration examples
802.1X RADIUS authentication configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 35, configure the AP to meet the following requirements:
· Use the RADIUS server to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting for 802.1X users.
· Authenticate all 802.1X users who access the AP through GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 in the ISP domain dm1X.
· Exclude domain names from the usernames sent to the RADIUS server.
· Use name as the authentication and accounting shared keys for secure RADIUS communication between the AP and the RADIUS server.
· Use ports 1812 and 1813 for authentication and accounting, respectively.
Configuration procedure
1. Assign an IP address to each interface, as shown in Figure 35. (Details not shown.)
2. On the AP, Configure a RADIUS scheme on the AP:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Security > AAA > RADIUS.
b. Add and configure a RADIUS scheme:
- Set the name of the RADIUS scheme to 802.1X.
- Configure the primary authentication server: set its IP address to 10.1.1.1, set the port number to 1812, set the shared key to name, and set the state to Active.
- Configure the primary accounting server: set its IP address to 10.1.1.1, set the port number to 1813, set the shared key to name, and set the state to Active.
- Set the format of usernames sent to the RADIUS server to Excludes the domain name.
3. Configure an ISP domain on the AP:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Security > AAA > ISP Domains.
b. Add and configure an ISP domain:
- Set the domain name to dm1X.
- Set the ISP domain state to Active.
- Set the service type to LAN access.
- Set the method and scheme for authentication, authorization, and accounting to RADIUS and 802.1X, respectively.
4. Configure 802.1X on the AP:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration. Click Add.
b. In the basic settings area, configure the service name and the SSID.
c. In the authentication settings area, select 802.1X and specify the domain name dm1X.
d. Click Apply.
5. Configure the RADIUS server:
¡ Add a user account on the server. (Details not shown.)
¡ Configure the authentication, authorization, and accounting settings. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
1. Access the Network Security > AAA > RADIUS page to verify brief information of the RADIUS scheme 802.1X.
2. Access the Network Security > AAA > ISP Domains page to verify brief information of the ISP domain dm1X.
3. Verify that the use can come online:
a. Use the configured username and password to log in.
b. Access the Network Security > Authentication > 802.1X page to verify that the number of online users is 1 on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
802.1X local authentication configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 36, add a user account with the username dotuser and password 12345 on the AP. Configure the AP to meet the following requirements:
· Perform local 802.1X authentication to control the network access of users on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
· Authenticate the users in the ISP domain abc.
· Specify port-based access control on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. After a user passes authentication on the port, all subsequent users can access the network without authentication.
Configuration procedure
1. Assign an IP address to each interface, as shown in Figure 36. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure a local user:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Security > User Management > Local Users.
b. Add and configure a local user:
- Set the username to dotuser.
- Set the password to 12345.
- Set the service type to LAN access.
3. Configure an ISP domain:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Security > AAA > ISP Domains.
b. Add and configure an ISP domain:
- Set the ISP domain name to abc.
- Set the ISP domain state to Active.
- Set the service type to LAN access.
- Configure the ISP domain to use local method for authentication and authorization of LAN users, and not perform accounting for LAN users.
4. Configure 802.1X:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration. Click Add.
b. In the basic settings area, configure the service name and the SSID.
c. In the authentication settings area, select 802.1X and specify the domain name abc.
d. Click Apply.
Verifying the configuration
1. Access the Network Security > User Management > Local Users page to verify the configuration of the local user dotuser.
2. Access the Network Security > AAA > ISP Domains page to verify brief information of the ISP domain abc.
3. Verify that the use can come online:
a. Use the configured username and password to log in.
b. Access the Network Security > Authentication > 802.1X page to verify that the number of online users is 1 on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
802.1X AKM configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 37, the switch functions as a DHCP server to assign IP addresses to the AP and client.
· Configure open system authentication and 802.1X authentication so that the client can access the network by using the login username abcdef and password 123456.
· Configure 802.1X as the AKM mode.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure the username abcdef and the password 123456 on the RADIUS server and make sure the RADIUS server and AP can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure RADIUS and an authentication domain.
3. Configure a wireless service:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Add a wireless service:
- Create a wireless service named service1.
- Set the SSID to service.
- Enable the wireless service.
4. Click Apply and Configure Advanced Settings, and then click the Authentication tab.
5. Configure 802.1X authentication:
¡ Set the security type to 802.1X authentication.
¡ Set the security mode to WPA.
¡ Select the CCMP cipher suite.
¡ Set the domain name to dom1.
6. Apply the wireless service.
7. Bind the wireless service service1 to the radio:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Select service service1 and click Bind to Radio.
c. Select the 5GHz radio of the AP and then click Bind.
