- Table of Contents
-
- 08-Radio Resources Management Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Radio management configuration
- 02-WLAN radio load balancing configuration
- 03-WLAN load balancing configuration
- 04-WLAN radio resource measurement configuration
- 05-Band navigation configuration
- 06-WLAN RRM configuration
- 07-Channel scanning configuration
- 08-Spectrum management configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-Radio management configuration | 411.96 KB |
1 Configuring radio management
Restrictions and guidelines: Radio management configuration
Radio management tasks at a glance
Enabling or disabling all radios
Enabling a radio to disable wireless services as scheduled
Configuring basic radio functions
Configuring 2.4 GHz radios to use the European channel gap for auto channel selection
Configuring the channel selection blacklist or whitelist
Setting the maximum transmit power
Setting the hardware retransmission limits
Setting the maximum number of clients that can associate with an AP
Configuring access services for 802.11b clients
Configuring 802.11g protection
Setting the maximum transmission distance
Enabling the continuous mode for a radio
Performing on-demand channel usage measurement
Setting the channel usage alarm threshold
Restoring the default bandwidth mode for all radios
Setting the channel calibration interval for supplement APs
Configuring the A-MPDU aggregation method
Configuring the A-MSDU aggregation method
Configuring the client dot11n-only feature
Setting the 802.11n bandwidth mode
Configuring 802.11n protection
Configuring 802.11ac functions
Configuring the client dot11ac-only feature
Setting the 802.11ac bandwidth mode
Configuring 802.11ax functions
Hardware compatibility with 802.11ax functions
Configuring the client dot11ax-only feature
Setting the 802.11ax bandwidth mode
Configuring the smart antenna feature
Configuring error packet ratio optimization and retransmission ratio optimization
Setting the radio channel usage threshold
Enabling radio environment monitoring
Display and maintenance commands for radio management
Radio management configuration examples
Example: Configuring basic radio functions
1 Configuring radio management
WA530 series and WA5500 series access points do not support the 802.11ax and 802.11gax radio types.
About radio management
Radio frequency (RF) is a rate of electrical oscillation in the range of 300 KHz to 300 GHz. WLAN uses the 2.4 GHz band and 5 GHz band radio frequencies as the transmission media. The 2.4 GHz band includes radio frequencies from 2.4 GHz to 2.4835 GHz. The 5 GHz band includes radio frequencies from 5.150 GHz to 5.350 GHz and from 5.725 GHz to 5.850 GHz.
The term "radio frequency" or its abbreviation RF is also used as a synonym for "radio" in wireless communication.
Radio mode
|
|
NOTE: · 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11ax are backward compatible. · In this document, the term "802.11ac" refers to both 802.11ac and 802.11gac and the term "802.11ax" refers to both 802.11ax and 802.11gax, unless otherwise specified. |
Table1-1 provides a comparison of these radio modes.
Table1-1 Comparison of 802.11 standards
|
IEEE standard |
Frequency band |
Maximum rate |
|
802.11a |
5 GHz |
54 Mbps |
|
802.11b |
2.4 GHz |
11 Mbps |
|
802.11g |
2.4 GHz |
54 Mbps |
|
802.11n |
2.4 GHz or 5 GHz |
600 Mbps |
|
802.11ac |
5 GHz |
6900 Mbps |
|
802.11gac |
2.4 GHz |
1600 Mbps |
|
802.11ax |
5 GHz |
9600 Mbps |
|
802.11gax |
2.4 GHz |
6900 Mbps |
Channel
A channel is a range of frequencies with a specific bandwidth.
The 2.4 GHz band has 14 channels. The bandwidth for each channel is 20 MHz and each two channels are spaced 5 MHz apart. Among the 14 channels, four groups of non-overlapping channels exist and the most commonly used one contains channels 1, 6, and 11.
The 5 GHz band can provide higher rates and is more immune to interference. There are 24 non-overlapping channels designated to the 5 GHz band. The channels are spaced 20 MHz apart with a bandwidth of 20 MHz. The available channels vary by country.
Transmit power
Transmit power reflects the signal strength of a wireless device. A higher transmit power enables a radio to cover a larger area but it brings more interference to adjacent devices. The signal strength decreases as the transmission distance increases.
Transmission rate
Transmission rate refers to the speed at which wireless devices transmit traffic. It varies by radio mode and spreading, coding, and modulation schemes. The following are rates supported by different types of radios:
· 802.11a—6 Mbps, 9 Mbps, 12 Mbps, 18 Mbps, 24 Mbps, 36 Mbps, 48 Mbps, and 54 Mbps.
· 802.11b—1 Mbps, 2 Mbps, 5.5 Mbps, and 11 Mbps.
· 802.11g—1 Mbps, 2 Mbps, 5.5 Mbps, 6 Mbps, 9 Mbps, 11 Mbps, 12 Mbps, 18 Mbps, 24 Mbps, 36 Mbps, 48 Mbps, and 54 Mbps.
· 802.11n—Rates for 802.11n radios vary by channel bandwidth. For more information, see "MCS."
· 802.11ac—Rates for 802.11ac radios vary by channel bandwidth and number of spatial streams (NSS). For more information, see "VHT-MCS."
· 802.11ax—Rates for 802.11ax radios vary by channel bandwidth and number of spatial streams (NSS). For more information, see "HE-MCS."
MCS
Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS) defined in IEEE 802.11n-2009 determines the modulation, coding, and number of spatial streams.
MCS types
802.11n MCSs are classified into the following types:
· Mandatory MCSs—Mandatory MCSs for an AP. To associate with an 802.11n AP, a client must support the mandatory MCSs for the AP.
· Supported MCSs—MCSs supported by an AP besides the mandatory MCSs. If a client supports both mandatory and supported MCSs, the client can use a supported rate to communicate with the AP.
· Multicast MCS—MCS for the rate at which an AP transmits multicast frames.
MCS parameters
An MCS is identified by an MCS index, which is represented by an integer in the range of 0 to 76. An MCS index is the mapping from MCS to a data rate.
Table1-2 through Table1-9 show sample MCS parameters for 20 MHz and 40 MHz.
When the bandwidth mode is 20 MHz, MCS indexes 0 through 15 are mandatory for APs, and MCS indexes 0 through 7 are mandatory for clients.
Table1-2 MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=1)
|
MCS index |
Number of spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
1 |
BPSK |
6.5 |
7.2 |
|
1 |
1 |
QPSK |
13.0 |
14.4 |
|
2 |
1 |
QPSK |
19.5 |
21.7 |
|
3 |
1 |
16-QAM |
26.0 |
28.9 |
|
4 |
1 |
16-QAM |
39.0 |
43.3 |
|
5 |
1 |
64-QAM |
52.0 |
57.8 |
|
6 |
1 |
64-QAM |
58.5 |
65.0 |
|
7 |
1 |
64-QAM |
65.0 |
72.2 |
Table1-3 MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=2)
|
MCS index |
Number of spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
|||
|
8 |
2 |
BPSK |
13.0 |
14.4 |
|
9 |
2 |
QPSK |
26.0 |
28.9 |
|
10 |
2 |
QPSK |
39.0 |
43.3 |
|
11 |
2 |
16-QAM |
52.0 |
57.8 |
|
12 |
2 |
16-QAM |
78.0 |
86.7 |
|
13 |
2 |
64-QAM |
104.0 |
115.6 |
|
14 |
2 |
64-QAM |
117.0 |
130.0 |
|
15 |
2 |
64-QAM |
130.0 |
144.4 |
Table1-4 MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=3)
|
MCS index |
Number of spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
|||
|
16 |
3 |
BPSK |
19.5 |
21.7 |
|
17 |
3 |
QPSK |
39.0 |
43.3 |
|
18 |
3 |
QPSK |
58.5 |
65.0 |
|
19 |
3 |
16-QAM |
78.0 |
86.7 |
|
20 |
3 |
16-QAM |
117.0 |
130.0 |
|
21 |
3 |
64-QAM |
156.0 |
173.3 |
|
22 |
3 |
64-QAM |
175.5 |
195.0 |
|
23 |
3 |
64-QAM |
195.0 |
216.7 |
Table1-5 MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=4)
|
MCS index |
Number of spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
|||
|
24 |
4 |
BPSK |
26.0 |
28.9 |
|
25 |
4 |
QPSK |
52.0 |
57.8 |
|
26 |
4 |
QPSK |
78.0 |
86.7 |
|
27 |
4 |
16-QAM |
104.0 |
115.6 |
|
28 |
4 |
16-QAM |
156.0 |
173.3 |
|
29 |
4 |
64-QAM |
208.0 |
231.1 |
|
30 |
4 |
64-QAM |
234.0 |
260.0 |
|
31 |
4 |
64-QAM |
260.0 |
288.9 |
Table1-6 MCS parameters (40 MHz, NSS=1)
|
MCS index |
Number of spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
1 |
BPSK |
13.5 |
15.0 |
|
1 |
1 |
QPSK |
27.0 |
30.0 |
|
2 |
1 |
QPSK |
40.5 |
45.0 |
|
3 |
1 |
16-QAM |
54.0 |
60.0 |
|
4 |
1 |
16-QAM |
81.0 |
90.0 |
|
5 |
1 |
64-QAM |
108.0 |
120.0 |
|
6 |
1 |
64-QAM |
121.5 |
135.0 |
|
7 |
1 |
64-QAM |
135.0 |
150.0 |
Table1-7 MCS parameters (40 MHz, NSS=2)
|
MCS index |
Number of spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
|||
|
8 |
2 |
BPSK |
27.0 |
30.0 |
|
9 |
2 |
QPSK |
54.0 |
60.0 |
|
10 |
2 |
QPSK |
81.0 |
90.0 |
|
11 |
2 |
16-QAM |
108.0 |
120.0 |
|
12 |
2 |
16-QAM |
162.0 |
180.0 |
|
13 |
2 |
64-QAM |
216.0 |
240.0 |
|
14 |
2 |
64-QAM |
243.0 |
270.0 |
|
15 |
2 |
64-QAM |
270.0 |
300.0 |
Table1-8 MCS parameters (40 MHz, NSS=3)
|
MCS index |
Number of spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
|||
|
16 |
3 |
BPSK |
40.5 |
45.0 |
|
17 |
3 |
QPSK |
81.0 |
90.0 |
|
18 |
3 |
QPSK |
121.5 |
135.0 |
|
19 |
3 |
16-QAM |
162.0 |
180.0 |
|
20 |
3 |
16-QAM |
243.0 |
270.0 |
|
21 |
3 |
64-QAM |
324.0 |
360.0 |
|
22 |
3 |
64-QAM |
364.5 |
405.0 |
|
23 |
3 |
64-QAM |
405.0 |
450.0 |
Table1-9 MCS parameters (40 MHz, NSS=4)
|
MCS index |
Number of spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
|||
|
24 |
4 |
BPSK |
54.0 |
60.0 |
|
25 |
4 |
QPSK |
108.0 |
120.0 |
|
26 |
4 |
QPSK |
162.0 |
180.0 |
|
27 |
4 |
16-QAM |
216.0 |
240.0 |
|
28 |
4 |
16-QAM |
324.0 |
360.0 |
|
29 |
4 |
64-QAM |
432.0 |
480.0 |
|
30 |
4 |
64-QAM |
486.0 |
540.0 |
|
31 |
4 |
64-QAM |
540.0 |
600.0 |
|
|
NOTE: · For all the MCS data rate tables, see IEEE 802.11n-2009. · Support for MCS indexes depends on the device model. |
VHT-MCS
Very High Throughput Modulation and Coding Scheme (VHT-MCS) defined in IEEE 802.11ac determines the wireless data rates.
