- Table of Contents
-
- 07-Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Basic IP routing configuration
- 02-Static routing configuration
- 03-RIP configuration
- 04-OSPF configuration
- 05-Policy-based routing configuration
- 06-IPv6 static routing configuration
- 07-RIPng configuration
- 08-OSPFv3 configuration
- 09-IPv6 policy-based routing configuration
- 10-Routing policy configuration
- 11-BGP configuration
- 12-IS-IS configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 10-Routing policy configuration | 177.00 KB |
Implementation of a routing policy
Routing policy tasks at a glance
Configuring an IPv4 prefix list
Configuring an IPv6 prefix list
Configuring an extended community list
Configuring the continue clause
Display and maintenance commands for routing policies
Routing policy configuration examples
Example: Configuring a routing policy for redistributing static routes to RIP
Example: Configuring a routing policy for redistributing IS-IS routes to OSPF
Example: Configuring a routing policy for IPv6 route redistribution
Configuring routing policies
About routing policies
Routing policies control routing paths by filtering and modifying routing information.
Routing policies can filter advertised, received, and redistributed routes, and modify attributes for specific routes.
Implementation of a routing policy
To configure a routing policy:
1. Configure filters based on route attributes.
2. Create a routing policy and apply filters to the routing policy.
Filters
Routing policies can use the following filters to match routes.
ACL
An ACL can match the destination or next hop of routes.
For more information about ACLs, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
IP prefix list
An IP prefix list matches the destination address of routes.
An IP prefix list can contain multiple items that specify prefix ranges. Each destination IP address prefix of a route is compared with these items in ascending order of their index numbers. A prefix matches the IP prefix list if it matches one item in the list.
AS path list
An AS path list matches the AS_PATH attribute of BGP routes. The AS_PATH attribute identifies the ASs through which a route has passed.
For more information about AS path lists, see "Configuring BGP."
Community list
A community list matches the COMMUNITY attribute of BGP routes. The COMMUNITY attribute identifies the community of BGP routes.
For more information about community lists, see "Configuring BGP."
Extended community list
An extended community list matches the extended community attribute (Route-Target for VPN and Site of Origin) of BGP routes.
RD list
A route distinguisher (RD) list matches the RD of routes.
An RD list is identified by an RD list number and can contain multiple items that specify RD ranges. Each item is identified by an index number. The RD of a route is compared with these items in ascending order of their index numbers. An RD matches the RD list if it matches one item in the list.
Tag list
A tag list matches the tag of IGP routes.
Routing policy
A routing policy can contain multiple nodes, which are in a logical OR relationship. A node with a smaller number is matched first. A route matches the routing policy if it matches one node (except the node configured with the continue clause) in the routing policy.
Each node has a match mode of permit or deny.
· permit—Specifies the permit match mode for a routing policy node. If a route meets all the if-match clauses of the node, it is handled by the apply clauses of the node. The route is not compared with the next node unless the continue clause is configured. If a route does not meet all the if-match clauses of the node, it is compared with the next node.
· deny—Specifies the deny match mode for a routing policy node. The apply and continue clauses of a deny node are never executed. If a route meets all the if-match clauses of the node, it is denied without being compared with the next node. If a route does not meet all the if-match clauses of the node, it is compared with the next node.
A node can contain a set of if-match, apply, and continue clauses.
· if-match clauses—Specify the match criteria that match the attributes of routes. The if-match clauses of different types are in a logical AND relationship and the if-match clauses of the same type are in a logical OR relationship. A route must meet if-match clauses of all types to match the node.
· apply clauses—Specify the actions to be taken on permitted routes, such as modifying a route attribute.
· continue clause—Specifies the next node. A route that matches the current node (permit node) must match the specified next node in the same routing policy. The continue clause combines the if-match and apply clauses of the two nodes to improve flexibility of the routing policy. After you configure a continue clause, a route can pass the routing policy even if it does not match the specified next node. To reject such a route, add a deny node without clauses.
Follow these guidelines when you configure if-match, apply, and continue clauses:
· If you only want to filter routes, do not configure apply clauses.
· If you do not configure any if-match clauses for a permit node, the node will permit all routes.
· Configure a permit node containing no if-match or apply clauses following multiple deny nodes to allow unmatched routes to pass.
