- Table of Contents
-
- 07-MPLS Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Basic MPLS configuration
- 02-Static LSP configuration
- 03-LDP configuration
- 04-MPLS TE configuration
- 05-Static CRLSP configuration
- 06-RSVP configuration
- 07-Tunnel policy configuration
- 08-MPLS L3VPN configuration
- 09-MPLS L2VPN configuration
- 10-VPLS configuration
- 11-MPLS OAM configuration
- 12-MCE configuration
- 13-Static SR over MPLS configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 07-Tunnel policy configuration | 89.40 KB |
Tunnel policy configuration examples
Exclusive tunnel configuration example
Preferred tunnel and tunnel selection order configuration example
Configuring tunnel policies
Overview
Tunnel policies enable a PE to forward traffic for each MPLS VPN over a preferred tunnel or over multiple tunnels. The tunnels supported by MPLS VPN include MPLS LSPs and MPLS TE tunnels.
For more information about MPLS TE, see "Configuring MPLS TE." For more information about MPLS VPNs, see "Configuring MPLS L2VPN," "Configuring VPLS," and "Configuring MPLS L3VPN."
Configuring a tunnel policy
Configuration guidelines
When you configure a tunnel policy, follow these guidelines:
· To select a preferred tunnel, create a tunnel policy and configure the preferred tunnel with the preferred-path command. The destination address of the preferred tunnel identifies a peer PE so the PE will forward traffic destined for that peer PE over the preferred tunnel.
¡ If you configure multiple preferred tunnels that have the same destination address in a tunnel policy, only the first configured tunnel takes effect.
¡ If the first tunnel is not available, the second tunnel is used, and so forth. No load balancing will be performed on these tunnels.
This method explicitly specifies an MPLS TE tunnel for an MPLS VPN, facilitating traffic planning. As a best practice, use this method.
· To select multiple tunnels for load sharing, create a tunnel policy and specify the tunnel selection order and the number of tunnels by using the select-seq load-balance-number command. A tunnel type closer to the select-seq keyword has a higher priority. The tunnels selected by this method are not fixed, complicating traffic planning. As a best practice, do not use this method.
If you configure both methods for a tunnel policy, the tunnel policy selects tunnels in the following steps:
1. If the destination address of a preferred tunnel identifies a peer PE, the tunnel policy uses the preferred tunnel to forward traffic destined for the peer PE.
2. If not, the tunnel policy selects tunnels as configured by the select-seq load-balance-number command.
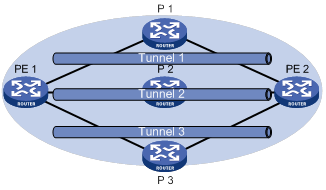
As shown in Figure 1, PE 1 and PE 2 have multiple tunnels in between and they are connected to multiple MPLS VPNs. You can control the paths for VPN traffic by using one of the following methods:
· Configure multiple tunnel policies, and specify a preferred tunnel for each policy by using the preferred-path command. Apply these policies to different MPLS VPNs to forward the traffic of each VPN over a specific tunnel.
· Configure one tunnel policy, and use the select-seq load-balance-number command to specify the tunnel selection order and the number of tunnels for load balancing. Apply the tunnel policy to MPLS VPNs to forward the traffic of every VPN over multiple tunnels.
The second method distributes traffic of a single VPN to multiple tunnels. The transmission delays on different tunnels can vary by a large amount. Therefore, the destination device or the upper layer application might take a great time to sequence the packets. As a best practice, do not use the second method.
Figure 1 MPLS VPN tunnel selection diagram
Configuration procedure
To configure a tunnel policy:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Create a tunnel policy, and enter tunnel policy view. |
tunnel-policy tunnel-policy-name |
By default, no tunnel policies exist. |
|
3. Configure tunnel selection methods. |
·
(Method 1) Configure a tunnel as a preferred
tunnel: ·
(Method 2) Configure the tunnel selection
order and the number of tunnels for load balancing: |
Configure one or both methods. By default, no preferred tunnels are configured. By default, only one tunnel is selected in LSP—CRLSP order. |
|
|
NOTE: For a VPN to exclusively use a tunnel, you can specify the tunnel as the preferred tunnel in a tunnel policy, and apply the policy only to that VPN. |
Displaying tunnel information
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display tunnel information. |
display mpls tunnel { all | statistics | [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] destination { ipv4-address | ipv6-address } } |
Tunnel policy configuration examples
Exclusive tunnel configuration example
Network requirements
PE 1 has multiple tunnels to reach PE 2: two MPLS TE tunnels on interface Tunnel 1 and Tunnel 2, and one LDP LSP tunnel.