VHT-MCS types
802.11ac VHT-MCSs are classified into the following types:
· Mandatory VHT-MCSs—Mandatory VHT-MCSs for an AP. To associate with an 802.11ac AP, a client must support the mandatory VHT-MCSs for the AP.
· Supported VHT-MCSs—VHT-MCSs supported by an AP besides the mandatory VHT-MCSs. If a client supports both mandatory and supported VHT-MCSs, the client can use a supported rate to communicate with the AP.
· Multicast VHT-MCS—VHT-MCS for the rate at which an AP transmits multicast frames.
VHT-MCS parameters
A VHT-MCS is identified by a VHT-MCS index, which is represented by an integer in the range of 0 to 9. A VHT-MCS index is the mapping from VHT-MCS to a data rate.
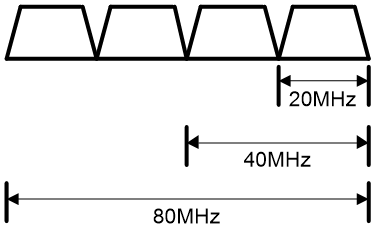
802.11ac supports the 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, and 160 MHz (80+80 MHz) bandwidth modes, and supports a maximum of eight spatial streams. 802.11gac supports the 20 MHz and 40 MHz bandwidth modes.
Table1-10 through Table1-21 show VHT-MCS parameters that are supported by an AP.
Table1-10 VHT-MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=1)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
6.5 |
7.2 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
13.0 |
14.4 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
19.5 |
21.7 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
26.0 |
28.9 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
39.0 |
43.3 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
52.0 |
57.8 |
|
6 |
64-QAM |
58.5 |
65.0 |
|
7 |
64-QAM |
65.0 |
72.2 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
78.0 |
86.7 |
|
9 |
Not valid |
||
Table1-11 VHT-MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=2)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
13.0 |
14.4 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
26.0 |
28.9 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
39.0 |
43.3 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
52.0 |
57.8 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
78.0 |
86.7 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
104.0 |
115.6 |
|
6 |
64-QAM |
117.0 |
130.0 |
|
7 |
64-QAM |
130.0 |
144.4 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
156.0 |
173.3 |
|
9 |
Not valid |
||
Table1-12 VHT-MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=3)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
19.5 |
21.7 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
39.0 |
43.3 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
58.5 |
65.0 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
78.0 |
86.7 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
117.0 |
130.0 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
156.0 |
173.3 |
|
6 |
64-QAM |
175.5 |
195.0 |
|
7 |
64-QAM |
195.0 |
216.7 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
234.0 |
260.0 |
|
9 |
256-QAM |
260.0 |
288.9 |
Table1-13 VHT-MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=4)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
26.0 |
28.9 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
52.0 |
57.8 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
78.0 |
86.7 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
104.0 |
115.6 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
156.0 |
173.3 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
208.0 |
231.1 |
|
6 |
64-QAM |
234.0 |
260.0 |
|
7 |
64-QAM |
260.0 |
288.9 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
312.0 |
346.7 |
|
9 |
Not valid |
||
Table1-14 VHT-MCS parameters (40 MHz, NSS=1)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
13.5 |
15.0 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
27.0 |
30.0 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
40.5 |
45.0 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
54.0 |
60.0 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
81.0 |
90.0 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
108.0 |
120.0 |
|
6 |
64-QAM |
121.5 |
135.0 |
|
7 |
64-QAM |
135.0 |
150.0 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
162.0 |
180.0 |
|
9 |
256-QAM |
180.0 |
200.0 |
Table1-15 VHT-MCS parameters (40 MHz, NSS=2)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
27.0 |
30.0 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
54.0 |
60.0 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
81.0 |
90.0 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
108.0 |
120.0 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
162.0 |
180.0 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
216.0 |
240.0 |
|
6 |
64-QAM |
243.0 |
270.0 |
|
7 |
64-QAM |
270.0 |
300.0 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
324.0 |
360.0 |
|
9 |
256-QAM |
360.0 |
400.0 |
Table1-16 VHT-MCS parameters (40 MHz, NSS=3)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
40.5 |
45.0 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
81.0 |
90.0 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
121.5 |
135.0 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
162.0 |
180.0 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
243.0 |
270.0 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
324.0 |
360.0 |
|
6 |
64-QAM |
364.5 |
405.0 |
|
7 |
64-QAM |
405.0 |
450.0 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
486.0 |
540.0 |
|
9 |
256-QAM |
540.0 |
600.0 |
Table1-17 VHT-MCS parameters(40 MHz, NSS=4)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
54.0 |
60.0 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
108.0 |
120.0 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
162.0 |
180.0 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
216.0 |
240.0 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
324.0 |
360.0 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
432.0 |
480.0 |
|
6 |
64-QAM |
486.0 |
540.0 |
|
7 |
64-QAM |
540.0 |
600.0 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
648.0 |
720.0 |
|
9 |
256-QAM |
720.0 |
800.0 |
Table1-18 VHT-MCS parameters (80 MHz, NSS=1)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
29.3 |
32.5 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
58.5 |
65.0 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
87.8 |
97.5 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
117.0 |
130.0 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
175.5 |
195.0 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
234.0 |
260.0 |
|
6 |
64-QAM |
263.0 |
292.5 |
|
7 |
64-QAM |
292.5 |
325.0 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
351.0 |
390.0 |
|
9 |
256-QAM |
390.0 |
433.3 |
Table1-19 VHT-MCS parameters (80 MHz, NSS=2)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
58.5 |
65.0 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
117.0 |
130.0 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
175.5 |
195.0 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
234.0 |
260.0 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
351.0 |
390.0 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
468.0 |
520.0 |
|
6 |
64-QAM |
526.5 |
585.0 |
|
7 |
64-QAM |
585.0 |
650.0 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
702.0 |
780.0 |
|
9 |
256-QAM |
780.0 |
866.7 |
Table1-20 VHT-MCS parameters (80 MHz, NSS=3)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
87.8 |
97.5 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
175.5 |
195.0 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
263.3 |
292.5 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
351.0 |
390.0 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
526.5 |
585.0 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
702.0 |
780.0 |
|
6 |
Not valid |
||
|
7 |
64-QAM |
877.5 |
975.0 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
1053.0 |
1170.0 |
|
9 |
256-QAM |
1170.0 |
1300.0 |
Table1-21 VHT-MCS parameters (80 MHz, NSS=4)
|
VHT-MCS index |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
800ns GI |
400ns GI |
||
|
0 |
BPSK |
117.0 |
130.0 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
234.0 |
260.0 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
351.0 |
390.0 |
|
3 |
16-QAM |
468.0 |
520.0 |
|
4 |
16-QAM |
702.0 |
780.0 |
|
5 |
64-QAM |
936.0 |
1040.0 |
|
6 |
64-QAM |
1053.0 |
1170.0 |
|
7 |
64-QAM |
1170.0 |
1300.0 |
|
8 |
256-QAM |
1404.0 |
1560.0 |
|
9 |
256-QAM |
1560.0 |
1733.3 |
|
|
NOTE: · For all the VHT-MCS data rate tables, see IEEE 802.11ac-2013. · Support for VHT-MCS indexes depends on the AP model. |
HE-MCS
High Efficiency Modulation and Coding Scheme (HE-MCS) defined in IEEE 802.11ax determines the wireless data rates.
HE-MCS types
802.11ax HE-MCSs are classified into the following types:
· Mandatory HE-MCSs—Mandatory HE-MCSs for an AP. To associate with an 802.11ax AP, a client must support the mandatory HE-MCSs for the AP.
· Supported HE-MCSs—HE-MCSs supported by an AP besides the mandatory HE-MCSs. If a client supports both mandatory and supported HE-MCSs, the client can use a supported rate to communicate with the AP.
· Multicast HE-MCS—HE-MCS for the rate at which an AP transmits multicast frames.
HE-MCS parameters
An HE-MCS is identified by an HE-MCS index, which is represented by an integer in the range of 0 to 11. An HE-MCS index is the mapping from HE-MCS to a data rate.
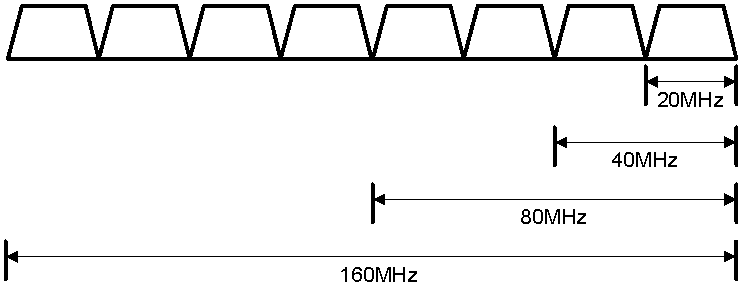
802.11ax supports the 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, and 160 MHz (80+80 MHz) bandwidth modes, and supports a maximum of eight spatial streams. 802.11gax supports the 20 MHz and 40 MHz bandwidth modes.