Routing policy tasks at a glance
To configure a routing policy, perform the following tasks:
1. (Optional.) Configure filters:
¡ Configuring an IPv4 prefix list
¡ Configuring an IPv6 prefix list
¡ Configuring a community list
¡ Configuring an extended community list
2. Configuring a routing policy
b. Configuring if-match clauses
d. Configuring the continue clause
Configuring an IPv4 prefix list
Restrictions and guidelines
If all the items are set to deny mode, no routes can pass the IPv4 prefix list. To permit unmatched IPv4 routes, you must configure the permit 0.0.0.0 0 less-equal 32 item following multiple deny items.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure an IPv4 prefix list.
ip prefix-list prefix-list-name [ index index-number ] { deny | permit } ip-address mask-length [ greater-equal min-mask-length ] [ less-equal max-mask-length ]
Configuring an IPv6 prefix list
Restrictions and guidelines
If all items are set to deny mode, no routes can pass the IPv6 prefix list. To permit unmatched IPv6 routes, you must configure the permit :: 0 less-equal 128 item following multiple deny items.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure an IPv6 prefix list.
ipv6 prefix-list prefix-list-name [ index index-number ] { deny | permit } ipv6-address { inverse inverse-prefix-length | prefix-length [ greater-equal min-prefix-length ] [ less-equal max-prefix-length ] }
Configuring an AS path list
About this task
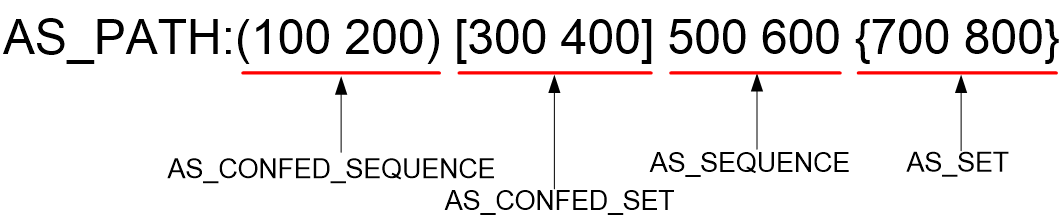
The AS_PATH attribute identifies the ASs through which a BGP route has passed. Figure 1 shows the AS_PATH attribute format in the BGP routing table.
The AS_PATH attribute value is a character string containing digits, parentheses, brackets, braces, and spaces. It is a sequence of the following AS path segments:
· AS_CONFED_SEQUENCE—Ordered set of member AS numbers in the local confederation that the UPDATE message has traversed.
· AS_CONFED_SET—Unordered set of member AS numbers in the local confederation that the UPDATE message has traversed.
· AS_SEQUENCE—Ordered set of ASs a route in the UPDATE message has traversed.
· AS_SET—Unordered set of ASs a route in the UPDATE message has traversed.
|
|
NOTE: The AS_PATH attribute of a BGP route might not contain all of the four AS path segments. |
An AS path list consists of regular expressions used for filtering BGP routes by their AS_PATH attributes. A regular expression can contain the special characters described in Table 1.
Table 1 Special characters supported in a regular expression
|
Description |
Example |
|
|
^ |
Matches the beginning of a line. |
Match a local route if its AS_PATH attribute is null: ip as-path { as-path-number| as-path-name } { deny | permit } ^$ |
|
$ |
Matches the end of a line. |
Match a route if it is originated from AS 100: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } 100$ |
|
. |
Matches any single character. |
Match a route if it has passed AS 100 but is not originated or received from AS 100: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } ._100_. |
|
* |
Matches the preceding character or string zero, one, or multiple times. |
Match a route if it has an AS_PATH attribute: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } .* |
|
+ |
Matches the preceding character or string one or multiple times. |
Match a route if its AS_PATH attribute value contains 5: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } 5+ |
|
x|y |
Matches the preceding or succeeding string. |
Match a route if it is originated from AS 100 or AS 200: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } 100$|200$ |
|
( ) |
Matches the string in the parentheses, usually used together with the plus sign (+) or asterisk sign (*). |
Match a route if its AS_PATH attribute value contains 123: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } (123)+ |
|
[xyz] |
Matches a single character in the brackets. |
Match a route if it is received from AS 10 through AS 19: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } ^1[0-9]$ |
|
[^xyz] |
Matches a single character that is not in the brackets. |
Match a route if its originating AS number does not end with 2 or 4: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } [^24]$ |
|
{n} |
Matches the preceding character n times. The number n must be a nonnegative integer. |
Match a route if its AS_PATH attribute value contains two 5: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } 5{2} |
|
{n,} |
Matches the preceding character n times or more. The number n must be a nonnegative integer. |
Match a route if its AS_PATH attribute value contains two or more consecutive 5: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } 5{2,} |
|
{n,m} |
Matches the preceding character n to m times or more. The numbers n and m must be nonnegative integers and n cannot be greater than m. |
Match a route if its AS_PATH attribute value contains one or more consecutive 5: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } 5{1,2} |
|
[a-z] |
Matches a single character within the specified range for only once. |
Match a route if its AS_PATH attribute value contains 0, 1, or 2: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit }[0-2] |