Two MPLS VPNs, vpna and vpnb, exist on PE 1. The VPN vpna exclusively uses the MPLS TE tunnel 1, and the VPN vpnb exclusively uses the MPLS TE tunnel 2.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure tunnel policies on PE 1:
# Create tunnel policy preferredte1, and configure tunnel 1 as the preferred tunnel.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] tunnel-policy preferredte1
[PE1-tunnel-policy-preferredte1] preferred-path tunnel 1
[PE1-tunnel-policy-preferredte1] quit
# Create tunnel policy preferredte2, and configure tunnel 2 as the preferred tunnel.
[PE1] tunnel-policy preferredte2
[PE1-tunnel-policy-preferredte2] preferred-path tunnel 2
[PE1-tunnel-policy-preferredte2] quit
2. Configure MPLS VPN instances and apply tunnel policies to the VPN instances:
# Create MPLS VPN instance vpna, and apply tunnel policy preferredte1 to it.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpna
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] tnl-policy preferredte1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] quit
# Create MPLS VPN instance vpnb, and apply tunnel policy preferredte2 to it.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpnb
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnb] route-distinguisher 100:2
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnb] vpn-target 100:2
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnb] tnl-policy preferredte2
Preferred tunnel and tunnel selection order configuration example
Network requirements
PE 1 has multiple tunnels to reach PE 2: two MPLS TE tunnels on interfaces Tunnel 1 and Tunnel 2, and one LDP LSP tunnel.
PE 1 has multiple MPLS VPN instances: vpna, vpnb, vpnc, vpnd, and vpne. Table 1 shows the tunnel policy that PE 1 uses for each VPN instance.
Table 1 Tunnel policies used for VPN instances
|
VPN instance |
Tunnel policy |
|
vpna, vpnb |
Use MPLS TE tunnel Tunnel 1 as the preferred tunnel. |
|
vpnc, vpnd |
Use MPLS TE tunnel Tunnel 2 as the preferred tunnel. |
|
vpne |
Uses one tunnel selected in LDP LSP-MPLS TE order. |
Configuration procedure
1. Configure tunnel policies on PE 1:
# Create tunnel policy preferredte1, and configure tunnel 1 as the preferred tunnel.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] tunnel-policy preferredte1
[PE1-tunnel-policy-preferredte1] preferred-path tunnel 1
[PE1-tunnel-policy-preferredte1] quit
# Create tunnel policy preferredte2, and configure tunnel 2 as the preferred tunnel.
[PE1] tunnel-policy preferredte2
[PE1-tunnel-policy-preferredte2] preferred-path tunnel 2
[PE1-tunnel-policy-preferredte2] quit
# Create tunnel policy select-lsp.
[PE1] tunnel-policy select-lsp
# Configure the policy to select only one tunnel in LDP LSP-MPLS TE order.
[PE1-tunnel-policy-select-lsp] select-seq lsp cr-lsp load-balance-number 1
[PE1-tunnel-policy-select-lsp] quit
2. Configure MPLS VPN instances and apply tunnel policies to the VPN instances:
# Create MPLS VPN instances vpna and vpnb, and apply tunnel policy preferredte1 to them.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpna
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] tnl-policy preferredte1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] quit
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpnb
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnb] route-distinguisher 100:2
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnb] vpn-target 100:2
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnb] tnl-policy preferredte1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnb] quit
# Create MPLS VPN instances vpnc and vpnd, and apply tunnel policy preferredte2 to them.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpnc
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnc] route-distinguisher 100:3
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnc] vpn-target 100:3
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnc] tnl-policy preferredte2
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnc] quit
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpnd
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnd] route-distinguisher 100:4
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnd] vpn-target 100:4
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnd] tnl-policy preferredte2
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpnd] quit
# Create MPLS VPN instance vpne, and apply tunnel policy select-lsp to it.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpne
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpne] route-distinguisher 100:5
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpne] vpn-target 100:5
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpne] tnl-policy select-lsp