Table1-22 through Table1-37 show HE-MCS parameters that are supported by an AP.
Table1-22 HE-MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=1)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
1 |
BPSK |
8 |
8.6 |
|
1 |
1 |
QPSK |
16 |
17.2 |
|
2 |
1 |
QPSK |
24 |
25.8 |
|
3 |
1 |
16-QAM |
33 |
34.4 |
|
4 |
1 |
16-QAM |
49 |
51.6 |
|
5 |
1 |
64-QAM |
65 |
68.8 |
|
6 |
1 |
64-QAM |
73 |
77.4 |
|
7 |
1 |
64-QAM |
81 |
86 |
|
8 |
1 |
256-QAM |
98 |
103.2 |
|
9 |
1 |
256-QAM |
108 |
114.7 |
|
10 |
1 |
1024-QAM |
122 |
129 |
|
11 |
1 |
1024-QAM |
135 |
143.4 |
Table1-23 HE-MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=2)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
2 |
BPSK |
16 |
17.2 |
|
1 |
2 |
QPSK |
32 |
34.4 |
|
2 |
2 |
QPSK |
48 |
51.6 |
|
3 |
2 |
16-QAM |
66 |
68.8 |
|
4 |
2 |
16-QAM |
98 |
103.2 |
|
5 |
2 |
64-QAM |
130 |
137.6 |
|
6 |
2 |
64-QAM |
146 |
154.8 |
|
7 |
2 |
64-QAM |
162 |
172 |
|
8 |
2 |
256-QAM |
196 |
206.4 |
|
9 |
2 |
256-QAM |
216 |
229.4 |
|
10 |
2 |
1024-QAM |
244 |
258 |
|
11 |
2 |
1024-QAM |
270 |
286.8 |
Table1-24 HE-MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=3)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
3 |
BPSK |
24 |
25.8 |
|
1 |
3 |
QPSK |
48 |
51.6 |
|
2 |
3 |
QPSK |
72 |
77.4 |
|
3 |
3 |
16-QAM |
99 |
103.2 |
|
4 |
3 |
16-QAM |
147 |
154.8 |
|
5 |
3 |
64-QAM |
195 |
206.4 |
|
6 |
3 |
64-QAM |
219 |
232.2 |
|
7 |
3 |
64-QAM |
243 |
258 |
|
8 |
3 |
256-QAM |
294 |
309.6 |
|
9 |
3 |
256-QAM |
324 |
344.1 |
|
10 |
3 |
1024-QAM |
366 |
387 |
|
11 |
3 |
1024-QAM |
405 |
430.2 |
Table1-25 HE-MCS parameters (20 MHz, NSS=4)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
4 |
BPSK |
32 |
34.4 |
|
1 |
4 |
QPSK |
64 |
68.8 |
|
2 |
4 |
QPSK |
96 |
103.2 |
|
3 |
4 |
16-QAM |
132 |
137.6 |
|
4 |
4 |
16-QAM |
196 |
206.4 |
|
5 |
4 |
64-QAM |
260 |
275.2 |
|
6 |
4 |
64-QAM |
292 |
309.6 |
|
7 |
4 |
64-QAM |
324 |
344 |
|
8 |
4 |
256-QAM |
392 |
412.8 |
|
9 |
4 |
256-QAM |
432 |
458.8 |
|
10 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
488 |
516 |
|
11 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
540 |
573.6 |
Table1-26 HE-MCS parameters (40 MHz, NSS=1)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
1 |
BPSK |
16 |
17.2 |
|
1 |
1 |
QPSK |
33 |
34.4 |
|
2 |
1 |
QPSK |
49 |
51.6 |
|
3 |
1 |
16-QAM |
65 |
68.8 |
|
4 |
1 |
16-QAM |
98 |
103.2 |
|
5 |
1 |
64-QAM |
130 |
137.6 |
|
6 |
1 |
64-QAM |
146 |
154.9 |
|
7 |
1 |
64-QAM |
163 |
172.1 |
|
8 |
1 |
256-QAM |
195 |
206.5 |
|
9 |
1 |
256-QAM |
217 |
229.4 |
|
10 |
1 |
1024-QAM |
244 |
258.1 |
|
11 |
1 |
1024-QAM |
271 |
286.8 |
Table1-27 HE-MCS parameters (40 MHz, NSS=2)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
2 |
BPSK |
32 |
34.4 |
|
1 |
2 |
QPSK |
66 |
68.8 |
|
2 |
2 |
QPSK |
98 |
103.2 |
|
3 |
2 |
16-QAM |
130 |
137.6 |
|
4 |
2 |
16-QAM |
196 |
206.4 |
|
5 |
2 |
64-QAM |
260 |
275.2 |
|
6 |
2 |
64-QAM |
292 |
309.8 |
|
7 |
2 |
64-QAM |
326 |
344.2 |
|
8 |
2 |
256-QAM |
390 |
413 |
|
9 |
2 |
256-QAM |
434 |
458.8 |
|
10 |
2 |
1024-QAM |
488 |
516.2 |
|
11 |
2 |
1024-QAM |
542 |
573.6 |
Table1-28 HE-MCS parameters (40 MHz, NSS=3)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
3 |
BPSK |
48 |
51.6 |
|
1 |
3 |
QPSK |
99 |
103.2 |
|
2 |
3 |
QPSK |
147 |
154.8 |
|
3 |
3 |
16-QAM |
195 |
206.4 |
|
4 |
3 |
16-QAM |
294 |
309.6 |
|
5 |
3 |
64-QAM |
390 |
412.8 |
|
6 |
3 |
64-QAM |
438 |
464.7 |
|
7 |
3 |
64-QAM |
489 |
516.3 |
|
8 |
3 |
256-QAM |
585 |
619.5 |
|
9 |
3 |
256-QAM |
651 |
688.2 |
|
10 |
3 |
1024-QAM |
732 |
774.3 |
|
11 |
3 |
1024-QAM |
813 |
860.4 |
Table1-29 HE-MCS parameters(40 MHz, NSS=4)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
4 |
BPSK |
64 |
68.8 |
|
1 |
4 |
QPSK |
132 |
137.6 |
|
2 |
4 |
QPSK |
196 |
206.4 |
|
3 |
4 |
16-QAM |
260 |
275.2 |
|
4 |
4 |
16-QAM |
392 |
412.8 |
|
5 |
4 |
64-QAM |
520 |
550.4 |
|
6 |
4 |
64-QAM |
584 |
619.6 |
|
7 |
4 |
64-QAM |
652 |
688.4 |
|
8 |
4 |
256-QAM |
780 |
826 |
|
9 |
4 |
256-QAM |
868 |
917.6 |
|
10 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
976 |
1032.4 |
|
11 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
1084 |
1147.2 |
Table1-30 HE-MCS parameters (80 MHz, NSS=1)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
1 |
BPSK |
34 |
36 |
|
1 |
1 |
QPSK |
68 |
72.1 |
|
2 |
1 |
QPSK |
102 |
108.1 |
|
3 |
1 |
16-QAM |
136 |
144.1 |
|
4 |
1 |
16-QAM |
204 |
216.2 |
|
5 |
1 |
64-QAM |
272 |
288.2 |
|
6 |
1 |
64-QAM |
306 |
324.4 |
|
7 |
1 |
64-QAM |
340 |
360.3 |
|
8 |
1 |
256-QAM |
408 |
432.4 |
|
9 |
1 |
256-QAM |
453 |
480.4 |
|
10 |
1 |
1024-QAM |
510 |
540.4 |
|
11 |
1 |
1024-QAM |
567 |
600.5 |
Table1-31 HE-MCS parameters (80 MHz, NSS=2)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mb/s) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
2 |
BPSK |
68 |
72 |
|
1 |
2 |
QPSK |
136 |
144.2 |
|
2 |
2 |
QPSK |
204 |
216.2 |
|
3 |
2 |
16-QAM |
272 |
288.2 |
|
4 |
2 |
16-QAM |
408 |
432.4 |
|
5 |
2 |
64-QAM |
544 |
576.4 |
|
6 |
2 |
64-QAM |
612 |
648.8 |
|
7 |
2 |
64-QAM |
680 |
720.6 |
|
8 |
2 |
256-QAM |
816 |
864.8 |
|
9 |
4 |
256-QAM |
906 |
960.8 |
|
10 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
1020 |
1080.8 |
|
11 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
1134 |
1201 |
Table1-32 HE-MCS parameters (80 MHz, NSS=3)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
3 |
BPSK |
102 |
108 |
|
1 |
3 |
QPSK |
204 |
216.3 |
|
2 |
3 |
QPSK |
306 |
324.3 |
|
3 |
3 |
16-QAM |
408 |
432.3 |
|
4 |
3 |
16-QAM |
612 |
648.6 |
|
5 |
3 |
64-QAM |
816 |
864.6 |
|
6 |
3 |
64-QAM |
918 |
973.2 |
|
7 |
3 |
64-QAM |
1020 |
1080.9 |
|
8 |
3 |
256-QAM |
1224 |
1297.2 |
|
9 |
4 |
256-QAM |
1359 |
1441.2 |
|
10 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
1530 |
1621.2 |
|
11 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
1701 |
1801.5 |
Table1-33 HE-MCS parameters (80 MHz, NSS=4)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
4 |
BPSK |
136 |
144 |
|
1 |
4 |
QPSK |
272 |
288.4 |
|
2 |
4 |
QPSK |
408 |
432.4 |
|
3 |
4 |
16-QAM |
544 |
576.4 |
|
4 |
4 |
16-QAM |
816 |
864.8 |
|
5 |
4 |
64-QAM |
1088 |
1152.8 |
|
6 |
4 |
64-QAM |
1224 |
1297.6 |
|
7 |
4 |
64-QAM |
1360 |
1441.2 |
|
8 |
4 |
256-QAM |
1632 |
1729.6 |
|
9 |
4 |
256-QAM |
1812 |
1921.6 |
|
10 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
2040 |
2161.6 |
|
11 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
2268 |
2402 |
Table1-34 HE-MCS parameters (160 MHz or 80+80 MHz, NSS=1)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
1 |
BPSK |
68 |
72.1 |
|
1 |
1 |
QPSK |
136 |
144.1 |
|
2 |
1 |
QPSK |
204 |
216.2 |
|
3 |
1 |
16-QAM |
272 |
288.2 |
|
4 |
1 |
16-QAM |
408 |
432.4 |
|
5 |
1 |
64-QAM |
544 |
576.5 |
|
6 |
1 |
64-QAM |
612 |
648.5 |
|
7 |
1 |
64-QAM |
681 |
720.6 |
|
8 |
1 |
256-QAM |
817 |
864.7 |
|
9 |
1 |
256-QAM |
907 |
960.7 |
|
10 |
1 |
1024-QAM |
1021 |
1080.9 |
|
11 |
1 |
1024-QAM |
1134 |
1201 |
Table1-35 HE-MCS parameters (160 MHz or 80+80 MHz, NSS=2)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
2 |
BPSK |
136 |
144.1 |
|
1 |
2 |
QPSK |
272 |
288.2 |
|
2 |
2 |
QPSK |
408 |
432.4 |
|
3 |
2 |
16-QAM |
544 |
576.5 |
|
4 |
2 |
16-QAM |
817 |
864.7 |
|
5 |
2 |
64-QAM |
1089 |
1152.9 |
|
6 |
2 |
64-QAM |
1225 |
1297.1 |
|
7 |
2 |
64-QAM |
1361 |
1441.2 |
|
8 |
2 |
256-QAM |
1633 |
1729.4 |
|
9 |
4 |
256-QAM |
1815 |
1921.5 |
|
10 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
2042 |
2161.8 |
|
11 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
2269 |
2401.9 |
Table1-36 HE-MCS parameters (160 MHz or 80+80 MHz, NSS=3)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
3 |
BPSK |
204 |
216.2 |
|
1 |
3 |
QPSK |
408 |
432.4 |
|
2 |
3 |
QPSK |
613 |
648.5 |
|
3 |
3 |
16-QAM |
817 |
864.7 |
|
4 |
3 |
16-QAM |
1225 |
1297.1 |
|
5 |
3 |
64-QAM |
1633 |
1729.4 |
|
6 |
3 |
64-QAM |
1838 |
1945.6 |
|
7 |
3 |
64-QAM |
2042 |
2161.8 |
|
8 |
3 |
256-QAM |
2450 |
2594.1 |
|
9 |
4 |
256-QAM |
2722 |
2882.4 |
|
10 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
3062 |
3242.6 |
|
11 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
3403 |
3602.9 |
Table1-37 HE-MCS parameters (160 MHz or 80+80 MHz, NSS=4)
|
HE-MCS index |
Spatial streams |
Modulation |
Data rate (Mbps) |
|
|
1600ns GI |
800ns GI |
|||
|
0 |
4 |
BPSK |
272 |
288.2 |
|
1 |
4 |
QPSK |
544 |
576.5 |
|
2 |
4 |
QPSK |
817 |
864.7 |
|
3 |
4 |
16-QAM |
1089 |
1152.9 |
|
4 |
4 |
16-QAM |
1633 |
1729.4 |
|
5 |
4 |
64-QAM |
2178 |
2305.9 |
|
6 |
4 |
64-QAM |
2450 |
2594.1 |
|
7 |
4 |
64-QAM |
2722 |
2882.4 |
|
8 |
4 |
256-QAM |
3267 |
3458.8 |
|
9 |
4 |
256-QAM |
3630 |
3843.1 |
|
10 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
4083 |
4323.5 |
|
11 |
4 |
1024-QAM |
4537 |