|
[^a-z] |
Matches a single character that is not in the specified range. |
Match a route if its AS_PATH attribute value contains digits other than 0, 1, or 2: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit }^ [^0-2]$ |
|
_ |
Matches a punctuation. The expression can begin or end with _. |
Match a route if it has passed AS101 100: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } 101_100_ |
|
\b |
Matches a word that starts with the pattern following \b or ends with the pattern preceding \b. |
Match a route if it is originated from AS 100: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } \b100$ |
|
\B |
Matches a word that contains the pattern but does not start or end with the pattern. |
Match a route if its AS_PATH attribute value starts with 1: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } { deny | permit } ^1\B |
|
\ |
Escape character. If a special character listed in this table follows \, the specific meaning of the character is removed. |
N/A |
|
\w |
Same as [A-Za-z0-9_], matches a digit, letter, or underscore. |
Match a route if its AS_PATH attribute value contains double digits: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } \w{2} |
|
\W |
Same as [^A-Za-z0-9_], matches a character that is not a digit, letter, or underscore. |
N/A |
|
\index |
Matches the specified string in the parentheses followed by \ twice. Each string in the parentheses is numbered from 1 in order. The index argument represents the sequence number of the string you want to match. If the parentheses contain n strings, you can specify the sequence number of the string in the range of 1 to n. |
Match a route if its AS_PATH attribute value contains two consecutive 1: ip as-path { as-path-number | as-path-name } (1)\1 |
|
|
NOTE: The regular expressions shown in Table 1 are used for illustration only. Other regular expressions might be available to achieve the same effect. |
Restrictions and guidelines
You can configure multiple items for an AS path list that is identified by a number. The relationship between the items is logical OR. A route matches the AS path list if it matches one item in the list.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure an AS path list.
ip as-path as-path-number { deny | permit } regular-expression
Configuring a community list
About this task
You can configure multiple items for a community list that is identified by a number. The relationship between the items is logical OR. A route matches the community list if it matches one item in the list.
An advanced community list matches the community attributes of BGP routes based on the regular expressions described in "Configuring an AS path list."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure a community list.
¡ Configure a basic community list.
ip community-list { basic-comm-list-num | basic basic-comm-list-name } { deny | permit } [ community-number&<1-32> | aa:nn&<1-32> ] [ internet | no-advertise | no-export | no-export-subconfed ] *
¡ Configure an advanced community list.
ip community-list { adv-comm-list-num | advanced adv-comm-list-name } { deny | permit } regular-expression
Configuring an extended community list
About this task
You can configure multiple items for an extended community list that is identified by a number. The relationship between the items is logical OR. A route matches the extended community list if it matches one item in the list.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure an extended community list.
ip extcommunity-list ext-comm-list-number [ index index-number ] { deny | permit } { rt route-target | soo site-of-origin }&<1-32>
Configuring an RD list
About this task
You can configure multiple items for an RD list that is identified by a number. The relationship between the items is logical OR. A route matches the RD list if it matches one item in the list.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure an RD list.
ip rd-list rd-list-number [ index index-number ] { deny | permit } route-distinguisher&<1-10>
Configuring a tag list
About this task
You can configure multiple items for a tag list. The relationship between the items is logical OR. A route matches the tag list if it matches one item in the list.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure a tag list.
route tag-list tag-list-number [ index index-number ] { deny | permit } tag-value&<1-32>
Configuring a routing policy
Creating a routing policy
About this task
A routing policy must have a minimum of one permit node. If all the nodes are in deny mode, no routes can pass the routing policy.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a routing policy and a node, and enter routing policy node view.
route-policy route-policy-name { deny | permit } node node-number
3. (Optional.) Configure a description for the routing policy node.
description text
Configuring if-match clauses
About this task
You can either specify no if-match clauses or multiple if-match clauses for a routing policy node. If no if-match clause is specified for a permit node, all routes can pass the node. If no if-match clause is specified for a deny node, no routes can pass the node.