Verifying the configuration
# View details about the wireless service service1 to verify that the configuration is correct.
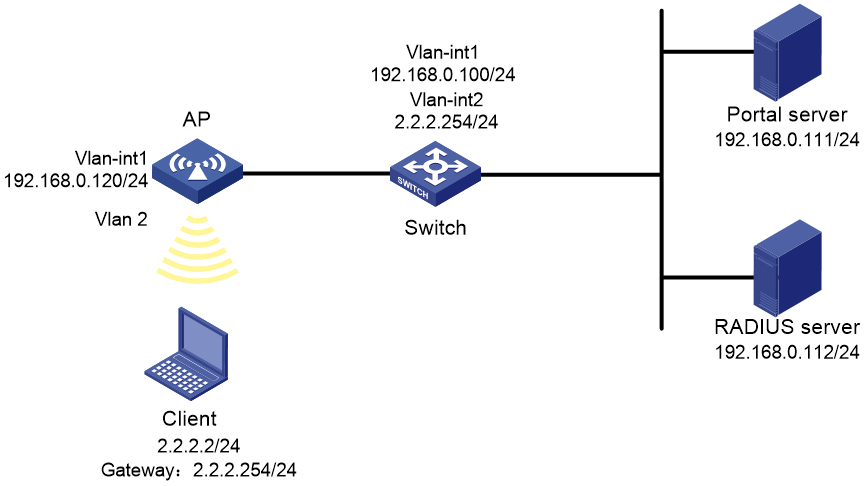
Direct IPv4 portal authentication configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 38, the AP directly forwards user traffic from the client. The client is assigned with a public IP address either manually or through DHCP. A portal server acts as both a portal authentication server and a portal Web server. A RADIUS server acts as the authentication/accounting server.
Configure direct portal authentication, so the client can access only the portal Web server before passing the authentication and access Internet resources after passing the authentication.
Configuration procedures
1. Configure IP addresses for the client, AP, and servers as shown in Figure 38 and make sure they can reach each other.
2. Configure the RADIUS server correctly to provide authentication and accounting functions.
3. Configure RADIUS and an authentication domain.
· Configure a wireless service:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Add a wireless service:
- Create a wireless service named service1.
- Set the SSID to service.
- Enable the wireless service.
4. Configure the portal authentication mode:
a. Click the edit icon for wireless service service1.
The advanced settings page opens.
b. Click the Authentication tab.
c. Select IPv4 Portal Authentication.
d. Set the domain name to dm1.
e. Set the server URL to newpt.
f. Set the BAS-IP to 192.168.0.110.
g. Click Apply.
5. Bind the wireless service1 to the radio:
a. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Services > Wireless Services Configuration.
b. Select service service1 and click Bind to Radio.
c. Select the 5GHz radio of the AP and then click Bind.
Verifying the configuration
# View details about the service service1 to verify that the configuration is correct.
System feature configuration examples
Device management configuration examples
Administrators configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 39, configure an administrator account with the username webuser and password 12345 on the AP to meet the following requirements:
· Allow the user to use the account to log in to the AP through HTTP.
· Perform local authentication for the user that uses the administrator account to log in to the AP.
· Assign the network-admin user role to the authenticated user.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure the VLAN and VLAN interface:
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Network Links > VLAN.
b. Create VLAN 2.
c. Access the edit page for VLAN 2 to perform the following tasks:
- Add the interface that connects to the admin's PC to the tagged port list.
- Create VLAN-interface 2.
- Assign the IP address 192.168.1.20/24 to VLAN-interface 2.
2. Configure an administrator account:
a. From the navigation pane, select System > Management > Administrators.
b. Create and configure an administrator account:
- Set the username and the password to webuser and hello12345, respectively.
- Select the network-admin user role.
- Specify HTTP and HTTPS as the permitted access types.
Verifying the configuration
1. Access the System > Management > Administrators page to verify that the administrator account is successfully added.
2. Enter http://192.168.1.20 in the address bar to verify the following items:
¡ You can use the administrator account to log in to the Web interface.
¡ After login, you can configure the device.
Local SSH server configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 40, configure the AP as a Stelnet server and the host as a Stelnet client, and establish an SSH connection between the two devices to meet the following requirements:
· The AP and host can reach each other. The AP uses password authentication to verify the host and the authentication process is finished on the AP locally.
· The network administrator can log in to the host with username client and password hello12345 and can perform all operations supported on the device.
|
|
NOTE: Stelnet client software has various types such as PuTTY and OpenSSH. This section takes PuTTY0.58 as an example to configuration a Stelnet client. |
Configuration procedure
1. Configure the SSH service. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Management Protocols > SSH. Enable the Stelnet service.
2. Configure VLANs and VLAN interfaces.
a. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Network Links > VLAN.
b. Create VLAN 2.
c. Access the edit page for VLAN 2 to perform the following tasks:
- Add interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 to the tagged port list.
- Create VLAN-interface 2.
- Assign the IP address 192.168.1.40/24 to VLAN-interface 2.
3. Configure an administrator account:
a. From the navigation pane, select System > Management > Administrators.
b. Create and configure an administrator account:
- Set the username and the password to client and hello12345, respectively.
- Select the network-admin user role.
- Specify SSH as the permitted access type.
Verifying the configuration
1. Run PuTTY.exe on the host.
2. Enter the Stelnet server IP address in the Host Name (or IP address) field and click Open.
3. Verify that you can use the username client and password hello12345 to access the AP configuration page successfully.