4803.9 |
|
|
NOTE: · For all the HE-MCS data rate tables, see IEEE 802.11ax. · Support for HE-MCS indexes depends on the AP model. |
Restrictions and guidelines: Radio management configuration
You can configure radios by using the following methods:
· Configure radios one by one in radio view.
· Assign APs to an AP group and configure the radios of the AP group in an AP group's radio view.
· Configure all radios in global configuration view.
For a radio, the settings made in these views for the same parameter take effect in descending order of radio view, an AP group's radio view, and global configuration view.
In a large-sized network, configure AP groups instead of any single AP as a best practice.
Radio management tasks at a glance
To configure radio management, perform the following tasks:
· Enabling or disabling radios
· Enabling a radio to disable wireless services as scheduled
· Configuring basic radio functions
· (Optional.) Configuring 802.11ac functions
· (Optional.) Configuring 802.11ax functions
· (Optional.) Configuring the smart antenna feature
· (Optional.) Configuring error packet ratio optimization and retransmission ratio optimization
· (Optional.) Setting the radio channel usage threshold
· (Optional.) Enabling radio environment monitoring
· (Optional.) Configuring ATF
Enabling or disabling radios
Enabling or disabling all radios
|
CAUTION: Disabling all radios terminates wireless services. Use it with caution. |
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature takes effect only on manual APs and online auto APs.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable or disable all radios.
wlan radio { enable | disable }
By default, radios are disabled unless they are already enabled in radio view or an AP group's radio view.
Enabling or disabling a radio
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Enable or disable the radio.
radio { enable | disable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio is enabled if the wlan radio enable command is executed in system view. If the wlan radio enable command is not executed in system view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, a radio is disabled unless it is already enabled by using the wlan radio enable command in system view.
Enabling a radio to disable wireless services as scheduled
system-view
2. Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Enable the radio to disable wireless services as scheduled.
radio scheduled-shutdown time-range range-name
By default, this feature is not configured.
Specifying a radio mode
About this task
Available radio functions vary by radio mode:
· For 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g radios, you can configure basic radio functions.
· For 802.11an and 802.11gn radios, you can configure basic radio functions and 802.11n functions.
· For 802.11ac and 802.11gac radios, you can configure basic radio functions, 802.11n functions, and 802.11ac functions.
· For 802.11ax and 802.11gax radios, you can configure basic radio functions, 802.11n functions, 802.11ac functions, and 802.11ax functions.
Restrictions and guidelines
Support for channels and transmit powers depends on the radio mode. When you change the mode of a radio, the system automatically adjusts the channel and power parameters for the radio.
When you change the radio mode in an AP group's radio view, the default settings for the radio mode related commands are restored.
Hardware and feature compatibility
The WA530 and WA5500 series do not support the 802.11ax and 802.11gax radio modes.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Specify a radio mode.
type { dot11a | dot11ac | dot11an | dot11ax | dot11b | dot11g | dot11gac | dot11gax | dot11gn }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the default setting for this command varies by AP model.
Configuring basic radio functions
Specifying a working channel
About this task
Perform this task to reduce interference from both wireless and non-wireless devices. You can manually specify a channel or configure the system to automatically select a channel for a radio.
When radar signals are detected on the working channel of a radio, one of the following events occurs:
· If the channel is automatically assigned, the radio changes its channel.
· If the channel is manually specified, the radio changes its channel, and switches back to the specified channel after 30 minutes and then starts the quiet timer. If no radar signals are detected within the quiet time, the radio starts to use the channel. If radar signals are detected within the quiet time, the radio changes it channel again.
Restrictions and guidelines
If you manually specify a channel in the range of 36 to 64, whether the 5.1 GHz band can be used outdoors depends on the device region.
· For outdoor devices that use the 5150 to 5250 Hz band:
¡ China—Not supported.
¡ EU—Not supported.
¡ US—Supported if the maximum effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) at any elevation angle above 30 degrees does not exceed 125mW and you are to deploy 1000 or fewer devices at a time. To install over 1000 devices at one deployment, contact Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and reduce the total transmit power.
¡ Canada—Not supported.
· For outdoor devices that use the 5250 to 5350 Hz band:
¡ China—Not supported.
¡ EU—Not supported.
¡ US—Supported if Depth First Search (DFS) is used.
¡ Canada—Supported if Depth First Search (DFS) is used.
Specifying a working channel
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Specify a working channel.
channel { channel-number | auto { lock | unlock } }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the AC automatically selects a channel for the radio and does not lock the channel.
Restoring the default working channel mode for all radios
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Restore the default working channel mode for all radios.
wlan radio channel default
In default working channel mode, the AC automatically selects a channel for a radio and the channel is unlocked.
This command takes effect on all APs associated with the AC, including offline APs.
Configuring 2.4 GHz radios to use the European channel gap for auto channel selection
About this task
By default, 2.4 GHz radios use non-European channel gap 5 to automatically select channels 1, 6, and 11. You can use this feature to enable the radios to use European channel gap 6 to automatically select channels 1, 7, and 13.
Restrictions and guidelines
Select a channel gap based on channel availability and interference conditions.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter global configuration view.
wlan global-configuration
3. Configure 2.4 GHz radios to use the European channel gap for auto channel selection.
auto-channel european-gap enable
By default, 2.4 GHz radios use the non-European channel gap for auto channel selection.
Configuring the channel selection blacklist or whitelist
About this task
If you configure the blacklist for an AP, the AP will not select channels in the blacklist. If you configure the whitelist for an AP, the AP will select only channels in the whitelist. You cannot configure both the channel selection blacklist and whitelist for the same AP.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature takes effect only on APs operating in auto channel selection mode.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Add the specified channels to the channel selection blacklist or whitelist.
channel auto-select { blacklist | whitelist } channel-number
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in AP group view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, no channel selection blacklist or the whitelist exists.
Setting the antenna type
About this task
Perform this task to set the antenna type for an AP. The antenna type setting for an AP must be consistent with the type of the antenna used on the AP.
To ensure that the Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) is within the correct range, the antenna gain automatically changes after you set the antenna type.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the antenna type.
antenna type antenna-type
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the antenna type is internal.
Setting the antenna gain
About this task
EIRP is the actual transmit power of an antenna, and it is the sum of the antenna gain and the maximum transmit power of the radio.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the antenna gain.
custom-antenna gain antenna-gain
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the antenna gain is 0 dBi.