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure if-match clauses, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· The if-match clauses of a routing policy node have a logical AND relationship. A route must meet all if-match clauses before it can be executed by the apply clauses of the node. If an if-match command exceeds the maximum length, multiple if-match clauses of the same type are generated. These clauses have a logical OR relationship. A route only needs to meet one of them.
· All IPv4 routes match a node if the if-match clauses of the node use only IPv6 ACLs. All IPv6 routes match a node if the if-match clauses of the node use only IPv4 ACLs.
· If the ACL used by an if-match clause does not exist, the clause is always matched. If no rules of the specified ACL are matched or the match rules are inactive, the clause is not matched.
· If the prefix list, community list, or extended community list used by an if-match clause does not exist, the clause is always matched. If no rules of the specified prefix list, community list, or extended community list are matched, the clause is not matched.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter routing policy node view.
route-policy route-policy-name { deny | permit } node node-number
3. Match routes whose destination, next hop, or source address matches an ACL or prefix list.
IPv4:
if-match ip { address | next-hop | route-source } { acl { ipv4-acl-number | name ipv4-acl-name } | prefix-list prefix-list-name }
IPv6:
if-match ipv6 { address | next-hop | route-source } { acl { ipv6-acl-number | name ipv6-acl-name } | prefix-list prefix-list-name }
By default, no ACL or prefix list match criterion is configured.
The ACL specified in an if-match clause must be a non-VPN ACL.
4. Configure BGP route match criteria.
¡ Match BGP routes whose AS_PATH attribute matches a specified AS path list.
if-match as-path as-path-number&<1-32>
¡ Match BGP routes whose COMMUNITY attribute matches a specified community list.
if-match community { { basic-community-list-number | name comm-list-name } [ whole-match ] | adv-community-list-number }&<1-32>
¡ Match BGP routes whose extended community attribute matches a specified extended community list.
if-match extcommunity ext-comm-list-number&<1-32>
¡ Match BGP routes having the specified local preference.
if-match local-preference preference
By default, no BGP route match criteria are configured.
5. Configure route match criteria.
¡ Match routes having the specified cost.
if-match cost cost-value
¡ Match routes having the specified output interface.
if-match interface { interface-type interface-number }&<1-16>
This command is not supported by BGP.
¡ Match routes having the specified route type.
if-match route-type { external-type1 | external-type1or2 | external-type2 | internal | nssa-external-type1 | nssa-external-type1or2 | nssa-external-type2 } *
¡ Match IGP routes having the specified tag value.
if-match tag tag-value
¡ Match IGP routes whose tag matches the specified tag list.
if-match tag-list tag-list-number
By default, no route match criteria are configured.
6. Match routes whose RD matches the specified RD list.
if-match rd-list rd-list-number
By default, no RD match criterion is configured.
Configuring apply clauses
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter routing policy node view.
route-policy route-policy-name { deny | permit } node node-number
3. Configure BGP route attributes.
¡ Set the AS_PATH attribute for BGP routes.
apply as-path as-number&<1-32> [ replace ]
¡ Delete the specified COMMUNITY attribute for BGP routes.
apply comm-list { comm-list-number | comm-list-name } delete
By default, no COMMUNITY attribute is deleted for BGP routes.
¡ Set the specified COMMUNITY attribute for BGP routes.
apply community { none | additive | { community-number&<1-32> | aa:nn&<1-32> | internet | no-advertise | no-export | no-export-subconfed } * [ additive ] }
¡ Set the extended community attribute for BGP routes.
apply extcommunity { rt route-target }&<1-32> [ additive ]
¡ Set a local preference for BGP routes.
apply local-preference preference
¡ Set the ORIGIN attribute for BGP routes.
apply origin { egp as-number | igp | incomplete }
¡ Set a preferred value for BGP routes.
apply preferred-value preferred-value
¡ Set a traffic index for BGP routes.
apply traffic-index { value | clear }
By default, no BGP route attributes are configured.