Setting the maximum transmit power
Restrictions and guidelines
The transmit power range supported by a radio varies by country code, channel, AP model, radio mode, antenna type, and bandwidth mode. If you change these attributes for a radio after you set the maximum transmit power, the configured maximum transmit power might be out of the supported transmit power range. If this happens, the system automatically adjusts the maximum transmit power to a valid value.
If you enable power lock, the locked power becomes the maximum transmit power. For more information about power lock, see "Configuring power lock."
This feature invalidates auto TPC for the specified radio. For more information about auto TPC, see "Configuring WLAN RRM."
Specifying the maximum transmit power
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the maximum transmit power.
max-power radio-power
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, a radio uses the supported maximum transmit power.
Restoring the default maximum transmit power for all radios
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Restore the default maximum transmit power for all radios.
wlan radio max-power default
This command takes effect on all APs associated with the AC, including offline APs.
Configuring power lock
About this task
If you enable power lock, the current power is locked and becomes the maximum transmit power. The locked power still takes effect after the AC restarts.
If you enable power lock, the current power is locked and becomes the maximum transmit power. The locked power still takes effect after the AP restarts.
If a radio enabled with power lock switches to a new channel that provides lower power than the locked power, the maximum power supported by the new channel takes effect.
Configuring power lock
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure power lock.
power-lock { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, power lock is disabled.
Restoring the default power lock state
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Restore the default power lock state.
wlan radio power-lock default
This command restores the default power lock state in radio view of all radios and AP group's radio view of all AP groups.
Setting transmission rates
About this task
Transmission rates are classified into the following types:
· Prohibited rates—Rates that cannot be used by an AP.
· Mandatory rates—Rates that the clients must support to associate with an AP.
· Supported rates—Rates that an AP supports. After a client associates with an AP, the client can select a higher rate from the supported rates to communicate with the AP. The AP automatically decreases or increases the transmission rate as interference signals, retransmission packets, or dropped packets increase or decrease.
· Multicast rate—Rate at which an AP transmits multicasts and broadcasts. The multicast rate must be selected from the mandatory rates.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the transmission rates for the radio.
rate { multicast { auto | rate-value } | { disabled | mandatory | supported } rate-value }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the default settings are as shown in Table1-38.
Table1-38 Default radio transmission rates in an AP group's radio view
|
Protocol |
Default radio transmission rates |
|
802.11a/802.11an/802.11ac/802.11ax |
· Prohibited rates—None. · Mandatory rates—6, 12, and 24. · Multicast rate—Selected from the mandatory rates. · Supported rates—9, 18, 36, 48, and 54. |
|
802.11b |
· Prohibited rates—None. · Mandatory rates—1 and 2. · Multicast rate—Selected from the mandatory rates. · Supported rates—5.5, and 11. |
|
802.11g/802.11gn/802.11gac/802.11gax |
· Prohibited rates—None. · Mandatory rates—1, 2, 5.5, and 11. · Multicast rate—Selected from the mandatory rates. · Supported rates—6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54. |
Setting the beacon interval
About this task
Perform this task to enable an AP to broadcast beacon frames at the specified interval. A short beacon interval enables clients to easily detect the AP but consumes more system resources.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the beacon interval.
beacon-interval interval
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the beacon interval is 100 TU.
Setting the DTIM interval
About this task
An AP periodically broadcasts a beacon compliant with the Delivery Traffic Indication Map (DTIM). After the AP broadcasts the beacon, it sends buffered broadcast and multicast frames based on the value of the DTIM interval. For example, if you set the DTIM interval to 5, the AP sends buffered broadcast and multicast frames every five beacon frames.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the DTIM interval.
dtim counter
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the DTIM interval is 1.
Setting the hardware retransmission limits
About this task
In wireless networks, unicast packets require acknowledgements. If a radio fails to receive the acknowledgement for a packet, it retransmits the packet.
You can set hardware retransmission limits for both large frames and small frames. Transmitting large frames requires a large buffer size and a long time because the system performs collision avoidance for large frames before transmission. Therefore, you can set a small hardware retransmission limit for large frames to save system buffer and transmission time.
Hardware and feature compatibility
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Feature compatibility |
|
WA6600 series |
WA6638 WA6638i WA6636 WA6630X WA6628 WA6628X WA6622 WA6620 WA6620X WA6620X-LI WA6620XE-LI |
No |
|
WA6500 series |
WA6528i |
Yes |
|
WA6300 series |
WA6338 WA6338-HI WA6338-LI WA6330 WA6330-LI WA6322 WA6322H WA6322H-LI WA6320 WA6320-C WA6320-D WA6320-SI WA6320S-C WA6320S-E WA6320H WA6320H-LI WA6320H-XEPON |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922 WAP922E WAP922H |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922X |
No |
|
WAP923 series |
WAP923 |
Yes |
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the hardware retransmission limit for small frames.
short-retry threshold count
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the hardware retransmission limit is 7 for small frames.
5. Set the hardware retransmission limit for large frames.
long-retry threshold count
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the hardware retransmission limit is 4 for large frames.
Setting the maximum number of clients that can associate with an AP
About this task
When the maximum number of clients is reached on an AP, the AP stops accepting new clients and hides its SSIDs. This prevents the AP from being overloaded.
This feature limits clients associated with the AP and the AC separately. If a radio is bound with two service templates enabled with client association at the AP and client association at the AC, the actual maximum number of clients allowed is twice the configured maximum number of clients allowed. In this case, configure this command based on the number of clients expected to come online on a radio.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the maximum number of clients that can associate with the AP.
client max-count max-number
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, no limit is set for the number of clients that can associate with an AP.
Configuring access services for 802.11b clients
About this task
To prevent low-speed 802.11b clients from decreasing wireless data transmission performance, you can enable an 802.11g, 802.11gac, or 802.11gn radio to disable access services for 802.11b clients.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure access services for 802.11b clients.
client dot11b-forbidden { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, a radio accepts 802.11b clients.
Configuring 802.11g protection
About this task
When both 802.11b and 802.11g clients exist in a WLAN, transmission collision might occur because they use different modulation modes. 802.11g protection can avoid such collision. It enables 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax devices to send RTS/CTS or CTS-to-self packets to inform 802.11b clients to defer access to the medium.
802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax devices send RTS/CTS or CTS-to-self packets before sending data only when 802.11b signals are detected on the channel.
802.11g protection automatically takes effect when 802.11b clients associate with an 802.11g, 802.11n (2.4 GHz), 802.11gac, or 802.11gax AP.
Hardware and feature compatibility
|
Series |
Model |
Feature compatibility |
|
WA6600 series |
WA6638 WA6638i WA6636 WA6630X WA6628 WA6628X WA6622 WA6620 WA6620X WA6620X-LI WA6620XE-LI |
No |
|
WA6500 series |
WA6528i |
Yes |
|
WA6300 series |
WA6338 WA6338-HI WA6338-LI WA6330 WA6330-LI WA6322 WA6322H WA6322H-LI WA6320 WA6320-C WA6320-D WA6320-SI WA6320S-C WA6320S-E WA6320H WA6320H-LI WA6320H-XEPON |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922 WAP922E WAP922H WAP922X |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922X |
No |
|
WAP923 series |
WAP923 |
Yes |
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature is applicable only to 802.11g, 802.11n (2.4 GHz), 802.11gac, and 802.11gax radios.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure 802.11g protection.
dot11g protection { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, 802.11g protection is disabled.
Setting the preamble type
About this task
A preamble is a set of bits in a packet header to synchronize transmission signals between sender and receiver. A short preamble improves network performance and a long preamble ensures compatibility with wireless devices using long preambles.
Hardware and feature compatibility
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Feature compatibility |
|
WA6600 series |
WA6638 WA6638i WA6636 WA6630X WA6628 WA6628X WA6622 WA6620 WA6620X WA6620X-LI WA6620XE-LI |
No |
|
WA6500 series |
WA6528i |
Yes |
|
WA6300 series |
WA6338 WA6338-HI WA6338-LI WA6330 WA6330-LI WA6322 WA6322H WA6322H-LI WA6320 WA6320-C WA6320-D WA6320-SI WA6320S-C WA6320S-E WA6320H WA6320H-LI WA6320H-XEPON |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922 WAP922E WAP922H |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922X |
No |
|
WAP923 series |
WAP923 |
Yes |
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature is applicable only to 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11gn radios.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the preamble type.
preamble { long | short }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, a short preamble is used.
Setting the maximum transmission distance
About this task
The strength of wireless signals gradually degrades as the transmission distance increases. The maximum transmission distance of wireless signals depends on the surrounding environment and on whether an external antenna is used.
· Without an external antenna—About 300 meters (984.25 ft).
· With an external antenna—30 km (18.64 miles) to 50 km (31.07 miles).
· In an area with obstacles—35 m (114.83 ft) to 50 m (164.04 ft).
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the maximum transmission distance.
distance distance
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the maximum transmission distance is 1 km (0.62 miles).
Enabling the continuous mode for a radio
About this task
This feature is used for network testing only. Do not use it under any other circumstances.
The feature enables continuous data packet sending at the specified rate. When the feature is enabled, do not perform any other operations except for changing the transmit rate.
For an 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11g radio, set the transmit rate. For an 802.11n radio, set the transmit rate or MCS index. For an 802.11ac or 802.11gac radio, set the transmit rate, MCS index, or VHT-MCS index.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Enable the continuous mode for the radio.
continuous-mode { mcs mcs-index | nss nss-index vht-mcs vhtmcs-index | rate rate-value }
By default, the continuous mode is disabled.
Performing on-demand channel usage measurement
About this task
This feature enables an AP to scan supported channels and display the channel usage after scanning. It takes about one second to scan a channel.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Perform on-demand channel usage measurement.
channel-usage measure
Setting the channel usage alarm threshold
About this task
If the actual channel usage exceeds the threshold, the device reports an alarm to the information center.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the channel usage alarm threshold.
channel-usage threshold threshold
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the channel usage alarm threshold is 90%.
Restoring the default bandwidth mode for all radios
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature might change the working channel of some radios and log off online clients. Please use this feature with caution.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Restore the default bandwidth mode for all radios.
wlan radio channel band-width default
Setting the channel calibration interval for supplement APs
About this task
A supplement AP is an AP deployed to remove a blind spot after the AC is powered on. Radios on supplement APs are not optimized by global DFS and may use a channel that conflicts with any other APs.
To resolve the issue, this feature is introduced to examine supplement APs periodically and adjust their radio channels if needed.
You can perform this task to set the channel calibration interval for supplement APs. The AC scans supplement APs at the interval and performs one-time DFS on conflicting radios. APs that have been adjusted are no longer considered as supplement APs.
Restrictions and guidelines
If new APs are added frequently, set a short interval as a best practice. Otherwise, set a long interval as a best practice.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the channel calibration interval for supplement APs.
wlan rrm supplement-ap calibration-channel interval minutes
By default, the channel calibration interval is 60 minutes for supplement APs.
Configuring 802.11n functions
|
|
NOTE: · Support for 802.11n functions depends on the device model. · 802.11n functions are applicable only to 802.11an, 802.11gn, 802.11ac, 802.11gac, 802.11ax, and 802.11gax radios. |
Configuring the A-MPDU aggregation method
About this task
A MAC Protocol Data Unit (MPDU) is a data frame in 802.11 format. MPDU aggregation aggregates multiple MPDUs into one aggregate MPDU (A-MPDU) to reduce additional information, ACK frames, and Physical Layer Convergence Procedure (PLCP) header overhead. This improves network throughput and channel efficiency.
All MPDUs in an A-MPDU must have the same QoS priority, source address, and destination address.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure the A-MPDU aggregation method.
a-mpdu { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the A-MPDU aggregation method is enabled.
Configuring the A-MSDU aggregation method
About this task
MSDU aggregation aggregates multiple MSDUs into one aggregate MSDU (A-MSDU) to reduce PLCP preamble, PLCP header, and MAC header overheads. This improves network throughput and frame forwarding efficiency.
All MSDUs in an A-MSDU must have the same QoS priority, source address, and destination address. When a device receives an A-MSDU, it restores the A-MSDU to multiple MSDUs for processing.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure the A-MSDU aggregation method.
a-msdu { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the A-MSDU aggregation method is enabled.
Configuring short GI
About this task
802.11 OFDM fragments frames to data blocks for transmission. It uses GI to ensure that the data block transmissions do not interfere with each other and are immune to transmission delays.
The GI used by 802.11a/g is 800 ns. 802.11n supports a short GI of 400 ns, which provides a 10% increase in data rate.
Both the 20 MHz and 40 MHz bandwidth modes support short GI.
Hardware and feature compatibility
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Feature compatibility |
|
WA6600 series |
WA6638 WA6638i WA6636 WA6630X WA6628 WA6628X WA6622 WA6620 WA6620X WA6620X-LI WA6620XE-LI |
No |
|
WA6500 series |
WA6528i |
Yes |
|
WA6300 series |
WA6338 WA6338-HI WA6338-LI WA6330 WA6330-LI WA6322 WA6322H WA6322H-LI WA6320 WA6320-C WA6320-D WA6320-SI WA6320S-C WA6320S-E WA6320H WA6320H-LI WA6320H-XEPON |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922 WAP922E WAP922H |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922X |
No |
|
WAP923 series |
WAP923 |
Yes |
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure short GI.
short-gi { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, short GI is enabled.
Configuring LDPC
About this task
802.11n introduces the Low-Density Parity Check (LDPC) mechanism to increase the signal-to-noise ratio and enhance transmission quality. LDPC takes effect only when both ends support LDPC.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-number
4. Configure LDPC.
ldpc { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, LDPC is enabled.
Configuring STBC
About this task
The Space-Time Block Coding (STBC) mechanism enhances the reliability of data transmission and does not require clients to have high transmission rates.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-number
4. Configure STBC.
stbc { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, STBC is enabled.
Setting MCS indexes
About this task
802.11n clients use the rate corresponding to the MCS index to send unicast frames. 802.11a/b/g clients use the 802.11a/b/g rate to send unicast frames.
If you do not set a multicast MCS index, 802.11n clients and the AP use the 802.11a/b/g multicast rate to send multicast frames. If you set a multicast MCS index, one of following events occurs:
· The AP and clients use the rate corresponding to the multicast MCS index to send multicast frames if only 802.11n and 802.11ac clients exist.
· The AP and clients use the 802.11a/b/g multicast rate to send multicast frames if any 802.11a/b/g clients exist.
When you set the maximum mandatory or supported MCS index, you are specifying a range. For example, if you set the maximum mandatory MCS index to 5, rates corresponding to MCS indexes 0 through 5 are configured as 802.11n mandatory rates.
Restrictions and guidelines
The multicast MCS index cannot be greater than the maximum mandatory MCS index.
The maximum supported MCS index cannot be smaller than the maximum mandatory MCS index.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the maximum mandatory MCS index.
dot11n mandatory maximum-mcs index
By default:
¡ In radio view, the default settings are as follows:
- No maximum mandatory MCS index is set if the maximum supported MCS index is set.
- The radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view if the maximum supported MCS index is not set.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, no maximum mandatory MCS index is set.
5. Set the maximum supported MCS index.
dot11n support maximum-mcs index
By default:
¡ In radio view, the default settings are as follows:
- The maximum supported MCS index is 76 if the maximum mandatory MCS index is set.
- The radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view if the maximum mandatory MCS index is not set.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the maximum supported MCS index is 76.
6. Set the multicast MCS index.
dot11n multicast-mcs index
By default:
¡ In radio view, the default settings are as follows:
- No multicast MCS index is set if the maximum supported MCS index or the maximum mandatory MCS index is set.
- The radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view if neither the maximum supported MCS index nor the maximum mandatory MCS index is set.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, no multicast MCS index is set.
Configuring the client dot11n-only feature
About this task
To prevent low-speed 802.11a/b/g clients from decreasing wireless data transmission performance, you can enable the client dot11n-only feature for an AP to accept only 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax clients.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure the client dot11n-only feature.
client dot11n-only { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the client dot11n-only feature is disabled.
Setting the 802.11n bandwidth mode
About this task
802.11n uses the channel structure of 802.11a/b/g, but it increases the number of data subchannels in each 20 MHz channel to 52. This improves data transmission rate.
802.11n binds two adjacent 20 MHz channels to form a 40 MHz channel (one primary channel and one secondary channel). This provides a simple way to double the data rate.
If the current channel of a radio does not support the specified bandwidth mode, the radio clears the channel configuration and selects another channel.
If the bandwidth mode is set to 40 MHz, the radio uses the 40 MHz bandwidth if two adjacent channels that can be bound together exist. If there are no adjacent channels that can be bound together, the radio uses the 20 MHz bandwidth.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the 802.11n bandwidth mode.
channel band-width { 20 | 40 [ auto-switch ] }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the bandwidth mode is 40 MHz for 802.11an radios and 20 MHz for 802.11gn radios.
Only 802.11gn radios support the auto-switch keyword.
Specifying a MIMO mode
About this task
Multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) enables a radio to send and receive wireless signals through multiple spatial streams. This improves system capacity and spectrum usage without requiring higher bandwidth.
A radio can operate in one of the following MIMO modes:
· 1x1—Sends and receives wireless signals through one spatial stream.
· 2x2—Sends and receives wireless signals through two spatial streams.
· 3x3—Sends and receives wireless signals through three spatial streams.
· 4x4—Sends and receives wireless signals through four spatial streams.
· 5x5—Sends and receives wireless signals through five spatial streams.
· 6x6—Sends and receives wireless signals through six spatial streams.
· 7x7—Sends and receives wireless signals through seven spatial streams.
· 8x8—Sends and receives wireless signals through eight spatial streams.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Specify a MIMO mode.
mimo { 1x1 | 2x2 | 3x3 | 4x4 | 5x5 | 6x6 | 7x7 | 8x8 }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
Configuring energy saving
About this task
After you enable the energy-saving feature, the MIMO mode of a radio automatically changes to 1x1 if no clients associate with the radio and the radio is not configured with WIPS.
Hardware and feature compatibility
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Feature compatibility |
|
WA6600 series |
WA6638 WA6638i WA6636 WA6630X WA6628 WA6628X WA6622 WA6620 WA6620X WA6620X-LI WA6620XE-LI |
No |
|
WA6500 series |
WA6528i |
Yes |
|
WA6300 series |
WA6338 WA6338-HI WA6338-LI WA6330 WA6330-LI WA6322 WA6322H WA6322H-LI WA6320 WA6320-C WA6320-D WA6320-SI WA6320S-C WA6320S-E WA6320H WA6320H-LI WA6320H-XEPON |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922 WAP922E WAP922H |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922X |
No |
|
WAP923 series |
WAP923 |
Yes |
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure energy saving.
green-energy-management { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, energy saving is disabled.
Configuring 802.11n protection
About this task
When both 802.11n and non-802.11n clients exist in a WLAN, transmission collision might occur because they use different modulation modes. 802.11n protection can avoid such collision. It enables 802.11n devices to send RTS/CTS or CTS-to-self packets to inform non-802.11n clients to defer access to the medium.
802.11n devices send RTS/CTS or CTS-to-self packets before sending data only when non-802.11n signals are detected on the channel.
802.11n protection automatically takes effect when non-802.11n clients associate with an 802.11n AP.
|
|
NOTE: 802.11n devices refer to 802.11nand 802.11ac devices. |
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure 802.11n protection.
dot11n protection { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, 802.11n protection is disabled.
Configuring 802.11ac functions
|
|
NOTE: · Support for 802.11ac depends on the device model. · 802.11ac functions are applicable only to 802.11ac, 802.11gac, 802.11ax, and 802.11gax radios. |
Setting NSSs
About this task
If an AP supports an NSS, it supports all VHT-MCS indexes for the NSS. 802.11ac clients that use the rate corresponding to the VHT-MCS index for the NSS to send unicast frames. Non-802.11ac clients use the 802.11a/b/g/n rate to send unicast frames.