4. Configure the route cost and cost type.
¡ Set a cost for routes.
apply cost [ + | - ] cost-value
By default, no cost is set for routes.
¡ Set a cost type for routes.
apply cost-type { external | internal | type-1 | type-2 }
By default, no cost type is set for routes.
5. Set the next hop for routes.
IPv4:
apply ip-address next-hop ip-address [ public | vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
IPv6:
apply ipv6 next-hop ipv6-address
By default, no next hop is set for routes.
The configuration does not apply to redistributed routes.
6. Configure route priorities.
¡ Set an IP precedence for matching routes.
apply ip-precedence { value | clear }
By default, no IP precedence is set.
¡ Set a preference.
apply preference preference
By default, no preference is set.
¡ Set a prefix priority.
apply prefix-priority { critical | high | medium }
By default, the prefix priority is low.
7. Set a tag value for IGP routes.
apply tag tag-value
By default, no tag value is set for IGP routes.
8. Set a backup link for fast reroute (FRR).
IPv4:
apply fast-reroute { backup-interface interface-type interface-number [ backup-nexthop ip-address ] | backup-nexthop ip-address }
IPv6:
apply ipv6 fast-reroute { backup-interface interface-type interface-number [ backup-nexthop ipv6-address ] | backup-nexthop ipv6-address }
By default, no backup link is set for FRR.
Configuring the continue clause
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure the continue clause to combine multiple nodes, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· If you configure an apply clause that sets different attribute values on all the nodes, the apply clause of the node configured most recently takes effect.
· If you configure the following apply clauses on all the nodes, the apply clause of each node takes effect:
¡ apply as-path without the replace keyword.
¡ apply cost with the + or – keyword.
¡ apply community with the additive keyword.
¡ apply extcommunity with the additive keyword.
· The apply comm-list delete clause configured on the current node cannot delete the community attributes set by the apply community clauses of the preceding nodes.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter routing policy node view.
route-policy route-policy-name { deny | permit } node node-number
3. Specify the next node to be matched.
continue [ node-number ]
By default, no continue clause is configured.
The specified next node must have a larger number than the current node.
Display and maintenance commands for routing policies
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display BGP AS path list information. |
display ip as-path [ as-path-number ] |
|
Display BGP community list information. |
display ip community-list [ basic-community-list-number | adv-community-list-number | name comm-list-name ] |
|
Display BGP extended community list information. |
display ip extcommunity-list [ ext-comm-list-number ] |
|
Display IPv4 prefix list statistics. |
display ip prefix-list [ name prefix-list-name ] |
|
Display RD list information. |
display ip rd-list [ rd-list-number ] |
|
Display IPv6 prefix list statistics. |
display ipv6 prefix-list [ name prefix-list-name ] |
|
Display tag list information. |
display route tag-list [ tag-list-number ] |
|
Display routing policy information. |
display route-policy [ name route-policy-name ] |
|
Clear IPv4 prefix list statistics. |
reset ip prefix-list [ prefix-list-name ] |
|
Clear IPv6 prefix list statistics. |
reset ipv6 prefix-list [ prefix-list-name ] |
Routing policy configuration examples
Example: Configuring a routing policy for redistributing static routes to RIP
Network configuration
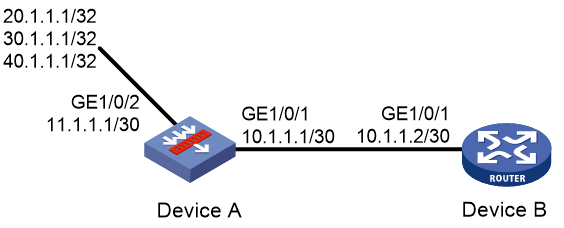
As shown in Figure 2, Device A exchanges routing information with Device B by using RIP.
On Device A, configure three static routes. Use a routing policy to configure Device B to redistribute networks 20.1.1.1/32 and 40.1.1.1/32 and block network 30.1.1.1/32.
Procedure
1. Configure Device A:
# Configure IP addresses for interfaces GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 30
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ip address 11.1.1.1 30
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Enable RIP on interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] rip 1 enable
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Configure three static routes and set the next hop of the three routes to 11.1.1.2.
[DeviceA] ip route-static 20.1.1.1 32 11.1.1.2
[DeviceA] ip route-static 30.1.1.1 32 11.1.1.2
[DeviceA] ip route-static 40.1.1.1 32 11.1.1.2
# Configure a routing policy.
[DeviceA] ip prefix-list a index 10 permit 30.1.1.1 32
[DeviceA] route-policy static2rip deny node 0
[DeviceA-route-policy-static2rip-0] if-match ip address prefix-list a
[DeviceA-route-policy-static2rip-0] quit
[DeviceA] route-policy static2rip permit node 10
[DeviceA-route-policy-static2rip-10] quit
# Enable RIP and apply routing policy static2rip to filter redistributed static routes.
[DeviceA] rip
[DeviceA-rip-1] import-route static route-policy static2rip
2. Configure Device B:
# Configure an IP address for interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.2 30
# Enable RIP.
[DeviceB] rip
[DeviceB-rip-1] quit
# Enable RIP on the interface.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] rip 1 enable
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display routing table information on Device B.
<Sysname> display ip routing-table
Destinations : 14 Routes : 14
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.0/30 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
10.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.3/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
20.0.0.0/8 RIP 100 1 10.1.1.1 GE1/0/1
40.0.0.0/8 RIP 100 1 10.1.1.1 GE1/0/1
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
224.0.0.0/4 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
224.0.0.0/24 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
Example: Configuring a routing policy for redistributing IS-IS routes to OSPF
Network configuration
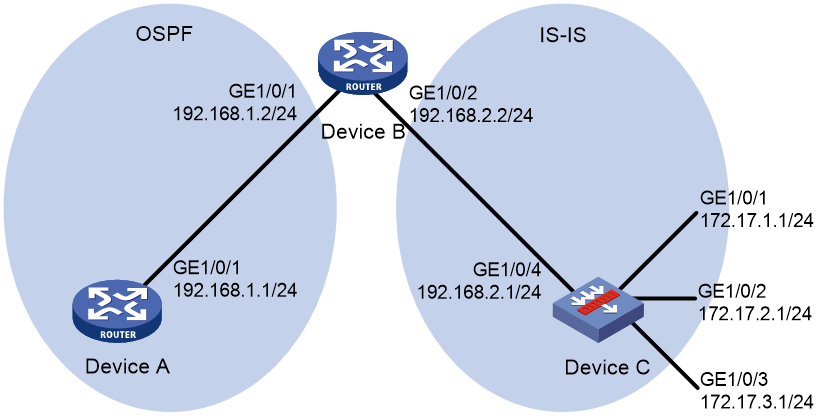
As shown in Figure 3, Device B exchanges routing information with Device A by using OSPF and with Device C by using IS-IS.
On Device B, enable route redistribution from IS-IS to OSPF. Use a routing policy to set the cost of route 172.17.1.0/24 to 100 and the tag of route 172.17.2.0/24 to 20.
Procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure IS-IS:
# Configure Device C.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] isis
[DeviceC-isis-1] is-level level-2
[DeviceC-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[DeviceC-isis-1] quit
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] isis enable
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] isis enable
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] isis enable
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] isis enable
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
# Configure Device B.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] isis
[DeviceB-isis-1] is-level level-2
[DeviceB-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[DeviceB-isis-1] quit
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] isis enable
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
3. Configure OSPF and route redistribution:
# Configure OSPF on Device A.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] ospf
[DeviceA-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceA-ospf-1] quit
# On Device B, configure OSPF and enable route redistribution from IS-IS to OSPF.
[DeviceB] ospf
[DeviceB-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceB-ospf-1] import-route isis 1