If you do not set a multicast NSS, 802.11ac clients and the AP use the 802.11a/b/g/n multicast rate to send multicast frames. If you set a multicast NSS and specify a VHT-MCS index, the following situations occur:
· The AP and clients use the rate corresponding to the VHT-MCS index to send multicast frames if all clients are 802.11ac clients.
· The AP and clients use the 802.11a/b/g/n multicast rate to send multicast frames if any non-802.11ac clients exist.
The maximum mandatory NSS or supported NSS determines a range of 802.11 rates. For example, if the maximum mandatory NSS is 5, rates corresponding to VHT-MCS indexes for NSSs 1 through 5 will be 802.11ac mandatory rates.
Restrictions and guidelines
The maximum supported NSS cannot be smaller than the maximum mandatory NSS and the multicast NSS cannot be greater than the maximum mandatory NSS.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the maximum mandatory NSS.
dot11ac mandatory maximum-nss nss-number
By default:
¡ In radio view, the default settings are as follows:
- If the multicast NSS or the maximum supported NSS is set, no maximum mandatory NSS is set.
- If neither the multicast NSS nor the maximum supported NSS is set, the radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, no maximum mandatory NSS is set.
5. Set the maximum supported NSS.
dot11ac support maximum-nss nss-number
By default:
¡ In radio view, the default settings are as follows:
- If the multicast NSS or the maximum mandatory NSS is set, the maximum supported NSS is 8.
- If neither the multicast NSS nor the maximum mandatory NSS is set, the radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the maximum supported NSS is 8.
6. Set the multicast NSS and specify a VHT-MCS index.
dot11ac multicast-nss nss-number vht-mcs index
By default:
¡ In radio view, the default settings are as follows:
- If the maximum supported NSS or the maximum mandatory NSS is set, no multicast NSS is set.
- If neither the maximum supported NSS nor the maximum mandatory NSS is set, the radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, no multicast NSS is set.
Configuring the client dot11ac-only feature
About this task
To prevent low-speed 802.11a/b/g/n clients from decreasing wireless data transmission performance, you can enable the client dot11ac-only feature for an AP to accept only 802.11ac and 802.11ax clients.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure the client dot11ac-only feature.
client dot11ac-only { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the client dot11ac-only feature is disabled.
Setting the 802.11ac bandwidth mode
About this task
802.11ac uses the channel structure of 802.11n and increases the maximum bandwidth from 40 MHz to 160 MHz. 802.11ac can bind two adjacent 20/40/80 MHz channels to form a 40/80/160 MHz channel.
The radio uses the specified 40/80 MHz bandwidth if adjacent channels can be bound to form a 40/80 channel. If adjacent channels cannot form a 40/80 channel, the radio uses the next available bandwidth lower than the specified one.
For example, the bandwidth mode is set to 80 MHz. The radio uses the 80 MHz bandwidth if adjacent channels that can be bound together exist. If adjacent channels that can be bound to an 80 MHz channel do not exist, but two adjacent channels that can be bound to a 40 MHz channel exist, the 40 MHz bandwidth is used. If no adjacent channels that can be bound together exist, the radio uses the 20 MHz bandwidth.
After you specifying a working channel, the system selects a secondary channel automatically. The working channel forwards all types of packets and the secondary channel forwards only data packets.
If the current channel of a radio does not support the specified bandwidth mode, the radio clears the channel configuration and selects another channel.
Figure1-1 802.11ac bandwidth modes
Restrictions and guidelines
802.11gac supports only the 20 MHz and 40 MHz bandwidth modes.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the 802.11ac bandwidth mode:
channel band-width { 20 | 40 | 80 | 160 }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the bandwidth mode is 80 MHz for 802.11ac radios.
5. Set the 802.11gac bandwidth mode:
channel band-width { 20 | 40 }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the bandwidth mode is 20 MHz for 802.11gac radios.
Configuring 802.11ax functions
|
|
NOTE: · Support for 802.11ax depends on the device model. · 802.11ax functions are applicable only to 802.11ax and 802.11gax radios. |
Hardware compatibility with 802.11ax functions
The WA530 series and WA5500 series do not support 802.11ax functions.
Setting NSSs
About this task
If an AP supports an NSS, it supports all HE-MCS indexes for the NSS. 802.11ax clients that use the rate corresponding to the HE-MCS index for the NSS to send unicast frames. Non-802.11ax clients use the 802.11a/b/g rate, or the rate corresponding to the MCS or VHT-MCS index for the NSS to send unicast frames.
If you do not set a multicast NSS, 802.11ax clients and the AP use the 802.11a/b/g/n/ac multicast rate to send multicast frames. If you set a multicast NSS and specify an HE-MCS index, the following situations occur:
· The AP and clients use the rate corresponding to the HE-MCS index to send multicast frames if all clients are 802.11ax clients.
· The AP and clients use the 802.11a/b/g/n/ac multicast rate to send multicast frames if any non-802.11ax clients exist.
The maximum mandatory NSS or supported NSS determines a range of 802.11 rates. For example, if the maximum mandatory NSS is 5, rates corresponding to HE-MCS indexes for NSSs 1 through 5 will be 802.11ax mandatory rates.
Restrictions and guidelines
The maximum supported NSS cannot be smaller than the maximum mandatory NSS and the multicast NSS cannot be greater than the maximum mandatory NSS.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the maximum mandatory NSS.
dot11ax mandatory maximum-nss nss-number
By default:
¡ In radio view, the default settings are as follows:
- If the multicast NSS or the maximum supported NSS is set, no maximum mandatory NSS is set.
- If neither the multicast NSS nor the maximum supported NSS is set, the radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, no maximum mandatory NSS is set.
5. Set the maximum supported NSS.
dot11ax support maximum-nss nss-number
By default:
¡ In radio view, the default settings are as follows:
- If the multicast NSS or the maximum mandatory NSS is set, the maximum supported NSS is 8.
- If neither the multicast NSS nor the maximum mandatory NSS is set, the radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the maximum supported NSS is 8.
6. Set the multicast NSS and specify an HE-MCS index.
dot11ax multicast-nss nss-number he-mcs index
By default:
¡ In radio view, the default settings are as follows:
- If the maximum supported NSS or the maximum mandatory NSS is set, no multicast NSS is set.
- If neither the maximum supported NSS nor the maximum mandatory NSS is set, the radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, no multicast NSS is set and no HE-MCS is specified.
Configuring the client dot11ax-only feature
About this task
To prevent low-speed 802.11a/b/g/n/ac clients from decreasing wireless data transmission performance, you can enable the client dot11ax-only feature for an AP to accept only 802.11ax clients.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure the client dot11ax-only feature.
client dot11ax-only { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the client dot11ax-only feature is disabled.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter radio interface view.
interface wlan-radio interface-number
3. Configure the client dot11ax-only feature.
client dot11ax-only { disable | enable }
By default, the client dot11ax-only feature is disabled.
Setting the 802.11ax bandwidth mode
About this task
802.11ax uses the channel structure of 802.11n and increases the maximum bandwidth from 40 MHz to 160 MHz. 802.11ax can bind two adjacent 20/40/80 MHz channels to form a 40/80/160 MHz channel.
The radio uses the specified 40/80/160 MHz bandwidth if adjacent channels can be bound to form a 40/80/160 channel. If adjacent channels cannot form a 40/80/160 channel, the radio uses the next available bandwidth lower than the specified one.
For example, the bandwidth mode is set to 80 MHz. The radio uses the 80 MHz bandwidth if adjacent channels that can be bound together exist. If adjacent channels that can be bound to an 80 MHz channel do not exist, but two adjacent channels that can be bound to a 40 MHz channel exist, the 40 MHz bandwidth is used. If no adjacent channels that can be bound together exist, the radio uses the 20 MHz bandwidth.
When the bandwidth mode is set to 80+80 MHz, the radio uses the 160 MHz bandwidth if two adjacent 80 MHz channels that can be bound together exist. If a 160 MHz channel cannot be formed but two non-adjacent 80 MHz channels are available, the radio uses the two 80 MHz channels to achieve the 160 MHz bandwidth.
After you specify a working channel, the device automatically selects a secondary channel. The working channel forwards all types of packets and the secondary channel forwards only data packets.
If the current channel of a radio does not support the specified bandwidth mode, the radio clears the channel configuration and selects another channel.
|
|
NOTE: Support for the 160 MHz and 80+80 MHz bandwidth modes depends on the device model. |
Figure1-2 802.11ax bandwidth modes
Restrictions and guidelines
802.11gax supports only the 20 MHz and 40 MHz bandwidth modes.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the 802.11ax bandwidth mode:
channel band-width { 20 | 40 | 80 | 160}
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the bandwidth mode is 80 MHz for 802.11ax radios.
Support for the 160 keywords depends on the AP model.
5. Set the 802.11gax bandwidth mode:
channel band-width { 20 | 40 [ auto-switch ] }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the bandwidth mode is 20 MHz for 802.11gax radios.
Configuring BSS coloring
About this task
BSS coloring enables the system to assign a color to each BSS and include the color ID in data packets for clients to identify if a packet comes from the associated AP. To avoid conflicts, clients that detect an 802.11ax data packet with the same color as its associated BSS will postpone transmission.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature is configurable only for 802.11ax radios.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view/an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure BSS coloring.
bss-color { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, the configuration in an AP group's radio view is used.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, BSS coloring is disabled.
Configuring the smart antenna feature
About this task
This feature is applicable only to 802.11n and 802.11ac radios.
The smart antenna feature enables an AP to automatically adjust the antenna parameters based on the client location and channel information to improve signal quality and stability.
You can configure a radio to operate in one of the following smart antenna modes:
· Auto—Uses the high availability mode for audio and video packets, and uses the high throughput mode for other packets.
· High-availability—Applicable to WLANs that require stable bandwidth, this mode reduces noise and interference impacts, and provides guaranteed bandwidth for clients.
· High-throughput—Applicable to WLANs that require high performance, this mode enhances signal strength and association capability.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure the smart antenna feature.
smart-antenna { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the smart antenna feature is enabled.