[DeviceB-ospf-1] quit
# Display the OSPF routing table on Device A to view the redistributed routes.
[DeviceA] display ospf routing
OSPF Process 1 with Device ID 192.168.1.1
Routing Tables
Routing for Network
Destination Cost Type NextHop AdvDevice Area
192.168.1.0/24 1 Transit 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0
Routing for ASEs
Destination Cost Type Tag NextHop AdvDevice
172.17.1.0/24 1 Type2 1 192.168.1.2 192.168.2.2
172.17.2.0/24 1 Type2 1 192.168.1.2 192.168.2.2
172.17.3.0/24 1 Type2 1 192.168.1.2 192.168.2.2
Total Nets: 4
Intra Area: 1 Inter Area: 0 ASE: 3 NSSA: 0
4. Configure filtering lists on Device B:
# Configure IPv4 basic ACL 2002 to permit route 172.17.2.0/24.
[DeviceB] acl basic 2002
[DeviceB-acl-ipv4-basic-2002] rule permit source 172.17.2.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceB-acl-ipv4-basic-2002] quit
# Configure IP prefix list prefix-a to permit route 172.17.1.0/24.
[DeviceB] ip prefix-list prefix-a index 10 permit 172.17.1.0 24
5. Configure a routing policy on Device B.
[DeviceB] route-policy isis2ospf permit node 10
[DeviceB-route-policy-isis2ospf-10] if-match ip address prefix-list prefix-a
[DeviceB-route-policy-isis2ospf-10] apply cost 100
[DeviceB-route-policy-isis2ospf-10] quit
[DeviceB] route-policy isis2ospf permit node 20
[DeviceB-route-policy-isis2ospf-20] if-match ip address acl 2002
[DeviceB-route-policy-isis2ospf-20] apply tag 20
[DeviceB-route-policy-isis2ospf-20] quit
[DeviceB] route-policy isis2ospf permit node 30
[DeviceB-route-policy-isis2ospf-30] quit
6. Apply the routing policy to route redistribution on Device B:
# On Device B, enable route redistribution from IS-IS to OSPF and apply the routing policy.
[DeviceB] ospf
[DeviceB-ospf-1] import-route isis 1 route-policy isis2ospf
[DeviceB-ospf-1] quit
# Display OSPF routing table information on Device A.
[DeviceA] display ospf routing
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 192.168.1.1
Routing Tables
Routing for Network
Destination Cost Type NextHop AdvRouter Area
192.168.1.0/24 1 Transit 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0
Routing for ASEs
Destination Cost Type Tag NextHop AdvRouter
172.17.1.0/24 100 Type2 1 192.168.1.2 192.168.2.2
172.17.2.0/24 1 Type2 20 192.168.1.2 192.168.2.2
172.17.3.0/24 1 Type2 1 192.168.1.2 192.168.2.2
Total Nets: 4
Intra Area: 1 Inter Area: 0 ASE: 3 NSSA: 0
The output shows that the cost of route 172.17.1.0/24 is 100 and the tag of route 172.17.2.0/24 is 20.
Example: Configuring a routing policy for IPv6 route redistribution
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 4:
· Run RIPng on Device A and Device B.
· Configure three static routes on Device A.
· On Device A, apply a routing policy to redistribute static routes 20::/32 and 40::/32 and deny route 30::/32.
Procedure
1. Configure Device A:
# Configure IPv6 addresses for interfaces GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipv6 address 10::1 32
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ipv6 address 11::1 32
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Enable RIPng on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ripng 1 enable
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Configure three static routes with next hop 11::2, and make sure the static routes are active.
[DeviceA] ipv6 route-static 20:: 32 11::2
[DeviceA] ipv6 route-static 30:: 32 11::2
[DeviceA] ipv6 route-static 40:: 32 11::2
# Configure a routing policy.
[DeviceA] ipv6 prefix-list a index 10 permit 30:: 32
[DeviceA] route-policy static2ripng deny node 0
[DeviceA-route-policy-static2ripng-0] if-match ipv6 address prefix-list a
[DeviceA-route-policy-static2ripng-0] quit
[DeviceA] route-policy static2ripng permit node 10
[DeviceA-route-policy-static2ripng-10] quit
# Enable RIPng and apply routing policy static2ripng to filter redistributed static routes on Device A.
[DeviceA] ripng
[DeviceA-ripng-1] import-route static route-policy static2ripng
2. Configure Device B:
# Configure the IPv6 address of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipv6 address 10::2 32
# Enable RIPng.
[DeviceB] ripng
[DeviceB-ripng-1] quit
# Enable RIPng on the interface.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ripng 1 enable
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display the RIPng routing table on Device B.
[DeviceB] display ripng 1 route
Route Flags: A - Aging, S - Suppressed, G - Garbage-collect
----------------------------------------------------------------
Peer FE80::7D58:0:CA03:1 on GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Destination 20::/32,
via FE80::7D58:0:CA03:1, cost 1, tag 0, A, 8 secs
Destination 40::/32,
via FE80::7D58:0:CA03:1, cost 1, tag 0, A, 3 secs
Local route
Destination 10::/32,
via ::, cost 0, tag 0, DOF