5. Specify a smart antenna mode.
smart-antenna policy { auto | high-availability | high-throughput }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the auto mode is used.
Configuring error packet ratio optimization and retransmission ratio optimization
About this task
This feature enables the device to recalculate the error packet ratio and retransmission ratio by using the specified indexes to get smaller ratio values.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the index for optimizing the error packet ratio.
wlan error-frame optimization value
By default, the index for optimizing the error packet ratio is not set.
3. Set the index for optimizing the retransmission ratio.
wlan retransmit-frame optimization value
By default, the index for optimizing the retransmission ratio is not set.
Setting the radio channel usage threshold
About the radio channel usage threshold
|
CAUTION: Adjusting the radio usage threshold might affect online clients. Please use this feature with caution. |
The system hides the SSID of a radio if the radio's channel usage exceeds the threshold. To associate with the radio when the SSID is hidden, clients must perform active scanning.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set the radio channel usage threshold.
sacp ssid-hide channel-usage-threshold threshold
By default:
¡ In AP view, an AP uses the configuration in AP group view.
¡ In AP group view, the radio channel usage threshold is 100%.
Enabling radio environment monitoring
About this task
This feature enables an AP to scan the wireless environment, collect environment data, and report the data to the AC periodically. The AC uses the data reported by APs to generate channel and neighbor reports. To view the reports, execute the display wlan rrm-status ap command.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Enable radio environment monitoring.
environment-monitor enable
By default:
¡ In radio view, the AP uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, radio environment monitoring is disabled.
Configuring ATF
|
|
NOTE: Support for this feature depends on the AP model. |
About this task
Air Time Fairness (ATF) ensures that every client has equal access to air time in the APs’ coverage area. With this feature, high-speed clients have more opportunities to use wireless resources. This practice enhances the forwarding efficiency for the entire network.
Enabling this feature might decrease the forwarding efficiency for low-speed clients. Consider the number of access clients and forwarding efficiency for high-speed clients when you configure this feature.
Hardware and feature compatibility
|
Hardware series |
Model |
Feature compatibility |
|
WA6600 series |
WA6638 WA6638i WA6636 WA6630X WA6628 WA6628X WA6622 WA6620 WA6620X WA6620X-LI WA6620XE-LI |
No |
|
WA6500 series |
WA6528i |
Yes |
|
WA6300 series |
WA6338 WA6338-HI WA6338-LI WA6330 WA6330-LI WA6322 WA6322H WA6322H-LI WA6320 WA6320-C WA6320-D WA6320-SI WA6320S-C WA6320S-E WA6320H WA6320H-LI WA6320H-XEPON |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922 WAP922E WAP922H WAP922X |
Yes |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922X |
No |
|
WAP923 series |
WAP923 |
Yes |
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Configure ATF.
atf { disable | enable }
By default:
In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in AP group view.
In an AP group's radio view, ATF is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for radio management
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Command |
|
|
Display information about the continuous mode. |
display wlan ap { all | name ap-name } continuous-mode |
|
Display AP radio information. |
display wlan ap { all | name ap-name } radio [ frequency-band { 5 | 2.4 } ] |
|
Display radio channel information. |
display wlan ap { all | name ap-name } radio channel |
|
Display radio type information. |
display wlan ap { all | name ap-name } radio type |
|
Display radio statistics. |
display wlan statistics ap { all | name ap-name } radio |
|
Reassign working channels. |
reset wlan channel all |
|
Clear radio statistics. |
reset wlan statistics ap { all | name ap-name } radio |
Radio management configuration examples
Example: Configuring basic radio functions
Network configuration
As shown in Figure1-3, create a manual AP and set the radio mode, working channel, and maximum transmit power to 802.11ax, channel 40, and 19 dBm, respectively.
Procedure
# Create manual AP ap1, and specify its model and serial ID.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA6330
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
# Enter radio view of radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1
# Set the radio mode to dot11ax.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] type dot11ax
# Configure radio 1 to work on channel 40.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] channel 40
# Set the maximum transmit power to 19 dBm.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] max-power 19
# Enable radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] return
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about all radios.
<AC> display wlan ap all verbose
Total number of APs: 1
Total number of connected APs: 1
Total number of connected manual APs: 1
Total number of connected auto APs: 0
Total number of connected common APs: 1
Total number of connected WTUs: 0
Total number of inside APs: 0
Maximum supported APs: 6144
Remaining APs: 6144
Total AP licenses: 128
local AP licenses: 0
Server AP licenses: 0
Remaining local AP licenses: 127
Sync AP licenses: 0
AP name : ap1
AP ID : 1
AP group name : default-group
State : Run
Backup Type : Master
Online time : 0 days 1 hours 25 minutes 12 seconds
System up time : 0 days 2 hours 22 minutes 12 seconds
Model : WA6330
Region code : CN
Region code lock : Disable
Serial ID : 219801A28N819CE0002T
MAC address : 0AFB-423B-893C
IP address : 192.168.1.50
UDP control port number : 65488
UDP data port number : N/A
H/W version : Ver.C
S/W version : V700R001B49D001
Boot version : 1.01
USB state : N/A
Power level : N/A
Power info : N/A
Description : wtp1
Priority : 4
Echo interval : 10 seconds
Echo count : 3 counts
Keepalive interval : 10 seconds
Discovery-response wait-time : 2 seconds
Statistics report interval : 50 seconds
Fragment size (data) : 1500
Fragment size (control) : 1450
MAC type : Local MAC & Split MAC
Tunnel mode : Local Bridging & 802.3 Frame & Native Frame
CAPWAP data-tunnel status : Down
Discovery type : Static Configuration
Retransmission count : 3
Retransmission interval : 5 seconds
Firmware upgrade : Enabled
Sent control packets : 1
Received control packets : 1
Echo requests : 147
Lost echo responses : 0
Average echo delay : 3
Last reboot reason : User soft reboot
Latest IP address : 10.1.0.2
Current AC IP : N/A
Tunnel down reason : Request wait timer expired
Connection count : 1
Backup IPv4 : Not configured
Backup IPv6 : Not configured
Ctrl-tunnel encryption : Disabled
Ctrl-tunnel encryption state : Not encrypted
Data-tunnel encryption : Disabled
Data-tunnel encryption state : Not encrypted
LED mode : Normal
Remote configuration : Disabled
EnergySaving Level : 0
AP type : Normal AP
Radio 1:
BSSID : 7848-59f6-3940
State : Up
Type : 802.11ax(5GHz)
Antenna type : internal
Client dot11ac-only : Disabled
Client dot11n-only : Disabled
Channel band-width : 20/40/80MHz
Active band-width : 20/40/80MHz
Secondary channel offset : SCB
Short GI for 20MHz : Supported
Short GI for 40MHz : Supported
Short GI for 80MHz : Supported
Short GI for 160MHz : Not supported
MIMO : 2*2
Green-Energy-Management : Disabled
A-MSDU : Enabled
A-MPDU : Enabled
LDPC : Supported
STBC : Supported
Operational VHT-MCS Set:
Mandatory : Not configured
Supported : NSS1 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
NSS2 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
Multicast : Not configured
Operational HT MCS Set:
Mandatory : Not configured
Supported : 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15
Multicast : Not configured
Channel : 40
Channel usage(%) : 0
Max power : 19 dBm
Operational rate:
Mandatory : 6, 12, 24 Mbps
Multicast : Auto
Supported : 9, 18, 36, 48, 54 Mbps
Disabled : Not configured
Distance : 1 km
ANI : Enabled
Fragmentation threshold : 2346 bytes
Beacon interval : 100 TU
Protection threshold : 2346 bytes
Long retry threshold : 4
Short retry threshold : 7
Frame aging time in cache : 2000 ms
Noise Floor : 0 dBm
Protection mode : cts-to-self
MU-TxBF : Disabled
SU-TxBF : Disabled
Continuous mode : N/A
Client dot11ax-only : Disabled
Operational HE-MCS Set:
Mandatory : Not configured
Supported : NSS1 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11
NSS2 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11
Multicast : Not configured
OFDMA random access RUs : Not Supported
Channel Width Set : 0x02
DL-OFDMA : Disabled
UL-OFDMA : Disabled
UL-MU-MIMO : Disabled
BSS-COLOR : Disabled
TWT negotiation : Disabled
HT protection mode : No protection
Radio 2:
BSSID : N/A
State : Down
Type : 802.11ax(2.4GHz)
Antenna type : internal
Client dot11ac-only : Disabled
Client dot11n-only : Disabled
Channel bandwidth : 20MHz
Operating bandwidth : 20MHz
Secondary channel mode : SCN
Short GI for 20MHz : Supported
Short GI for 40MHz : Supported
Short GI for 80MHz : Not supported
Short GI for 160MHz : Not supported
MIMO : 2*2
Green-Energy-Management : Disabled
A-MSDU : Enabled
A-MPDU : Enabled
LDPC : Supported
STBC : Supported
Operational VHT-MCS set:
Mandatory : Not configured
Supported : Not configured
Multicast : Not configured
Operational HT MCS set:
Mandatory : Not configured
Supported : 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15
Multicast : Not configured
Channel : 6(auto)
Channel usage(%) : 0
Max power : 20 dBm
Operational rate:
Mandatory : 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps
Multicast : Auto
Supported : 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 Mbps
Disabled : Not configured
Distance : 1 km
ANI : Enabled
Fragmentation threshold : 2346 bytes
Beacon interval : 100 TU
Protection threshold : 2346 bytes
Long retry threshold : 4
Short retry threshold : 7
Frame aging time in cache : 2000 ms
Noise floor : 0 dBm
Protection mode : cts-to-self
MU-TxBF : Disabled
SU-TxBF : Disabled
Continuous mode : N/A
Client dot11ax-only : Disabled
Operational HE-MCS Set:
Mandatory : Not configured
Supported : NSS1 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11
NSS2 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11
Multicast : Not configured
OFDMA random access RUs : Not Supported
DL-OFDMA : Disabled
UL-OFDMA : Disabled
UL-MU-MIMO : Disabled
BSS-COLOR : Disabled
TWT negotiation : Disabled
ATF : Disabled
HT protection mode : No protection